Enrichment and recovery of zinc from a high zinc blast furnace ash by hydrocyclone method
-
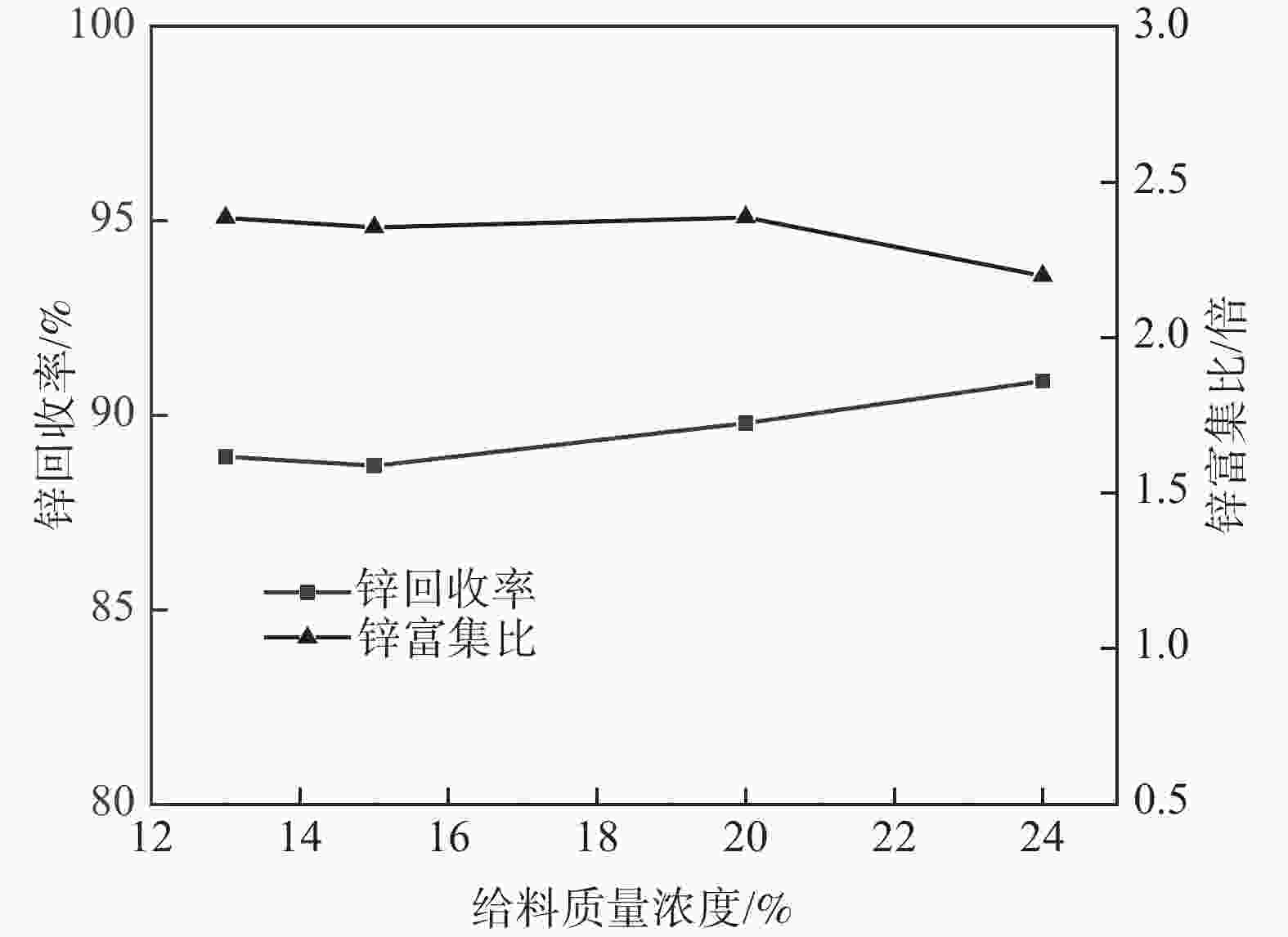
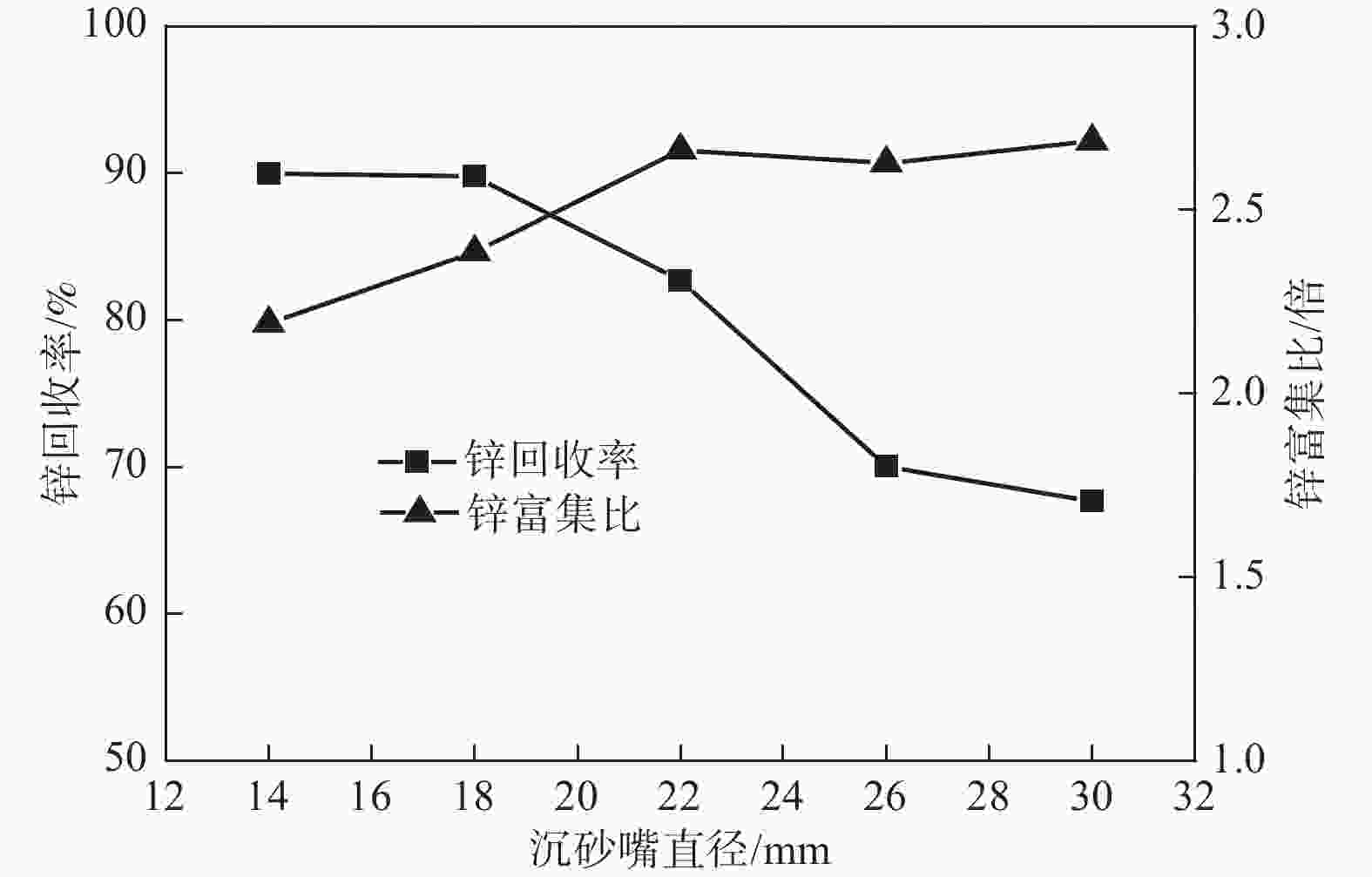
摘要: 为了充分回收利用高炉灰中的有价元素,通过对四川某钢铁企业钒钛磁铁矿炼铁所产高锌高炉灰的理化性质进行分析,提出采用水力旋流法对该高炉灰中的锌进行富集/回收,重点考察了给料质量浓度、沉砂嘴直径等关键参数对锌富集/回收效果的影响,并进一步开展了200 kg级规模的高炉灰扩大试验进行验证。结果显示:锌回收率随给料质量浓度的增大而略有增大,随沉砂嘴直径的减小而显著增大,锌品位的富集比变化趋势则与锌回收率相反。在给料质量浓度15%~20%、沉砂嘴直径为14~18 mm、深度回收锌级数3的条件下,总锌回收率可达97%左右,第一级的锌富集比可达2.4倍左右,第三级贫锌高炉灰锌品位可降低至0.8%左右。扩大试验结果表明,高炉灰总锌回收率为96%,第一级水力旋流富锌高炉灰锌品位可达26%,第三级贫锌高炉灰锌含量可降至1%以下,满足作为炼铁原料回用的需求。此项研究有望为高锌高炉灰的资源化高效利用提供数据支撑。Abstract: In order to fully recover and utilize the valuable elements in the blast-furnace ash, the physical and chemical properties of the high-zinc blast-furnace ash produced by the ferro-smelting of vanadium titanium magnetite in a Sichuan iron and steel enterprise were analyzed. The hydrocyclone method was proposed to enrich/recover zinc in the blast-furnace ash. The influences of key parameters such as the feed mass concentration and the diameter of the settling nozzle on the zinc enrichment/recovery effect were investigated. And further, a 200 kg blast furnace ash scale expansion experiment was carried out to verify. The results show that the zinc recovery rate slightly increases with the increase of the feed mass concentration and significantly increases with the decreases of the diameter of the underflow nozzle. The enrichment multiple change trend of zinc grade is opposite to that of the zinc recovery rate. Under the conditions of feeding mass concentration of 15~20 %, diameter of settling nozzle of 14~18 mm and depth recovery of zinc grade 3, the total zinc recovery rate can reach about 97%, the enrichment ratio of zinc in the first stage can reach about 2.4 times, and the grade of zinc in the third stage zinc-poor blast ash can be reduced to about 0.8 %. The expanded test results indicate that the recovery rate of total zinc in blast-furnace ash is 96%, the grade of zinc in the first stage zinc-rich blast-furnace ash can reach 26 %, and the content of zinc in the third stage zinc-poor blast-furnace ash can be reduced to less than 1.0 %, which meets the demand for recycling as iron making raw material. The results of this study are expected to provide data support for the resource utilization of high zinc blast furnace ash.
-
表 1 高炉灰主要元素组成
Table 1. Main elemental composition of blast furnace dust
% Al C Fe Zn K Na Ti Ca Mg Mn Cl P Pb S Si V 1.39 16.30 29.20 13.85 0.45 0.15 2.23 2.72 4.71 0.14 2.55 0.03 1.40 0.54 2.89 0.10 表 2 高炉灰的矿物组成
Table 2. Mineral composition of blast furnace ash
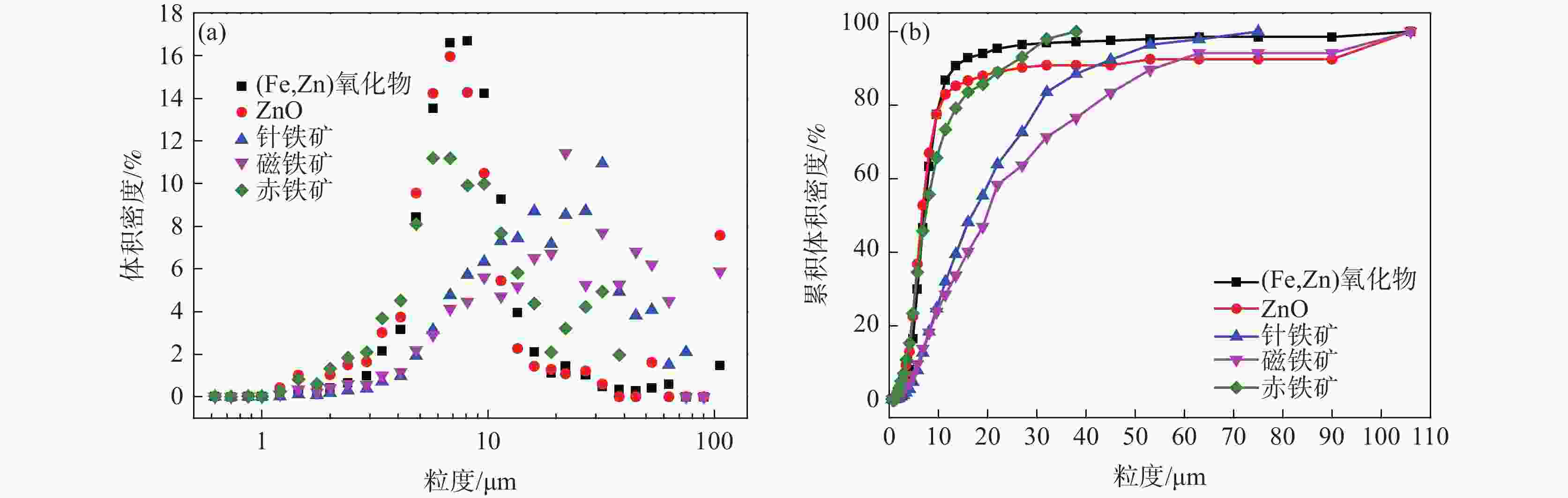
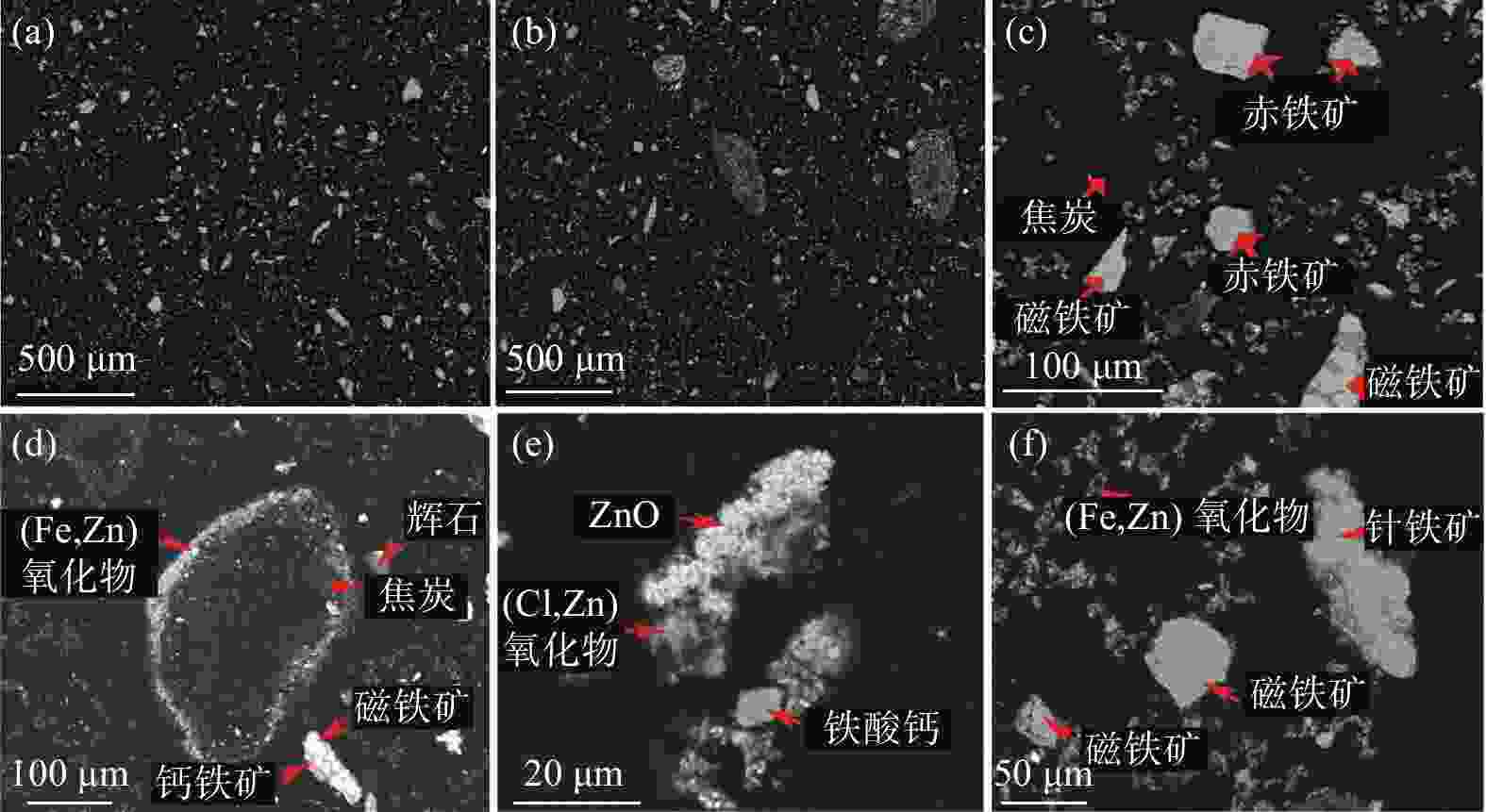
% (Fe,Zn)氧化物 焦炭 ZnO 针铁矿 磁铁矿 赤铁矿 白云母 石英 辉石 铁橄榄石 玻璃相 钛闪石 31.50 16.30 13.38 11.07 7.47 3.58 2.13 1.60 1.15 1.07 0.91 0.92 表 3 高炉灰中Zn、Fe、C元素的赋存状态
Table 3. Occurrence states of Zn, Fe and C elements in blast furnace ash
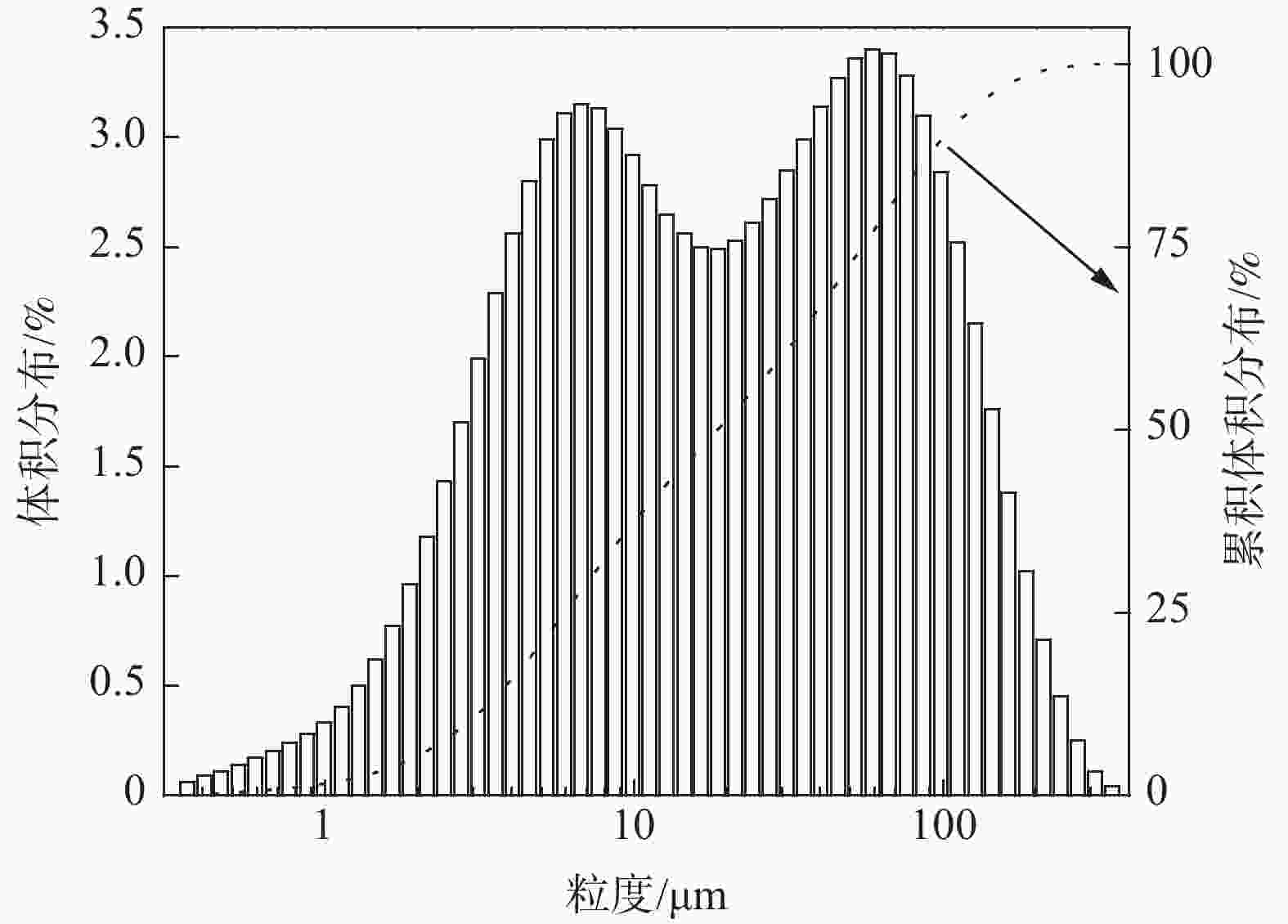
% (Fe,Zn)氧化物 焦炭 ZnO 针铁矿 磁铁矿 赤铁矿 白云母 石英 辉石 铁橄榄石 玻璃相 钛闪石 C 95.00 Fe 30.31 0.10 3.40 32.49 15.24 7.72 0.69 0.09 0.82 1.90 0.43 0.47 Zn 52.94 0.10 39.08 0.80 0.41 0.81 0.27 0.09 0.66 0.20 0.08 表 4 Zn、Fe、C元素的粒度分布情况
Table 4. Particle size distribution of Zn, Fe, and C elements
粒级/μm 产率/% 元素含量/% 元素分布率/% C Fe Zn C Fe Zn +200 1.34 62.0 8.62 7.64 5.33 0.39 0.72 125~200 3.26 66.3 9.75 4.33 13.90 1.07 1.00 106~125 7.24 46.9 22.38 2.76 21.81 5.46 1.41 74~106 2.27 34.8 28.00 2.30 5.08 2.14 0.37 50~74 7.99 26.5 33.62 2.30 13.60 9.05 1.29 30~50 27.11 13.5 40.75 3.15 23.51 37.21 6.02 −30 50.78 5.14 26.12 24.94 16.76 44.67 89.20 表 5 高炉灰中锌的回收扩大试验条件和结果
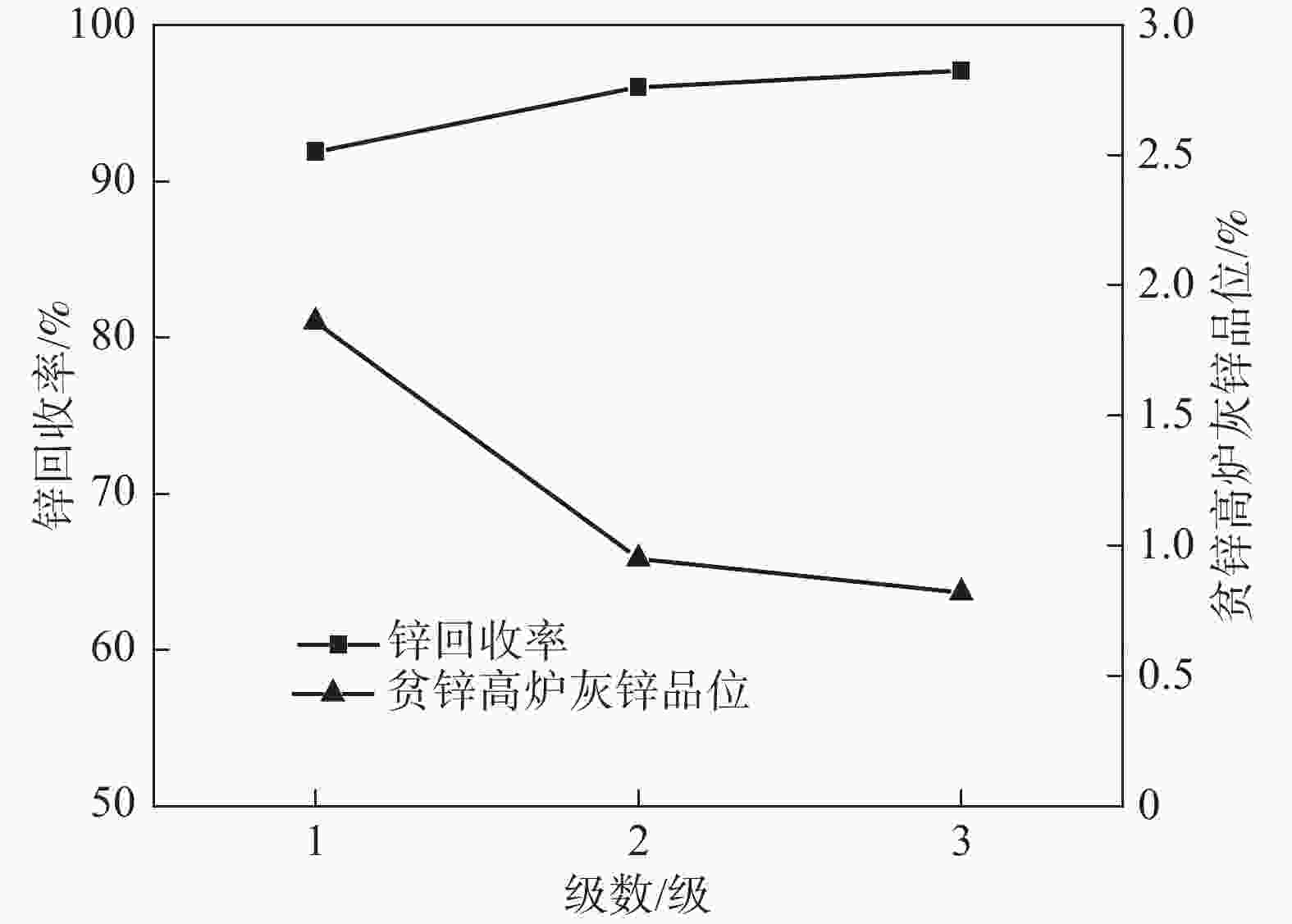
Table 5. Experimental conditions and results of the expansion test for zinc recovery from blast furnace slag
原料锌
品位/%级数 给料质量
浓度/%沉砂嘴
直径/mm贫锌高炉
灰锌品位/%富锌高炉
灰锌品位/%富锌高炉
灰锌回收率/%富锌高炉
灰锌总回收率/%12.47 1 18 18 2.09 26.95 90.24 96.38 2 17 16 0.95 14.72 4.99 3 17 14 0.79 1.67 1.15 -
[1] ZENG G W. Review on utilization technologies of blast-furnace gas sludge[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2015,35(3):279-283. (曾冠武. 高炉瓦斯泥综合利用技术述评[J]. 化工环保, 2015,35(3):279-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2015.03.011ZENG G W. Review on utilization technologies of blast-furnace gas sludge[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2015, 35(3): 279-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2015.03.011 [2] WANG Z J, LI Y, TANG J Y, et al. Status and progress of resource recovery and utilization of dust and sludge in the steel industry[J]. Jiangxi Metallurgy, 2023,43(2):87-94. (王钟建, 李岩, 唐境言, 等. 钢铁产业尘泥资源化回收利用现状与进展[J]. 江西冶金, 2023,43(2):87-94.WANG Z J, LI Y, TANG J Y, et al. Status and progress of resource recovery and utilization of dust and sludge in the steel industry[J]. Jiangxi Metallurgy, 2023, 43(2): 87-94. [3] TIAN S L, ZHANG H, CAO Y D, et al. Technology status on treatment and recovery of steel sludge[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2023,52(2):70-75. (田释龙, 张辉, 曹远栋, 等. 钢铁尘泥的处理回收技术现状[J]. 云南冶金, 2023,52(2):70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0308.2023.02.012TIAN S L, ZHANG H, CAO Y D, et al. Technology status on treatment and recovery of steel sludge[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2023, 52(2): 70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0308.2023.02.012 [4] FENG S, CHEN K. Theoretical research and practice on zinc loading of Hansteel 3200 m3 BF[J]. 2023, 31(3): 5-7, 32. (冯帅, 陈奎. 邯钢3200 m3高炉锌负荷的理论研究与实践[J]. 河南冶金, 2023, 31(3): 5-7, 32.FENG S, CHEN K. Theoretical research and practice on zinc loading of Hansteel 3200 m3 BF[J]. 2023, 31(3): 5-7, 32. [5] SHANG H X, LI H M, WEI R F, et al. Present situation and prospect of iron and steel dust and sludge utilization technology[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019,54(3):9-17. (尚海霞, 李海铭, 魏汝飞, 等. 钢铁尘泥的利用技术现状及展望[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(3):9-17.SHANG H X, LI H M, WEI R F, et al. Present situation and prospect of iron and steel dust and sludge utilization technology[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019, 54(3): 9-17. [6] WANG Z J, SOHN I. A review on reclamation and reutilization of ironmaking and steelmaking slags[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2019,5(1):127-140. doi: 10.1007/s40831-018-0201-5 [7] ZHENG H Y, SUN Y, ZHANG S L, et al. Comprehensive utilization of blast furnace gas sludge[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2019,37(7):79-82. (郑虹雨, 孙艳, 张树立, 等. 高炉瓦斯泥的综合利用[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2019,37(7):79-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2019.07.025ZHENG H Y, SUN Y, ZHANG S L, et al. Comprehensive utilization of blast furnace gas sludge[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2019, 37(7): 79-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2019.07.025 [8] FISHER L V, BARRON A. The recycling and reuse of steelmaking slags-a review[J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 2019,146:244-255. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.010 [9] XIAO X, ZHANG S F, SHER F et al. A review on recycling and reutilization of blast furnace dust as a secondary resource[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2021,7:340-357. doi: 10.1007/s40831-021-00377-9 [10] WANG Z H, GUO J, GUO, H J, et al. Thermodynamic and experimental study of high-temperature roasting of blast furnace gas ash for recovery of metallic zinc and iron[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2024,31:108-120. doi: 10.1007/s42243-023-01021-4 [11] JIN Y L, YAN X M, SUN Y J, et al. Analysis and development of comprehensive utilization of ferrous solid waste combined with Zn in iron and steel enterprises[J]. Shandong Metallurgy, 2022,44(1):5-8,14. (金永龙, 闫献民, 孙宇佳, 等. 钢铁企业含锌固废综合利用技术分析和发展[J]. 山东冶金, 2022,44(1):5-8,14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4620.2022.1.sdyj202201002JIN Y L, YAN X M, SUN Y J, et al. Analysis and development of comprehensive utilization of ferrous solid waste combined with Zn in iron and steel enterprises[J]. Shandong Metallurgy, 2022, 44(1): 5-8,14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4620.2022.1.sdyj202201002 [12] YAN J L, YANG Y H, ZHANG J H. Preconcentration test of zinc-containing substance in ultra-fine blast furnace ash by hydrocyclone[J]. Modern Mining, 2023,39(4):107-109. (闫金磊, 杨义红, 张建辉. 超细粒高炉灰中含锌物的水力旋流器预富集试验[J]. 现代矿业, 2023,39(4):107-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2023.04.028YAN J L, YANG Y H, ZHANG J H. Preconcentration test of zinc-containing substance in ultra-fine blast furnace ash by hydrocyclone[J]. Modern Mining, 2023, 39(4): 107-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2023.04.028 [13] SHI S Y, MA A Y, LI G J, et al. Research on comprehensive utilization status of zinc metallurgical solid waste slag[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2019,34(13):7-8. (石升友, 马爱元, 李国江, 等. 锌冶金固废渣综合利用现状研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2019,34(13):7-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.13.003SHI S Y, MA A Y, LI G J, et al. Research on comprehensive utilization status of zinc metallurgical solid waste slag[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 34(13): 7-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2019.13.003 [14] JIN Y L, LIU S Y, QIN G Q, et al. Energy efficiency analysis of typical technologies for disposal ferrous solid waste combined with Zn in steel plants[J]. Energy for Metallurgical Industry, 2022,41(3):18-22. (金永龙, 刘思远, 秦国旗, 等. 典型的处置钢铁企业含锌固废工艺的能效分析[J]. 冶金能源, 2022,41(3):18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1617.2022.03.004JIN Y L, LIU S Y, QIN G Q, et al. Energy efficiency analysis of typical technologies for disposal ferrous solid waste combined with Zn in steel plants[J]. Energy for Metallurgical Industry, 2022, 41(3): 18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1617.2022.03.004 [15] PENG G J, ZHAO Z H, YAN C M, et al. Optimization study of flotation process for one high silicon low-grade lead-zinc ore in Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2024,53(6):44-50. (彭光继, 赵泽辉, 严川明, 等. 云南某高硅低品位铅锌矿浮选工艺优化研究[J]. 云南冶金, 2024,53(6):44-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0308.2024.06.008PENG G J, ZHAO Z H, YAN C M, et al. Optimization study of flotation process for one high silicon low-grade lead-zinc ore in Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Metallurgy, 2024, 53(6): 44-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0308.2024.06.008 [16] GAO X R, DUAN X X, ZHENG Y M, et al. Summary of research progress on comprehensive utilization of blast furnace gas ash[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2023,41(S2):609-611, 617. (高熙然, 段学新, 郑艳梅, 等. 高炉瓦斯灰综合利用研究进展综述[J]. 环境工程, 2023,41(S2):609-611, 617.GAO X R, DUAN X X, ZHENG Y M, et al. Summary of research progress on comprehensive utilization of blast furnace gas ash[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2023, 41(S2): 609-611, 617. [17] CHEN W Y, YANG T Q, LI Q Y et al. Characteristic analysis and separation of zinc and iron from zinc containing metallurgical dust[J]. Nonferrous Metals(Extractive Metallurgy), 2023(9):126-136. (陈王媛, 杨通清, 李奇勇, 等. 含锌冶金尘泥特性分析及锌铁分离[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2023(9):126-136.CHEN W Y, YANG T Q, LI Q Y et al. Characteristic analysis and separation of zinc and iron from zinc containing metallurgical dust[J]. Nonferrous Metals(Extractive Metallurgy), 2023(9): 126-136. [18] CAO K, HU L G, JIA Y M. Application of hydrocyclone separation technology in dezincification engineering of gas scrubbing slime[J]. Metallurgical Power, 2006(5):52-55, 58. (曹克, 胡利光, 贾永铭. 水力旋流分离技术在瓦斯泥脱锌工程中的研究[J]. 冶金动力, 2006(5):52-55, 58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6764.2006.05.019CAO K, HU L G, JIA Y M. Application of hydrocyclone separation technology in dezincification engineering of gas scrubbing slime[J]. Metallurgical Power, 2006(5): 52-55, 58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6764.2006.05.019 [19] WANG W, FU G T, LIU J M, et al. Feasibility study on iron-carbon separation and zinc selection from low zinc blast furnace ash[J]. Modern Mining, 2024,40(2):173-175. (王伟, 付贵泰, 刘金明, 等. 低锌高炉灰选锌与铁炭分离可行性研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2024,40(2):173-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2024.02.043WANG W, FU G T, LIU J M, et al. Feasibility study on iron-carbon separation and zinc selection from low zinc blast furnace ash[J]. Modern Mining, 2024, 40(2): 173-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2024.02.043 [20] WANG W, SUN W, WANG J, et al. Research and application of enrichment of fine zinc minerals in ash from blast furnace by hydrocyclone[J]. Modern Mining, 2019,35(4):233-234. (王伟, 孙伟, 王建, 等. 水力旋流器富集高炉灰中的微细粒锌矿物的研究与实践[J]. 现代矿业, 2019,35(4):233-234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2019.04.073WANG W, SUN W, WANG J, et al. Research and application of enrichment of fine zinc minerals in ash from blast furnace by hydrocyclone[J]. Modern Mining, 2019, 35(4): 233-234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2019.04.073 [21] YANG G H, YANG X H, LIU P K, et al. Experimental study on iron collection and zinc decrease from blast furnace sludge with three-product hydrocyclones[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2021,49(10):15-20. (杨光辉, 杨兴华, 刘培坤, 等. 三产品旋流器瓦斯泥集铁降锌试验研究[J]. 流体机械, 2021,49(10):15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0329.2021.10.003YANG G H, YANG X H, LIU P K, et al. Experimental study on iron collection and zinc decrease from blast furnace sludge with three-product hydrocyclones[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2021, 49(10): 15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0329.2021.10.003 [22] ZHANG Z C, ZHANG Y K, LIU P K, et al. The influence of straight pipe length of the bottom outlet on the separation performance of the hydrocyclone[J]. Metal Mine, 2021(11):158-164. (张智宸, 张悦刊, 刘培坤, 等. 旋流器底流口直管段长度对分离性能的影响研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2021(11):158-164.ZHANG Z C, ZHANG Y K, LIU P K, et al. The influence of straight pipe length of the bottom outlet on the separation performance of the hydrocyclone[J]. Metal Mine, 2021(11): 158-164. [23] PAN M, WU H, WNAG Q, et al. Application research on improving classification efficiency of hydrocyclone in Zhangzhuang mine[J]. Modern Mining, 2021,37(7):160-161, 164. (潘猛, 吴红, 王琦, 等. 张庄矿提高水力旋流器分级效率应用研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2021,37(7):160-161, 164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2021.07.042PAN M, WU H, WNAG Q, et al. Application research on improving classification efficiency of hydrocyclone in Zhangzhuang mine[J]. Modern Mining, 2021, 37(7): 160-161, 164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2021.07.042 [24] LUO Y L. Experimental study on grading filtration of fine-grained mineral slurry in a concentrator[J]. Modern Mining, 2024,40(11):150-152, 156. (罗渊林. 某选矿厂细粒级矿泥分级过滤试验研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2024,40(11):150-152, 156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2024.11.033LUO Y L. Experimental study on grading filtration of fine-grained mineral slurry in a concentrator[J]. Modern Mining, 2024, 40(11): 150-152, 156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2024.11.033 -




 下载:
下载: