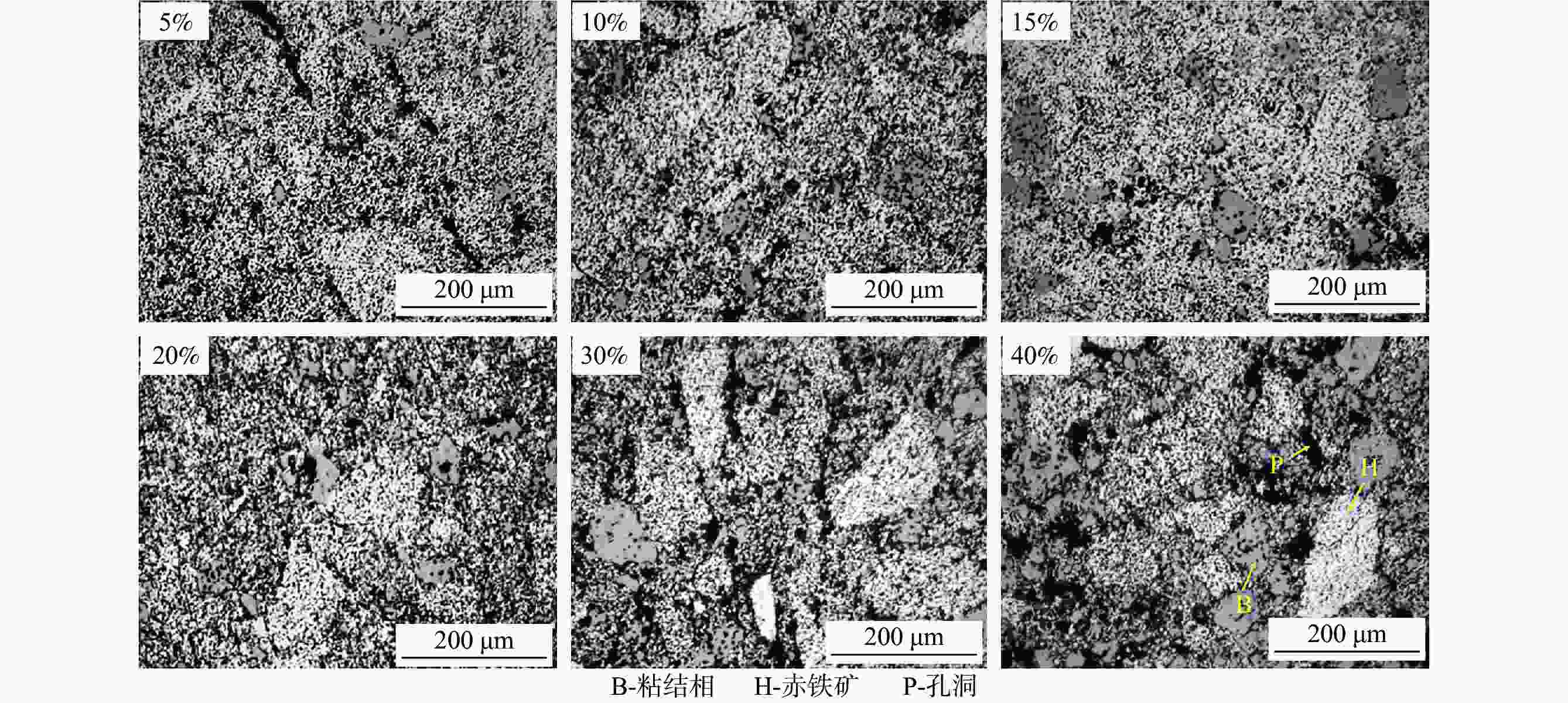
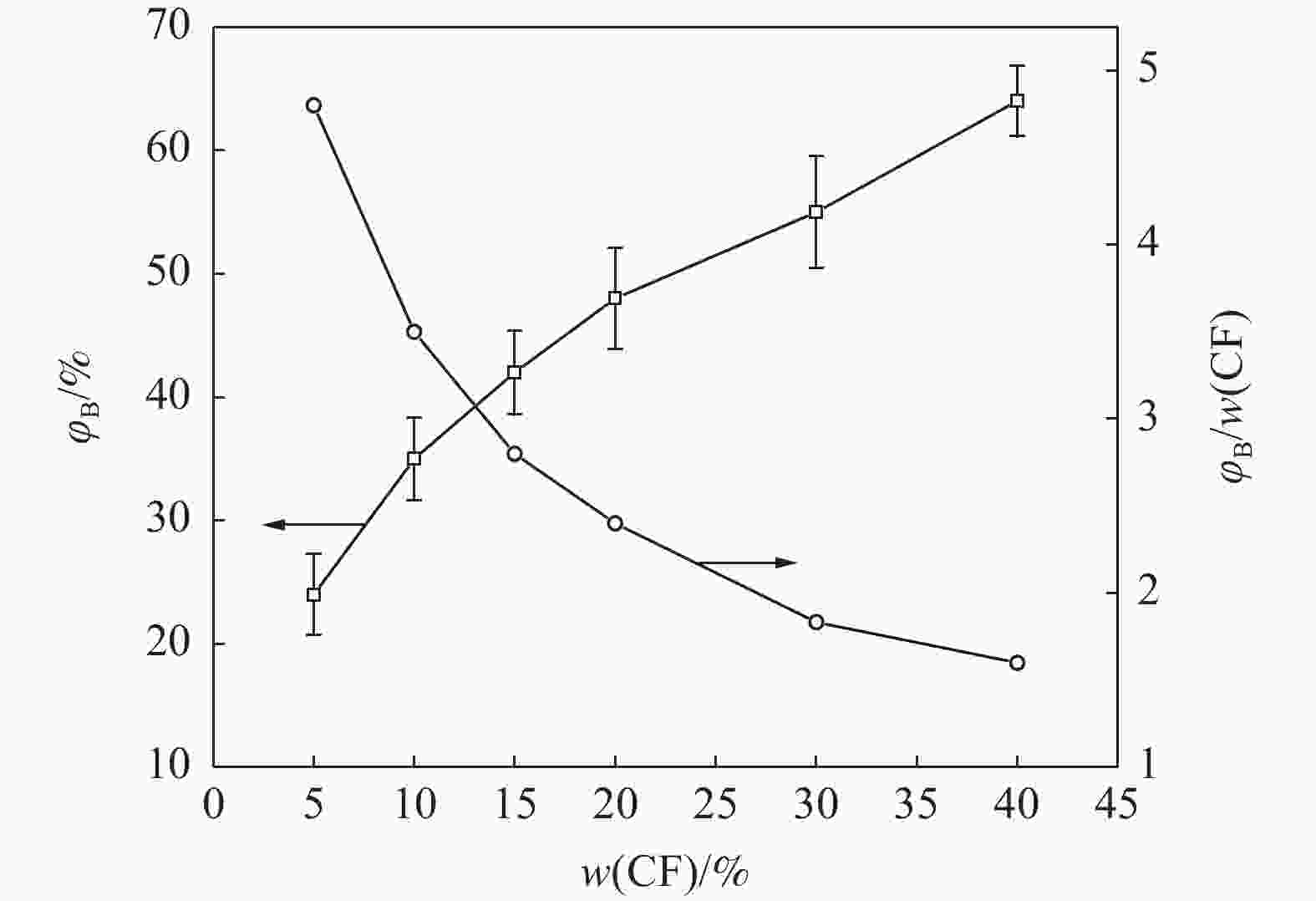
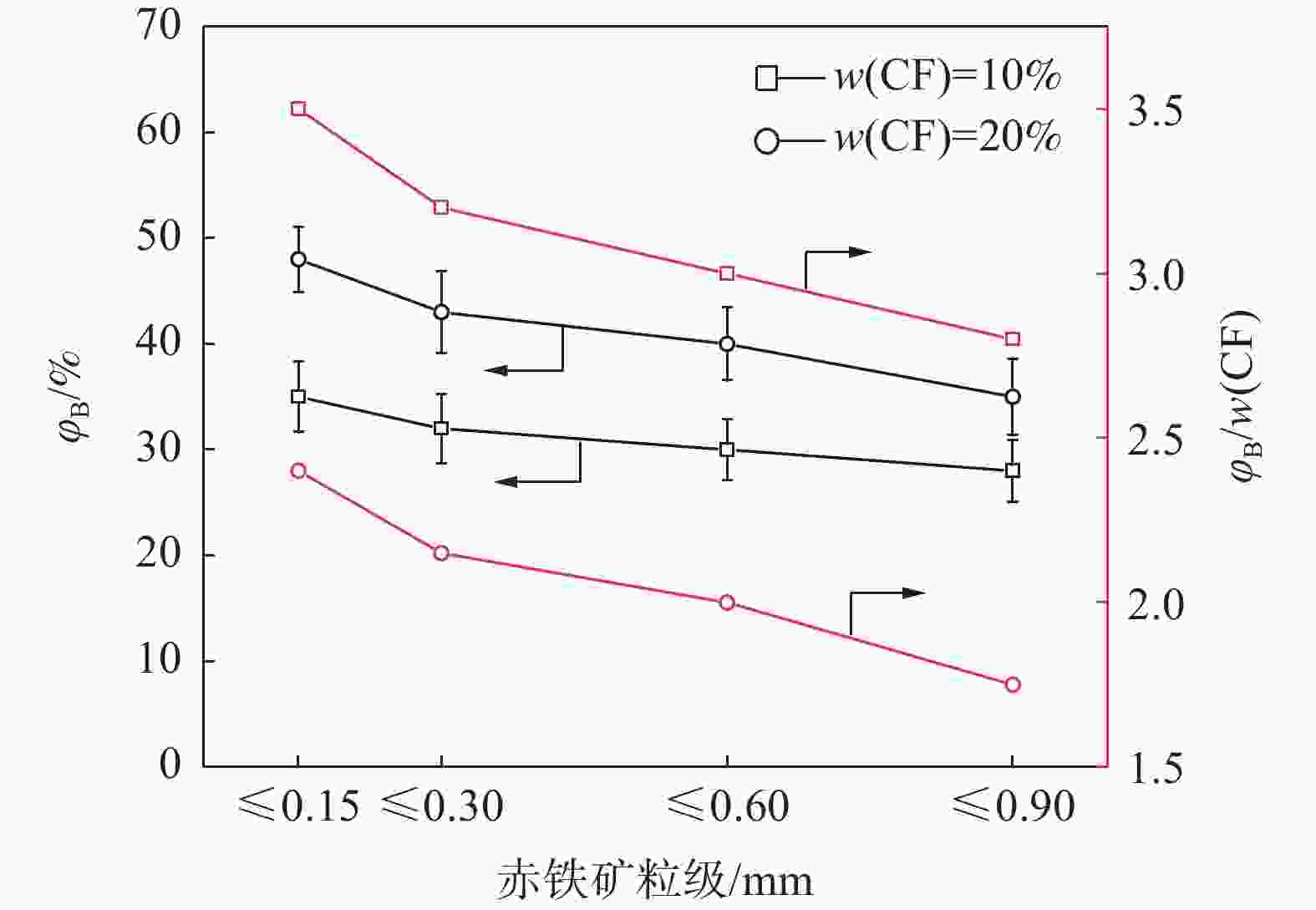
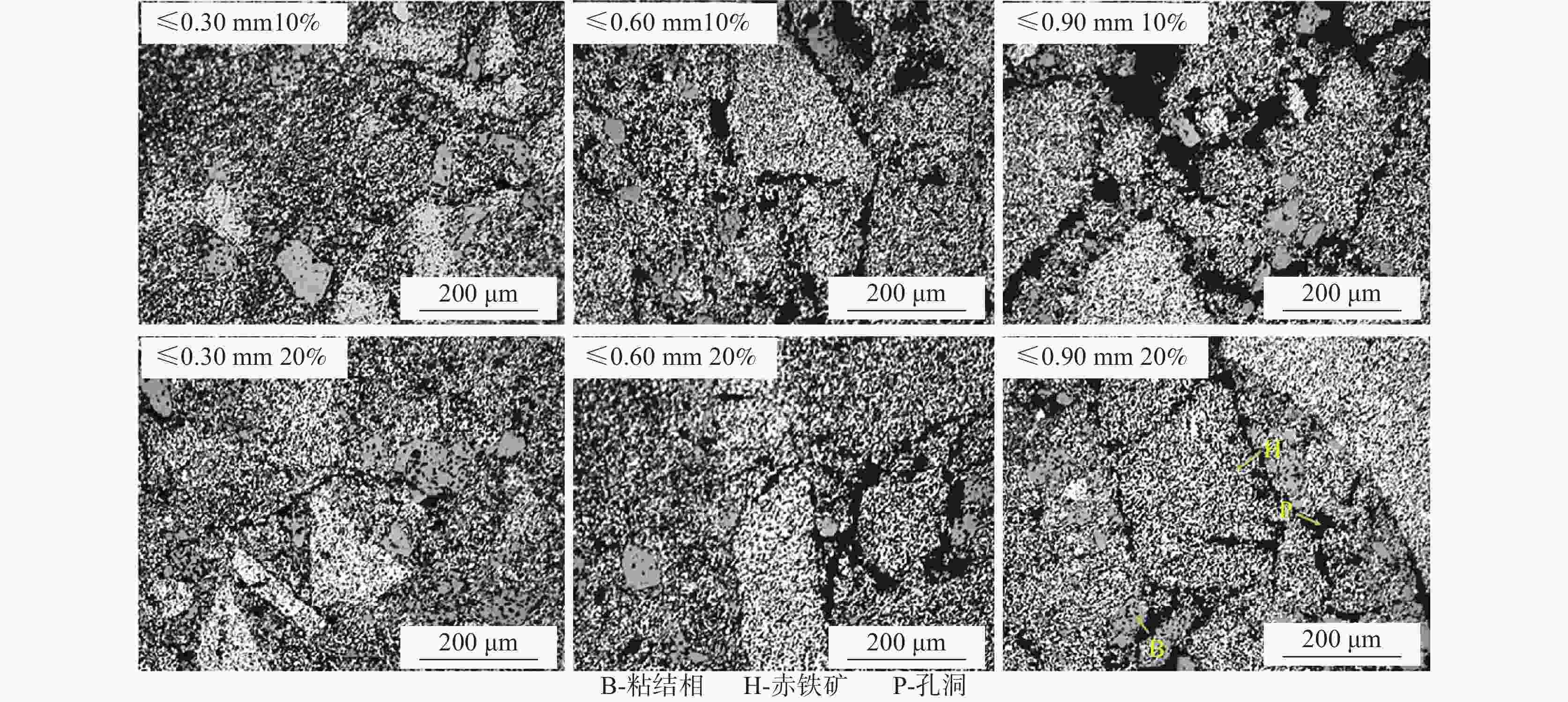
Effect of particle size composition of iron ore fines on the suitable amount of bonding phase in sintering process
-
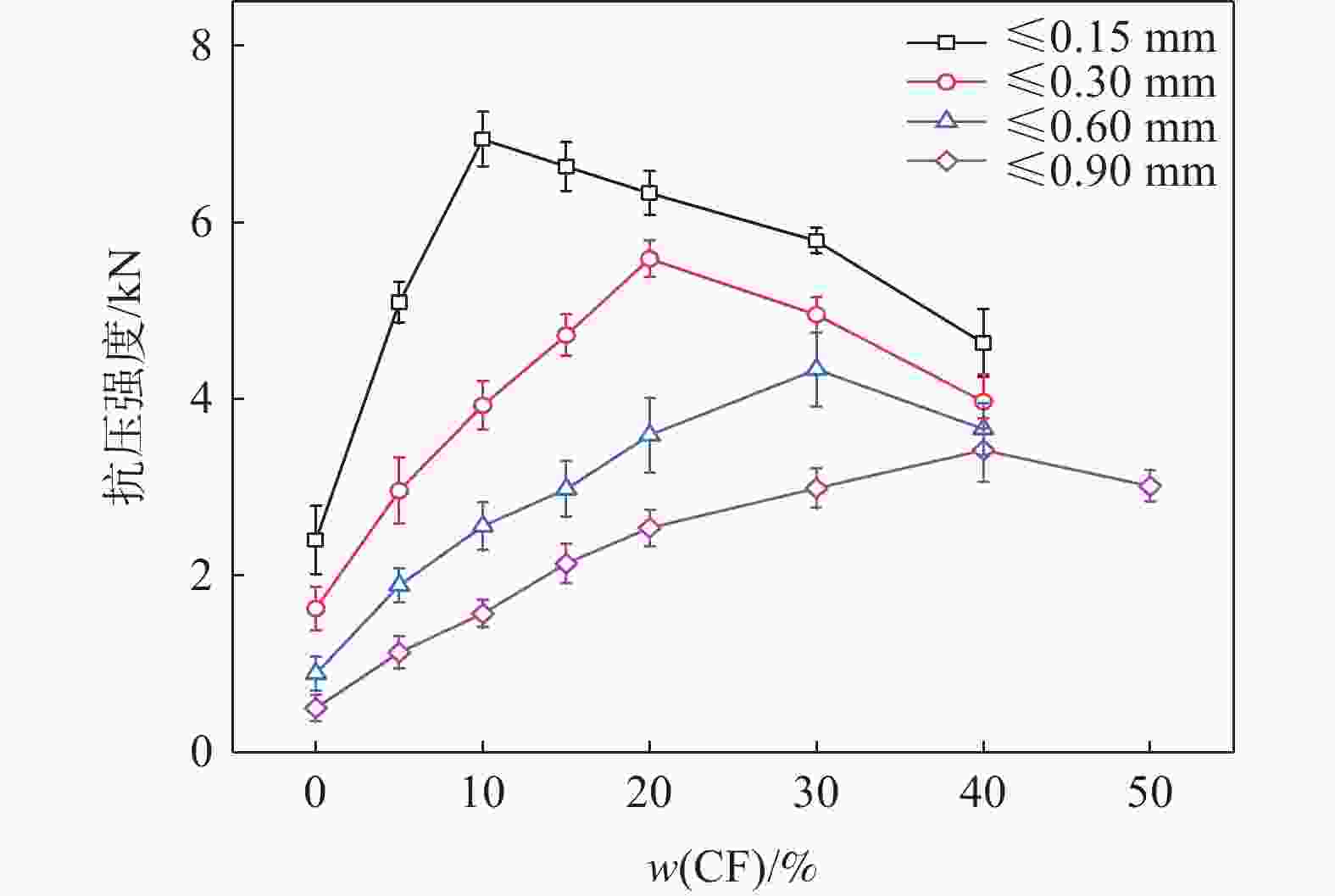
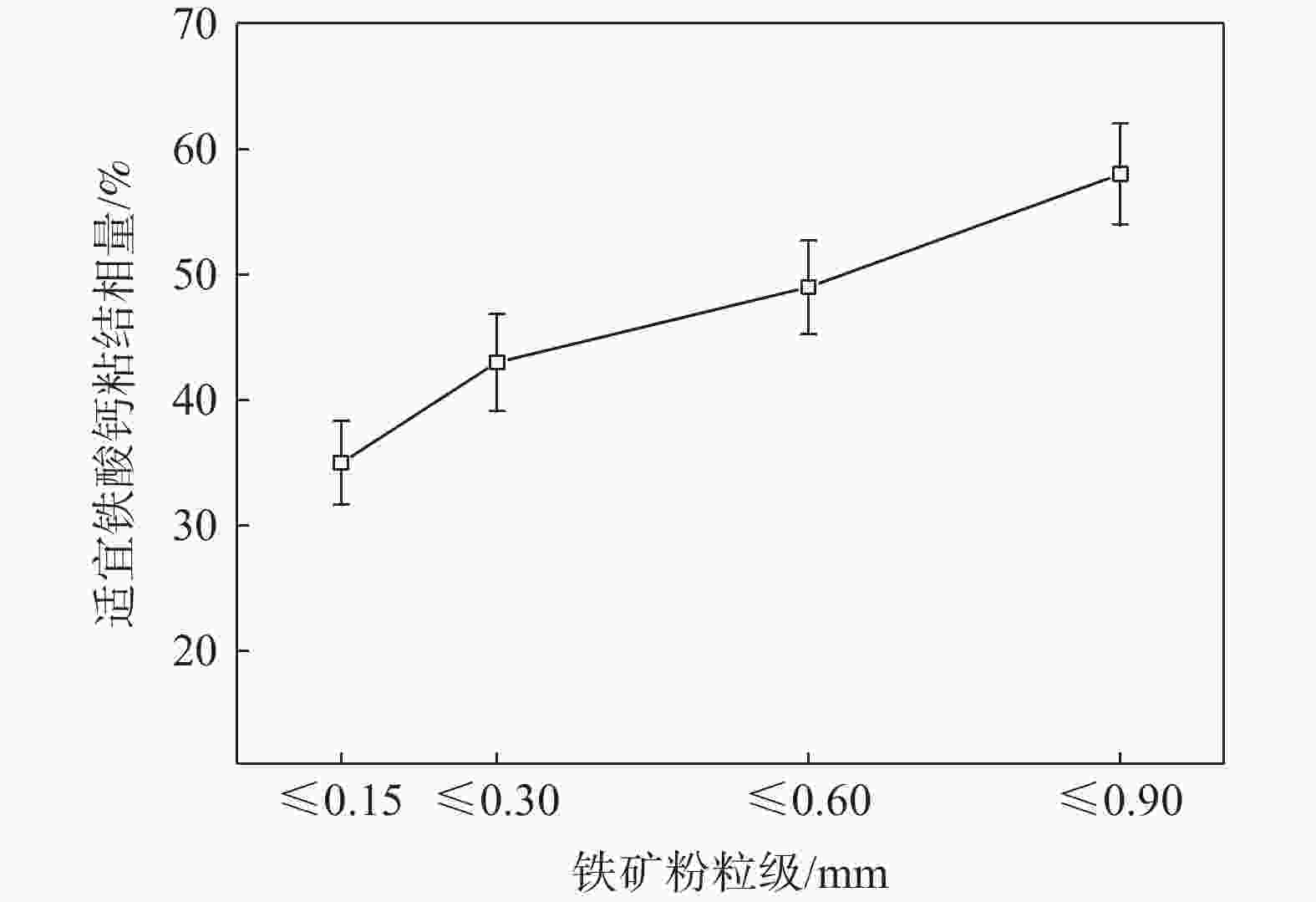
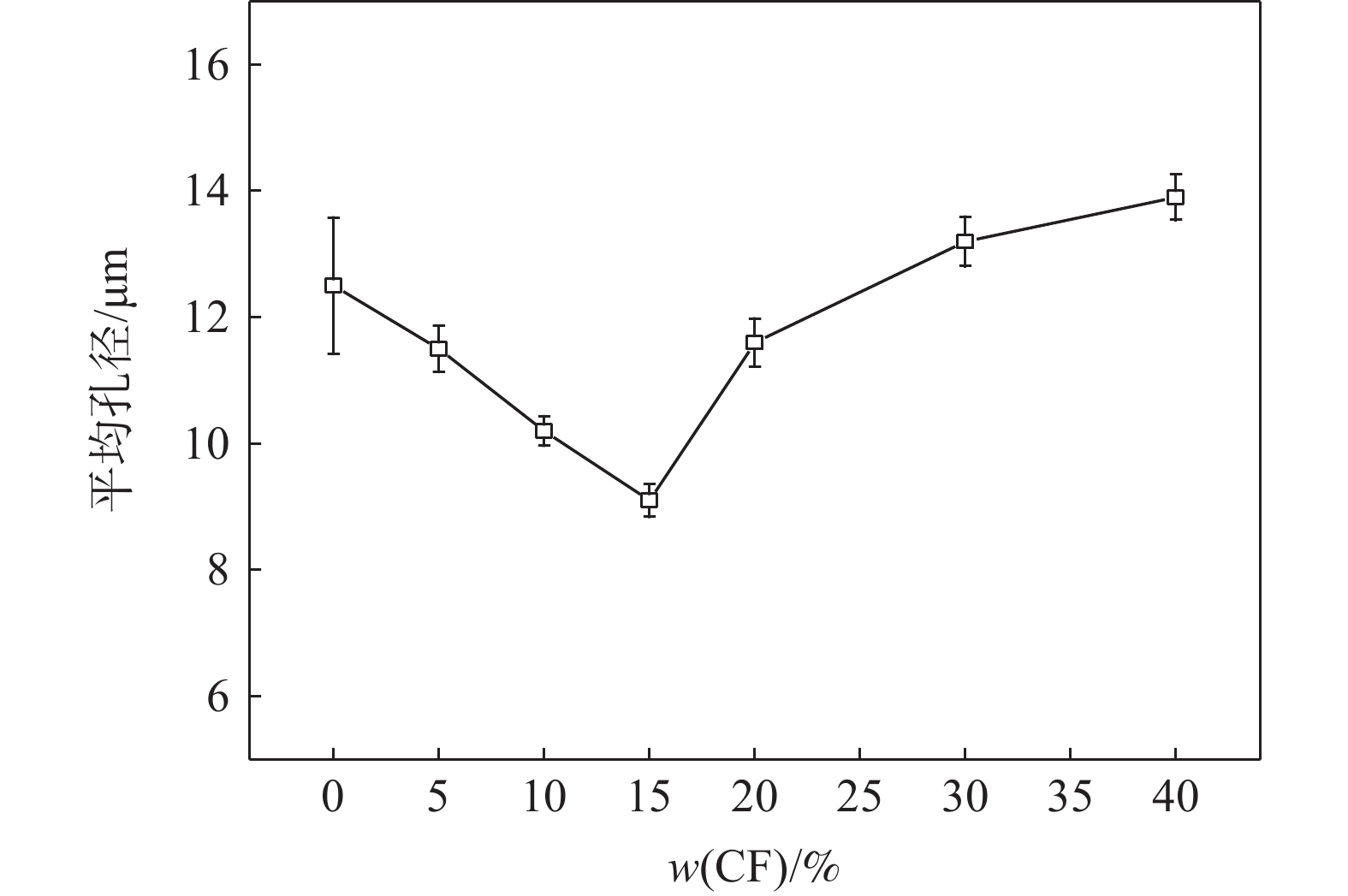
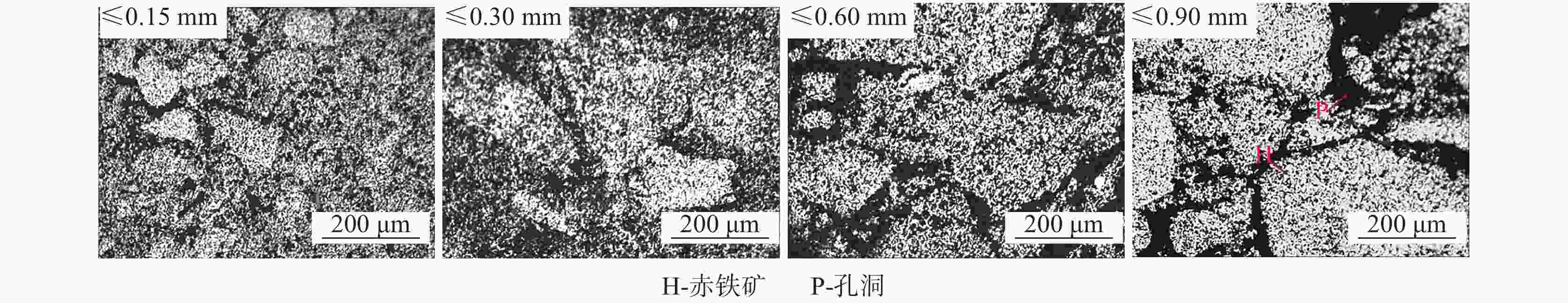
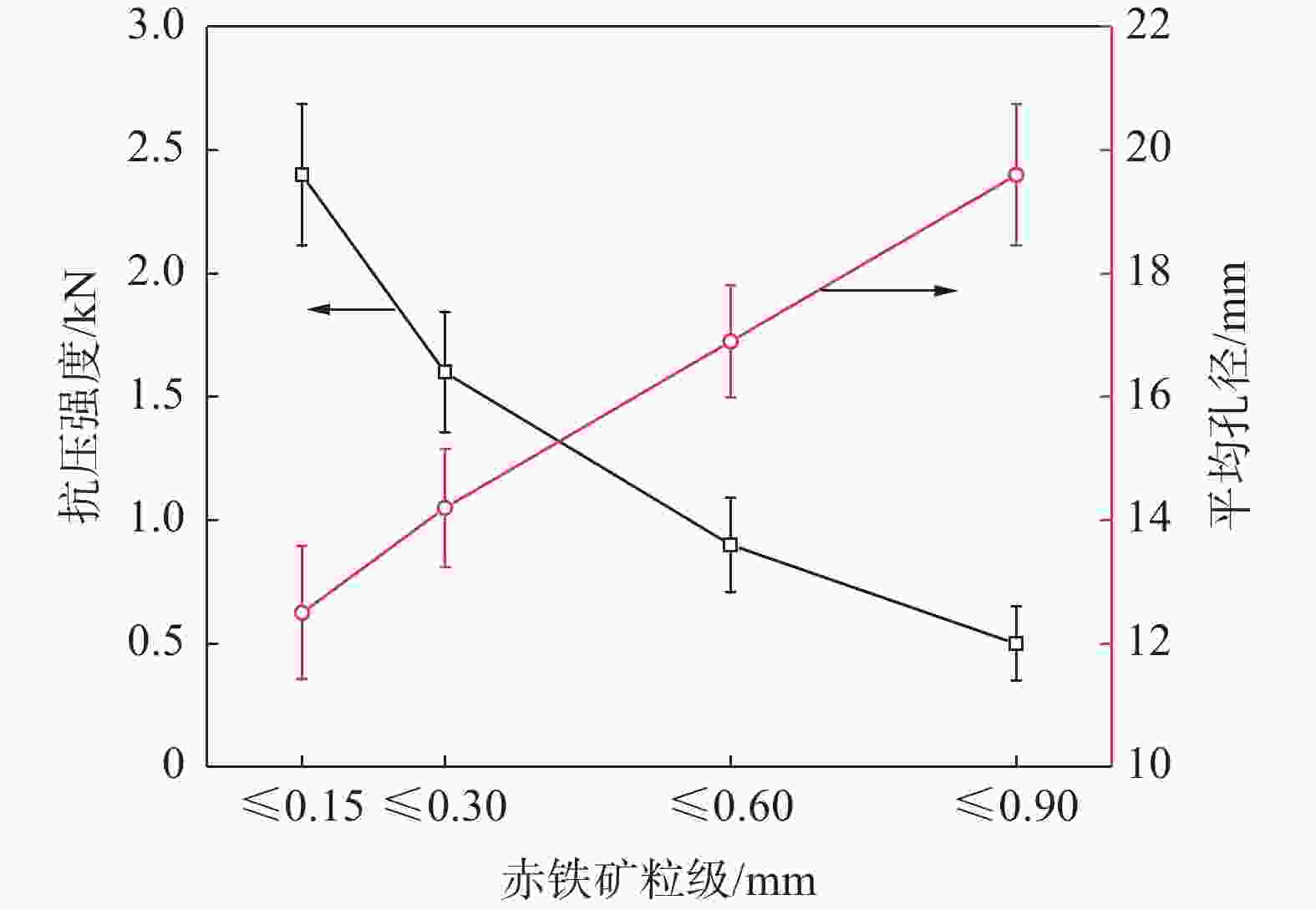
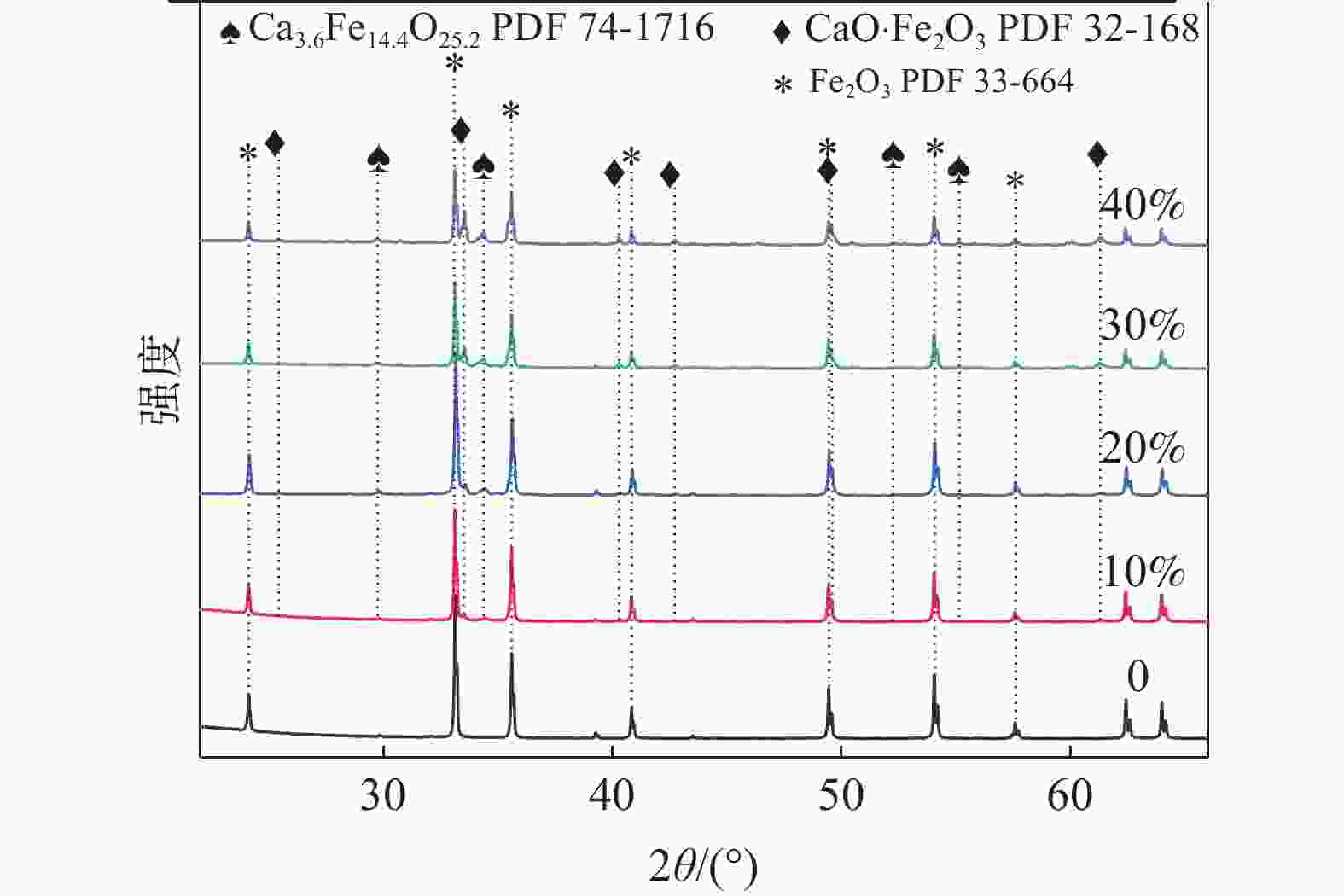
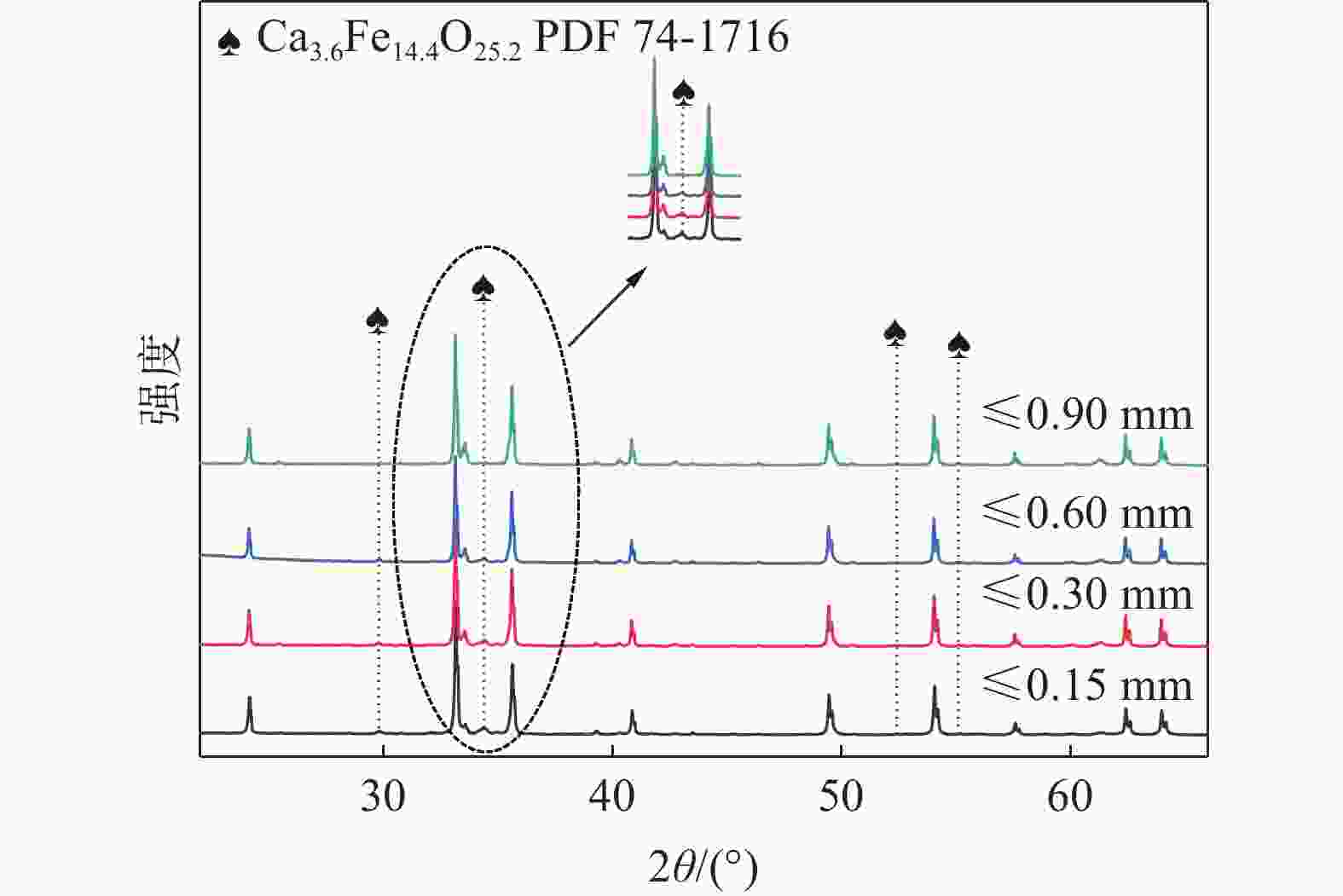
摘要: 铁酸钙是高碱度烧结矿的主要黏结相,其生成量与烧结矿质量有着密切关系,而适宜的黏结相量也是烧结过程中节能降碳的一个重要因素。以铁酸一钙(CF)为初始黏结相,用赤铁矿(Fe2O3)模拟铁矿粉,研究铁矿粉粒度组成对烧结中适宜的黏结相量的影响。结果表明,随着铁矿粉粒级的增加,获得同一抗压强度时烧结试样所需的黏结相量增加。相同粒度范围下,随着CF含量增加,抗压强度呈先增大后减小的变化趋势,其最大值对应于该粒度下适宜的黏结相量。不同粒级范围下,随着Fe2O3粒级的增加,最大抗压强度呈下降趋势。同时,适宜黏结相量向增加方向偏移。试验还发现,CF与Fe2O3反应有低熔点液相—高铁铁酸钙(Ca3.6Fe14.4O25.2)生成,增加了烧结中黏结相量。新相Ca3.6Fe14.4O25.2的生成随着CF含量增加和Fe2O3粒级减小而增加,揭示了初始黏结相与实际黏结相生成量的关系。Abstract: Calcium ferrite is main bonding phase in high-basicity sinter, its formation is closely related to the sinter quality, and the appropriate amount of bonding phase is also an important factor of energy saving and carbon reduction in the sintering process. In this work, mono-calcium ferrite (CF) as an initial bonding phase and pre-sintered hematite (Fe2O3) powder as iron ore fines were used to investigate the influence of particle size composition of iron ore fines on the appropriate amount of bonding phase in sintering process. The results show that the amount of bonding phase needed for obtaining the same compressive strength of sintered samples increases with the increase of iron ore fines size. At same particle size range of iron ore fines, the compressive strength increases first and then decreases with increase of CF addition, and its maximum value should be corresponding to the suitable amount of bonding phase. At different particle size range, the maximum compressive strength decreases with increase of iron ore fines size, simultaneous the suitable amount of bonding phase shiftes to the direction of increasing bonding phase amount. Besides, CF reacts with Fe2O3 to form a calcium rich-ferrate (Ca3.6Fe14.4O25.2) with the low melting point, increasing the amount of bonding phase in sintering process. The Ca3.6Fe14.4O25.2 formation as a new phase increases with the increase of CF addition and the decrease of iron ore fines size, which revealed the relationship of amount between actual bonding phase and initial one in sintering process.
-
Key words:
- sinter /
- iron ore fines /
- particle size /
- bonding phase /
- CF /
- compression strength
-
表 1 试样的混合组成
Table 1. Mixed compositions of samples
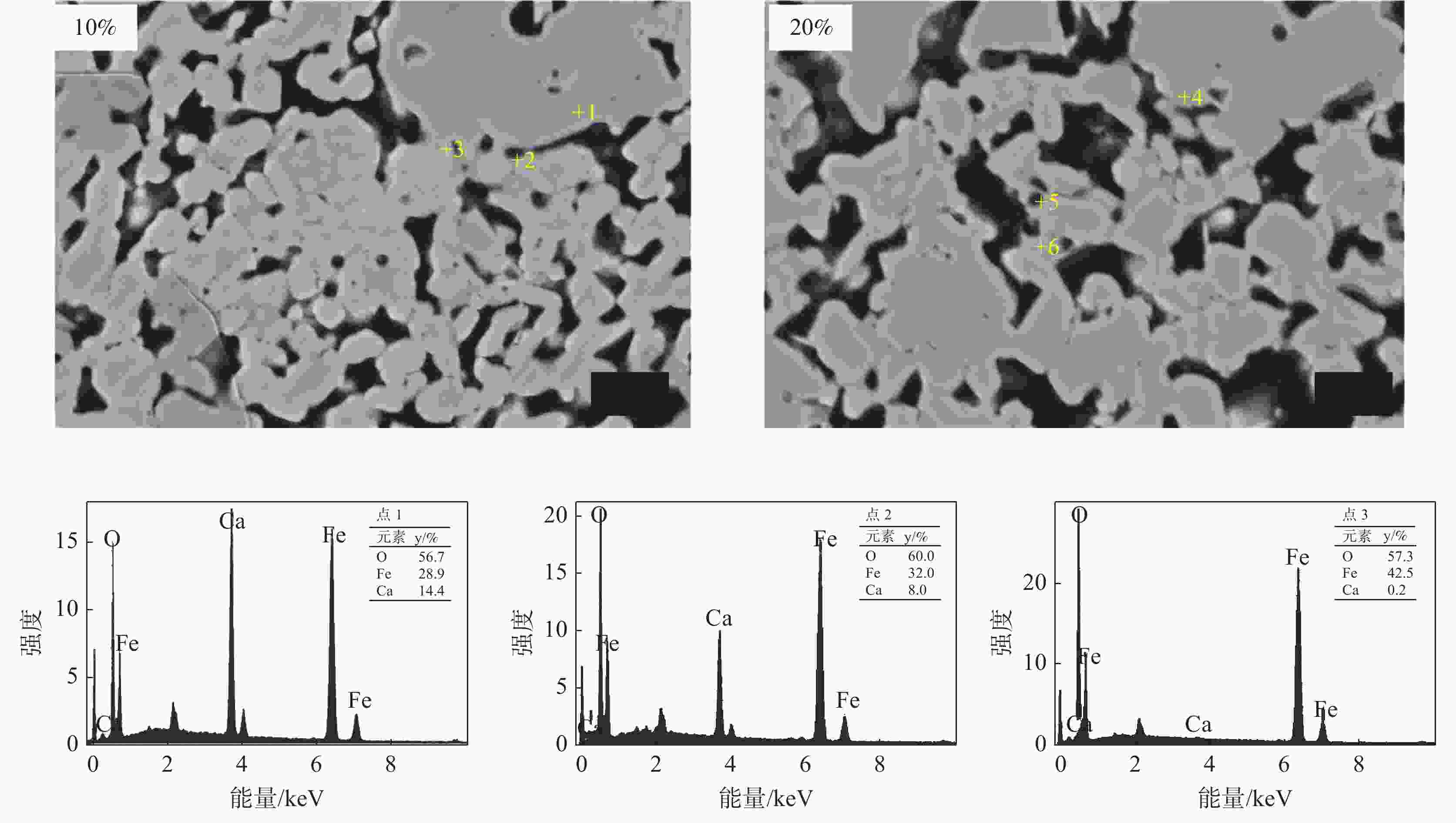
试样 成分组成/g w(CF)/% w(Fe2O3)/% CF Fe2O3 1 0.00 4.00 0 100 2 0.20 3.80 5 95 3 0.40 3.60 10 90 4 0.60 3.40 15 85 5 0.80 3.20 20 80 6 1.20 2.80 30 70 7 1.60 2.40 40 60 8 2.00 2.00 50 50 表 2 粒级≤0.15 mm赤铁矿粉中加入不同量CF烧结试样断面EDS分析结果
Table 2. EDS result of cross-section of sintered sample of ≤0.15 mm hematite fines with different amounts of CF
w(CF)/% 位置 元素含量(y/%) 物相 Fe Ca O 10 P1 28.9 14.4 56.7 CF P2 32.0 8.0 60.0 Ca3.6Fe14.4O25.2 P3 42.5 0.2 57.3 Fe2O3 20 P4 27.9 14.1 58.0 CF P5 32.5 7.6 59.9 Ca3.6Fe14.4O25.2 P6 41.8 0.2 58.0 Fe2O3 -
[1] 龙红明. 铁矿粉烧结原理与工艺[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2010: 5-9.Long Hongming. Sintering principle and technology of iron ore powder[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2010: 5-9. [2] 范晓慧. 铁矿烧结优化配矿原理与技术[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2013: 62-72.Fan Xiaohui. Principle and technology of optimized ore blending by sintering of iron ore[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013: 62-72. [3] 郭兴敏. 烧结过程铁酸钙生成及其矿物学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1999: 59-64.Guo Xingmin. Formation of calcium ferrite during sintering and its mineralogy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1999: 59-64. [4] Mumme W G, Clout J M F, Gable R W. The crystal structure of SFCA-I, Ca3.18Fe3+14.66Al 1.34Fe2+0.82O28, a homologue of the aenigmatite structure type and new crystal structure refinements of ß-CFF, Ca2.99Fe3+14.30Fe2+0.55O25 and Mg-free SFCA, Ca2.45Fe3+9.04Al1.74Fe2+0.16Si0.6O20[J]. Neues Jahrbuch für Mineralogie-Abhandlungen, 1998,173(1):93−117. [5] Xin R F, Du Y, Guo X M. Effect of alumina on crystallization behavior of calcium ferrite in Fe2O3-CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 system[J]. Materials, 2022,15(15):5257. doi: 10.3390/ma15155257 [6] Ding X, Guo X M. The formation process of silico ferrite of calcium (SFC) from binary calcium ferrite[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2014,45(4):1221−1231. doi: 10.1007/s11663-014-0041-z [7] Liu Zhengjian, Wang Jiabao, Zhang Jianliang, et al. Status of energy consumption and prospect of consumption reduction technology in blast furnace[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2022,14(1):1−14. (刘征建, 王家保, 张建良, 等. 高炉能耗现状及降耗技术展望[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2022,14(1):1−14.Liu Zhengjian, WangJiabao, Zhang Jianliang, et al. Status of energy consumption and prospect of consumption reduction technology in blast furnace[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2022, 14(1): 1-14. [8] Dong J J, Wang G, Gong Y G, et al. Effect of high alumina iron ore of gibbsite type on sintering performance[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2014,42(1):34−40. [9] Peng J, Zhang L, Liu L X, et al. Relationship between liquid fluidity of iron ore and generated liquid content during sintering[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2017,48(1):538−544. doi: 10.1007/s11663-016-0827-2 [10] Lv X W, Bai C G, Deng Q Y, et al. Behavior of liquid phase formation during iron ores sintering[J]. ISIJ International, 2022,51(5):722−727. [11] Wu Shengli, Du Jianxin, Ma Hongbin, et al. Self-intensity of bonding phase in iron ores during sintering[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2005,27(4):69−72. (吴胜利, 杜建新, 马洪斌, 等. 铁矿粉烧结黏结相自身强度特性[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2005,27(4):69−72.Wu Shengli, Du Jianxin, Ma Hongbin, et al. Self-intensity of bonding phase in iron ores during sintering[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2005, 27(4): 69-72. [12] Huang Zhucheng, Jiang Yuan, Mao Xiaoming, et al. Study on rational distribution of fuel in sintering iron ore[J]. Journal of Central South University: Natural Science Edition, 2006,(5):884−890. (黄柱成, 江源, 毛晓明, 等. 铁矿烧结中燃料合理分布研究[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2006,(5):884−890.Huang Zhucheng, Jiang Yuan, Mao Xiaoming, et al. Study on rational distribution of fuel in sintering iron ore[J]. Journal of Central South University: Natural Science Edition, 2006(5): 884-890. [13] Liu Lina, Han Xiuli. A review on influence of sintering quality[J]. Journal of Hebei Institute of Technology, 2006,28(2):18−22. (刘丽娜, 韩秀丽. 影响烧结矿质量的因素[J]. 河北理工学院学报, 2006,28(2):18−22.Liu Lina, Han Xiuli. A review on influence of sintering quality[J]. Journal of Hebei Institute of Technology, 2006, 28(2): 18-22. [14] 陈耀铭. 烧结球团矿微观结构[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2011: 69.Chen Yaoming. Microstructure of sintered pellets[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2011: 69. [15] 张汉泉. 烧结球团理论与工艺[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2015: 70-75.Zhang Hanquan. Theory and technology of sintered pellets[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industrial Press, 2015: 70-75. [16] 李光森. 黏结相对烧结矿强度的影响机理及其合理组分的探讨[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2008: 4-6.Li Guangsen. Discussion on the influence mechanism of bonding on the strength of sinter and its reasonable components[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2008: 4-6. [17] Chen Hong, Zhang Meifang. Study on reactivity of iron ore powder[J]. Bao-Steel Technology, 2001,(5):35−38. (陈宏, 张美芳. 铁矿粉反应性研究[J]. 宝钢技术, 2001,(5):35−38.Chen Hong, Zhang Meifang. Study on reactivity of iron ore powder[J]. Bao-Steel Technology, 2001(5): 35-38. [18] Gao Feng. Production practice of high precision powder and low silicon sintering in TISCO[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2004,29(6):38−41. (高峰. 太钢高精粉低硅烧结生产实践[J]. 烧结球团, 2004,29(6):38−41.Gao Feng. Production practice of high precision powder and low silicon sintering in TISCO[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2004, 29(6): 38-41. [19] Hida Y, Okazaki J, Itoh K, et al. Formation mechanism of acicular calcium ferrite of iron ore sinter[J]. Tetsu-to-Hagane, 1987,73(15):1893−1900. doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane1955.73.15_1893 [20] Scarlett N V Y, Madsen I C, Pownceby M I, et al. In situ X-ray diffraction analysis of iron ore sinter phases[J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2004,37(3):362−368. doi: 10.1107/S002188980400353X [21] Scarlett N V Y, Pownceby M I, Madsen I C, et al. Reaction sequences in the formation of silico-ferrites of calcium and aluminum in iron ore sinter[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2004,35B(5):929−936. [22] 李光森, 金明芳, 姜鑫, 等. 烧结矿黏结相熔化特性的研究[C]//中国钢铁年会论文集. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007.Li Guangsen, Jin Mingfang, Jiang Xin, et al. Research on melting characteristics of sinter bonding phase[C]// Proceedings of China Steel Annual Conference. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007. [23] Liu Ran, Liu Chaoqing, Lü Qing, et al. Study on liquid phase generation of vanadium-titanium sinter with moderate titanium content[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014,35(5):72−77. (刘然, 刘朝卿, 吕庆, 等. 中钛型钒钛烧结矿液相量的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014,35(5):72−77.Liu Ran, Liu Chaoqing, Lv Qing, et al. Study on liquid phase generation of vanadium-titanium sinterwith moderate titanium content[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014, 35(5): 72-77. [24] Cores A, Babich A, Muniz M, et al. The influence of different iron ores mixtures composition on the quality of sinter[J]. ISIJ International, 2010,50(8):1089−1098. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.50.1089 [25] Webster N A S, Pownceby M I, Madsen I C, et al. Effect of oxygen partial pressure on the formation mechanisms of complex Ca-rich ferrites[J]. ISIJ International, 2013,53(5):774−781. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.53.774 [26] Webster N A S, Churchill J G, Tufaile F, et al. Fundamentals of silico-ferrite of calcium and aluminium(SFCA) and SFCA-Ⅰ iron ore sinter bonding phase formation: effects of titanmagnetite-based ironsand and titanium addition[J]. ISIJ International, 2016,56(10):1715−1722. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2016-162 [27] Webster N A S, Pownceby M I, Pattel R. Fundamentals of silico-ferrite of calcium and aluminium(SFCA) and SFCA-Ⅰ iron ore sinter bonding phase formation: effects of mill scale addition[J]. Power Diffraction, 2017,32(S2):85−89. doi: 10.1017/S088571561700080X [28] Ding X, Guo X M, Ma C Y, et al. Effect of SiO2 on the crystal structure stability of SFC at 1473 K (1200 ℃)[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2015,46(2):1147−1153. [29] Guo H, Guo X M. Effect of aluminum dissolved in hematite on formation of calcium ferrites at 1473 K[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2018,49B:1974−1984. [30] Wang Ruying. The study on microhardness of sinter[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 1995,(3):9−13. (王如英. 烧结矿显微硬度的研究[J]. 烧结球团, 1995,(3):9−13.Wang Ruying. The study on microhardness of sinter[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 1995(3): 9-13. [31] Qiao Ruiqing, Du Hegui. Formation mechanism of micropores in low fluoride sinter and its influence on sinter strength[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 1999,11(6):1. (乔瑞庆, 杜鹤桂. 低氟烧结矿微气孔的形成机理及对烧结矿强度的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 1999,11(6):1.Qiao Ruiqing, Du Hegui. Formation mechanism of micropores in low fluoride sinter and its influence on sinter strength[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 1999, 11(6): 1. -




 下载:
下载: