Effect of electroplating time and temperature on hydrogen diffusion coefficient of U78CrV steel
-
摘要: 氢能使钢材产生氢脆,导致材料的力学性能降低。而氢原子对钢的危害作用由扩散产生,因此了解氢原子在钢中的扩散行为对防治氢鼓泡和氢脆有重要意义。利用电化学氢渗透技术,施加恒定阴极电流,分别通过改变试样电镀时间、试验温度,对U78CrV钢进行氢渗透参数的研究。分析了不同电镀时间、不同试验温度对U78CrV钢的氢扩散系数的影响。研究结果表明:电镀时间过短和过长都会使得阳极极化电流降低,影响氢原子电离形成氢离子,当电镀时间360 s时形成的镍层效果最好。试验温度的升高会提高氢的渗透量和氢扩散系数,氢在U78CrV钢的扩散激活能为19 371 J/mol,氢扩散系数与温度的关系式为
$ \mathit{D}=3.14\times {10}^{-3}\exp\left(-\dfrac{19\;371}{\mathit{R}\mathit{T}}\right) $ 。Abstract: Hydrogen can cause hydrogen embrittlement of steel, resulting in a decrease in the material's mechanical properties. The harmful effect of hydrogen atoms on steel is caused by diffusion. Therefore, understanding the diffusion behavior of hydrogen atoms in steel is significant in preventing hydrogen bubbling and embrittlement. In this paper, electrochemical hydrogen permeation technology is used, a constant cathode current is applied, and the hydrogen permeation parameters of U78CrV steel are studied by changing the sample plating time and test temperature, respectively. The influence of different plating times and test temperatures on the hydrogen diffusion coefficient of U78CrV steel is analyzed. The research results show that too short and too long electroplating time will reduce the anodic polarization current and affect the ionization of hydrogen atoms to form hydrogen ions. When the electroplating time is 360 seconds, the nickel layer formed has the best effect. The increase in the test temperature will increase the hydrogen permeability and diffusion coefficient. The activation energy of hydrogen diffusion in U78CrV steel is 19371 J/mol. -
0. 引言
钢轨作为铁路运输系统的重要组成部分,是保证铁路运输安全及运量的首要因素。其主要组织为珠光体,珠光体组织对氢含量敏感性较高。氢渗透入钢的内部聚集产生白点,或在应力作用下使钢轨产生氢致断裂,造成氢脆,损害钢的物理特性,引起很多重大事故[1-2]。当金属和合金在含氢的环境中服役时,氢化物的形成、氢侵蚀和内部氢聚集会导致其强度降低、延展性下降,脆性增大和开裂[3],这是存在于钢等高强度材料中的常见效应,称为氢脆(HE)[4]。氢鼓泡是氢原子进入钢中,并在其中聚集形成的。因此了解氢原子在钢中的扩散对防治氢鼓泡和氢脆有重要意义。
氢在材料中的扩散系数是表征氢扩散行为的重要参数之一。测定氢在金属中扩散系数的方法包括渗透法、内耗法、热萃取法和同位素示踪法等[5]。其中渗透法应用较多,包括气相及电化学渗透法,通过确定原子渗透量来计算氢扩散系数。气相渗透法适用温度范围大,最高温度可达800 ℃。因此多用于高温测定氢扩散系数,但试验装置结构复杂,操作繁琐,损耗费用高。电化学渗透法由于Devanathan[6]的创新,利用双电解池法研究氢扩散,使得试验过程简便、重复性好并且测量精度高,在室温环境下被广泛应用。具体测定方式又包括逐步法、电化学交流法和非稳态时间滞后法等[5,7]。
由于环境污染增大了钢轨接触到氢的机会,使钢轨出现氢脆现象,但关于U78CrV钢轨钢氢脆的基础理论研究却很少。钢轨服役条件多为室温,因此采用电化学渗透技术进行研究。但电化学渗透技术对试样表面要求较高,试样表面催化层对试验影响很大。笔者采用非稳态时间滞后法测定U78CrV钢的氢扩散系数,改进参比电极减少与试样之间的距离,提高精度。采用镍作为催化层,研究电镀时间、温度对其氢扩散系数的影响,确定室温条件下的氢扩散系数,为防治氢脆提供理论数据。
1. 试验
1.1 试样准备
试验用的钢样为U78CrV钢(攀钢生产重轨钢),主要成分如表1所示。将其加工为厚度1.0 mm,尺寸为30 mm×30 mm的试样。
表 1 试样U78CrV钢的主要化学成分Table 1. Main chemical composition of U78CrV steel% C Si Mn Cr V S 0.78 0.70 0.79 0.32 0.08 0.012 试样由600#、800#、1000#、1500#和2000#的砂纸分别打磨,再用水溶性抛光膏抛光,去除试样的锈迹和污染物。用蒸馏水冲洗并吹干,再将试样放在无水乙醇中进行超声波清洗10 min,取出后用蒸馏水清洗,用烘箱烘干水分,备用。
1.2 氢扩散系数测定
1.2.1 双电解池氢扩散试验原理
本次试验采用双电解池氢扩散法测量材料的氢渗透特性。测试装置见图1,其工作原理为:双弹簧夹将金属薄片固定在两个电解池装置的中间连通位置(保证试样将两边电解池分隔)并用垫圈密封,倒入电解液,防止漏液。电流源连通的电解池称为阴极池即充氢侧,电化学工作站连通的电解池称为阳极池即释氢侧。试样的有效测试区域(与电解液接触面积)为4.91 cm2的圆形区域。
辅助电极作为阳极,试样作为阴极(充氢反应),采用恒电流源施加一定的直流电流,阴极表面将发生析氢反应,产生吸附在试样表面的氢原子,大部分氢原子吸附在表面的过程中会复合成氢分子逸出,其余部分的氢原子在渗透作用下向试样对面渗透扩散。
阳极池发生释氢反应。辅助电极作为阴极,试样作为阳极,电化学工作站在中间施加恒定的电位,使通过扩散作用出现在阳极的氢原子被氧化成H+,电化学工作站监测记录产生的阳极电流随充氢时间变化的瞬时曲线,由此得出试样的氢扩散系数。试样的阳极面在阳极极化过程中发生氧化反应,产生的极化电流会影响H原子氧化产生的极化电流。
1.2.2 电镀试验
氧化反应会使试样阳极面产生一层氧化膜,妨碍H原子的渗出,将导致氢扩散系数的检测值偏低。渗透到阳极面的H原子会继续复合成氢气,并在其表面逸出,影响H原子的极化电流,造成检测值不准确。此外阳极面还易发生电化学腐蚀。因此可在试样阳极面制备电镀催化层来降低阳极极化和电化学腐蚀对试验的影响,同时防止试样本身产生的阳极极化电流导致的氢渗透电流测量误差。催化层通常为钯或镍,二者效果无太大区别,考虑经济因素,催化层采用镍层。镀镍可以避免试样被腐蚀(阳极溶解),而且H对镍具有较高的超电位,可以防止原子氢复合,产生阳极电流,保证试验结果的准确性。
具体电镀工艺包括:①除油:配制80 g/L的NaOH溶液超声波清洗试样3 min;②侵蚀:再使用37%盐酸处理试样15 s,清理钢试样表面的氧化膜,取出后冲洗掉试样表面盐酸,并用烘箱烘干水分;③电镀:处理完成的试样为阴极,铂片为阳极,采用10 mA/cm2的恒定电流密度在电镀液(配比为每升含250 g NiSO4:7H2O+45 gNiCl2-6H2O+40 gH3BO4)中进行电镀。通过改变电镀时间的长短,探究其对氢扩散试验的影响。电镀结束后取出试样,用去离子水清洗并吹干。
1.2.3 氢扩散试验
在氢扩散试验中,阴极池采用0.5 mol/L的H2SO4溶液作为充氢电解液,并添加2 g/L的硫脲作为毒化剂,使得H原子更易渗入试样。阳极池电解液采用0.2 mol/L的NaOH溶液。饱和甘汞电极(SCE)作为三电极中的参比电极(RE),铂片作为三电极的辅助电极(CE)。为保证辅助电极的电流密度均匀降低极化,铂片面积为9 cm2。阳极池施加恒电位阳极极化,极化电位为300 mV(vsSCE)。试验之前向电解池中通氩气30 min以排除溶解氧对阳极氧化的影响,排气完成后将电解池密封,整个试验在密封环境中完成。连接好整个试验装置,在试样的阳极面施加氧化电位300 mV(vsSCE),等阳极池背底电流降到2 μA/cm2以下时,开启恒电流源在试样阴极面施加恒电流进行充氢。
本次试验分为两部分:①探究电镀时间对试验的影响,时间分别为50、120、180、360 s和600 s,充氢电流密度为10 mA/cm2,试样厚度为1 mm,试验温度为25 ℃;②探究温度对试验的影响,试验温度分别为25、35、45、55、65 ℃,试验时间为3 h,试样厚度为1 mm,充氢电流密度为10 mA/cm2。由式(1)、(2)可得到氢渗透的动力学参数[8]。
$$ {N}_{\infty }=\frac{{I}_{\infty }}{FA}=\frac{{J}_{\infty }}{F} $$ (1) $$ {D}_{{\rm{eff}}}={L}^{2}/6{t}_{L} $$ (2) 式中,
$ {N}_{\infty } $ 为氢扩散通量,mol/(cm2·s);$ {I}_{\infty } $ 为饱和阳极电流,A;A为试样与溶液的接触面积,cm2;$ {J}_{\infty } $ 为饱和阳极电流密度,A/cm2;$ F $ 为法拉第常数,96485 C/mol;$ L $ 为试样的厚度,mm;$ {t}_{L} $ 为滞后时间($ \dfrac{I}{{I}_{\infty }}=0.63 $ 的时间,$ I $ 为阳极电流),s;$ {D}_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{f}\mathrm{f}} $ 为氢的有效扩散系数,cm2/s。2. 结果与讨论
2.1 电镀时间的影响
使用电化学渗透双电解池法测定试样的氢扩散系数之前,需要对试样的阳极面进行镀镍处理。电镀时间会影响镍在试样阳极面的附着程度,因此本试验探究电镀时间(50、120、180、360 s和600 s)对氢扩散试验的影响。
由图2可以看出,电镀时间过短或者过长都会影响H原子被电离成H+过程。电镀时间过短,试样表面镍层较薄且不均匀。此时,镍层无法抑制H原子复合成H分子,导致阳极电流较低,影响试验稳定性。电镀时间过长,试样表面镍层过厚,H原子无法穿透镍层,不能在阳极面被电离成H+,同样会造成阳极极化电流偏低。
由图2(a)可知,电镀时间为50 s时,测得的阳极极化电流极低,而且呈下降趋势,说明此时测得的阳极极化电流不是电解H形成的电流,可能是溶液中的背底电流。图2(b)和(c)中极化电流呈上升趋势,图2(b)中曲线变化幅度大,极化电流也较低,说明阳极侧有H原子被电离,但数量较少而且不够稳定;图2(c)中极化电流增大,H原子被电离数目增多,但无法获得饱和阳极电流。图2(d)显示试样被电镀360 s后,试验测得的阳极电流持续增大,且可以检测到饱和阳极电流,可以很好地完成渗氢试验。电镀600 s后(图2(e)),阳极极化电流值极小,曲线呈上升趋势,变化幅度较大,说明镍层阻碍了H原子的移动,大部分H原子无法穿透镍层,被电离的H原子数量减少。
2.2 试验温度的影响
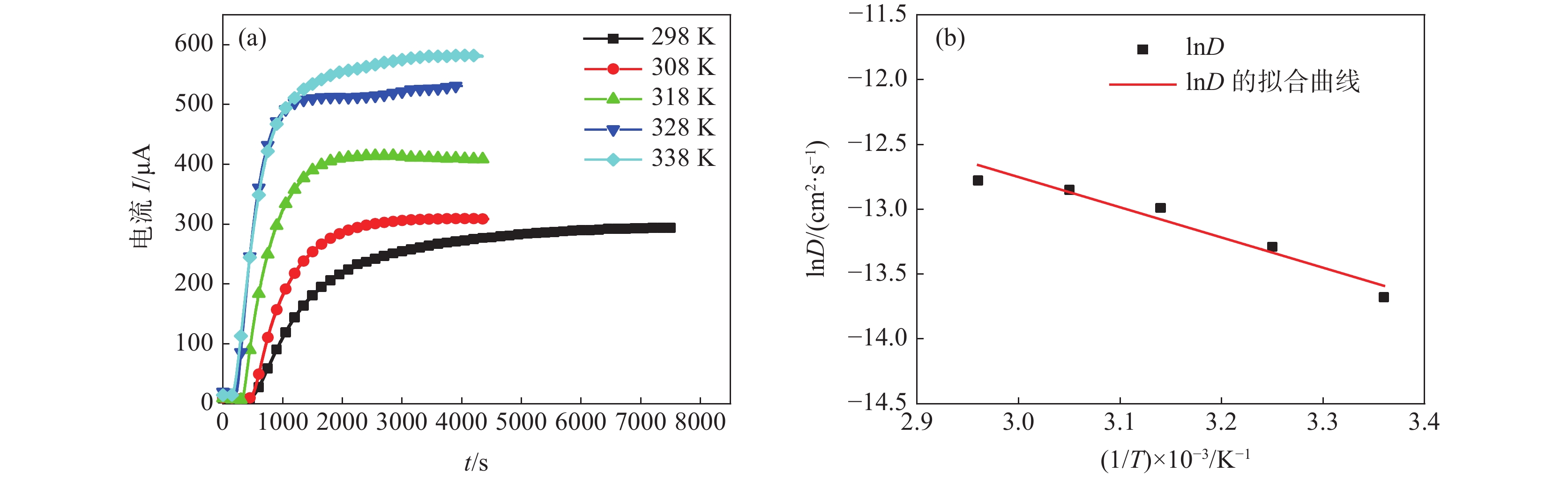
试验获得的阳极极化电流随阴极充氢时间的变化如图3(a)所示。根据公式(1)和(2)所求得的氢扩散参数列于表2。由图3(a)可知,阳极极化曲线达到稳态时的稳态电流值随测试温度(25~65 ℃)的升高而变大,氢扩散通量也随之增大,同时氢扩散的穿透时间随之减小。这表明随着温度的升高,渗透进入试样的氢原子数量增多,扩散到试样阳极面,被电离的氢原子数量也变多,所以会出现稳态电流和氢扩散通量增大的现象。此外,穿透时间随温度的上升而减小说明升高温度会使氢原子在材料内部晶格间的扩散速率增加,减少了扩散渗透的时间。
表 2 U78CrV钢在不同温度时的氢扩散参数Table 2. Hydrogen diffusion parameters of U78CrV steel at different temperaturesT/℃ $ {N}_{\infty } $×1010/(mol∙cm−2∙s−1) $ {t}_{L} $/s $ {D}_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{f}\mathrm{f}} $×106/(cm2∙s−1) 25 6.20 1548 1.14 35 6.51 1065 1.69 45 8.64 771 2.29 55 11.20 680 2.60 65 12.25 627 2.82 温度的升高也使U78CrV钢的氢扩散系数增大,根据扩散理论,氢的扩散系数与温度的关系符合Arrehnius公式,即
$$ D={D}_{0}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p}(-Q/{\rm{R}}T) $$ (3) 其中,
$ {D}_{0} $ 为扩散指数,cm2/s;$ Q $ 为扩散激活能,J;R为气体常数,8.314 J/(mol·K)。利用表2中的数据可以得出
$ \ln D $ 与$ 1/T $ 的关系,如图3(b)所示。由图3(b)可以看出,$ \ln D $ 与$ 1/T $ 呈良好的线性关系。对直线进行拟合可以求出氢原子在U78CrV钢中的扩散激活能$ Q= $ 19371 J/mol,扩散指数$ {D}_{0} $ =3.14×10−3cm2/s。由此可以得出,氢在U78CrV钢中的扩散系数和温度的关系式为:$$ D=3.14\times {10}^{-3}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p}\left(-\frac{19\;371}{RT}\right) $$ (4) 3. 结论
1)使用电化学渗透双电解池法测定试样的氢扩散系数之前,需对试样阳极面进行镀镍处理。试验表明电镀时间过短或者过长都会影响H原子被电离成H+的行为,造成阳极极化电流降低。当电镀时间为360 s时,可以形成稳定的阳极电流,说明此镍层可以抑制H原子复合成氢分子,而且不会阻碍H原子的移动。
2)建立了双电解池氢扩散装置,研究了不同温度下的氢扩散系数,发现升高温度将增加氢扩散通量、减少扩散时间,扩散激活能
$ Q= $ 19371 J/mol,扩散指数$ {D}_{0} $ =3.14×10−3cm2/s,氢扩散系数D会随温度的升高而增大,得到关系式:$ D=3.14\times {10}^{-3}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{x}\mathrm{p}\left(-\dfrac{19\;371}{RT}\right) $ 。利用氢扩散系数,可以预判重轨钢U78CrV钢在不同温度下的氢脆敏感性,对实际生产和维护具有重要意义。 -
表 1 试样U78CrV钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of U78CrV steel
% C Si Mn Cr V S 0.78 0.70 0.79 0.32 0.08 0.012 表 2 U78CrV钢在不同温度时的氢扩散参数
Table 2. Hydrogen diffusion parameters of U78CrV steel at different temperatures
T/℃ $ {N}_{\infty } $×1010/(mol∙cm−2∙s−1) $ {t}_{L} $/s $ {D}_{\mathrm{e}\mathrm{f}\mathrm{f}} $×106/(cm2∙s−1) 25 6.20 1548 1.14 35 6.51 1065 1.69 45 8.64 771 2.29 55 11.20 680 2.60 65 12.25 627 2.82 -
[1] Zhang Jianliang, Xiao Qing'an, Xiao Lei, et al. Development and steelmaking application of magnesium containing alkaline earth metal composite alloy[J]. Ferroalloy, 2001,4(159):1−7. (张建良, 肖清安, 肖雷, 等. 含镁碱土金属复合合金的开发与炼钢应用[J]. 铁合金, 2001,4(159):1−7. [2] Wang Zhen, Liu Jing, Zhang Shiqi, et al. Effect of strain rate on hydrogen embrittlement sensitivity of hydrogen precharged DP780 steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Corrosion and Protection, 2022,42(1):106−112. (王贞, 刘静, 张施琦, 等. 应变速率对预充氢DP780钢氢脆敏感性的影响[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2022,42(1):106−112. doi: 10.11902/1005.4537.2020.259 [3] Saini N, Pandey C, Mahapatra M M. Effect of diffusible hydrogen content on embrittlement of P92 steel[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(27):17328−17338. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.05.214 [4] Dwivedi S K, Vishwakarma M. Hydrogen embrittlement in different materials: A review[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018,43(46):21603−21616. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.09.201 [5] 崔国文. 缺陷、扩散与烧结[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1990.Cui Guowen. Defects, diffusion and sintering [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1990. [6] Devanathan M A V, Stachurski M. The adsorption and diffusion of electrolytic hydrogen in palladium[C]//Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1962, 270(1340): 90-102. [7] Haq A J, Muzaka K, Dunne D P, et al. Effect of microstructure and composition on hydrogen permeation in X70 pipeline steels[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013,38(5):2544−2556. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.11.127 [8] 褚武杨. 氢损伤和滞后断裂[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1988.Chu Wuyang. Hydrogen damage and delayed fracture [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1988. -






 下载:
下载:
































 下载:
下载: