Industrial study on modification of sulfide in Y1Cr13free-cutting stainless steel by tellurium
-
摘要: 借助金相显微镜、扫描电子显微镜,Image-Pro Plus图像分析软件等手段分析了碲改质Y1Cr13不锈钢中硫化物的效果并进行了对比。结果表明,当钢中加入0.011%的碲时MnS夹杂周围析出了MnTe夹杂,促使了硫化物夹杂粗化,大多数硫化物的形貌呈椭球状、纺锤状且分布弥散,同时碲增强了硫化物夹杂的抗变形能力。钢中加碲后,硫化物纺锤率由未改质前的55.4%提高到了86.5%,硫化物评级由未改质前的3-1级下降到了2-2级,硫化物形态及评级得到了显著提升。切削试验表明,钢中未加碲时,在切削速率分别为180、360、560 r/min时,切削后所得C型屑百分比分别为53%、59%、64%,且工件切削表面粗糙度Ra分别为3.407、2.112、4.186 μm,然而当钢中添加碲后,切削后所得C型屑百分比分别为86%、90%、93%,且工件切削表面粗糙度Ra分别为2.302、1.978、3.220 μm。因此,钢中添加碲后,显著提升了钢的切削性能。Abstract: The effect of sulfide modification by Te was analyzed and compared by means of metallographic microscopy, scanning electron microscope and Image-Pro Plus image analysis software. The results show that MnTe inclusions precipitated around the MnS inclusions when 0.011% Te added to the steel, resulting in the coarsening of sulfide inclusions. The morphology of most sulfides is ellipsoidal and spindle with dispersive distribution. Te enhanced the deformation resistance ability of sulfide inclusions. After adding Te to steel, the spindle percentage of sulfide inclusions increased from 55.4% to 86.5% compared to non-addition of Te. The sulfide rating decreased from 3-1 to 2-2. Thus, the sulfide morphology and rating are significantly improved. The machining test shows that when the cutting speed was 180 , 360 and 560 r/min, the percentage of C-chip obtained after cutting was 53%, 59% and 64%, respectively, and the surface roughness (Ra) value of workpiece was 3.407, 2.112 and 4.186 μm, respectively. However, when the Te powder was added to the steel, the percentage of C-chip obtained after cutting was 86%, 90% and 93%, and the surface roughness (Ra) of workpiece after cutting was 2.302, 1.978 and 3.220 μm, respectively. Therefore, the cutting property of steel was improved with Te addition.
-
Key words:
- Y1Cr13 stainless steel /
- sulfides /
- tellurium modification /
- cutting performance
-
0. 引言
不锈钢具有耐腐蚀、耐高温等优良特性,被广泛应用于各个领域,因此其消费量每年都在不断增加[1]。Y1Cr13又称416不锈钢,是一种硫含量较高的易切削不锈钢,主要用于电机、电气元件的生产[2-3],由于钢中含有大量的硫化物,而这些硫化物具有良好的变形能力,在轧制过程中沿轧制方向延展成长条状,过细的硫化物降低了切屑的断屑性,并恶化钢材的横向性能[4-7] ,还容易导致轧制过程劈头开裂的发生。因此,有必要对硫化物的形态进行调控,将硫化物形貌向椭球状方向调控。
目前,向钢中添加碲元素对硫化物进行改质处理被认为是控制硫化物形态的有效途径。Katoh等[8]研究了钢中碲含量对轧制后硫化物长宽比的影响,发现当Te/S值通常小于0.2%时,钢中的所有碲均有效地作用于MnS的球化。张硕等[9]研究发现向钢中添加一定含量的碲元素,会在MnS硫化物的表面形成碲、锰、铁的复合相。李杰等[10]研究发现303Cu不锈钢中加入碲,可以减少小尺寸夹杂物的数量,增多大尺寸夹杂物的数量,增大夹杂物平均等效直径和平均面积,夹杂物和基体的硬度均先增大后减小。Zheng等[11]通过在1600 ℃下向钢液中加入不同量的碲,研究了碲对硫化物形成的影响,发现凝固期间和凝固后分别形成了粗晶和细晶硫化物,这两种类型都显示出链状模式。Shen等[12]研究了碲在易切削钢中的应用,对Te对MnS硫化物的改性规律进行了总结和阐述,结果表明,当钢中加入少量的Te,可以显著降低钢中硫化物的长宽比,提高球化率。Wu等[13]研究了Te对MnS硬度的影响,结果表明,Te的添加可以提高MnS的硬度,因此添加Te后的MnS在轧制过程中更不易变形,依然可以保持良好的形态,有利于提高轧材的成材率。Xie等[14]研究了Te对Y1Cr17不锈钢中含碲固溶体形态和成分特征的影响,结果表明,Te使夹杂物沿晶界分布且尺寸增大,降低了固溶体中Nb和Fe的含量,提高了Cr的含量,对含Te固溶体中S的含量有很大的影响。但目前碲改质处理缺乏大规模工业试验的相关报道。
由于某钢厂生产的Y1Cr13不锈钢中硫化物形态控制水平较低,导致了轧材劈头开裂、切削性能差等问题。因此,笔者通过向Y1Cr13不锈钢生产工艺中添加碲开展工业试验研究,以改质钢中硫化物夹杂的形态,并进一步提升钢的切削性能。借助金相显微镜、扫描电子显微镜,Image-Pro Plus图像分析软件等手段分析了钢中夹杂物的形态和分布,并研究了碲对Y1Cr13不锈钢改质的效果,以及开展了切削试验研究。
1. 试验材料与方法
1.1 试验材料
Y1Cr13易切削不锈钢的生产工艺为:40 t电炉→AOD→LF→连铸→轧制,在LF精炼末期,向钢中添加含碲包芯线进行硫化物改质。1#、2#、3#试样为含碲易切削钢盘条,碲含量为0.0110%,化学成分见表1,碲含量为北京钢研纳克国家钢铁材料测试中心检测。相同工艺不含碲的盘条为原样。图1为工业试验喂线的现场照片及包芯线。
表 1 试验钢的主要化学成分Table 1. Main chemical compositions of the experimental steels% 试样 C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Te 原样 0.13 0.45 1.15 0.03 0.34 17.25 0.04 碲改质 0.12 0.44 1.17 0.03 0.35 17.14 0.04 0.011 1.2 硫化物测试及切削试验
原样轧材的断面尺寸为Ø16 mm,1#样为Ø16 mm、2#为Ø8 mm和3#样为Ø5.5 mm,按GB/T10561-2005《钢中非金属硫化物含量的测定》对试样进行取样,对观察面进行打磨、抛光、烘干后,采用蔡司金相显微镜(OM)结合Image-Pro Plus专业图像分析软件对硫化物进行评级及统计,采用SEM和EDS对试样中典型硫化物的形貌和成分进行分析。
切削试验取四个试样的盘条进行测试,切削设备为C61320型车床,其中61代表卧式机床,320为最大加工件回转直径,试验刀具为YW2硬质合金机夹式车刀。先将轧材车去外皮,然后在不同切削转速参数下进行车削试验,每次切削后收集切屑并对切削后的轧材表面粗糙度进行检测,检测标准采用日本JIS94标准。表面粗糙度测量原理为:检测时金刚石仿形探头在检测表面上移动,然后将探头的移动转换为电信号的波动,通过放大器将试样表面形貌记录下来,最终形成表面粗糙度曲线图和相应的数值。本次检测表面粗糙度探头移动速度为0.50 mm/s,每段移动距离为0.8 mm,评定长度为4.0 mm。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 碲对硫化物评级的影响
A类硫化物评级是钢中品质的一个重要判断指标,分别对Y1Cr13不锈钢原样及碲改质的不同规格轧材中A类硫化物进行评级,具体分析碲对硫化物改质的工业效果。
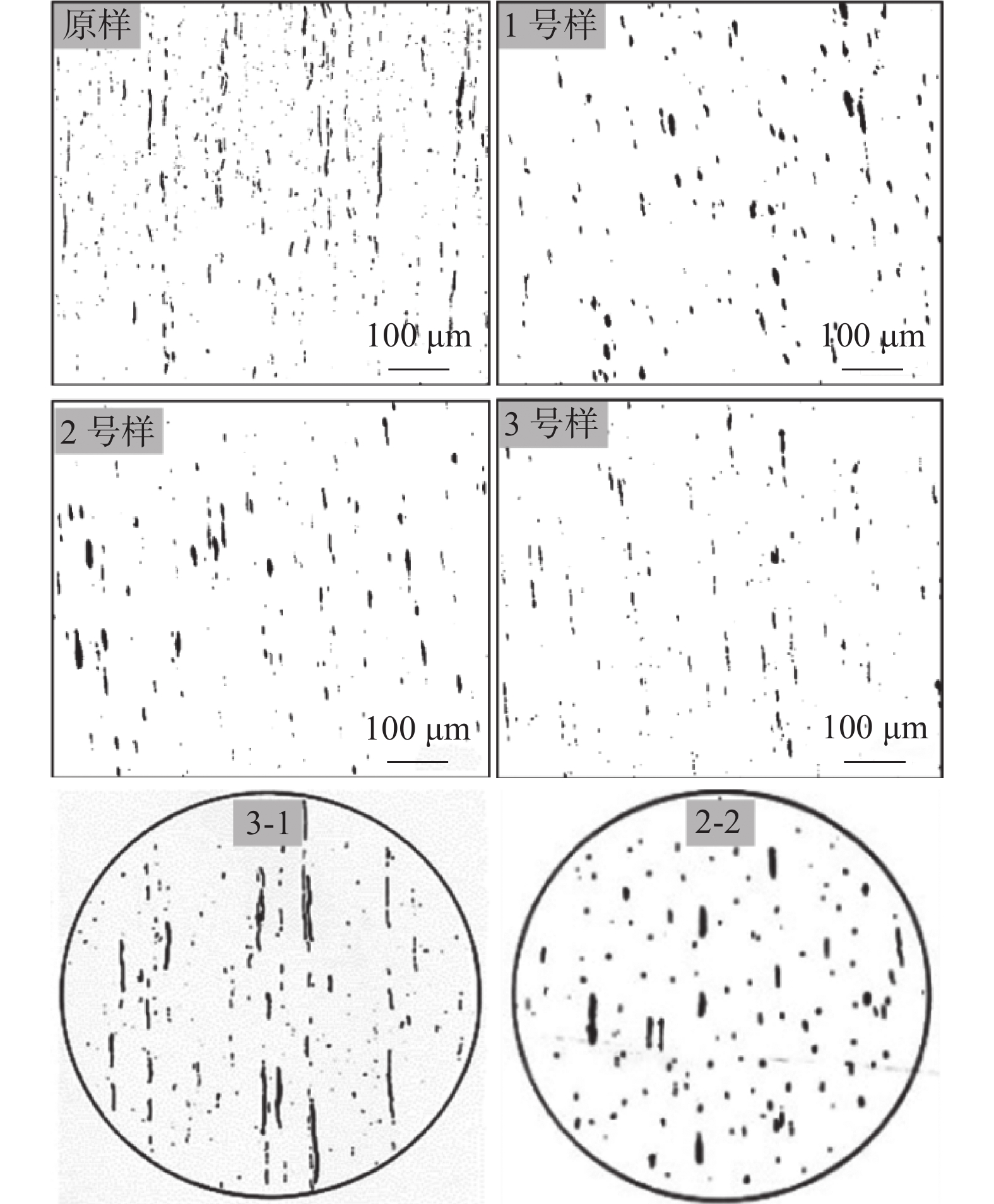
根据国家标准GB/T 10561-2005/ISO 4967:1998(E),对轧材原样和碲改质后的轧材试样中A类硫化物分别选取20个100倍视场进行国标评级,且由于Y1Cr13不锈钢属于高硫易切削不锈钢,采用德国标准DIN 50602-1985评级方式更为准确。按GB/T10561-2005《钢中非金属夹杂物的测定》进行制样,在光学显微镜100×的放大倍数下拍照20张,选取最恶劣的一张金相照片与图谱进行比对,为了更好地与黑白图谱标准比较,采用ImageJ图像处理软件对金相照片进行了黑白翻转,得到各试样的评级结果如图2所示,各样品的综合评级结果如表2所示。
表 2 Y1Cr13不锈钢原样及碲改质轧材A类硫化物评级对比Table 2. Grade of type A inclusions in Y1Cr13 stainless steel and Te modified rolled bars样品 国标评级(GBT 10516-2005 ) 德标评级 原样 粗系4.5级,细系5.5级 3-1级 1#样 粗系4.0级,细系2.5级 2-2级 2#样 粗系4.0级,细系4.0级 2-2级 3#样 粗系2.5级,细系3.0级 2-2级 未改质原样中硫化物细系总长度在1 956~2666 μm,粗系总长度在998~1630 μm。按照国标最恶劣视场作为评级的原则,未改质原样评级为细系5.5级,粗系4.5级。工业试验进行碲改质后,1#样轧材中硫化物细系总长度在570~824 μm,粗系总长度在814~1581 μm,2#样轧材中硫化物细系总长度在735~1505 μm,粗系总长度在918~1512 μm,3#样轧材中硫化物细系总长度在534~1125 μm,粗系总长度在476~854 μm。
对比未改质原样轧材和碲改质工业试验后的轧材硫化物国标和德标评级,可以看出,适量碲的添加明显改善了硫化物的形态,粗系和细系评级均降低,硫化物德标评级由原来的3-1级降低到2-2级。
2.2 碲对硫化物形态的影响
利用金相显微镜观察硫化物形貌并拍照记录,在×100、×200和×500视场下对钢中的硫化物进行观察和检测,图3为未改质的轧材原样和不同直径Te改质轧材中典型硫化物不同倍数视场下的金相照片。从图3中可以看出,在轧制状态下,其中轧材原样中硫化物多为细长条状,1#样、2#样和3#样为碲改质后不同规格的轧材试样,碲改质后的同规格1#样与未改质的轧材原样相比,硫化物多呈椭球状或纺锤状分布,长条状硫化物大大减少,硫化物分布更加细小弥散和均匀,随着轧材直径的减小,轧制压缩比增大,理论上硫化物变形量增大,但2#样和3#样中硫化物仍能保持良好的形态,说明碲改质后的轧制过程中,硫化物的抗变形能力增强,硫化物的形态得到了很大改善。
利用IPP 6.0软件对各试样中硫化物的尺寸、数量及长宽比等进行统计,结果如表3及图4所示。分析图表可知Te改质直径为16 mm轧材的硫化物的平均面积与等效直径均大于未改质直径为16 mm的轧材,表明Te具有粗化MnS的作用。未改质原样总长宽比为6.79,Te改质后的1#样、2#样和3#样总长宽比分别为3.65、3.89和3.31,说明Te改质后硫化物总长宽比降低,并且Te改质后轧材中长宽比在1~3的硫化物所占的比例与未改质轧材相比也均有所提高,从图4可以看出碲改质轧材中硫化物长宽比主要分布在3以内,长宽比小于3的硫化物所占比例分别为86.5%、80.3%和91.2%,形态趋于短粗条状;相比而言,未改质轧材中硫化物长宽比较大,其中硫化物长宽比分布在3以内的夹杂物占比为55.4%,长宽比大于3的夹杂物占比为44.6%,较碲改质轧材多,表明Te改质后轧材中球状或椭球状硫化物增加,有利于降低对钢材横向性能的影响。
表 3 轧材硫化物统计Table 3. Statistics of the inclusions in the rolled bars样品 规格/mm 硫化物平均面积/μm2 硫化物平均等效直径/μm 硫化物密度/(个·mm−2) 总长宽比 原样 Ø16 5.4 2.2 4232 6.79 1#样 Ø16 24.07 5.70 1624 3.65 2#样 Ø8 13.71 4.78 1853 3.89 3#样 Ø5.5 9.95 3.32 2245 3.31 利用扫描电子显微镜观察硫化物形态,如图5所示,未改质原样中硫化物为灰色硫化物,大多呈细长条形,尺寸在20~30 μm左右,在Te改质后,轧材中硫化物主要为灰色硫化物和复合硫化物,灰色硫化物呈椭球形或纺锤形,尺寸在10~20 μm左右,分布弥散,说明在轧制后,不同直径轧材中的硫化物均能保持良好的形态,复合硫化物为白色物质附着在灰色硫化物的两端。
利用能谱对四个试样中典型硫化物进行分析,如图6所示。由图6可知,未改质原样为MnS夹杂物,在Te改质后,MnS周围析出MnTe,形成MnS-MnTe复合夹杂物。
2.3 碲改质对切削性能的影响
目前,评价切削性能的指标主要包括:刀具切削寿命、刀具的断屑性(切屑形貌)、表面光洁度。刀具的切削寿命往往需要长时间的切削才能测定,由于本试验在实验室进行,无法进行长时间切削来测定刀具的切削寿命,故采用刀具的断屑性和表面光洁度来评价碲改质对切削性能的影响。
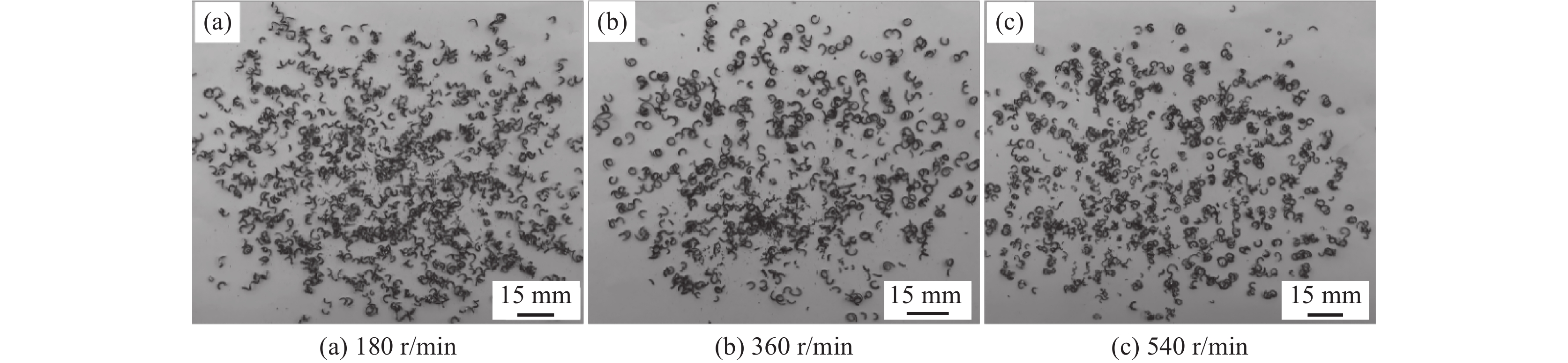
对未改质原样轧材和碲改质轧材进行切削,切削参数为:转速依次为180、360 r/min和560 r/min,切削深度ap=1.0 mm,进给量f=0.10 mm/r,在切削过程中收集切屑,切屑形貌如图7、8所示。
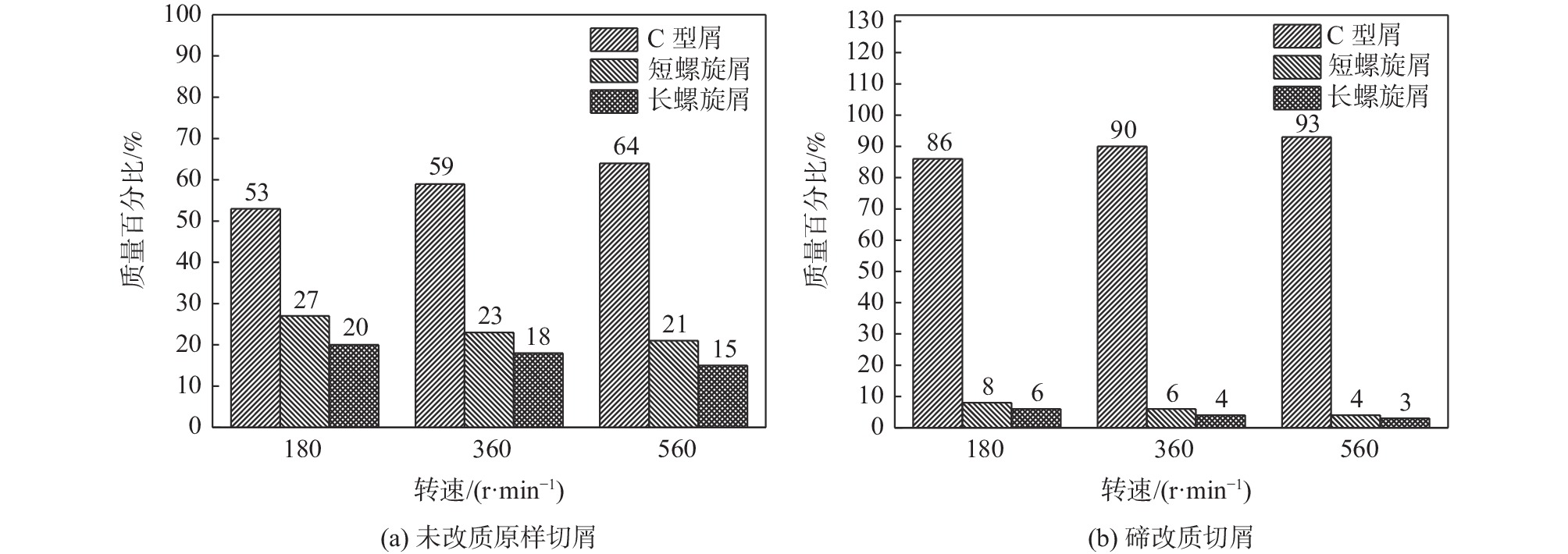
由图7、8可知,改质前后C型屑的比例都随着转速的增加而增加,且相同转速下,碲改质后能够降低切屑长度,并增加了C型屑的比例,切屑长度越长,说明钢材在切削过程中排屑能力越差,由于切削时切屑热量主要是由切屑带走,所以切屑长度越短,说明钢材越易切削,碲改质后钢材的切屑长度均较未改质处理短,所以碲改质处理能够增加钢材的切削加工性能。
为了对切屑进行细致的分析,接下来对切屑进行分类,从切屑形貌可以发现,切屑大致分为三类:长螺旋屑(>2圈)、短螺旋屑(≤2圈)、C型屑,如图9所示,其中长螺旋屑容易缠绕在刀具上,划伤工件表面或损坏刀具,切削过程应避免此类屑的形成。短螺旋屑也是一种相对较好的屑形,切屑的产生比较平稳且易于清除,一般在精加工时要求形成该类屑形。C型屑是一种非常好的切屑形状,该类切屑容易排出,而且不会对工件表面产生影响。本次切削试验对轧材切削性能的评判主要以C型屑为主。
为了更准确地分析切屑形态对切削性能的影响,对上述不同类型的切屑进行分类后统计该类型屑所占的质量百分比,其统计结果如图10所示。从图10可以看出,碲改质前后切屑的形状主要为C型屑,转速在180、360 r/min和560 r/min下,未改质原样轧材切屑中C型屑的比例依次为53%、59%、64%,碲改质轧材切屑中C型屑的比例依次为86%、90%、93%,在相同转速下,碲改质轧材的C型屑比例均明显增加,说明碲的添加可以提升工件的切削性能。
结合切屑形态和切屑统计结果可以看出,在切削速率为180、360 r/min和560 r/min下,碲改质后C型屑的比例均较未改质的高,所以碲的添加使轧材的切削性能得到了改善。
使用表面粗糙度测量仪对切削试样的表面光洁度进行测量。工件表面形貌的粗糙度为Ra、Ry、Rz,其中Ra为在测量长度L内轮廓偏距绝对值的算术平均值,Ry为测量长度L内最高点和最低点之间的距离,Rz为在测量长度内5个最高点的平均值与5个最低点的平均值之和。结合实际生产,本次试验选取Ra作为表面粗糙值的比较对象。对每个切削后的试样表面测量三个点的表面粗糙度并求取平均值,不同转速下表面粗糙度的值如表4所示。
表 4 切削钢表面粗糙度统计Table 4. Statistics of surface roughness of the machining steels转速/
(r·min−1)Ra/µm 原样 碲改质 测定值 平均值 测定值 平均值 180 3.155,3.276,3.790 3.407 2.184,2.449,2.274 2.302 360 2.165,2.074,2.098 2.112 1.977,1.903,2.055 1.978 560 4.000,4.392,4.167 4.186 3.199,3.187,3.274 3.220 由表4中数据可以发现,工件表面粗糙度值均在560 r/min时最大,在360 r/min时最小。当进给量f=0.1 mm/r、切削深度ap=0.5 mm时,转速在180、360 r/min和560 r/min下,碲改质后的轧材表面平均粗糙度Ra值均小于原样轧材,说明碲改质后的轧材在切削后轧材表面光洁度较好,原样轧材表面光洁度不如碲改质轧材。因此,在相同表面粗糙度的要求下,未改质原样轧材的加工效率不如碲改质后的轧材,从而切削加工性能不如碲改质后的轧材,说明Te改质之后的Y1Cr13不锈钢具有优良的切削性能。
有研究表明,加入到钢水中的Te能迅速包围在MnS夹杂周围,生成规则圆整的MnS+MnTe共生物,使硫化物形态改善并弥散均匀地分布于钢中,破坏了金属基体的连续性,使切屑易于碎断,进而使得钢的切削加工性得到极大的改善[15]。
3. 结论
1) 碲改质工业试验结果表明:碲改质后硫化物大小、数量、分布、形貌明显优化;硫化物评级由未改质前的3-1级下降到了2-2级,硫化物评级得到了显著提升;未改质轧材中的硫化物纺锤率为55.4%,总长宽比为6.79,碲改质轧材中的硫化物纺锤率分别为86.5%,80.3%、91.2%,总长宽比分别为3.65、3.89和3.31;说明碲改质后的Y1Cr13不锈钢中硫化物纺锤率提高,硫化物形态得到改善。
2) 切削试验中当转速在180、360 r/min和560 r/min下,进给量f=0.10 mm/r,切削深度ap=1.0 mm时,未改质原样轧材切削所得C型屑所占切屑质量百分比分别为53%、59%、64%,切削后工件表面粗糙度Ra分别为3.407、2.112、4.186 μm;碲改质轧材切削所得C型屑所占切屑质量百分比分别为86%、90%、93%,切削后工件表面粗糙度Ra分别为2.302、1.978、3.220 μm;说明碲改质后的Y1Cr13不锈钢切削性能提高。
-
表 1 试验钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of the experimental steels
% 试样 C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Te 原样 0.13 0.45 1.15 0.03 0.34 17.25 0.04 碲改质 0.12 0.44 1.17 0.03 0.35 17.14 0.04 0.011 表 2 Y1Cr13不锈钢原样及碲改质轧材A类硫化物评级对比
Table 2. Grade of type A inclusions in Y1Cr13 stainless steel and Te modified rolled bars
样品 国标评级(GBT 10516-2005 ) 德标评级 原样 粗系4.5级,细系5.5级 3-1级 1#样 粗系4.0级,细系2.5级 2-2级 2#样 粗系4.0级,细系4.0级 2-2级 3#样 粗系2.5级,细系3.0级 2-2级 表 3 轧材硫化物统计
Table 3. Statistics of the inclusions in the rolled bars
样品 规格/mm 硫化物平均面积/μm2 硫化物平均等效直径/μm 硫化物密度/(个·mm−2) 总长宽比 原样 Ø16 5.4 2.2 4232 6.79 1#样 Ø16 24.07 5.70 1624 3.65 2#样 Ø8 13.71 4.78 1853 3.89 3#样 Ø5.5 9.95 3.32 2245 3.31 表 4 切削钢表面粗糙度统计
Table 4. Statistics of surface roughness of the machining steels
转速/
(r·min−1)Ra/µm 原样 碲改质 测定值 平均值 测定值 平均值 180 3.155,3.276,3.790 3.407 2.184,2.449,2.274 2.302 360 2.165,2.074,2.098 2.112 1.977,1.903,2.055 1.978 560 4.000,4.392,4.167 4.186 3.199,3.187,3.274 3.220 -
[1] Lin Qizeng, Li Cheng. Rapidly developing stainless steel industry in China[J]. Iron and Steel, 2006,41(12):1−2. (林企曾, 李成. 迅速发展的中国不锈钢工业[J]. 钢铁, 2006,41(12):1−2. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2006.12.001 [2] Wu Hailong, Huang Yun, Huang Zhi, et al. Experimental research on the abrasive belt grinding turbine blades material 1Cr13 stainless steel[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2011,487(1):452−453. [3] Cardoso P H S, Kwietniewski C, Porto J P, et al. The influence of delta ferrite in the AISI 416 stainless steel hot workability[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003,351(1):1−2. [4] Domizzi G, Anteri G, Ovejero-Garcia J. Influence of sulphur content and inclusion distribution on the hydrogen induced blister cracking in pressure vessel and pipeline steels[J]. Corrosion Science, 2001,43(2):325−326. doi: 10.1016/S0010-938X(00)00084-6 [5] Li Yanmei, Zhu Fuxian, Cui Fengping, et al. Analysis on formation mechanism of delamination defect in medium and heavy steel plate[J]. Journal of Northeast University:Natural Science Edition, 2007,28(7):1002−1003. (李艳梅, 朱伏先, 崔凤平, 等. 中厚钢板分层缺陷的形成机制分析[J]. 东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2007,28(7):1002−1003. [6] Li Tai. Hot forging crack analysis and improvement measures of non-uenched and tempered steel F45MnVS[J]. Special Steel, 2015,36(5):28−30. (李泰. 非调质钢F45MnVS热顶锻裂纹分析和改进工艺措施[J]. 特殊钢, 2015,36(5):28−30. [7] Chen Xiaokang, Yang Shufeng, Li Jingshe. Inclusion modification of E36 ship plate steel containing yttrium[J]. China Metallurgy, 2019,29(12):25−26. (陈晓康, 杨树峰, 李京社. 含钇E36船板钢硫化物改性[J]. 中国冶金, 2019,29(12):25−26. [8] A. Mahmutoviü, M. Rimac. Modification of non-metallic inclusions by tellurium in austenitic stainless steel[J]. Journal of Trends in the Development of Machinery and Associated Technology, 2015, 19(1): 53-56. [9] Zhang Shuo, Yang Shufeng, Li Jingshe, et al. Control of MnS inclusion morphology in Y15 free-cutting steel by tellurium treatment[J]. Iron and Steel, 2017,52(9):27−29. (张硕, 杨树峰, 李京社, 等. 碲处理控制Y15易切削钢中MnS硫化物形貌[J]. 钢铁, 2017,52(9):27−29. [10] Li Jie, Zhu Qiangbin, Fu Jianxun, et al. Morphology of MnS inclusions in tellurium modified 303Cu stainless steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium , 2020,41(6):135−136. (李杰, 朱强斌, 付建勋, 等. 碲改质303Cu不锈钢中MnS夹杂物形态[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(6):135−136. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.06.024 [11] Zheng L, Malfliet A, Wollants P, et al. Effect of surfactant Te on the formation of MnS inclusions in steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2017,48(5):2447−2448. doi: 10.1007/s11663-017-1050-5 [12] Shen Ping, Yang Qiankun, Zhang Dong, et al. Application of tellurium in free-cutting steels[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2018,25(8):787−789. doi: 10.1007/s42243-018-0123-2 [13] Wu Xiangyu, Wu Liangping, Fu Jianxun, et al. Modification of sulfide by Te in Y1Cr13 free-cutting stainless steel[J]. Metallurgical Research & Technology, 2020,117(1):107−108. [14] Xie Jianbo, Wu Liangping, Fu Jianxun, et al. Morphology and composition characteristics of solid solution in Te-treated Y1Cr17 steel[J]. Emerging Materials Research, 2020,9(4):1145−1146. doi: 10.1680/jemmr.19.00138 [15] Hao Yuan, Zhu Pingshun. Effect of tellurium on cast steel[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 1991,(3):53−54. (郝远, 朱平顺. 碲在铸钢中的作用[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 1991,(3):53−54. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘松涛,伦明睿,陈炜,周茂华,唐佳丽,付建勋. 碲对Cr12MoV冷作模具钢加工性能的影响. 机械工程材料. 2025(01): 38-43 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载:











 下载:
下载:






 百度学术
百度学术











