Study on the influence of highly oxygen enrichment and H2-rich oxygen blast furnace atmospheres on softening-melting behaviors of vanadium titanomagnetite mixed burden
-
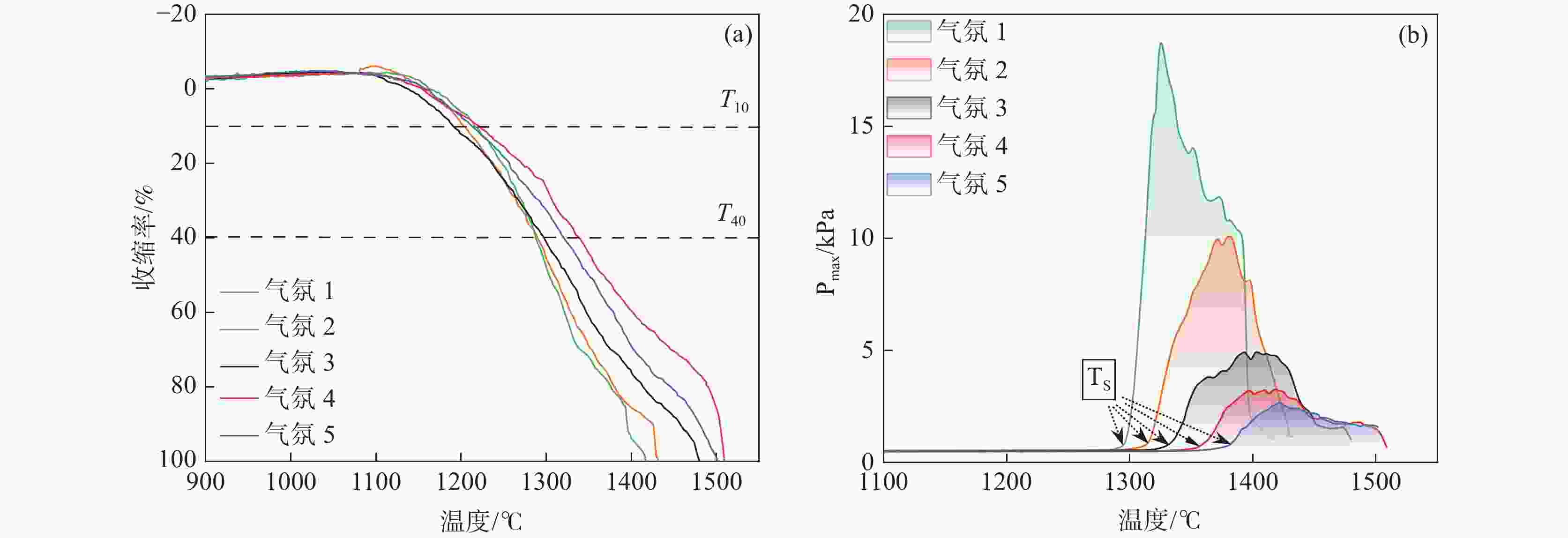
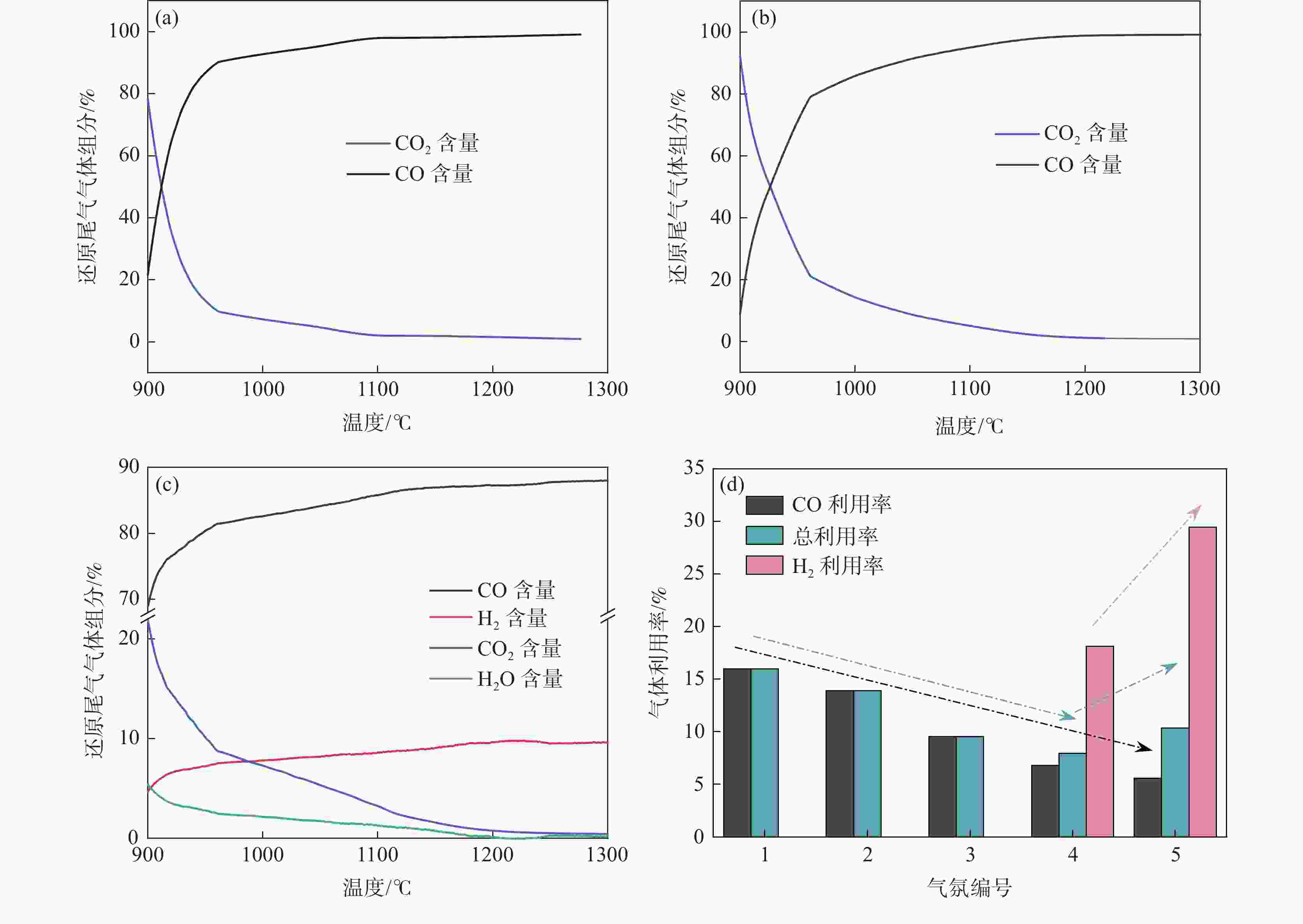
摘要: 探讨了高炉富氧、全氧及全氧富氢气氛对钒钛磁铁矿混合炉料软熔性能、透气性及气体利用率的影响规律。结果表明,高炉富氧气氛下,炉料软化开始温度下降,软化结束温度、熔化开始温度、滴落温度升高,软化区间、熔化区间变宽,但透气性指数下降,气体利用率降低;全氧富氢气氛条件下,通过引入H2,炉料软化开始温度、软化结束温度、熔化开始温度升高,软化区间变宽,熔化区间变窄,透气性能进一步得到改善,H2利用率增加。进一步研究表明,还原气体成分的变化对炉渣和铁水的化学成分产生了重要影响,富氧气氛下炉渣中Ti(C,N)含量显著降低,全氧富氢气氛下炉渣中TiC含量及铁水中[Si]、[Ti]、[V]含量均显著提高。研究为钒钛矿高炉冶炼过程中的绿色低碳技术提供了理论依据,为提高钒钛磁铁矿高炉冶炼效率并减少碳排放提供了重要的基础试验支持。Abstract: This study investigates the effects of oxygen-enriched, oxygen blast furnace, and H2-rich oxygen blast furnace atmospheres on the softening-melting behaviors, permeabilities, and gas utilization efficiency of vanadium titanomagnetite mixed burden. The results indicate that under oxygen-rich blast furnace atmosphere, the softening start temperature of furnace burden decreases, while the softening end temperature, melting start temperature, and dripping temperature increase. Consequently, both the softening and melting intervals become widened. However, the permeabilities and total reduction gas utilization efficiency decline. Under the H2-rich oxygen blast furnace atmosphere, the introduction of H2 leads to an increase in the softening start temperature, softening end temperature, and melting start temperature. Additionally, the softening interval expands, while the melting interval narrows, resulting in the improved gas permeability and enhanced H2 utilization efficiency. Further investigation reveals that variations in the reducing gas compositions significantly influence the chemical compositions of both slags and hot metals. Under the oxygen-enriched atmosphere, the Ti(C,N) content in slag decreases markedly, whereas under fully oxygen-enriched, H2-rich conditions, the TiC content in the slag, as well as [Si], [V] and [Ti] concentrations in hot metal, increase substantially. This study provides a theoretical basis for green low-carbon technologies in vanadium titanomagnetite smelting, and offers important experimental support for improving smelting efficiency and reducing carbon emissions.
-
表 1 钒钛炉料主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of the vanadium titanomagnetite feeds
% TFe FeO CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MgO TiO2 V2O5 S P R2 烧结矿 49.50 8.88 13.86 7.06 2.84 2.10 3.02 0.21 0.07 0.04 1.96 球团矿 54.88 <0.50 0.57 3.86 3.53 3.03 9.75 0.72 <0.01 <0.01 0.15 表 2 焦炭化学成分
Table 2. Chemical composition of the coke
% FCad Mt St Vdaf Ad K2O Na2O CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 Fe2O3 Total 85.88 0.23 0.63 1.09 0.08 0.10 0.49 7.24 0.13 3.73 1.03 12.80 注:M为水分;V为挥发分;FC为固定碳;A为灰分。 表 3 软熔试验还原气组分(体积分数)
Table 3. Compositions of the reducing gases used during the softening and melting tests
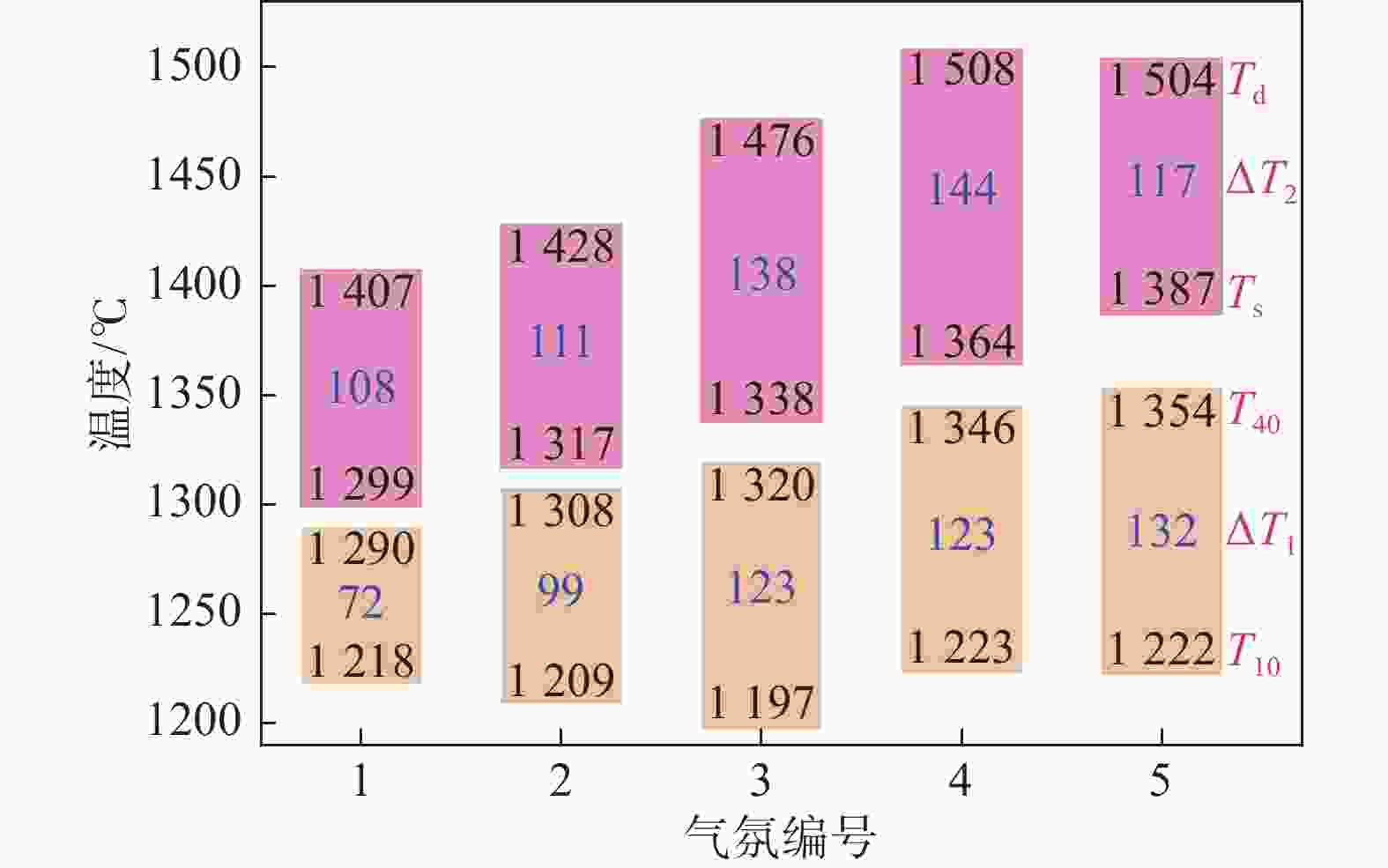
% 编号 N2 CO H2 普通高炉气氛 1 70 30 0 富氧高炉气氛 2 35 65 0 全氧高炉气氛 3 0 100 0 全氧高炉富氢气氛 4 0 90 10 5 0 80 20 表 4 不同气氛下钒钛混合炉料软熔试验特征参数
Table 4. Characteristic parameters of the softening and melting experiments for vanadium titanomagnetite mixed burden under different atmospheres
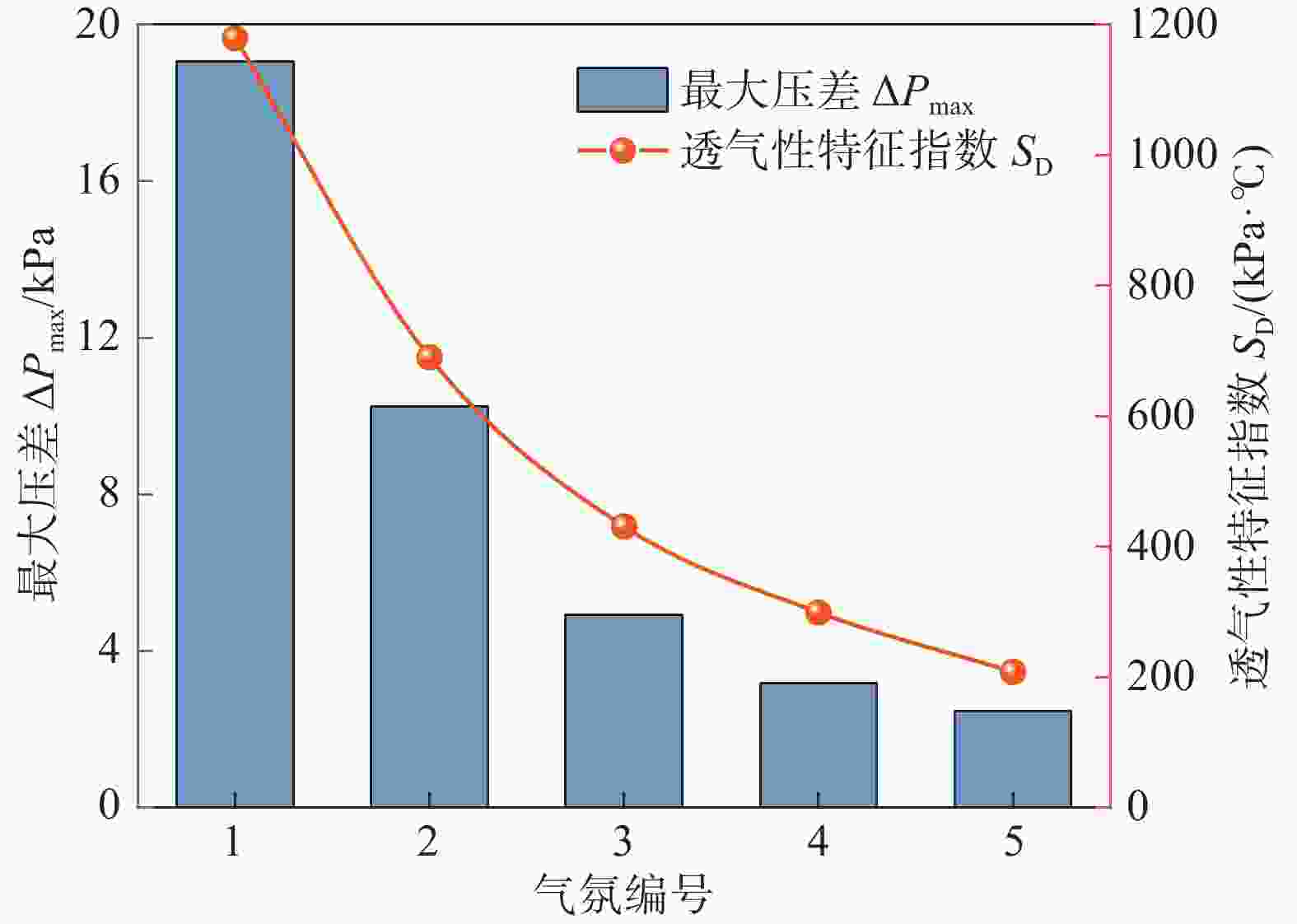
气氛编号 T10/℃ T40/℃ ΔT1/℃ TS/℃ TD/℃ ΔT2/℃ ΔPmax/kPa SD 1 1218 1290 72 1299 1407 108 19.05 1179.45 2 1209 1308 99 1317 1428 111 10.24 689.96 3 1197 1320 123 1338 1476 138 4.93 430.97 4 1223 1346 123 1364 1508 144 3.18 299.31 5 1222 1354 132 1387 1504 117 2.47 208.03 表 5 不同气氛条件下熔滴试验后炉渣化学成分
Table 5. Chemical compositions of slags after softening-melting experiments under different atmospheres
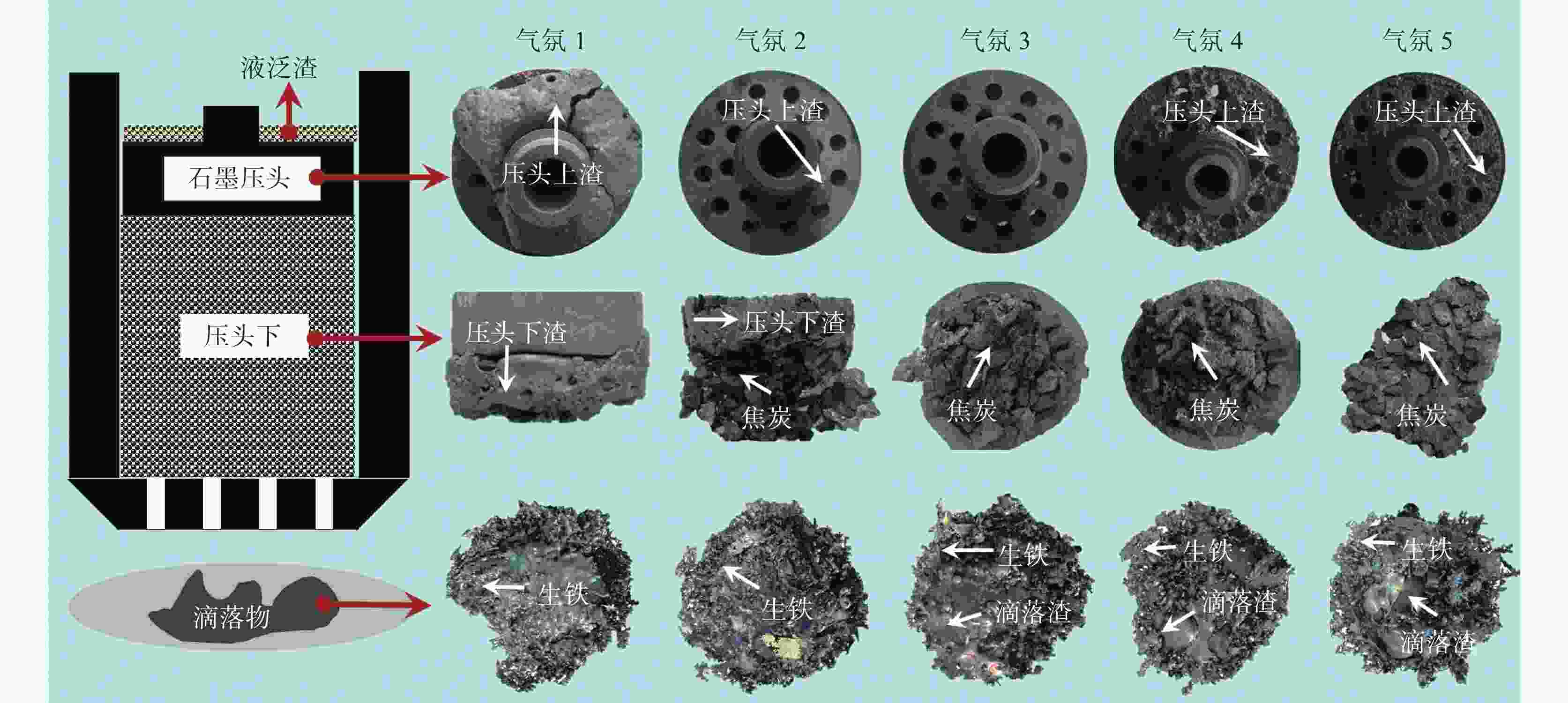
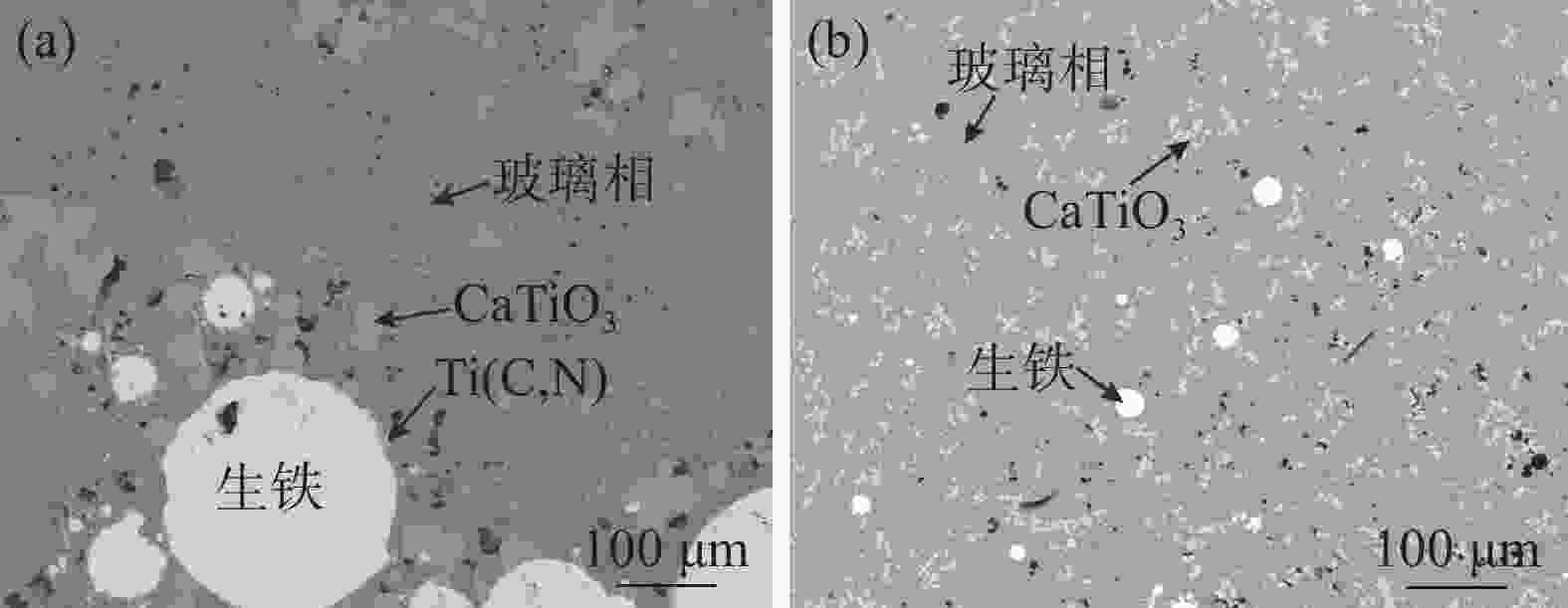
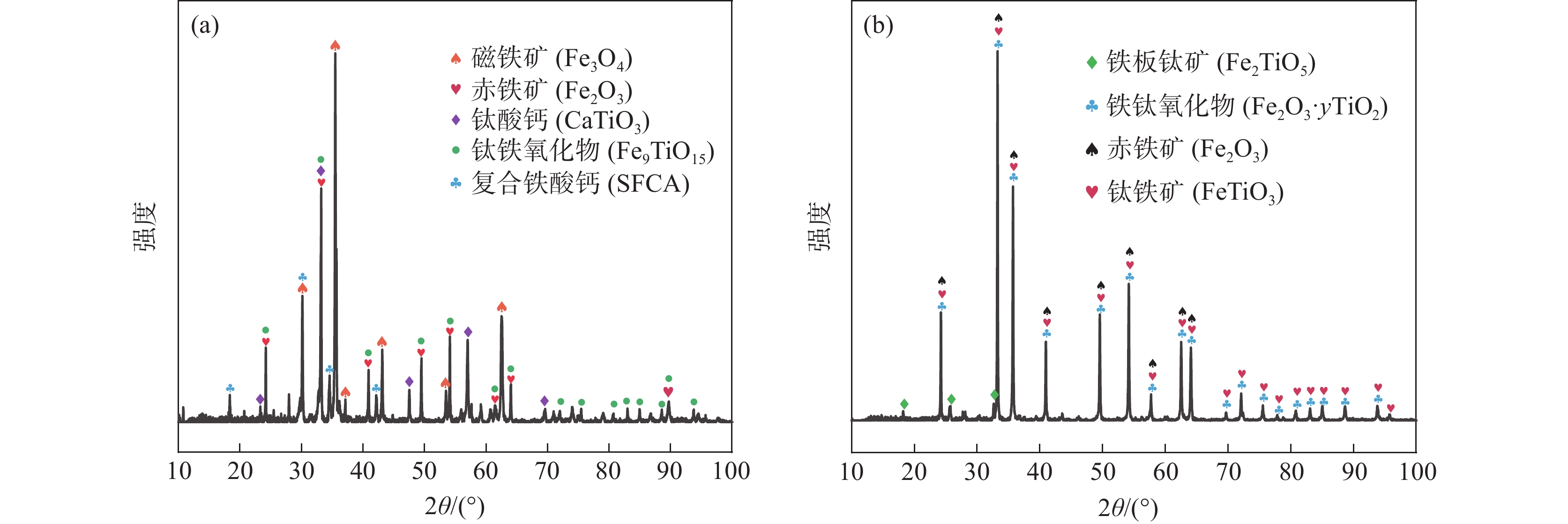
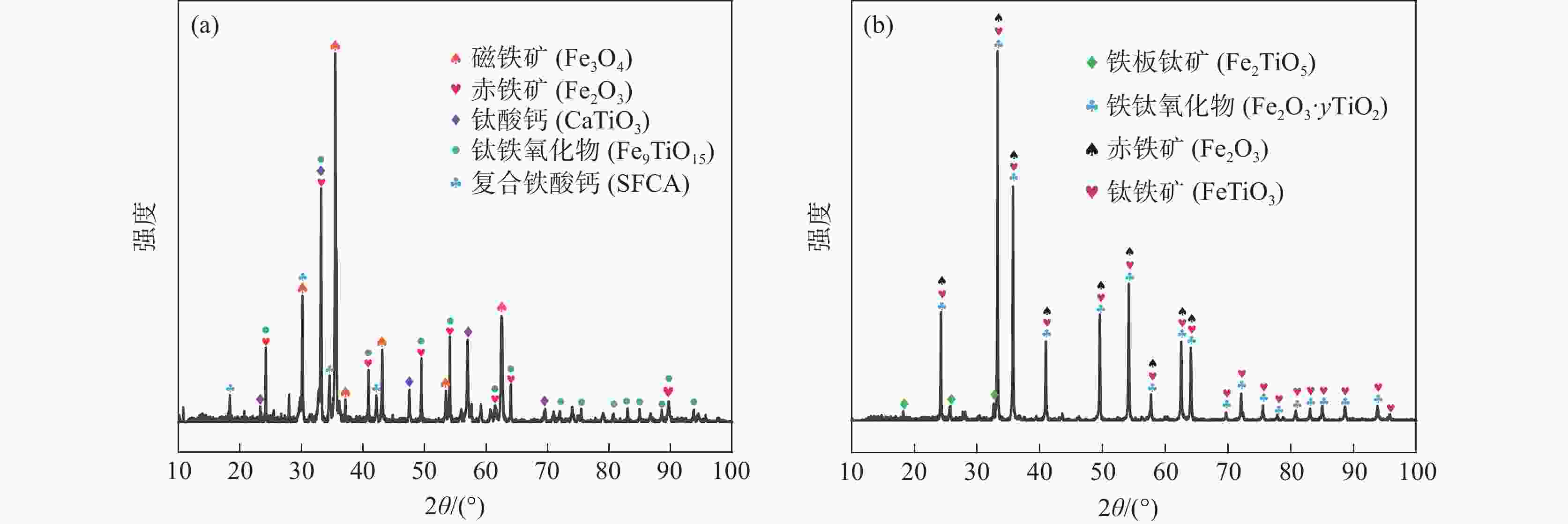
气氛序号 样品部位 MFe/% 渣成分/% FeO Al2O3 CaO MgO SiO2 TiO2 V2O5 Ti(C,N) R2 1 压头上渣 4.20 5.43 11.75 29.26 6.15 22.26 22.24 1.09 1.82 1.31 2 压头上渣 2.50 3.77 12.23 29.57 6.79 22.72 22.60 1.08 1.24 1.30 4 压头上渣 3.40 4.86 12.70 28.42 7.23 21.86 21.52 0.95 2.46* 1.30 5 压头上渣 2.30 3.30 13.14 28.11 7.70 21.46 21.41 0.85 4.04* 1.31 1 压头下渣 26.40 7.60 11.04 27.34 6.92 20.89 21.88 1.09 3.24 1.31 2 压头下渣 21.50 6.07 11.51 27.52 8.51 20.87 22.52 1.03 1.98 1.32 3 滴落渣 1.90 3.94 12.88 27.92 9.41 21.37 23.59 0.76 0.12* 1.31 4 滴落渣 4.30 2.56 12.67 27.72 9.58 21.52 23.56 0.64 1.73* 1.29 5 滴落渣 6.30 2.13 13.06 28.14 9.13 21.32 23.53 0.62 2.07* 1.32 注:*样品仅存在TiC,无TiN存在。 表 6 不同气氛条件下熔滴试验后滴落铁化学成分
Table 6. Chemical compositions of the dripping iron samples after softening-melting experiments under different atmospheres
% 气氛编号 C S Si Ti V 1 4.500 0.098 0.009 0.023 0.011 2 4.300 0.092 0.012 0.028 0.019 3 3.440 0.081 0.040 0.033 0.038 4 2.840 0.078 0.265 0.215 0.150 5 2.600 0.050 0.495 0.561 0.187 -
[1] DU H G. Principle of smelting vanadium titanium magnetite in blast furnace[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1996. (杜鹤桂. (1996). 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1996.DU H G. Principle of smelting vanadium titanium magnetite in blast furnace[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1996. [2] DENG J, XUE X, LIU G G. Present situation and development of comprehensive utilization of vanadium titanomagnetite resources in Pangang[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2007, 6(2): 83-86. (邓君, 薛逊, 刘功国. 攀钢钒钛磁铁矿资源综合利用现状与发展[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2007, 6(2): 83-86.DENG J, XUE X, LIU G G. Present situation and development of comprehensive utilization of vanadium titanomagnetite resources in Pangang[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2007, 6(2): 83-86. [3] USUI T, KAWABATA H, ONO-NAKAZATO H. Fundamental experiments on the H2 gas injection into the lower part of a blast furnace shaft[J]. ISIJ international, 2002, 42: 14-18. [4] WANG H T, CHU M S, GUO T L, et al. Mathematical simulation on blast furnace operation of coke oven gas injection in combination with top gas recycling[J]. Steel Research International, 2016, 87(5): 539-549. doi: 10.1002/srin.201500372 [5] XIA Z X, JIANG Z Y, Zhang X R, et al. The CO2 reduction potential for the oxygen blast furnace with CO2 capture and storage under hydrogen-enriched conditions[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2022), 121: 103793. [6] TIAN B S. Research and practice on low carbon smelting technology of hydrogen-rich carbon cycle blast furnace at Bayi steel[J]. Xinjiang Iron and Steel, 2021, 4(4): 1-3. (田宝山. 八钢富氢碳循环高炉低碳冶炼技术研究与实践[J]. 新疆钢铁, 2021, 4(4): 1-3.TIAN B S. Research and practice on low carbon smelting technology of hydrogen-rich carbon cycle blast furnace at Bayi steel[J]. Xinjiang Iron and Steel, 2021, 4(4): 1-3. [7] HIGUCHI K, MATSUZAKI S, SAITO K, et al. Improvement in reduction behavior of sintered ores in a blast furnace through injection of reformed coke oven gas[J]. ISIJ International, 2020, 60(10): 2218-2227. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2020-063 [8] PAN Y Z, ZHANG A J, LIN L, et al. Correlation between reduction degree and softening and melting properties of pellets[C]// Proceedings of the 10th international symposium on high-temperature metallurgical processing. San Antonio, 2019: 523-530. [9] QIE Y N, JIN Y T, KANG Y, et al. Influence of hydrogen-rich on softening and melting property of blast furnace burden with vanadium and titanium[J]. Iron & Steel, 2023, 58(5): 31-38. (郄亚娜, 靳亚涛, 康媛, 等. 高炉富氢对钒钛矿软熔滴落性能的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2023, 58(5): 31-38.QIE Y N, JIN Y T, KANG Y, et al. Influence of hydrogen-rich on softening and melting property of blast furnace burden with vanadium and titanium[J]. Iron & Steel, 2023, 58(5): 31-38. [10] CHEN B J, JIANG T, WEN J, et al. High-chromium vanadium–titanium magnetite all-pellet integrated burden optimization and softening–melting behavior based on flux pellets[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2024, 31(3): 498-507. doi: 10.1007/s12613-023-2719-1 [11] DENG Q Y. Study on the formation conditions and regulation mechanism of titanium carbonitride during blast furnace smelting of vanadium-titanium magnetite[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012. (邓青宇. 钒钛磁铁矿高炉冶炼过程中碳氮化钛形成条件与调控机制研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2012.DENG Q Y. Study on the formation conditions and regulation mechanism of titanium carbonitride during blast furnace smelting of vanadium-titanium magnetite[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012. [12] QIE Y N, LÜ Q, LIU X J, et al. Effect of hydrogen addition on softening and melting reduction behaviors of ferrous burden in gas-injection blast furnace[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2018, 49(5): 2622-2632. doi: 10.1007/s11663-018-1299-3 [13] XIN R, ZHAO J B, GAO X D, et al. Softening-melting properties and slag evolution of vanadium titano-magnetite sinter in hydrogen-rich gases[J]. Crystals, 2023, 13(2): 103390. [14] LIU R W, PAN Z H, LI J X, et al. Study on softening-melting characteristics of iron bearing material in oxygen blast furnace[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2022, 34(6): 534-542. (刘荣伟, 潘中华, 李家新, 等. 氧气高炉含铁炉料软熔特性研究[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2022, 34(6): 534-542.LIU R W, PAN Z H, LI J X, et al. Study on softening-melting characteristics of iron bearing material in oxygen blast furnace[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2022, 34(6): 534-542. [15] LÜ B B. Basic research on gas cycle coupling hydrogen-rich blast furnace ironmaking[D]. Beijing, Beijing University of Science and Technology, 2024. (吕斌斌. 煤气循环耦合富氢高炉炼铁基础研究[D]. 北京, 北京科技大学, 2024.LÜ B B. Basic research on gas cycle coupling hydrogen-rich blast furnace ironmaking[D]. Beijing, Beijing University of Science and Technology, 2024. [16] LÜ Q, QIE Y N, LIU X J, et al. Effect of hydrogen addition on reduction behavior of iron oxides in gas-injection blast furnace[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2017, 648: 79-90. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2016.12.009 [17] MAO X D. Basic research on the reaction behavior of iron oxides with H2-CO mixed gas[D]. Beijing, Beijing University of Science and Technology, 2023. (毛旭东. 铁氧化物与H2-CO混合气体反应行为的基础研究[D]. 北京, 北京科技大学, 2023.MAO X D. Basic research on the reaction behavior of iron oxides with H2-CO mixed gas[D]. Beijing, Beijing University of Science and Technology, 2023. [18] XIE H E, HU P, ZHENG K, et al. Study on phase and chemical composition of V-Ti sinter during softening, melting and dripping process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(2): 107-117. (谢洪恩, 胡鹏, 郑魁, 等. 钒钛烧结矿软熔滴落过程中的物相组成及化学成分变化规律研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022, 43(2): 107-117.XIE H E, HU P, ZHENG K, et al. Study on phase and chemical composition of V-Ti sinter during softening, melting and dripping process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(2): 107-117. [19] WANG W Z, YU K. Theory and practice of smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite in blast furnace[J]. Journal of Northeast Institute of Technology, 1984(4): 41-48,125-126. (王文忠, 余琨. 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿的理论与实践[J]. 东北工学院学报, 1984(4): 41-48,125-126.WANG W Z, YU K. Theory and practice of smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite in blast furnace[J]. Journal of Northeast Institute of Technology, 1984(4): 41-48,125-126. [20] DIAO R S. A new understanding of vanadium titanomagnetite smelting in blast furnace[J]. Iron & Steel, 1999(6): 14-16,40. (刁日升. 对高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿问题的新认识[J]. 钢铁, 1999(6): 14-16,40.DIAO R S. A new understanding of vanadium titanomagnetite smelting in blast furnace[J]. Iron & Steel, 1999(6): 14-16,40. [21] CHEN M, CHEN B X, JIANG Y, et al. Study of Ti(C, N) Formations in TiO2-Containing Slags[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2025, 56: 1018-1028. doi: 10.1007/s11663-024-03410-w [22] QIE Y N, SHANGGUAN D Y, LI Y Z, et al. Formation of primary slag and carburizing behavior of metal iron in cohesive zone of Hydrogen-rich blast furnace[J]. ISIJ International, 2024), 64(9): 1360-1366. [23] GUO X S, YU J B, ZHANG Y J, et al. Mechanism of desulfurization from liquid iron by hydrogen plasma arc melting[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2018, 49(6): 2951-2955. doi: 10.1007/s11663-018-1345-1 -




 下载:
下载: