Overview of non-quenched and tempered steel for automotive
-
摘要: 分析了国内外非调质钢在汽车零部件领域的发展历程及现状,重点分析了非调质钢的强韧化技术措施、硫化物形态和分布的控制技术,以及材料偏析的控制措施。非调质钢强韧化主要通过成分及生产工艺优化和组织优化两个途径实现,硫化物形态和分布可以从冶炼、凝固和轧制等过程进行调控,硫化物偏析可以从凝固过程和连铸工艺进行改善。未来,随着非调质钢市场的发展及品种需求的进一步提升,非调质钢将向着多品种化、微合金高强化、易切削化、高速化及高可靠性方向进一步发展。Abstract: In this paper the development history and status quo of non-quenched and tempered steel for making auto parts worldwidely had been described, and the technologies such as strengthening & toughening, sulfide form and distribution control, and material segregation control had been highlighted. The strength and toughening of non-quenched and tempered steel are mainly realized through two approaches: composition and production process optimization and microstructure optimization. Sulfide morphology and distribution can be regulated from smelting, solidification, and rolling processes, and sulfide segregation can be improved from solidification process and continuous casting process. In the future, with the development of the non-quenched and tempered steel market and the further improvement of variety demand, non-quenched and tempered steel will further develop in the direction of multi-variety, micro-alloying high strengthen, easy cutting, high speed, and high reliability.
-
0. 引言
非调质钢是以中碳锰钢为基础,加入钒、钛、铌等微合金化元素,使这些元素在加热时固溶于奥氏体,而在钢的冷却过程中,这些元素在钢中的固溶度随着温度的降低而减小,这些微合金元素会以细小的合金碳化物或氮化物的形式在先共析铁素体和珠光体中析出,并与母相保持共格关系,使钢强韧化[1-2]。
非调质钢在热轧、锻造或正火状态下的力学性能可达到或接近调质钢,又可避免调质过程中淬火造成的变形开裂,简化了矫直工序,提高了锻件的成品率,减少了生产工序,缩短了生产周期,又降低了生产成本[3]。据统计,应用非调质钢每生产1 t零件可节省750~1000 kWh的电能或节省 420~810 m3的天然气,节省零件制造的能耗约为30%~40%,降低零件制造成本25%~38%[4]。此外,将非调质钢应用于制造汽车零部件还可实现汽车的轻量化,例如汽车转向节、前悬臂、胀断连杆和曲轴等采用非调质钢制造后轻量化效果可达10%~29%[5-6]。
由于非调质钢具有上述优点,所以被广泛应用于制造发动机连杆、曲轴、凸轮轴、套管叉、半轴、轮毂、紧固件轴销类零件、转向节等零部件[7]。日本90%以上汽车的曲轴、连杆均采用非调质钢制造[8],而韩国和欧洲采用非调质钢生产的汽车锻钢件的比例也占到80%[9]。
1. 国内外非调质钢发展历程及现状
1.1 国外非调质钢的发展历程及现状
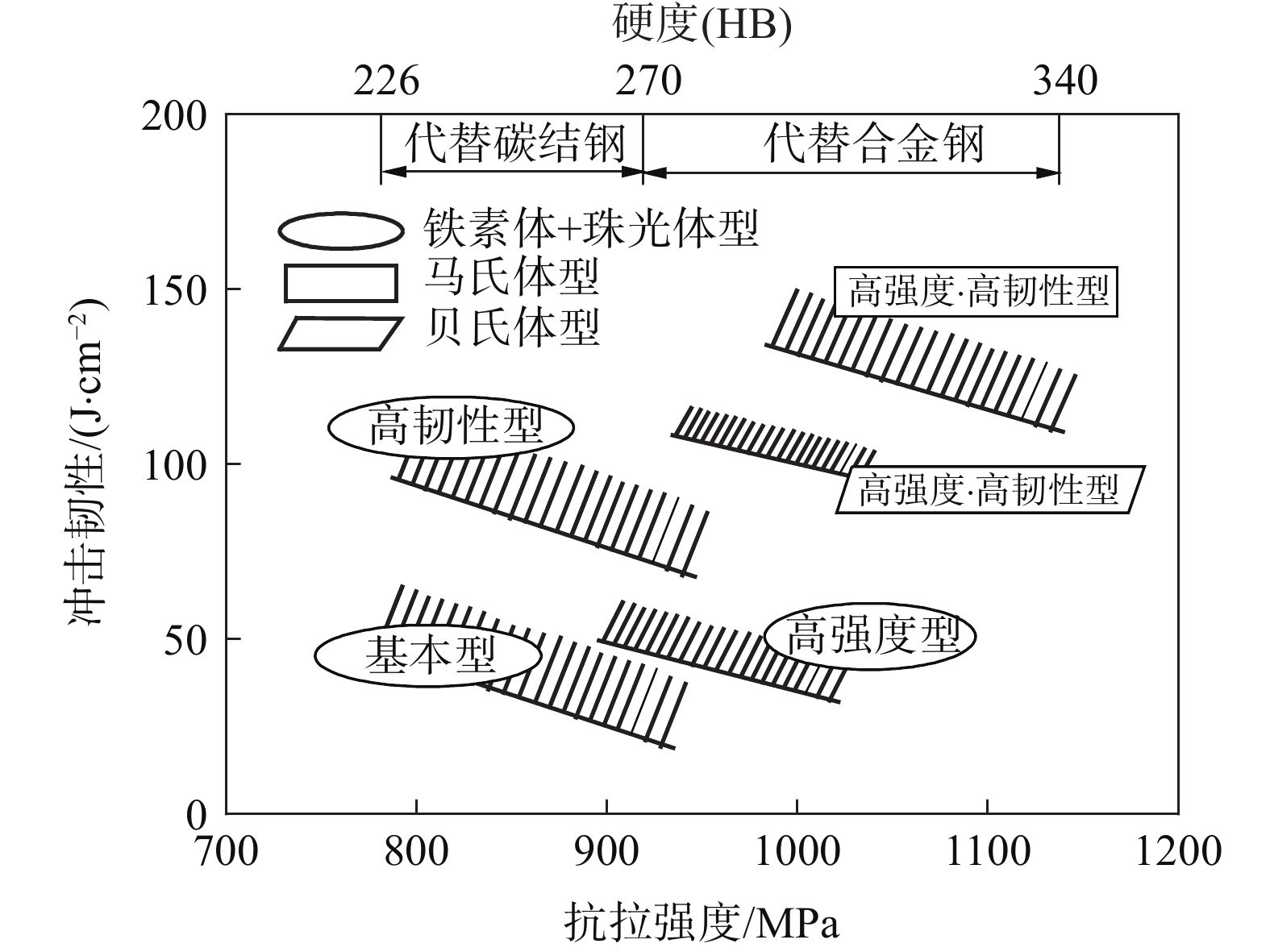
非调质钢的发展主要经历了三个阶段[10]。20世纪70年代前期,由于石油危机导致世界各国纷纷开始研制非调质钢,用以代替一般的碳素结构钢和低合金结构钢。到80年代前期,德国蒂森公司率先开发了一类非调质钢,以49MnVS3为代表钢号提供给汽车工业,逐渐取代了40Cr和50Mn 等一系列的调质钢,用于制造汽车的锻造曲轴[11]。之后,又开发了第二代、第三代和复合微合金化非调质钢。第二代非调质钢主要是以38MnVS6为代表的铁素体-珠光体型非调质钢[12],相比第一代非调质钢,第二代非调质钢主要通过降低碳含量、提升微合金元素Si、Mn、Ti含量等方式实现韧性提升。第三代非调质钢包括以20MnCrMo7和25MnCrV等为代表的贝氏体型非调质钢以及以NQF10MAT和KNF5MC等为代表的马氏体型非调质钢[13-15],具有低碳含量、高强韧性的特点,通过相变强化的方式得到贝氏体或马氏体,提高强韧性。国外生产的非调质钢代表钢种如表1所示,生产的非调质钢强韧性匹配情况如图1所示[16]。
表 1 国外生产的非调质钢代表钢种及成分性能情况Table 1. Steel grade and composition properties of typical non-quenched and tempered steel produced abroad产地 代表钢种 主要成分/% 用途 强度级别/MPa C Si Mn S V Ti N 德国 49MnVS3 0.47 0.20 0.85 0.050 0.10 0.014 曲轴 850 C70S6 0.70 0.20 0.50 0.060 0.03 0.015 连杆 900 38MnVS6 0.38 0.65 1.40 0.030 0.10 0.017 活塞 850 美国 44MnSiVS6 0.44 0.65 1.45 0.025 0.16 0.015 0.017 曲轴 950 瑞典 V-2906 0.45 0.30 0.70 0.050 0.10 0.017 曲轴 850 V-2908 0.38 0.55 1.40 0.050 0.016 曲轴 800 日本 S38CMS1 0.38 0.55 1.45 0.060 0.014 曲轴 800 SVh40C 0.40 0.20 0.75 0.020 0.05 0.010 曲轴 800 36MnVS4 0.38 0.65 1.00 0.070 0.25 0.017 连杆 950  图 1 不同强度级别非调质钢的强韧性匹配情况[16]Figure 1. Matching situation of strength and toughness of different strength grades of non-quenched and tempered steel
图 1 不同强度级别非调质钢的强韧性匹配情况[16]Figure 1. Matching situation of strength and toughness of different strength grades of non-quenched and tempered steel目前,日本六大汽车主机厂中55%轴类件、75%锻件实现非调质钢化,转向、传动系统热锻件几乎全部非调质化,在汽车机构件中约20%~30%采用了非调质钢,远高于国内企业的份额[17-18]。
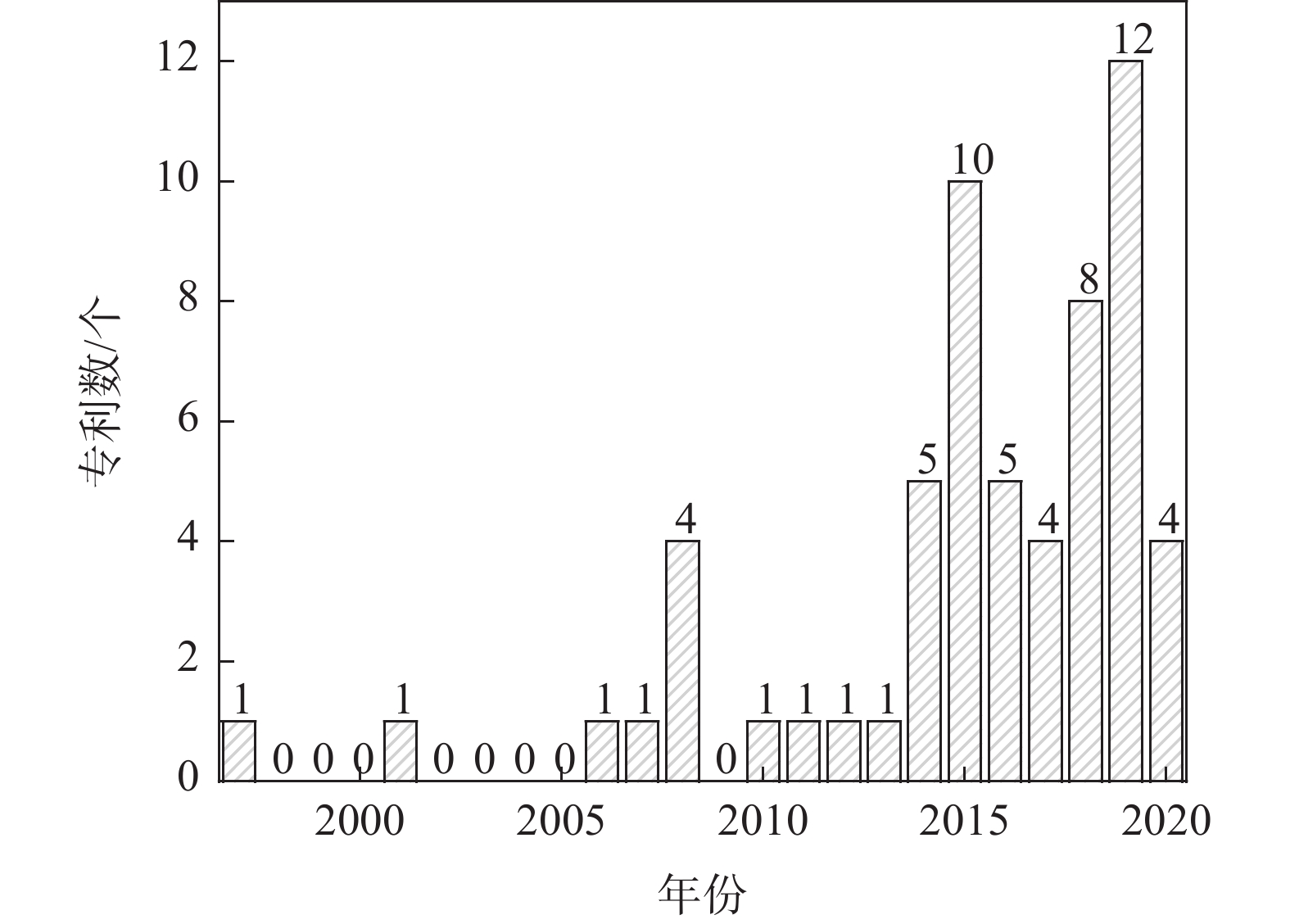
德温特世界专利索引数据库表明,1963~2020年期间各国汽车零部件用非调质钢专利可搜索到1077条,如图2所示。1971~1998年期间的年申请量较少,1999~2016年期间年申请量开始缓慢增长,从2017年开始,年申请量大幅增加,可见非调质钢至今还是各国发展的重点钢种。
1971~2020年期间,国外汽车零部件用非调质钢相关专利申请数量排名前10的申请人如表2所示。全球的非调质钢市场产业集中度较高,主要的钢铁生产企业包括新日铁(日本制铁株式会社)、蒂森克虏伯、神户制钢和大同特殊钢,这四家公司的产品占据了全球市场份额的52.38%[19]。新日铁、神户制钢、大同特殊钢、住友金属等日本钢铁企业则建立了各自的非调质钢体系,掌握着非调质钢研发与生产的高端技术。
表 2 国外汽车零部件用非调质钢相关专利主要申请人分析Table 2. Analysis of the main applicants for foreign patents related to non-quenched and tempered steel for auto parts申请人 专利数/个 日本制铁株式会社 127 大同特殊钢株式会社 54 株式会社神户制钢所 50 JFE钢铁株式会社 30 韩国现代汽车公司 25 本田技研工业株式会社 18 安塞乐米塔尔 18 日本爱知制钢株式会社 18 丰田自动车株式会社 17 日产自动车株式会社 17 1.2 国内非调质钢的发展历程及现状
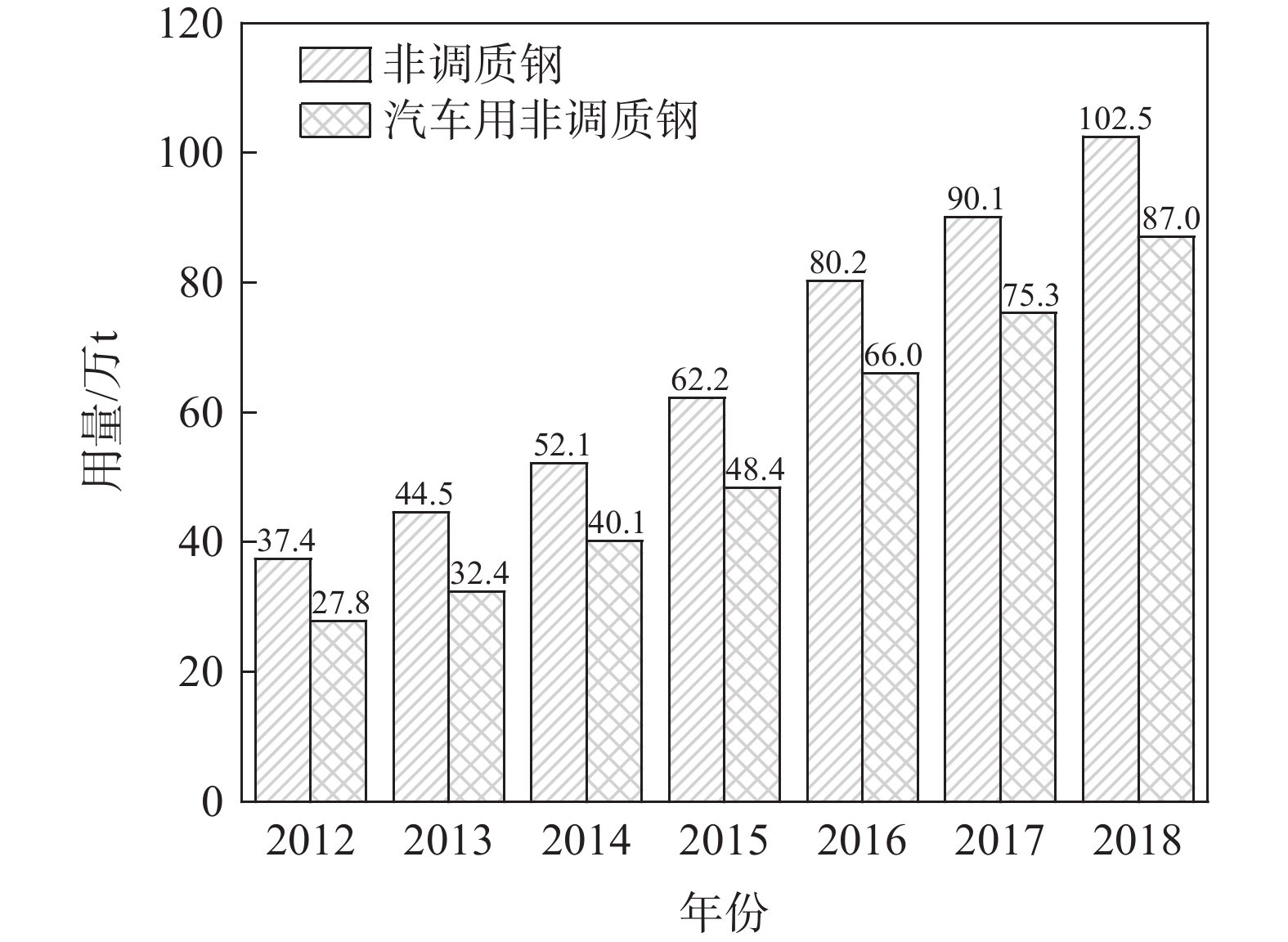
相较于其它国家,我国的非调质钢开发并不算晚。“六五”期间即起步,“九五”和“十五”主要面向轿车用非调质钢的开发并扩大非调质钢的应用数量和范围,“十一五”期间取得了突出的进步。汽车用非调质钢是非调质钢的主要部分,用量占比超过50%,如图3所示[20]。至2018年,我国非调质钢行业产量102.5万t,其中汽车领域需求量约87万t,用量占比约为84.9%。
 图 3 2012~2018年我国非调质钢用量及占比情况[20]Figure 3. The consumption and proportion of non-quenched and tempered steel in China from 2012 to 2018
图 3 2012~2018年我国非调质钢用量及占比情况[20]Figure 3. The consumption and proportion of non-quenched and tempered steel in China from 2012 to 2018随着我国汽车产量和汽车保有量的增加,2022年底全国机动车保有量已达到4.17亿辆,其中汽车3.19亿辆[21],所造成的汽车行业节能减排的压力亦随之增加。由于非调质钢在汽车行业中的广泛应用,生产成本显著降低[22],国内汽车零部件用非调质钢在最近10多年得到了快速发展。1963~2020年国内的汽车零部件用非调质钢专利如图4所示,最早的申请年份为1997年,2001~2013年期间申请量较少,到2014年申请量开始显著增加。
目前,非调质钢在国内主要应用在汽车曲轴、连杆、活塞、转向节、工程机械半轴、活塞杆上。一汽、上汽、东风等主机厂所用胀断连杆均已采用46MnVS5、38MnSiVS4非调质钢生产,东风、康明斯等大马力商用车主机厂、发动机厂大量使用了由C38N2、48MnV非调质钢所生产的曲轴[23]。
2. 非调质钢的品质要求
随着汽车零部件朝着高性能、长寿命、轻量化、安全性、低成本、零缺陷、易加工等方向发展,对非调质钢的切削性能、高强韧性的匹配、内部偏析控制等都提出了更高的要求。
2.1 非调质钢的强韧化技术
提高非调质钢强韧性主要通过成分及生产工艺优化和组织优化两途径 [1,24]。
2.1.1 成分及生产工艺优化
为了提高铁素体-珠光体型非调质钢的强韧性,可以通过降低钢中的C含量,提高其Si、Mn含量,通过固溶强化方式改善强韧性;也可以通过加入V、Ti、Nb、N等微合金元素,经过热加工后析出碳化物和氮化物,由于析出强化和细晶强化的作用提高非调质钢的强韧性[25];利用氧化物冶金技术形成晶内铁素体[24],以细晶强化方式提高非调质钢强韧性。
1)碳作为钢中最重要的强化元素,合理控制碳含量是控制钢材强度高低的基础。在一定范围内增加碳含量会增加珠光体含量,提高材料强度,但会使韧性下降。因此,可以在提高其它合金元素含量或采取其它强化手段的方式保证强度的条件下,通过降低钢中的碳含量,从而提高钢的韧性。
2)锰元素是扩大奥氏体相区元素,可与奥氏体无限互溶,但在铁素体中溶解度较低,钢中加入一定量锰元素能以固溶强化方式强化珠光体和铁素体,提升珠光体含量,并且减小珠光体片层间距,使渗碳体变薄,提升钢材韧性。硅元素是铁素体形成元素,能促进铁素体形成和均匀分布,从而提高韧性。因此,可适当提高钢中的锰和硅含量。
3)微合金元素的复合加入可加强元素析出强化的作用,如在49MnVS3中添加微量Ti,通过Ti-V复合微合金化,再经过适宜的锻造工艺,可实现晶粒细化,奥氏体平均晶粒尺寸从110 μm左右降至40 μm左右。加Ti与不加Ti钢裂纹产生能量相近,而含Ti钢组织晶粒细化导致晶界增多,裂纹扩展阻力加大,裂纹扩展能量提高,从而韧性提高[26]。单一元素微合金化很难得到性能更好的非调质钢,因此通常在非调质钢中采用复合添加微合金元素的方法。
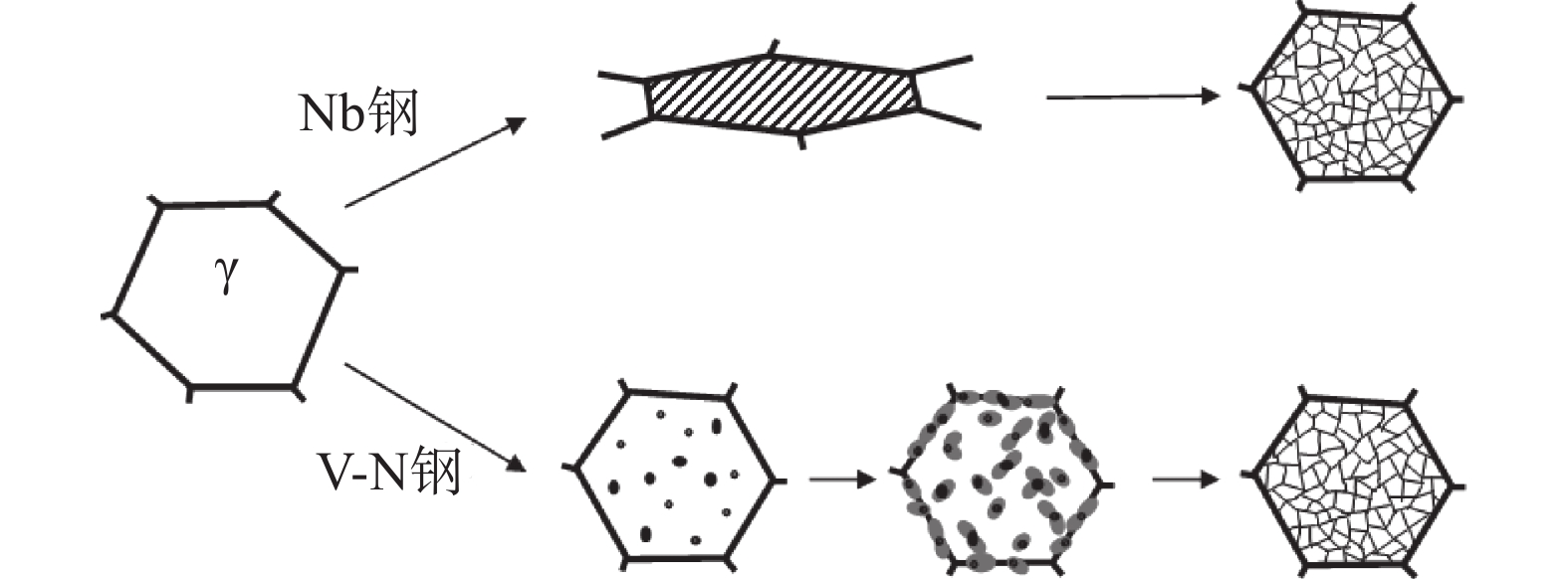
4)日本新日铁公司的研究人员提出氧化物冶金(Oxides Metallurgy)技术,该技术通过控制钢中氧化物夹杂(Al2O3、MnO、FeO、(Ti,Mn)2O3)的成分、数量和分布状态,以细晶强化方式达到提升钢材强韧性的目的。钢中细小弥散的氧化物夹杂作为晶内铁素体形核的核心,使细小针状铁素体在奥氏体晶内析出,进而分割、细化晶粒,从而使钢的强韧性得到提升[27]。钢中的V与N析出形成的VN与晶内铁素体晶格共格,成为晶内铁素体形核核心,促进形成晶内铁素体(intragranular ferrite, IGF)组织,大幅提高材料的强韧性[28]。V-N钢技术路线为:V-N合金钢成分设计→奥氏体中析出VN颗粒→晶内铁素体形核长大→相变→细化晶粒[29]。V-N钢晶粒细化原理见图5。
 图 5 V-N钢晶粒细化原理[16]Figure 5. The grain refinement principle of the V-N steel
图 5 V-N钢晶粒细化原理[16]Figure 5. The grain refinement principle of the V-N steel2.1.2 组织优化
为使铁素体-珠光体型非调质钢的热轧材或锻造材达到要求的性能,钢的化学成分在一定范围内,通过制定合理的热轧/锻工艺,如钢坯加热温度、材的轧制温度及轧/锻后的冷却速度等,调控非调质钢的组织(铁素体、珠光体等的比例,铁素体晶粒的大小等),调控加热、轧制和冷却过程的微合金化元素Nb、V、Ti的析出相数量及分布,从而获得较为理想的组织,提高非调质钢的强韧性。
除此之外,还可以通过改变非调质钢的基体组织提高非调质钢的强韧性。在中碳钢的基础上降低钢中碳含量,添加Mo、Ni、W、B、Si等贝氏体转变区扩大元素,控制冷却速度,开发出以贝氏体为基体的贝氏体型非调质钢[30];进一步降低碳含量,开发以马氏体为基体的低碳马氏体组织型非调质钢。
2.2 硫化物形态和分布控制技术
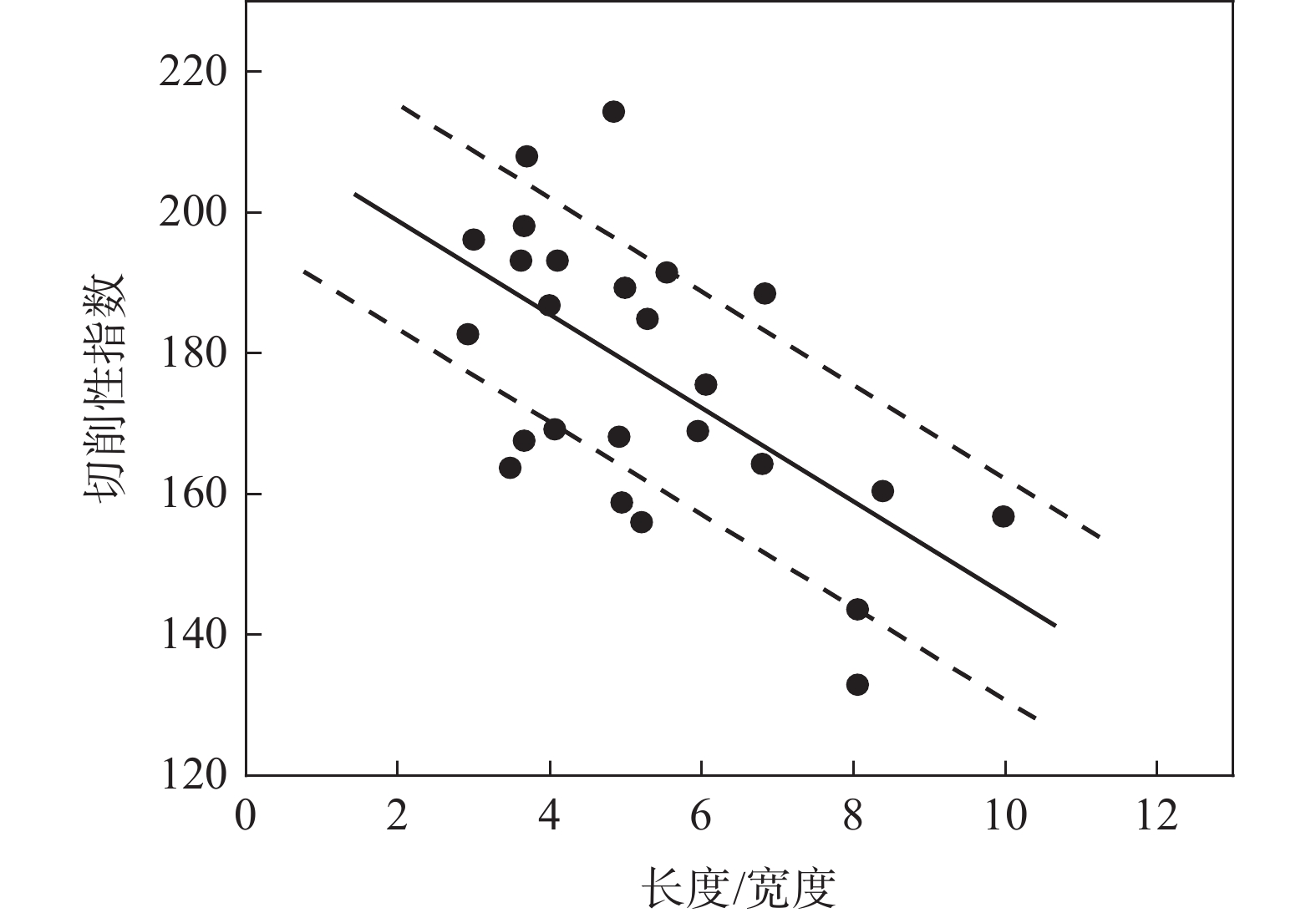
非调质钢主要依靠加入一定含量的硫形成硫化物夹杂来改善切削性能。由于非调质钢中有较高的锰,硫元素主要以MnS的形式存在于钢中。在切削过程中容易在硫化锰夹杂处形成应力集中源,使切屑容易碎断,从而提高非调质钢的切削性能[31]。非调质钢的切削性能通常与硫化物的大小及形貌有很大的关联,硫化物通常等效面积越大,材料的切削性能越好; 硫化物长宽比越小、形貌越接近椭球状,材料的切削性能越好;随着硫化物夹杂长宽比的降低,钢材切削性指数逐渐升高[32],图6为硫化物形状对切削性能的影响。
 图 6 硫化物形状对切削性能的影响[32]Figure 6. The influence of sulfide shape on cutting performance
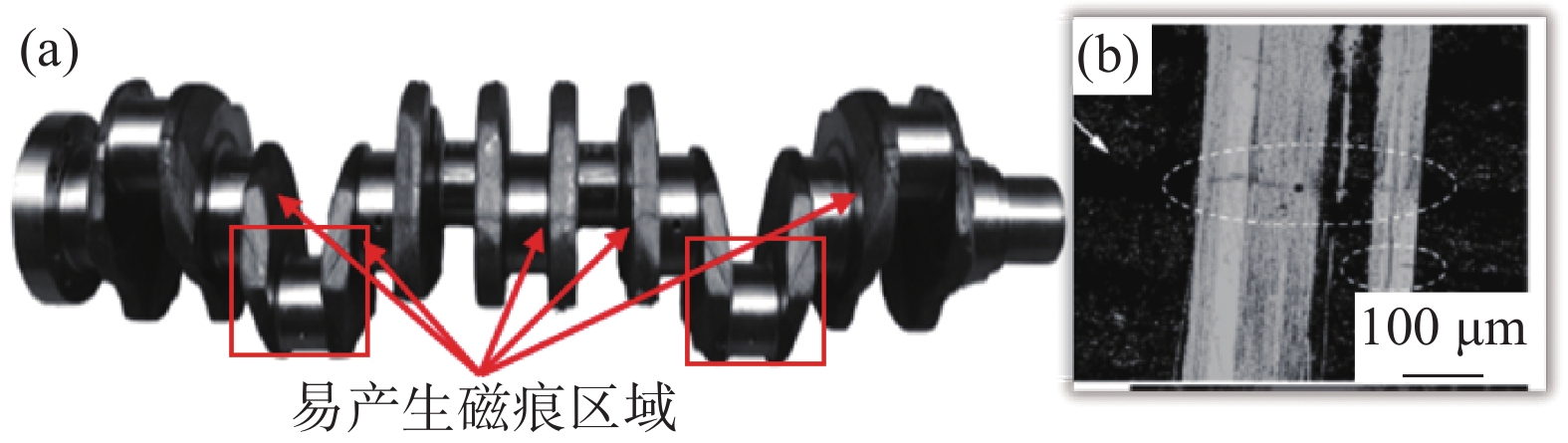
图 6 硫化物形状对切削性能的影响[32]Figure 6. The influence of sulfide shape on cutting performance由于MnS是塑性夹杂物,硬度比钢基体软,故轧制/锻造后易形成长条状硫化物,会导致产品各向异性,并降低曲轴的疲劳强度,长条状的硫化物在大变形的部位易导致硫化物累积,在磁探伤时产生“磁痕缺陷”,会导致汽车曲轴在探伤时磁痕超标而判废[33],如图7所示。
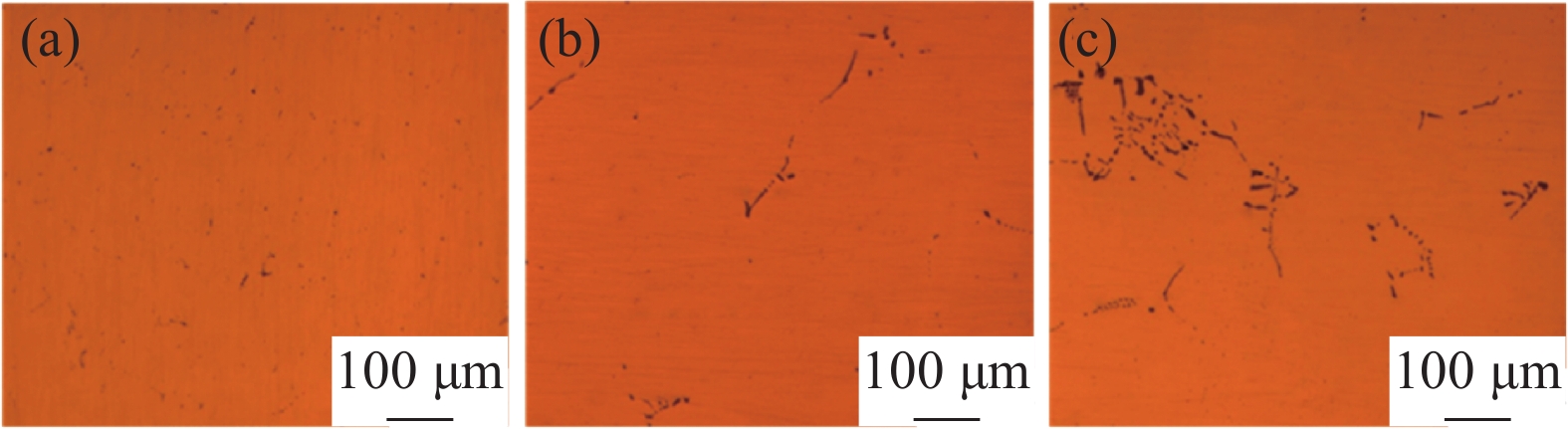
硫是强偏析性元素,MnS在接近凝固温度时才析出,导致MnS在凝固末期出现沿晶界偏聚,硫化物在铸坯中心部位富集,导致出现大量团簇状硫化物聚集,降低非调质钢的性能,特别是对疲劳性能造成危害[34]。图8是国内某厂C70S6非调质钢铸坯三个位置的硫偏析情况。中碳非调质钢在凝固过程中受易偏析元素碳和硫局部严重偏析聚集的影响,产生严重的碳偏析和硫化物偏析[35],降低零部件的使用寿命,甚至导致零部件突然失效。
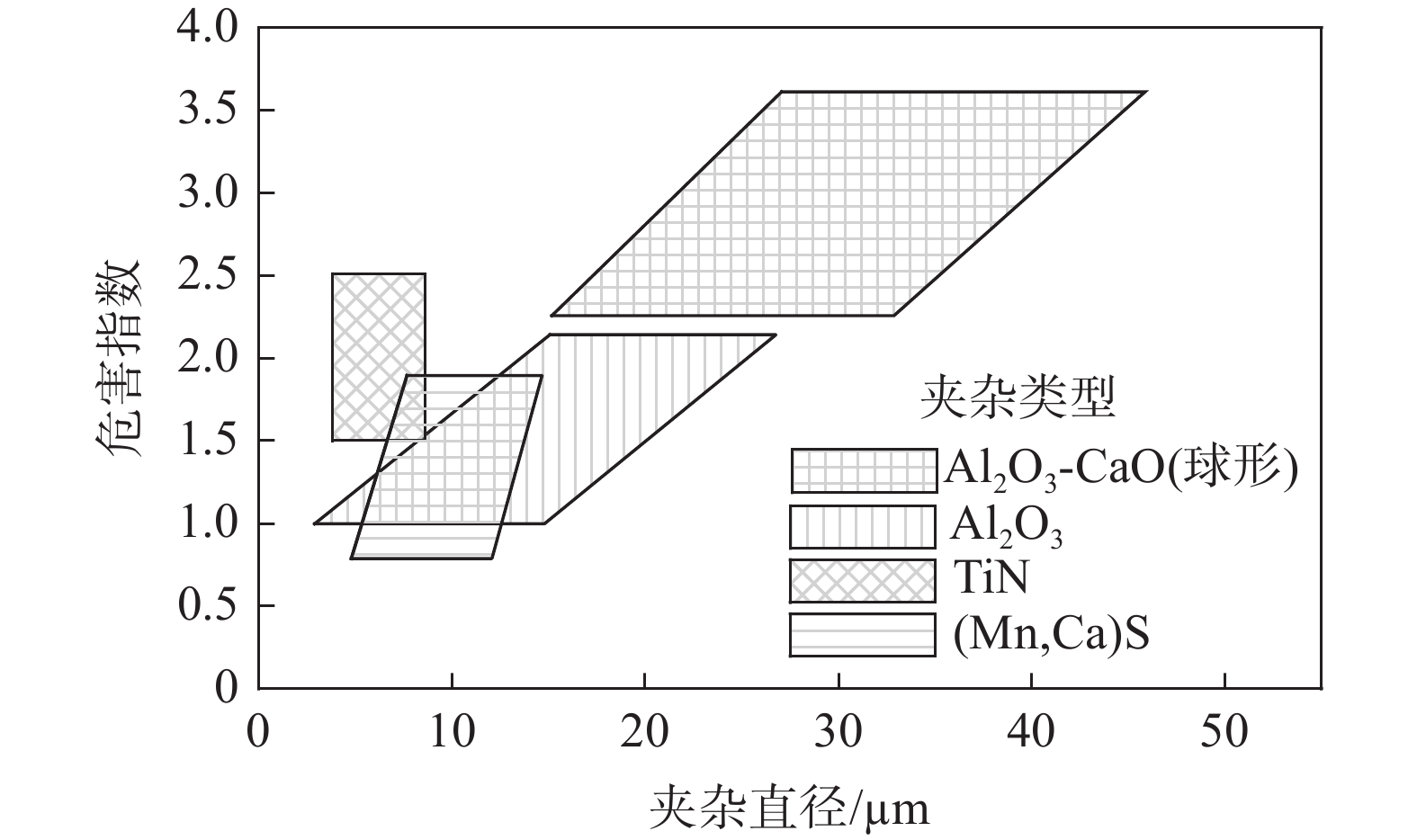
图9为四种类型的非金属夹杂物尺寸对疲劳性能的影响,同种类型的夹杂物尺寸越小对疲劳性能的危害程度越低,但团簇状夹杂物会严重降低非调质钢的疲劳性能。
 图 9 非金属夹杂物种类和尺寸对疲劳性能的影响[33]Figure 9. Influence of the type and size of non-metallic inclusions on fatigue performance of non-quenched and tempered steel
图 9 非金属夹杂物种类和尺寸对疲劳性能的影响[33]Figure 9. Influence of the type and size of non-metallic inclusions on fatigue performance of non-quenched and tempered steel因此,为减小硫化物夹杂对非调质钢疲劳性能的危害,同时提高切削性能,可以通过硫化物调控使硫化物细化、分布均匀,得到纺锤状的硫化物夹杂。目前硫化物夹杂物控制主要采用以下几种方法:
1)在冶炼过程中,通过向钢中加入Ca、Mg、Te、RE等改质剂[36-45],这些物质在钢中形成大量的细小弥散的氧化物,并以氧化物为核心形成硫化物,使硫化物改质为“内硬外软的”的复合夹杂物,将MnS变成不容易变形、硬度较高的纺锤状(椭球状)硫化物,改善材料的切削性能;
2)在凝固过程中,通过控制钢液凝固速率、二冷水强度及MnS夹杂物的偏析等,改善MnS夹杂物的形态及分布;
3)在轧制过程中,通过控制轧制温度、变形量以及分段轧制等[46],破碎MnS夹杂物,改善MnS夹杂物的形态比及分布;
4)在热处理过程中,通过控制热处理温度、升温速率、保温时间、热后冷却速率等都会对硫化物的形态、数量等产生一定的影响,改善MnS夹杂物的形态及数量[47-49]。
以上改善硫化物形态的方法,目前国内仍是第1)种方法应用较多且效果较显著;氧化物冶金技术、凝固过程控制硫化物形态的关键技术仍然有待进一步研究;轧制工艺改善硫化物对低硫钢有一定作用,但对半硫钢及高硫钢仍不理想;热处理在实际生产过程中会大幅度增加生产工序成本,且对钢材的晶粒度、脱碳等性能都会产生不利的影响。
2.3 非调质钢偏析及控制
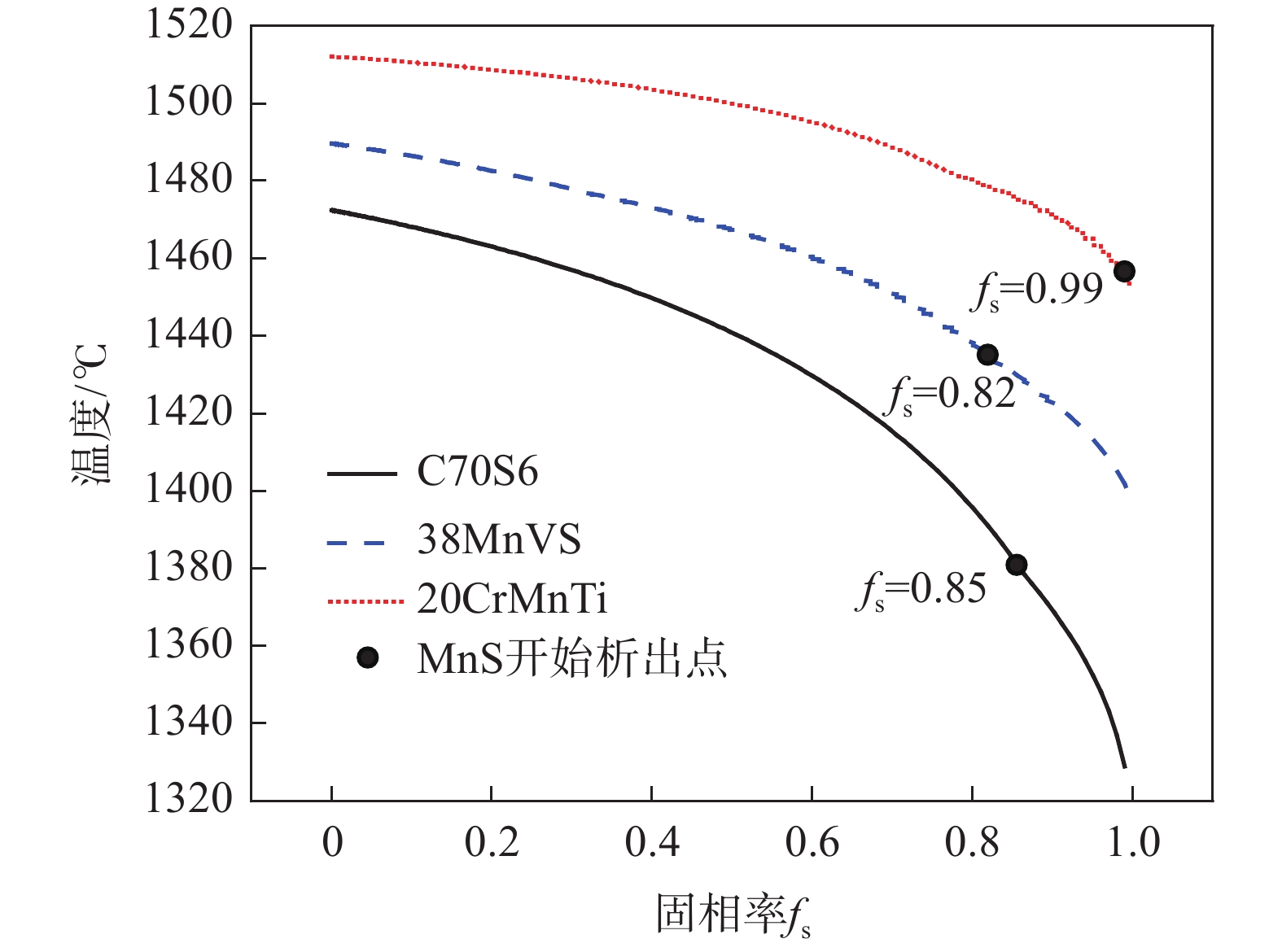
为改善非调质钢的切削性能,通常在非调质钢中添加0.03%~0.07%的硫元素。由于非调质钢中通常含有较高的Mn元素,所以在高锰硫比的情况下,硫在钢中通常以MnS形式存在。图10所示为C70S6、38MnVS、20CrMnTi中的MnS的析出曲线[50]。
 图 10 含硫钢凝固分率与温度的关系[50]Figure 10. Relationship between solidification rate and temperature of sulfur-containing steel
图 10 含硫钢凝固分率与温度的关系[50]Figure 10. Relationship between solidification rate and temperature of sulfur-containing steel目前非调质钢碳偏析和硫化物偏析的机理及控制技术相对较为成熟,可以从凝固和工艺方向进行控制。从凝固方向可采用以下方法:①低过热度的控制。等轴晶比例随过热度增加而降低,而等轴晶比例增加,碳中心偏析降低。目前连铸可将过热度稳定控制在10~35 ℃,在这个范围内过热度对碳偏析的改善甚微;②降低拉速。拉速降低,等轴晶率增加,由于拉速的降低,钢水在结晶区停留时间延长,促进了中心等轴晶的生长。但是,过低的拉速影响生产节奏,降低生产效率,且容易导致断浇;③夹杂物改质。在冶炼过程中,通过喂入Ca、Mg、RE等包芯线进行改质,使硫化物进行复合化,通过增加异质形核点提高硫化物的析出时机,减少硫化物的偏析。
从连铸工艺角度,主要方法包括:①电磁搅拌的控制。电磁搅拌是改善偏析最重要的手段之一,它能改变溶质场的分布,对宏观偏析产生重要影响[51]。电磁搅拌包括结晶器电磁搅拌、二冷电磁搅拌和末端电磁搅拌,它们可以单独使用或组合使用,对于中碳非调质钢,组合使用对偏析的改善效果更佳。电磁搅拌可有效减少枝晶搭桥,减少柱状区的比例,减少硫化物、碳化物的偏析;②轻压下技术的控制。轻压下技术使在连铸坯的凝固末端通过设备施加压力来产生一定的压下量,从而消除或减弱在凝固收缩的作用下凝固末端中心缩孔,并且使凝固末端液芯富集溶质的钢液向未凝固部位流动,使富集的溶质元素在未凝固钢液中重新分配,起到改善中心偏析的作用,从而使连铸坯的凝固组织成分更均匀。但在实际生产中,钢种成分、浇铸断面和浇铸工艺等会发生波动,所以轻压下工艺参数实施的实际效果需进行大量的理论计算及生产实践试验。
3. 非调质钢主要发展研究方向
1)多品种化发展
虽然已逐步开发有铁素体-珠光体型、贝氏体型、马氏体型非调质钢,但是目前国内仍以铁素体-珠光体型为主,贝氏体、马氏体型非调质钢应用偏少,而且在汽车零部件领域应用也仍以曲轴、连杆为主,推广较慢;另外,铁素体-珠光体型、贝氏体型、马氏体型非调质钢牌号仍然偏少,且都是以引入国外的为主,自主开发偏少。
2)微合金高强化
目前开发的非调质钢主要是通过加入较高含量的Nb、V合金,与钢中的C、N等形成析出相,充分发挥析出强化的作用。但过量的Nb、V在钢中只是发挥固溶强化作用,强化效果甚微。因此,要根据强度不同要求,依据N、C与Nb、V的化学配比的理论计算,结合适当的轧制工艺,采取增N节Nb、V,节约合金用量。另外,加强Al、Ti代替Nb、V合金析出强化方式的研究,降低高价格合金的使用,从而降低非调质钢的生产成本。
3)非调质钢的易切削化
前期为追求非调质钢的易切削性,主要是通过增加钢中硫含量,目前非调质钢的硫含量普遍控制在0.040%~0.070%。加入大量的硫引起钢中硫化物偏聚严重,硫化物形态控制难度加剧,虽然硫化物形态控制技术有了一定提高,但是仍带来大量硫化物引起的零部件失效问题,如曲轴的磁痕、疲劳寿命降低等。适当降低钢中的硫含量,控制在0.020%~0.040%,通过添加Te、RE等硫化物改质剂,结合连铸过程硫化物偏析控制技术,充分改善钢中硫化物的形态及分布,大幅度提高球状或纺锤状硫化物的比例,降低硫化物的不利影响。
4)高速化及高可靠性
随着新能源汽车的快速发展,汽车动力传动轴的转速成倍提高,由原来最高3000 r/min提升到6000 r/min以上,瞬间扭矩会成倍地增加,对轴类材料的强度、塑性、冲击性能、疲劳性能等提出比传统燃油汽车更高的要求,对材料的洁净度、夹杂物、偏析、带状组织等要求更加严苛外,材料在拉压状态(tension)、旋转弯曲(bending)的疲劳性能S-N曲线也成为普遍的要求。
4. 结语
1)近二十年国内非调质钢的开发、应用发展较为迅速,但是在汽车零部件应用范围、品种开发能力以及产品质量控制等方面与国外相比仍存在一定差距。
2)目前非调质钢强韧化主要通过成分及生产工艺优化和组织优化两个途径实现,硫化物形态和分布可以从冶炼、凝固、轧制和热处理等过程进行调控,碳、硫偏析可以从凝固过程和连铸工艺两方面进行改善。
3)未来非调质钢在汽车零部件应用方面应重点在多品种发展研究、微合金高强化、易切削、高速化及高可靠性方向等方面开展研究。
-
图 1 不同强度级别非调质钢的强韧性匹配情况[16]
Figure 1. Matching situation of strength and toughness of different strength grades of non-quenched and tempered steel
图 3 2012~2018年我国非调质钢用量及占比情况[20]
Figure 3. The consumption and proportion of non-quenched and tempered steel in China from 2012 to 2018
图 5 V-N钢晶粒细化原理[16]
Figure 5. The grain refinement principle of the V-N steel
图 6 硫化物形状对切削性能的影响[32]
Figure 6. The influence of sulfide shape on cutting performance
图 9 非金属夹杂物种类和尺寸对疲劳性能的影响[33]
Figure 9. Influence of the type and size of non-metallic inclusions on fatigue performance of non-quenched and tempered steel
图 10 含硫钢凝固分率与温度的关系[50]
Figure 10. Relationship between solidification rate and temperature of sulfur-containing steel
表 1 国外生产的非调质钢代表钢种及成分性能情况
Table 1. Steel grade and composition properties of typical non-quenched and tempered steel produced abroad
产地 代表钢种 主要成分/% 用途 强度级别/MPa C Si Mn S V Ti N 德国 49MnVS3 0.47 0.20 0.85 0.050 0.10 0.014 曲轴 850 C70S6 0.70 0.20 0.50 0.060 0.03 0.015 连杆 900 38MnVS6 0.38 0.65 1.40 0.030 0.10 0.017 活塞 850 美国 44MnSiVS6 0.44 0.65 1.45 0.025 0.16 0.015 0.017 曲轴 950 瑞典 V-2906 0.45 0.30 0.70 0.050 0.10 0.017 曲轴 850 V-2908 0.38 0.55 1.40 0.050 0.016 曲轴 800 日本 S38CMS1 0.38 0.55 1.45 0.060 0.014 曲轴 800 SVh40C 0.40 0.20 0.75 0.020 0.05 0.010 曲轴 800 36MnVS4 0.38 0.65 1.00 0.070 0.25 0.017 连杆 950 表 2 国外汽车零部件用非调质钢相关专利主要申请人分析
Table 2. Analysis of the main applicants for foreign patents related to non-quenched and tempered steel for auto parts
申请人 专利数/个 日本制铁株式会社 127 大同特殊钢株式会社 54 株式会社神户制钢所 50 JFE钢铁株式会社 30 韩国现代汽车公司 25 本田技研工业株式会社 18 安塞乐米塔尔 18 日本爱知制钢株式会社 18 丰田自动车株式会社 17 日产自动车株式会社 17 -
[1] 董成瑞. 微合金非调质钢[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2000.Dong Chengrui. Microalloyed non quenched and tempered steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000. [2] Deardo A J, Hua M J, Cho K G, et al. On strength of microalloyed steels: an interpretive review[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2013,25(9):1074−1082. [3] Thewillis G, Naylor D J. New alloys help cut the cost of forged steel components[J]. Metals and Materials, 1981,(12):21−28. [4] 米丰亮. 非调质钢C38+N曲轴组织和力学性能研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2018.Mi Fengliang. Regulation of microstructure and mechanical properties of C38+N crankshaft of non quenched and tempered steel[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2018. [5] Mibourn D. Vanadium microalloyed non-quench and temper forging steels[R]. Chongqing: International Vanitec Technology Committee, 2011: 1-35. [6] Chen Yunbo, Ma Mingtu, Wang Guodong. Resent progress of non-quenched and tempered steel for automotive sheet[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2014,16(2):4−17, 45. (陈蕴博, 马鸣图, 王国栋. 汽车用非调质钢的研究进展[J]. 中国工程科学, 2014,16(2):4−17, 45.Chen Yunbo, Ma Mingtu, Wang Guodong. Resent progress of non-quenched and tempered steel for automotive sheet[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2014, 16(2): 4-17+45. [7] Chen Silian, Hui Weijun, Wang Lianhai, et al. Research and development of energy-saving high performance microalloyed forging steels[J]. Iron & Steel, 2014,49(6):1−7. (陈思联, 惠卫军, 王连海, 等. 节能低成本高品质非调质钢的研发[J]. 钢铁, 2014,49(6):1−7.Chen Silian, Hui Weijun, Wang Lianhai, et al. Research and development of energy-saving high performance microalloyed forging steels[J]. Iron & Steel, 2014, 49(06): 1-7. [8] Miao Taosheng, Jiang Peng. Application research on non-quenched and tempered steel for automotive forging of crankshaft and connecting rod[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2010,35(6):1−5. (缪桃生, 蒋鹏. 非调质钢在汽车曲轴、连杆锻件上的应用研究[J]. 锻压技术, 2010,35(6):1−5.Miao Taosheng, Jiang Peng. Application research on non-quenched and tempered steel for automotive forging of crankshaft and connecting rod[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2010, 35(6): 1-5. [9] Dong Han. Understanding of developing high quality special steel industry[J]. China Steel, 2011,(10):10−13. (董瀚. 对发展高品质特殊钢产业的认识[J]. 中国钢铁业, 2011,(10):10−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5115.2011.10.004Dong Han. Understanding of developing high quality special steel industry[J]. China Steel, 2011(10): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5115.2011.10.004 [10] Zhou Yazhuo, Jin Wenhui, Yu Qin, et al. Development trend on crankshaft materials of non quenched and tempered steel[J]. Heat Treatment Technology and Equipment, 2018,39(4):61−65. (周亚倬, 金文辉, 于勤, 等. 非调质钢曲轴用材发展趋势[J]. 热处理技术与装备, 2018,39(4):61−65.Zhou Yazhuo, Jin Wenhui, Yu Qin, et al. Development trend on crankshaft materials of non quenched and tempered steel[J]. Heat Treatment Technology and Equipment, 2018, 39(04): 61-65. [11] Naylor D J. Review of international activity on microalloyed engineering steels[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 1989,16(4):246−252. [12] Liu Donglin, Tan Li, Liu Pan, et al. The application of 38MnVS6 non quenched and tempered steel on automobile steering knuckle[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2014,43(2):80−81, 85. (刘栋林, 谭利, 刘攀, 等. 38MnVS6非调质钢在汽车转向节上的应用[J]. 热加工工艺, 2014,43(2):80−81, 85.Liu Donglin, Tan Li, Liu Pan, et al. The application of 38 MnVS6 non quenched and tempered steel on automobile steering knuckle [J]. Hot Working Technology, 2014, 43(02): 80-81+85. [13] Buchmayr B. Critical assessment 22: bainitic forging steels[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2016,32(6):517−522. doi: 10.1080/02670836.2015.1114272 [14] Liu Jie, Wu Dan, Yang Xiujuan, et al. Research status and development trend of non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021,50(23):1−6, 10. (刘洁, 吴丹, 杨秀娟, 等. 非调质钢的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 热加工工艺, 2021,50(23):1−6, 10.Liu Jie, Wu Dan, Yang Xiujuan, et al. Research status and development trend of non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021, 50(23): 1-6+10. [15] Merkel C, Engineer J. Hochfester bainitischer stahl 20MnCrMo7 für umformanwendungen[J]. Schmiede Journal, 2014(2): 38-41. [16] Wang Xiaoning, Fang Gang, Li Yang, et al. Application status and development of automotive non quenched and tempered steel[J]. Automobile Technology & Material, 2014,(9):52−58. (王小宁, 方刚, 李阳, 等. 汽车用非调质钢的应用现状与发展[J]. 汽车工艺与材料, 2014,(9):52−58.Wang Xiaoning, Fang Gang, Li Yang, et al. Application status and development of automotive non quenched and tempered steel[J]. Automobile Technology & Material, 2014(09): 52-58. [17] Gu Zhimin, Zhang Qingjun, Zhu Liguang, et al. Recent progress in non-quenched-tempered and its application[J]. Journal of North China University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2012,34(3):59−63. (谷志敏, 张庆军, 朱立光, 等. 非调质钢的研究进展及其实践[J]. 河北联合大学学报(自然科学版), 2012,34(3):59−63.Gu Zhimin, Zhang Qingjun, Zhu Liguang, et al. Recent progress in non-quenched-tempered and its application[J]. Journal of North China University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition) , 2012, 34(03): 59-63. [18] 吴玮. 汽车零部件用非调质钢的应用和发展[J]. 世界钢铁, 2009, 9(4): 62-68.Wu Wei. Application and development of non-quenched and tempered steel for automotive parts[J]. World Iron & Steel, 2009, 9(4): 62-68. [19] 市场调研报告. 全球及中国非调质钢市场现状及未来趋势走向分析报告, QYResearch预测: 2019-2025全球与中国非调质钢市场现状及未来发展趋势[EB/OL]. (2020-10-27) [2023-07-02]. https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/84287755.Market research report analysis. Report on the current situation and future trends of the global and Chinese non quenched and tempered steel market, QYResearch Forecast: 2019-2025 Current situation and future development trends of the global and Chinese non quenched and tempered steel market [EB/OL]. (2019-09-26) [2022-05-15]. https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/84287755. [20] 智研咨询. 2018年中国非调质钢行业产量82.4万吨, 预计2020年市场规模将超过60亿元[EB/OL]. (2019-03-21) . https://www.chyxx.com/industry/201903/723554.html.Zhiyanzixun. In 2018, China's non quenched and tempered steel industry produced 824000 tons, and it is expected that the market size will exceed 6 billion yuan by 2020 [EB/OL]. (2019-03-21) .https://www.chyxx.com/industry/201903/723554.html. [21] 全国新能源汽车保有量达1310万辆[N]. 新能源汽车报, 2023-01-16(5).The total number of new energy vehicles in China has reached 13.1 million [N] .New Energy Vehicle News, 2023-01-16 (5). [22] 马鸣图. 双相钢——物理和力学冶金第2版[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2009: 1-12.Ma Mingtu. Duplex steels - physical and mechanical metallurgy 2nd Edition[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009: 1-12. [23] Huo Dongmei, Xiao Bangguo, Yang Weining, et al. Summary of the standard“Non-quenched and tempered steel for automobile crankshaft and connecting rod"[J]. Metallurgical Economy and Management, 2020,(3):41−43. (霍咚梅, 肖邦国, 杨伟宁, 等. 《汽车曲轴和连杆用非调质圆钢》团体标准综述[J]. 冶金经济与管理, 2020,(3):41−43.Huo Dongmei, Xiao Bangguo, Yang Weining, et al. Summary of the standard“Non-quenched and tempered steel for automobile crankshaft and connecting rod"[J]. Metallurgical economy and management, 2020(03): 41-43. [24] Zhu Shuaishuai, Wang Zhangzhong, Mao Xiangyang, et al. A review about strengthening-toughening technologies for ferrite-pearlite non-quenched and tempered steels[J]. Materials Reports, 2016,30(9):122−126. (朱帅帅, 王章忠, 毛向阳, 等. 铁素体-珠光体型非调质钢强韧化技术研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2016,30(9):122−126.Zhu Shuaishuai, Wang Zhangzhong, Mao Xiangyang, et al. A review about strengthening-toughening technologies for ferrite-pearlite non-quenched and tempered steels[J]. Materials Reports, 2016, 30(09): 122-126. [25] Chen Silian, Zhao Xiaoli, Hui Weijun, et al. Precipitation behavior of medium-carbon steel for fracture splitting connecting rod[J]. Iron & Steel, 2015,50(7):77−83. (陈思联, 赵晓丽, 惠卫军, 等. 胀断连杆用中碳非调质钢的析出强化行为[J]. 钢铁, 2015,50(7):77−83.Chen Silian, Zhao Xiaoli, Hui Weijun, et al. Precipitation behavior of medium-carbon steel for fracture splitting connecting rod[J]. Iron & Steel, 2015, 50(07): 77-83. [26] Jha G, Sharma R, Jha C N, et al. Medium carbon microalloyed steel 49MnVS3: development towards improved quality[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 1997,50(2):181−190. [27] Chen Yunbo, Ma Wei, Jin Kang. Development on improving the strength & toughness of microalloyed steels[J]. Materials Reports, 2000,(8):3−7. (陈蕴博, 马炜, 金康. 强韧微合金非调质钢的研究动向[J]. 材料导报, 2000,(8):3−7.Chen Yunbo, Ma Wei, Jin Kang. Development on lmproving the strength & toughness of microalloyed steels[J]. Materials Reports, 2000(08): 3-7. [28] Song Yu, Wu Guoping, Wu Tianli. Application of oxide metallurgy technique in improving microstructure and property of steels[J]. China Metallurgy, 2012,22(6):1−7, 11. (宋宇, 武国平, 吴天礼. 氧化物冶金技术在改善钢材组织和性能中的应用[J]. 中国冶金, 2012,22(6):1−7, 11.Song Yu, Wu Guoping, Wu Tianli. Application of oxide metallurgy technique in lmproving microstructure and property of steels[J]. China Metallurgy, 2012, 22(06): 1-7+11. [29] Yu Yang, Pan Tao. New technology opens up new space - rapid development and application of vanadium nitrogen alloying technology[J]. China Metallurgy, 2005,(2):44−45. (于杨, 潘涛. 新技术开启新空间−迅猛发展应用的钒氮合金化技术[J]. 中国冶金, 2005,(2):44−45.Yu Yang, Pan Tao. New technology opens up new space - rapid development and application of vanadium nitrogen alloying technology[J]. China Metallurgy, 2005(02): 44-45. [30] Chen Silian, Hui Weijun, Shao Chengwei, et al. Effect of controlled cooling on microstructure and properties of medium-carbon high-vanadium microalloyed steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2015,50(8):77−82. (陈思联, 惠卫军, 邵成伟, 等. 控制冷却对中碳高钒非调质钢组织性能的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2015,50(8):77−82.Chen Silian, Hui Weijun, Shao Chengwei, et al. Effect of controlled cooling on microstructure and properties of medium-carbon high-vanadium microalloyed steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2015, 50(08): 77-82. [31] Liu H T, Chen W Q. Research on recovery for adding low melting point metal bismuth to eco-friendly Bi–S based free cutting steel[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2014,41(5):355−359. [32] Mohla P P, Beech J. The formation of sulphide inclusions in cast steel[J]. Brit Foundryman, 1968,61(12):453−460. [33] 马鸣图. 汽车用非调质钢的进展[C]//全国高品质特殊钢生产技术研讨会暨中国金属学会特殊钢学术年会.济南:中国金属学会, 2021.Ma Mingtu. Development of non quenched and tempered steels for automobiles[C]// National High Quality Special Steel Production Technology Seminar and Special Steel Academic Annual Meeting of China Metal Society. Jinan:China Metal Society,2021. [34] Wang Zhanhua, Hui Weijun, Zhang Yongjian, et al. High-cycle fatigue properties of microalloyed medium-carbon forging steel 45MnVS with modified sulfide[J]. Iron & Steel, 2021,56(10):117−126. (王占花, 惠卫军, 张永健, 等. 硫化物变性处理45MnVS非调质钢的高周疲劳性能[J]. 钢铁, 2021,56(10):117−126.Wang Zhanhua, Hui Weijun, Zhang Yongjian, et al. High-cycle fatigue properties of microalloyed medium-carbon forging steel 45 MnVS with modified sulfide[J]. Iron & Steel, 2021, 56(10): 117-126. [35] Zhou Zhiwei, Tian Jun, Xu Yifeng. Distribution of inclusions in non-quenched and tempered steel billets[J]. Steelmaking, 2019,35(5):68−74. (周志伟, 田俊, 徐益峰. 非调质钢铸坯中夹杂物的分布[J]. 炼钢, 2019,35(5):68−74.Zhou Zhiwei, Tian Jun, Xu Yifeng. Distribution of inclusions in non-quenched and tempered steel billets[J]. Steelmaking, 2019, 35(05): 68-74. [36] Qiao Xueliang, Sun Peizhen. Quantitative study on Ca content and sulfide morphology in free cutting steel[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1995,23(1):121−123. (乔学亮, 孙培祯. 易切削钢中Ca含量与硫化物形态的定量研究[J]. 华中理工大学学报, 1995,23(1):121−123.Qiao Xueliang, Sun Peizhen. Quantitative study on Ca content and sulfide morphology in free cutting steel[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1995, 23(1): 121-123. [37] Larsson A, Ruppi S. Structure and composition of built-up layers on coated tools during turning of Ca-treated steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2001,313(1-2):160−169. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(01)00964-9 [38] Ai Kenan, Xie Jianbo, Zeng Zhiqi, et al. Effect of Mg on microstructure and sulfide in non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019,31(4):361−367. (艾克南, 谢剑波, 曾志崎, 等. 镁对非调质钢中组织及硫化物的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2019,31(4):361−367.Ai Kenan, Xie Jianbo, Zeng Zhiqi, et al. Effect of Mg on microstructure and sulfide in non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2019, 31(04): 361-367. [39] Feng Shunhuai. Development of free cutting steel at home and abroad in the 1980s[J]. Manufacturing Technology & Machine Tool, 1994,(7):51−54. (封顺怀. 80年代国内外易切削钢的发展[J]. 制造技术与机床, 1994,(7):51−54.Feng Shunhuai. Development of free cutting steel at home and abroad in the 1980 s[J]. Manufacturing Technology & Machine Tool, 1994(07): 51-54. [40] Lou Dechun, Wu Xiaochun. Prediction of rare earth inclusion in free cutting steel[J]. Research on Iron and Steel, 1995,(3):29−33, 28. (娄德春, 吴晓春. 易切削钢中稀土夹杂物类型的预测[J]. 钢铁研究, 1995,(3):29−33, 28.Lou Dechun, Wu Xiaochun. Prediction of rare earth inclusion in free cutting steel[J]. Research on Iron and Steel, 1995(03): 29-33+28. [41] Yao Dengyuan, Wu Huajie, Lu Pengyan, et al. Effect of Ca treatment on sulfides morphology in S-bearing non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2017,27(4):11−16. (姚登元, 吴华杰, 陆鹏雁, 等. 钙处理对含硫非调质钢中硫化物形态的影响[J]. 中国冶金, 2017,27(4):11−16.Yao Dengyuan, Wu Huajie, Lu Pengyan, et al. Effect of Ca treatment on sulfides morphology in S-bearing non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. China Metallurgy, 2017, 27(04): 11-16. [42] Shen P, Yang Q K, Zhang D, et al. The effect of tellurium on the formation of MnTe-MnS composite Inclusions in non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Metals, 2018,8(8):639(1−12). [43] Shen P, Zhou L, Yang Q K, et al. Modification of MnS inclusion by tellurium in 38MnVS6 micro-alloyed steel[J]. Metallurgical Research and Technology, 2020,117(6):615(1−8). [44] Xie Xiaoyu, Gu Chao, Wang Min, et al. Manganese sulfide inclusion control technology in medium and high sulfur steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2021,56(12):52−61. (谢啸宇, 顾超, 王敏, 等. 中高硫钢中硫化锰夹杂物控制技术[J]. 钢铁, 2021,56(12):52−61.Xie Xiaoyu, Gu Chao, Wang Min, et al. Manganese sulfide inclusion control technology in medium and high sulfur steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2021, 56(12): 52-61. [45] Hu Tao, Zhong Liangmei, Zhou Lei, et al. The practice of tellurium to control the form of sulfide in non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2022,38(1):63−67. (胡涛, 钟亮美, 周蕾, 等. 碲对非调质钢中硫化物形态调控的实践[J]. 炼钢, 2022,38(1):63−67.Hu Tao, Zhong Liangmei, Zhou Lei, et al. The practice of tellurium to control the form of sulfide in non-quenched and tempered steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2022, 38(01): 63-67. [46] 吴华杰. 二次开坯轧制对含硫钢硫化物形态分布的影响[C]//2021年全国炉外精炼论文集.贵阳: 北京金属学会, 2021: 619-625.Wu Huajie. Effect of secondary bloom rolling on sulfide morphology distribution of sulfur-containing steel[C]//2021 Proceedings of National off Furnace Refining.Guiyang: Beijing Metal Society, 2021: 619-625. [47] Shao X J, Wang X H, Ji C X, et al. Morphology, size and distribution of MnS inclusions in non-quenched and tempered steel during heat treatment[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2015,22(5):483−491. doi: 10.1007/s12613-015-1097-8 [48] Shao Xiaojing, Wang Xinhua, Wang Wanjun, et al. lnfluence of isothermal treatment on sulfides in YF45MnV steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2010,31(10):80−84. (邵肖静, 王新华, 王万军, 等. 等温热处理对YF45MnV钢中硫化物的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2010,31(10):80−84.Shao Xiaojing, Wang Xinhua, Wang Wanjun, et al. lnfluence of isothermal treatment on sulfides in YF45 MnV steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2010, 31(10): 80-84. [49] Shao X J, Wang X H, Jiang M, et al. Effect of heat treatment conditions on shape control of large-sized elongated MnS inclusions in resulfurized free-cutting steels[J]. ISIJ International, 2011,51(12):1995−2001. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.51.1995 [50] 刘辉. 含硫钢凝固过程硫化锰析出及生长行为研究[D]. 上海: 上海大学, 2019.Liu Hui. The precipitation and growth behavior of MnS during solidification in resulphurised steel[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2019. [51] 许伟阳. 连铸齿轮钢矩形坯碳“锭型”偏析的形成与控制[D]. 北京: 钢铁研究总院, 2011.Xu Weiyang. The formation and control of carbon segregation of gear steel in the bloom casting process[D]. Beijing: Central Iron and Steel Research Institute, 2011. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 韩中奎,陈子瞻,潘昭帅,代涛,杜力普,李杰,高天明. 2035年我国碲资源供需形势分析. 中国矿业. 2025(02): 297-305 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 徐晓春,王杨,邓伟. 1000 MPa级汽车锁环用非调质钢的开发. 上海金属. 2025(02): 59-63 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术











