Efficient metallurgical extraction of vanadium slag: mechanochemically enhanced sodium salt roasting vanadium extraction process
-
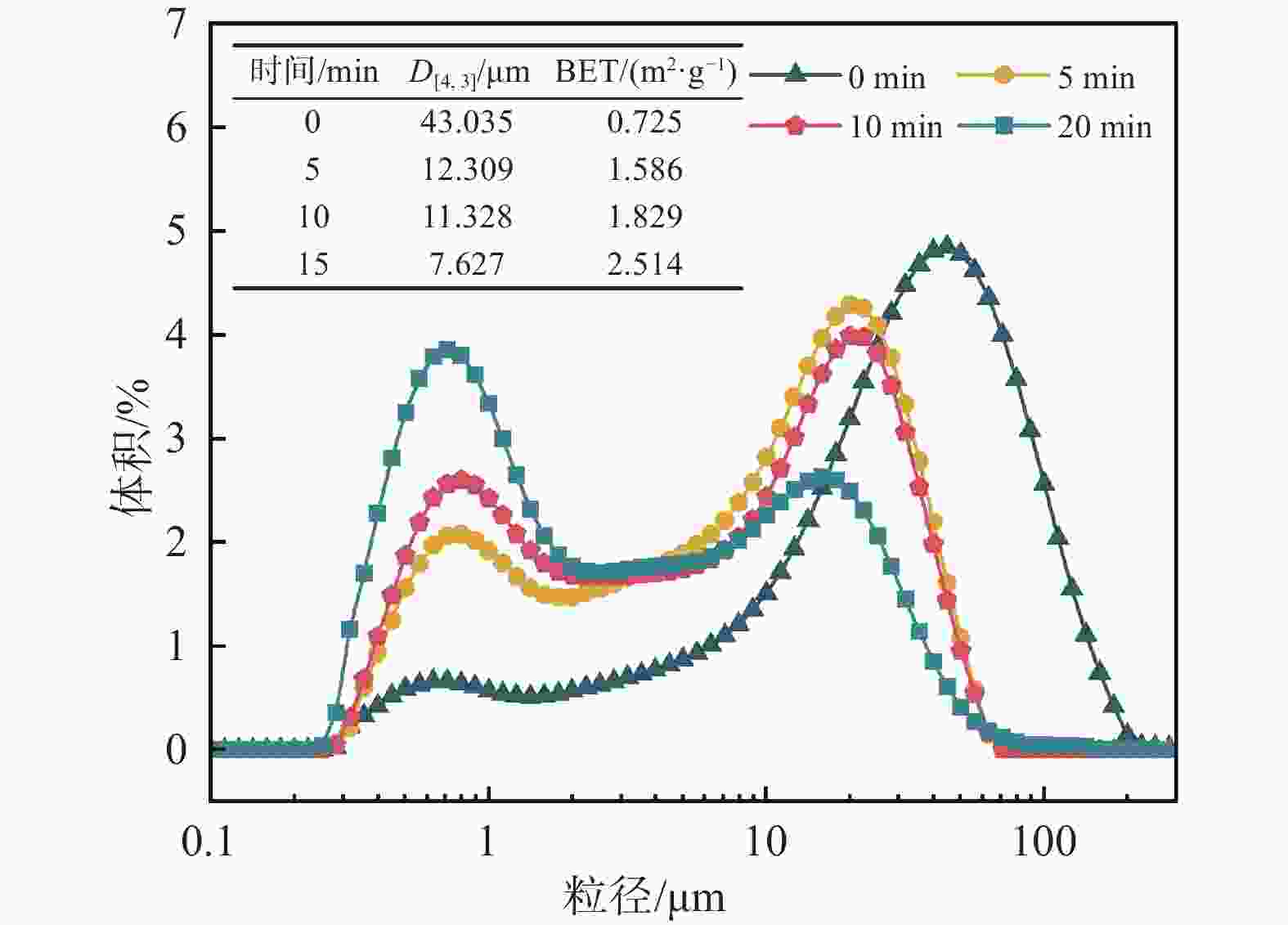
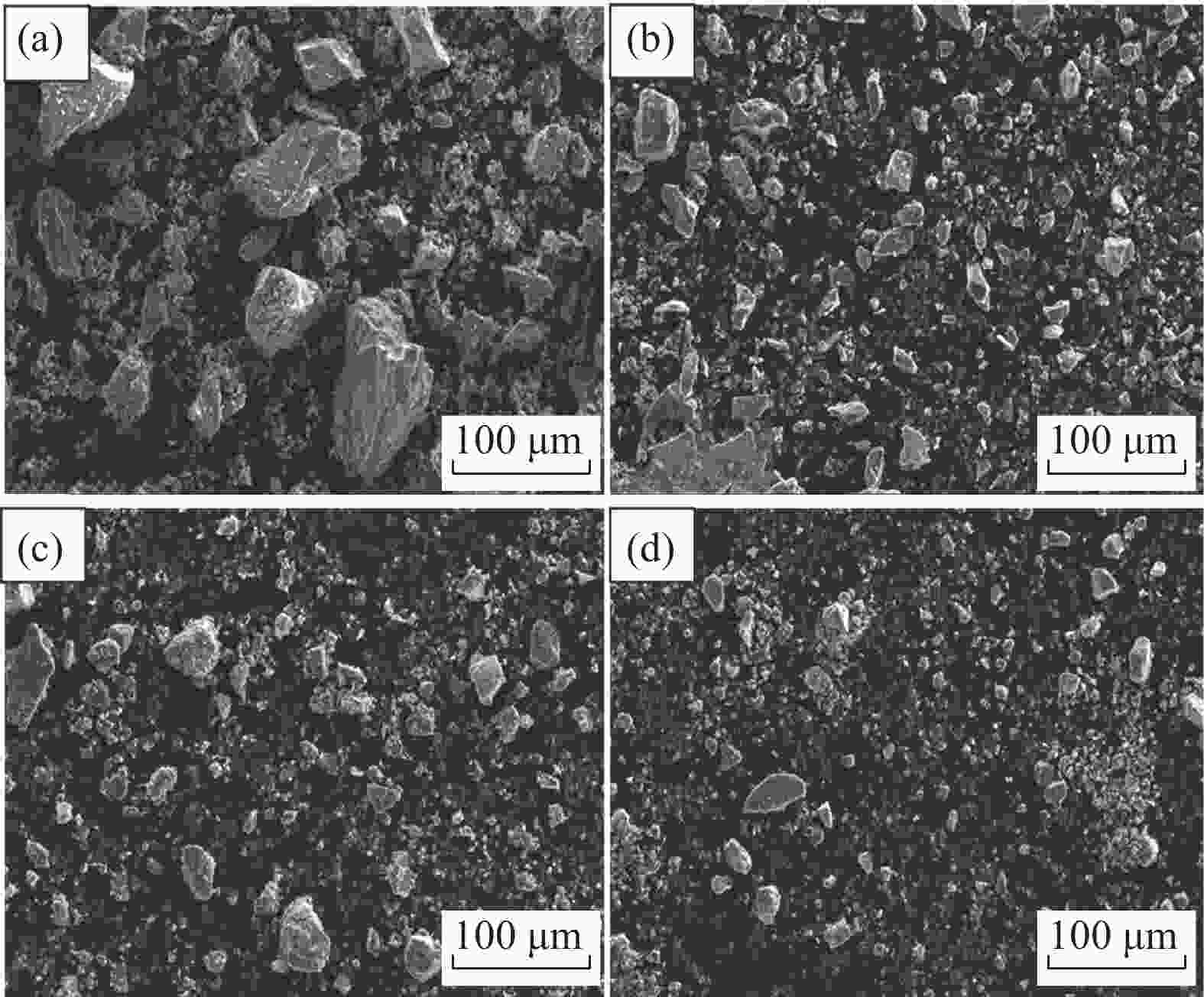
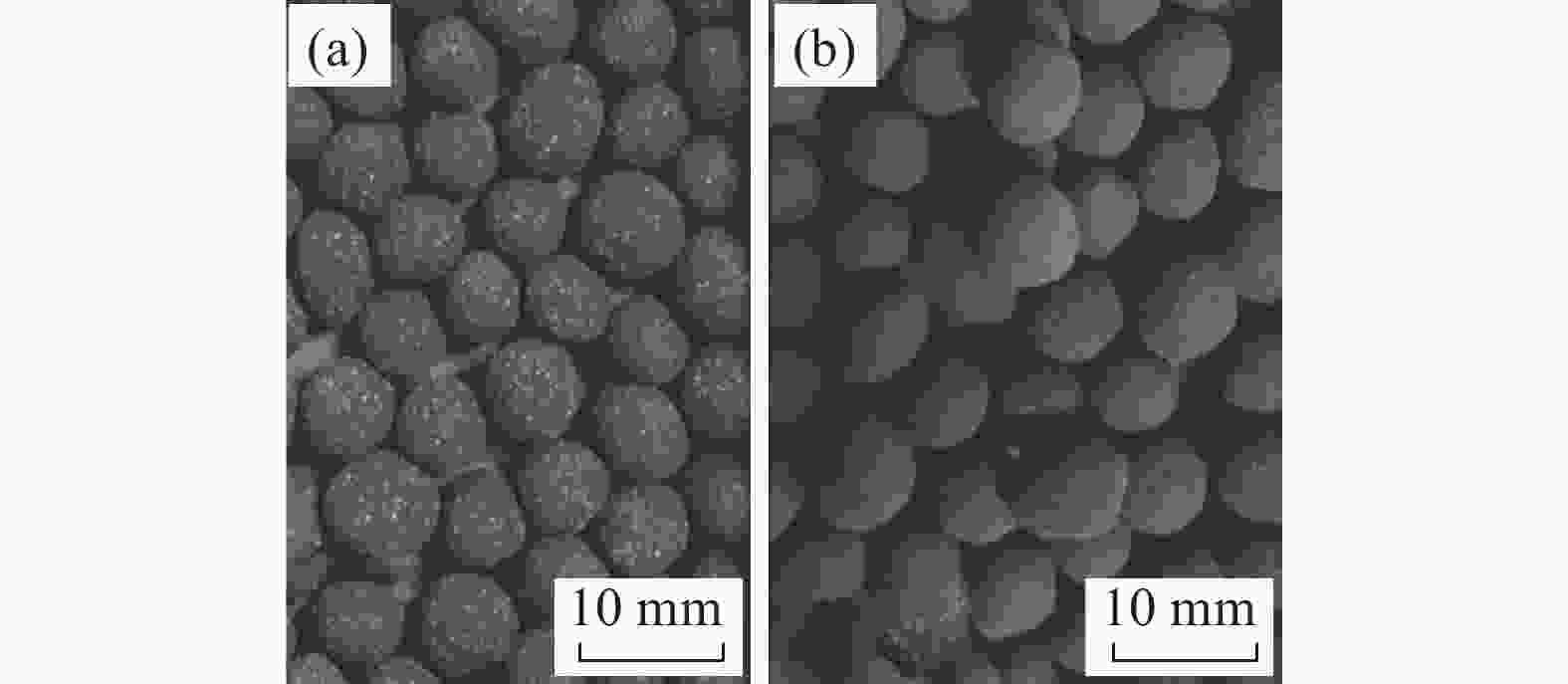
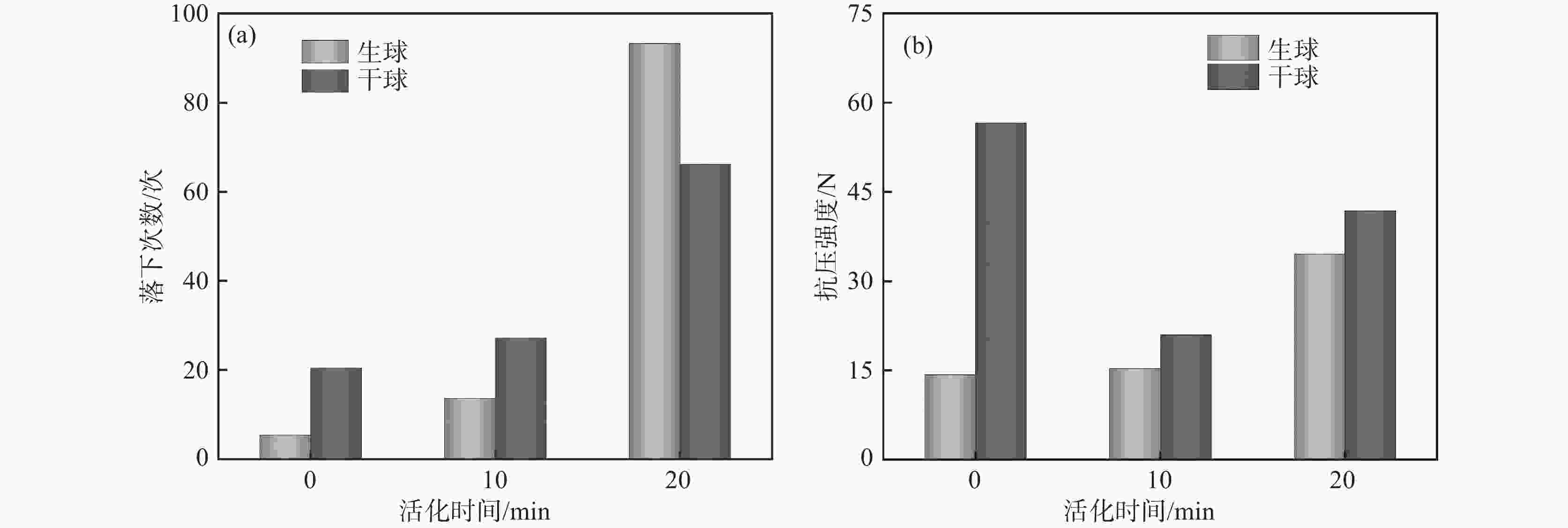
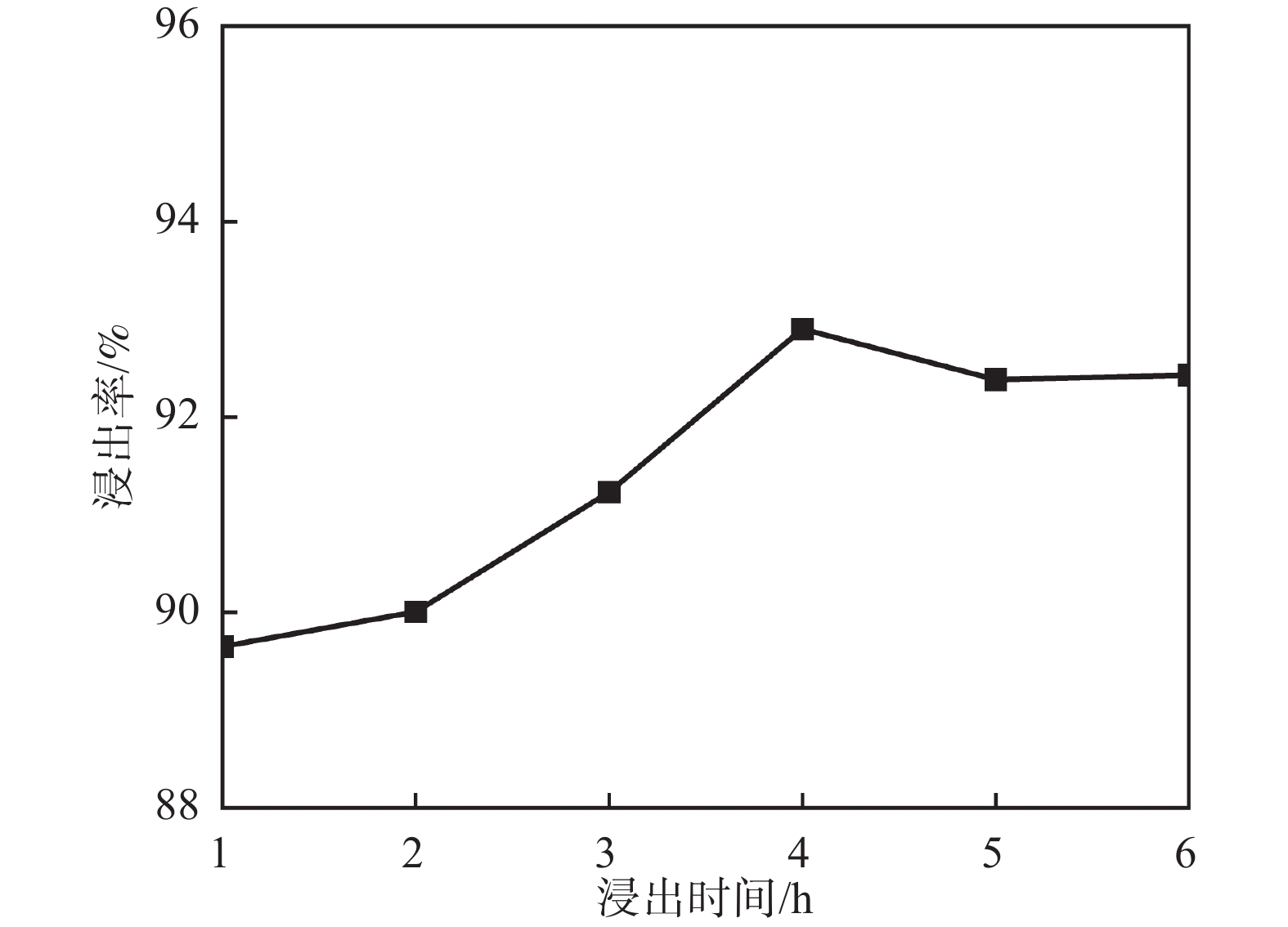
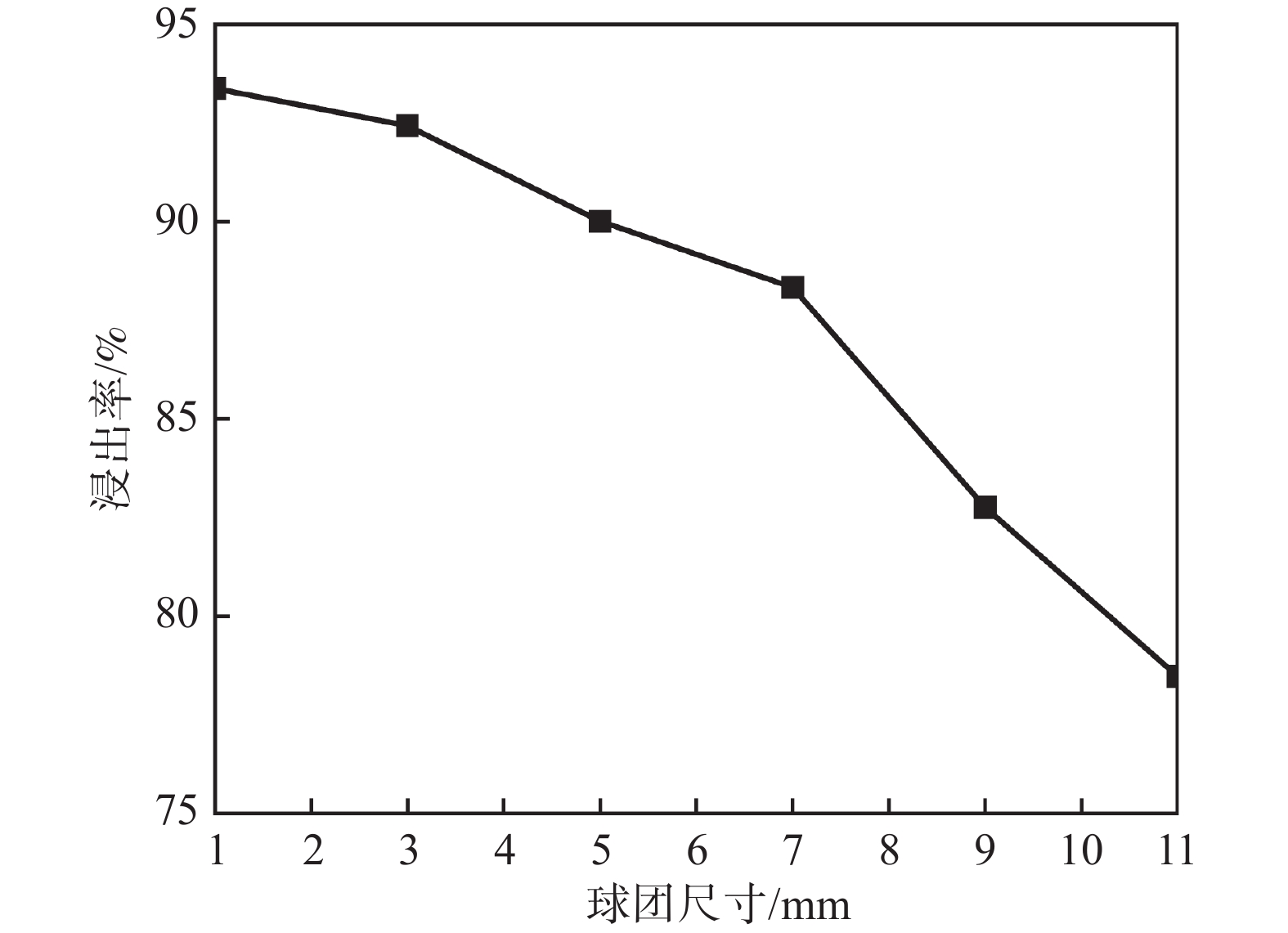
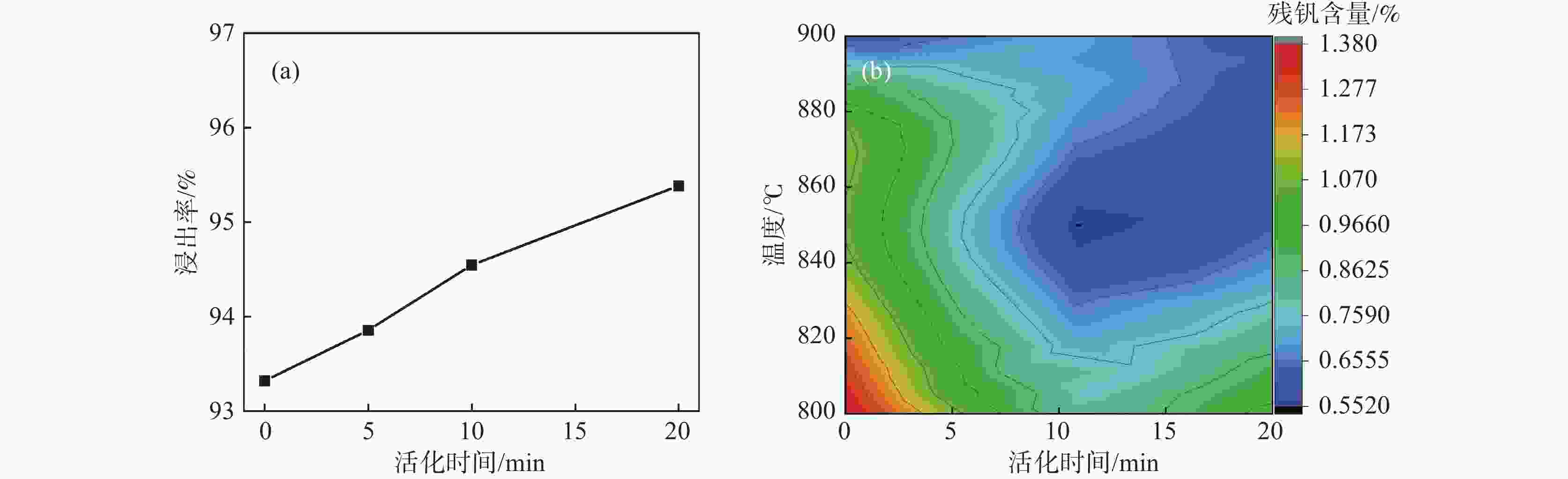
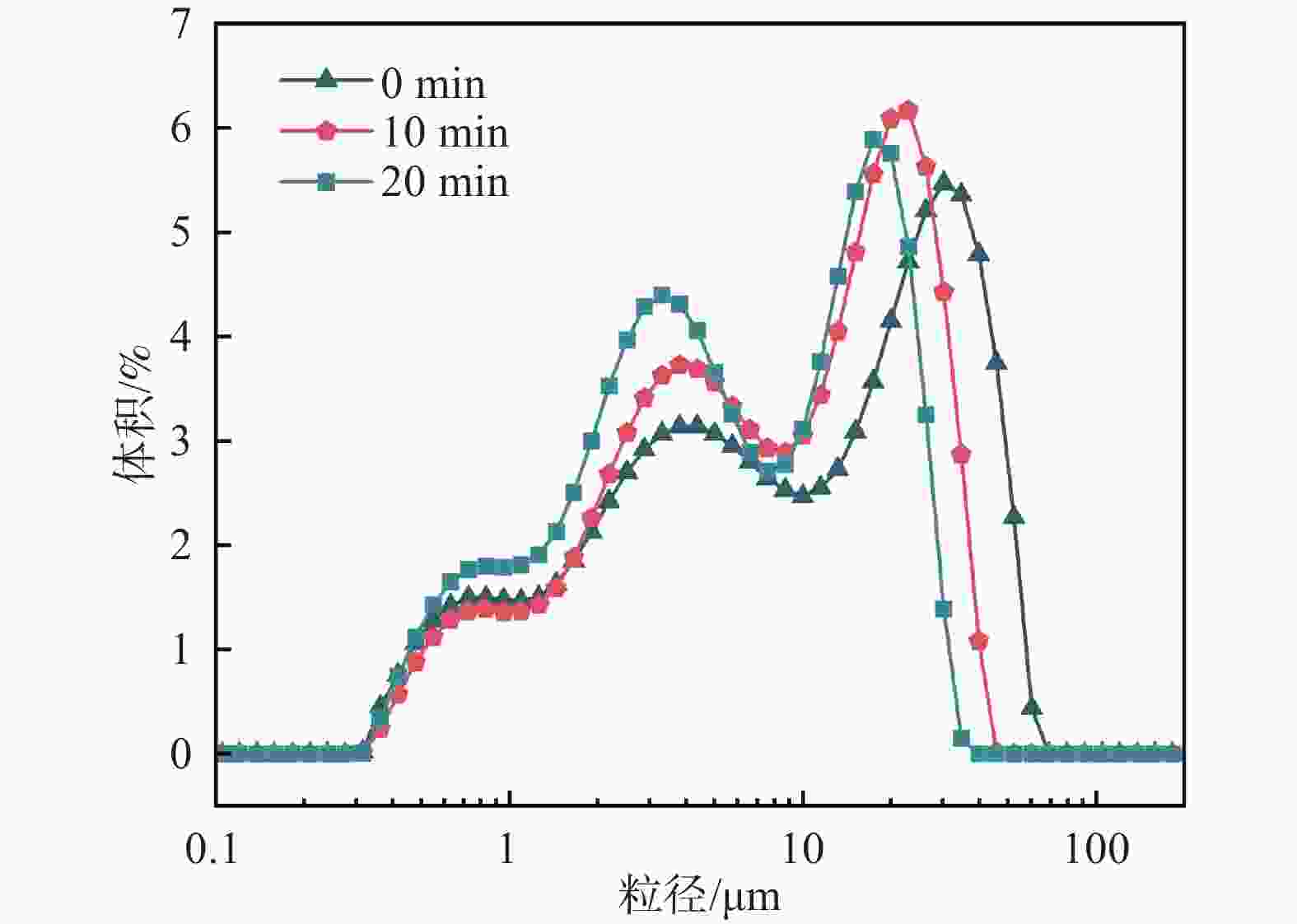
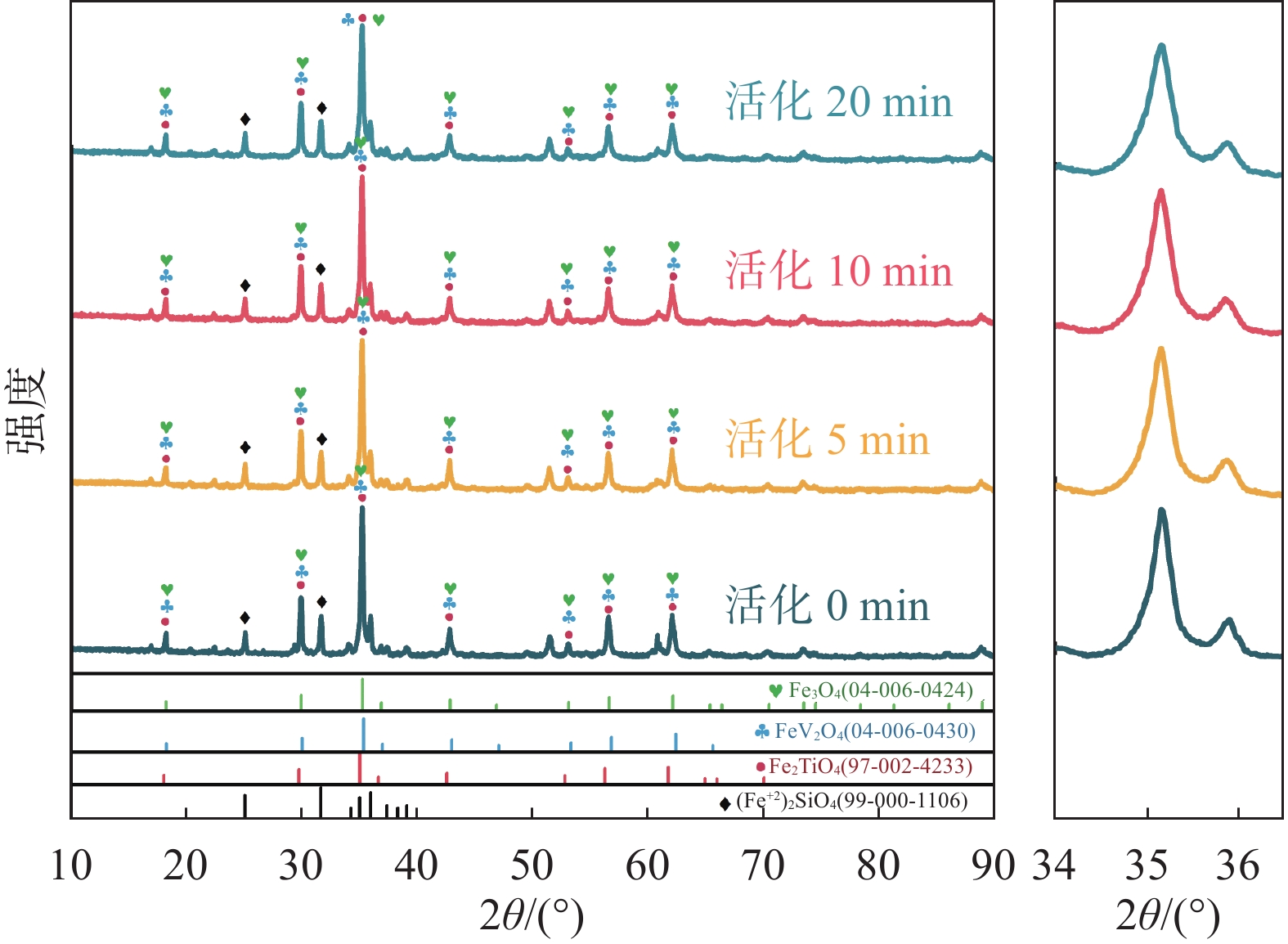
摘要: 针对钒渣钠化焙烧-水浸提钒工艺一次焙烧转化率低、高温回转窑结圈等技术难题,提出了机械活化-造球协同预处理强化钒渣提钒技术。通过高能球磨活化促进钒渣物相解离与微观结构调控,提升其反应活性,并通过造球工艺改善原料传热均匀性与氧化速率,提高回转窑处理效率。采用XRD、激光粒度分析和BET比表面积等测定手段,系统分析了活化前后钒渣的物理化学性质及焙烧转浸变化规律。结果表明,机械活化会导致晶格畸变引起衍射峰宽化,且将钒渣平均粒径从43.035 μm降至7.627 μm,比表面积从0.725 m2/g升至2.514 m2/g;机械活化可显著提高钒渣混料球团的下落强度与抗压强度;钒渣最佳焙烧温度降低50 ℃,一次焙烧钒浸出率达到95.38%。新技术在低温下实现了钒收率提高,有效避免了回转窑结圈,是一种高效提钒技术。Abstract: To resolve the low conversion rate in single-pass roasting and ring formation in rotary kilns during conventional sodium roasting-water leaching process, this study proposed an innovative mechanical activation-granulation co-pretreatment technology. High-energy ball milling was introduced to promote phase dissociation and microstructure modification of vanadium slag, significantly enhancing its reactivity. Granulation process was optimized to improve heat transfer uniformity and oxidation rate of raw materials. Through XRD, laser particle size analysis, and BET measurements, the physicochemical evolution of vanadium slag was systematically characterized. Results indicate that mechanical activation can cause lattice distortion and diffraction peak broadening. It reduces the average particle size of vanadium slag from 43.035 μm to 7.627 μm and increases the specific surface area from 0.725 m2/g to 2.514 m2/g. The optimal roasting temperature is reduced by 50 °C, achieving a 95.38% vanadium leaching rate in single-pass roasting. This technology not only improves vanadium yield at lower temperatures but also effectively prevents rotary kiln ring formation, enabling an efficient and clean extraction process.
-
Key words:
- vanadium slag /
- mechanical activation /
- sodium roasting /
- leaching rate
-
表 1 钒渣的化学成分
Table 1. Main composition of vanadium slag
% TFe MFe SiO2 V2O5 TiO2 Cr2O3 CaO P2O5 39.35 1.42 15.28 9.52 8.72 2.96 2.30 0.458 -
[1] KIM W S, KIM D S, KUZNETSOV A V. Simulation of coupled turbulent flow and heat transfer in the wedge-shaped pool of a twin-roll strip casting process[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2000,43(20):3811-3822. doi: 10.1016/S0017-9310(00)00013-2 [2] LIU J S, DING X Y, XUE X X, et al. Research progress of comprehensive utilization of vanadium extraction tailings[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021,56(7):152-160. (刘金生, 丁学勇, 薛向欣, 等. 提钒尾渣资源化综合利用的研究进展[J]. 钢铁, 2021,56(7):152-160.LIU J S, DING X Y, XUE X X, et al. Research progress of comprehensive utilization of vanadium extraction tailings[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021, 56(7): 152-160. [3] LI L J, CHEN D H, BAI R G, et al. High-efficiency clean vanadium-extracting technique of vanadium slag blank calcination[J]. Hebei Metallurgy, 2014(12):29-33. (李兰杰, 陈东辉, 白瑞国, 等. 钒渣空白焙烧高效清洁提钒技术[J]. 河北冶金, 2014(12):29-33.LI L J, CHEN D H, BAI R G, et al. High-efficiency clean vanadium-extracting technique of vanadium slag blank calcination[J]. Hebei Metallurgy, 2014(12): 29-33. [4] WANG C Q, LIU W H, LIU H Q, et al. Research on sintering phenomenon during calcination of vanadium slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013,34(6):6-11. (王春琼, 刘武汉, 刘恢前, 等. 钒渣钙化焙烧烧结现象研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2013,34(6):6-11. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2013.06.002WANG C Q, LIU W H, LIU H Q, et al. Research on sintering phenomenon during calcination of vanadium slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013, 34(6): 6-11. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2013.06.002 [5] WU E H, LI J, XU Z, et al. Extraction of vanadium from high-chromium vanadium-bearing titano-magnetite concentrate pelles by oxidizing and Na-activation roasting and water leaching[J]. Chinese Journal Rare Metals, 2022,46(12):1599-1608. (吴恩辉, 李军, 徐众, 等. 高铬型钒钛铁精矿球团氧化钠化焙烧-水浸提钒研究[J]. 稀有金属, 2022,46(12):1599-1608.WU E H, LI J, XU Z, et al. Extraction of vanadium from high-chromium vanadium-bearing titano-magnetite concentrate pelles by oxidizing and Na-activation roasting and water leaching[J]. Chinese Journal Rare Metals, 2022, 46(12): 1599-1608. [6] FU Z B, JIANG L, LI M, et al. Simultaneous extraction of vanadium and chromium from Vanadium-chromium slag by sodium roasting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(4):1-6. (付自碧, 蒋霖, 李明, 等. 钒铬渣钠化焙烧同步提取钒和铬[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(4):1-6.FU Z B, JIANG L, LI M, et al. Simultaneous extraction of vanadium and chromium from Vanadium-chromium slag by sodium roasting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(4): 1-6. [7] MA, J, MA B Z, AN Y R, et al. Recovery of vanadium from rapid-cooling converter vanadium slag by sodium roasting and water leaching[J]. JOM, 2024,76(12):7047-7059. doi: 10.1007/s11837-024-06546-x [8] TENG A J, XUE X X, ZHANG X F. Research on microwave roasting for sodiumizing vandalite for vanadium recovery[C]. China Metallurgical Society, Ironmaking Branch, 2017: 632-638. (滕艾均, 薛向欣, 张学飞. 钒渣钠化提钒的微波焙烧研究[C]. 中国金属学会炼铁分会, 2017: 632-638.TENG A J, XUE X X, ZHANG X F. Research on microwave roasting for sodiumizing vandalite for vanadium recovery[C]. China Metallurgical Society, Ironmaking Branch, 2017: 632-638. [9] DENG, R R, XIAO H, XIE Z M, et al. A novel method for extracting vanadium by low temperature sodium roasting from converter vanadium slag[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2020,28(8):2208-2213. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2020.03.038 [10] LI Q W, LIU F Q, DENG X B, et al. Study on roasting Pangang converter vanadium slag with soda in laboratory[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012,33(4):7-11. (李千文, 刘丰强, 邓孝伯, 等. 攀钢转炉钒渣钠化焙烧实验室研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2012,33(4):7-11. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2012.04.002LI Q W, LIU F Q, DENG X B, et al. Study on roasting Pangang converter vanadium slag with soda in laboratory[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012, 33(4): 7-11. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2012.04.002 [11] XIANG J Y, HUANG Q Y, LÜ X W, et al. Effect of mechanical activation treatment on the recovery of vanadium from converter slag[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2017,48(5):2759-2767. [12] PETER B. Mechochemistry in nanoscience and minerals engineering[M]. Germany: Springer Science & Business Media, 2008: 257-292. [13] HUANG Q Y, XIANG J Y, PEI G S et al. Mechanical activation on extraction of vanadium from vanadium slag by calcification roasting-acid leaching process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2020,30(4):858-865. (黄青云, 向俊一, 裴贵尚, 等. 机械活化强化钒渣钙化提钒工艺[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2020,30(4):858-865. doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-35745HUANG Q Y, XIANG J Y, PEI G S et al. Mechanical activation on extraction of vanadium from vanadium slag by calcification roasting-acid leaching process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2020, 30(4): 858-865. doi: 10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2020-35745 [14] XIANG J Y. Fundamental study on the optimization of vanadium extraction from LD converter slag by calcification based process and the comprehensive utilization of tailings[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2018. (向俊一. 转炉钒渣钙化提钒工艺优化及提钒尾渣综合利用基础研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2018.XIANG J Y. Fundamental study on the optimization of vanadium extraction from LD converter slag by calcification based process and the comprehensive utilization of tailings[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2018. [15] YAO N, XING C, HU Q W. Analysis on influencing factors of compressive strength of carbon-burdened double-layer pelleting[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2021,46(6):89-94. (姚娜, 兴超, 胡启武. 内配碳双层球团抗压强度的影响因数分析[J]. 烧结球团, 2021,46(6):89-94.YAO N, XING C, HU Q W. Analysis on influencing factors of compressive strength of carbon-burdened double-layer pelleting[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing, 2021, 46(6): 89-94. -




 下载:
下载: