Establishment of a constitutive model of aviation stainless steel 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb considering the coupling effects of strain, strain rate and temperature
-
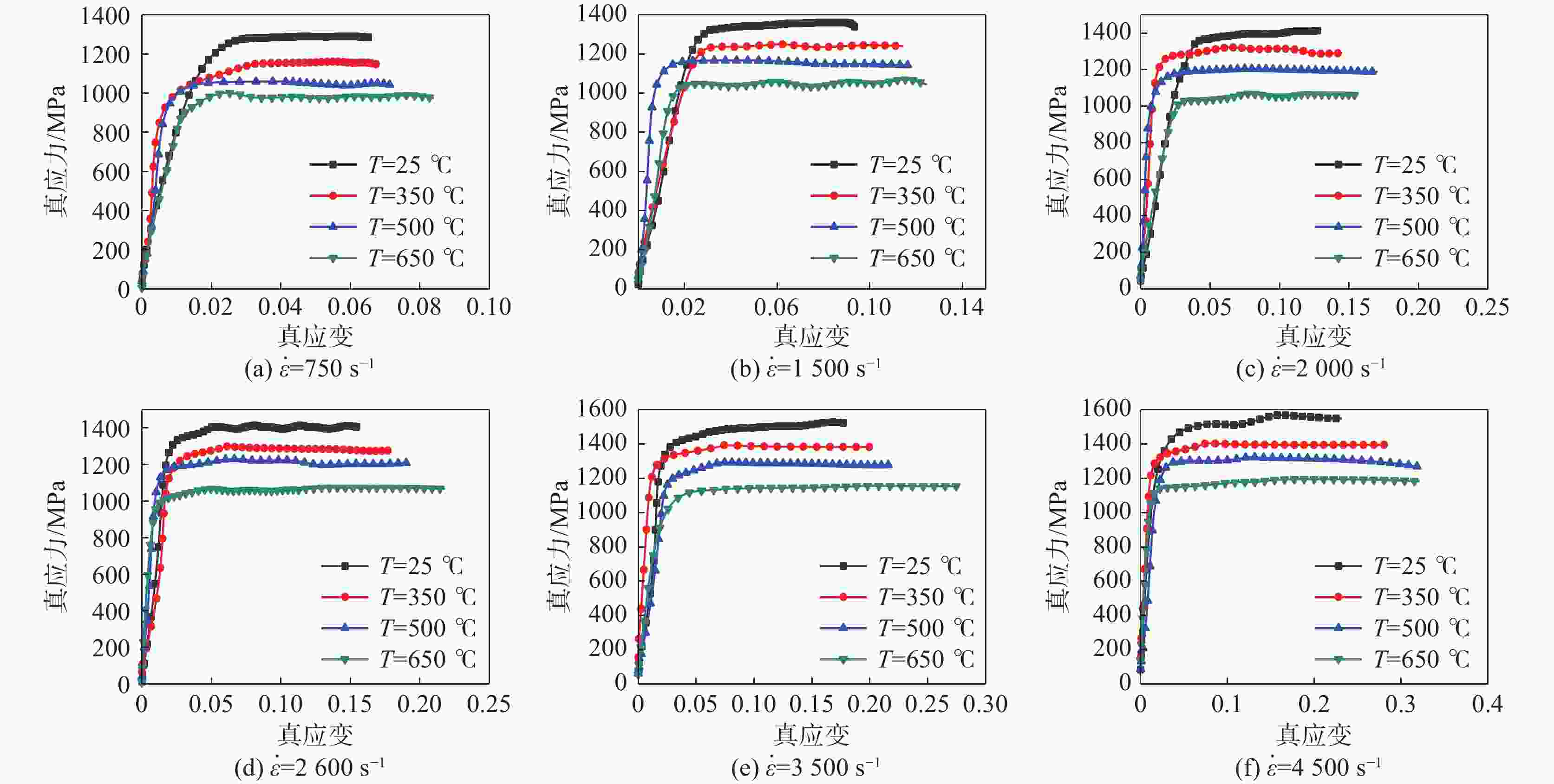
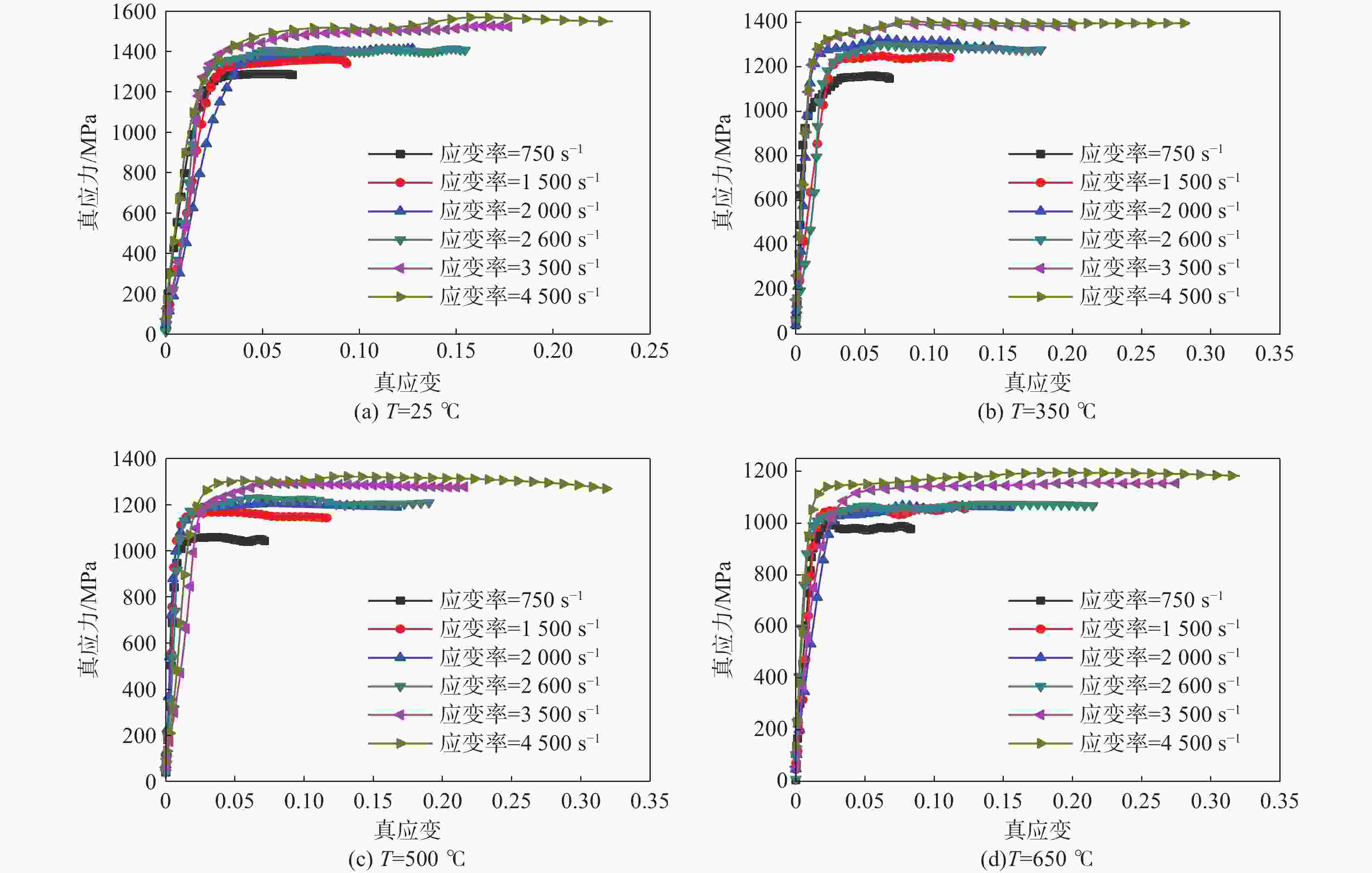
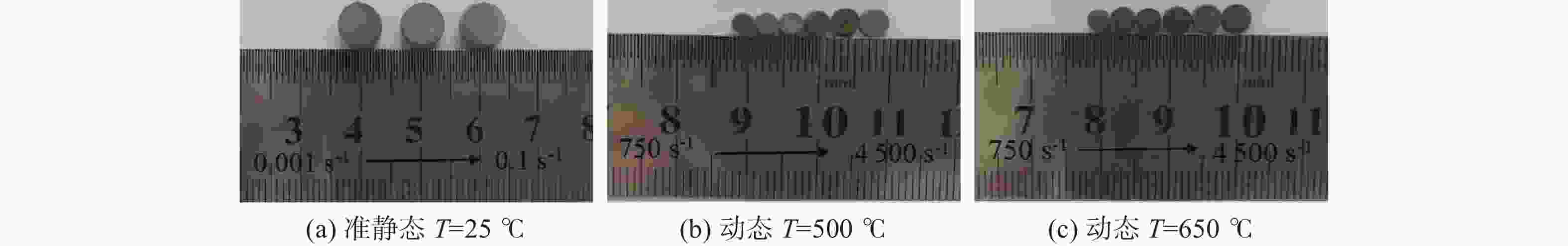
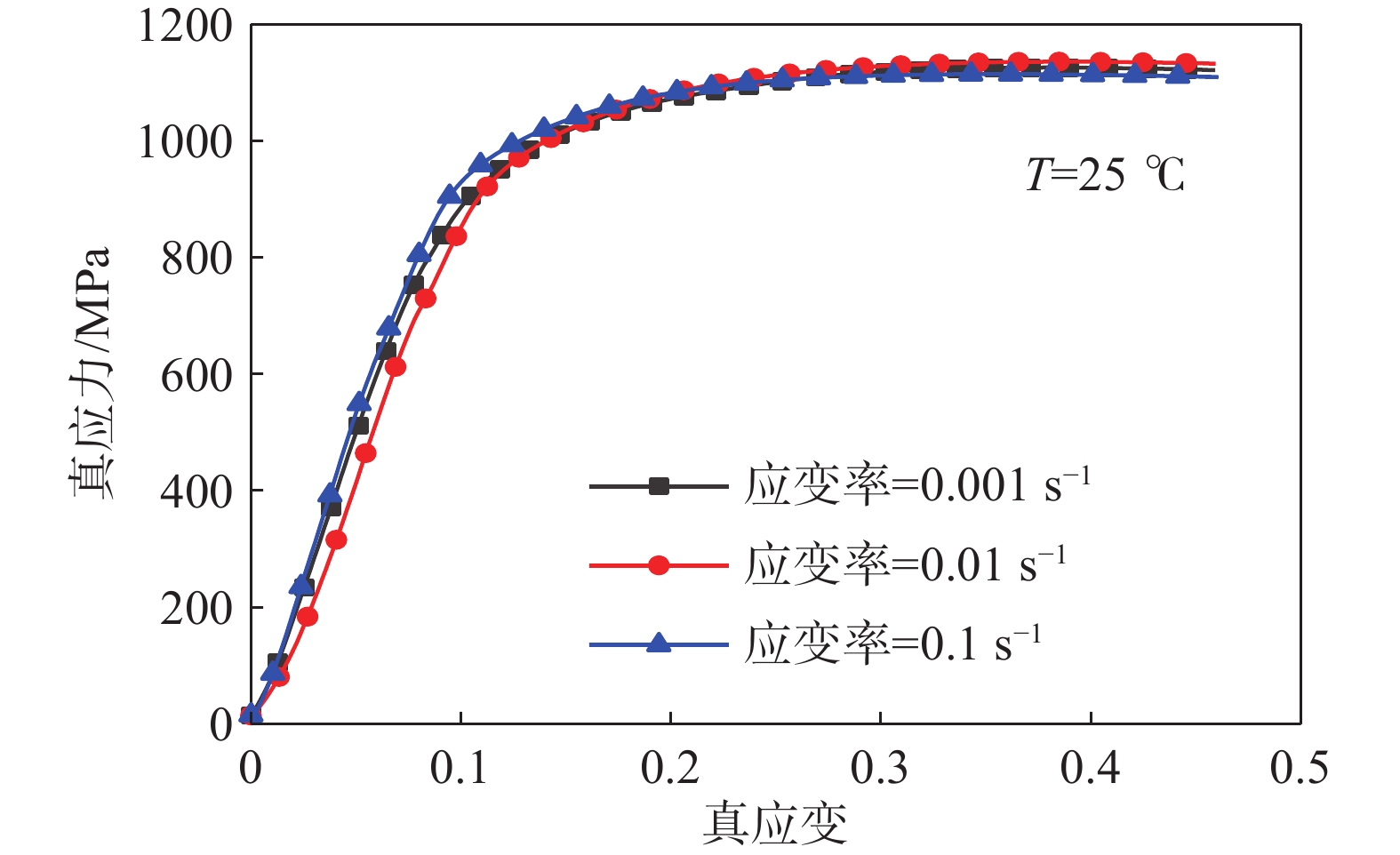
摘要: 航空不锈钢0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb具有优良的特性,广泛应用在各个机械的重要零部件上,零件的加工过程伴随着大应变、高温和高应变率,基于此考虑耦合关系建立能够真实反映切削力学性能的本构模型,为切削仿真提供可靠的数据。以航空不锈钢0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb为研究对象,利用万能试验机(UTM5305)和高温分离式霍普金森试验装置(Split Hopkinson Pressure Bar,SHPB,ALT1000)分别进行准静态压缩试验(温度为25 ℃,应变率为0.1、0.01、0.001s−1)和动态冲击试验(温度为25、350、500、650 ℃,应变率为750、
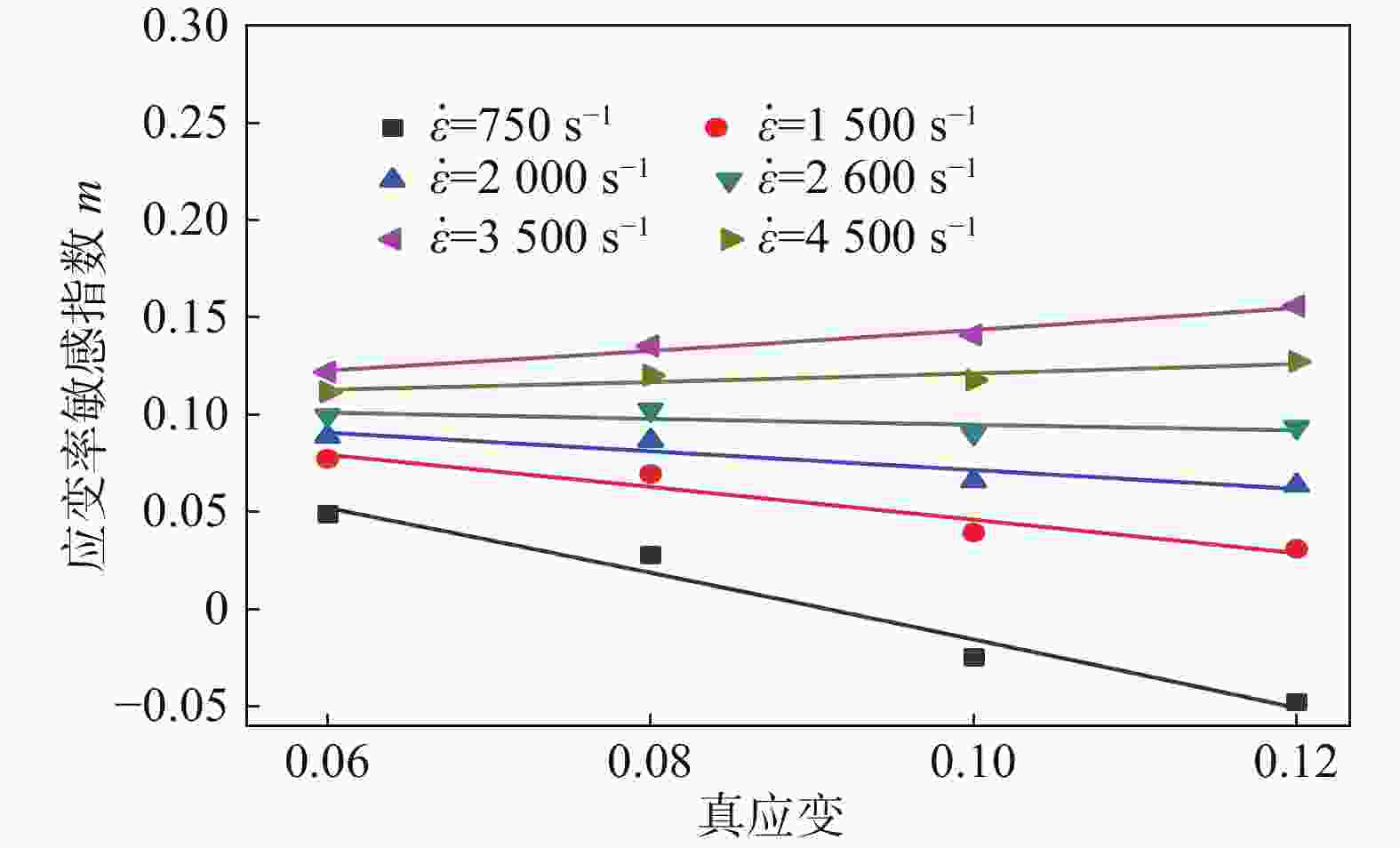
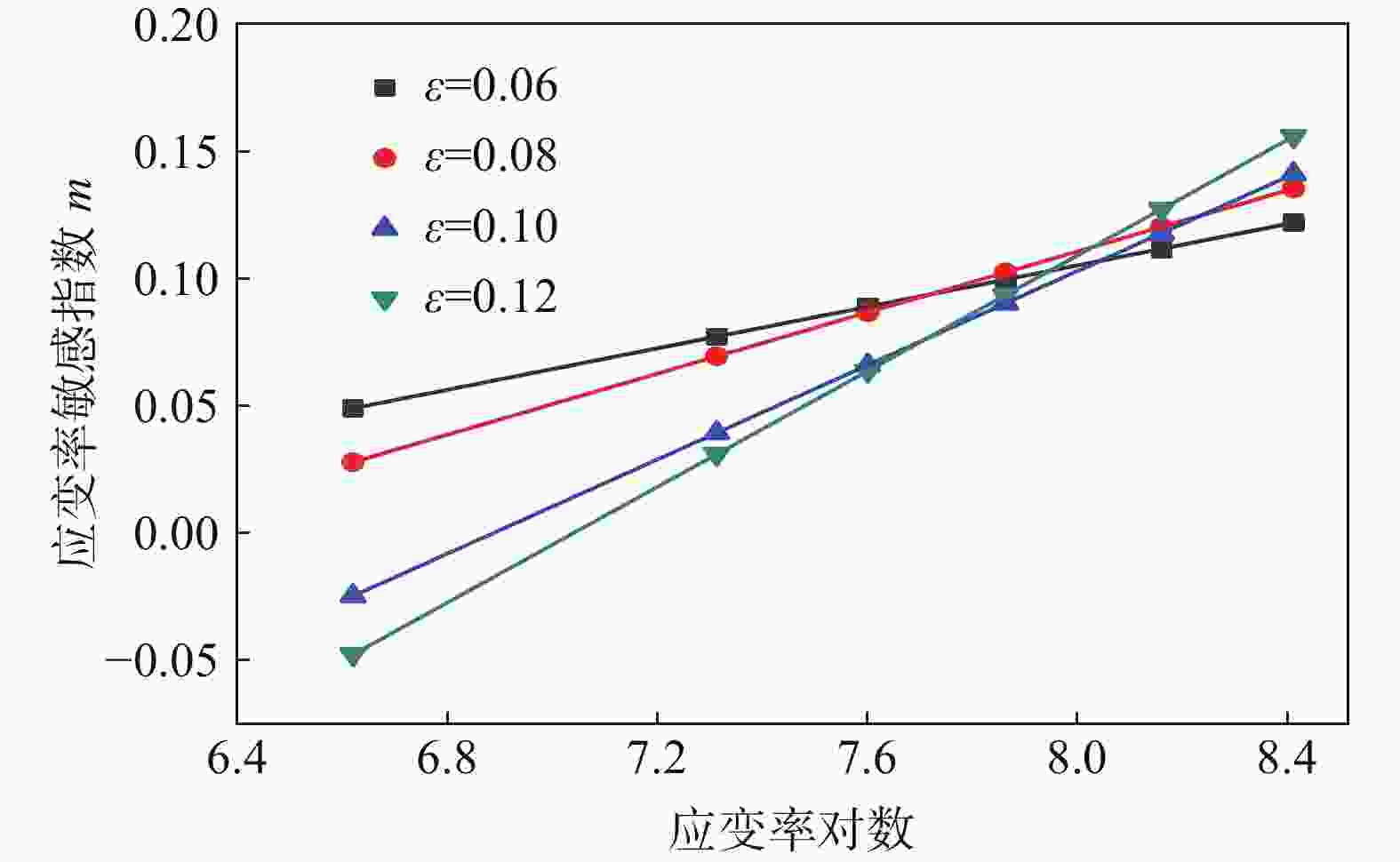
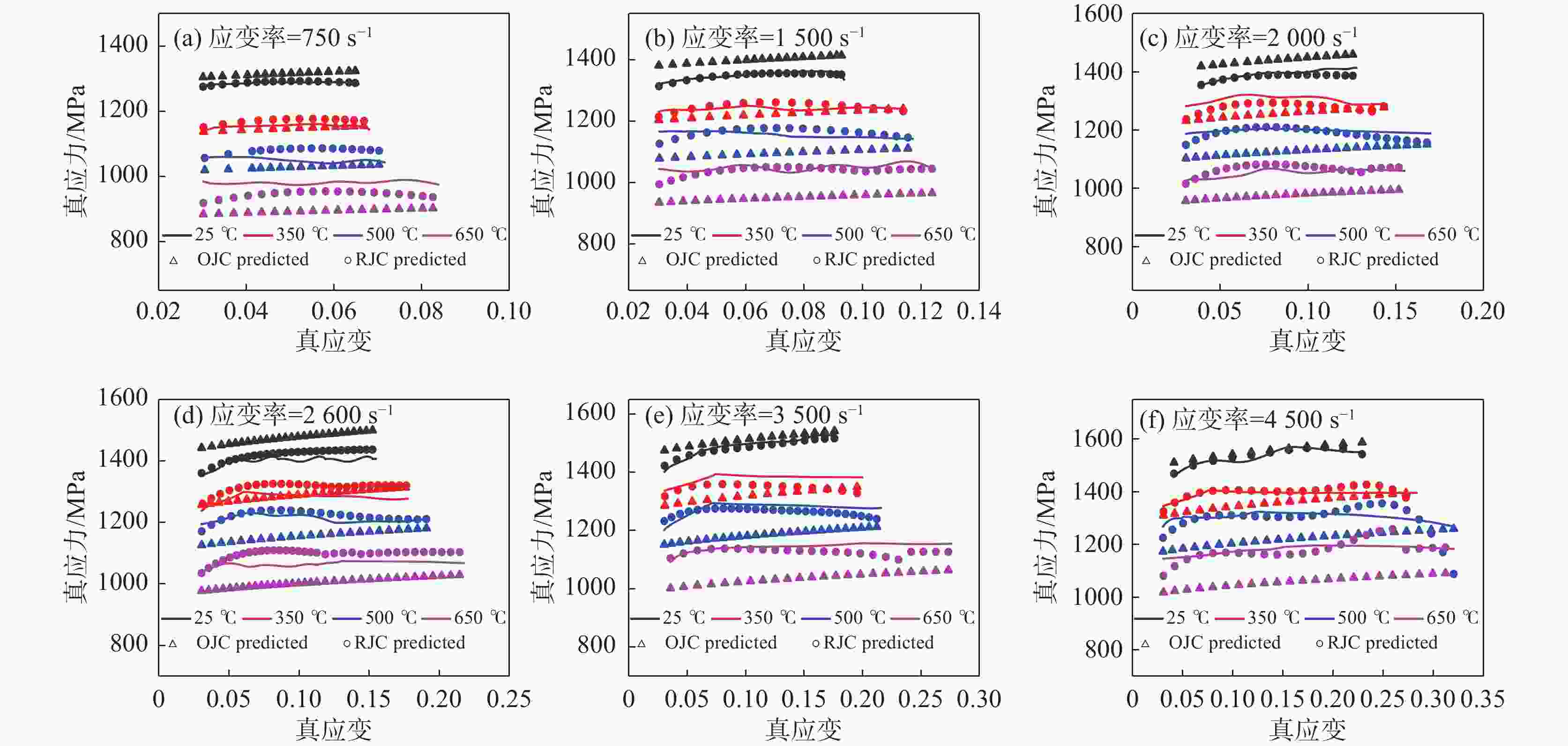
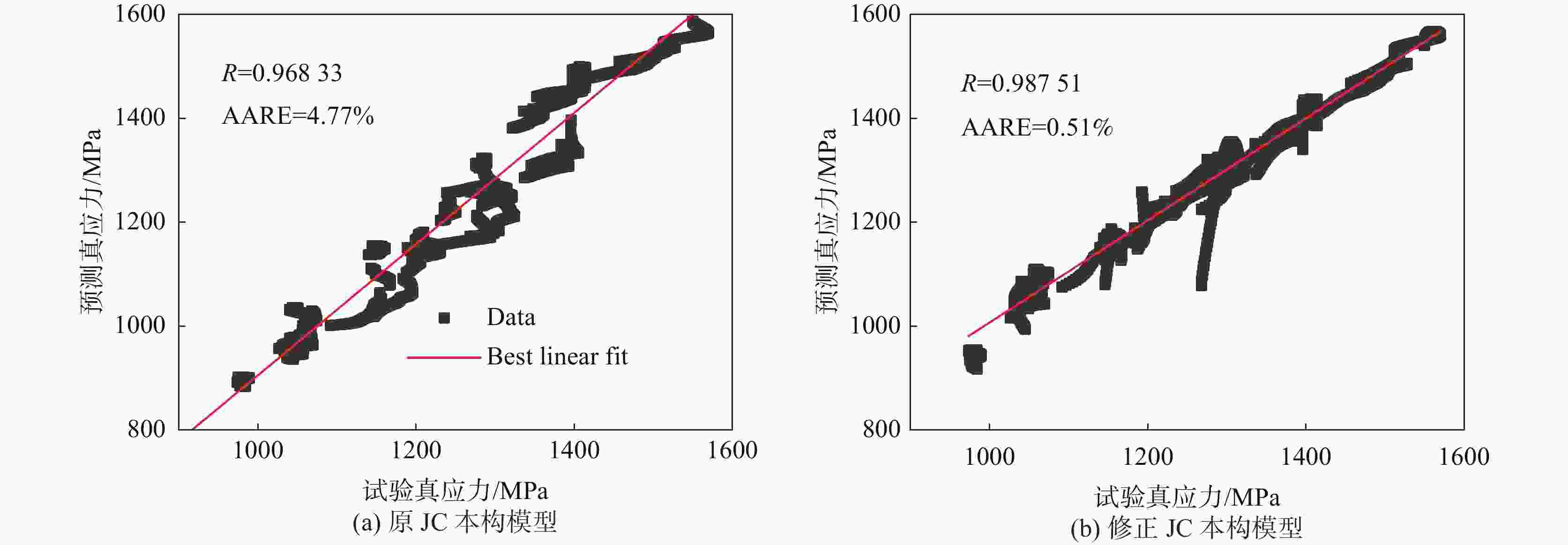
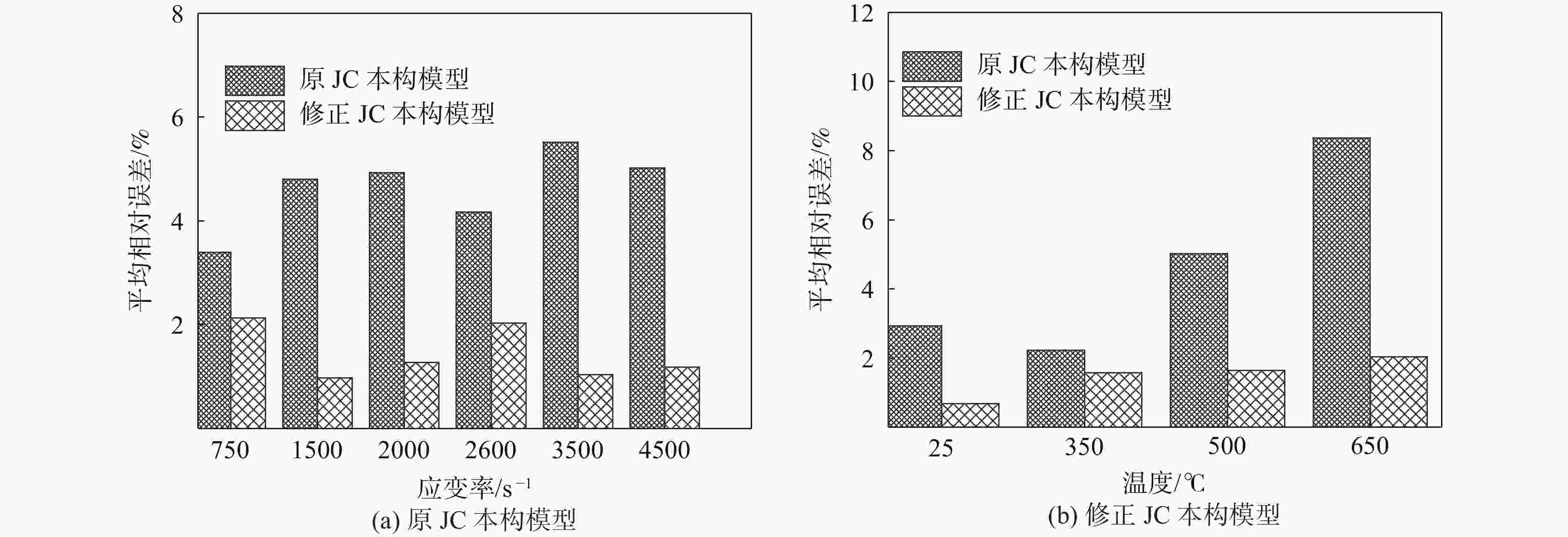
1500 、2000、2600 、3500 、4500 s−1),获得该材料的应力应变关系,并分析其力学性能,结果表明该材料具有应变硬化效应、温度软化效应、应变率强化效应和增塑效应。综合应变、应变率和温度三者相互作用,建立耦合作用下的Johnson-Cook(JC)本构方程,统计分析了试验数据与预测数据(原JC本构方程和修正JC本构方程数据),原JC本构方程的相关系数(R)和平均相对误差(AARE)分别为0.96833 和4.77%;修正JC本构方程的相关系数(R)和平均相对误差(AARE)分别为0.987513 和0.51%,表明修正JC本构方程更加准确、可靠预测高应变率下应力应变的关系。Abstract: The aviation stainless steel 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb has excellent characteristics and is widely used in important parts of various machines. The machining process of these parts is accompanied by large strain, high temperature and high strain rate. Based on this coupling relationship, a constitutive model that can truly reflect the cutting mechanical properties is established to provide reliable data for cutting simulation. This paper sets the aviation stainless steel 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb as the research object, and uses the universal testing machine (UTM5305) and the split Hopkinson Pressure Bar (SHPB, ALT1000) to carry out the quasi-static compression tests (temperature: 25 ℃, strain rate: 0.1, 0.01, 0.001 s−1) and dynamic impact tests (temperature: 25, 350, 500 and 650 ℃, strain rate: 750,1500 ,2000 ,2600 ,3500 and4500 s−1), respectively. The stress-strain relationship of the material is obtained, and its mechanical properties are analyzed. It is shown that the material exhibits strain hardening effect, temperature softening effect, strain rate strengthening effect and plasticizing effect. Combining the interaction of strain, strain rate and temperature, the Johnson-Cook (JC) constitutive equation under the coupling action is established. The test data and prediction data (the original and modified JC constitutive equation) are statistically analyzed. The correlation coefficient (R) and the average phase error (AARE) of the original JC constitutive equation are0.96833 and 4.77%, respectively. The correlation coefficient (R) and average relative error (AARE) of the modified JC constitutive equation are0.987513 and 0.51%, respectively, indicating that the modified JC constitutive equation is more accurate and reliable in predicting the stress-strain relationship at high strain rates. -
表 1 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel
% C Si Cr Ni Mn P S Cu Nb Fe 0.06 0.80 16.25 3.60 0.82 0.030 0.022 3.83 0.28 Bal. 表 2 准静态下不同应变率和应变处的强化指数$ n $
Table 2. Strengthening exponent $ n $ at different strain rates and strains under quasi-static state
$ \dot \varepsilon /{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}} $ n $ \varepsilon $=0.20 $ \varepsilon $=0.25 $ \varepsilon $=0.30 $ \varepsilon $=0.35 $ \varepsilon $=0.40 $ \varepsilon $=0.45 0.001 0.1418 0.1250 0.0625 0.0335 0.0210 0.0425 0.01 0.1612 0.0849 0.0611 0.0239 0.0119 0.0390 0.1 0.1187 0.0644 0.0260 0.0004 0.0145 0.0267 表 3 准静态试样变形量
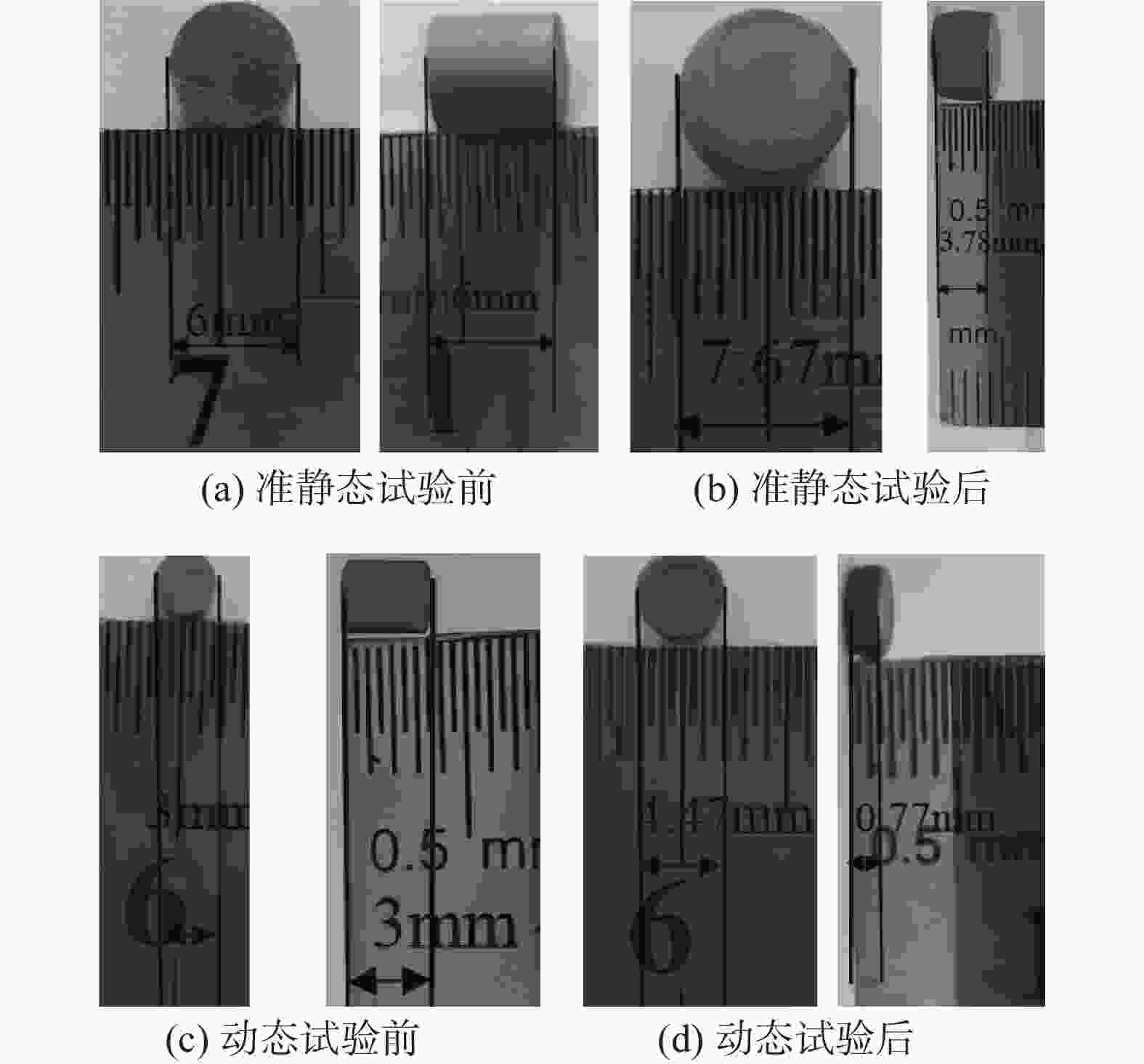
Table 3. Deformation of quasi-static specimens
应变率/$ {{\text{s}}^{ - 1}} $ 直径/mm 厚度/mm 0.001 7.29 4.31 0.01 7.43 4.11 0.1 7.67 3.78 表 4 动态试样变形量(T=25 ℃和T=650 ℃)
Table 4. Deformation of quasi-static specimens
T/℃ $ \dot \varepsilon /{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}} $ $ d/{\text{mm}} $ $ h/{\text{mm}} $ 25 750 3.12 2.68 1500 3.18 2.47 2 000 3.64 2.06 2600 3.77 1.86 3500 4.01 1.65 4500 4.42 0.76 650 750 3.36 2.40 1500 3.55 2.22 2 000 3.71 1.97 2600 4.13 1.56 3500 4.37 1.51 4500 4.47 0.77 表 5 应变项参数值
Table 5. Parameter values of strain item
B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 509.01581 5908.2858 − 21498.54 35937.295 − 23318.67 表 6 应变率项参数值
Table 6. Parameter values of strain rate item
C0 C1 C2 C3 C4 − 2.42266 0.69941 − 0.06371 0.00192 − 11.18017 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 3.04559 − 9.69615 1.58625 0.18026 − 0.06239 表 7 温度项参数值
Table 7. Parameter values of temperature item
a0 a1 a2 a3 a4 a5 − 67.50836 9.61375 − 118.52129 333.90202 15.06135 − 1.08320 a6 a7 a8 a9 a10 0.02552 1.07963 0.00000 − 3.53005 0.39414 -
[1] 郭亚欢. 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢热处理工艺及性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2011.Guo Yahuan. Effect of heat treatment processes on properties of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb steel[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2011. [2] 吕义郎. 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢薄壁环形件胀形工艺研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2018.Lü Yilang. Bulging process of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel thin-walled ring research[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2018. [3] 夏德贵. 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb马氏体沉淀硬化不锈钢耐海水腐蚀性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2007.Xia Degui. Seawater corrosion resistance property of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb martensitic precipitation hardening stainless steel[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2007. [4] 朱凯旋. 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb燃气轮机叶片材料砂带磨削的表面质量研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2006.Zhu Kaixuan. Study on surface quality of the material 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb gas turbine blade ground by coated abrasive belt[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2006. [5] Remington B A, Bazan G, Belak J, et al. Materials science under extreme conditions of pressure and strain rate[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 2004,35(9):2587−2607. [6] Tian Xianhua, Yan Kuicheng, Zhao Jun, et al. Properties at elevated temperature and high strain rate and establishment of Johnson-Cook constitutive model for GH2132[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2022,33(7):872−881. (田宪华, 闫奎呈, 赵军, 等. GH2132高温高应变率下力学性能分析与Johnson-Cook本构模型的建立[J]. 中国机械工程, 2022,33(7):872−881.Tian Xianhua, Yan Kuicheng, Zhao Jun, et al. Properties at elevated temperature and high strain rate and establishment of Johnson-Cook constitutive model for GH2132[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 33(7): 872-881. [7] Jamwal A, Agrawal R, Sharma M, et al. Application of optimization techniques in metal cutting operations: A biliometric analysis[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020,38(1):365−370. [8] Zhang Jilin, Jia Haishen, Yi Xiangbin, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties and comparison of two constitutive models for martensitic stainless steel 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb[J]. Materials Research Express, 2021,8(10):106501. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ac29f5 [9] Chen G, Ren C, Yang X, et al. Evidence of thermoplastic instability about segmented chip formation process for Ti-6Al-4V alloy based on the finite-element method[J]//Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 225(6): 1407-1417. [10] Shi Jing, Zhang Weiqiang, Guo Jin. Constitutive model of plastic deformation for metal[J]. Materials Reports, 2010,24(4):82−85. (是晶, 张伟强, 郭金. 金属塑性变形的本构模型研究[J]. 材料导报, 2010,24(4):82−85.Shi Jing, Zhang Weiqiang, Guo Jin. Constitutive model of plastic deformation for metal[J]. Materials Reports, 2010, 24(4): 82-85. [11] Zhan Lishui, Liu Cheng, Ye Junqing, et al. Research on refinement of heat treatment for improving hardness of 17-4PH (0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb) forgings[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2021,46(9):212−215. (占立水, 刘成, 叶俊青, 等. 改善17-4PH(0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb)锻件硬度的热处理精细化研究[J]. 锻压技术, 2021,46(9):212−215.Zhan Lishui, Liu Cheng, Ye Junqing, et al. Research on refinement of heat treatment for improving hardness of 17-4 PH (0 Cr17 Ni4 Cu4 Nb) forgings[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2021, 46(9): 212-215. [12] He Li. Vacuum heat treatment of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel base[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2021,46(8):189−192. (贺利. 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢底座的真空热处理[J]. 金属热处理, 2021,46(8):189−192.He Li. Vacuum heat treatment of 0 Cr17 Ni4 Cu4 Nb stainless steel base[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2021, 46(8): 189-192. [13] Zhang Xuezhen, Lü Kang, Shi Yaocheng, et al. Study on drill thrust and chip in ultrasonic vibration drilling of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2018,46(19):53−55, 66. (张学忱, 吕康, 史尧臣, 等. 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb超声振动钻削的钻削力和切屑研究[J]. 机床与液压, 2018,46(19):53−55, 66.Zhang Xuezhen, Lv Kang, Shi Yaocheng, et al. Study on drill thrust and chip in ultrasonic vibration drilling of 0 Cr17 Ni4 Cu4 Nb[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2018, 46(19): 53-55, 66. [14] Hu Chunyan, Liu Xinling, Tao Chunhu, et al. Failure analysis on 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb screws[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2012,(12):21−23, 28. (胡春燕, 刘新灵, 陶春虎, 等. 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb钢制螺钉断裂原因分析[J]. 材料工程, 2012,(12):21−23, 28.Hu Chunyan, Liu Xinling, Tao Chunhu, et al. Failure analysis on 0 Cr17 Ni4 Cu4 Nb screws[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2012(12): 21-23, 28. [15] He Zhu, Zhao Shougen, Yang Jialing, et al. Experimental investigation of the dynamic material property of stainless steel: 0Crl7Ni4Cu4Nb[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2007,25(3):418−421. (何著, 赵寿根, 杨嘉陵, 等. 0Crl7Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢动态力学性能研究[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2007,25(3):418−421.He Zhu, Zhao Shougeng, Yang Jialing, et al. Experimental investigation of the dynamic material property of stainless steel: 0 Crl7 Ni4 Cu4 Nb[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering, 2007, 25(3): 418-421. [16] 王建军. 典型金属塑性流动中反常应力峰及其本构关系[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2017.Wang Jianjun. Anomalous stress peak in the plastic flow of typical metals and its constitutive model[D]. Xi, an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2017. [17] Johnson G R, Cook W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1983,21:541−548. [18] Liang R, Khan A S. A critical review of experimental results and constitutive models for BCC and FCC metals over a wide range of strain rates and temperatures[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 1999,15(9):869−890. doi: 10.1016/S0749-6419(99)00016-9 [19] 王礼立. 冲击动力学进展[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 1992.Wang Lili. Advances in impact dynamics[M]. Beijng: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 1992. [20] Fang Jian, Wei Yijing, Wang Chengzhong. Analytical measurement and mechanical study on the tensile strain hardening exponent[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2003,10(3):12−17. (方健, 魏毅静, 王承忠. 拉伸应变硬化指数的解析测定及力学分析[J]. 塑性工程报, 2003,10(3):12−17.Fang Jian, Wei Yijing, Wang Chengzhong. Analytical measurement and mechanical study on the tensile strain hardening exponent[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2003, 10(3): 12-17. [21] Sun Xuewei, Ling Yongzhuo, Sun Jisong, et al. A method of determinig strain-hardening exponents[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 1995,17(4):27−28. (孙学伟, 令永卓, 孙吉松, 等. 材料硬化指数n的确定方法[J]. 机械强度, 1995,17(4):27−28.Sun Xuewei, Ling Yongzhuo, Sun Jisong, et al. A method of determinig strain-hardening exponents[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 1995, 17(4): 27-28. [22] 曹育菡. Ni-Co-Cr-Fe基高熵合金的应变强化研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2020.Cao Yuhan. Study on strain hardening of Ni-Co-Cr-Fe based high entropy alloys[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2020. [23] 王相宇. 高温合金GH4169的切削加工性评价方法和本构模型研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2016.Wang Xiangyu. Study on cutting performance evaluation and constitutive model of superalloy GH4169[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2016. [24] 姬芳芳. 高速切削GH4169切削区材料塑性行为研究[D]. 长春: 长春工业大学, 2018.Ji Fangfang. Study on cutting performance evaluation and constitutive model of superalloy GH4169[D]. Changchun: Changchun Industrial College, 2018. [25] Wang Xiangyu, Huang Chuanzhen, Zou Bin. Dynamic behavior and a modified Johnson–Cook constitutive model of Inconel 718 at high strain rate and elevated temperature[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2013, 58(15): 385-390. [26] Yang Xuemei, Guo Hongzhen, Yao Zekun. Strain rate sensitivity, temperature sensitivity, and strain hardening during the isothermal compression of BT25y alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2016,31(18):2863−2875. doi: 10.1557/jmr.2016.294 [27] Tang Changguo, Zhu Jinhua, Zhou Huijiu. Phenomena and analysis of plastisity-increasing induced by high strain rate for some metallic materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 1996,(1):19−24. (唐长国, 朱金华, 周惠久. 金属材料拉伸的高应变率增塑现象及分析[J]. 材料研究学报, 1996,(1):19−24.Tang Changguo, Zhu Jinhua, Zhou Huijiu. Phenomena and analysis of plastisity-increasing induced by high strain rate for some metallic materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 1996(1): 19-24. [28] 冯端. 金属物理学-金属力学性能[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999.Feng Duan. Metal physics-metal mechanical properties[M]. Beijng: Science Press, 1999. [29] 李庆生. 材料强度学[M]. 太原: 山西科学教育出版社, 1999.Li Qingsheng. Material strength[M]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Science Education Press, 1999. [30] 李川平. Ti6Al4V钛合金动态本构模型与高速切削有限元模拟研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2011.Li Chuangping. The research on dynamic constitutive model of Ti6Al4V titanium alloy and finite element simulation of high-speed cutting[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2011. [31] Niu D X, Zhao C, Li D X, et al. Constitutive modeling of the flow stress behavior for the hot deformation of Cu-15Ni-8Sn alloys[J]. Frontiers in Materials, 2022,7(12):577867. [32] Ma Bin, Li Ping, Liang Qiang. Comparison on high-temperature flow behavior of HNi55-7-4-2 alloy predicted by modified JC model and BP-ANN algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2021,45(1):92−99. (马斌, 李平, 梁强. 基于修正JC模型和BP-ANN算法预测HNi55-7-4-2合金高温流变行为的对比[J]. 机械工程材料, 2021,45(1):92−99.Ma Bing, Li Ping, Liang Qiang. Comparison on high-temperature flow behavior of HNi55-7-4-2 alloy predicted by modified JC model and BP-ANN algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2021, 45(1): 92-99. [33] Su Nan, Chen Minghe, Xie Lansheng, et al. Dynamic mechanical characteristics and constitutive model of TC2 Ti-alloy[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2021,35(3):201−208. (苏楠, 陈明和, 谢兰生, 等. TC2钛合金的动态力学特征及其本构模型[J]. 材料研究学报, 2021,35(3):201−208.Su Nan, Chen Minghe, Xie Lansheng, et al. Dynamic mechanical characteristics and constitutive model of TC2 Ti-alloy[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 35(3): 201-208. [34] Jia Haishen, Luo Wencui, Zhang Jilin, et al. Study on dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of 022Cr18Ni14Mo2 stainless steel under impact load[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(2):178−185. (贾海深, 罗文翠, 张继林, 等. 冲击载荷下022Cr18Ni14Mo2不锈钢动态力学特性及其本构模型研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(2):178−185. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.02.027Jia Haishen, Luo Wencui, Zhang Jilin, et al. Study on dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of 022 Cr18 Ni14 Mo2 stainless steel under impact load[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(2): 178-185. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.02.027 -




 下载:
下载: