Effect of Cr on the properties of 460 MPa anti-seismic and fire-resistant construction steel
-
摘要: 设计了两种不同Cr含量460 MPa级抗震耐火建筑用钢,并进行了室温和高温机械性能检测,0.4%Cr和0.8%Cr试验钢的性能均满足抗震钢屈强比≤0.83,并且耐火钢600 ℃保温3 h后屈服强度≥307 MPa的标准。JMatPro热力学软件对460 MPa级抗震耐火建筑用钢的析出相进行计算,采用光学显微镜和透射电子显微镜方法对钢中的析出相进行了分析。结果表明,试验钢随Cr含量的升高,室温抗拉强度升高,屈强比降低,具有更好的抗震性能。Cr的增加,减少了高温稳定性较差的析出相的析出,降低了析出相中Mo的含量,促使Mo更多地溶入基体中,从而提高了抗震钢的高温固溶强化作用和耐火性能。Abstract: The anti-seismic and fire-resistant 460 MPa construction steels with different Cr content were designed to analyze the microstructure, performance at room temperature and elevated temperature. Both 0.4%Cr and 0.8%Cr steels meet the standards of anti-seismic and fire-resistant steel, that is, yield ratio is less than 0.83 and yield strength is more than 307 MPa after 3 hours soaking at 600 ℃. The precipitations were simulated and analyzed by simulation software and using OM and TEM. It is concluded that increasing Cr content has an effect on improving of yield stress at room temperature and the reduction of yield strength ratio. With the increase of Cr content, high elevated temperature instability precipitations and the content of Mo in the precipitations can be decreased and Mo in the matrix can be raised. It has a positive effect on enhanced high elevated temperature solution strengthening and fire-resistance of construction steel because of Mo solid solutions.
-
Key words:
- construction steel /
- Cr /
- anti-seismic /
- fire-resistance /
- yield ratio
-
表 1 460 MPa级抗震耐火钢的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of 460 MPa anti-seismic and fire-resistant construction steel
% 钢号 C Si Mn Cr Mo Nb+Ti Cu+Ni Al P S 1# 0.055 0.25 1.39 0.40 0.27 0.047 0.55 0.03 0.0052 0.0041 2# 0.056 0.24 1.37 0.80 0.26 0.046 0.56 0.03 0.0052 0.0041 表 2 460 MPa级抗震耐火钢工艺参数
Table 2. Technology parameters of 460 MPa anti-seismic and fire-resistant construction steel
编号 一阶段开轧
温度/℃一阶段终轧
温度/℃二阶段开轧
温度/℃二阶段终轧
温度/℃二次轧制
厚度/mm开冷
温度/℃终冷
温度/℃冷却速率/
(℃·s−1)1# 1020 982 860 826 60 783 342 9.20 2# 1020 986 860 828 60 786 348 9.14 表 3 室温和高温机械性能
Table 3. Mechanical properties of experimental steels at room temperature and elevated temperature
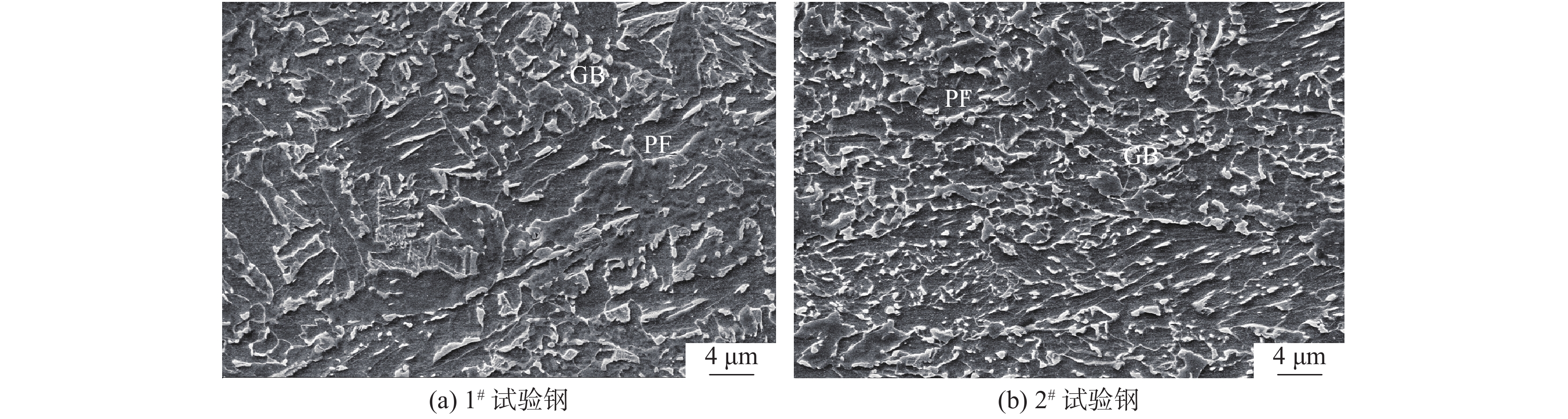
编号 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 屈强比 断后延伸率/% −40 ℃冲击功/J 高温屈服强度/MPa 高温抗拉强度/MPa 1# 538.7 693.2 0.78 21.0 209.6 379.8 429.9 2# 543.1 723.3 0.75 20.3 231.4 407.8 466.2 表 4 马奥岛平均尺寸与体积分数
Table 4. Average size and volume fraction of the MA constituents in the tested steels
编号 平均尺寸/μm 体积分数/% 1# 0.64 3.19 2# 0.49 2.23 表 5 试验钢大尺寸析出物平均尺寸和体积分数
Table 5. Average size and volume fraction of the MA constituents in the tested steels
编号 平均尺寸/nm 体积分数/% 1# 75.4 0.011 2# 67.9 0.008 -
[1] Ishii T, Fujisawa S, Ohmori A. Overview and application of steel materials for high-rise building[J]. JFE Technical Reports, 2008,(21):1−7. [2] Yoshifumi S. Recent trend and future direction in the technology for structural steels used in buildings[J]. Nippon Steel Technical Reports, 2007,(387):7−9. [3] Li Chunzhi, Ma Longteng, Tian Zhihong, et al. Research of high performance Q460 Structural steel with fire resistant and weather resistant[J]. China Metallurgy, 2018,28(7):19−23. (李春智, 马龙腾, 田志红, 等. 高性能Q460耐火耐候结构钢的研发[J]. 中国冶金, 2018,28(7):19−23. [4] Wan Weiguo, Wu Jiecai, Wu Baoqiao, et al. Research on properties and process of fire-resistant steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2005,15(7):33−37. (完卫国, 吴结才, 吴保桥, 等. 耐火钢的性能及工艺研究[J]. 中国冶金, 2005,15(7):33−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9356.2005.07.008 [5] Liu Qingchun, Yong Qilong, Zheng Zhiwang. Effect of vanadium on microstructure and high temperature properties of fire-resistant steels[J]. Iron and Steel, 2016,51(7):76−80. (刘庆春, 雍岐龙, 郑之旺. 钒对耐火钢显微组织及高温性能的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2016,51(7):76−80. [6] Ma Longteng, Wang Yanfeng, Di Guobiao, et al. Microstructural stability of Q60FRW fire-resistant steel[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2019,47(10):82−89. (马龙腾, 王彦峰, 狄国标, 等. Q460FRW耐火钢的组织稳定性[J]. 材料工程, 2019,47(10):82−89. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2018.001141 [7] Wang Lianqing, Ma Wenjiang, Wang Hongying. Research on the mechanical properties of 460 MPa fire-resistant steel at high temperature[J]. Steel Construction, 2019,34(11):110−112. (王连庆, 马文江, 王红缨. 460 MPa耐火钢高温力学性能研究[J]. 钢结构, 2019,34(11):110−112. [8] Zhang Zhengyan, Yong Qilong, Sun Xinjun. Microstructure and mechanical properties of precipitation strengthened fire-resistant Steel containing high Nb and low Mo[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2015,22(4):337−342. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(15)30009-1 [9] Liu Jixiong Wang Qingfeng Li Pinghe. Study on weld ability of high toughness refractory and weather resistant construction steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2002,37(12):40−44. (刘继雄, 王青峰, 李平和. 高性能耐火耐侯建筑用钢焊接性能研究[J]. 钢铁, 2002,37(12):40−44. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2002.12.012 [10] Gladman T. The physical metallurgy of microalloyed steels[M]. London: CRC Press LLC, 2002. [11] Li Pinghe, Liu Jixiong, Chen Xiao. Study on microstructure of high performance fire-resistant and weathering construction steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2005,40(6):72−75. (李平和, 刘继雄, 陈晓. 高性能耐火耐侯建筑结构用钢的显微组织研究[J]. 钢铁, 2005,40(6):72−75. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2005.06.020 [12] (王艳华. 超超临界汽轮机耐热钢组织和性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2006.)Wang Yanhua. Study on microstructure and properties of heat-resistant steel for ultra-supercritical steam[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2006. [13] (万荣春. 耐火钢中Mo的强化机理及其替代研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2012.)Wan Rongchun. Study on strengthening mechanism of Mo and replacement of Mo in f ire-resistant steel[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2012. -





 下载:
下载: