Influence of flow control devices on the flow field of a double-strand slab tundish based on numerical simulation and water modeling
-
摘要: 为研究控流装置对某钢厂78 t大型双流对称中间包内钢液流场的影响规律,采用数值模拟计算与水模拟试验相结合的方法研究了不同的控流装置变化的影响。在欧拉-欧拉框架下对原始条件中间包1∶1建模,研究了有无坝孔、坝与长水口间距、堰与长水口间距、湍流抑制器高度、堰距中间包底部间距和坝高度对双流中间包内钢液流场的影响。结果表明:随着湍流抑制器高度加大,堰距中间包底部间距减小,中间包钢液平均停留时间显著增加,死区体积分数显著减小。另外,坝无孔可有效抑制短路流的发展,延长钢液的流动距离,增加平均停留时间。增大坝与长水口的间距,平均停留时间先增大后减小;增大堰与长水口的间距,通过坝孔直接流向出钢口的短路流得到发展,平均停留时间呈减小趋势。Abstract: In order to study the influence of flow control devices on the molten steel flow field in a 78 ton large double strand symmetrical tundish in a certain steel plant, a combined method of numerical simulation and water modeling was adopted to investigate the effects of changes in different flow control devices. The 1:1 modeling of the prototype tundish under the Euler-Euler framework was established to study the influence of the presence or absence of dam holes, the distance between dam and ladle shroud, the distance between weir and ladle shroud, the height of turbulence inhibitor, the distance between weir and bottom of tundish and the height of dam on the molten steel flow field in the double strand tundish. The results show that with increasing the height of turbulence inhibitor, and decreasing the distance between weir and the bottom of tundish, the average residence times of molten steel in tundish increase obviously, and the volume fractions of dead zone decrease significantly. In addition, the dam without holes can effectively inhibit the development of short-circuit flow, extend the flow distance of the molten steel and increase the average residence time. When the distance between the dam and the ladle shroud is increased, the average residence time first increases and then decreases. With increasing the distance between weir and ladle shroud, the short-circuit flow to steel outlet through dam holes is developed, and the average residence time decreases.
-
Key words:
- tundish /
- numerical simulation /
- flow control devices /
- flow field tracer /
- average residence time
-
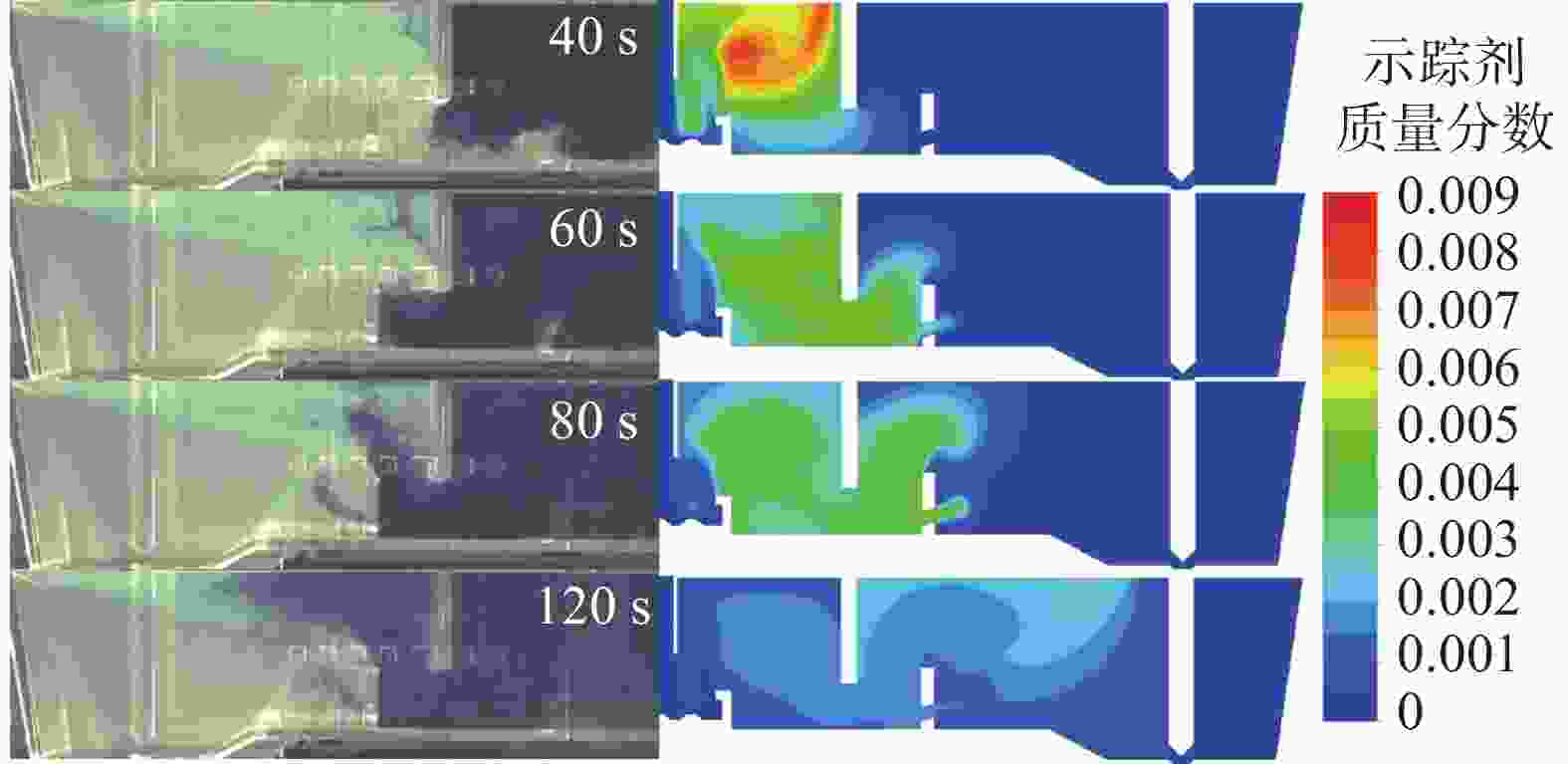
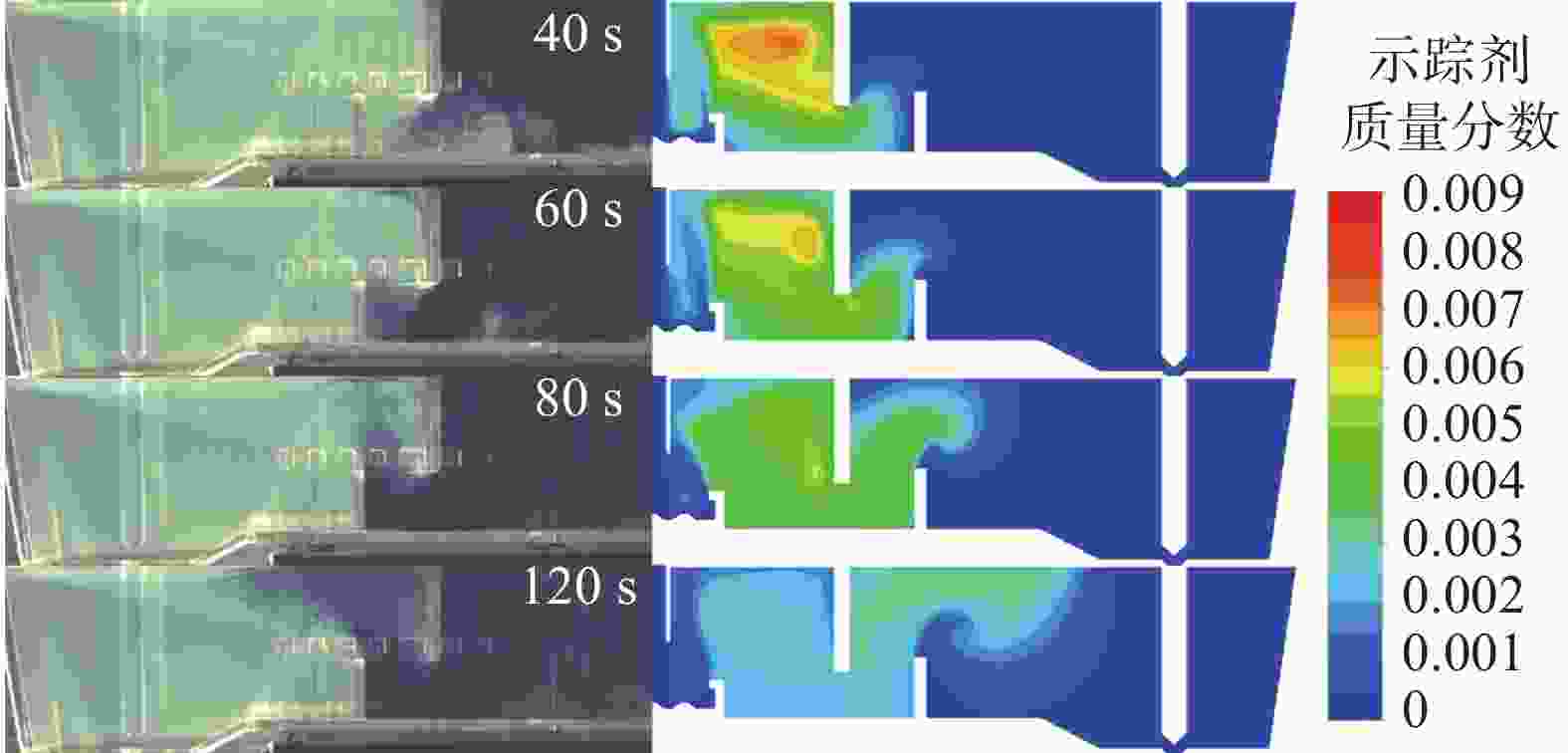
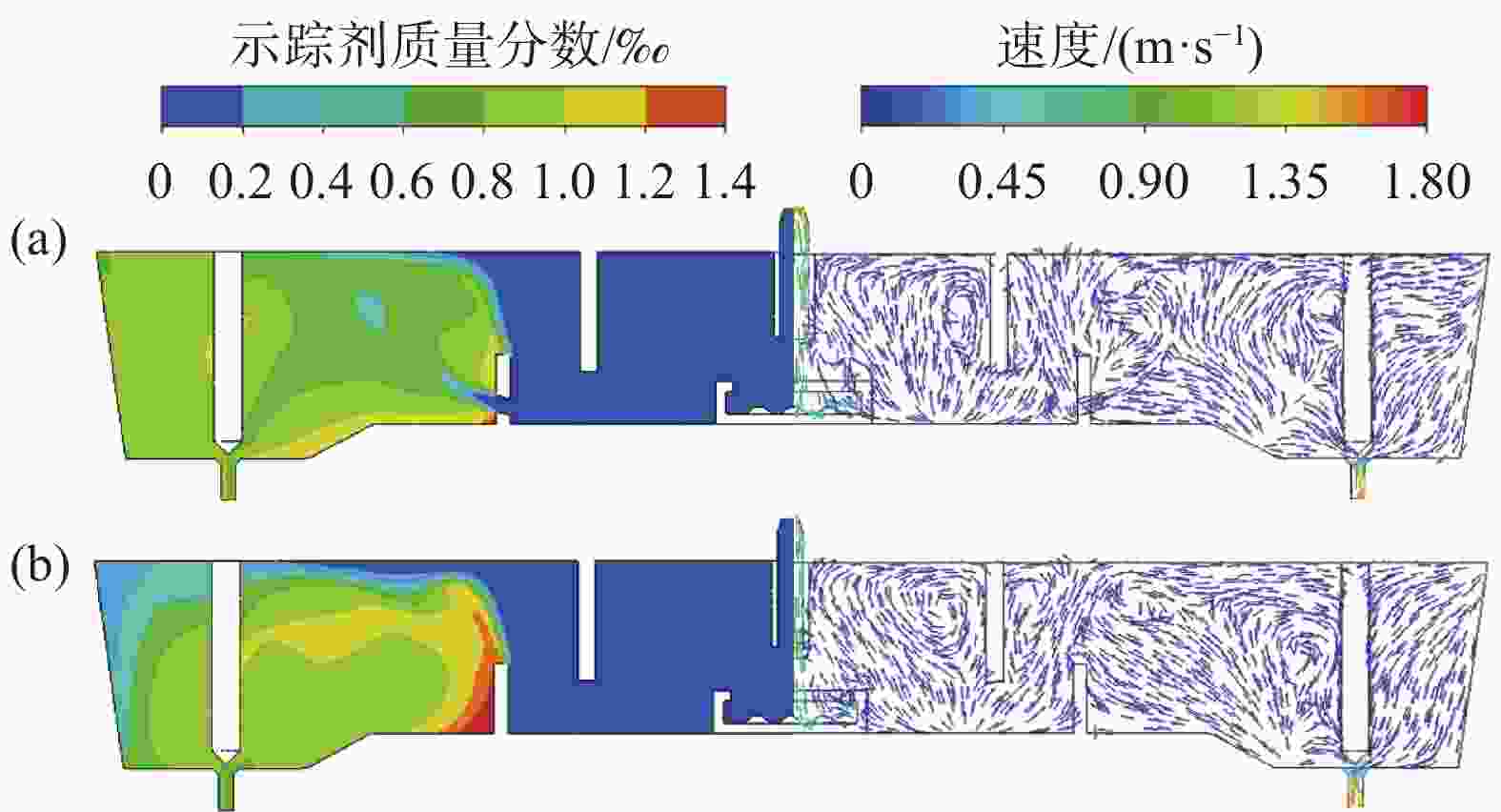
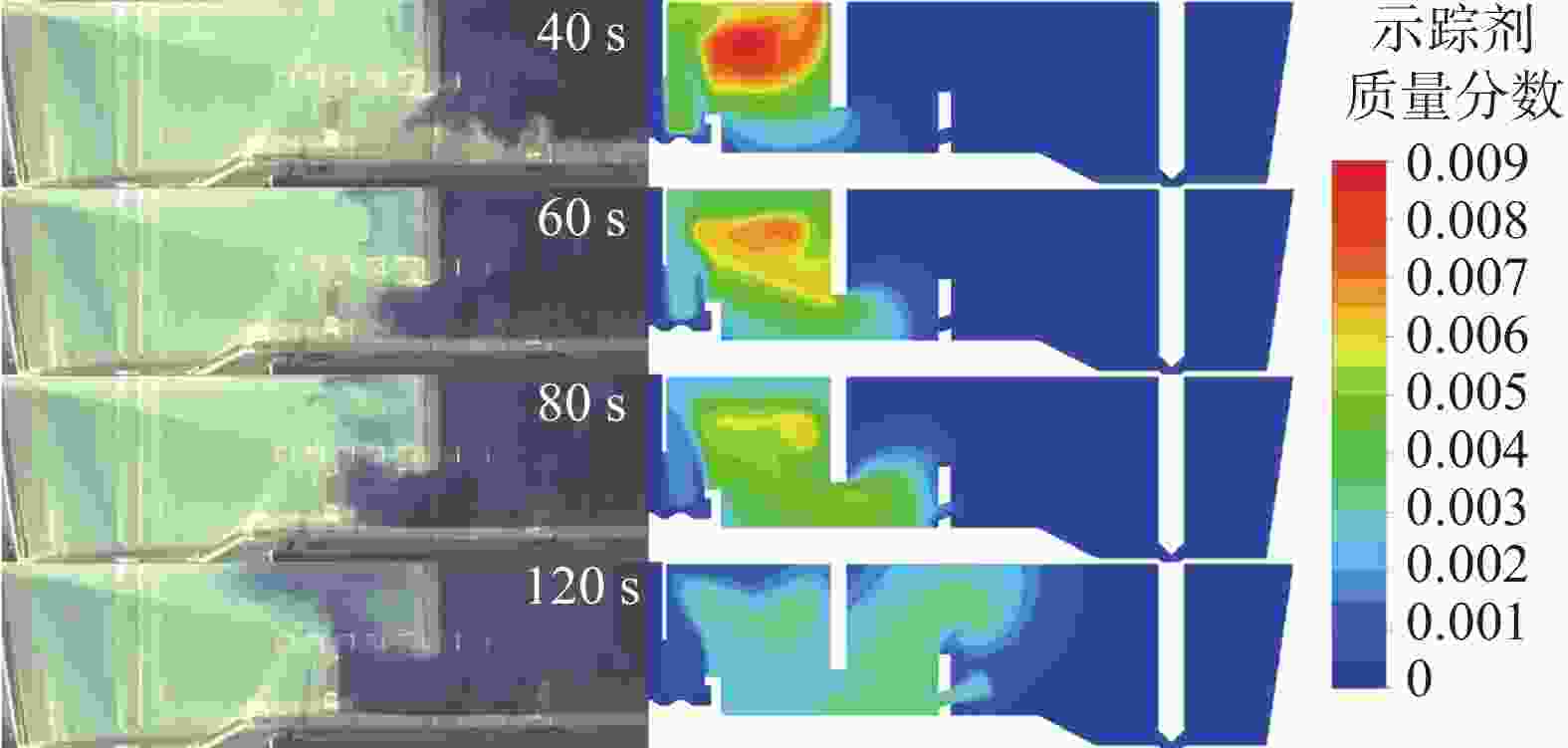
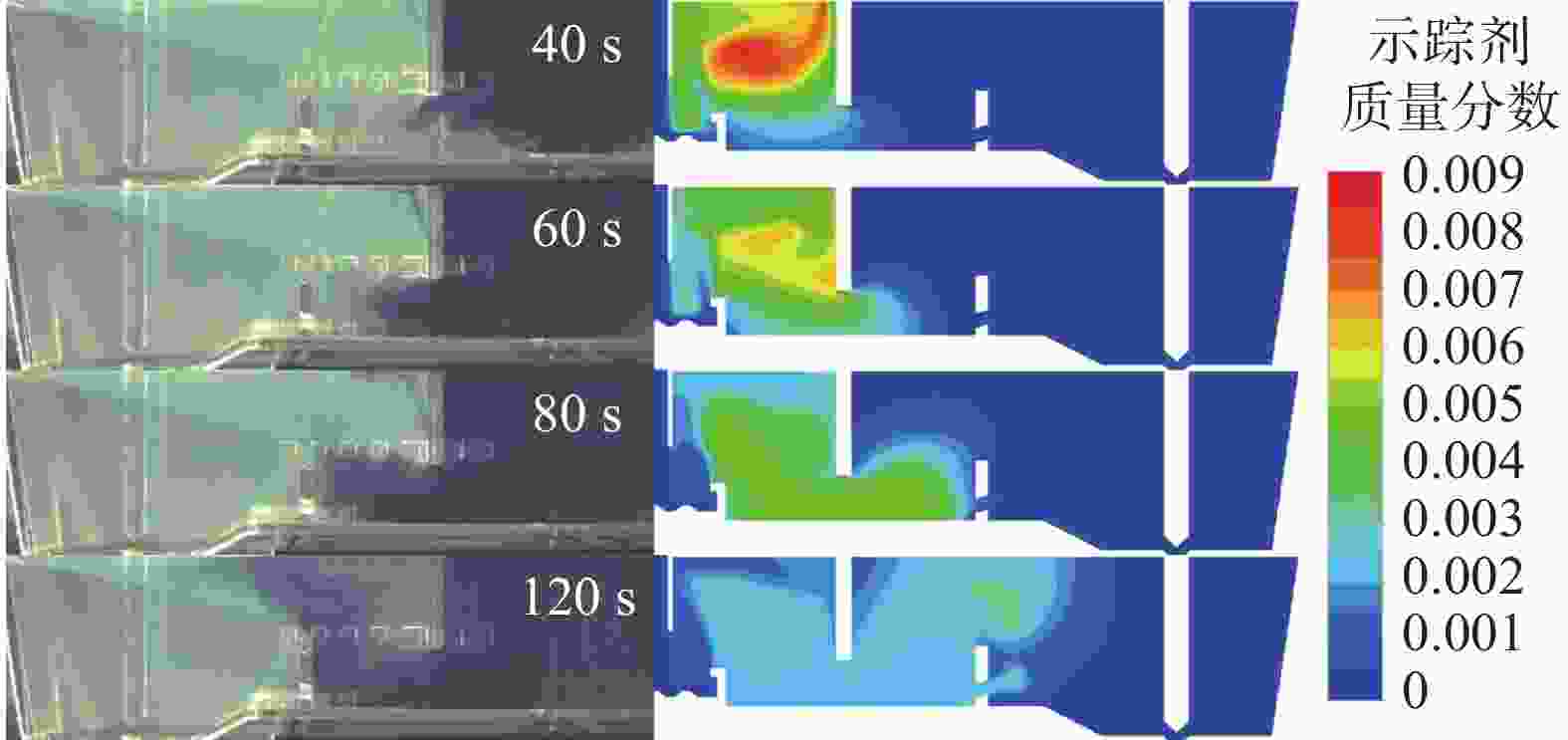
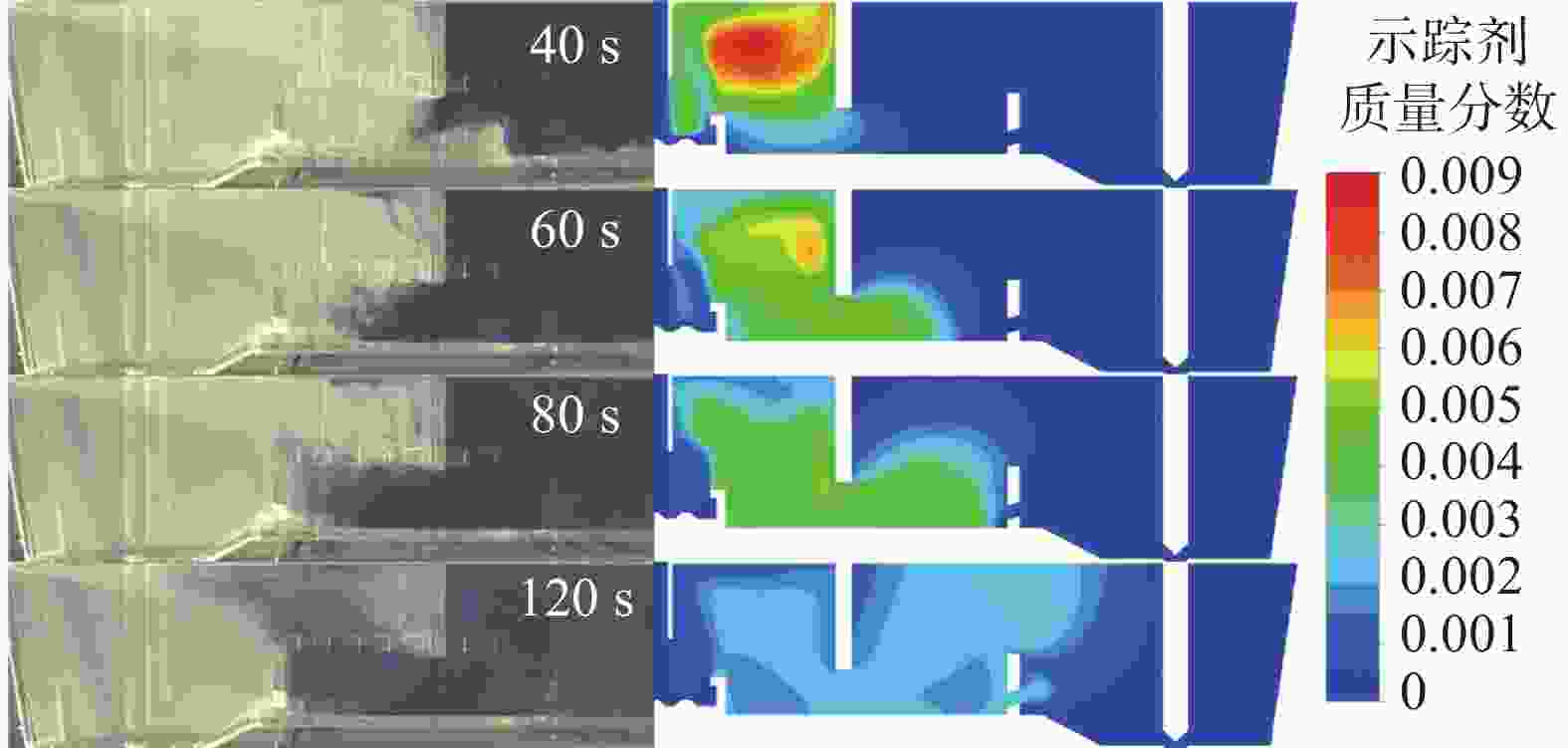
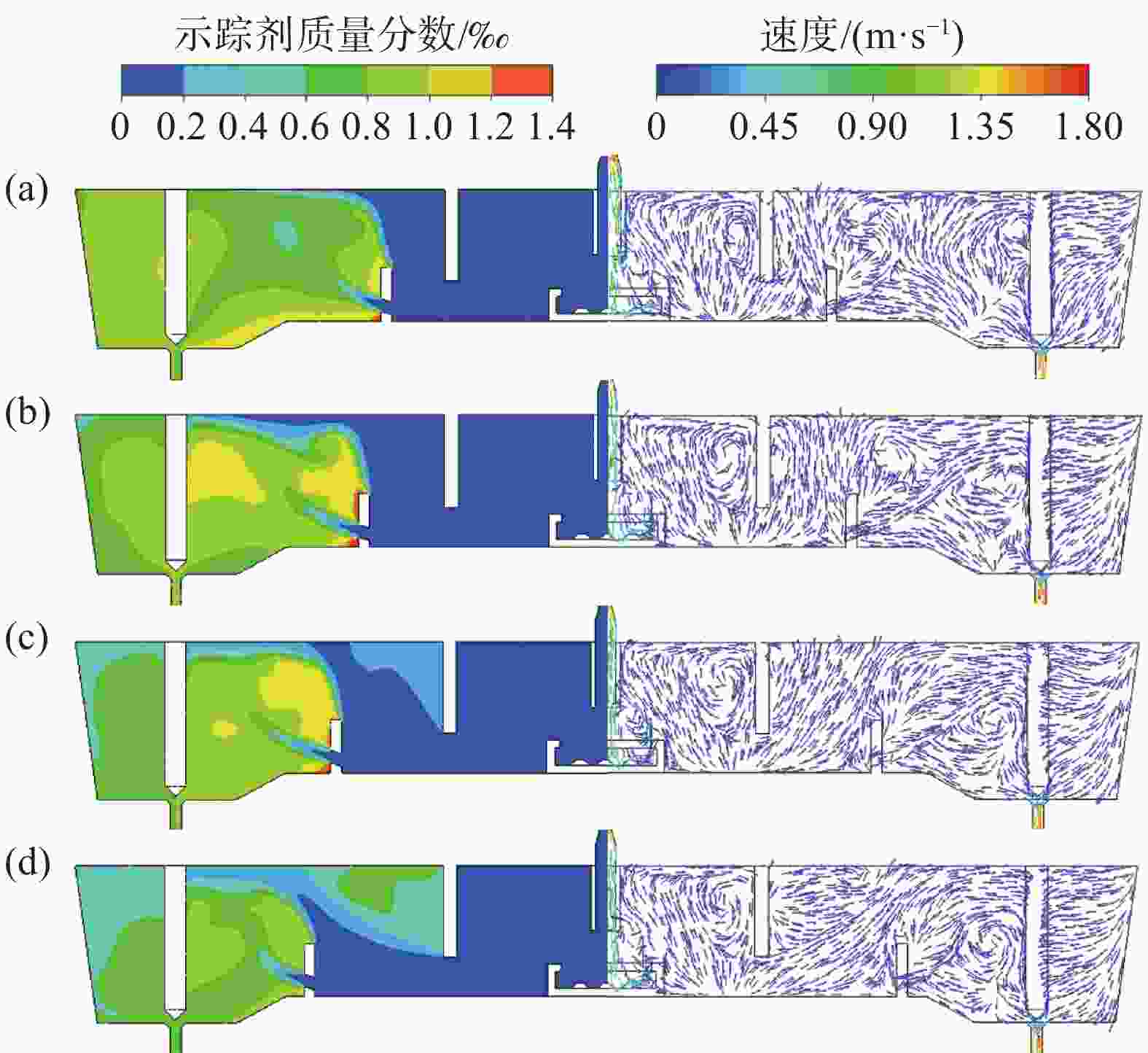
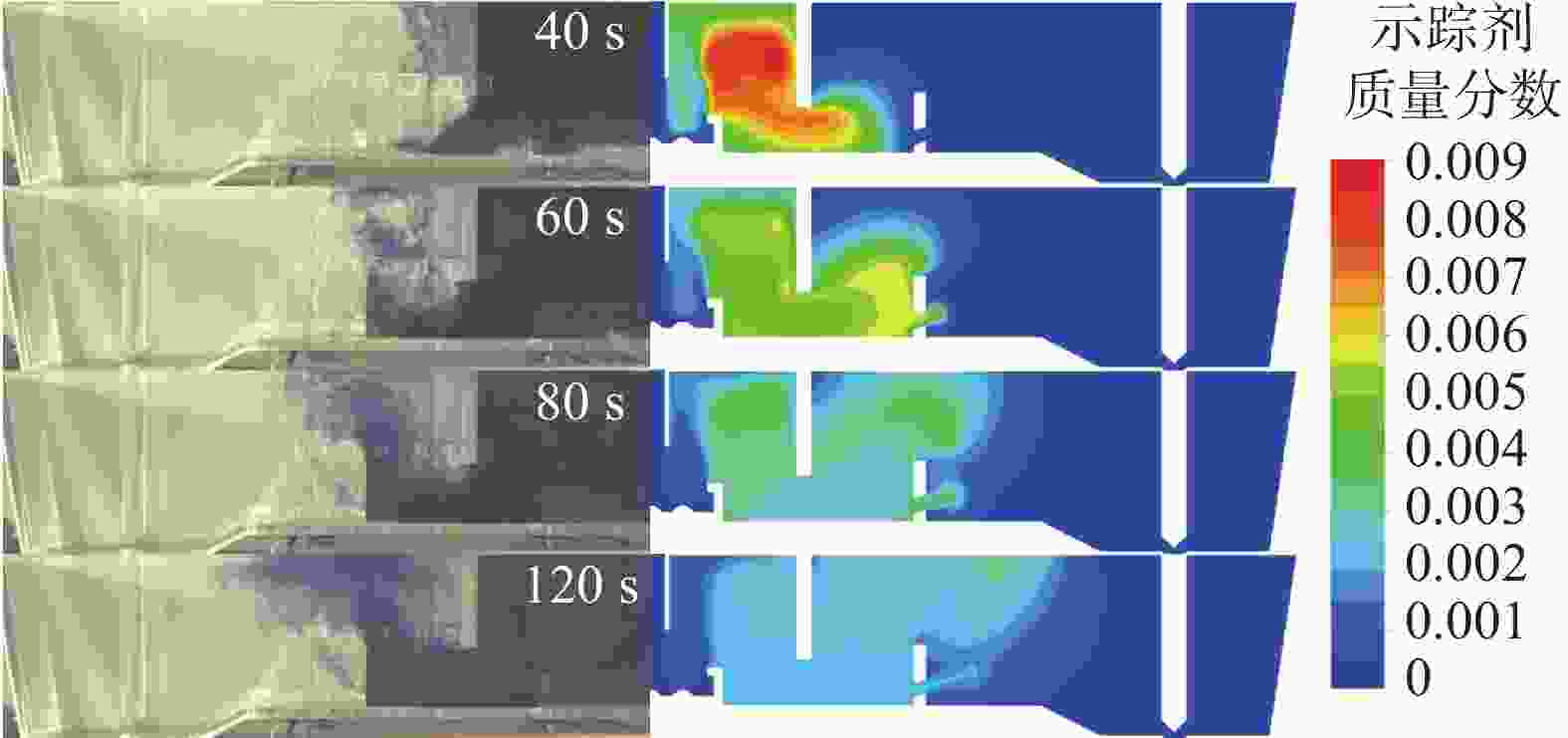
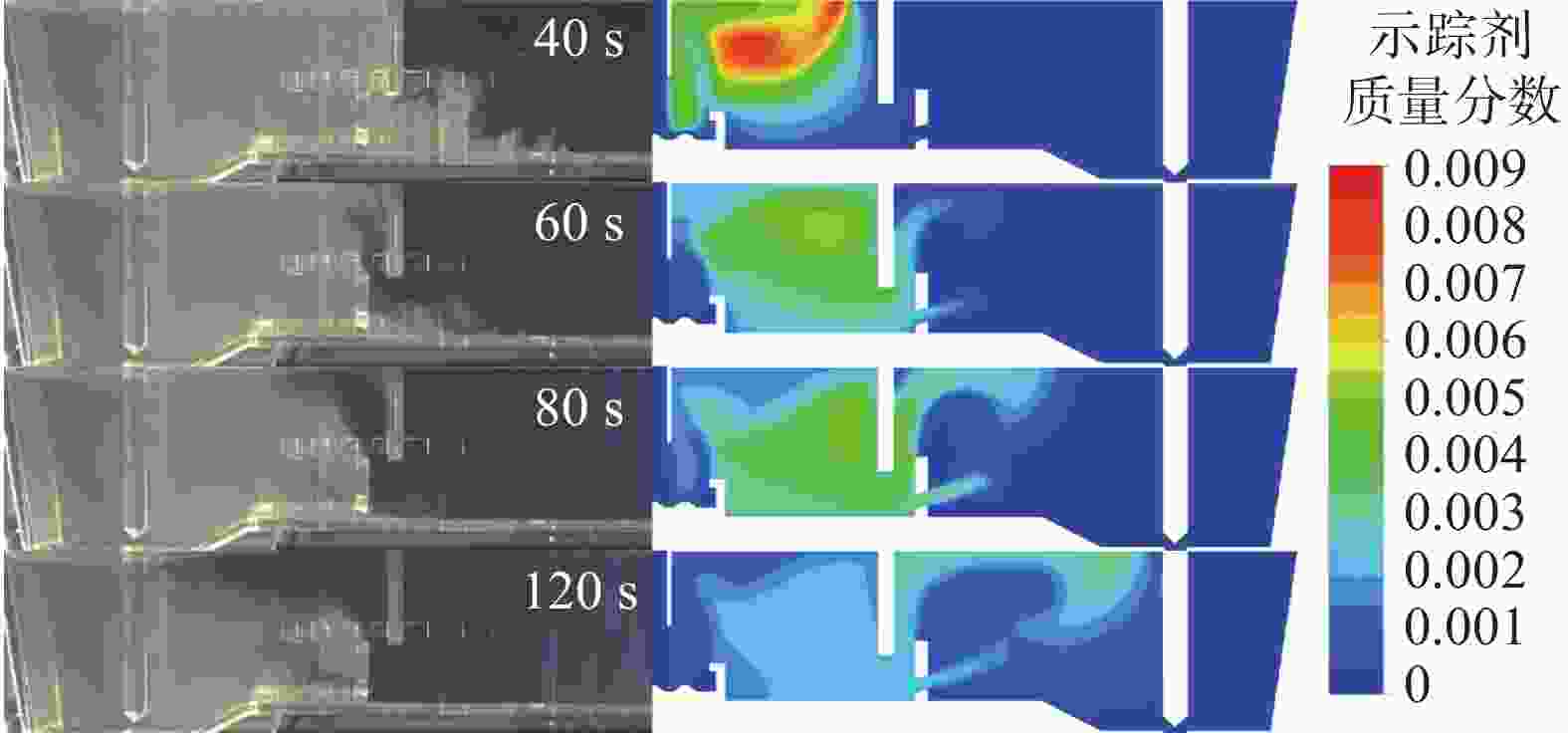
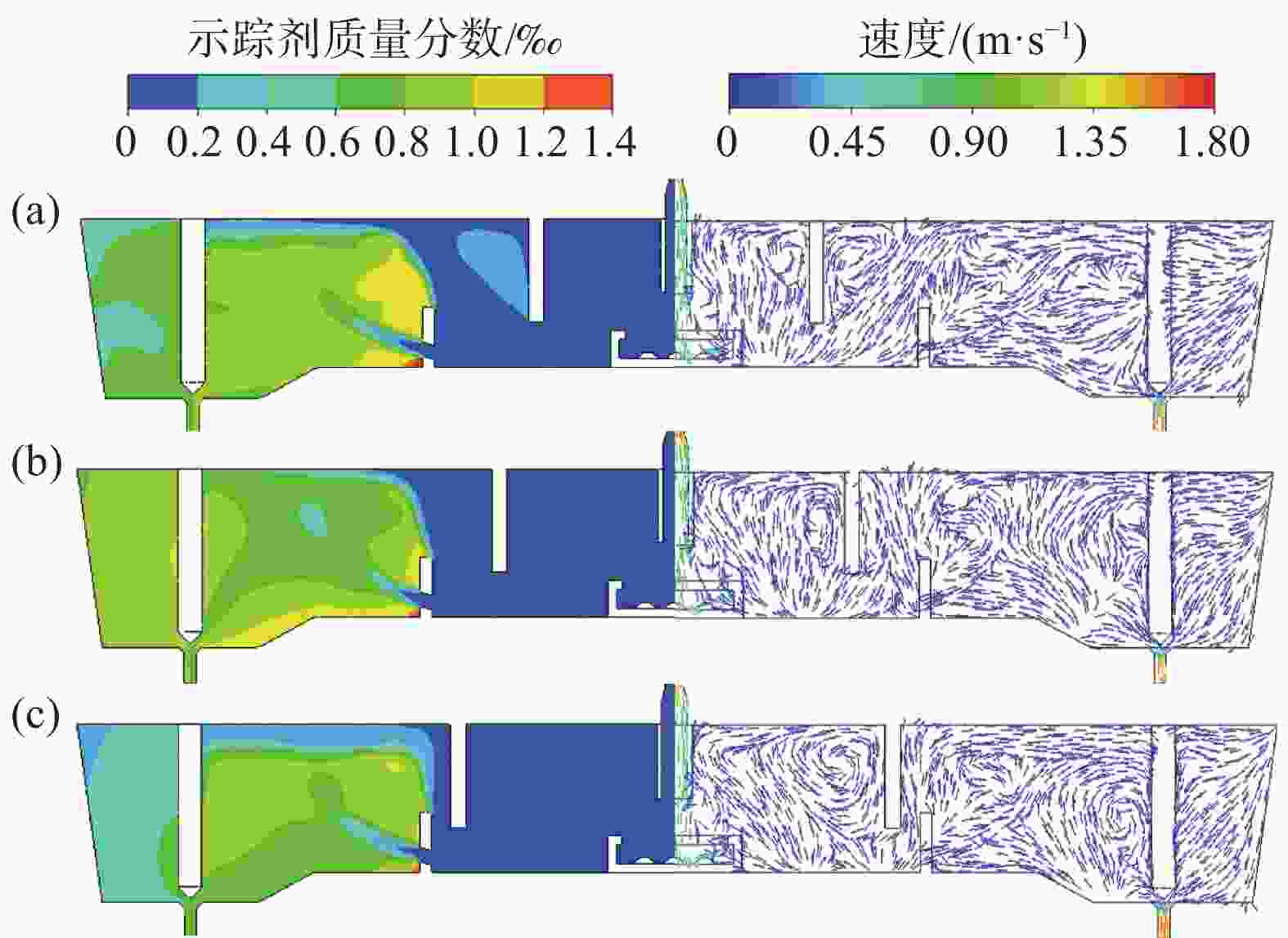
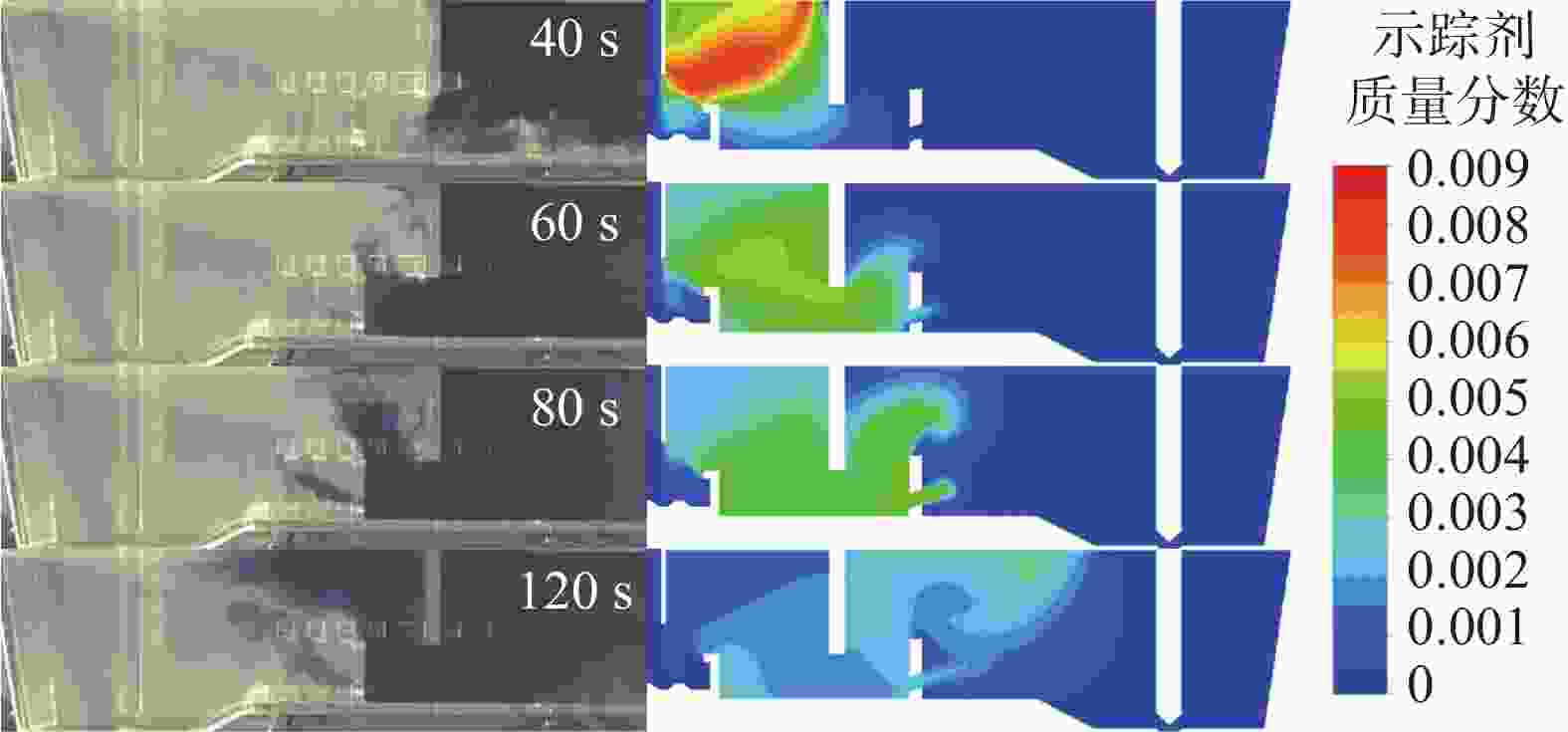
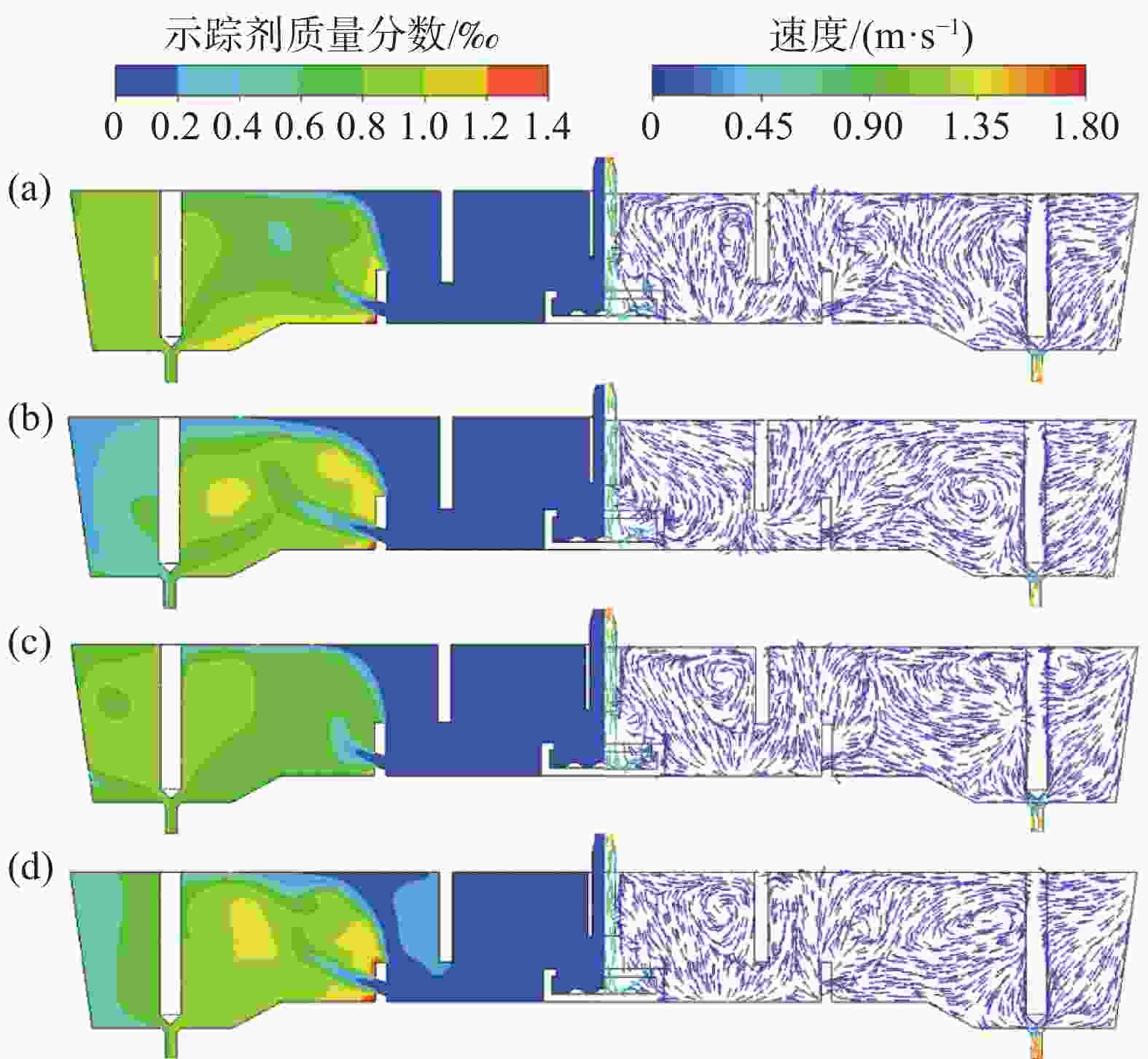
图 13 湍流抑制器高度、堰距中间包底部间距和坝高度对中间包示踪剂分布和速度分布的影响(
1000 s)(a) 原始条件;(b) 湍流抑制器高度300 mm;(c) 堰距中间包底部间距400 mm;(d) 坝高度300 mm
Figure 13. Effect of the height of the turbulence inhibitor, the distance between the weir and the tundish bottom, and the height of the dam on the distribution of tracer and velocity in the tundish at
1000 s表 1 中间包的主要物性参数
Table 1. Main parameters of the industrial tundish
表 2 中间包数值模拟试验方案
Table 2. Experimental plan of tundish numerical simulation
方案 坝孔 坝与长
水口的
间距/mm堰与长
水口的
间距/mm湍流抑
制器高
度/mm堰距中间
包底部间
距/mm坝高度/
mm1 有 1631.5 1131.5 250 300 400 2 无 1631.5 1131.5 250 300 400 3 有 1800 1131.5 250 300 400 4 有 2000 1131.5 250 300 400 5 有 2200 1131.5 250 300 400 6 有 1631.5 900 250 300 400 7 有 1631.5 1400 250 300 400 8 有 1631.5 1131.5 300 300 400 9 有 1631.5 1131.5 250 400 400 10 有 1631.5 1131.5 250 300 300 注:表中斜体字为与中间包原始参数的对比试验数据 表 3 坝孔对中间包流场参数的影响
Table 3. Effect of dam holes on the flow field parameters in the tundish
坝孔 平均停留
时间/s混合区体积
分数/%活塞区体积
分数/%死区体积
分数/%有 694.3 27.44 54.51 18.13 无 712.5 31.49 52.53 15.98 表 4 坝与长水口的间距对中间包流场参数的影响
Table 4. Effect of the distance between the dam and ladle shroud on the flow field parameters in the tundish
坝与长水口
的间距/mm平均停留
时间/s混合区体积
分数/%活塞区体积
分数/%死区体积
分数/%1631.5 694.3 27.44 54.51 18.13 1800 718.6 31.3 53.44 15.23 2000 706.7 29.68 54.13 16.66 2200 687.5 27.72 53.35 18.93 表 5 堰与长水口的间距对中间包流场参数的影响
Table 5. Effect of the distance between the weir and ladle shroud on the flow field parameters in the tundish
堰与长水口
的间距/mm平均停留
时间/s混合区体积
分数/%活塞区体积
分数/%死区体积
分数/%900 737.9 33.36 53.65 12.98 1131.5 694.3 27.44 54.51 18.13 1400 686.0 20.9 59.75 19.1 表 6 湍流抑制器高度、堰距中间包底部间距和坝高度对中间包流场参数的影响
Table 6. Effect of the height of the turbulence inhibitor, the distance between the weir and the tundish bottom, and the height of the dam on the RTD curves in the tundish
方案 平均停留
时间/s混合区体积
分数/%活塞区体积
分数/%死区体积
分数/%1 694.3 27.44 54.51 18.13 8 723.5 30.88 54.44 14.68 9 662.1 21.24 56.84 21.92 10 717.8 31.38 53.27 15.35 -
[1] BAO Y P, WANG M. Development trend of tundish metallurgical technology[J]. Continuous Casting, 2021,40(5):2-11. (包燕平, 王敏. 中间包冶金技术发展趋势[J]. 连铸, 2021,40(5):2-11.BAO Y P, WANG M. Development trend of tundish metallurgical technology[J]. Continuous Casting, 2021, 40(5): 2-11. [2] SAHAI Y. Tundish technology for casting clean steel: A review[J]. Metall Mater Trans B, 2016,47(4):2095-2106. doi: 10.1007/s11663-016-0648-3 [3] BRAUN A, WARZECHA M, PFEIFER H. Numerical and physical modeling of steel flow in a two-strand tundish for different casting conditions[J]. Metall Mater Trans B, 2010,41(3):549-559. doi: 10.1007/s11663-010-9347-7 [4] LIU Y B, YANG J. Progress in tundish flow field control technology[J]. Continuous Casting, 2021(5):12-33. (刘逸波, 杨健. 中间包流场控制技术的进展[J]. 连铸, 2021(5):12-33.LIU Y B, YANG J. Progress in tundish flow field control technology[J]. Continuous Casting, 2021(5): 12-33. [5] JHA P K, RAO P S, DEWAN A. Effect of height and position of dams on inclusion removal in a six strand tundish[J]. ISIJ Int, 2008,48(2):154-160. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.48.154 [6] LING H T, ZHANG L F. Numerical simulation of the growth and removal of inclusions in the molten steel of a two-strand tundish[J]. Jom, 2013,65(9):1155-1163. doi: 10.1007/s11837-013-0689-x [7] MAZUMDAR D, GUTHRIE R I L. The physical and mathematical modelling of continuous casting tundish systems[J]. ISIJ Int, 1999,39(6):524-547. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.39.524 [8] SAHAI Y, EMI T. Melt flow characterization in continuous casting tundishes[J]. ISIJ Int, 1996,36(6):667-672. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.36.667 [9] LEI H. New insight into combined model and revised model for RTD curves in a multi-strand tundish[J]. Metall Mater Trans B, 2015,46(6):2408-2413. doi: 10.1007/s11663-015-0435-6 [10] LING H T, XU R, WANG H J, et al. Multiphase flow behavior in a single-strand continuous casting tundish during ladle change[J]. ISIJ Int, 2020,60(3):499-508. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2019-506 [11] ZHANG J J, GAO W F, CAO T Y, et al. Experiment on hydraulic model of optimization of flow field in 60 t two-strand tundish[J]. Steel Making, 2013,29(5):61-64. (张剑君, 高文芳, 曹同友, 等. 武钢60 t双流连铸中间包流场优化试验研究[J]. 炼钢, 2013,29(5):61-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1043.2013.05.016ZHANG J J, GAO W F, CAO T Y, et al. Experiment on hydraulic model of optimization of flow field in 60 t two-strand tundish[J]. Steel Making, 2013, 29(5): 61-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1043.2013.05.016 [12] ZHANG H, WANG J H, FANG Q, et al. Research progress on numerical simulation of transient tundish casting[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2021,44(6):401-412. (张华, 王家辉, 方庆, 等. 中间包非稳态浇注过程数值模拟研究进展[J]. 辽宁科技大学学报, 2021,44(6):401-412.ZHANG H, WANG J H, FANG Q, et al. Research progress on numerical simulation of transient tundish casting[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2021, 44(6): 401-412. [13] LIU C, XIAO A D, HE Z, et al. Numerical investigation on motion and removal of inclusions in continuous casting tundish with multiorifice filter [J]. Steel Res Int, 2022, 93(12). [14] QU T P, JIANG M F, WANG D Y. Physical and numerical simulation on characteristic of fluid flow in four-strand tundish[J]. China Metallurgy, 2009,19(1):6-11. (屈天鹏, 姜茂发, 王德永. 四流中间包钢液流动行为的数学物理模拟[J]. 中国冶金, 2009,19(1):6-11.QU T P, JIANG M F, WANG D Y. Physical and numerical simulation on characteristic of fluid flow in four-strand tundish[J]. China Metallurgy, 2009, 19(1): 6-11. [15] SINGH R K, PAUL A, RAY A K. Modelling of flow behaviour in continuous casting tundish[J]. Scandinavian Journal of Metallurgy, 2003,32(3):137-146. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0692.2003.00635.x [16] SONG L N, TIE Z P. Metallurgical effects of commonly used flow control devices in asymmetric tundish[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2023,35(6):692-703. (宋丽娜, 铁占鹏. 非对称中间包常用控流装置冶金效果的数值模拟[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2023,35(6):692-703.SONG L N, TIE Z P. Metallurgical effects of commonly used flow control devices in asymmetric tundish[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2023, 35(6): 692-703. [17] LIU D X, GONG W, ZHU J J, et al. Numerical simulation optimization of flow field in slab tundish using flow control device[J]. Continuous Casting, 2023(2):10-18. (刘东旭, 龚伟, 朱江江, 等. 控流装置对板坯中间包流场的数值模拟优化[J]. 连铸, 2023(2):10-18.LIU D X, GONG W, ZHU J J, et al. Numerical simulation optimization of flow field in slab tundish using flow control device[J]. Continuous Casting, 2023(2): 10-18. [18] TACKE K-H, LUDWIG J C. Steel flow and inclusion separation in continuous casting tundishes[J]. Steel Research, 1987,58(6):262-270. doi: 10.1002/srin.198700877 [19] LI M W, LI Y H, DONG C. Numerical simulation of the effect of flow holes on the behavior of fluid in tundish[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020,30(6):55-62. (李茂旺, 李怡宏, 董超. 流钢孔对中间包流体行为影响的数值模拟[J]. 中国冶金, 2020,30(6):55-62.LI M W, LI Y H, DONG C. Numerical simulation of the effect of flow holes on the behavior of fluid in tundish[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020, 30(6): 55-62. [20] ZHANG S J, ZHU M Y. Water model study of removal mechanism of inclusion in continuous casting tundish[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2007,43(9):1004-1008. (张胜军, 朱苗勇. 连铸中间包夹杂物去除机理的水模型研究[J]. 金属学报, 2007,43(9):1004-1008. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2007.09.019ZHANG S J, ZHU M Y. Water model study of removal mechanism of inclusion in continuous casting tundish[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2007, 43(9): 1004-1008. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2007.09.019 [21] LI N, BAO Y P, LIN L, et al. Study on the influence of slag retaining wall on flow field in slab continuous casting tundish[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014,35(3):83-87. (李宁, 包燕平, 林路, 等. 挡渣墙对板坯连铸中间包流场的影响研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014,35(3):83-87. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.03.018LI N, BAO Y P, LIN L, et al. Study on the influence of slag retaining wall on flow field in slab continuous casting tundish[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014, 35(3): 83-87. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.03.018 [22] PATIL S P, VISWANATHAN N N. Numerical investigation of single-strand slab casting tundish flow with heat transfer and inclusion transport[J]. Trans Indian Inst Met, 2021,74(2):369-379. doi: 10.1007/s12666-020-02129-x [23] SAHAI Y, AHUJA R. Fluid flow and mixing of melt in steelmaking tundishes[J]. Ironmak Steelmak, 1986,13(5):241-247. [24] ZHU H H, WANG M, YAO C, et al. Numerical simulation of inclusion removal behavior in six strand T-type tundish[J]. China Metallurgy, 2022,32(8):89-97. (祝航航, 王敏, 姚骋, 等. 六流T型中间包夹杂物去除行为的数值模拟[J]. 中国冶金, 2022,32(8):89-97.ZHU H H, WANG M, YAO C, et al. Numerical simulation of inclusion removal behavior in six strand T-type tundish[J]. China Metallurgy, 2022, 32(8): 89-97. [25] MADIAS J, MARTIN D, FERREYRA M, et al. Design and plant experience using an advanced pouring box to receive and distribute the steel in a six strand tundish[J]. ISIJ Int, 1999,39(8):787-794. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.39.787 [26] MORALES R, LOPEZ S, PALAFOX J, et al. Numerical and modeling analysis of fluid flow and heat transfer of liquid steel in a tundish with different flow control devices[J]. ISIJ Int, 1999,39(5):455-462. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.39.455 [27] ZHANG L, HUANG Y W, YANG S B, et al. Water model experimental study on turbulence controller of continuous casting tundish[J]. Iron & Steel, 2002(12):17-18. (张立, 黄耀文, 杨时标, 等. 连铸中间包湍流控制器水模实验研究[J]. 钢铁, 2002(12):17-18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2002.12.005ZHANG L, HUANG Y W, YANG S B, et al. Water model experimental study on turbulence controller of continuous casting tundish[J]. Iron & Steel, 2002(12): 17-18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2002.12.005 [28] MERDER T, PIEPRZYCA J. Optimization of two-strand industrial tundish work with use of turbulence inhibitors: physical and numerical modeling[J]. Steel Research International, 2012,83(11):1029-1038. doi: 10.1002/srin.201200059 [29] WANG L, YANG J, LIU Y B. Numerical investigation for effects of polydisperse argon bubbles on molten steel flow and liquid slag entrapment in a slab continuous casting mold[J]. Metall Mater Trans B, 2022,53(6):3707-3721. doi: 10.1007/s11663-022-02634-y [30] WANG G, YUN M, ZHANG C, et al. Flow mechanism of molten steel in a single-strand slab caster tundish based on the residence time distribution curve and data[J]. ISIJ Int, 2015,55(5):984-992. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.55.984 [31] FANG Q, ZHANG H, WANG J, et al. Effect of electromagnetic stirrer position on mold metallurgical behavior in a continuously cast bloom[J]. Metall Mater Trans B, 2020,51(4):1705-1717. doi: 10.1007/s11663-020-01849-1 -




 下载:
下载: