Prediction of primary carbide size in high carbon chromium bearing steel
-
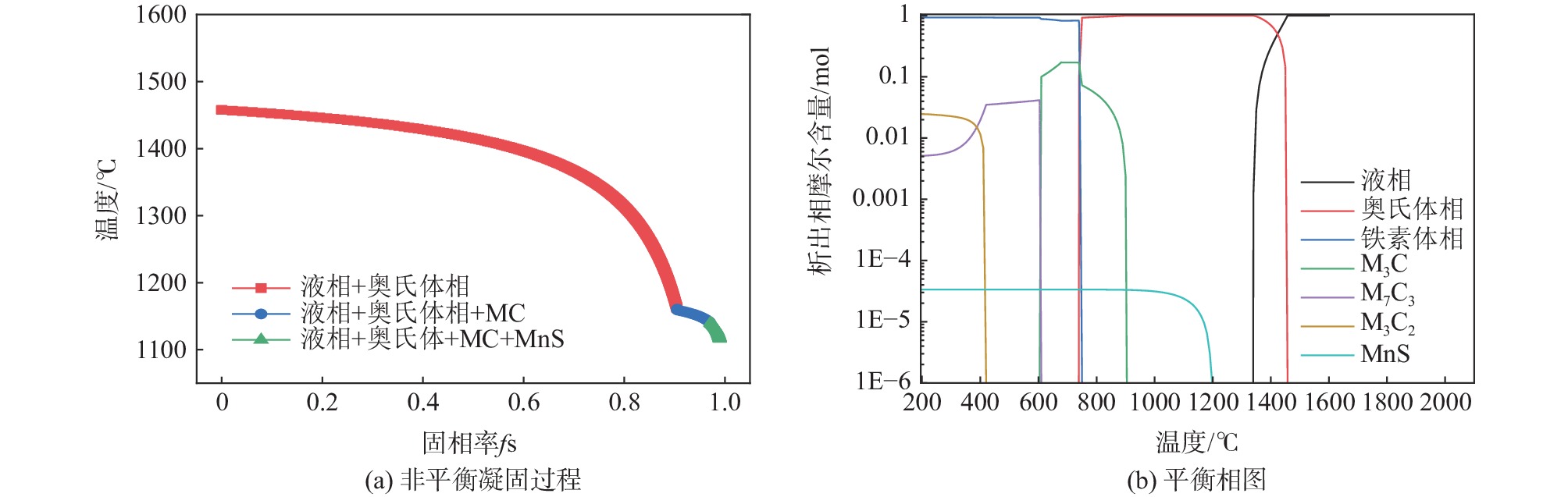
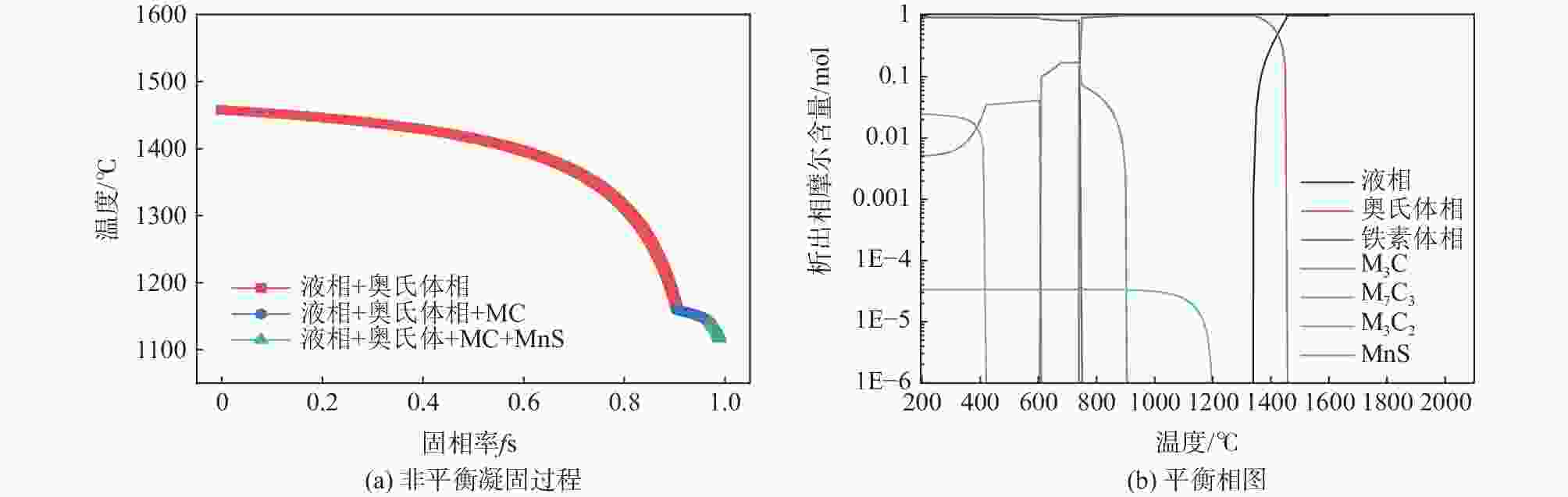
摘要: 采用Thermo-Calc热力学计算软件对轴承钢凝固过程相转变规律、初生碳化物物相类型、初生碳化物析出温度进行热力学分析。基于Scheil偏析模型和Goto模型对轴承钢凝固过程中初生碳化物粒子尺寸进行预测,并通过热模拟试验和碳化物显微形貌定量分析对预测结果进行试验验证。计算结果表明,轴承钢凝固过程初生碳化物为(Fe,Cr)C型碳化物,析出温度为
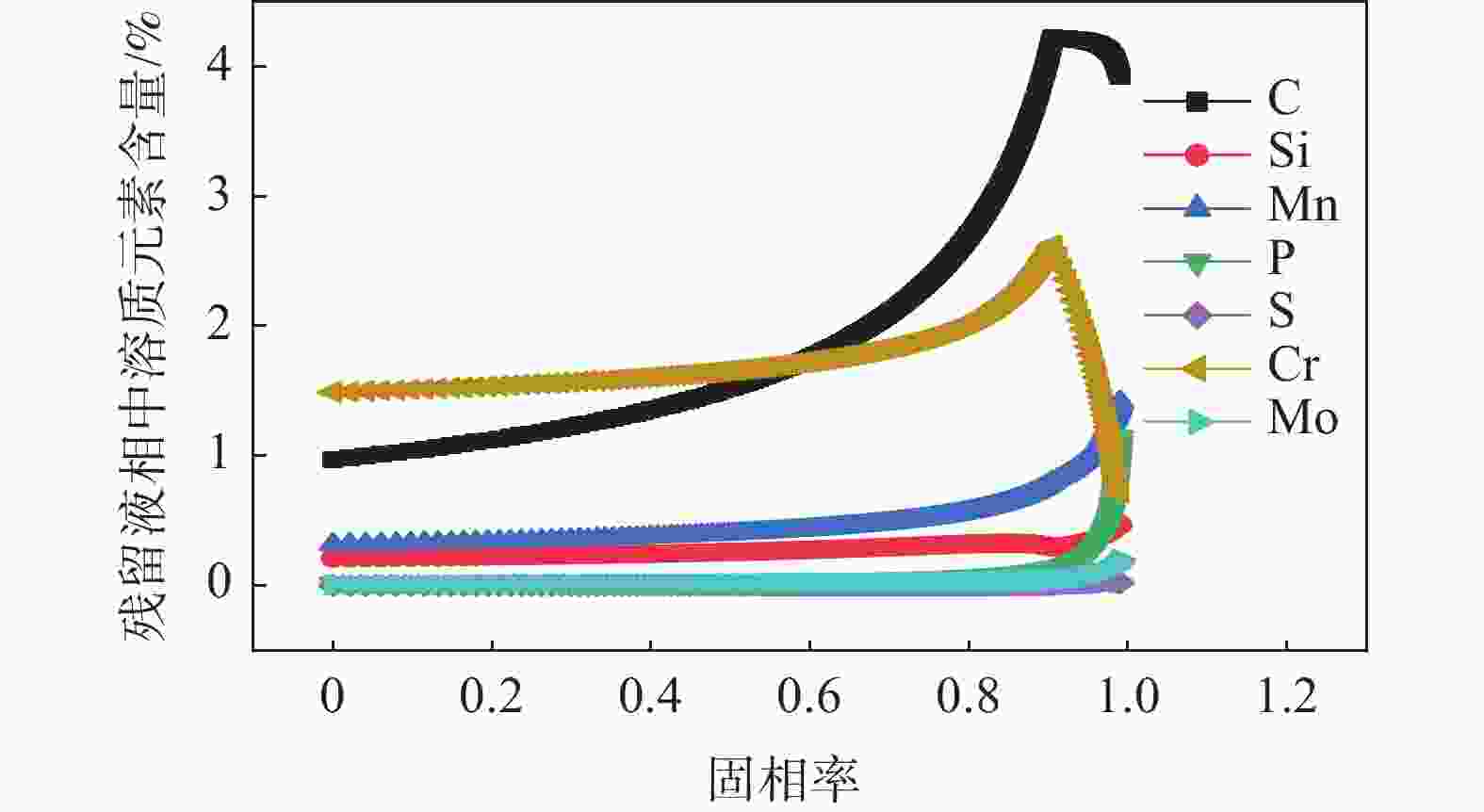
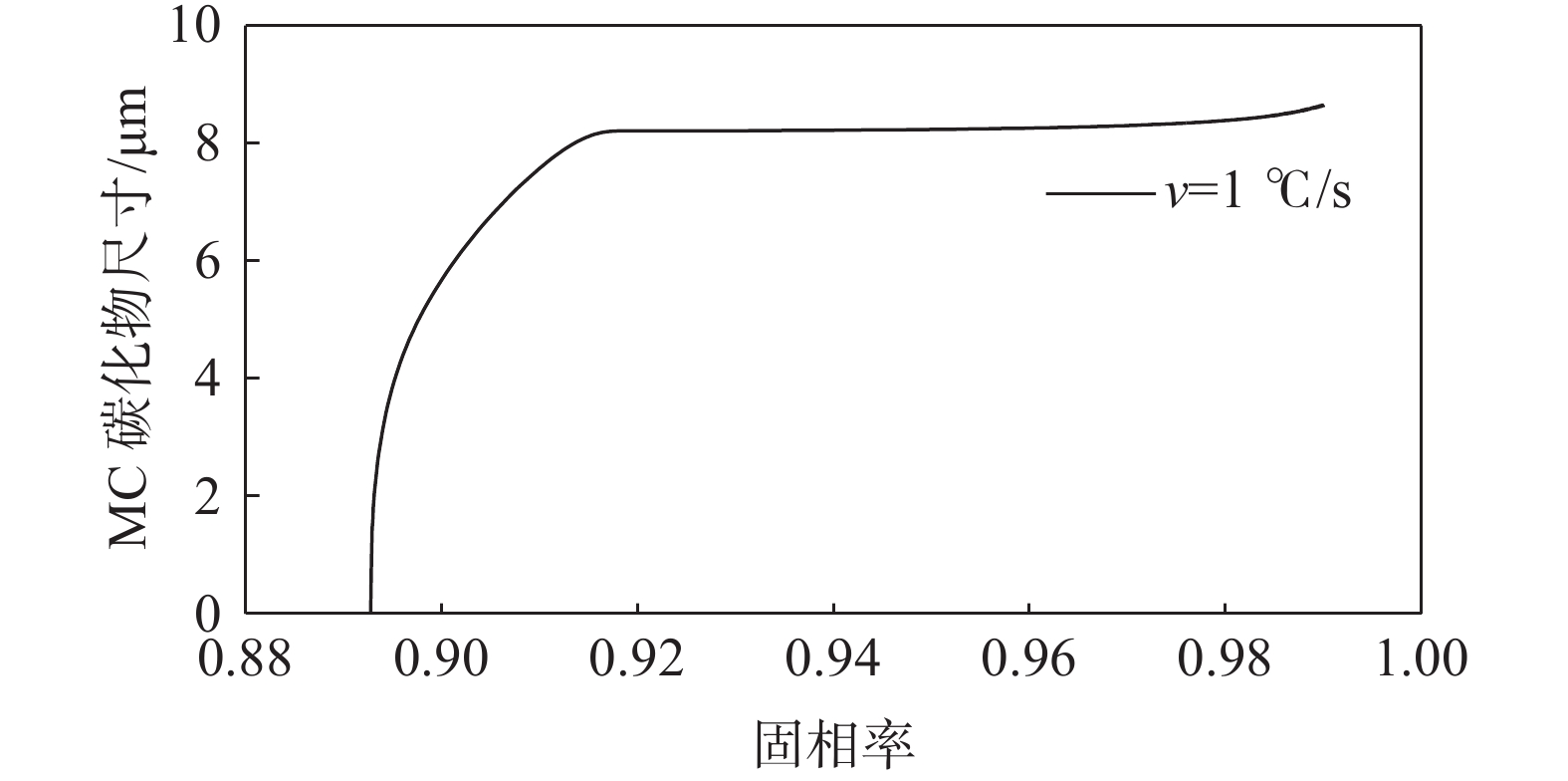
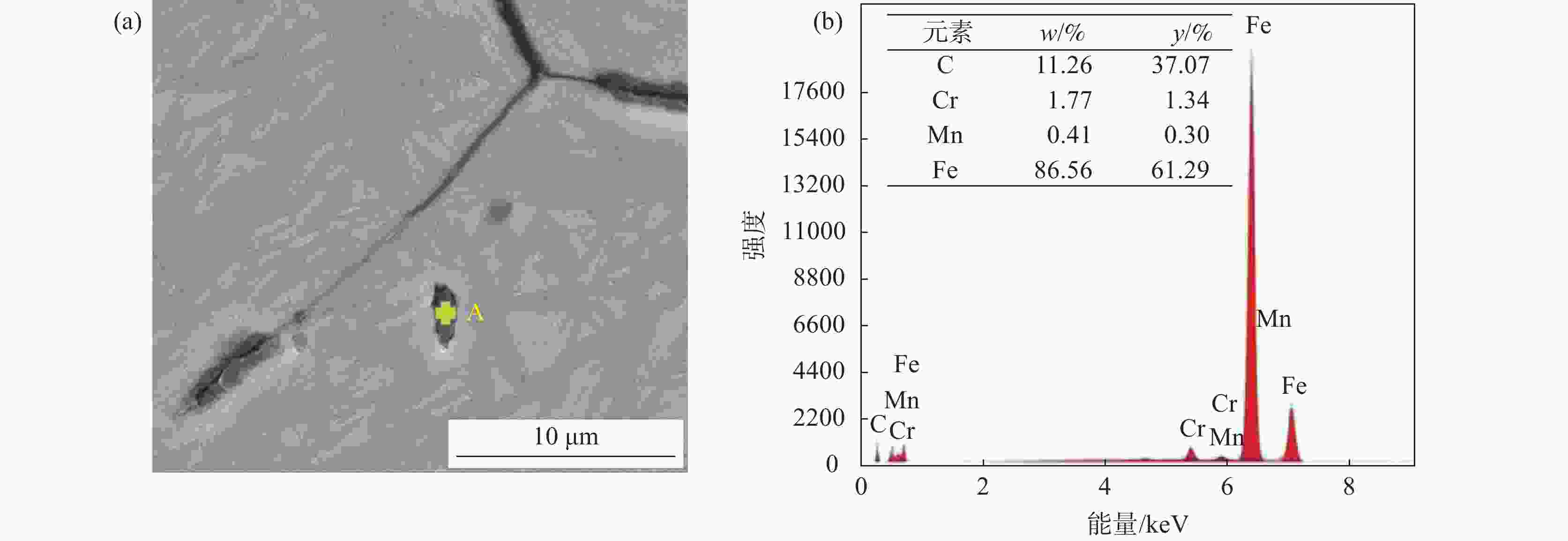
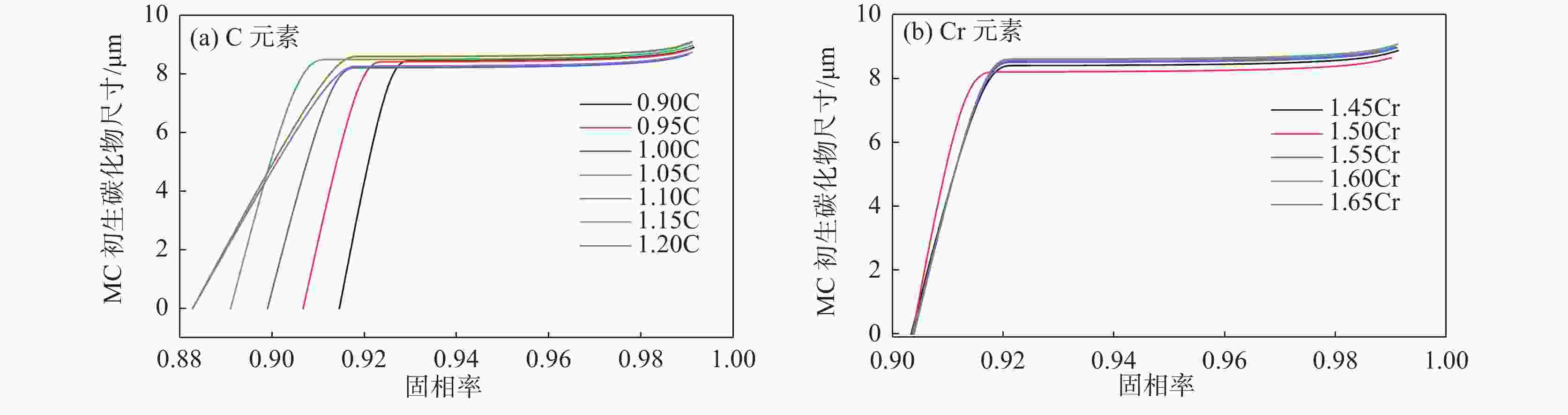
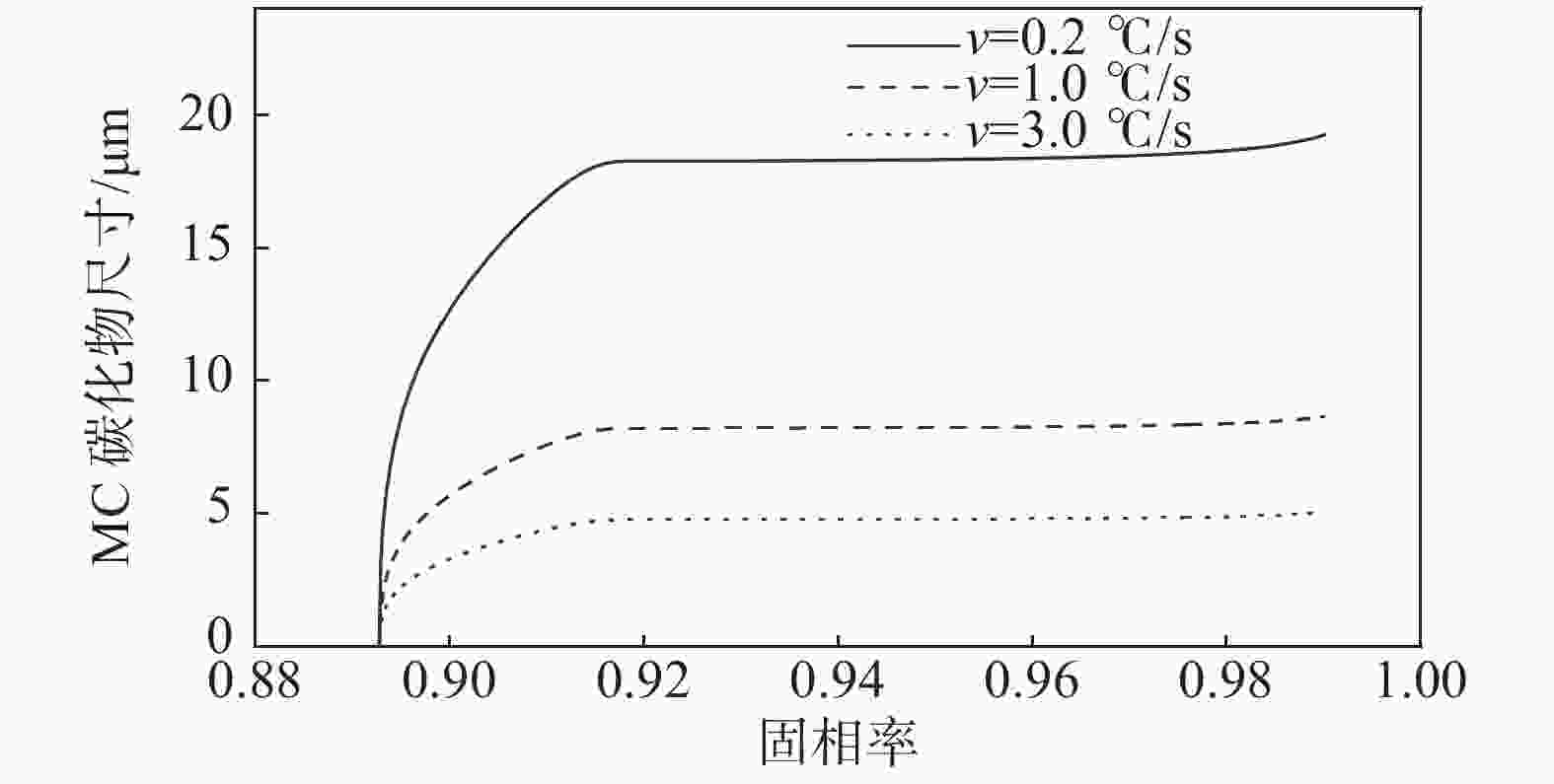
1158 ℃。其析出行为主要是凝固末端残留液相中C和Cr元素偏析所引起的,当固相率为0.92时,残留液相中C元素的质量分数达到4.12%;残留液相中的Cr元素质量分数达到2.59%,初生碳化物尺寸为8.2 μm。此外,钢液中C元素的增加可以使初生碳化物析出温度提高,初生碳化物尺寸增大。但是,凝固过程中初生碳化物的尺寸主要是由冷却速率决定的,当冷却速率由0.2 ℃/s增加到3 ℃/s时,初生碳化物最大尺寸由19.25 μm减小至5.02 μm,其影响机制是冷却速率增大会使初生碳化物晶体各界面附近原子扩散速率降低,使得碳化物晶体各界面各向异性生长受阻,最终导致初生碳化物尺寸减小。Abstract: A Thermo-Calc thermodynamic calculation software was used to conduct thermodynamic analysis on the phase transformation, primary carbide phase type, and primary carbide precipitation temperature during solidification process of bearing steel. Based on both Scheil segregation model and Goto model, the size of primary carbide particles during solidification process of bearing steel was predicted, and the predicted results were experimentally verified through thermal simulation tests and quantitative analysis of carbide microscopic morphology. The results show that primary carbides during solidification process of bearing steel are (Fe, Cr) C carbides and its precipitation temperature is1158 ℃. The precipitation behavior is mainly caused by the segregation of C and Cr in the residual liquid phase at the end of solidification. When the solid phase ratio is 0.92, the mass fraction of C in the residual liquid phase reaches 4.12%; The mass fraction of Cr element in the residual liquid phase reached 2.59%, and the size of primary carbides reached 8.2 μm. In addition, the precipitation temperature of primary carbides and the size of primary carbides can be increased with the increase of solute C in molten steel. However, the size of primary carbides during solidification is mainly determined by the cooling rate. When the cooling rate is increased from 0.2 ℃/s to 3 ℃/s, the maximum size of primary carbides increases from 19.25 μm reduced to 5.02 μm. The influence mechanism is that increasing cooling rate will reduce the diffusion rate of atoms near the interfaces of primary carbide crystal, which will hinder the anisotropic growth of carbide crystal interfaces, and ultimately lead to decreasing primary carbide size.-
Key words:
- bearing steel /
- primary carbides /
- goto model /
- growth behavior /
- cooling rate /
- solute element /
- dynamics
-
表 1 GCr15轴承主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of GCr15 bearing steel
% C Si Mn P S Cr Al 0.97 0.21 0.32 0.017 0.001 1.49 0.0019 -
[1] 顾超. 高品质轴承钢疲劳寿命预测模型及夹杂物影响规律研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2019.Gu Chao. Study on the fatigue life prediction model and the influence of inclusions on high quality bearing steel[D].Beijing: Beijing University of Science and Technology, 2019. [2] Wang Kun, Hu Feng, Zhou Wen, et al. Research status and development trend of bearing steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020,30(9):119−128. (王坤, 胡锋, 周雯, 等. 轴承钢研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 中国冶金, 2020,30(9):119−128.Wang Kun, Hu Feng, Zhou Wen, Wu Kaiming. Research Status and Development Trend of Bearing Steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020, 30 (09): 119-128 [3] Lü Haotian, Yang Liang, Chen Hao, et al. Long life design of bearing steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020,30(11):16−22. (吕皓天, 杨亮, 陈浩, 等. 轴承钢的长寿命化设计[J]. 中国冶金, 2020,30(11):16−22.Lv Haotian, Yang Liang, Chen Hao, et al. Long Life Design of Bearing Steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020, 30 (11): 16-22 [4] 关健. 航空滚动轴承用M50钢的接触疲劳损伤行为研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.Guan Jian. Study on contact fatigue damage behavior of M50 steel for aerospace rolling bearings[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019. [5] Zheng Kai, Cao Wenquan, Yu Feng, et al. Research and development status and progress of high temperature stainless carburizing bearing steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2022,57(7):125−136. (郑凯, 曹文全, 俞峰, 等. 高温不锈渗碳轴承钢的研发现状与进展[J]. 钢铁, 2022,57(7):125−136.Zheng Kai, Cao Wenquan, Yu Feng, et al. Research and Development Status and Progress of High Temperature Stainless Carburizing Bearing Steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2022, 57 (07): 125-136 [6] 呙如兵. 高速列车轴箱轴承材料微观结构及力学性能演化规律研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2019.Guo Rubing. Study on microstructure and mechanical property evolution of high-speed train axle box bearing materials[D].Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019. [7] 马泽铭. 高速列车轴承微观组织与力学性能演化规律及断裂机理研究[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学, 2021.Ma Zeming. Study on the evolution law and fracture mechanism of microstructure and mechanical properties of high speed train bearings[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang Railway University, 2021. [8] 韩伟. 高速精密机床球轴承力学特性分析[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2016.Han Wei. Mechanical characteristics analysis of ball bearings in high speed and precision machine tools[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2016. [9] 安立愿, 李朋, 刘德义, 等. 352226X2-2RZ轴承渗碳内圈剥离失效分析[J]. 大连交通大学学报, 2020, 40(1): 80-84.An Liyuan, Li Peng, Liu Deyi, et al. Failure analysis on peeling of carburized inner ring of 352226X2-2RZ bearing[J]. Journal of Dalian Jiaotong University, 2020, 40 (1): 80-84. [10] Fu Hanwei, Cui Yinan, Zhang Chi, et al. Progress in research on rolling contact fatigue of bearing steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020,30(9):11−23. (付悍巍, 崔一南, 张弛, 等. 轴承钢滚动接触疲劳研究进展[J]. 中国冶金, 2020,30(9):11−23.Fu Humiwei, Cui Yinan, Zhang Chi, et al. Progress in research on rolling contact fatigue of bearing steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020, 30 (09): 11-23 [11] Liu Ye, Yin Qing, Li Feng, et al. Quality evaluation of ultra long fatigue life bearing steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020,30(9):37−40. (刘烨, 尹青, 李锋, 等. 超长疲劳寿命轴承钢的质量评价[J]. 中国冶金, 2020,30(9):37−40.Liu Ye, Yin Qing, Li Feng, et al. Quality Evaluation of Ultra Long Fatigue Life Bearing Steel[J]. China Metallurgical Journal, 2020, 30 (09): 37-40 [12] Khan F A. The effect of soaking on segregation and primary-carbide dissolution in ingot-cast bearing steel[J]. Metal, 2018,8(10):1−18. [13] Li G, Ke L, Peng W, et al. Effects of natural aging and variable loading on very high cycle fatigue behavior of a bearing steel GCr15[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2022,(119):103360. [14] Zhang J W, Shiozawa K, Lu L T, et al. Fatigue fracture behavior of bearing steel GCr15 in very high cycle regime[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2008,44-46:119−126. [15] Yu Feng, Chen Xingpin, Xu Haifeng, et al. Current status of metallurgical quality and fatigue performance of rolling bearing steels and development direction of high-end bearing steels[J]. Journal of Metals, 2020,56(4):513−522. (俞峰, 陈兴品, 徐海峰, 等. 滚动轴承钢冶金质量与疲劳性能现状及高端轴承钢发展方向[J]. 金属学报, 2020,56(4):513−522.Yu Feng, Chen Xingpin, Xu Haifeng, et al. Current status of metallurgical quality and fatigue performance of rolling bearing steels and development direction of high-end bearing steels[J]. Journal of Metals, 2020, 56 (04): 513-522 [16] Zhu Zuchang, Yang Yitao. Research progress in the first, second, and third generation bearing steels and their heat treatment technologies (III)[J]. Heat Treatment Technology and Equipment, 2019,40(2):67−74. (朱祖昌, 杨弋涛. 第一、二、三代轴承钢及其热处理技术的研究进展(三)[J]. 热处理技术与装备, 2019,40(2):67−74.Zhu Zuchang, Yang Yitao. Research Progress in the First, Second, and Third Generation Bearing Steels and Their Heat Treatment Technologies (III)[J]. Heat Treatment Technology and Equipment, 2019, 40 (2): 67-74 [17] Xiao Maoguo, Li Donghui, Lü Xinyang, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and properties of high CrCoMo bearing steel[J]. Journal of Material Heat Treatment, 2018,39(8):75−81. (肖茂果, 李东辉, 吕新杨, 等. 热处理对高Cr-Co-Mo轴承钢组织与性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2018,39(8):75−81.Xiao Maoguo, Li Donghui, Lv Xinyang, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and properties of high Cr Co Mo bearing steel[J]. Journal of Material Heat Treatment, 2018, 39 (08): 75-81 [18] 王升千. GCr15轴承钢低倍检验孔洞的形成机理及控制研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2016.Wang Shengqian. Study on the formation mechanism and control of macroscopic inspection holes in GCr15 bearing steel[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Science and Technology, 2016. [19] 库尔兹, 费希尔, 李建国, 等. 凝固原理[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2010.Kurtz, Fisher, Li Jianguo, et al. Fundamentals of solidification[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2010. [20] Goto H, Miyazawa K, Honma H. Effect of the primary oxide on the behavior of the oxide precipitating during solidification of steel[J]. ISIJ International, 1996,36(5):537−542. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.36.537 [21] 熊辉辉. 钢中碳化物析出及其界面行为的第一性原理研究[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2019.Xiong Huihui. First-principles study on carbide precipitation and interfacial behavior in steel[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2019. [22] Du N, Liu H, Cao Y, et al. Formation mechanism of MC and M2C primary carbides in as-cast M50 bearing steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2021,174:111011-111024. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2021.111011 [23] Li Shanshan, Chen Yun, Gong Tongzhao, et al. Effect of cooling rate on solidification and precipitation mechanism of liquid precipitated carbide in high carbon chromium bearing steel[J]. Journal of Metals, 2022,58(8):1024−1034. (李闪闪, 陈云, 巩桐兆, 等. 冷速对高碳铬轴承钢液析碳化物凝固析出机制的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2022,58(8):1024−1034.Li Shanshan, Chen Yun, Gong Tongzhao, et al. Effect of cooling rate on solidification and precipitation mechanism of liquid precipitated carbide in high carbon chromium bearing steel[J]. Journal of Metals, 2022, 58 (08): 1024-1034 [24] Song W, Choi P P, Inden G, et al. On the spheroidized carbide dissolution and elemental partitioning in high carbon bearing steel 100Cr6[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2014,45A(2):595−606. doi: 10.1007/s11661-013-2048-5 -




 下载:
下载: