Development of hot metal pre-dephosphorization agent based on the resource utilization of sludge in continuous casting swirl wells
-
摘要: 为了利用连铸旋流井沉泥开发铁水预脱磷剂以期实现沉泥的资源化,基于连铸旋流井沉泥的成分分析及脱磷热力学计算,配制了w(CaO):w(沉泥)=0、7%、14%、20%、25%、30%的预脱磷剂,进行了熔化性能测定及脱磷效果评价试验。结果表明,连铸旋流井沉泥中(Fe2O3+FeO)含量较高、碱度为0.86,其作为配制脱磷剂的基料在热力学上可行。随着CaO配加比例由0增加至30%,脱磷剂的熔点先降低后升高,熔速先增大后减小,当w(CaO):w(沉泥)=20%时,脱磷剂熔点最低,熔速最快。随着CaO配加比例由14%增加至25%,渣剂的脱磷率先上升后下降,金属Fe回收率逐渐增加,当w(CaO):w(沉泥)=20%时,脱磷率和Fe回收率分别为73.6%和86.76%,可同时实现深度脱磷和铁元素高效回收。Abstract: In order to develop a P-removal agent for molten iron by using the sludge from the continuous casting swirl well to realize the resource utilization, the pre-dephosphorization agent with w(CaO): w(sludge) =0, 7%, 14%, 20%, 25% and 30% was prepared, and the melting performance measurement and P removal evaluation experiment were carried out based on the composition analysis and thermodynamic calculation. The results show that the sludge contains high quantity of (Fe2O3+FeO) and has an alkalinity of 0.86, and it is thermodynamically feasible as the base material for the preparation of pre-dephosphorization agent. With the increase of CaO from 0 to 30%, the melting point of the P-removal agent decreases first and then increases, and the melting rate rises first and then declines. When w(CaO): w(sludge) = 20%, the melting point of the P-removal agent is the lowest and the melting rate is the fastest. With the increase of CaO from 14% to 25%, the P removal rate first increases and then decreases, and the recovery rate of Fe gradually rises. Overall, when w(CaO): w(sludge)=20%, the removal rate of P and recovery rate of Fe are 73.6% and 86.76%, respectively, both deep removal of P and efficient ferrite recovery can be achieved at the same time.
-
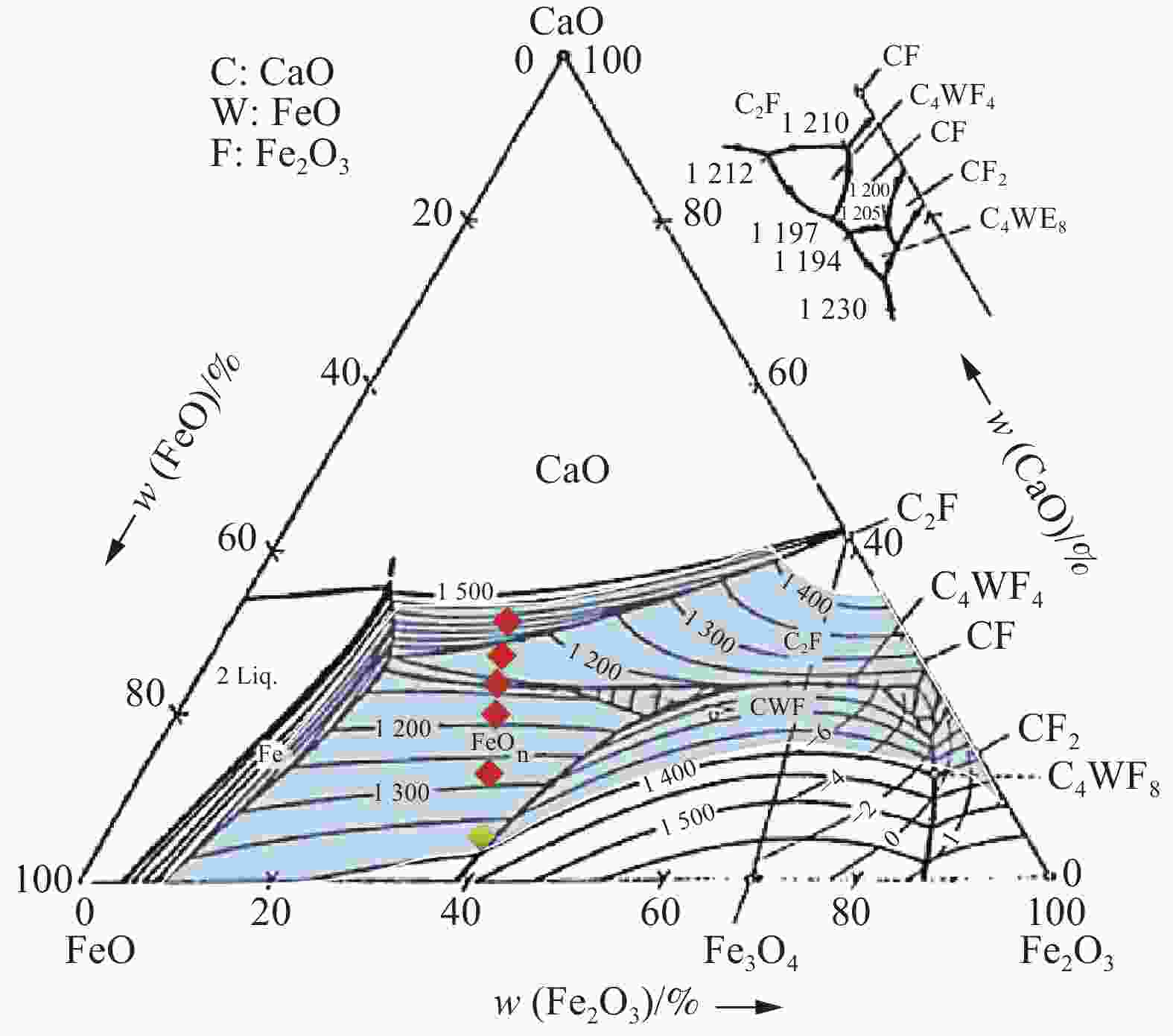
图 2 Fe2O3-FeO-CaO三元相图[12]
Figure 2. Fe2O3-FeO-CaO ternary phase diagram
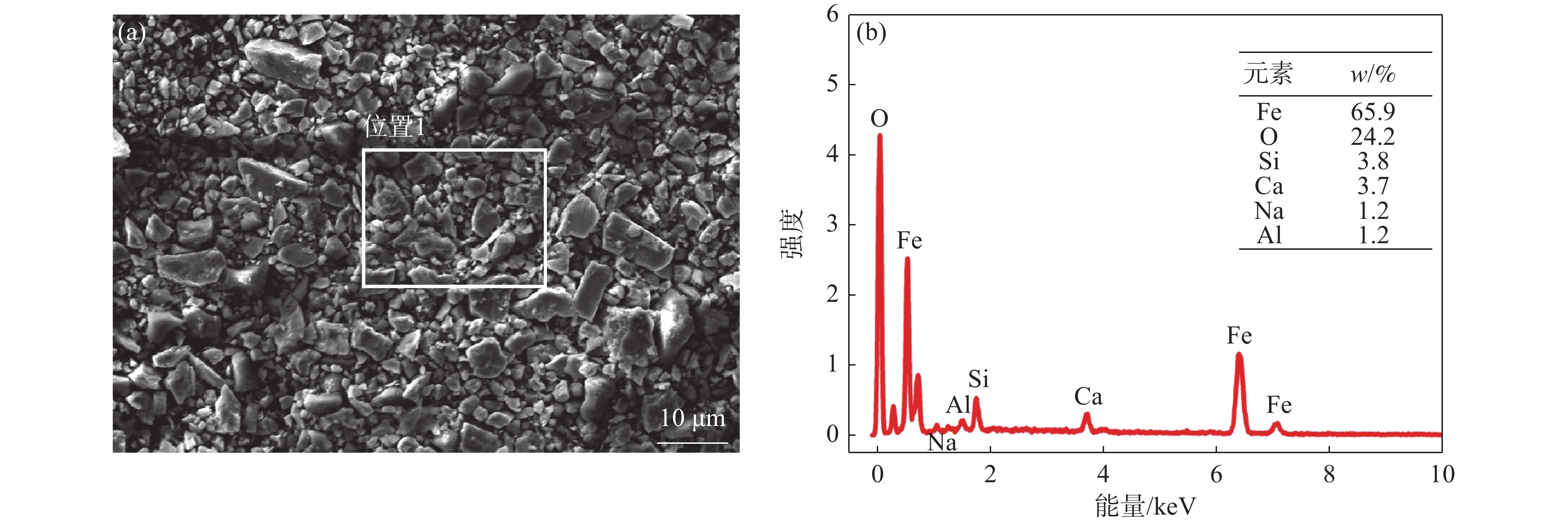
表 1 旋流井沉泥化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of sludge in continuous
% TFe MFe Fe2O3 FeO CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MnO Na2O K2O P2O5 C 62.20 0.61 36.38 46.49 4.69 5.46 1.29 0.94 0.82 0.19 0.045 0.63 表 2 部分氧化物的光学碱度[10]
Table 2. Optical alkalinity of some oxides
CaO Fe2O3 FeO SiO2 Al2O3 MnO Na2O K2O $ \mathit{\Lambda}_{\mathrm{B}} $ 1.00 0.48 0.51 0.48 0.60 0.59 1.15 1.40 表 3 各组分摩尔分数
Table 3. Molar fraction of each component
CaO Fe2O3 FeO SiO2 Al2O3 MnO Na2O K2O $ x'_{\mathrm{B}} $ 0.077 0.208 0.593 0.084 0.012 0.012 0.012 0.002 表 4 脱磷渣剂化学成分
Table 4. Chemical compositions of the pre-dephosphoriza
% 编号 w(CaO):
w(沉泥)Fe2O3 FeO CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MnO Na2O K2O 1 0 37.79 48.3 4.87 5.67 1.34 0.98 0.85 0.2 2 7 35.23 45.02 11.32 5.28 1.25 0.91 0.79 0.18 3 14 33.00 42.16 16.96 4.95 1.17 0.85 0.74 0.17 4 20 31.29 39.99 21.24 4.70 1.11 0.81 0.70 0.16 5 25 30.01 38.34 24.48 4.51 1.06 0.77 0.68 0.15 6 30 28.81 36.84 27.47 4.32 1.02 0.74 0.65 0.15 表 5 熔点和熔速测定试验结果
Table 5. Results of the melting point and melting velocity
编号 w(CaO):
w(沉泥)/%软化温度
平均值/ ℃熔化温度
平均值/ ℃流动温度
平均值/ ℃熔化
速度/s1 0 1323.3 1352.3 1382.4 152.6 2 7 1223.0 1303.4 1321.0 117.6 3 14 1135.7 1195.1 1253.3 65.4 4 20 1128.2 1155.0 1216.4 30.6 5 25 1179.7 1222.2 1246.6 52.3 6 30 1231.3 1261.0 1302.6 95.3 表 6 不同取样时间测得铁水中的P含量
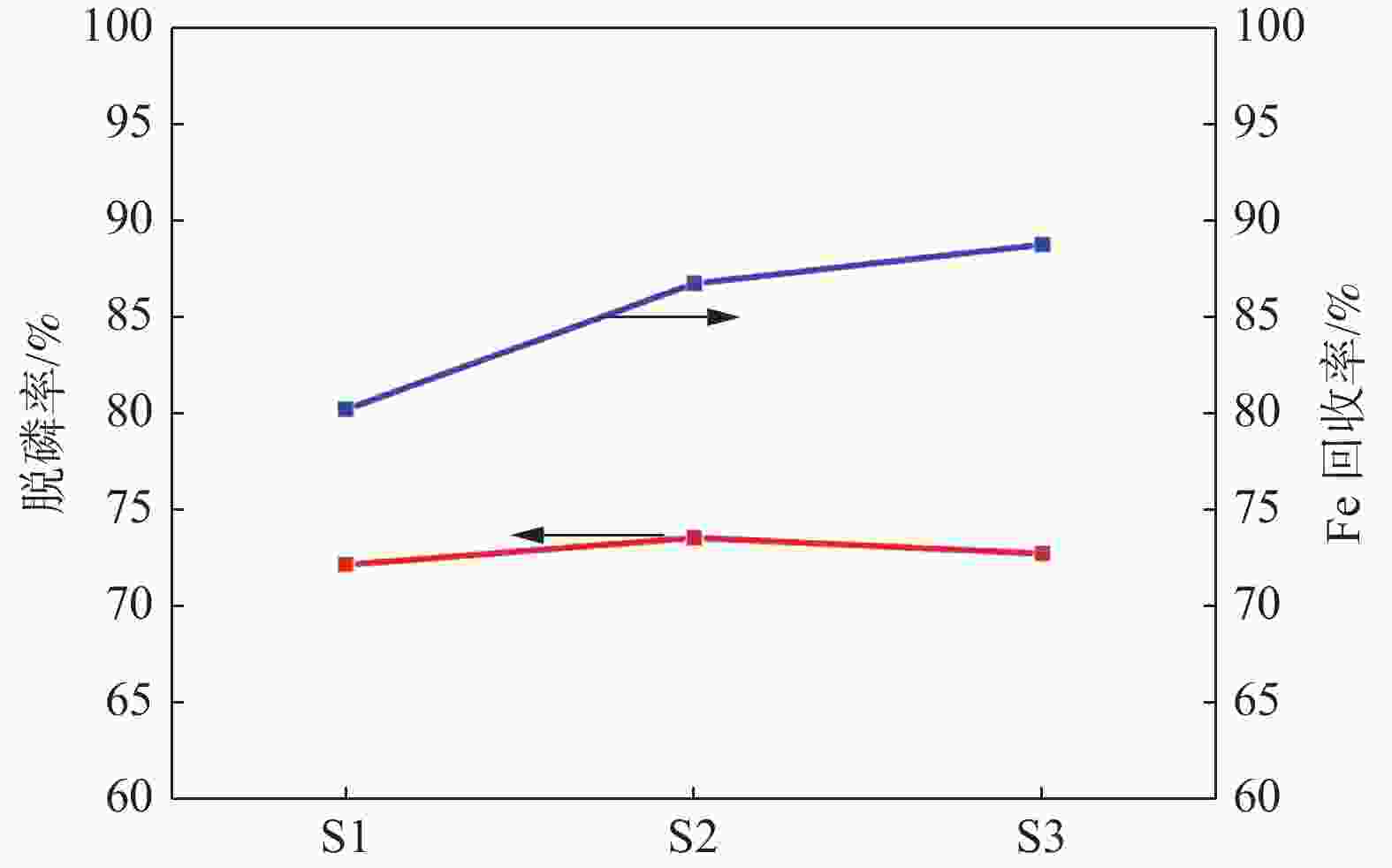
Table 6. The P content in molten iron measured at different sampling time
编号 w[P]/% 脱磷率/% 0 min 3 min 5 min 10 min 15 min 20 min S1 0.413 0.165 0.123 0.118 0.109 0.115 72.2 S2 0.414 0.150 0.132 0.112 0.107 0.109 73.6 S3 0.412 0.153 0.115 0.104 0.105 0.112 72.8 -
[1] PAN F F. Study on the reaction behavior between CaO-Fe2O3 based slag and the hot metal[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2020. (潘飞飞. CaO-Fe2O3基渣系与铁水反应行为研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2020.PAN F F. Study on the reaction behavior between CaO-Fe2O3 based slag and the hot metal[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2020. [2] LIU Q, WANG C Y, JI L L. Present situation and development of hot metal pretreatment process[J]. Metallurgical Equipment, 2022(S1):149-155. (刘倩, 王长勇, 季乐乐. 铁水预处理工艺现状与发展[J]. 冶金设备, 2022(S1):149-155.LIU Q, WANG C Y, JI L L. Present situation and development of hot metal pretreatment process[J]. Metallurgical Equipment, 2022(S1): 149-155. [3] WANG Y M, TAO L, GUO H Y, et al. Dephosphorization influence factors in converter hot metal pretreatment[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020,55(9):29-37. (王雨墨, 陶林, 郭皓宇, 等. 转炉铁水预处理脱磷的影响因素[J]. 钢铁, 2020,55(9):29-37.WANG Y M, TAO L, GUO H Y, et al. Dephosphorization influence factors in converter hot metal pretreatment[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020, 55(9): 29-37. [4] ZHAO J X. Researches on secondary dephosphurizaition[J]. Steelmaking, 1995(6):25-29. (赵俊学. 炉外脱磷剂研究概况[J]. 炼钢, 1995(6):25-29.ZHAO J X. Researches on secondary dephosphurizaition[J]. Steelmaking, 1995(6): 25-29. [5] DU F. The development of hot metal dephosphorization pretreatment[J]. Shanghai Metals, 1999(6):16-20. (杜锋. 铁水脱磷预处理工艺的发展[J]. 上海金属, 1999(6):16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.1999.06.003DU F. The development of hot metal dephosphorization pretreatment[J]. Shanghai Metals, 1999(6): 16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.1999.06.003 [6] LIU Y Q, LUO L, ZHANG P, et al. Development of green recycling system of hot slag and molten steel at Shougang Jingtang[J]. China Metallurgy, 2018,28(6):25-31, 42. (刘延强, 罗磊, 张鹏, 等. 首钢京唐热态渣、钢绿色循环利用体系开发[J]. 中国冶金, 2018,28(6):25-31, 42.LIU Y Q, LUO L, ZHANG P, et al. Development of green recycling system of hot slag and molten steel at Shougang Jingtang[J]. China Metallurgy, 2018, 28(6): 25-31, 42. [7] XU B, WANG Z D, DING J Y. LT-Dust and BOF slag as hot metal dephosphorization fluxes at Baosteel.[J]. Baosteel technology, 2006(1):6-9. (徐兵, 王兆达, 丁建勇. 宝钢LT灰及转炉渣用于铁水预处理脱磷剂的实践[J]. 宝钢技术, 2006(1):6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0716.2006.01.002XU B, WANG Z D, DING J Y. LT-Dust and BOF slag as hot metal dephosphorization fluxes at Baosteel.[J]. Baosteel technology, 2006(1): 6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0716.2006.01.002 [8] SUN G B. Efficiency enhancement mechanism of fluorine-free steel-making dephosphorizer made from collected dust and its harm reducing effect[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2022. (孙国斌. 除尘灰基无氟炼钢脱磷剂增效机理与降害作用研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2022.SUN G B. Efficiency enhancement mechanism of fluorine-free steel-making dephosphorizer made from collected dust and its harm reducing effect[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2022. [9] WU Q A, ZHU B L, LI D J. The preliminary study of the pretreatment of medium phosphorus hot metal(semi-steel)[J]. East China Metallurgical Institute Newspaper, 1986(4):1-10. (吴淇澳, 朱本立, 李大经. 中磷铁水(半钢)预处理初探[J]. 华东冶金学院报, 1986(4):1-10.WU Q A, ZHU B L, LI D J. The preliminary study of the pretreatment of medium phosphorus hot metal(semi-steel)[J]. East China Metallurgical Institute Newspaper, 1986(4): 1-10. [10] HUANG X H. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013: 298-299. (黄希祜. 钢铁冶金原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2013: 298-299.HUANG X H. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2013: 298-299. [11] ZHANG H B, DONG L Y, CHEN D F, et al. Thermodynamic analysis of dephosphorization for high phosphorus hot metal and experimental study[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009,9(S1):137-141. (张洪彪, 董凌燕, 陈登福, 等. 高磷铁水脱磷的热力学分析及实验研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2009,9(S1):137-141. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2009.z1.027ZHANG H B, DONG L Y, CHEN D F, et al. Thermodynamic analysis of dephosphorization for high phosphorus hot metal and experimental study[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009, 9(S1): 137-141. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2009.z1.027 [12] M. Allibert, et al. Slag atlas[M]. Düsseldorf: Verlag Stahleisen GmbH, 1981: 58-59. -




 下载:
下载: