Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni3Al based intermetallic designed based on 'cluster plus connected atom' model
-
摘要: Ni3Al金属间化合物的室温脆性问题极大地限制了其应用。通过“团簇加连接原子”模型对Ni3Al金属间化合物进行成分和结构解析及成分设计,通过Co、Fe部分取代团簇壳层上的Ni,Ti部分取代连接原子Al,设计出六种合金。并对其显微组织及力学性能进行了表征。结果表明:六种合金的显微组织均由Ni3Al相(γ′相)、NiAl相(BCC)和少量共晶析出的第三相所构成,且通过TEM分析证实了基体为Ni3Al相。相比于Ni3Al金属间化合物,合金的室温强度、硬度和塑性均有大幅度的提升。分析其原因是由于基体为Ni3Al相,保持了合金基体的强度和硬度,当Ni3Al基体中析出少量的BCC相时,进一步提高合金的强度和硬度,而当BCC含量过高时,合金的强度和硬度降低,塑性升高。
-
关键词:
- Ni3Al金属间化合物 /
- "团簇加连接原子"模型 /
- 相分析 /
- 力学性能
Abstract: The room temperature brittleness of Ni3Al intermetallic compounds significantly limits its application. Accordingly, in this paper, the composition and structure of Ni3Al intermetallic compounds are analyzed, and the composition is designed by the 'cluster plus connected atom' model. Six alloys were designed by replacing some Ni on the cluster shell with Co and Fe and replacing some connecting atom Al with Ti. Simultaneously the microstructure and mechanical properties of these alloys were characterized. The results show that the microstructures of all six alloys are composed of the Ni3Al phase (γ′ phase), NiAl phase (BCC), and a small amount of eutectic precipitated third phase, and the formation of the Ni3Al phase is confirmed by TEM analysis. The alloy designed in this paper has improved room temperature strength, hardness, and plasticity compared to the Ni3Al intermetallic compound. The reason is that the formation of the Ni3Al phase as the matrix improves the strength and hardness. When a small amount of BCC phase precipitates in the Ni3Al matrix, it helps further to improve the strength and hardness of the alloy. In comparison, the high concentration of BCC decreased the strength and hardness and increased the plasticity. -
0. 引言
Ni3Al作为一种典型的金属间化合物,具有良好的机械性能,例如高温强度高、出色的抗氧化性和耐腐蚀性以及优异的抗蠕变性能等[1-3],此外,Ni3Al在一定温度范围内屈服强度随着温度升高而增加,因此成为了最具吸引力的金属间化合物之一。但是由于金属间化合物共有的本征脆性问题,极大地限制了它的应用,因此如何改善Ni3Al基金属间化合物的塑性是当前领域的研究热点。
早期研究发现,在Ni3Al中添加微量的B元素可以很好地改善其塑性[4-6]。然而其在室温下强度和延展性不能很好地协调,且影响了合金的热稳定性,以至于这种改性方式不能被广泛使用[7]。文献[8]以最近邻配位多面体为基元描述复杂合金相的结构特征,总结出合金相的常见团簇类型,提出了一种基于团簇的固体结构描述方法,即“团簇加连接原子”模型,可用于描述各类复杂合金的短结构特征。该模型已经在部分准晶[9-10]、非晶[11-12]和固溶体合金[13-16]之中得到了验证,但对于金属间化合物的成分设计则较少应用。
为了更好地协调Ni3Al金属间化合物室温下的的强度和延展性,笔者尝试采用“团簇加连接原子”模型对Ni3Al金属间化合物进行结构解析和成分设计,并且通过对比分析不同成分合金的微观组织和性能,得出合金成分设计对微观组织和性能的影响,结果表明设计的合金显著改善了Ni3Al金属间化合物的室温脆性问题。也为Ni3Al金属间化合物的室温强塑性改善提供了一种有效的设计思路。
1. 基于“团簇加连接原子”模型的Ni3Al成分解析及设计
“团簇加连接原子”模型中的团簇是指以某个原子为中心的由截断距离[17]所决定的最近邻的配位多面体,而连接原子则位于团簇之间的间隙位置,即次近邻壳层,表示成统一的团簇成分式即:[团簇](连接原子)x,其中x为连接原子的个数。基于该模型对Ni3Al金属间化合物进行解析,Ni3Al为Cu3Au型L12面心立方结构(γ′相),其晶体结构如图1所示。Ni3Al中镍的含量占主体,因此以Al为中心原子,此时最邻近的原子壳层依次为Ni12,Al6和Ni24壳层。它们的位置距离中心原子为0.25258 nm,0.35720 nm,0.43748 nm。根据其截断距离,可确定团簇结构为立方八面体团簇[Al-Ni12],剩余的Al原子则作为连接原子,最终得到的团簇堆垛模式为[Al-Ni12]Al3[18]。依据Ni3Al的团簇结构表达式,对其成分进行设计。Ti和Al元素性质相似,可用Ti替代部分Al元素,以减少其在基体中的溶解度,促进γ′相的析出,增强合金的强度和硬度[19]。Fe和Co的性质和Ni相似,在原子替换时可最大程度的保障Ni3Al的特征,并且Fe和Co部分替换Ni会降低有序结构的电子密度,有助于抑制脆性六角形或四方有序相的形成。同时为保证Ni3Al的晶体结构,Ni原子的个数必须大于等于6,据此设计出[Al-(Ni6-Co5-Fe)]AlTi2、[Al-(Ni6-Co5-Fe)]Al2Ti、[Al-(Ni7-Co4-Fe)]AlTi2、[Al-(Ni7-Co4-Fe)]Al2Ti、[Al-(Ni8-Co3-Fe)]AlTi2和[Al-(Ni8-Co3-Fe)]Al2Ti六种成分式,同时加入少量的硼(~2%,原子分数)以改善合金的晶界塑性,并分别编号为1#、2#、3#、4#、5#、6#,具体成分列于表1。
2. 材料制备及试验方法
2.1 样品制备
在纯氩气保护下用水冷铜坩埚非自耗真空电弧熔炼方法制备合金,严格按照设计目标值配料,全部采用高纯原料颗粒(临沂研创新材料科技有限公司)配料,所用高纯金属原料的纯度为Ni:99.95% , Fe:99.9%, Co:99.98%,Al:99.99%,Ti:99.9%和B:99.95%,熔炼真空度3 mPa,温度1550 ℃左右,且为保证合金的均匀性,至少经过6次反复熔炼,熔炼后铸态样品的的实际化学成分如表2所示。
表 2 各合金的实际化学成分组成Table 2. Actual chemical compositions of each alloy% 合金 Ni Co Fe Al Ti 1# 41.535 33.998 6.14 6.666 11.661 2# 42.519 35.496 6.331 10.099 5.555 3# 47.751 27.994 6.835 6.409 11.011 4# 49.099 28.429 6.502 10.084 5.886 5# 54.601 21.197 6.371 6.36 11.471 6# 56.407 21.356 6.468 9.97 5.799 2.2 微观组织分析
样品经打磨抛光后通过X射线衍射分析技术(XRD, Empyrean, PANalytical B·V, Netherlands)分析合金的晶体结构和相组成,Cu-Kα(λ=0.154056 nm)作为入射射线,扫描速度为4 °/min,扫描角度范围为20 °~110 °。用X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF,Panaco,Axios,Netherlands)测量合金实际的化学组成成分。
表 1 基于团簇加连接原子模型设计的合金成分Table 1. Alloy composition list based on cluster plus linked atom model合金 原子替换 原子百分比/% 加B后的原子百分比/% 加B后的质量百分比/% 1# [Al-(Ni6-Co5-Fe)]AlTi2 Ni37.5Co31.25Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5 (Ni37.5Co31.25Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5)98B2 Ni41.2Co34.4Fe6.5Al6.3Ti11.2B0.4 2# [Al-(Ni6-Co5-Fe)]Al2Ti Ni37.5Co31.25Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.2 (Ni37.5Co31.25Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.25)98B Ni42.2Co35.3Fe6.7Al9.7Ti5.7B0.4 3# [Al-(Ni7-Co4-Fe)]AlTi2 Ni43.75Co25Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5 (Ni43.75Co25Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5)98B2 Ni48Co27.6Fe6.5Al6.3Ti11.2B0.4 4# [Al-(Ni7-Co4-Fe)]Al2Ti Ni43.75Co25Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.25 (Ni43.75Co25Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.25)98B2 Ni49.2Co28.3Fe6.7Al9.7Ti5.7B0.4 5# [Al-(Ni8-Co3-Fe)]AlTi2 Ni50Co18.75Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5 (Ni50Co18.75Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5)98B2 Ni54.9Co20.7Fe6.5Al6.3Ti11.2B0.4 6# [Al-(Ni8-Co3-Fe)]Al2Ti Ni50Co18.75Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.25 (Ni50Co18.75Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.25)98B2 Ni56.3Co21.2Fe6.7Al9.7Ti5.7B0.4 将打磨抛光后的样品进行腐蚀,腐蚀液成分为5 g FeCl3+25 mL HCl+25 mL C2H5OH,腐蚀时间控制在5~10 s,随后用金相显微镜(OM,LEICA,DMi8,Germany)观察其显微组织。用场发射电子探针(EPMA, JXA-8530F PLUS, Jeol, Japan)测试合金中元素的分布和化学组成。用电解双喷法制备透射样品(电解双喷仪,TenuPol-5,Struers,Denmark),工作电压为20 kV,工作温度为243 K,双喷液为体积分数为8%的高氯酸酒精溶液,双喷完成后用酒精清洗。使用透射电子显微镜(Transmission Electron Microscopy, TEM)观察合金的微观形貌,使用其附带的EDS分析元素组成和分布,使用高分辨TEM图像(High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy, HRTEM)和选区电子衍射花样(Selected Area Electron Diffraction, SAED)分析合金晶体结构。
2.3 力学性能表征
通过电火花切割机在每个合金上取出5个Ø4 mm×6 mm的小圆柱,并对样品表面进行打磨,随后对其进行室温压缩(CSS电子万能试验机,CSS-7210,长春试验机研究所,中国长春),压缩速度为0.5 mm/min。
使用HVS-1000A数显显微硬度计测量合金的硬度,测量过程中加载载荷500 g,并保持15 s,每个样品至少测量七个点,去掉最大值和最小值,然后取其剩余五个的平均值作为合金维氏硬度。
3. 试验结果及讨论
3.1 X射线衍射分析
图2为合金的XRD衍射图谱,由图2可知,合金主要由Ni3Al(γ′相)和NiAl(BCC)两相构成。与Ni3Al的标准衍射峰相对比,试验所得衍射峰和标准峰位对比略有偏移,是由结构中部分原子被替换产生了不同程度的晶格畸变所致。其中1#、3#和5#合金结构中的3个连接原子Al被(Al+2Ti)替换,其Ti含量较高,合金中的Ni3Al的衍射峰较强;而2#、4#和6#合金中3个连接原子Al 被(2Al+Ti)替代,Al含量较高,其衍射图中NiAl相衍射峰较强。
3.2 微观组织分析
从图3可以看出合金的显微组织均以Ni3Al相为基体,部分NiAl相析出,且含少量的第三相,且每种合金的相含量均有所不同(见表3)。当合金中Ti、Al含量恒定不变时,随着Ni含量的增加,Ni3Al相的体积分数逐渐增加,相对的NiAl相的体积分数逐渐减少。5#合金中Ni3Al的体积分数明显高于1#和3#合金,同时6#合金中Ni3Al的体积分数也明显高于2#和4#合金。而Ti元素相较于Al元素也促进了Ni3Al相的形成,1#、3#、5#合金中含有较多的Ti,其Ni3Al相的体积分数明显高于2#、4#、6#合金。
表 3 合金各相所占体积分数Table 3. Volume fraction of each phase in the alloy合金 体积分数/% NiAl相 Ni3Al相 第三相 1# 29 65 6 2# 46 50 4 3# 27 68 5 4# 44 52 4 5# 8 88 4 6# 42 54 4 图4显示,1#合金中Ni3Al基体中富集Ni和Al元素,还含有一部分Ti和Co元素,以及微量的Fe元素,B元素含量极少。NiAl相中富集Ni元素和Al元素,Co、Ti元素含量较Ni3Al相更少,还含有微量的Fe元素,B元素含量极少。合金中含有部分共晶析出的第三相,是由Co、Ti、Fe、B元素富集产生,Ni、Al含量极少。2#合金中Ni3Al相和NiAl相元素分布和1#合金类似,合金中仍含有部分共晶区域所形成的第三相,如图4(b)所示。
为了进一步表征合金的显微组织,对合金样品进行了TEM测试。图5为1#合金铸态TEM图,分别在区域i和区域ⅱ进行选区电子衍射(SAED),其衍射图如图5(b)和5(k)所示。
 图 5 1#合金在不同区域的明场相(a和m),位置i和ii和iii的选区电子衍射花样(b,k,n),位置i的高分辨图像以及在图中区域Ⅱ傅里叶变化图像(c),位置ii的高分辨图像以及在图中Ⅲ区域的傅里叶变化图像(l),位置iii的高分辨图像以及在图中Ⅴ区域的傅里叶变化图像(o),Ⅰ区域的成分分布(d~j),区域Ⅳ成分分布(p~u)Figure 5. The bright field phase (a and m) of 1# alloy in different regions, the selected area electron diffraction pattern (b, k, n) of positions i and ii and iii, the high-resolution image of position i and the FFT image (c) of region II in the figure, the high-resolution image of position ii and the FFT image (l) of region III in the figure, the high-resolution image of position iii and the FFT image (o) of region V in the figure, and the composition distribution (d-J) of the region I, regional IV component distribution (p-u)
图 5 1#合金在不同区域的明场相(a和m),位置i和ii和iii的选区电子衍射花样(b,k,n),位置i的高分辨图像以及在图中区域Ⅱ傅里叶变化图像(c),位置ii的高分辨图像以及在图中Ⅲ区域的傅里叶变化图像(l),位置iii的高分辨图像以及在图中Ⅴ区域的傅里叶变化图像(o),Ⅰ区域的成分分布(d~j),区域Ⅳ成分分布(p~u)Figure 5. The bright field phase (a and m) of 1# alloy in different regions, the selected area electron diffraction pattern (b, k, n) of positions i and ii and iii, the high-resolution image of position i and the FFT image (c) of region II in the figure, the high-resolution image of position ii and the FFT image (l) of region III in the figure, the high-resolution image of position iii and the FFT image (o) of region V in the figure, and the composition distribution (d-J) of the region I, regional IV component distribution (p-u)图5中区域i的SADE图显示出在原有的衍射斑点中还存在一些较弱衍射花样,是在FCC基体中形成的有序化合物,即L12结构,晶带轴为[110]。在该区域选区拍摄高分辨图像,如图5(c)所示。选取区域Ⅱ进行傅里叶转变(FFT),出现了γ′相的衍射斑点,证明了基体为Ni3Al结构(γ′相)。区域ⅱ的衍射花样如图5(k)所示,其为NiAl相在[100]晶带轴下的电子衍射花样,其高分辨图中无其他相的存在,如图5(l)所示。同时在合金中还析出一些共晶组织,主要由Co和Ti元素形成,其明场像如图5(m)所示。通过其SAED、HR-TEM图及对应选区傅里叶转变图得出,此共晶相的原子排列更密,晶面间距较大,在不同方向分别为0.9167 nm和0.8808 nm。
3.3 合金的铸态力学性能
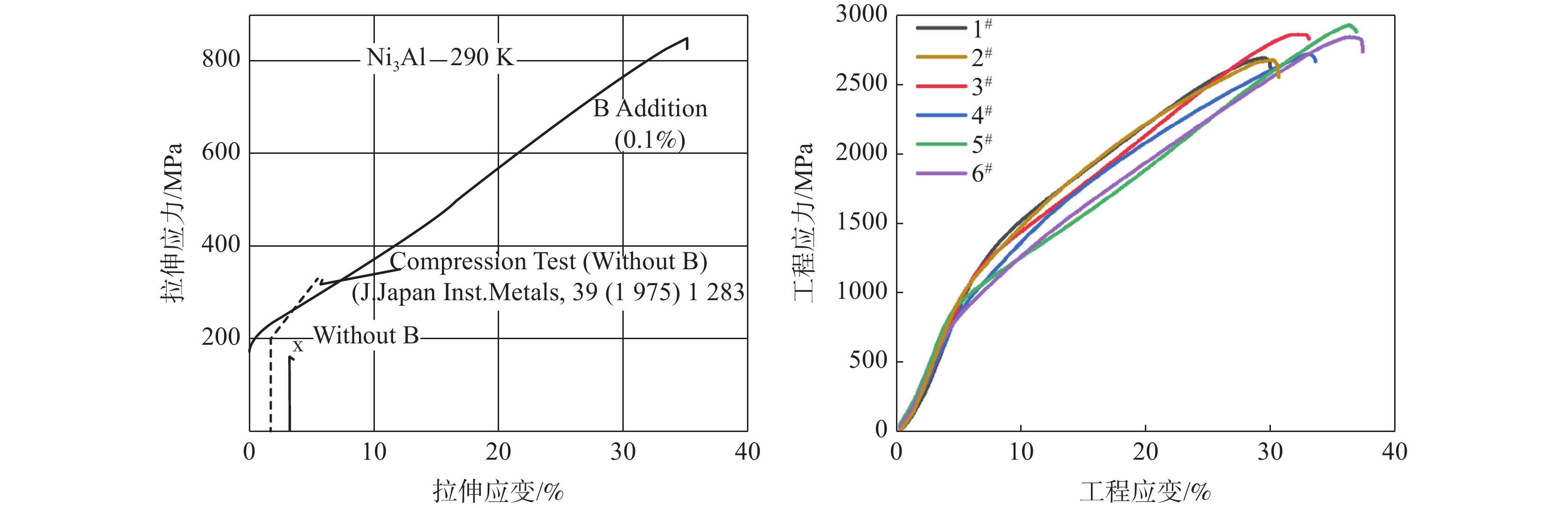
Ni3Al金属间化合物和设计合金的室温压缩曲线见图6,可见设计合金的屈服强度和塑性相较于Ni3Al金属间化合物都有了很好的提升。其中1#合金的屈服强度最高,达到1350 MPa,而Ni3Al金属间化合物的室温压缩屈服强度仅为200 MPa;6#样品的塑性较好,最大压缩率为37%,而Ni3Al金属间化合物的塑性几乎没有。通过表4可以看出所有合金的显微硬度(HV)均在470 之上,最高可以达到558 ,与Ni3Al金属间化合物(HV 160)相比,其室温下的显微硬度也显著提高[7]。
表 4 合金的显微硬度Table 4. Microhardness of alloy合金 显微硬度(HV) 屈服强度/MPa 最大压缩率/% 1# 558 1350 29 2# 500 1200 30 3# 528 1250 34 4# 484 1050 35 5# 508 1100 37 6# 470 900 37 综前文所述,所设计合金均以Ni3Al(γ′相)为基体,γ′相的形成提高了基体的强度和硬度,降低了基体的塑性。当基体中析出少量NiAl(BCC)相时,可以对合金起到进一步强化作用,合金的屈服强度和硬度均有所提升,1#合金的强度和硬度高于3#和5#合金。而当NiAl含量超过30%时,合金的强度和硬度开始降低,而塑性有所提高,2#、4#、6#合金的强度和硬度低于1#、3#、5#,而塑性相对较高[20-22]。
4. 结论
1) 根据“团簇加连接原子”模型对Ni3Al基金属间化合物进行成分设计,制备出六种合金,其金相组织主要由Ni3Al相(γ′相)和NiAl相(BCC)以及少量共晶析出的第三相组成。
2) 合金中部分Ti元素替换连接原子位置的Al元素有助于促进FCC相的形成。合金中Al、Ti元素的量恒定不变时,Ni元素含量的提高有助于FCC相的形成。
3) 合金的HRTEM图中证实了合金中基体为γ′相。
4) 所设计的合金相比于Ni3Al金属间化合物,强度、硬度和塑性均有所提升。
5) Ni3Al(γ′相)基体的形成提高了基体的强度和硬度,塑性相对较低。当γ′相基体中析出少量的BCC相时,有助于进一步提高合金的强度和硬度。而当BCC含量过高(超过30%)时,强度和硬度又开始降低,塑性升高。
-
图 5 1#合金在不同区域的明场相(a和m),位置i和ii和iii的选区电子衍射花样(b,k,n),位置i的高分辨图像以及在图中区域Ⅱ傅里叶变化图像(c),位置ii的高分辨图像以及在图中Ⅲ区域的傅里叶变化图像(l),位置iii的高分辨图像以及在图中Ⅴ区域的傅里叶变化图像(o),Ⅰ区域的成分分布(d~j),区域Ⅳ成分分布(p~u)
Figure 5. The bright field phase (a and m) of 1# alloy in different regions, the selected area electron diffraction pattern (b, k, n) of positions i and ii and iii, the high-resolution image of position i and the FFT image (c) of region II in the figure, the high-resolution image of position ii and the FFT image (l) of region III in the figure, the high-resolution image of position iii and the FFT image (o) of region V in the figure, and the composition distribution (d-J) of the region I, regional IV component distribution (p-u)
表 2 各合金的实际化学成分组成
Table 2. Actual chemical compositions of each alloy
% 合金 Ni Co Fe Al Ti 1# 41.535 33.998 6.14 6.666 11.661 2# 42.519 35.496 6.331 10.099 5.555 3# 47.751 27.994 6.835 6.409 11.011 4# 49.099 28.429 6.502 10.084 5.886 5# 54.601 21.197 6.371 6.36 11.471 6# 56.407 21.356 6.468 9.97 5.799 表 1 基于团簇加连接原子模型设计的合金成分
Table 1. Alloy composition list based on cluster plus linked atom model
合金 原子替换 原子百分比/% 加B后的原子百分比/% 加B后的质量百分比/% 1# [Al-(Ni6-Co5-Fe)]AlTi2 Ni37.5Co31.25Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5 (Ni37.5Co31.25Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5)98B2 Ni41.2Co34.4Fe6.5Al6.3Ti11.2B0.4 2# [Al-(Ni6-Co5-Fe)]Al2Ti Ni37.5Co31.25Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.2 (Ni37.5Co31.25Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.25)98B Ni42.2Co35.3Fe6.7Al9.7Ti5.7B0.4 3# [Al-(Ni7-Co4-Fe)]AlTi2 Ni43.75Co25Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5 (Ni43.75Co25Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5)98B2 Ni48Co27.6Fe6.5Al6.3Ti11.2B0.4 4# [Al-(Ni7-Co4-Fe)]Al2Ti Ni43.75Co25Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.25 (Ni43.75Co25Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.25)98B2 Ni49.2Co28.3Fe6.7Al9.7Ti5.7B0.4 5# [Al-(Ni8-Co3-Fe)]AlTi2 Ni50Co18.75Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5 (Ni50Co18.75Fe6.25Al12.5Ti12.5)98B2 Ni54.9Co20.7Fe6.5Al6.3Ti11.2B0.4 6# [Al-(Ni8-Co3-Fe)]Al2Ti Ni50Co18.75Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.25 (Ni50Co18.75Fe6.25Al18.75Ti6.25)98B2 Ni56.3Co21.2Fe6.7Al9.7Ti5.7B0.4 表 3 合金各相所占体积分数
Table 3. Volume fraction of each phase in the alloy
合金 体积分数/% NiAl相 Ni3Al相 第三相 1# 29 65 6 2# 46 50 4 3# 27 68 5 4# 44 52 4 5# 8 88 4 6# 42 54 4 表 4 合金的显微硬度
Table 4. Microhardness of alloy
合金 显微硬度(HV) 屈服强度/MPa 最大压缩率/% 1# 558 1350 29 2# 500 1200 30 3# 528 1250 34 4# 484 1050 35 5# 508 1100 37 6# 470 900 37 -
[1] Xu Songbo. A new generation of high temperature structural material-intermetallic compound Ni3Al[J]. Shanghai Nonferrous Metals, 1997,(2):88−92. (徐颂波. 新一代高温结构材料──金属间化合物Ni3Al[J]. 上海有色金属, 1997,(2):88−92. [2] Gong Shengkai, Shang Yong, Zhang Ji, et al. Research progress and application of typical intermetallic based high temperature structural materials in China[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 2019,55(9):1067−1076. (宫声凯, 尚勇, 张继, 等. 我国典型金属间化合物基高温结构材料的研究进展与应用[J]. 金属学报, 2019,55(9):1067−1076. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00148 [3] Sauthoff G. Physical metallurgy and processing of intermetallic compounds[M]. Stoloff N S, Sikka V K. London: Chapman & Hall, 1997. [4] Aoki K. Ductilization of L12 intermetallic compound Ni3Al by microalloying with boron[J]. Materials Transactions, 1990,31(6):443−448. doi: 10.2320/matertrans1989.31.443 [5] Orban R L, Lucaci M. Effect of small iron, chromium and boron additions as alloying elements on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni3Al[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2007,23:123−126. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.23.123 [6] Lapshin O, Savitskii A, Ovcharenkon V. Mathematical model of Ni3Al compound synthesis from powder mixture under pressure[J]. Journal of Materials Synthesis and Processing, 2002,10(5):257−261. doi: 10.1023/A:1023042109294 [7] Yang T, Zhao Y L, Li W P, et al. Ultrahigh-strength and ductile superlattice alloys with nanoscale disordered interfaces[J]. Science, 2020,369(6502):427−432. doi: 10.1126/science.abb6830 [8] Dong C, Wang Q, Qiang J B, et al. From clusters to phase diagrams: composition rules of quasicrystals and bulk metallic glasses[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2007,40(15):273−291. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/40/15/R01 [9] Chen H, Wang Q, Wang Y, et al. Composition rule for Al–transition metal binary quasicrystals[J]. Philosophical Magazine, 2010,90(30):3935−3946. doi: 10.1080/14786435.2010.502144 [10] Chen H, Qiang J, Wang Q, et al. A cluster-resonance criterion for Al-TM quasicrystal compositions[J]. Israel Journal of Chemistry, 2011,51(11-12):1226−1234. doi: 10.1002/ijch.201100139 [11] Wang Z, Dong D, Qiang J, et al. Ti-based glassy alloys in Ti-Cu-Zr-Sn system[J]. Science China Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 2013,56(7):1419−1422. doi: 10.1007/s11433-013-5104-7 [12] Wang Y, Wang Q, Zhao J, et al. Ni–Ta binary bulk metallic glasses[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2010,63(2):178−180. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.03.044 [13] Zhu C L, Wang Q, Li F W, et al. Cluster-based bulk metallic glass formation in Fe-Si-B-Nb alloy systems[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2009,144:012048. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/144/1/012048 [14] Wang Q, Li Q, Li X, et al. Microstructures and stability origins of β-(Ti, Zr)-(Mo, Sn)-Nb alloys with low young's modulus[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2015,46(9):3924−3931. doi: 10.1007/s11661-015-3011-4 [15] Ma Rentao, Hao Chuanpu, Wang Qing, et al. "Cluster plus connected atom" model and composition design of Ti-Mo-Nb-Zr solid solution alloy with low elastic bcc structure[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 2010,46(9):1034−1040. (马仁涛, 郝传璞, 王清, 等. 低弹bcc结构Ti-Mo-Nb-Zr固溶体合金的“团簇+连接原子”模型及其成分设计[J]. 金属学报, 2010,46(9):1034−1040. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2010.00039 [16] Zha Qianfeng, Liu Enxue, Dong Chuang, et al. Composition design of high strength martensitic precipitation hardening stainless steel based on cluster model[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 2012,48(10):1201−1206. (查钱锋, 刘恩雪, 董闯, 等. 基于团簇模型的高强度马氏体沉淀硬化不锈钢成分设计[J]. 金属学报, 2012,48(10):1201−1206. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2012.00053 [17] Dong D, Zhang S, Wang Z, et al. Nearest-neighbor coordination polyhedral clusters in metallic phases defined using Friedel oscillation and atomic dense packing[J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2015,48(6):2002−2005. doi: 10.1107/S1600576715018920 [18] Zhang J, Wang Q, Wang Y, et al. Revelation of solid solubility limit Fe/Ni = 1/12 in corrosion resistant Cu-Ni alloys and relevant cluster model[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2010,25(2):328−336. doi: 10.1557/JMR.2010.0041 [19] Ding J, Jiang S, Li Y, et al. Microstructure evolution behavior of Ni3Al (γ′) phase in eutectic γ-γ′ of Ni3Al-based alloy[J]. Intermetallics, 2018,98:28−33. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2018.04.010 [20] Wang W R, Wang W L, Yeh J W. Phases, microstructure and mechanical properties of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys at elevated temperatures[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014,589:143−152. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.084 [21] Wrwa B, Wlw B, Scw B, et al. Effects of Al addition on the microstructure and mechanical property of AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys[J]. Intermetallics, 2012,26:44−51. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2012.03.005 [22] Rao J C, Diao H Y, Ocelík V. et al. Secondary phases in AlxCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloys: An in-situ TEM heating study and thermodynamic appraisal[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017,131:206−220. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2017.03.066 -






 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载: