Microstructure and properties of ultra-high strength diffusion-bonded joint between TC21 titanium alloy and G50 steel
-
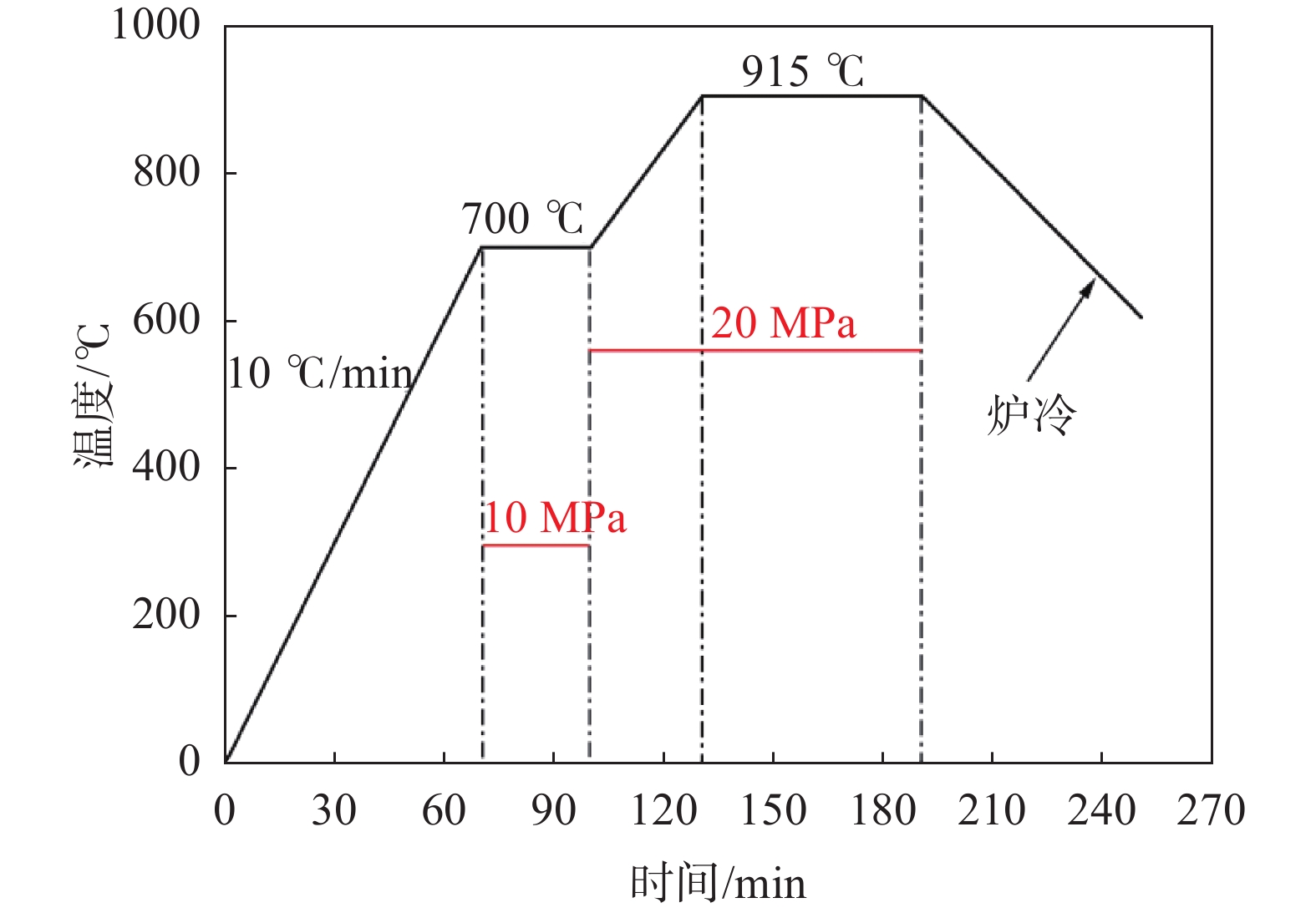
摘要: 使用改进的真空扩散焊接方法制备了TC21钛合金及G50高强钢的超高强扩散焊接头。在刚性模具约束下,以V/Cu为过渡层,在915 ℃保温60 min进行焊接,焊接压力为20 MPa。与传统扩散焊工艺不同,待焊件接头处于三向压应力状态,使焊接界面处金属塑性流动及元素扩散更充分,可有效消除界面孔洞、微孔等缺陷,所制备的接头抗拉强度达752 MPa,为目前研究报道的钛钢接头强度最高值。界面分析显示,TC21/V、V/Cu界面处无析出相,Cu/G50界面处析出富铁相,拉伸时接头从富铁相处断裂。Abstract: An ultra-high strength joint between TC21 titanium alloy and G50 high-strength steel had been prepared by an improved diffusion bonding in this study. Under the constraints of a rigid mold, the diffusion bonding using the V and Cu as interlayers was carried out at 915 ℃ for 60 minutes with an axial load of 20 MPa. Unlike the traditional diffusion bonding processes where the joint was under unidirectional compressive stress, the bonded samples in this study were subjected to triaxial compressive stress state, which promoted more sufficient metal flow and elemental diffusion at the interfaces. This effectively eliminated interfacial defects such as voids and micro-pores. The tensile strength of the joint was as high as 752 MPa, which was so far the highest that have been reported in the literature for the joints between titanium and steel prepared by diffusion bonding. The interface analysis showed that there were no precipitates at the TC21/V and V/Cu interfaces, and Fe-rich precipitates were observed at the Cu/G50 interface. In the tensile test, the fracture occurred in the interface between Cu and G50, resulting from the Fe-rich precipitates.
-
表 1 TC21钛合金及G50高强钢力学性能
Table 1. Tensile properties of the base metals of TC21 and G50
基材 抗拉强度/MPa 屈服强度/MPa 延伸率/% TC21 1262 1117 12.5 G50 1750 1510 12.3 表 2 TC21钛合金及G50高强钢基材化学成分
Table 2. Chemical compositions of the base metals of TC21 and G50
% 基材 Fe Ti Al Ni Nb Cr Mo Zr Sn Si Mn C TC21 Bal. 6.64 1.78 3.18 2.10 1.96 0.01 G50 Bal. 4.51 0.03 1.10 0.60 1.80 0.70 0.29 表 3 TC21/V/Cu/G50扩散焊接接头力学性能
Table 3. Mechanical properties of TC21/V/Cu/G50 diffusion bonded joint
MPa 编号 抗拉强度 1# 756 2# 751 3# 749 平均值 752 -
[1] KUNDU S, SAM S, CHATTERJEE S. Interface microstructure and strength properties of Ti-6Al-4V and microduplex stainless steel diffusion bonded joints[J]. Materials & Design, 2011,32(5):2997-3003. [2] VELMURUGAN C, SENTHILKUMAR V SARALA S, et al. Low temperature diffusion bonding of Ti-6Al-4V and duplex stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2016(234):272-279. [3] ZHANG Y, SUN D Q, GU X Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical property improvement of dissimilar metal joints for TC4 Ti alloy to 301L stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2018(53):2942-2955. [4] ELREFAEY A, TILLMANN W. Solid state diffusion bonding of titanium to steel using a copper base alloy as interlayer[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009,209(5):2746-2752. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.06.014 [5] WANG T, ZHANG B G, CHEN G Q, et al. High strength electron beam welded titanium-stainless steel joint with V/Cu based composite filler metals[J]. Vacuum, 2013(94):41-47. [6] GAO Q, JIANG X S, SUN H L, et al. Interfacial reaction and microstructure investigation of 4J36/Ni/Cu/V/TC4 diffusion-bonded joints[J]. Materials Letters, 2021 (305): 130809. [7] HE P, ZHANG B G, FENG J C, et al. Diffusion bonding of TiAl to 40Cr steel with interlayers Ti/V/Cu and V/Cu[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology, 2000(4):53-57. (何鹏, 张秉刚, 冯吉才, 等. 以Ti/V/Cu、V/Cu为中间层的TiAl合金与40Cr钢的扩散连接[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2000(4):53-57.HE P, ZHANG B G, FENG J C, et al. Diffusion bonding of TiAl to 40Cr steel with interlayers Ti/V/Cu and V/Cu[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology, 2000(4): 53-57. [8] LIU Y, JIANG X S, SUN H L, et al. Interfacial reaction and microstructure investigation of TC4/V/Cu/Co/316L diffusion-bonded joints[J], Materials Letters, 2020 ( 261): 127140. [9] HE P, ZHANG J H, ZHOU R L, et al. Diffusion bonding technology of a titanium alloy to a stainless steel web with an Ni interlayer[J]. Materials Characterization, 1999, 43(5): 287-292. [10] SONG T F, JIANG X S, SHAO Z Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of vacuum diffusion bonded joints between Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy and AISI316L stainless steel using Cu/Nb multi-interlayer[J]. Vacuum, 2017(145):68-76. [11] CHEN K X, LI Z X, WANG Z D, et al. Morphological evolution of Fe-rich precipitates in a Cu-2.0Fe alloy during isothermal treatment[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2023,59(12):1665-1674. (陈凯旋, 李宗烜, 王自东, 等. Cu-2.0Fe合金等温处理过程中富Fe析出相的形态演变[J]. 金属学报, 2023,59(12):1665-1674.CHEN K X, LI Z X, WANG Z D, et al. Morphological evolution of Fe-rich precipitates in a Cu-2.0Fe alloy during isothermal treatment[J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2023, 59(12): 1665-1674. [12] SUN H, HAN Y, LI Y. Microstructure and strength of diffusion bonding W alloy/304 stainless steel joint using a Cu interlayer[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2023(113):106188. [13] DENG Y Q, SHENG G M, XU C, et al. Evaluation of the microstructure and mechanical properties of diffusion bonded joints of titanium to stainless steel with a pure silver interlayer[J]. Materials & Design, 2013(46):84-87. [14] KUNDU S, MISHRA B, OLSON D L, et al. Interfacial reactions and strength properties of diffusion bonded joints of Ti64 alloy and 17-4PH stainless steel using nickel alloy interlayer[J]. Materials & Design, 2013 (51): 714-722. -





 下载:
下载: