Study on fluidized leaching of calcified vanadium slag clinker
-
摘要: 利用散式直管流化床进行了钙法钒渣熟料流态化浸出工艺研究,测定了熟料颗粒的粒度分布并分成7个粒级开展试验,首先计算出不同粒级下的临界速率及带出速率,考察了钒渣粒度对表观流化速率、停留时间分布以及钒浸出率的影响。结果表明,不同粒级的临界流化速率和停留时间差异较大,且存在显著的短路或者沟流现象,需分级处理,其中−39 μm颗粒的浸出效果最好,尾渣残钒为0.54%,钒浸出率可达94%。Abstract: The fluidized leaching process of calcified vanadium slag clinker was studied in a particulate fluidized bed reactor. The particle size distribution of the clinker was determined and seven size fractions were divided for the experiments. The critical velocity and entrainment velocity of different size fractions were firstly calculated. The effects of clinker particle size on the apparent fluidization velocity, residence time and vanadium leaching rate were investigated. The results show that the critical fluidization velocity and residence time distribution of different particle size fractions are quite different, and there exists significant short circuit or channeling which needs to be treated by stages. The best vanadium leaching efficiency of 94% can be obtained for particles lower than 39 μm, with the residual vanadium content of the tailing at 0.54%.
-
Key words:
- vanadium extracaction /
- vanadium slag /
- roasted calcium /
- clinker /
- fluidization leaching
-
0. 引言
钒渣钙法提钒工艺采用氧化钙或碳酸钙为焙烧添加剂,具有良好的经济性和环保性[1-3],目前已在西昌钒厂得到应用。将转炉钒渣破碎分选后与钙盐混合,经回转窑高温焙烧得到熟料,然后采用硫酸浸出得到酸性含钒溶液。但由于钒渣粒度较细,−95 μm颗粒含量接近80%,且浸出液固比受到后续沉钒工艺限制,导致浸出过程中存在料浆分散性较差,局部酸浓度高以及pH控制不稳定的问题,浸出效果波动较大。
流态化浸出技术可以让固体颗粒被赋予流体特性,具有较高的传质传热效率以及良好的混合均匀性等特点[4-5],在氧化锌烟尘[6-7]、钛铁矿[8-9]、赤泥[10]等细粒级物料的浸出或洗涤中获得了广泛的应用,并取得良好的效果[11]。
白瑞国等公开了一种钒渣全湿法流态化提钒的方法,钒渣不经过焙烧直接加入硫酸浸出,并在浸出过程中通入氧气,浸出酸耗较高且杂质被大量溶出[12]。郭继科等公开了一种钠盐钒渣熟料流态化提钒的方法[13],结果表明,钒渣流态化浸出具有一定可行性。但钙法钒渣熟料的性质和浸出条件与上述研究存在较大差别,其流态化浸出工艺仍需进一步研究。
同时由于西昌钙化钒渣熟料整体粒度较细且粒度分布较宽,各粒级的矿物组成和密度也有较大差异,导致流态化浸出的条件难以确定,操作窗口较窄。因此笔者首先针对钙化熟料按颗粒粒径和钙化熟料的物性参数进行了分级,计算出了各粒级的流化参数,临界流态化速度Umf和带出速度Ut的计算方法,并对影响流态化浸出的主要因素,如流化速率、停留时间等进行试验研究,分析其影响规律。
1. 试验原料与方法
1.1 试验原料
试验用钙化熟料取自攀钢西昌钒制品分公司钙化提钒生产线,主要化学成分见表1。
表 1 钙化熟料主要化学成分Table 1. Main chemical compositions of calcified vanadium slag clinker% V2O5 TFe SiO2 MnO TiO2 Al2O3 MgO CaO Cr2O3 P2O5 16.10 25.50 13.77 9.17 11.52 1.52 1.86 8.16 1.91 0.13 从表1可以看出,钒渣熟料中元素种类较多,物相主要包括钒酸钙、氧化铁、铁橄榄石、铁板钛矿、石英、硅酸钙以及未反应完的石灰石等。熟料粒度组成及密度分析结果见表2,可以看出,自生产现场取得的钙化熟料粒度分布范围较宽,+180 μm和−39 μm 都有一定比例分布,而且钙化熟料整体颗粒较细,其中在63 μm以下占比达到58.45%。而较宽的粒度分布对于流态化浸出则易出现分层现象,细颗粒钙化熟料会随着流化介质速度增大较快达到流态化,而粗颗粒熟料仍处于固定床阶段,形成分层现象。同时不同粒级颗粒的密度也存在较大差别,表明其矿物组成也存在一定区别。因此需要通过试验确定钙化熟料适合流态化浸出的合理粒径参数。
表 2 钙化熟料粒度分布及密度Table 2. Particle size distribution and density of calcified vanadium slag clinker粒度/μm 含量/% 密度/(g·cm−3) +180 5.85 2.95 −180~+125 7.58 3.17 −125~+95 7.62 3.27 −95~+74 13.47 3.24 −74~+63 7.03 3.33 −63~+39 31.75 3.44 −39 26.70 3.58 试验用硫酸为分析纯,配制为1∶1(体积比)稀硫酸。
1.2 试验设备
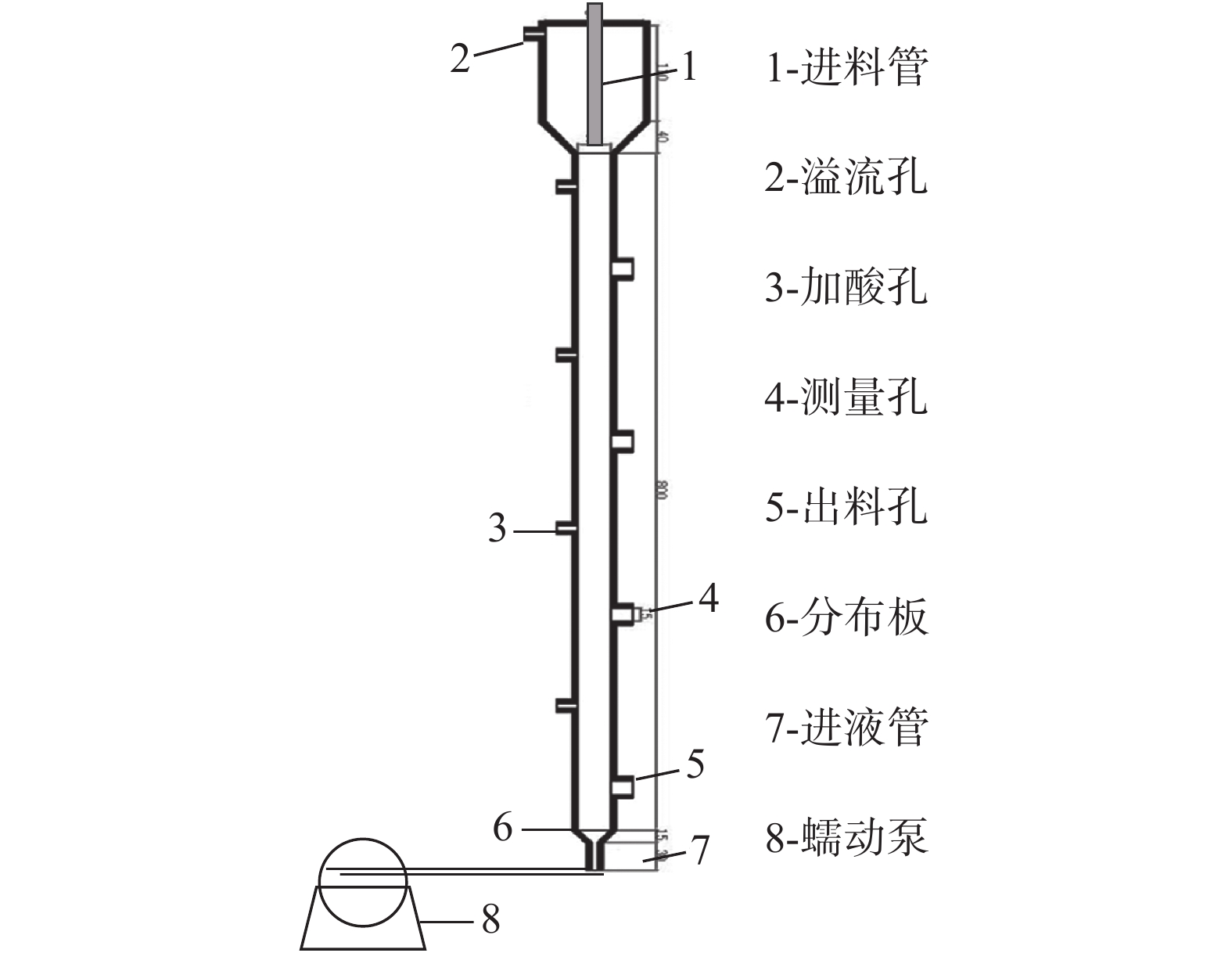
试验装置为内径3 cm,高80 cm的有机玻璃直管柱,分布板孔径为1 mm,采用等边三角形排列,柱身均匀设置了孔位以进行出料及加酸测pH等操作,顶部设有内径9 cm、高15 cm的溢流管,设备结构如图1所示。
1.3 试验方法
流态化浸出试验:采用连续浸出方式,在上部将钒渣钙化熟料造浆后连续给入流化床内,同时在下部出料孔同时抽出料浆,从而保持流化床内料浆固体浓度稳定。再将预先加热至50 ℃并调节pH=2.8的硫酸溶液从底部加入,加入流量按照设定值,从而保证物料实现流态化浸出,流量通过蠕动泵控制,同时从加酸孔加酸控制浸出过程pH,反应设定时间后取浸出残渣进行固液分离,残渣经洗涤、烘干后分析TV,计算钒浸出率。
停留时间试验:采用脉冲法测定各粒级颗粒的停留时间,在反应器的入口注入示踪剂,在反应器的出口或其他地点检测示踪剂的响应,分析测量数据,就可以定量地确定示踪剂所代表的反应物在反应器中停留时间的分布。由于钙化残渣中钾含量很低,因此试验采用K2SO4作为示踪剂,浓度为1 mol/L。具体实施方式为在流态化浸出达到稳定运行后,在反应器料浆注入口快速加入5 mL K2SO4溶液,同时每隔一定时间在上部出口收集一次料浆,测定料浆中钾离子的浓度。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 流态化参数计算
首先对原始钙化熟料按颗粒粒径进行了分级,依据测定的钙化熟料的物性参数,计算出各粒级物料的临界流化速度和带出速度,结果如表3所示,其中钒渣钙化熟料近似看做球形颗粒,则其在临界状态时的床层空隙率为0.4,形状系数设置为1.0。根据厄冈经验公式计算临界状态下的床层压降和临界流化速度,带出速度用颗粒在静置流体中的沉降速度表示。
表 3 各粒级颗粒的临界流化速度和带出速度Table 3. Critical fluidization velocity and entrainment velocity of different size fractions粒级/μm 平均粒径/μm 临界流化速度
Umf/(cm·s−1)带出速度
Ut/(cm·s−1)+180 180 0.47 2.31 −180~+125 150 0.37 2.02 −125~95 111 0.21 1.70 −95~+74 85 0.12 0.99 −74~+63 68 8.30×10−2 0.66 −63~+39 49 4.58×10−2 0.36 −39 39 3.00×10−2 0.24 从表3可以看出,随着粒度增加,各粒级的临界流化速度和带出速度均显著增加,−125~+95 μm粒级的临界流化速度已经和−39 μm粒级的带出速度接近,表明二者无法同时实现流化,在实际应用中最少也要以95 μm为分界进行分级,分出两个粒级颗粒进行流化浸出。为进一步分析各粒级颗粒的流化特性,需要将钙化钒渣熟料按以上7个粒度进行筛分分级处理。
2.2 不同粒度的流化速率试验
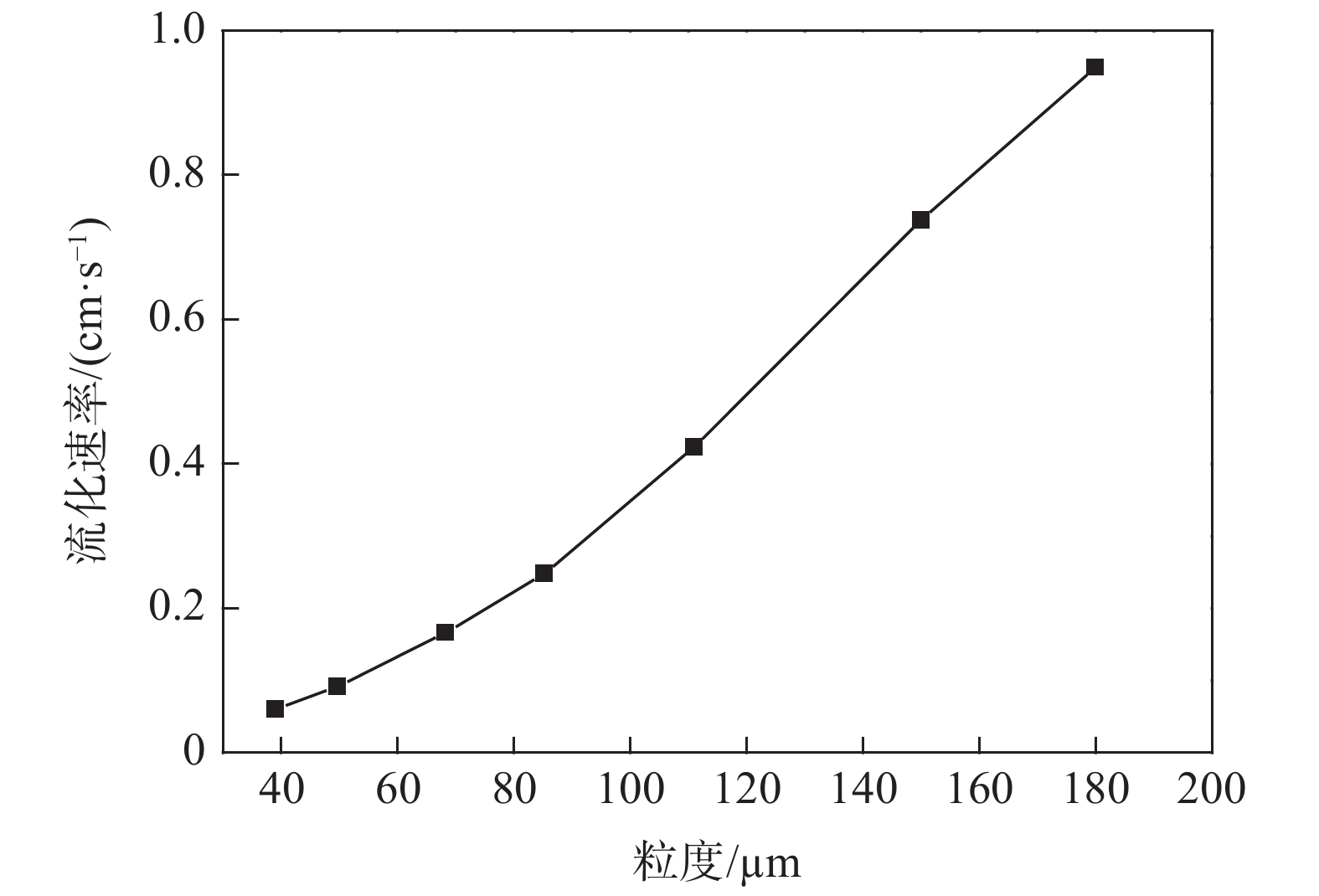
依据表3中计算出的流态化参数,首先开展了不同粒级的颗粒流化速率试验,观察不同流速下颗粒的运动状态,从而确定适宜的表观流化速率,试验结果如图2所示。
从图2可以看出,随着粒度增加,流化速率相应上升且基本呈线性相关。粒度由−39 μm增大到+180 μm时,相应的表观流化速率由0.06 cm/s增长到0.94 cm/s,表明浸出所需的液体量也大幅增加,对控制液固比和浸出液钒浓度不利。同时对比通过计算得到的理论临界流化速率,可以看出实际速率较计算结果呈倍数关系升高,表明计算结果具有较好的指导作用。
2.3 粒度对钒浸出的影响
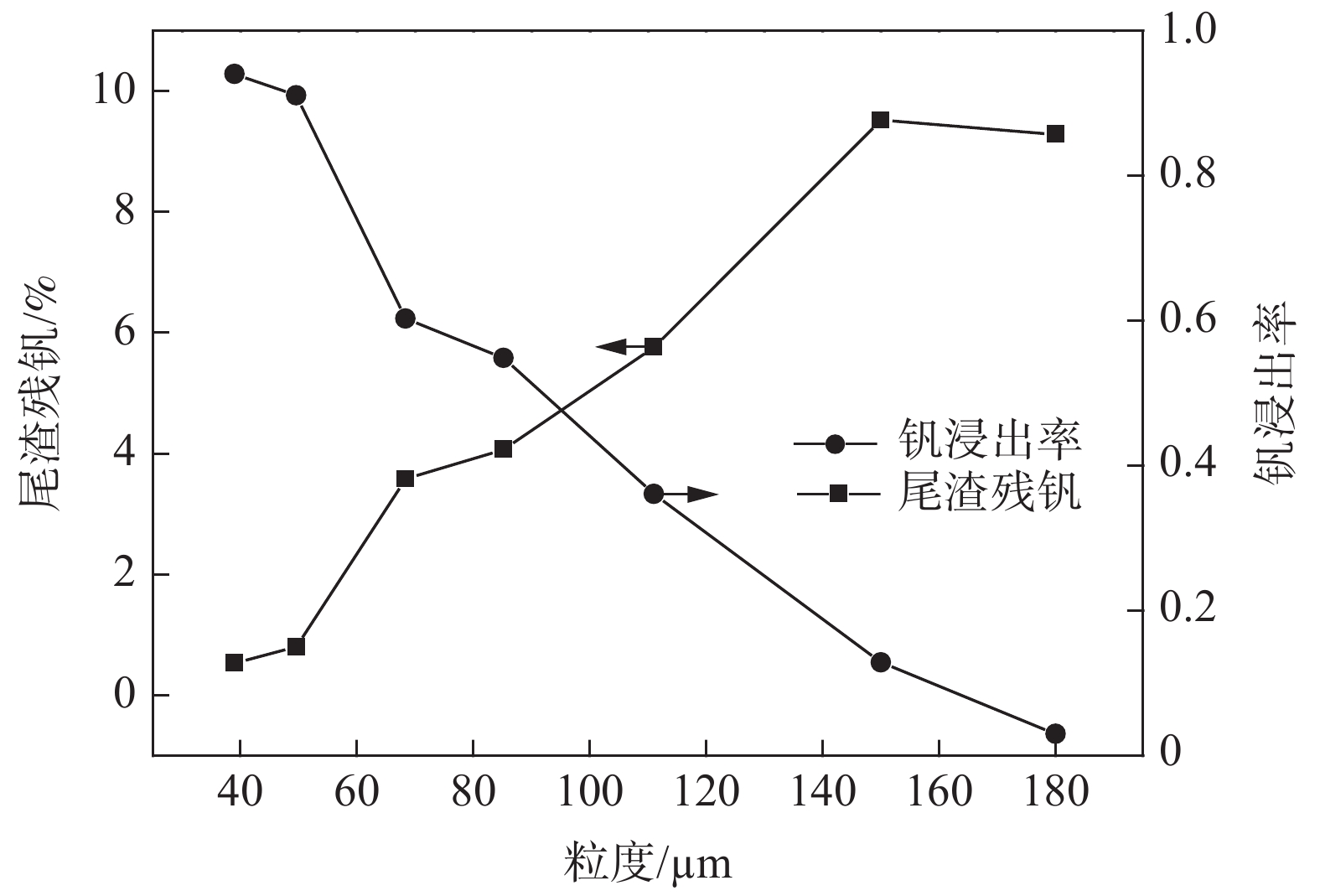
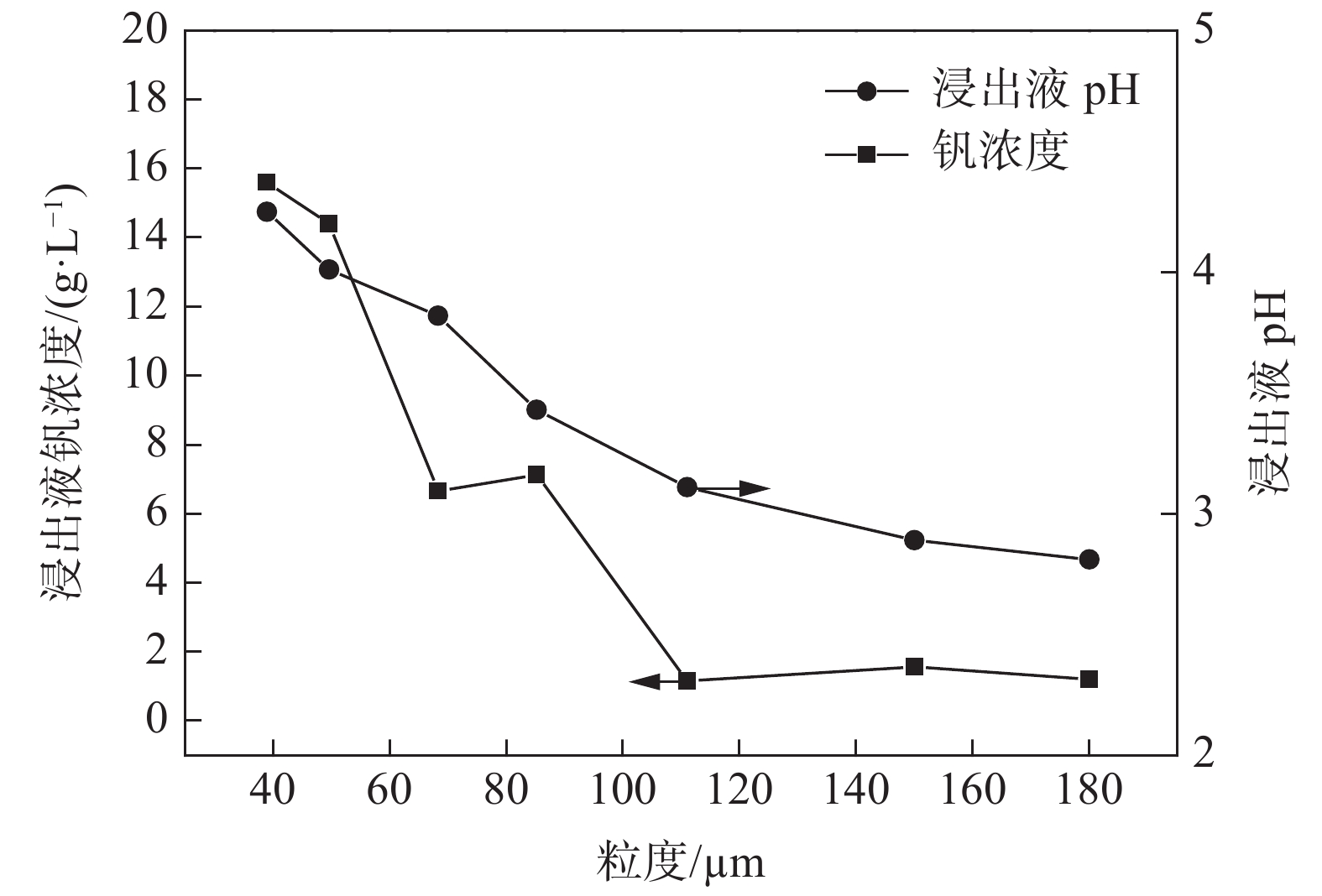
由于不同粒度颗粒的流化速率不同,浸出过程的液固比也相应受到影响,浸出液中钒浓度也有较大区别。从图3可以看出,粒度与钒浸出率呈反比,最小的−39 μm颗粒钒浸出率达到了94%,而粒度最大的+180 μm颗粒浸出率仅有不到10%。初步判断这是由于较大颗粒对应的流速过快,一方面加热功率限制导致实际反应温度无法达到要求,另一方面则是停留时间不足,颗粒流化效果较差。同时在试验中同时观察到尽管−39 μm的颗粒浸出率较高,但由于液体流速很低,柱身上部呈层流状态,混匀效果较差,且易在柱下部出现局部固体浓度过高和结块的现象,表明熟料粒度过大或过小均不利于实现流态化浸出。
从图4可以看出,浸出液pH和钒浓度是同步降低的,浸出液pH越低,表明其中硫酸未被有效利用,熟料中的钒也就没有反应进入溶液。计算可知各粒级的实际液固比分别为3.8、4.1、4.7、6.6、6.9、9.2、14.3。表明粒度125 μm以上的颗粒酸液是过量的,但反应不充分,浸出液需要循环。而细颗粒需要反应时间更短,反应速率更快,在后期进行混合粒度的熟料浸出时可以考率缩短其停留时间。
2.4 粒度对停留时间的影响
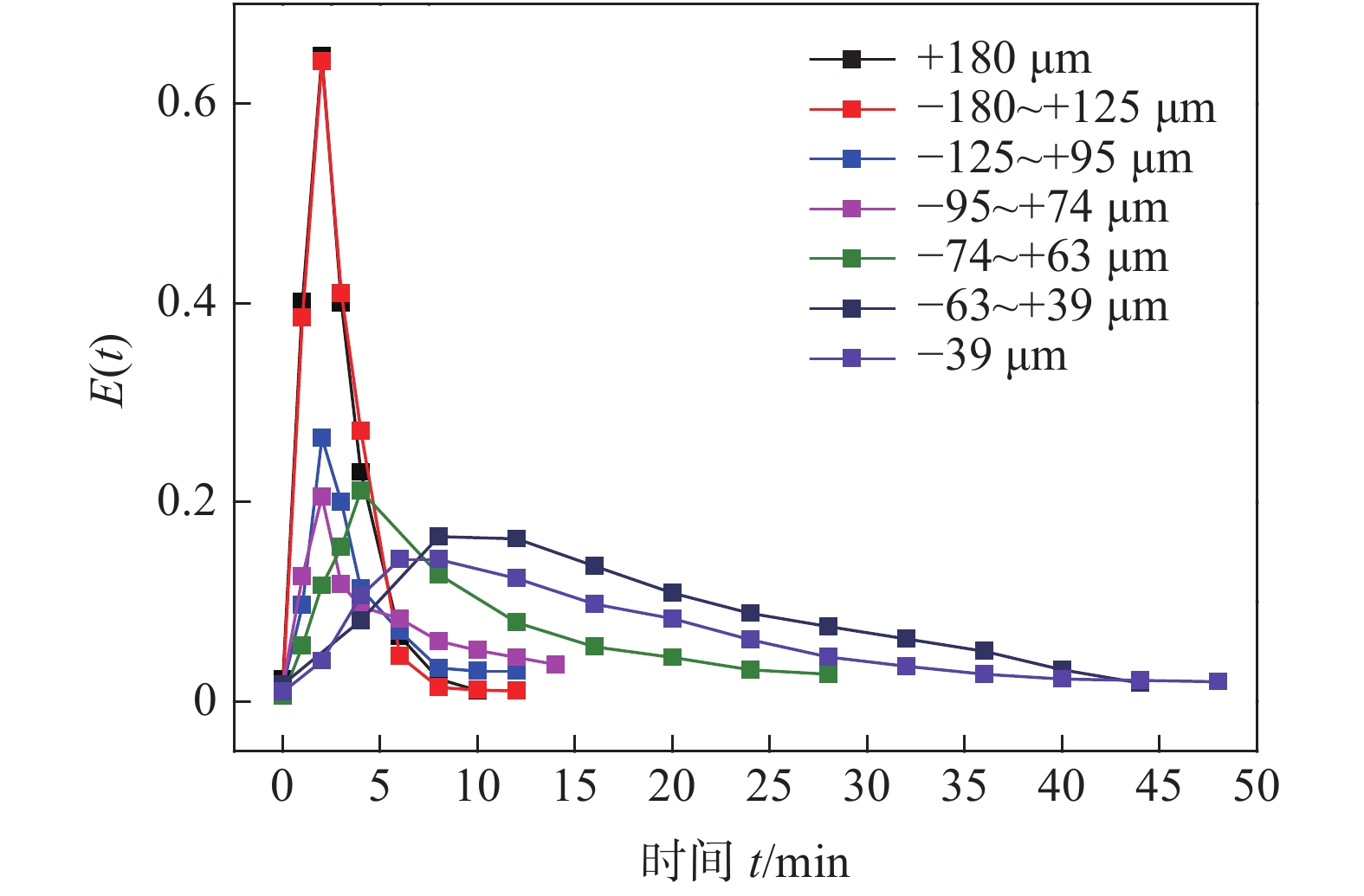
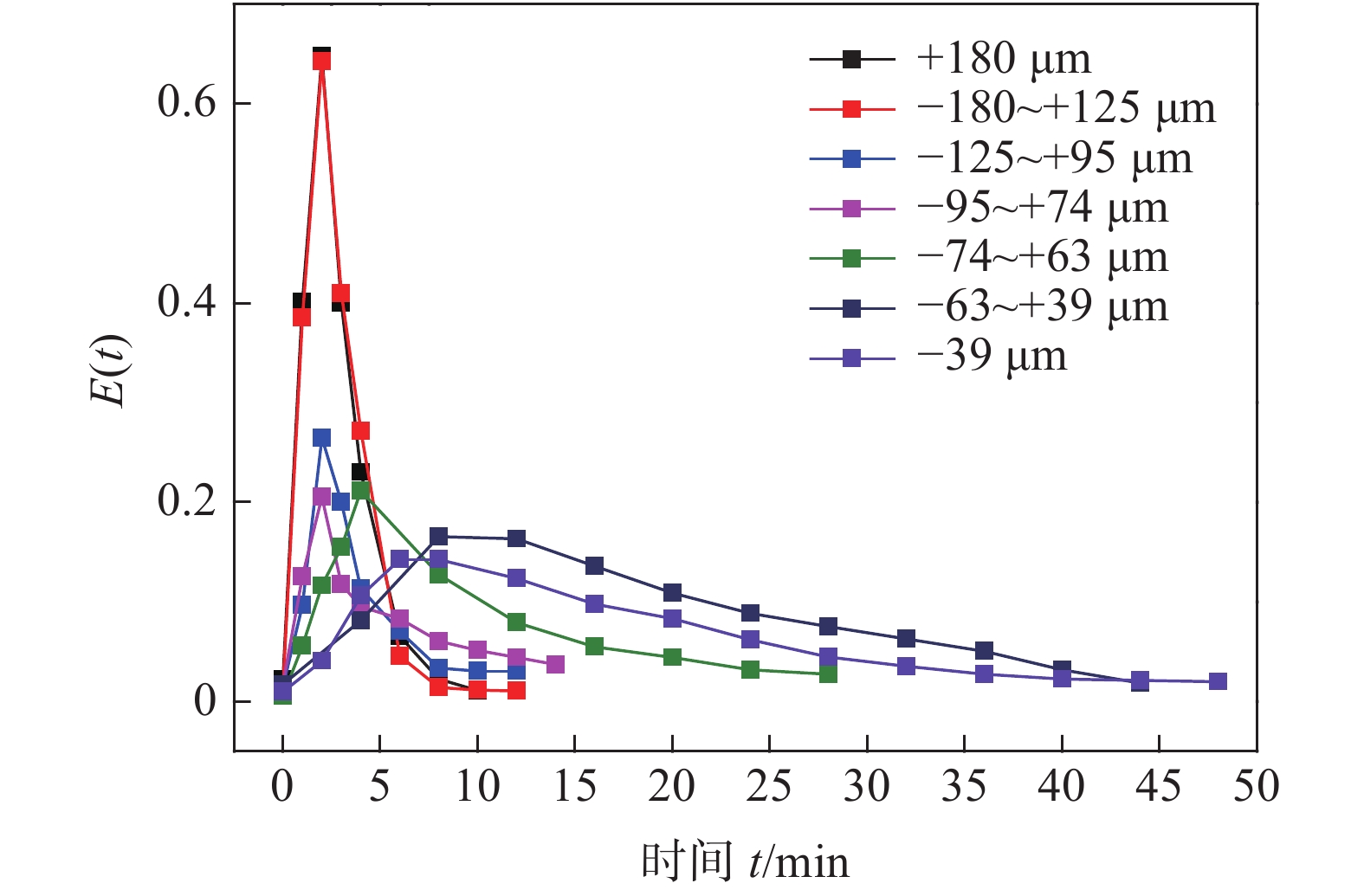
为了进一步考察各粒级颗粒在流化床内的返混程度,确定颗粒反应是否均匀充分,需要对其停留时间进行研究,试验采用脉冲示踪法。停留时间分布(RTD)是指出口寿命分布密度函数E(t),一般通过测量液体中示踪离子浓度来判断液体停留时间。
$$\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\! E(t){\rm{d}}t\!=\!\frac{{\text{单位时间流出的寿命在}}{{t}}{\text{到}}{{t}}+{\rm{d}}t{\text{之间的粒子数}}}{{\text{单位时间进入反应器的流体粒子总数}}}$$ (1) E(t)按定义满足归一化条件,即
$\displaystyle\int \nolimits_0^\infty {{E}}\left( {{t}} \right){\rm{d}}t$ =1。为便于对比,一般用粒子停留时间分布的均值来表示平均停留时间
${t_m}$ ,方差${\sigma ^2}$ 代表停留时间分散的程度。平均停留时间tm及方差
$\sigma^2 $ 的定义:$$ {t_m} = \mathop \int \limits_{\rm{0}}^\infty t{{E}}\left( {{t}} \right){\rm{d}}t $$ (2) $${\sigma ^2} = \int_0^\infty {(t - {t_m}} {)^2}E(t) = \int_0^\infty {{t^2}} E(t){\rm{d}}t - t_m^2$$ (3) 试验以钾离子为指示剂,试验结果如图5所示。
从图5可以看出,随着粒度减小,停留时间迅速上升,计算可知,+180 μm到−39 μm颗粒的平均停留时间tm分别为2.9、3.1、4.0、5.4、7.8、15.3、18.1 min,停留时间随粒度增加而显著减小,但从图5可以看出均存在着显著的拖尾现象。随着粒度越大,颗粒停留时间分布峰值出现得较早,表明在流化床内存在短路或者沟流现象,部分物料因短路快速排出,在床内的停留时间较短。同时,非短路物料停留时间延长,返混程度增加,使得停留时间分布分散。
同时可以看出,流态化浸出相对常规搅拌浸出所需时间(约90 min)大为缩短[2-3],但是粗颗粒的浸出效果较差,这是由于不同粒级的颗粒浸出动力学速率和实际停留时间存在矛盾,粒度越大则浸出动力学速率越慢,但其停留时间越短,导致流化浸出效果较差。此外流态化浸出的液固比较大,浸出液中钒浓度偏低,因此下一步考虑采用多级的流态化浸出,将浸出液循环以提高钒浓度。
3. 结论
1)计算出不同粒级下的的临界速率及带出速率,并对不同粒级的颗粒进行流化速率试验。粒度由−39 μm增大到+180 μm时,相应的表观流化速率由0.06 cm/s增长到0.94 cm/s。钒渣粒度与钒浸出率呈反比,−39 μm颗粒的尾渣残钒为0.54%,钒浸出率可达94%,而+180 μm颗粒浸出率则不到10%。
2)采用脉冲示踪法分析了颗粒的停留时间分布,确定不同粒级颗粒在一定流化速率下的停留时间变化规律。随着粒度从−39 μm增加到+180 μm,停留时间从15.3 min降低到2.9 min,且停留时间曲线分布峰值出现得较早,表明在流化床内存在短路或者沟流现象。而部分物料因短路快速排出,在床内的停留时间较短,非短路物料停留时间延长,返混程度增加,使得停留时间分布分散。
3)流态化浸出可显著改善浸出过程动力学,缩短浸出时间,−39 μm颗粒停留时间为18.1 min,尾渣残钒即可降低至0.54%,相对常规搅拌浸出所需时间大为缩短,但对物料的粒度要求较为严格,浸出过程存在液固比过大的问题,需要进一步研究。
-
表 1 钙化熟料主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of calcified vanadium slag clinker
% V2O5 TFe SiO2 MnO TiO2 Al2O3 MgO CaO Cr2O3 P2O5 16.10 25.50 13.77 9.17 11.52 1.52 1.86 8.16 1.91 0.13 表 2 钙化熟料粒度分布及密度
Table 2. Particle size distribution and density of calcified vanadium slag clinker
粒度/μm 含量/% 密度/(g·cm−3) +180 5.85 2.95 −180~+125 7.58 3.17 −125~+95 7.62 3.27 −95~+74 13.47 3.24 −74~+63 7.03 3.33 −63~+39 31.75 3.44 −39 26.70 3.58 表 3 各粒级颗粒的临界流化速度和带出速度
Table 3. Critical fluidization velocity and entrainment velocity of different size fractions
粒级/μm 平均粒径/μm 临界流化速度
Umf/(cm·s−1)带出速度
Ut/(cm·s−1)+180 180 0.47 2.31 −180~+125 150 0.37 2.02 −125~95 111 0.21 1.70 −95~+74 85 0.12 0.99 −74~+63 68 8.30×10−2 0.66 −63~+39 49 4.58×10−2 0.36 −39 39 3.00×10−2 0.24 -
[1] Yin Danfeng, Peng Yi, Sun Zhaohui, et al. Influencing factors of calcified roasting and thermal analysis to the process of vanadium slag produced from Pangang[J]. Metal Mine, 2012,(4):91−94. (尹丹凤, 彭毅, 孙朝晖, 等. 攀钢钒渣钙化焙烧影响因素研究及过程热分析[J]. 金属矿山, 2012,(4):91−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2012.04.024 [2] Fu Zibi. Experimental research on vanadium extraction by calcified roasting and acid leaching[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014,35(1):1−6. (付自碧. 钒渣钙化焙烧—酸浸提钒试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014,35(1):1−6. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.01.001 [3] Ye Lu. Research on dissolution of vanadium in acid leaching process of calcified roasting clinker with vanadium slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(5):20−25. (叶露. 钒渣钙化焙烧熟料酸浸过程钒溶解规律研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(5):20−25. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.05.004 [4] Li Hongzhong, Kwauk Mooson. Review and prospect of fluidization science and technology[J]. CIESC Jorunal, 2013,64(1):52−62. (李洪钟, 郭慕孙. 回眸与展望流态化科学与技术[J]. 化工学报, 2013,64(1):52−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2013.01.008 [5] (张楚. 快速流态化统一动力学模型的构建与模拟研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2013.)Zhang Chu. Research on the unified model for fast fluidization dynamics: construction and simulation[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2013. [6] Zhang Yuanfu, Chen Jiarong Huang Guangyu, et al. Study on fluidization leaching germanium-bearing smoke of zinc oxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 1999,23(2):90−94. (张元福, 陈家蓉, 黄光裕, 等. 氧化锌烟尘的流态化浸出研究[J]. 稀有金属, 1999,23(2):90−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.1999.02.003 [7] (王辉. 锌焙砂流态化浸出新工艺研究[C]//中国科学技术协会首届学术年会论文集. 杭州: 中国科学技术协会学会学术部, 1999: 993.)Wang Hui. Study on new fluidization leaching process of zinc calcine[C]//Proceedings of the First Academic Annual Meeting of China Association for Science and Technology. Hangzhou: Academic Department of China Association for Science and Technology, 1999: 993. [8] Ouyang Hongyong, Yang Zhi, Xiong Xueliang, et al. Study on elevated temperature curve and fluidization leaching behaviour of ilmenite in microwave field[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2010,30(2):73−75. (欧阳红勇, 杨智, 熊雪良, 等. 微波场中钛铁矿的升温曲线及流态化浸出行为研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2010,30(2):73−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2010.02.019 [9] Li Dongqin. Study on particles residence time distribution in low-temperature chlorinator[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(3):30−33. (李冬勤. 低温氯化炉内颗粒停留时间分布研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(3):30−33. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.03.005 [10] Li Xiaobin, Li Bin, Peng Zhihong, et al. Fluidization washing of the red mud[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2010,10(3):445−450. (李小斌, 李斌, 彭志宏, 等. 赤泥流态化洗涤[J]. 过程工程学报, 2010,10(3):445−450. [11] Jiao Weitang, Feng Xudong. Study of rtd in two-phase circulating fluidized bed[J]. Journal of Beijing Technology and Business University (Natural Science Edition), 2005,23(5):14−16. (焦伟堂, 冯旭东. 气液两相循环流化床停留时间分布的研究[J]. 北京工商大学学报(自然科学版), 2005,23(5):14−16. [12] (白瑞国, 李兰杰, 陈东辉, 等. 钒渣全湿法流态化提钒的方法, 中国专利: CN104674015A[P]. 2015.)Bai Ruiguo, Li Lanjie, Chen Donghui, et al. Wet fluidization method for vanadium extraction from vanadium slag, Chinese patent: CN104674015A[P]. 2015. [13] (郭继科, 付自碧, 殷兆迁, 等. 钠化钒渣流态化提钒的方法, 中国专利: CN106086441A[P]. 2016.)Guo Jike, Fu Zibi, Yin Zhaoqian, et al. Fluidized vanadium extraction from sodium vanadium slag, Chinese patent: CN106086441A[P]. 2016. -





 下载:
下载:













 下载:
下载: