Study on microstructure evolution and austenitizing process of 1800 MPa grade ultra-high strength hot stamping steels
-
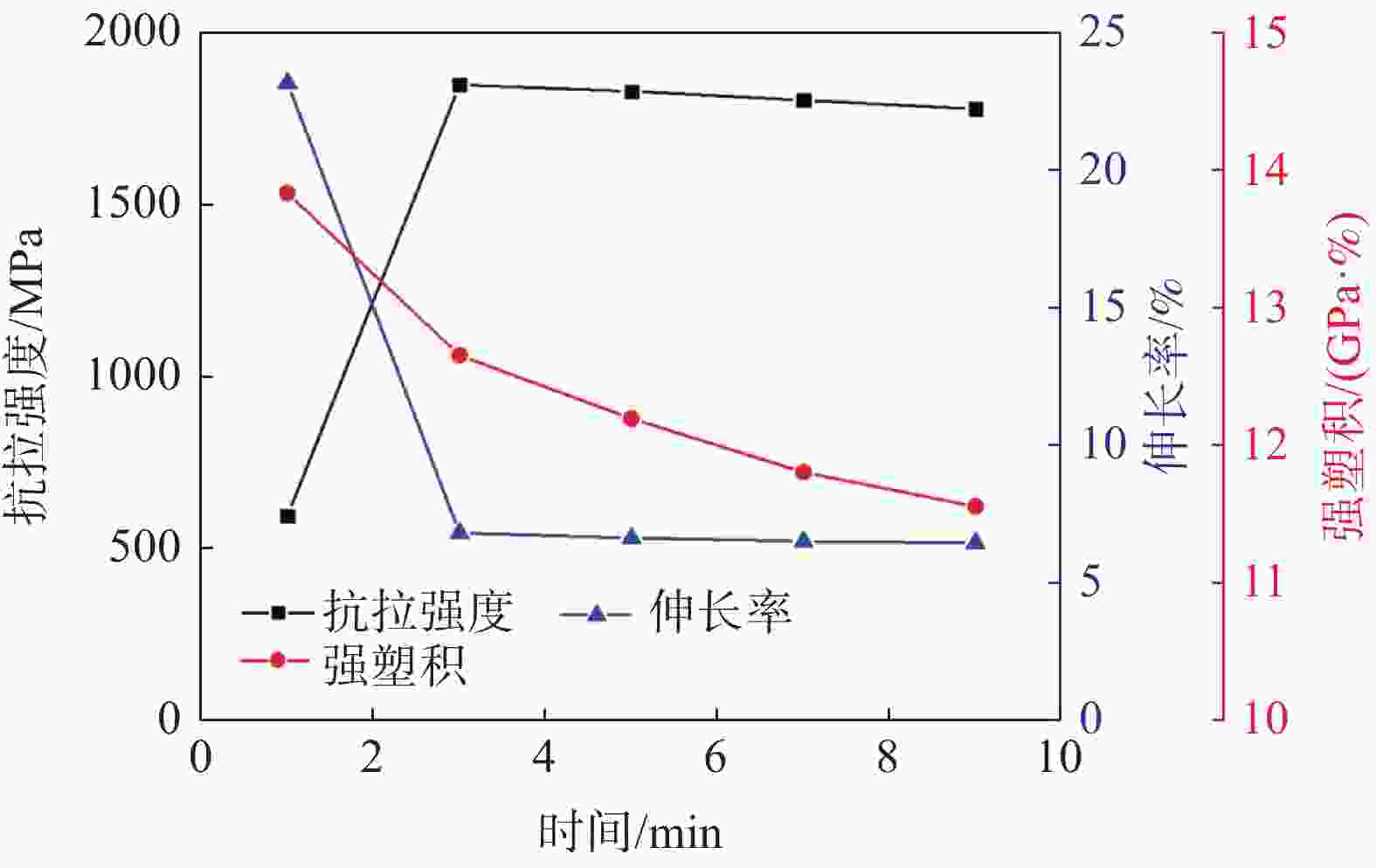
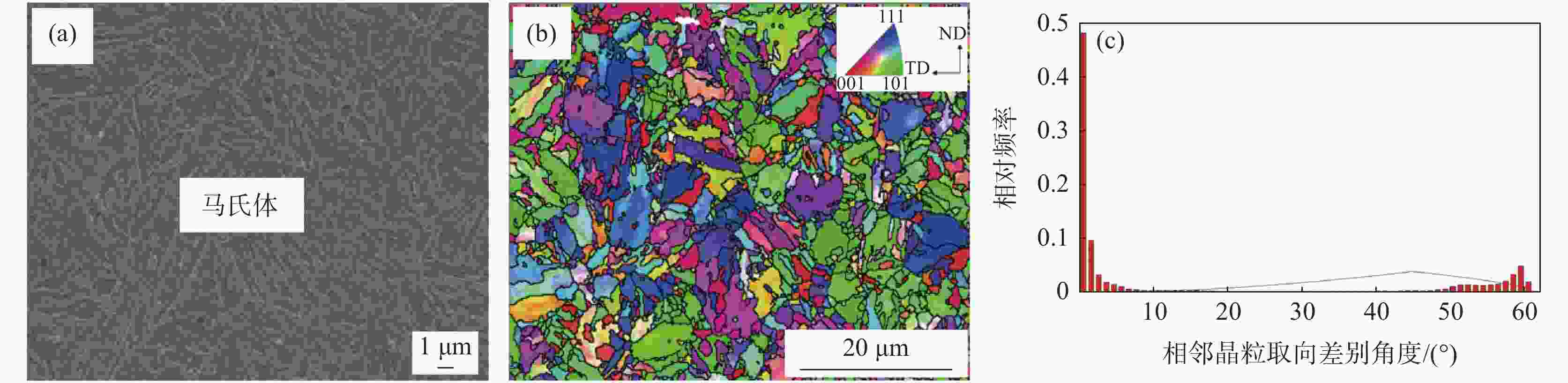
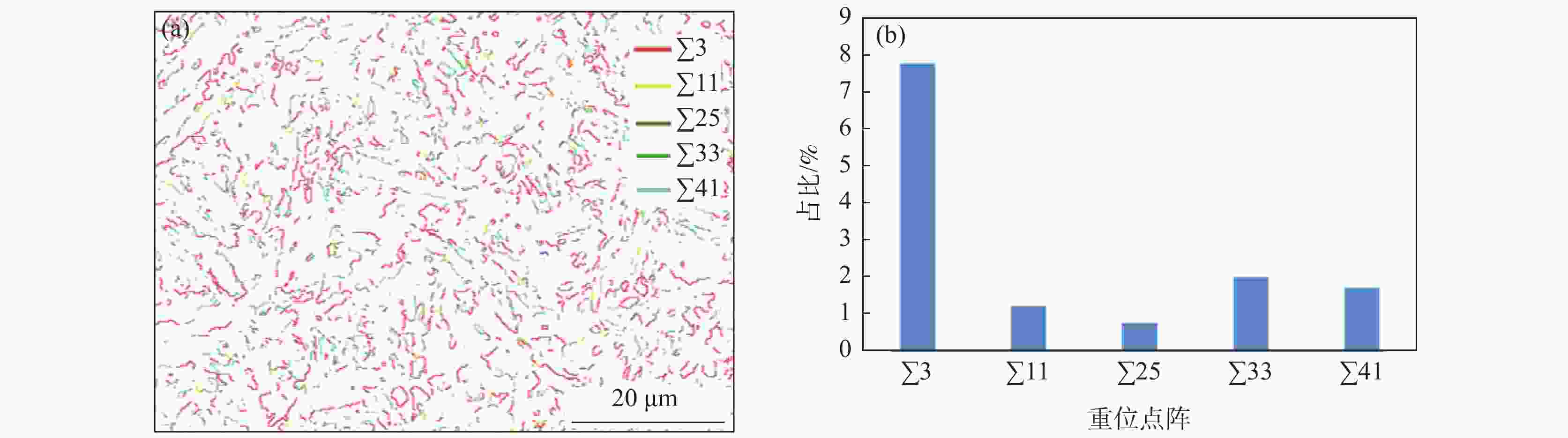
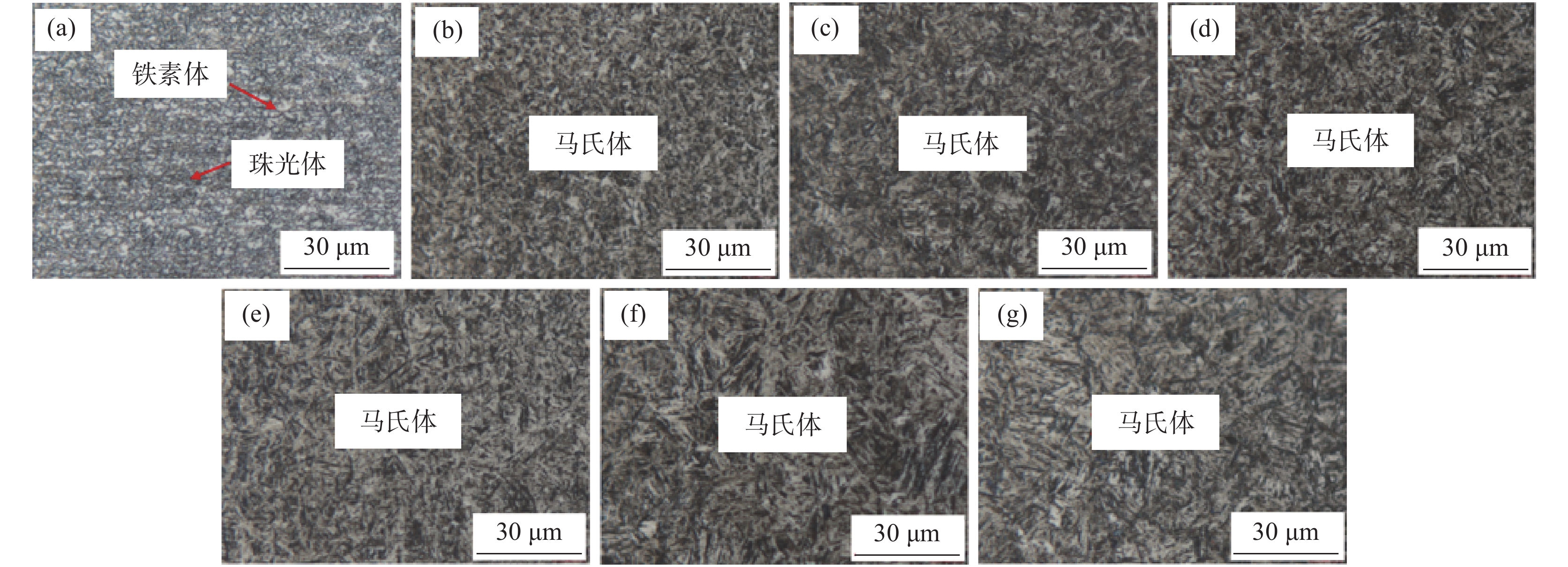
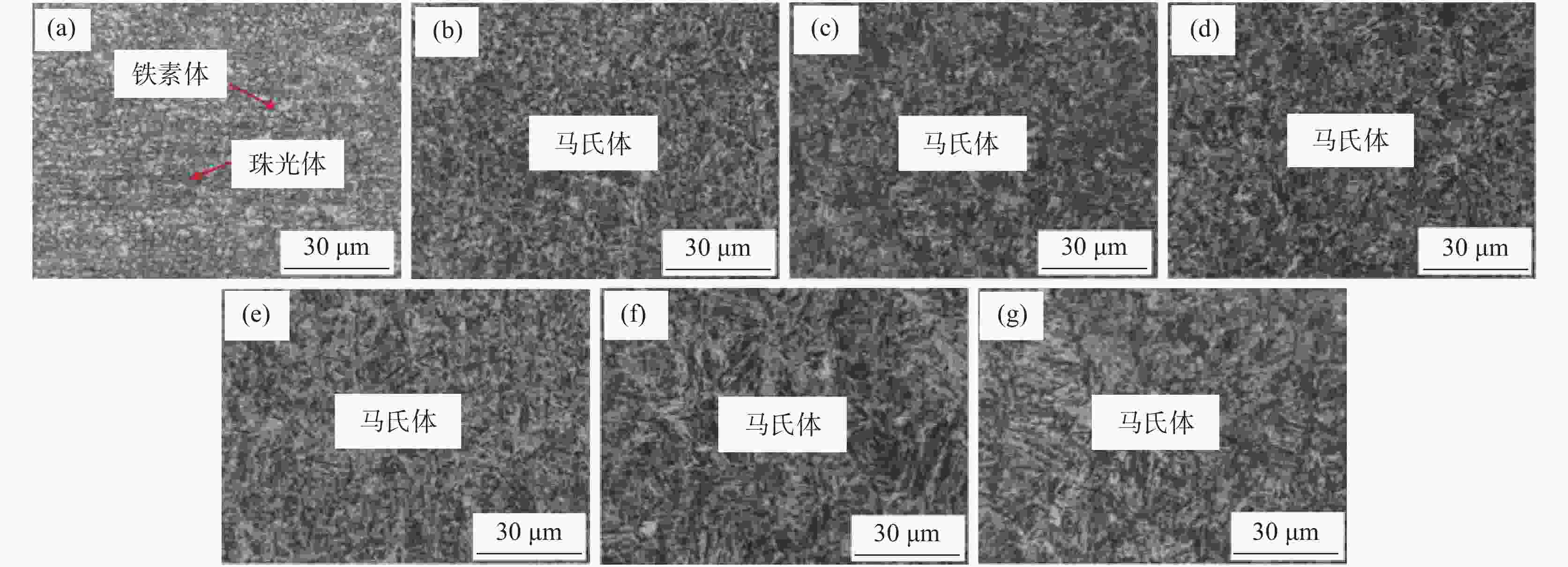
摘要: 对不同奥氏体化温度及保温时间条件下的
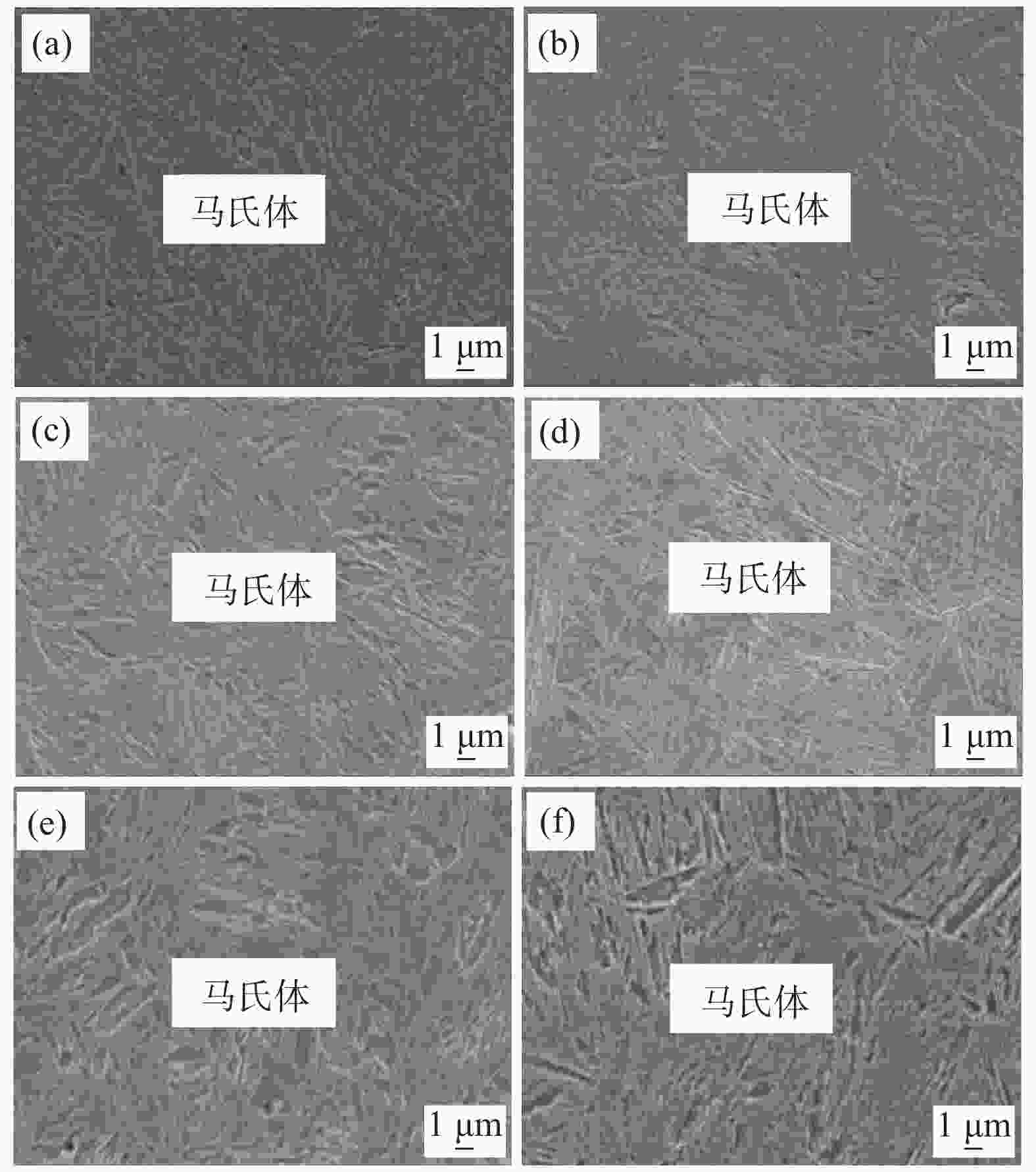
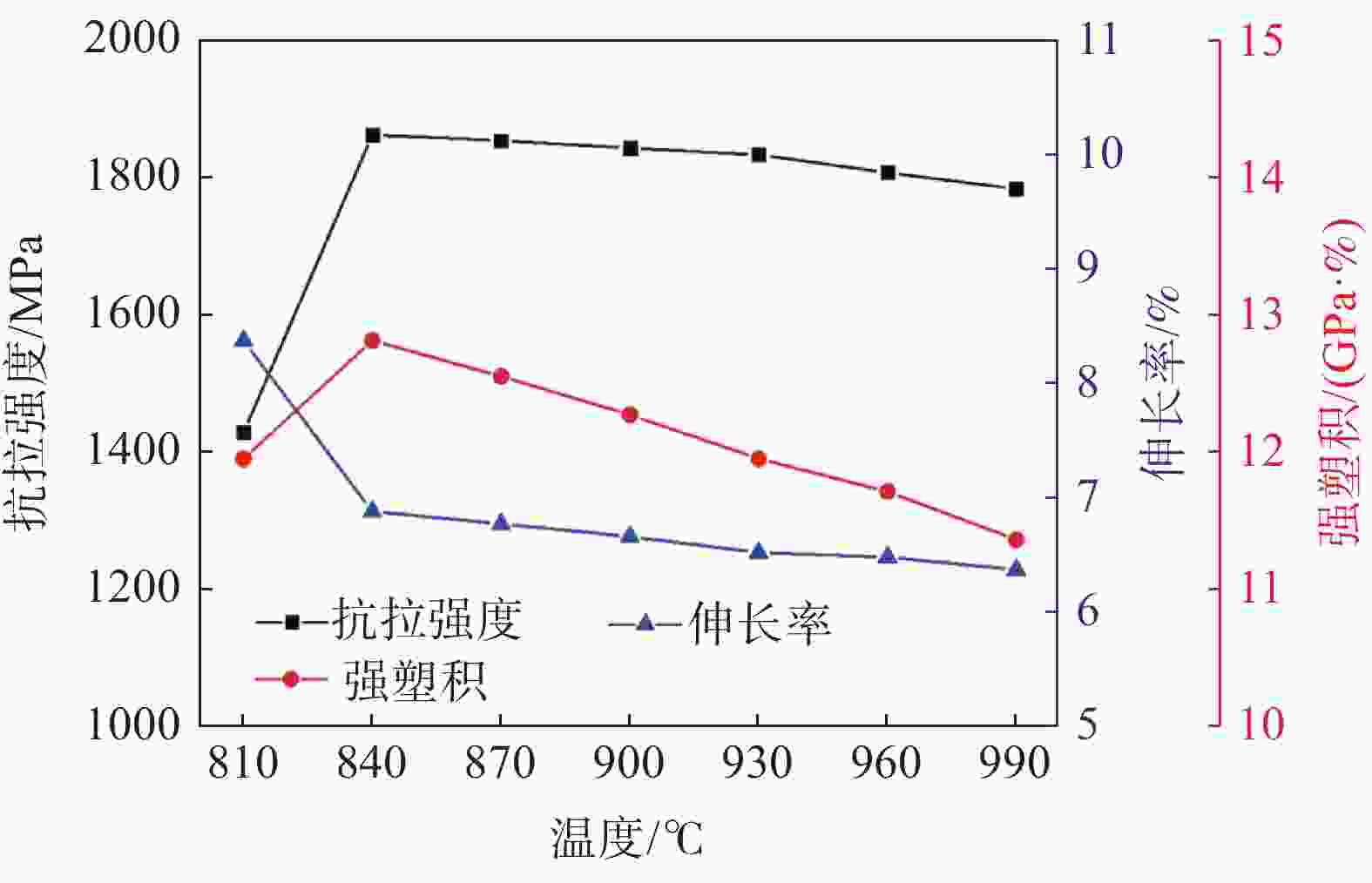
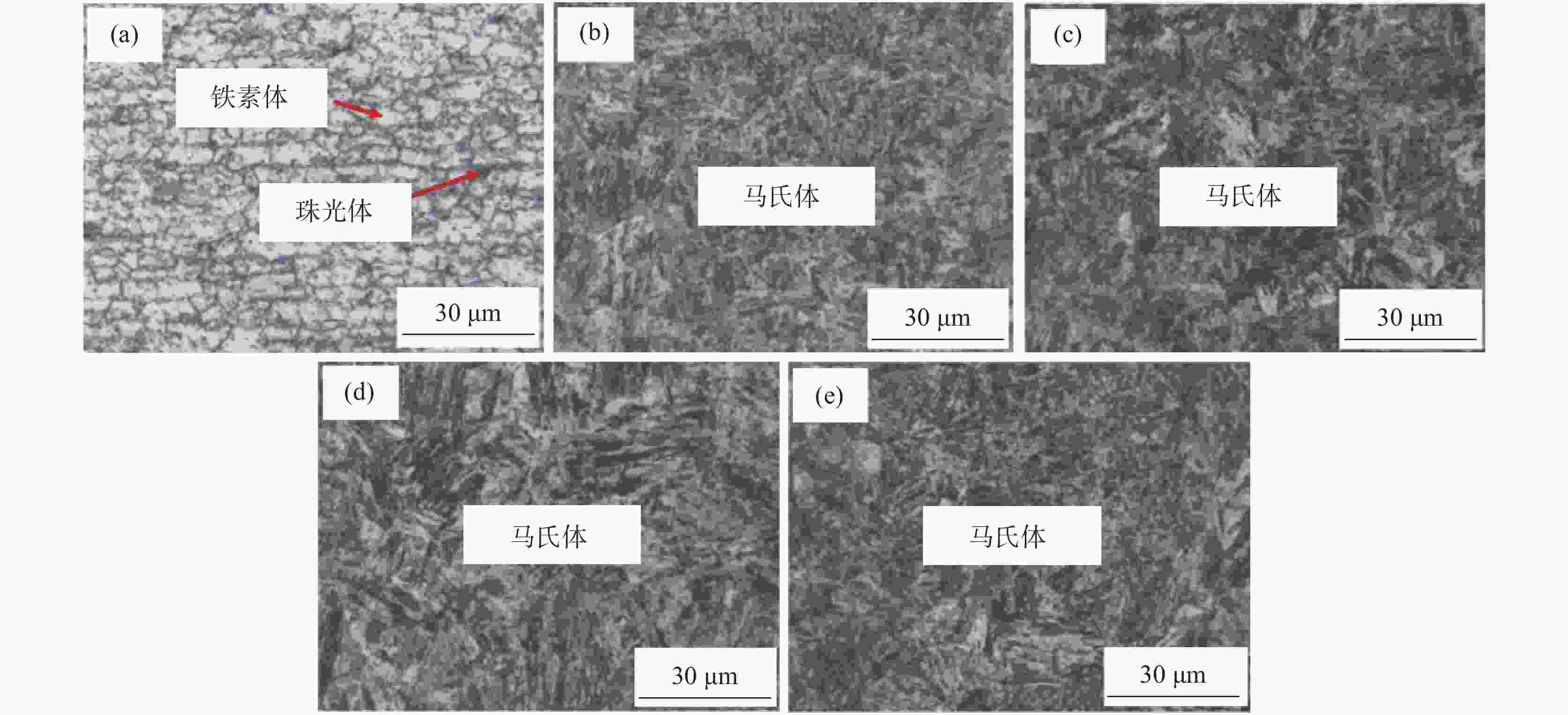
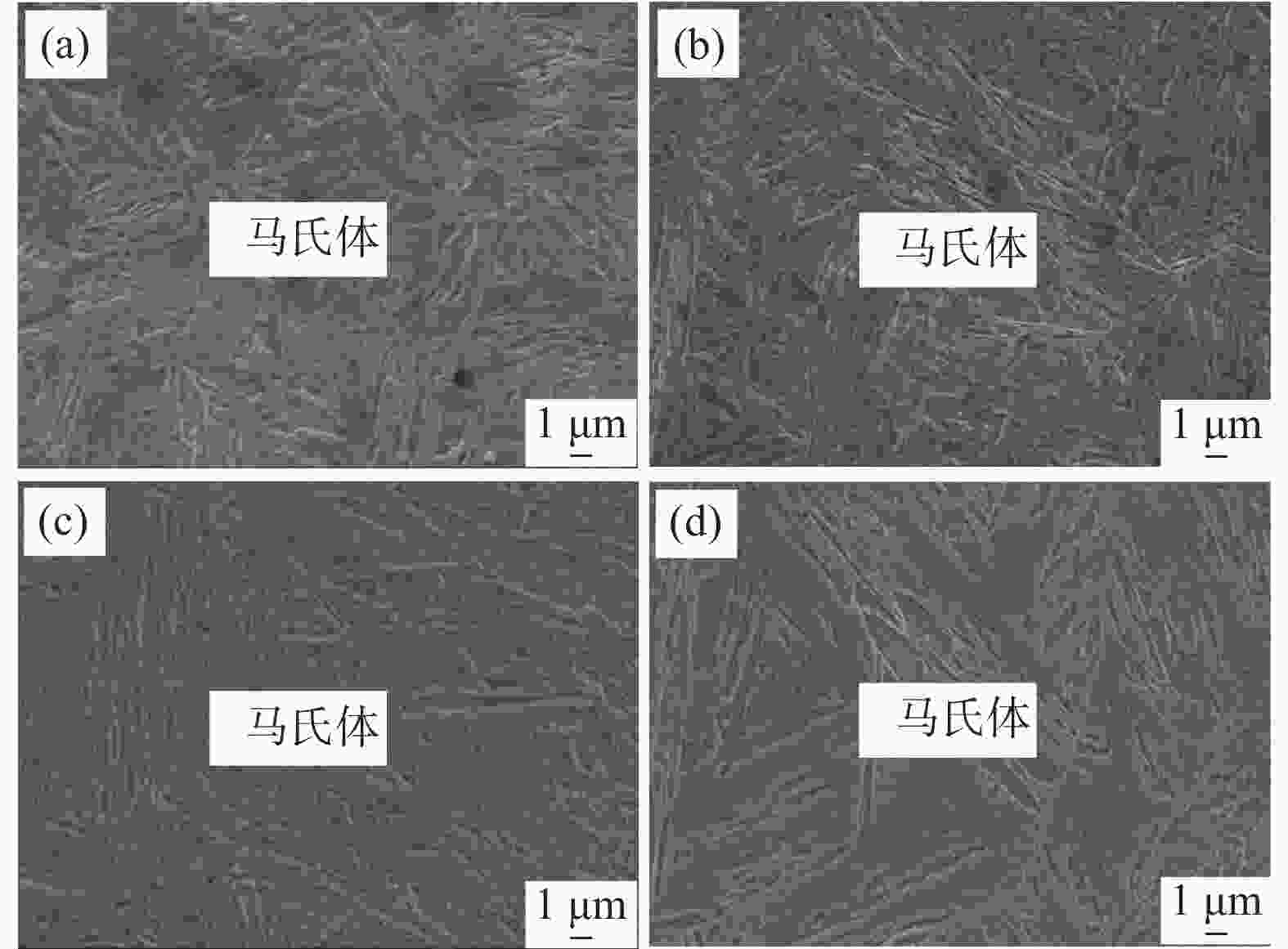
1800 MPa级超高强热成形钢组织性能演变进行了试验研究,确定了最佳的热成形奥氏体化工艺制度。结果表明,当奥氏体化温度及保温时间分别达到840 ℃、3 min时,1800 MPa级超高强热成形钢淬火后的组织均为马氏体,且马氏体组织随着奥氏体化温度的升高及保温时间的增加逐渐粗大,抗拉强度逐渐下降。当奥氏体化温度为840 ℃时,抗拉强度、伸长率及强塑积分别可以达到1861.3 MPa、6.88%、12.81 GPa·%;当保温时间为3 min时,抗拉强度、伸长率及强塑积分别可以达到1851.28 MPa、6.84%、12.66 GPa·%。最佳奥氏体化工艺制度为:奥氏体化温度840 ℃,保温时间3 min。Abstract: The evolution of microstructures and properties of 1800 MPa ultra-high strength hot stamping steels under different austenitizing temperatures and holding times were experimentally studied in this paper, and the optimum hot stamping austenitizing process was established. The results show that when the austenitizing temperature and holding time reach 840 ℃ and 3 min, respectively, the quenched microstructures of the hot stamping steel is consisted of martensite, and the martensite becomes coarser with the increase in temperature and holding time. The tensile strength decreases gradually with the increase of the austenitizing temperature and holding time. When the austenitizing temperature is 840 ℃, the tensile strength, elongation and strength-ductility product can reach1861.3 MPa, 6.88% and 12.81 GPa·%, respectively. When the holding time is 3 min, the tensile strength, elongation and strength-ductility product can reach1851.28 MPa, 6.84% and 12.66 GPa·%, respectively. The austenitizing temperature of 840 ℃ and holding time of 3 min are selected as the optimum austenitizing parameters. -
表 1
1800 MPa级热成形钢主要化学成分Table 1. Main composition of
1800 MPa hot stamping steel% C Mn Si Al B Cr Ti Nb 0.29 1.40 0.26 0.04 0.003 0.25 0.027 0.051 -
[1] Zhang Y, Lai X, Zhu P. Lightweight design of automobile component using high strength steel based on dent resistance[J]. Materials & Design, 2006,27(1):64−68. [2] Li Jixiong , Wang Daoyong . Study on application of MSOT method for lightweight design of automobile body structure[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 12(10): 1-15. [3] Zheng Songlin. Lightweight design of automobile drive shaft based on the characteristics of low amplitude load strengthening[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011,24(6):1111. doi: 10.3901/CJME.2011.06.1111 [4] Novotny S, Geiger M. Process design for hydroforming of lightweight metal sheets at elevated temperatures[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Tech, 2003,138(1-3):594−599. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00042-6 [5] Lechler J , Merklein M. Hot stamping of ultra high strength steels as a key technology for lightweight construction[C]// Materials Science & Technology Conference and Exhibition, MS&T'08. Germany: University Erlangen-Nuremberg, 2008. [6] Mori K I. New hot stamping processes of automobile lightweight ultra-high strength steel parts[J]. Journal of the Japan Society for Technology of Plasticity, 2012,53(613):98−102. doi: 10.9773/sosei.53.98 [7] Xu Yunsong, Gong Yu, Du Hao, et al. A newly-designed hot stamping plus non-isothermal Q&P process to improve mechanical properties of commercial QP980 steel[J]. International Journal of Lightweight Materials and Manufacture, 2019,3(1):26−35. [8] Hu Ping , Liang Ying, He Bin. Hot stamping advanced manufacturing technology of lightweight car body[C]//The Formability of High-Strength Steel for Hot Stamping. Singapore: Springer, 2017: 165-192. [9] De Castro M R, Monteiro W A, Politano R. Enhancements on strength of body structure due to bake hardening effect on hot stamping steel[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019,100(1/4):771−782. [10] Scharifi E, Schade T, Ademaj A, et al. Characterization of mechanical properties, macroscopic deformation behavior and microstructure of functionally graded 22MnB5 steel[J]. Steel Research International, 2021,92(7):16. [11] Reitz A, Grydin O, Schaper M. Characterization of phase transformations during graded thermo-mechanical processing of press-hardening sheet steel 22MnB5[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2020,51:5628−5638. doi: 10.1007/s11661-020-05976-x [12] Zhang Y, Wang W, Liu K, et al. Thermomechanical analysis on the frictional contact behavior of a high-strength steel 22MnB5–die steel H13 tribopair at 800 °C by experiment and finite-element simulation[C]//ARCHIVE Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part J Journal of Engineering Tribology , 2021, (208-210): 1994-1996. [13] Kong Ling, Peng Yan. In situ observation on microstructure evolution of 22MnB5 in hot stamping process[J]. Metallurgical Research and Technology, 2019,116(2):209. doi: 10.1051/metal/2018082 [14] Liu S, Long M, Zhang S, et al. Study on the prediction of tensile strength and phase transition for ultra-high strength hot stamping steel[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020,9(6):14244−14253. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.10.043 [15] Liu S, Ai S, Long M, et al. Evolution of microstructures and mechanical properties of Nb-V alloyed ultra-high strength hot stamping steel in austenitizing process[J]. Materials, 2022,15:8197. doi: 10.3390/ma15228197 -




 下载:
下载: