Microstructure and mechanical properties of TA16 bar with different heat treatment temperatures
-
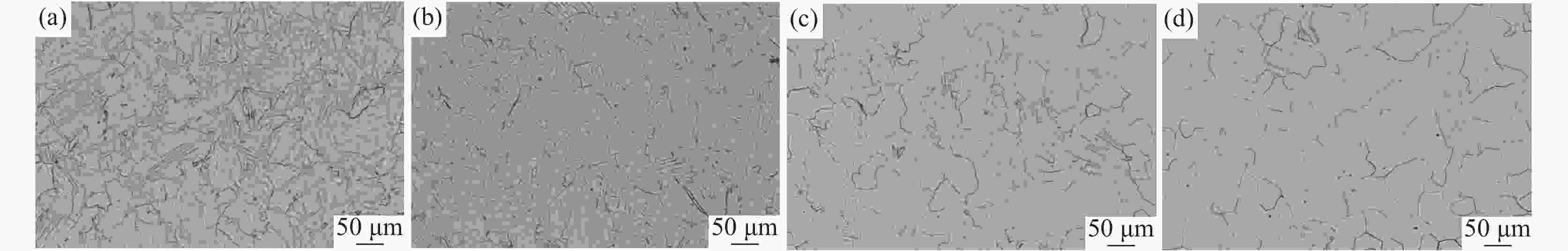
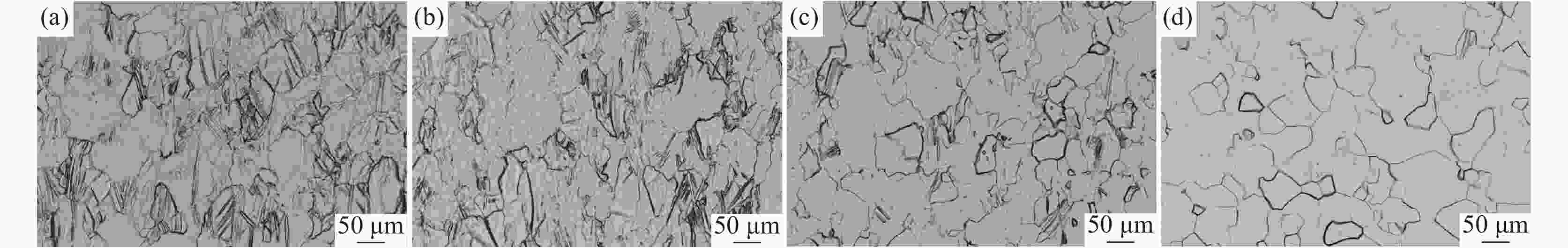
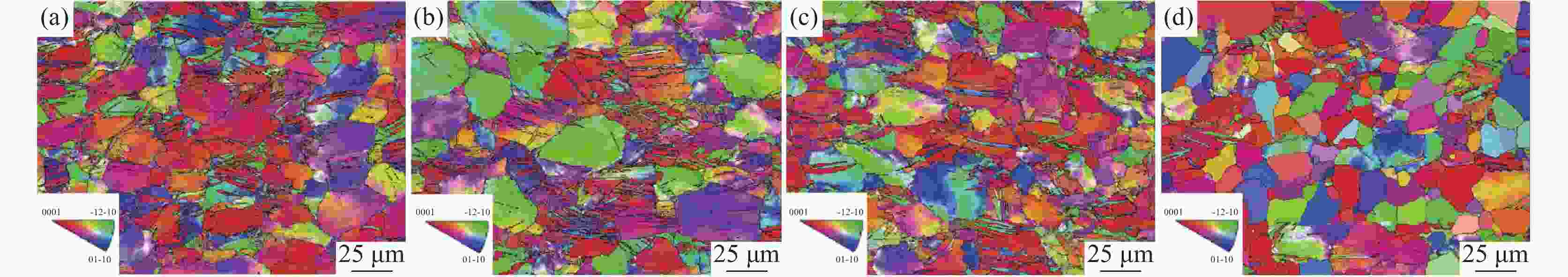
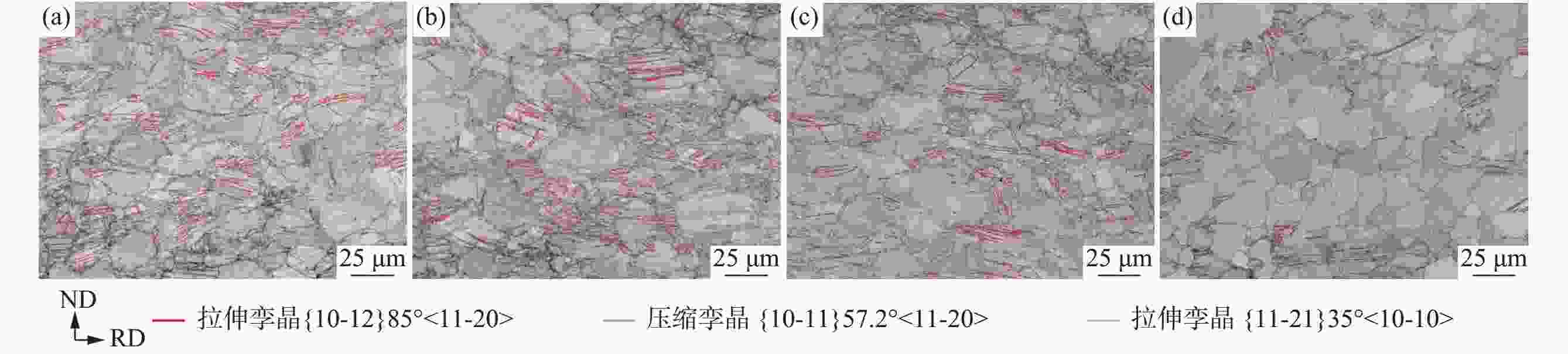
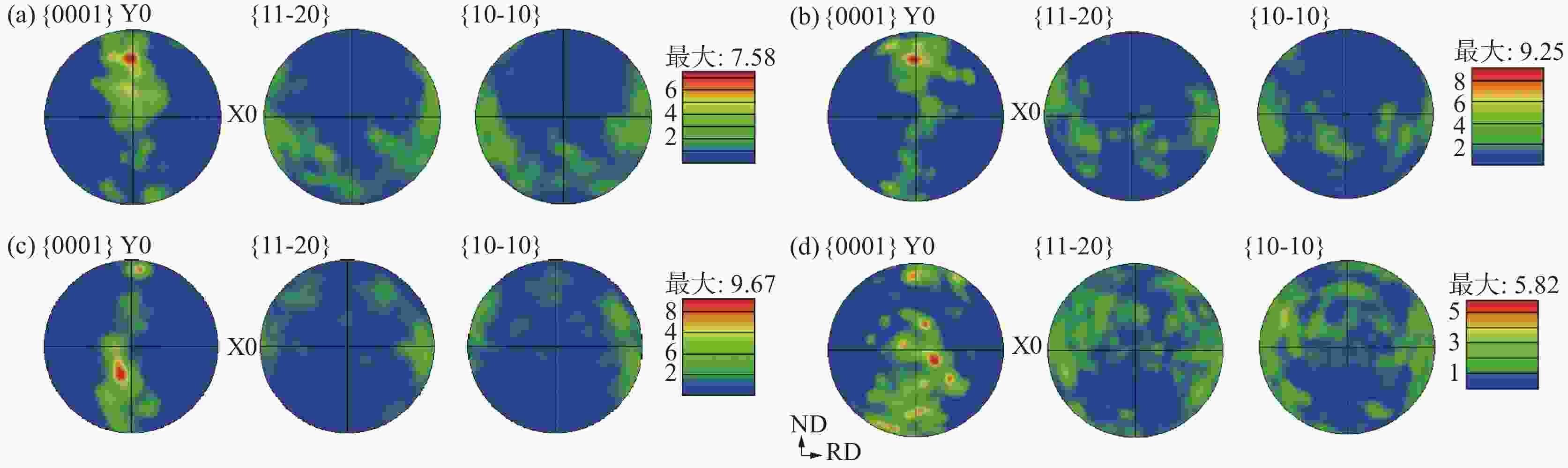
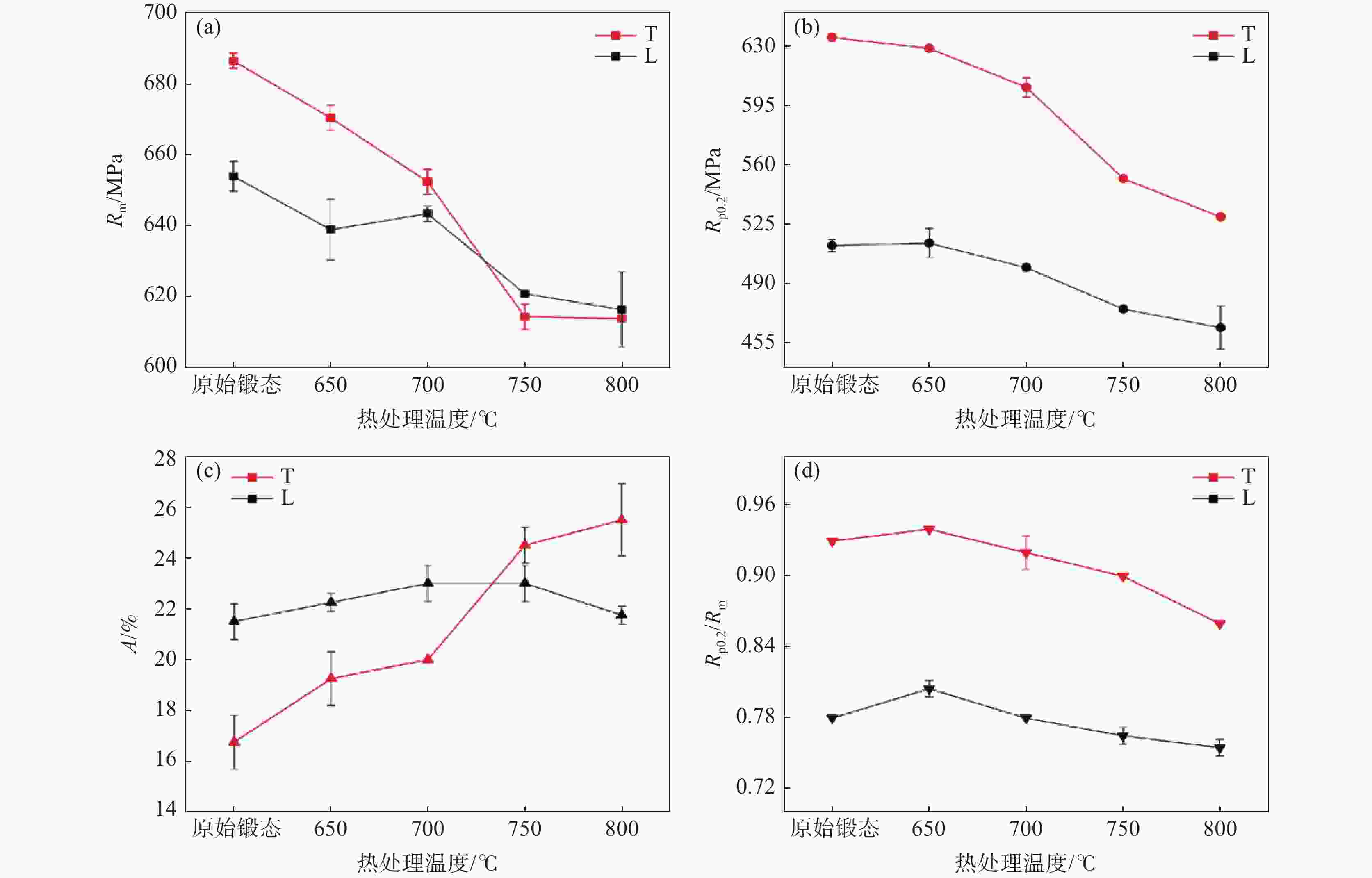
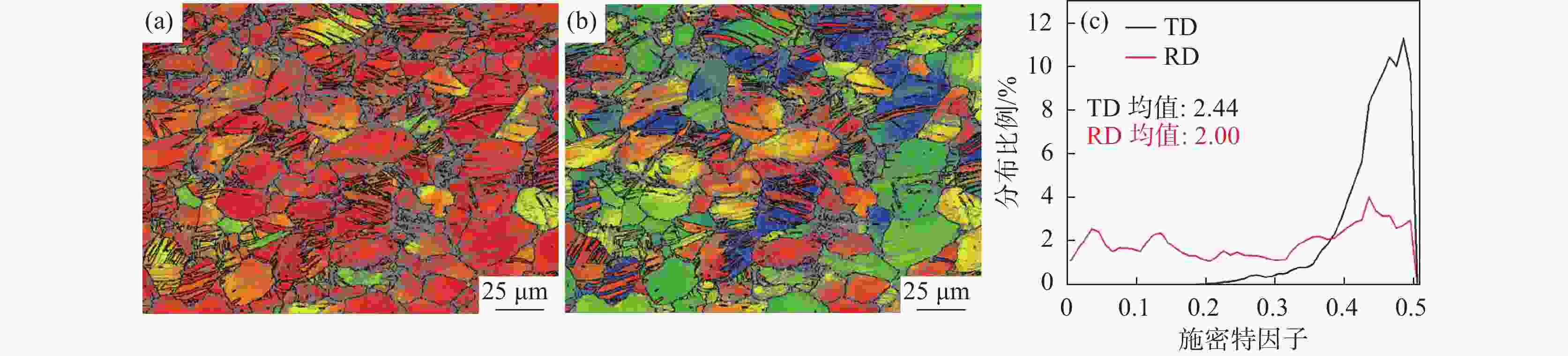
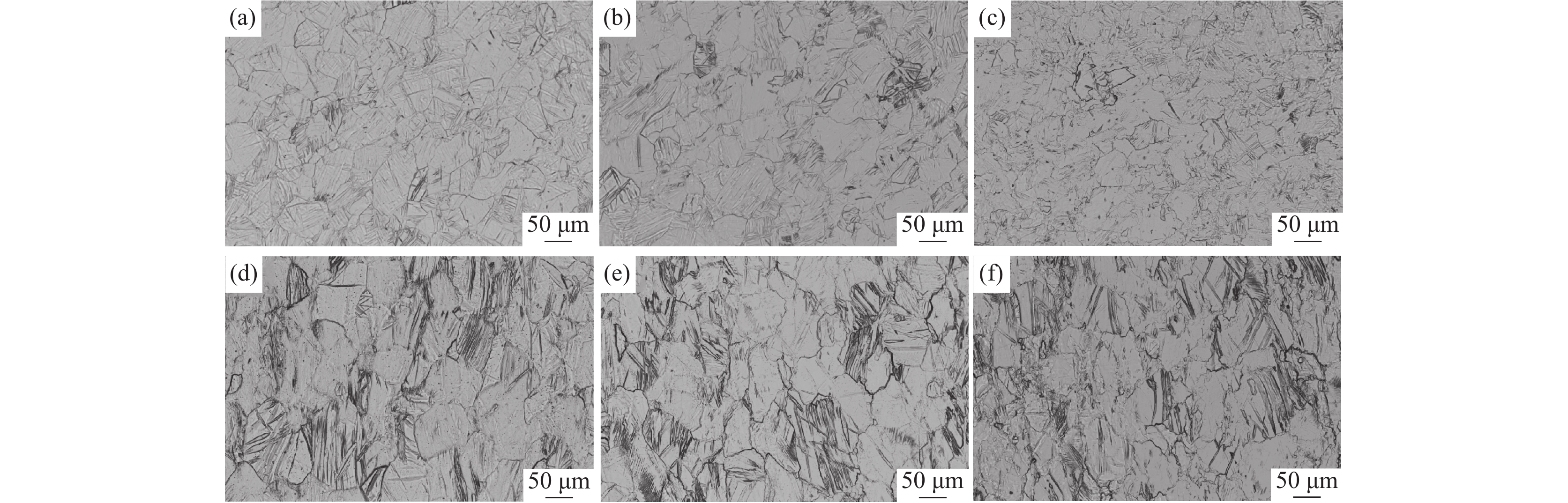
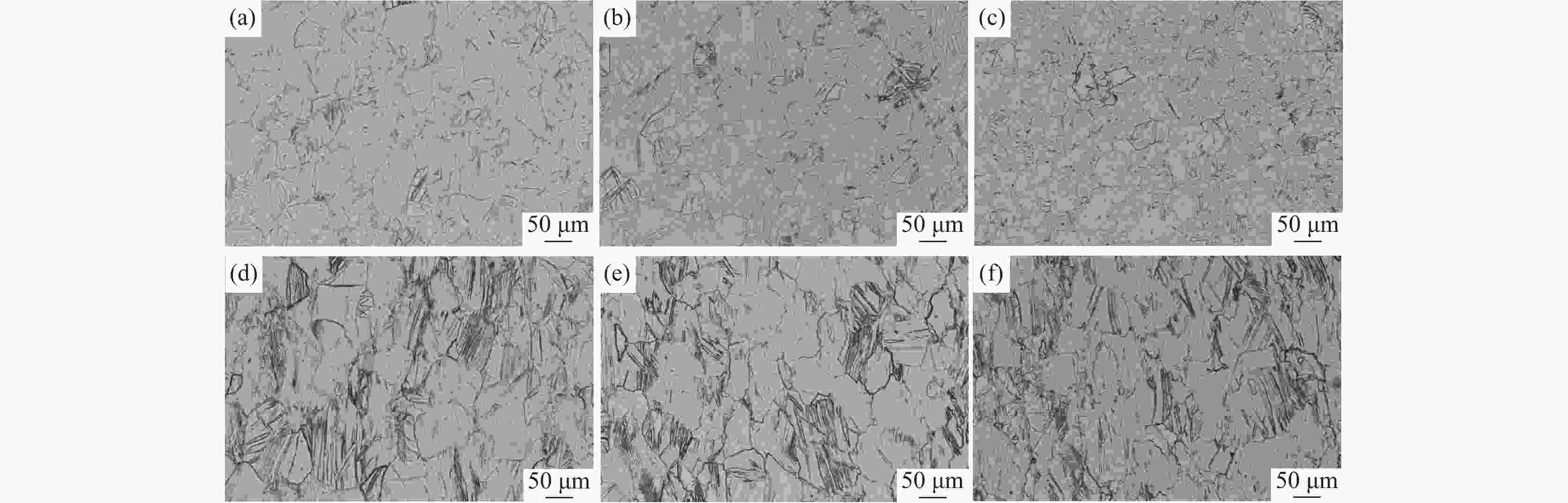
摘要: 研究了热处理温度对Ø230 mm的TA16棒材微观组织、织构和力学性能的影响。结果表明:锻棒横纵向样原始组织为拉长的变形等轴组织,大晶粒内部分布着孪晶,横向样抗拉强度、屈服强度高于纵向样;随着退火温度的升高,横纵向样组织由拉长的变形晶粒逐渐趋于等轴化;原始锻态{10-12}拉伸孪晶含量最多,且随着热处理温度的升高,{10-12}拉伸孪晶在逐渐减少,当热处理温度升高至800 ℃时,孪晶完全消失,再结晶晶粒逐渐长大;原始锻态织构主要集中在{0001}//RD取向,与ND有一定夹角,当热处理温度升高至750 ℃时,织构强度降低,织构类型发生变化,集中在{0001}//ND取向,且与RD有一定夹角;且随着热处理温度的升高,横纵向样的抗拉强度、屈服强度、屈强比整体均呈下降趋势,延伸率逐渐升高。Abstract: The effect of heat treatment temperature on the microstructure, texture, and mechanical properties of Ø230 mm TA16 bar was studied. The results show that the original microstructure of the forged bar is an elongated and deformed equiaxed structure in both horizontal and vertical directions. Twin crystals are distributed inside the large grains. The tensile strength and yield strength of the transverse sample are higher than those of the longitudinal sample. With the heat treatment temperature increases, the transverse and longitudinal microstructures gradually shift from elongated deformed grains to equiaxed grains.The original forged {10-12} has the highest content of tensile twins, and as the heat treatment temperature increases, the {10-12} tensile twins gradually decrease. When the heat treatment temperature rises to 800 ℃, the twins completely disappear, and the recrystallized grains gradually grow. The original forged texture is mainly concentrated in the {0001}//RD orientation, with a certain angle with ND. When the heat treatment temperature rises to 750 ℃, the texture strength decreases and the texture type changes, concentrated in {0001}//ND orientation, with a certain angle with RD. As the heat treatment temperature increases, the overall tensile strength, yield strength, and yield ratio of the transverse and longitudinal samples show a decreasing trend, while the elongation gradually increases.
-
Key words:
- TA16 /
- heat treatment /
- recrystallization /
- twin crystals /
- texture /
- tensile strength
-
表 1 TA16钛合金化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of TA16 alloy
% 部位 Al Zr O N H Fe C 上 2.27 2.26 0.11 0.0058 0.0011 0.079 0.0085 中 2.21 2.34 0.11 0.0030 0.0012 0.089 0.0073 下 2.14 2.22 0.11 0.0034 0.00088 0.085 0.013 表 2 热处理制度
Table 2. Heat treatment processes
工艺编号 热处理制度 温度/℃ 时长/h 方式 1# 650 1 AC 2# 700 1 AC 3# 750 1 AC 4# 800 1 AC -
[1] CHEN W, XIAO L, SUN Q Y, et al. Effect of the initial grain size on grain refinement in Ti-2Al-2.5Zr alloy subjected to multi-impact process[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A-Structural Materials Properties Microstructure and Processing, 2012,554:86-94. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.06.019 [2] CHEN W, XIAO L, SUN Q, et al. Effect of the initial grain size on grain refinement in Ti-2Al-2.5Zr alloy subjected to multi-impact process[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2012, 554: 86-94. [3] TANG Z P, PENG C F, HE X. Effects of hydrogen on fatigue crack propagation rate of Ti-2Al-2.5Zr titanium alloy[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2003,24(6):555-558. [4] XIAO H E, BAO S, JUN Y, et al. Effects of hydrogen on fatigue property for Ti-2Al-2.5Zr titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2002(27). [5] WANG S, LI P, WU Y, et al. Micromechanical behavior of Ti-2Al-2.5Zr alloy under cyclic loading using crystal plasticity modeling[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2022(161): 106890. [6] WANG S, NING Z, LI P, et al. Study on the crack nucleation mechanism of Ti-2Al-2.5 Zr alloy in low cycle fatigue: Quasi in-situ experiments and crystal plasticity simulation[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2023,165:103604. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2023.103604 [7] LI H, YU J, JIA W, et al. Investigation on the plastic anisotropic deformation behavior of Α-phase titanium alloy Ti-2Al-2.5Zr: Mechanism analysis and crystal plasticity modeling[J]. SSRN, 2024. [8] XIE L J, ZHU S P. Effect of extrusion speed on hot extrusion forming of TA16 titanium alloy tube blank[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2021(19):132-133. (谢林均, 朱栓平. 挤压速度对TA16钛合金管坯热挤压成型的影响[J]. 世界有色金属, 2021(19):132-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2021.19.065XIE L J, ZHU S P. Effect of extrusion speed on hot extrusion forming of TA16 titanium alloy tube blank[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2021(19): 132-133. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2021.19.065 [9] ZHANG Y F, YU Z T, YU S, et al. Effects of cold rolling and heat treatment on microstructure and properties of TA16 titanium alloy tubes[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2012,29(3):11-13. (张亚峰, 于振涛, 余森, 等. 冷轧及热处理对TA16钛合金管材组织与性能的影响[J]. 钛工业进展, 2012,29(3):11-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2012.03.003ZHANG Y F, YU Z T, YU S, et al. Effects of cold rolling and heat treatment on microstructure and properties of TA16 titanium alloy tubes[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2012, 29(3): 11-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2012.03.003 [10] WU J, WANG L, LIU X. Evolution of microstructure and microtexture in Ti-2A1-2.5Zr during one pass cold Pilgering[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2022,51(4):1145-1151. (吴军, 王理, 刘肖, 等. Ti-2Al-2.5Zr单道次皮尔格轧制过程中显微组织和织构的演化(英文)[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2022,51(4):1145-1151.WU J, WANG L, LIU X. Evolution of microstructure and microtexture in Ti-2A1-2.5Zr during one pass cold Pilgering[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2022, 51(4): 1145-1151. [11] LUO Q, WANG L, LIU S W. Effects of hydrogen on the performance of the TA16 titanium alloy[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2011,34(2):51-54. (罗强, 王理, 刘思维. 氢对TA16钛合金性能影响研究[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2011,34(2):51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2011.02.015LUO Q, WANG L, LIU S W. Effects of hydrogen on the performance of the TA16 titanium alloy[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2011, 34(2): 51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2011.02.015 [12] HE X, SHEN B L, YUE J, et al. Effects of hydrogen on fatigue property for Ti-2Al-2.5Zr titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2002,027(12):10-13. (何晓, 沈保罗, 岳俊, 等. 氢对Ti-2Al-2.5Zr钛合金疲劳性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2002,027(12):10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6051.2002.12.004HE X, SHEN B L, YUE J, et al. Effects of hydrogen on fatigue property for Ti-2Al-2.5Zr titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2002, 027(12): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6051.2002.12.004 [13] ZHANG C, LI B, WU J, et al. Effect of surface nanocrystallization on thermomechanical fatigue behavior of Ti-2Al-2.5Zr alloy tube[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2024,419:112976. doi: 10.1016/j.nucengdes.2024.112976 [14] CHEN G, CHU T, CUI Y, et al. Effect of surface nanocrystallization on high-cycle fatigue behavior of Ti-2Al-2.5Zr alloy tube[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2022,158:106735. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2022.106735 [15] CHEN S C, WANG L, LI Y L. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of TA16 alloy rods[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2018,43(12):195-199. (陈胜川, 王璐, 李永林, 等. 热处理对TA16合金棒材组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2018,43(12):195-199.CHEN S C, WANG L, LI Y L. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of TA16 alloy rods[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2018, 43(12): 195-199. [16] CHEN H Q, ZHAO X D, CHAI Y S, et al. Recovery and recrystallization during thermo-mechanical processing of Ti-6.5Al-1.5Zr-3.5Mo-0.3Si alloy[C]//Materials Science Forum. Trans Tech Publications Ltd, 2014, 783: 549-555. [17] YANG G, SUN L J, ZHANG L N, et al. Annihilation of deformation twins and formation of annealing twins[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2009,21(2):39-43. (杨钢, 孙利军, 张丽娜, 等. 形变孪晶的消失与退火孪晶的形成机制[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2009,21(2):39-43.YANG G, SUN L J, ZHANG L N, et al. Annihilation of deformation twins and formation of annealing twins[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2009, 21(2): 39-43. [18] CHEN C, HAN D S, SONG Y T, et al. Thermal stability of deformation twins in cryogenic rolled CP-Ti[J]. Materials Characterization, 2023,196:112587. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2022.112587 [19] YAN C K, QU S J, FENG A H, et al. Recent advances of deformation twins in titanium and titanium alloys[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2019,43(5):449-460. (闫辰侃, 曲寿江, 冯艾寒, 等. 钛及钛合金形变孪晶的研究进展[J]. 稀有金属, 2019,43(5):449-460.YAN C K, QU S J, FENG A H, et al. Recent advances of deformation twins in titanium and titanium alloys[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2019, 43(5): 449-460. [20] XU Y L, WU X W, LAI M J, et al. Research progress on titanium alloys deformation textures and their influences[J]. Foundry Technology, 2022,43(12):1021-1031. (许亚利, 吴小文, 赖敏杰, 等. 钛合金变形织构及其影响研究进展[J]. 铸造技术, 2022,43(12):1021-1031.XU Y L, WU X W, LAI M J, et al. Research progress on titanium alloys deformation textures and their influences[J]. Foundry Technology, 2022, 43(12): 1021-1031. [21] BIELER T R, SEMIATIN S L. The origins of heterogeneous deformation during primary hot working of Ti-6Al-4V[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2002,18(9):1165-1189. doi: 10.1016/S0749-6419(01)00057-2 [22] UTA E, GEY N, BOCHER P, et al. Texture heterogeneities in αp/αs titanium forging analysed by EBSD-relation to fatigue crack propagation[J]. Journal of microscopy, 2009,233(3):451-459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.2009.03141.x [23] LÜTJERING G, WILLIAMS J C. Titanium[M]. 2nd edition. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2007. [24] ROY S, SUWAS S. Unique texture transition during sub β-transus annealing of warm-rolled Ti-6Al-4V alloy: Role of orientation dependent spheroidization[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 154:1-7. -




 下载:
下载: