Study on the precipitation kinetics of carbides in austenite and ferrite of microalloyed steels
-
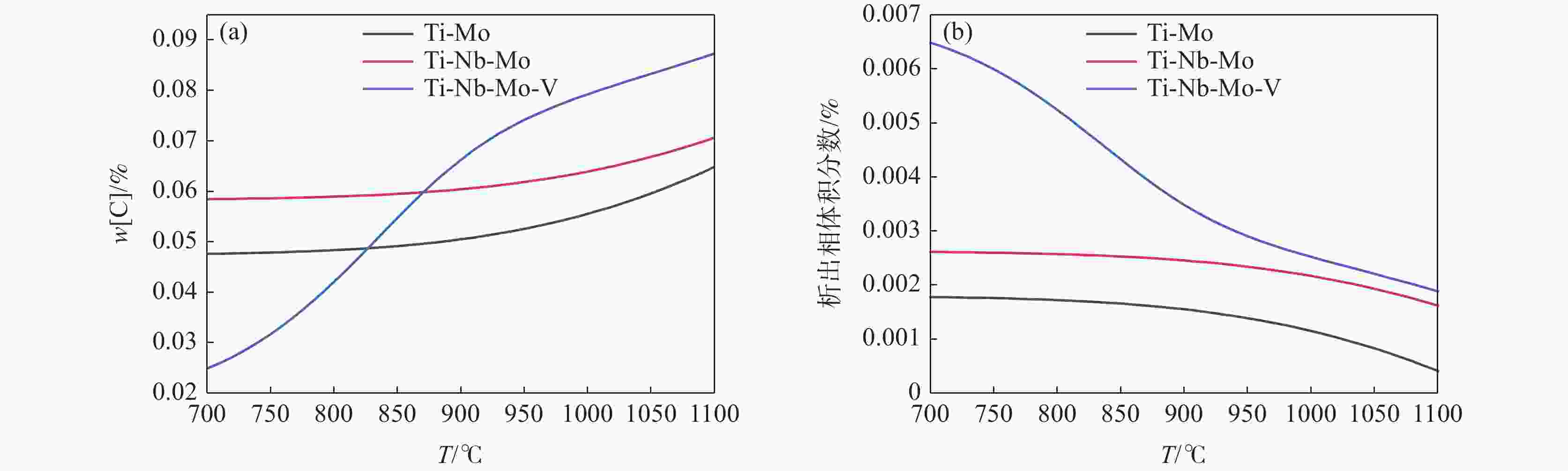
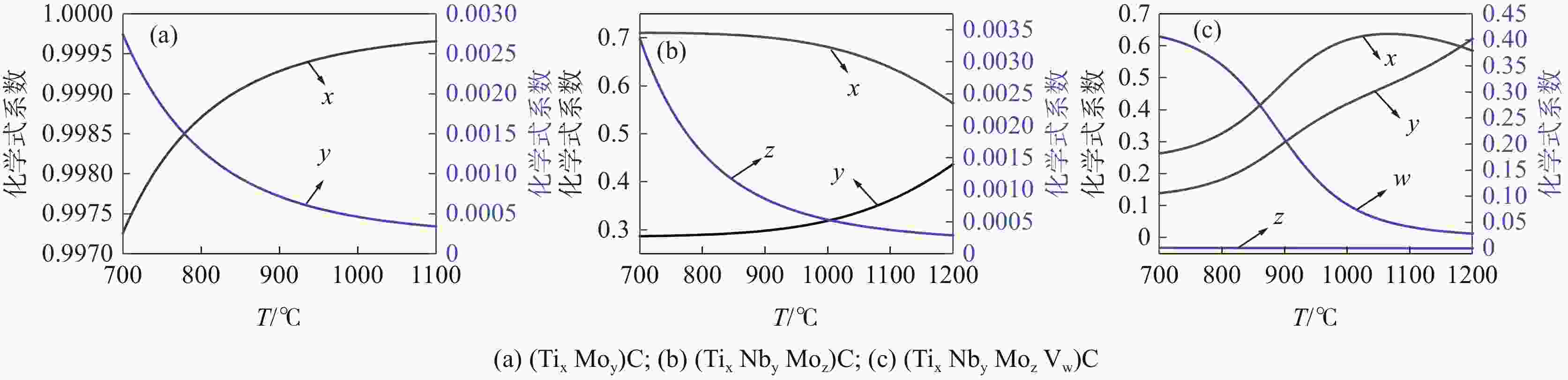
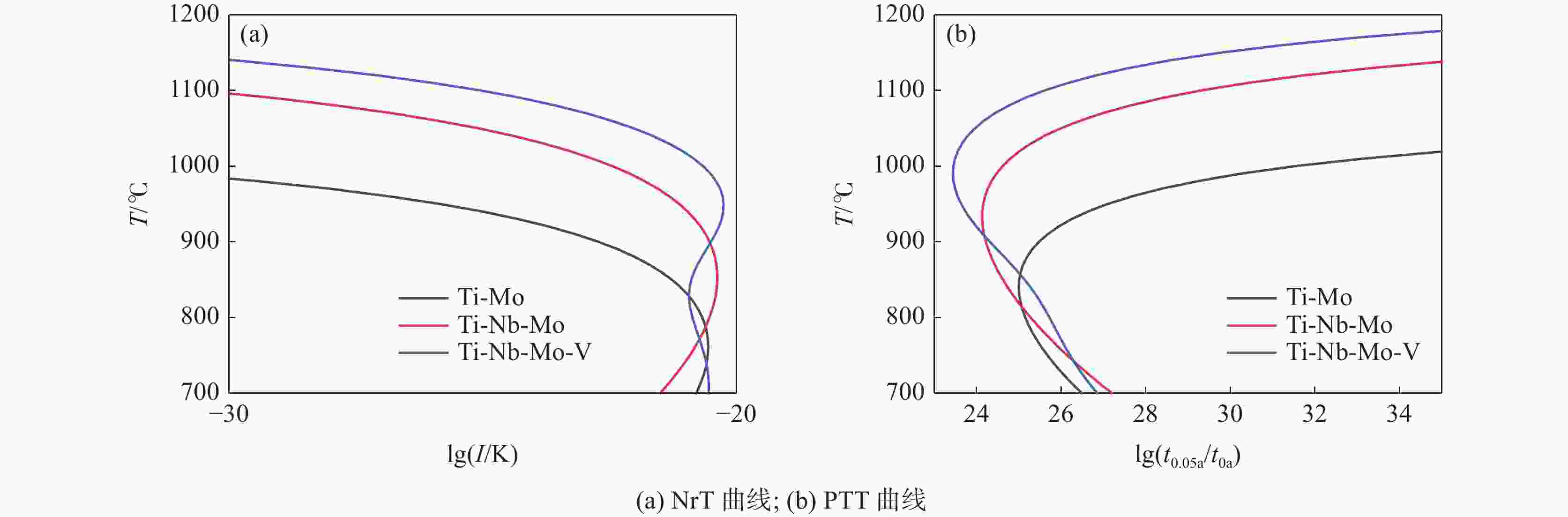
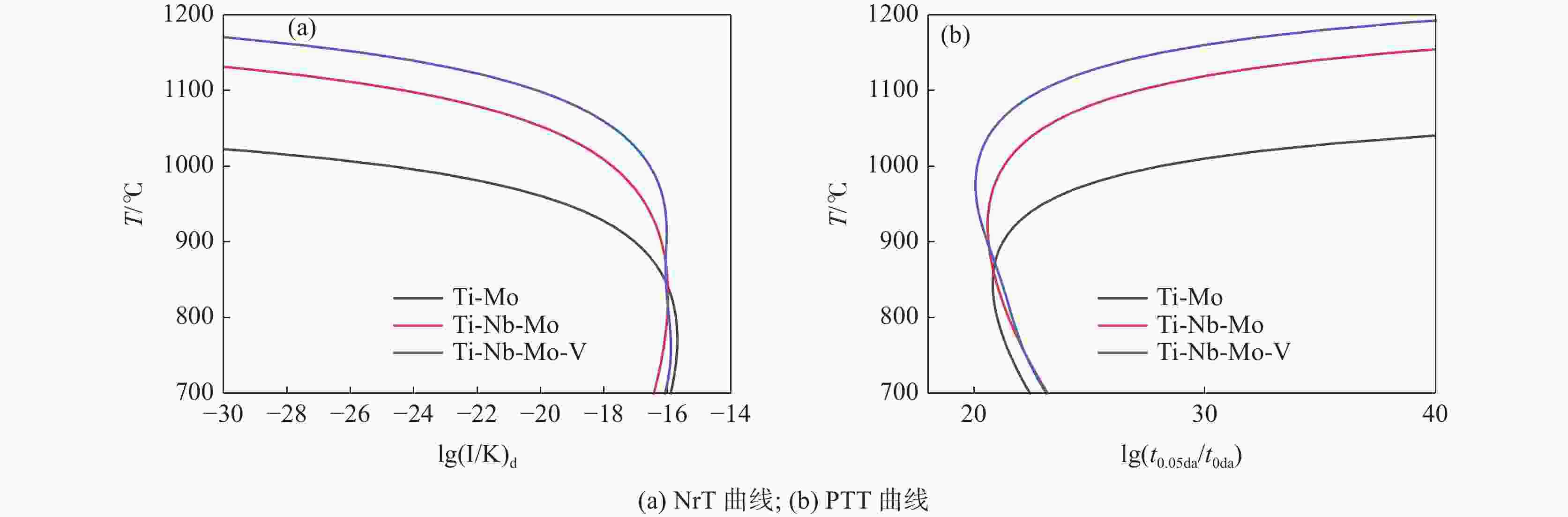
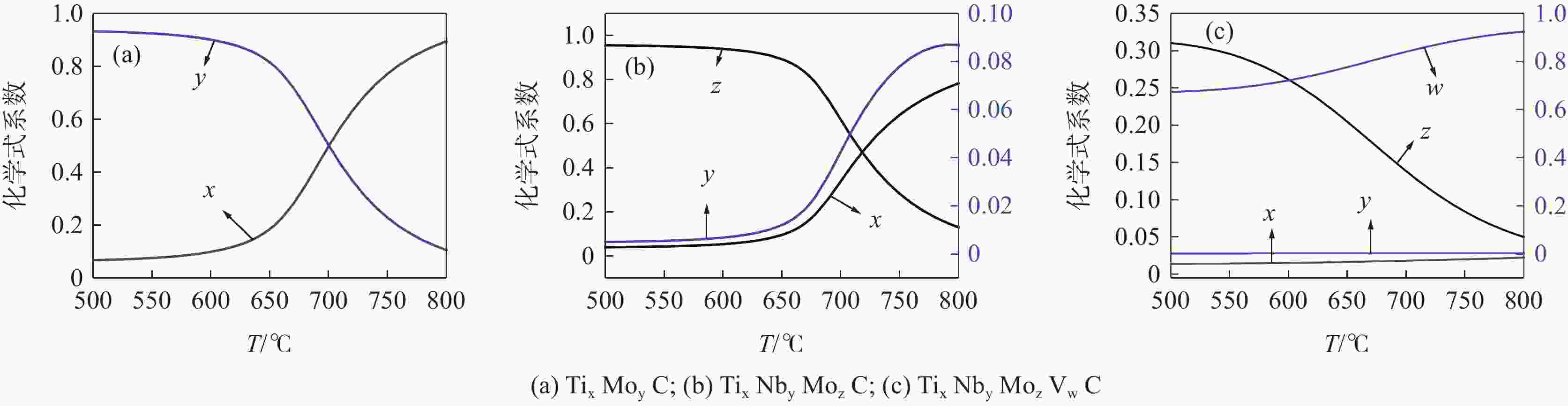
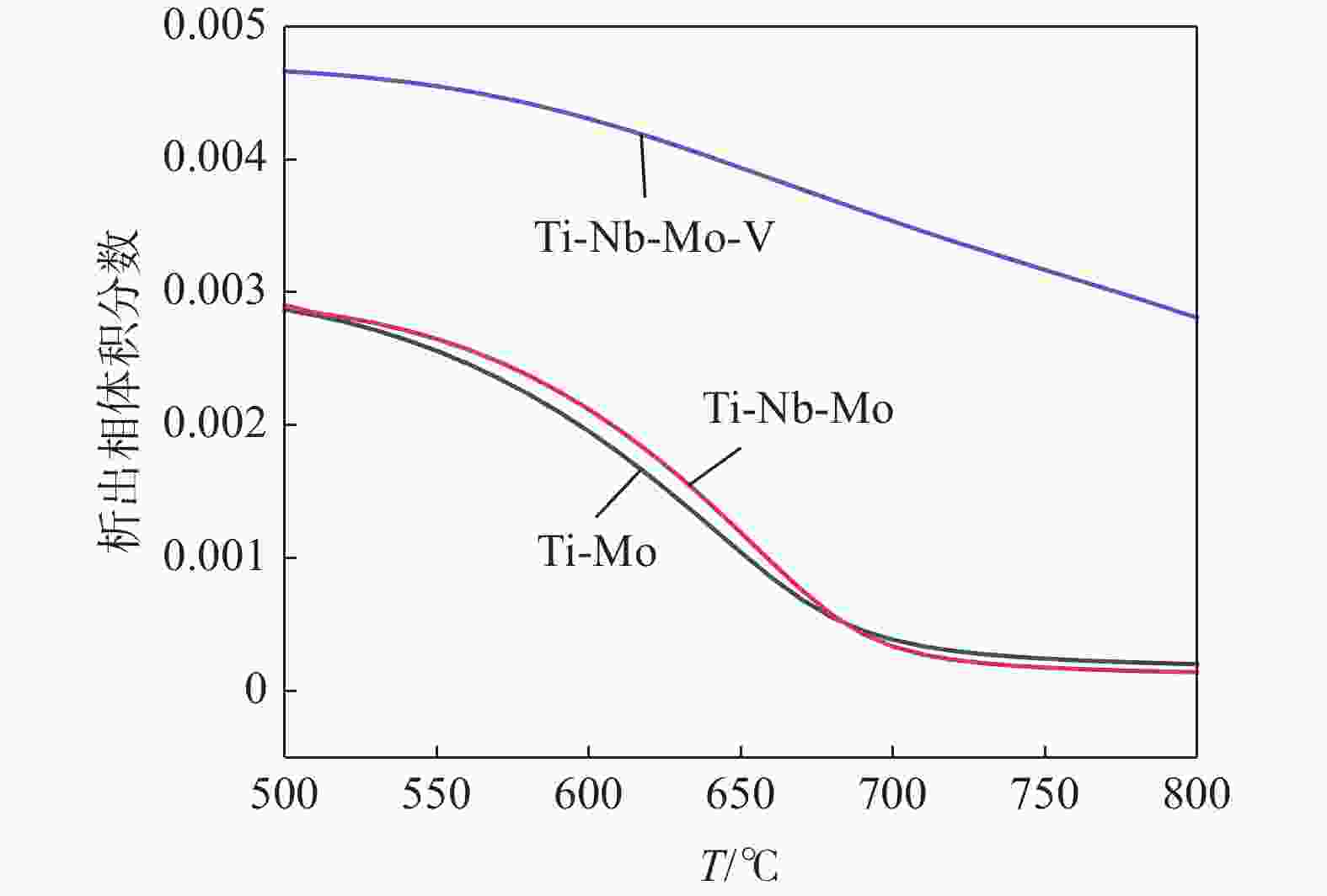
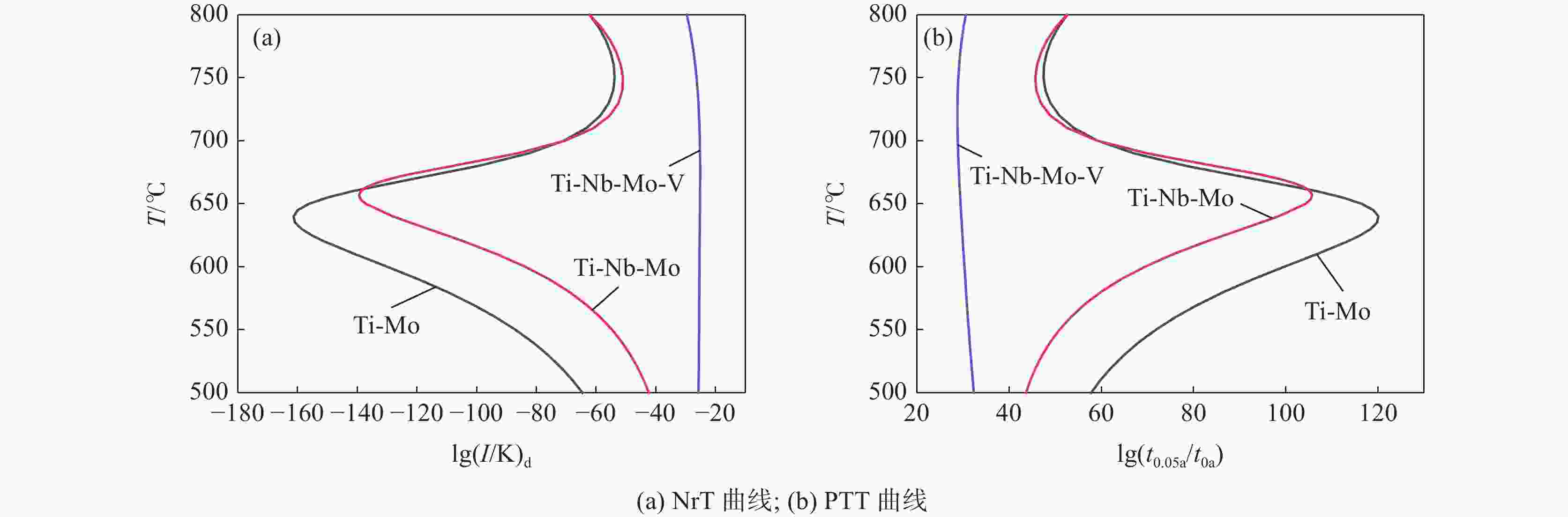
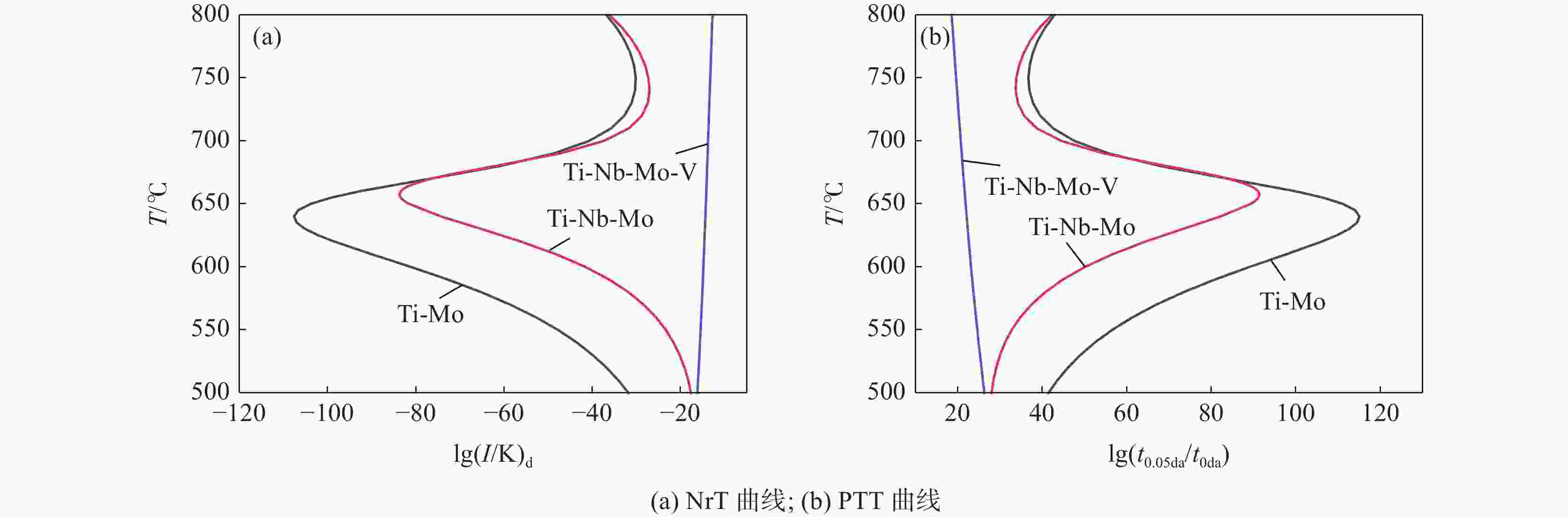
摘要: 根据多元复合析出相的固溶热力学计算和经典形核长大动力学理论,研究了Ti-Mo、Ti-Nb-Mo和Ti-Nb-Mo-V复合微合金化钢中碳化物在奥氏体(γ)和铁素体(α)中沉淀析出规律。研究表明,在γ区,Ti-Mo钢中析出相主要为富Ti的(Ti, Mo)C粒子,在较高温度区间,Ti-Nb-Mo和Ti-Nb-Mo-V钢中主要析出富Ti富Nb的碳化物粒子。在α区,Ti-Mo和Ti-Nb-Mo钢中析出相主要为富Mo的碳化物粒子,Ti-Nb-Mo-V钢主要析出富V的碳化物粒子。Ti-Mo、Ti-Nb-Mo钢中析出相在γ中沉淀析出的PTT曲线和NrT曲线分别呈“C”和反“C”形,而(Ti, Nb, Mo, V)C在奥氏体中沉淀析出NrT曲线呈反“ε”形,随着温度降低开始析出时间先缩短后延长。(Ti, Nb, Mo, V)C在高温奥氏体区形核速率最快,(Ti, Nb, Mo)C次之,(Ti, Mo)C最慢,且对应形核的最快析出温度依次升高。在铁素体区,(Ti, Mo)C和(Ti, Nb, Mo)C的PTT曲线和NrT曲线分别呈现“ε”形和反“ε”形。Ti-Nb-Mo-V钢中碳化物在整个铁素体区的形核速率快于Ti-Mo和Ti-Nb-Mo钢。Abstract: According to the solid solution thermodynamic calculation of the multi-composite precipitated phases and the classical nucleation growth kinetic theory, the deposition and precipitation of carbides in austenite (γ) and ferrite (α) phases in Ti-Mo, Ti-Nb-Mo and Ti-Nb-Mo-V composite microalloyed-steels were studied. It is shown that in γ phase, the precipitates in Ti-Mo steel are mainly Ti-enriched (Ti, Mo) C particles. In the higher temperature range, Ti-Nb-Mo and Ti-Nb-Mo-V steels mainly precipitate carbide particles enriched in Ti and Nb. In the ferritic zone, the precipitates in Ti-Mo and Ti-Nb-Mo steels are mainly Mo-enriched carbide particles, while in Ti-Nb-Mo-V steel, V-enriched carbide particles are mainly precipitated. The PTT and NrT curves of the precipitated phases in Ti-Mo and Ti-Nb-Mo steels show "C" and reverse "C" shapes, respectively, while the NrT curves of (Ti, Nb, Mo, V) C precipitated in austenite show reverse shapes "ε". As the temperature decreases, the precipitation time first decreases and then prolongs. The nucleation rate of (Ti, Nb, Mo, V) C is the fastest in the high-temperature austenitic zone, followed by (Ti, Nb, Mo) C, and that of (Ti, Mo) C is the slowest. The corresponding fastest nucleation precipitation temperature increases in sequence. In the ferritic region, the PTT and NrT curves of (Ti, Mo) C and (Ti, Nb, Mo) C are presented "ε" form and reverse "ε" shape, respectively. The nucleation rate of carbides in Ti-Nb-Mo-V steel is faster in the entire ferritic zone than in Ti-Mo and Ti-Nb-Mo steels.
-
Key words:
- microalloy steel /
- carbides /
- thermodynamic calculation /
- precipitation kinetics /
- PTT curves
-
表 1 Ti-Mo、Ti-Nb-Mo和Ti-Nb-Mo-V钢的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of Ti-Mo, Ti-Nb-Mo and Ti-Nb-Mo-V steels
% 编号 钢种 C Si Mn N Ti Mo Nb V 1# Ti-Mo 0.07 0.23 1.5 0.003 0.1 0.28 0 0 2# Ti-Nb-Mo 0.09 0.23 1.5 0.003 0.1 0.28 0.07 0 3# Ti-Nb-Mo-V 0.11 0.23 1.5 0.003 0.1 0.28 0.07 0.25 表 2 复合微合金钢中碳化物在奥氏体/铁素体中析出动力学的相关参数
Table 2. Parameters related to the precipitation kinetics of carbides in γ/α in composite microalloy steels
析出相 固溶度积 M元素的扩散
激活能/kJ点阵常数/nm 线胀系数$ \mathrm{\alpha }/{\mathrm{K}}^{-1} $ TiC γ 2.75-7000/T 251 0.4318 $ 7.86\times {10}^{-6} $ α 4.4-9575/T 248 NbC γ 2.96-7510/T 266.5 0.4469 $ 7.02\times {10}^{-6} $ α 5.43-10960/T 252 MoC γ 4.251-3468/T 240 0.4277 $ 6.88\times {10}^{-6} $ α 6.163-7583/T 229 VC γ 6.72-9500/T 264 0.4182 $ 8.29\times {10}^{-6} $ α 4.55-8300/T 241 表 3 Ti-Mo、T-Nb-Mo和Ti-Nb-Mo-V钢中碳化物在奥氏体中均匀形核的形核参量
Table 3. Uniform nucleation parameters of carbides in austenite in Ti-Mo, T-Nb-Mo and Ti-Nb-Mo-V steels
T/ ℃ Ti-Mo Ti-Nb-Mo Ti-Nb-Mo-V lg(I/K) lg(t0.05 a/t0 a) lg(I/K) lg(t0.05 a/t0 a) lg(I/K) lg(t0.05 a/t0 a) 700 −20.79 26.49 −21.50 27.20 −20.55 26.85 750 −20.56 25.68 −20.92 26.14 −20.63 26.21 800 −20.67 25.15 −20.53 25.27 −20.87 25.72 850 −21.28 25.01 −20.38 24.62 −20.89 25.13 900 −22.72 25.47 −20.53 24.22 −20.50 24.31 950 −25.85 27.10 −21.13 24.16 −20.25 23.63 1000 −33.14 31.54 −22.45 24.61 −20.66 23.45 1050 −55.11 45.80 −25.09 25.99 −22.02 23.96 1100 −194.45 138.33 −30.60 29.31 −25.04 25.61 表 4 Ti-Mo、Ti-Nb-Mo和Ti-Nb-Mo-V钢中碳化物在奥氏体中位错线上形核的计算结果
Table 4. Calculation results of carbide nucleation in austenite dislocation line in Ti-Mo, Ti-Nb-Mo and Ti-Nb-Mo-V steels
T/ ℃ Ti-Mo Ti-Nb-Mo Ti-Nb-Mo-V lg(I/K)d lg(t0.05 da/t0 da) lg(I/K)d lg(t0.05 da/t0 da) lg(I/K)d lg(t0.05 da/t0 da) 700 −15.90 22.41 −16.43 23.19 −16.08 23.13 750 −15.71 21.57 −16.17 22.25 −15.90 22.24 800 −15.74 21.00 −16.01 21.49 −15.95 21.65 850 −16.09 20.80 −16.00 20.93 −16.06 21.15 900 −17.03 21.25 −16.19 20.61 −16.03 20.57 950 −19.22 22.98 −16.70 20.66 −16.10 20.12 1000 −24.71 28.05 −17.74 21.28 −16.56 20.13 1050 −42.61 45.56 −19.83 22.98 −17.68 20.85 1100 −167.31 169.90 −24.29 27.09 −20.10 22.90 表 5 试验钢中碳化物在铁素体中均匀形核的计算结果
Table 5. Calculation results of uniform nucleation of carbides in ferrite in experimental steels
T/℃ Ti-Mo Ti-Nb-Mo Ti-Nb-Mo-V lg(I/K) lg(t0.05 a/t0 a) lg(I/K) lg(t0.05 a/t0 a) lg(I/K) lg(t0.05 a/t0 a) 500 −64.57 57.76 −43.81 44.65 −25.71 32.34 550 −87.03 71.80 −54.66 50.90 −25.51 31.24 600 −129.97 99.61 −83.74 69.41 −25.38 30.31 650 −156.16 116.42 −137.18 104.27 −25.20 29.46 700 −70.89 59.21 −70.52 59.20 −25.27 28.85 750 −53.80 47.46 −51.04 45.66 −26.36 28.99 800 −62.22 52.60 −62.15 52.53 −29.61 30.60 表 6 试验钢中碳化物在铁素体中位错线上形核的计算结果
Table 6. Calculation results of carbide nucleation in ferrite dislocation in experimental steels
T/℃ Ti-Mo Ti-Nb-Mo Ti-Nb-Mo-V lg(I/K) lg(t0.05 a/t0 a) lg(I/K) lg(t0.05 a/t0 a) lg(I/K) lg(t0.05 a/t0 a) 500 −31.79 41.50 −18.37 28.80 −16.1589 26.34 550 −47.79 56.56 −23.77 33.21 −15.4401 24.65 600 −81.13 89.09 −42.06 50.63 −14.8082 23.18 650 −103.85 111.15 −81.54 89.34 −14.2538 21.90 700 −40.7 47.64 −37.35 44.52 −13.7491 20.74 750 −30.17 36.75 −27.27 33.88 −13.2546 19.65 800 −36.86 42.97 −36.17 42.25 −12.7449 18.59 -
[1] Chen Zihao, Zhang Ke, Fu Xibin, et al. Effect of V content on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-V composite microalloy steel[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2021,21(7):827−835. (陈子豪, 张可, 付锡彬, 等. V含量对Ti-V复合微合金钢组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021,21(7):827−835. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.221107Chen Zihao, Zhang Ke, Fu Xibin, et al. Effect of V content on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-V composite microalloy steel[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2021, 21(7): 827-835. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.221107 [2] Zhou Dan, Chai Xiyang, Liang Fengrui, et al. Effects of V, V-N and V-Nb microalloying on microstructure and properties of high-strength ship plate steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019,44(6):60−64. (周丹, 柴希阳, 梁丰瑞, 等. V、V-N与V-Nb微合金化对高强船板钢组织与性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2019,44(6):60−64.Zhou Dan, Chai Xiyang, Liang Fengrui, et al. Effects of V, V-N and V-Nb microalloying on microstructure and properties of high-strength ship plate steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019, 44(6): 60-64. [3] Li Jing, Yuan Shaoqiang, Chu Xiangzhi. Dissolution behavior of the second phase in Nb-Ti microalloy steel[J]. Foundry Technology, 2017,38(9):2087−2089, 2095. (李敬, 苑少强, 褚祥治. Nb-Ti微合金钢中第二相的溶解行为[J]. 铸造技术, 2017,38(9):2087−2089, 2095.Li Jing, Yuan Shaoqiang, Chu Xiangzhi. Dissolution behavior of the second phase in Nb-Ti microalloy steel[J]. Foundry Technology, 2017, 38(9): 2087-2089, 2095. [4] Zheng Y X, Wang Q, Zhu L G, et al. Microstructure evolution and carbide precipitation behavior of microalloyed TS800TB steel during hot rolling and coiling processes[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2022,840:142902. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.142902 [5] Zheng Y X, Shen W, Zhu L G, et al. Effects of composition and strain rate on hot ductility of Cr-Mo-alloy steel in the two-phase region[J]. High Temperature Materials and Processes, 2021,40(1):228−240. doi: 10.1515/htmp-2021-0025 [6] Zheng Y X, Wang F M, Chang R. Effect of compound addition of Nb-B on hot ductility of Cr-Mo alloy steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2018,715:194−204. [7] Zhang D Q, Liu G, Zhang K, et al. Effect of Nb microalloying on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties in low carbon medium manganese steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2021,824:1−13. [8] Zhang K, Wang H, Sun X J, et al. Precipitation behavior and microstructural evolution of ferritic Ti-V-Mo complex microalloyed steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica (English Letters), 2018,31(9):9. [9] Nidhi Bansal G, Atul G, Mohit B. Effect of cold work, ageing on hardness and ultimate tensile strength of microalloyed steel[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2022,6671:116−123. [10] Liu H L, Yang B, Chen Y, et al. Precipitation law of vanadium in microalloyed steel and its performance influencing factors[J]. Materials, 2022,15(22):8146−8146. doi: 10.3390/ma15228146 [11] Pravendra Pratap S, Sadhan G, Suhrit M. Strengthening behaviour and failure analysis of hot-rolled Nb+V microalloyed steel processed at various coiling temperatures[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2022,859:144210. [12] 刘欣. 钒含量对Nb-V-Ti微合金钢析出行为及组织性能的影响[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2019.Liu Xin. Effect of vanadium content on precipitation behavior and microstructure properties of Nb-V-Ti microalloy steel[D]. Shengyang: Northeastern University, 2019. [13] Ni Lingling, Zhang Ke, Yuan Wenyang, et al. Effect of austenite deformation temperature on precipitation kinetics, microstructure and hardness of Ti-V composite microalloy steel[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2021,12(6):64−71. (倪玲玲, 张可, 袁文洋, 等. 奥氏体变形温度对Ti-V复合微合金钢析出动力学及组织和硬度的影响[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2021,12(6):64−71.Ni Lingling, Zhang Ke, Yuan Wenyang, et al. Effect of austenite deformation temperature on precipitation kinetics, microstructure and hardness of Ti-V composite microalloy steel[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2021, 12(6): 64-71. [14] 甘晓龙. V对Ti-Mo微合金钢第二相析出行为及组织性能的影响研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2019.Gan Xiaolong. Study on the effect of V on the second phase precipitation behavior and microstructure properties of Ti-Mo microalloy steel[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2019. [15] Yao Na, Xing Chao. Precipitation kinetics of composite carbides in Nb-Ti-V-Mo microalloy steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(4):142−149. (姚娜, 兴超. Nb-Ti-V-Mo微合金钢中复合碳化物的析出动力学[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(4):142−149.Yao Na, Xing Chao. Precipitation kinetics of composite carbides in Nb-Ti-V-Mo microalloy steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(4): 142-149. [16] Zhang Ke, Sun Xinjun, Zhang Mingya, et al. Kinetics of precipitation and precipitation of (Ti, V, Mo)C in γ/α in Ti-V-Mo composite microalloy steel[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 2018,54(8):1122−1130. (张可, 孙新军, 张明亚, 等. Ti-V-Mo复合微合金钢中(Ti, V, Mo)C在γ/α中沉淀析出的动力学[J]. 金属学报, 2018,54(8):1122−1130.Zhang Ke, Sun Xinjun, Zhang Mingya, et al. Kinetics of precipitation and precipitation of (Ti, V, Mo)C in γ/α in Ti-V-Mo composite microalloy steel[J]. Acta Metallurgical Sinica, 2018, 54(8): 1122-1130. [17] 杨海林. Ti-Nb微合金化高强钢强韧化机理及组织性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2021.Yang Hailin. Study on the toughening mechanism and microstructure properties of Ti-Nb microalloyed high-strength steel[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2021. [18] Bu Fanzheng, Wang Yubin, Zheng Lianhui, et al. Nanocarbide precipitation behavior during tempering of Ti-Mo microalloy steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2018,30(11):928−934. (卜凡征, 王玉斌, 郑连辉, 等. Ti-Mo微合金钢回火过程中纳米碳化物析出行为[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2018,30(11):928−934.Bu Fanzheng, Wang Yubin, Zheng Lianhui, et al. Nanocarbide precipitation behavior during tempering of Ti-Mo microalloy steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2018, 30(11): 928-934. [19] Liu Xiang, Du Qunli, Li Xin. Effect of heating process on austenitic grain growth of Nb-Ti microalloy steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019,54(9):116−120, 131. (刘祥, 杜群力, 李新. 加热工艺对Nb-Ti微合金钢奥氏体晶粒长大的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(9):116−120, 131. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20180424Liu Xiang, Du Qunli, Li Xin. Effect of heating process on austenitic grain growth of Nb-Ti microalloy steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019, 54(9): 116-120, 131. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn0449-749x.20180424 [20] 易航. Ti-Mo-V复合微合金钢中第二相析出行为及组织性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2020.Yi Hang. Study on second phase precipitation behavior and microstructure properties in Ti-Mo-V composite microalloy steel[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2020. [21] Yu Yinjun, Zhao Shiyu, Zhang Ke, et al. Effect of isothermal cooling time on microstructure transformation and hardness of Ti-V-Mo composite microalloy steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2021,46(6):95−101. (于银俊, 赵时雨, 张可, 等. 温冷却时间对Ti-V-Mo复合微合金钢组织转变及硬度的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2021,46(6):95−101.Yu Yinjun, Zhao Shiyu, Zhang Ke, et al. Effect of isothermal cooling time on microstructure transformation and hardness of Ti-V-Mo composite microalloy steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2021, 46(6): 95-101. [22] 韩荣. Ti-V-Mo复合微合金化温成形汽车钢的强化机理研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2022.Han Rong. Study on strengthening mechanism of Ti-V-Mo composite microalloy thermoformed automotive steel[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2022. [23] 雍岐龙. 钢铁材料中的第二相[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2006.Yong Qilong. Secondary phases in steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2006. -





 下载:
下载: