Impurities composition prediction and control of FeV50 alloy by aluminothermal reduction
-
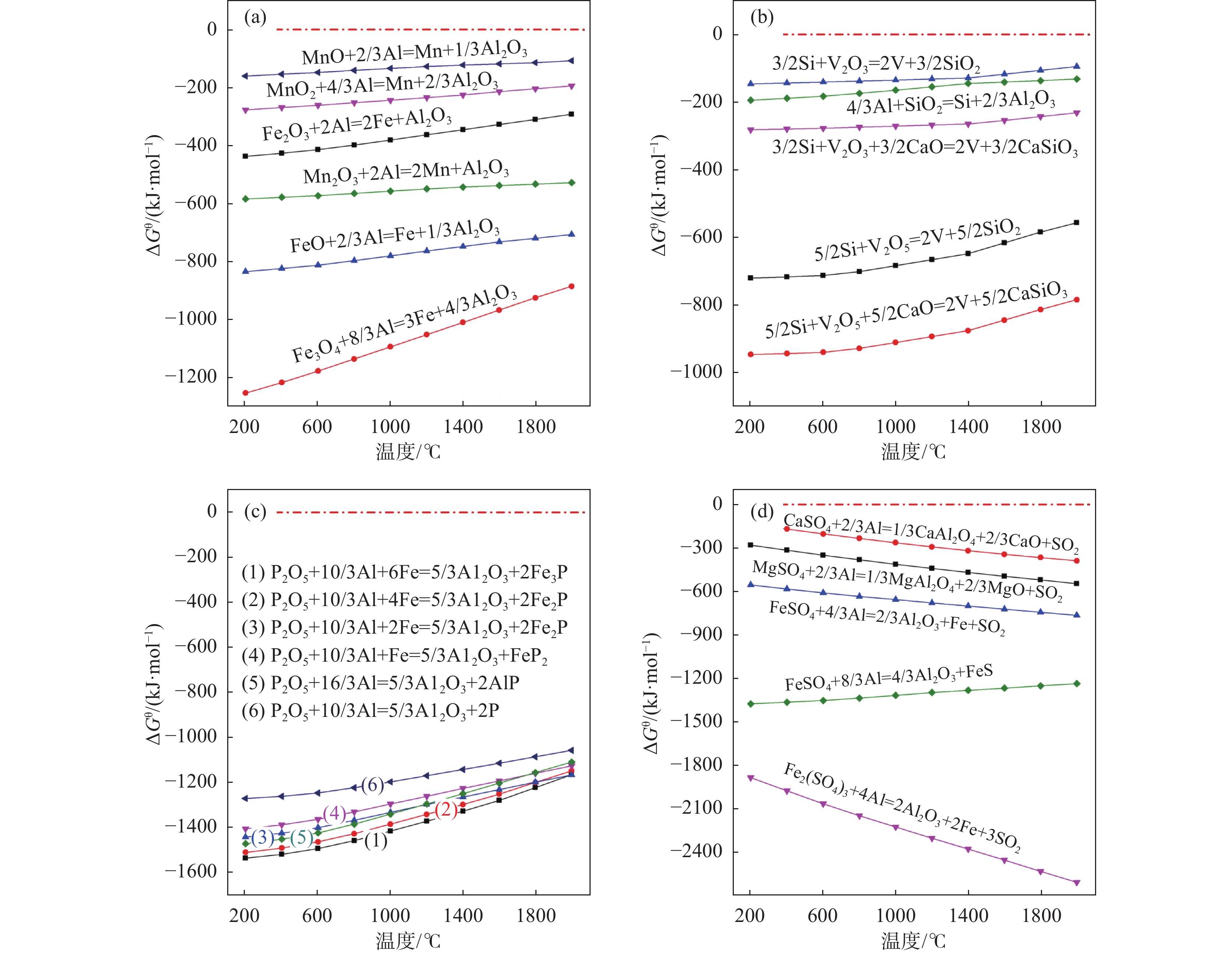
摘要: 分析了铝热还原FeV50合金制备过程典型杂质元素的热力学行为及其赋存状态,考察了特定熔渣特性条件下杂质元素在熔渣和合金中的分配规律,制定了原料杂质元素的控制标准。结果表明:铝热还原体系典型杂质元素迁移及其赋存状态与熔炼阶段和熔渣特性相关。铝热还原过程中,Fe、Mn、Si、C、P、S等弱还原性杂质元素在热力学上具有被金属铝还原并进入合金相的可行性,还原后的Fe、Mn、Si元素以单质形式存在,而C、P、S则可能与合金基体元素V和Fe反应生成VC、Fe3P和FeS。铝热反应结束后,合金中非金属杂质逐渐向熔渣扩散,其扩散能力主要由熔渣特性决定。在以钒氧化物还原为主导的特定熔渣组成条件下,Si、Mn、C、P和S在合金中的平均分配系数分别为76.9%、89.7%、255.0%、87.6%和28.7%,对应满足FeV50-A标准要求的单位原料杂质控制上限分别为4.0%、1.0%、0.6%、0.13%和0.12%。Abstract: The thermodynamic behavior of typical impurity elements in the preparation process of FeV50 alloy by aluminum thermal reduction and their stable occurrence state in the alloy were analyzed, and the distribution law of impurity elements under specific slag characteristics conditions was investigated.The control standards for impurity elements were established. The results indicate that the migration and occurrence of typical impurity elements in aluminum thermal reduction system are related to the smelting stage and slag characteristics. During the aluminum thermal reduction process, weak reducing impurity elements such as Fe, Mn, Si, C, P, S, etc. have the thermodynamic feasibility to be reduced by metallic aluminum and entering the alloy phase. The reduced Fe, Mn, and Si exist in elemental form, while C, P, and S may react with the alloy matrix elements V and Fe to form VC, Fe3P, and FeS, respectively. After the aluminothermal reaction, non-metallic impurities in the alloy gradually diffuse into the slag, and their diffusion ability is mainly determined by the characteristics of the slag. Under specific slag composition conditions dominated by vanadium oxide reduction, the average distribution coefficients of Si, Mn, C, P and S in the alloy are 76.9%, 89.7%, 255.0%, 87.6% and 28.7%, and the corresponding upper limits of impurity control for unit raw materials that meet the FeV50-A standard requirements are 4.0%, 1.0%, 0.6%, 0.13%, and 0.12%, respectively.
-
Key words:
- aluminothermal reduction /
- FeV50 /
- alloy composition /
- distribution regularity /
- control standards
-
表 1 试验原料化学成分及杂质含量分布
Table 1. Chemical compositions and impurities content of raw materials
原料 纯度 /% 杂质元素含量 /% 标准 Si Mn C P S 钒源 V2O3 60.8~64.5* 0.02~0.10 0~0.25 0~0.10 0~0.04 0~0.04 GB/T 40301–2021 V2O5 98.0~99.2 0.02~0.15 0~0.30 0~0.05 0~0.05 0~0.04 YB/T 5304–2017 FeV 47.6~51.8* 0.30~2.00 0~0.45 0~0.25 0~0.10 0~0.05 GB/T 4139–2012 PD 12.3~ 16.8* 0.50~3.00 0~0.35 0~0.45 0~0.10 0~0.15 QB–2021 EM 16.2~25.5* 0.30~2.50 0~0.15 0~0.35 0~0.15 0~0.15 QB–2021 铁源 Fe 99.4~99.7 0~0.10 0~0.10 0~0.15 0~0.04 0~0.05 QB–2021 BMIG 95.3~97.8 0~0.25 0~0.20 0~0.20 0~0.08 0~0.10 QB–2021 还原剂 Al 99.0~99.5 0~0.05 0~0.05 0~0.06 0~0.05 0~0.05 QB–2021 造渣剂 CaO 90.0~93.5 0~0.20 0~0.05 0~0.15 0~0.05 0~0.06 QB–2021 注:*为TV 表 2 FeV50合金成分标准(GB/T 4139-2012)
Table 2. Composition standards of FeV50 alloy (GB/T 4139-2012)
牌号 成分要求/% V C Si P S Al FeV50-A 48.0~55.0 ≤0.4 ≤2.0 ≤0.06 ≤0.04 ≤1.5 FeV50-B 48.0~55.0 ≤0.6 ≤3.0 ≤0.10 ≤0.06 ≤2.5 FeV50-C 48.0~55.0 ≤5.0 ≤3.0 ≤0.10 ≤0.06 ≤0.5 表 3 不同牌号钒铁合金冶炼原料的典型杂质的控制标准
Table 3. Control standards for typical impurities of raw materials in different grades of ferrovanadium alloy
牌号 原料杂质控制上限/% Si Mn C P S FeV50-A 4.0 1.0 0.6 0.13 0.12 FeV50-B 4.0 1.0 0.8 0.18 0.15 分配比 56.9~93.4 80.6~96.8 79.3~98.6 0~63.5 -
[1] HUANG D X. Vanadium recovery steelmaking[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000: 16-17 (黄道鑫. 提钒炼钢[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2000: 16-17.HUANG D X. Vanadium recovery steelmaking[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000: 16-17 [2] YANG C F, ZHANG Y Q, WANG R Z. Metallurgical principles and applications of vanadium steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2012: 20-25. (杨才福, 张永权, 王瑞珍. 钒钢冶金原理与应用[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2012: 20-25.YANG C F, ZHANG Y Q, WANG R Z. Metallurgical principles and applications of vanadium steel[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2012: 20-25. [3] YU B, SUN Z H, ZHOU H, et al. Theoretical application and factors influencing casting settlement of FeV50 alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2017,39(12):1822-1827. (余彬, 孙朝晖, 周恒, 等. FeV50合金浇铸沉降理论的应用及其影响因素[J]. 工程科学学报, 2017,39(12):1822-1827.YU B, SUN Z H, ZHOU H, et al. Theoretical application and factors influencing casting settlement of FeV50 alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2017, 39(12): 1822-1827. [4] ZHU S Y. Technical research on smelting high ferrovanadium by electroaluminothermal method[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993,14(1):37-39. (朱胜友. 电铝热法冶炼高钒铁的技术研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1993,14(1):37-39.ZHU S Y. Technical research on smelting high ferrovanadium by electroaluminothermal method[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993, 14(1): 37-39. [5] YU B, YUAN T C, SHI J J, et al. Preparation of high-quality FeV50 alloy by an improved SHS-EAH multi-stage process[J]. Ceramics International, 2023,49(10):15114-15121. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.01.094 [6] XIAN Y. Effects of Al content on phase transformation in FeV50 alloy and its mechanism[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012,33(5):14-18. (鲜勇. Al含量对FeV50合金相变的影响及机理研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2012,33(5):14-18.XIAN Y. Effects of Al content on phase transformation in FeV50 alloy and its mechanism[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012, 33(5): 14-18. [7] XIAN Y, ZHENG H X, ZHAI Q J, et al. A two-dimensional structure map for prediction of the transition-metal laves phases[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2016,125:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2016.08.023 [8] YE M F, YU B, HUANG Y, et al. Trend and control of P in FeV50 smelting process of large-scale tilting furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(4):36-41. (叶明峰, 余彬, 黄云, 等. P元素在倾翻炉FeV50冶炼中的走向与控制[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(4):36-41. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.04.006YE M F, YU B, HUANG Y, et al. Trend and control of P in FeV50 smelting process of large-scale tilting furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(4): 36-41. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.04.006 [9] TANG Z X, ZHANG S C, HU J L. Aluminum and oxygen equilibrium relation and deep desulfurization in smelting cast steel[J]. Foundry Equipment and Technology, 2014,6:44-45. (唐钟雪, 张生存, 胡进林. 铸钢冶炼过程中的Al、O平衡关系及深度脱S处理[J]. 铸造设备与工艺, 2014,6:44-45.TANG Z X, ZHANG S C, HU J L. Aluminum and oxygen equilibrium relation and deep desulfurization in smelting cast steel[J]. Foundry Equipment and Technology, 2014, 6: 44-45. [10] YU B, SUN Z H, PAN C, et al. Study on carbon content control for FeV80 alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017,38(5):37-41. (余彬, 孙朝晖, 潘成, 等. FeV80合金碳含量控制研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017,38(5):37-41.YU B, SUN Z H, PAN C, et al. Study on carbon content control for FeV80 alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017, 38(5): 37-41. -





 下载:
下载: