Construction of constitutive model for GH4169 alloy under high temperature and high strain rate
-
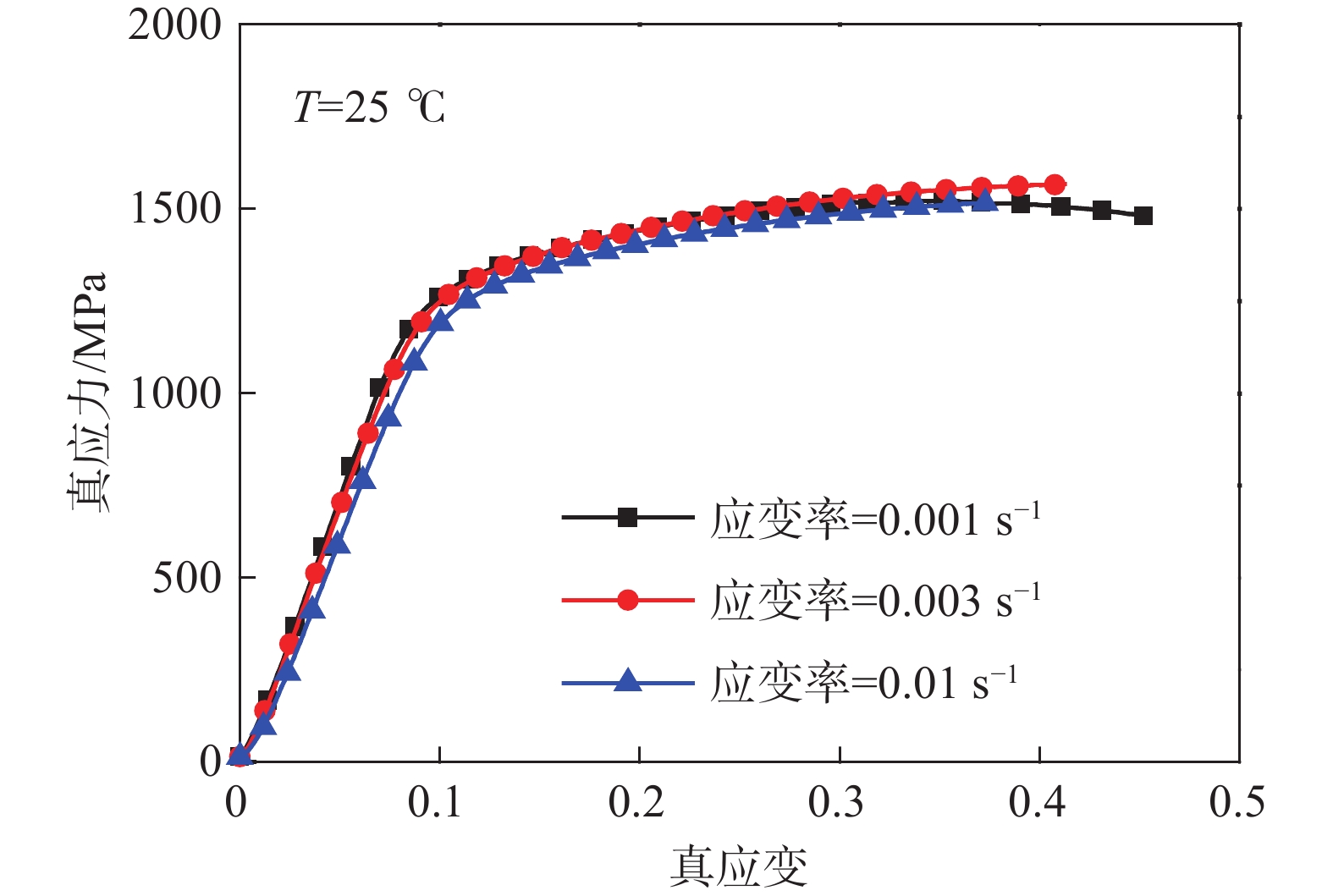
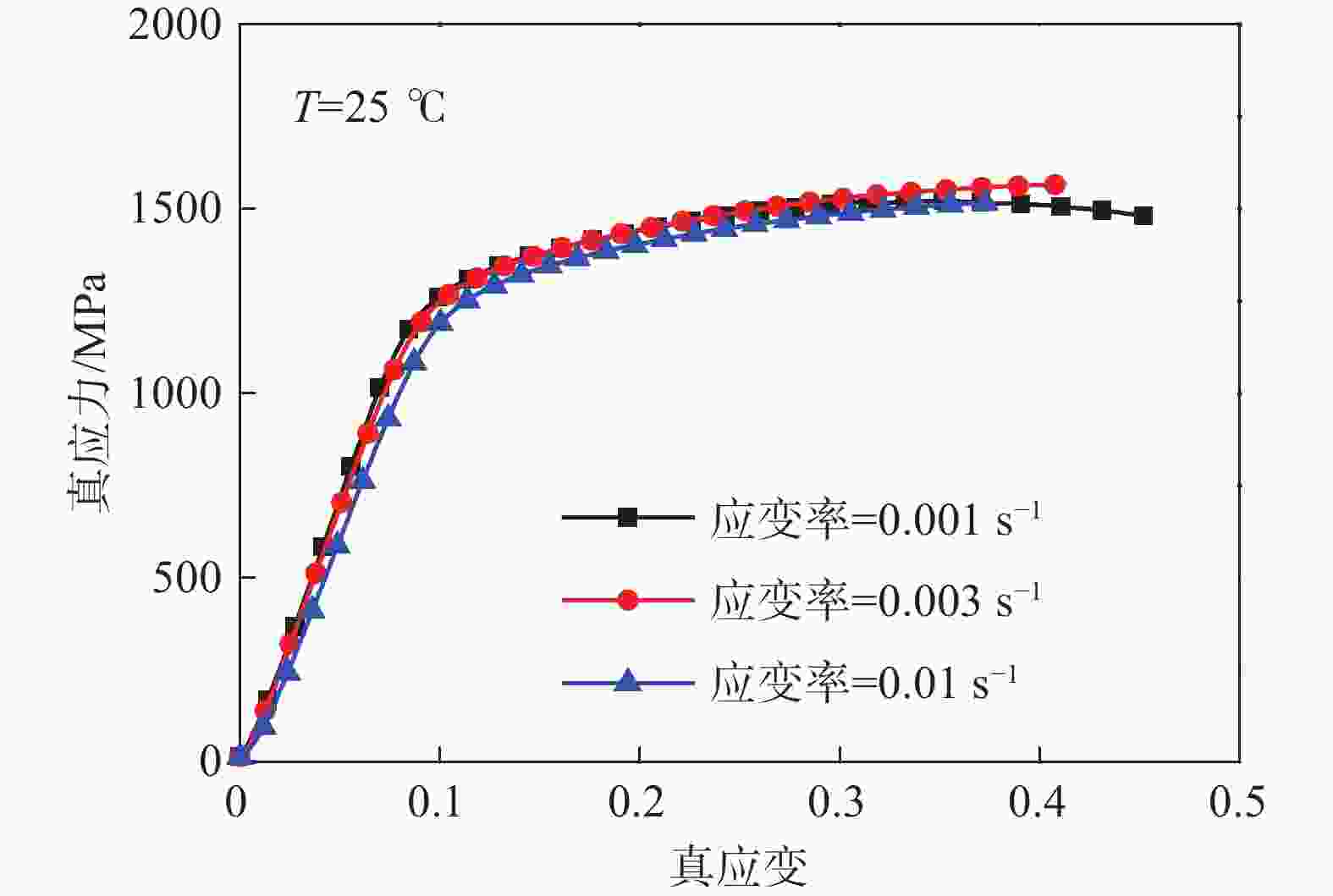
摘要: 利用万能试验机(UTM5305)和霍普金森动态试验装置(ALT
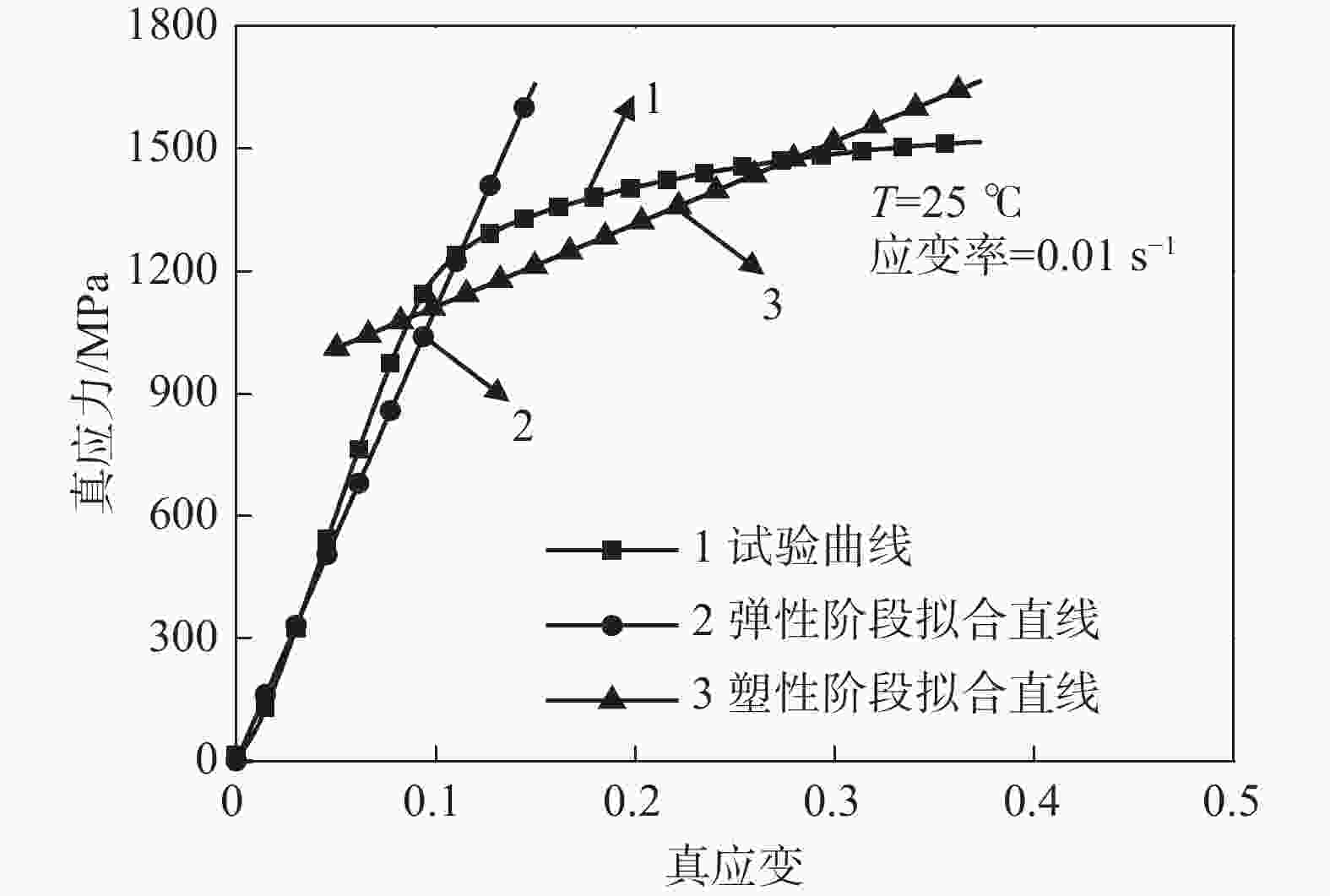
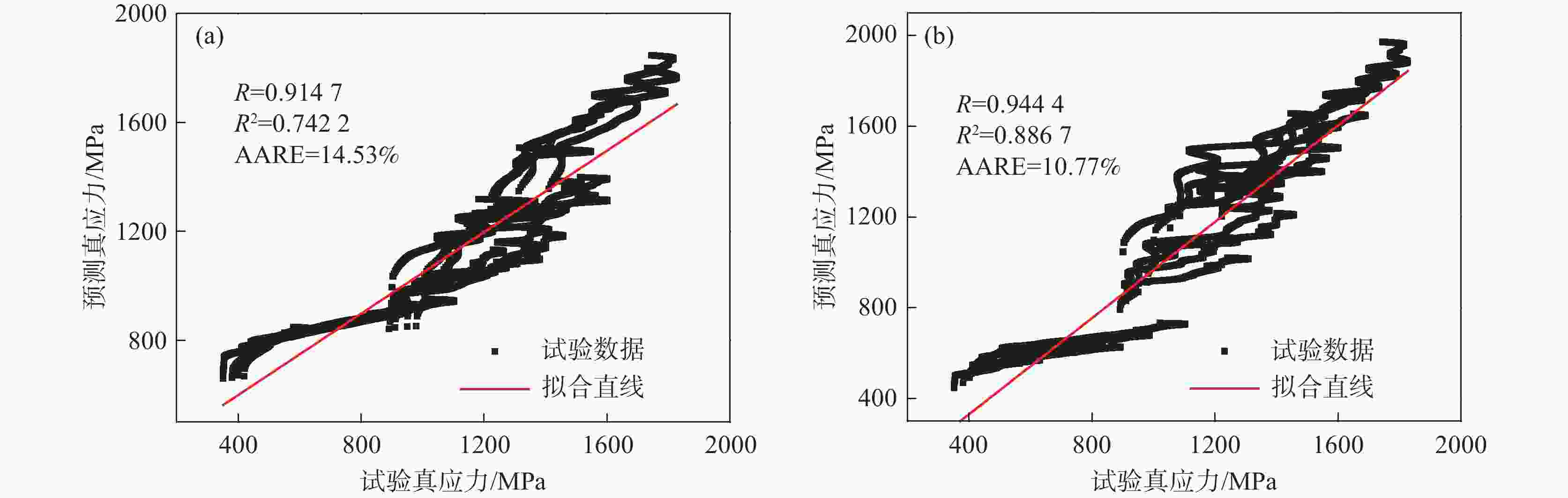
1000 )对GH4169合金分别进行准静态压缩试验和动态冲击试验,获得常温下应变率为0.001、0.003、0.1 s−1的准静态试验数据;以及温度为25、600、750、900 ℃和应变率为1500 、2500 、3500 、4500 s−1的动态试验数据,构建了Johnson-Cook(JC)本构模型及其修正模型。研究显示,材料的塑性硬化、热软化和速率敏感性都得到了体现,尤其在温度升至900 ℃时,软化效应尤为突出;原始JC本构方程的相关系数(r)为0.9147 ,决定系数(R2)为0.7422 ,平均相对误差(AARE)为14.53%,修正后的JC本构方程相关系数(r)提高至0.9444 ,决定系数(R2)提高至0.8867 ,平均相对误差(AARE)下降至10.77%,相较原始JC本构模型在预测精度和可靠性方面有显著提升,能够可靠正确描述材料的应力-应变行为。Abstract: The quasi-static compression test and dynamic impact test of GH4169 alloy were carried out by universal testing machine (UTM5305) and Hopkinson dynamic testing device (ALT 1000), respectively. The quasi-static test data of strain rates of 0.001, 0.003 and 0.1 s–1 at room temperature were obtained. The Johnson-Cook (JC) constitutive model and its modified model were constructed from the dynamic test data at temperatures of 25, 600, 750, 900 ℃ and strain rates of1500 ,2500 ,3500 ,4500 s–1. The result shows that the plastic hardening, thermal softening and rate sensitivity of the material happen, especially when the temperature rises to 900 degrees Celsius, the softening effect is particularly prominent. The correlation coefficient (r) of the original JC constitutive equation is0.9147 , the coefficient of determination (R2) is0.7422 , and the average relative error (AARE) is 14.53%. The revised JC constitutive equation correlation coefficient (r) is increased to0.9444 , and the coefficient of determination (R2) is increased to0.8867 . The average relative error (AARE) is reduced to 10.77%, which significantly improves the prediction accuracy and reliability compared with the original JC constitutive model, and can be used to predicate the stress-strain behavior of materials.-
Key words:
- GH4169 alloy /
- modified constitutive model /
- high temperature /
- high strain rate /
- prediction accuracy
-
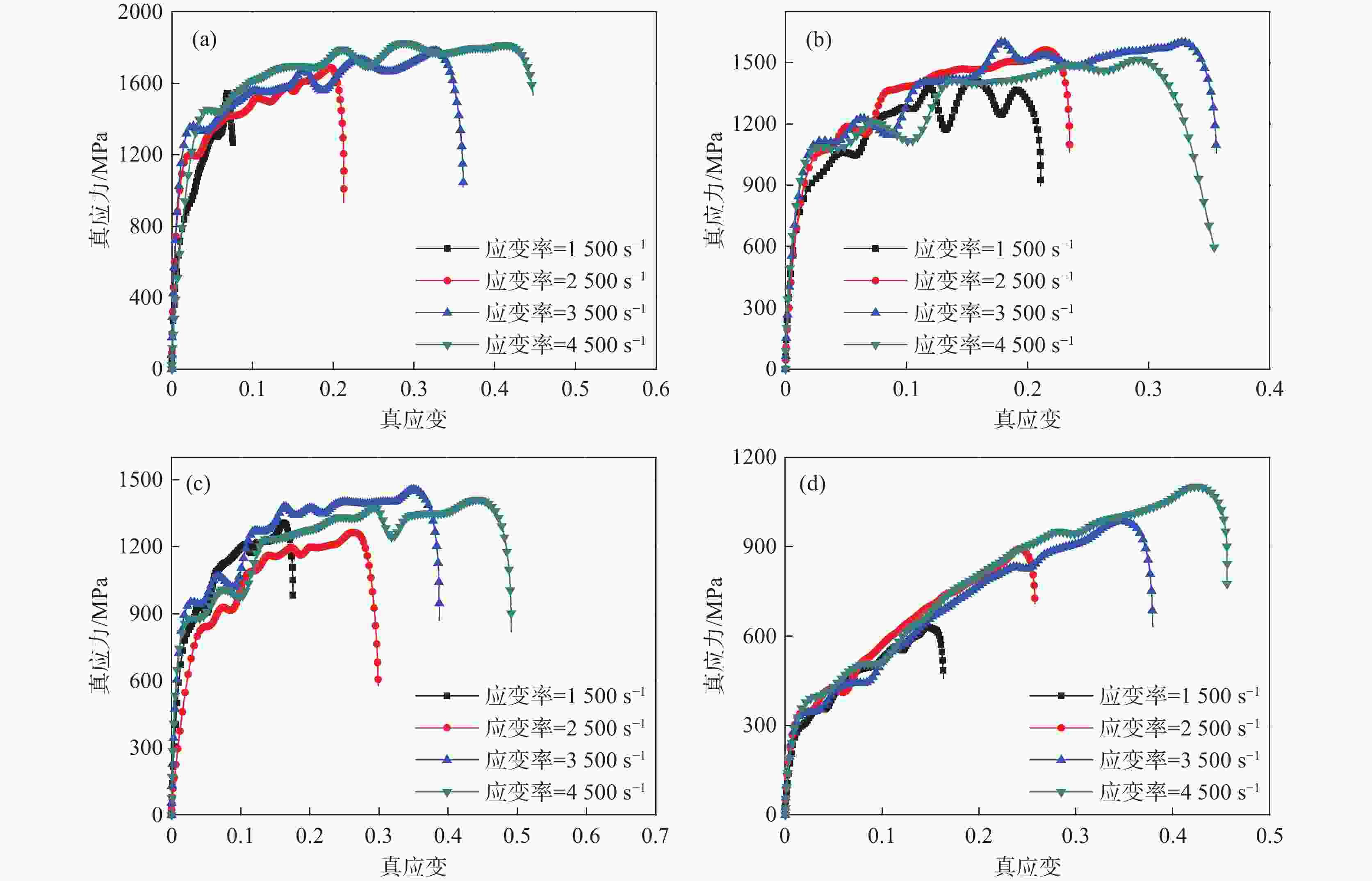
图 3 高温合金GH4169
1500 、2500 、3500 、4500 s−1的真应力-应变曲线(a) $ \dot{\varepsilon}=1\ 500\text{ }\text{s}^{-1} $; (b) $ \dot{\varepsilon}=2\ 500\text{ }\text{s}^{-1} $; (c) $ \dot{\varepsilon}=3\ 500\text{ }\text{s}^{-1} $ ; (d) $ \dot{\varepsilon}=4\ 500\text{ }\text{s}^{-1} $
Figure 3. True stress-strain curves for high-temperature alloy GH4169 under different strain rates
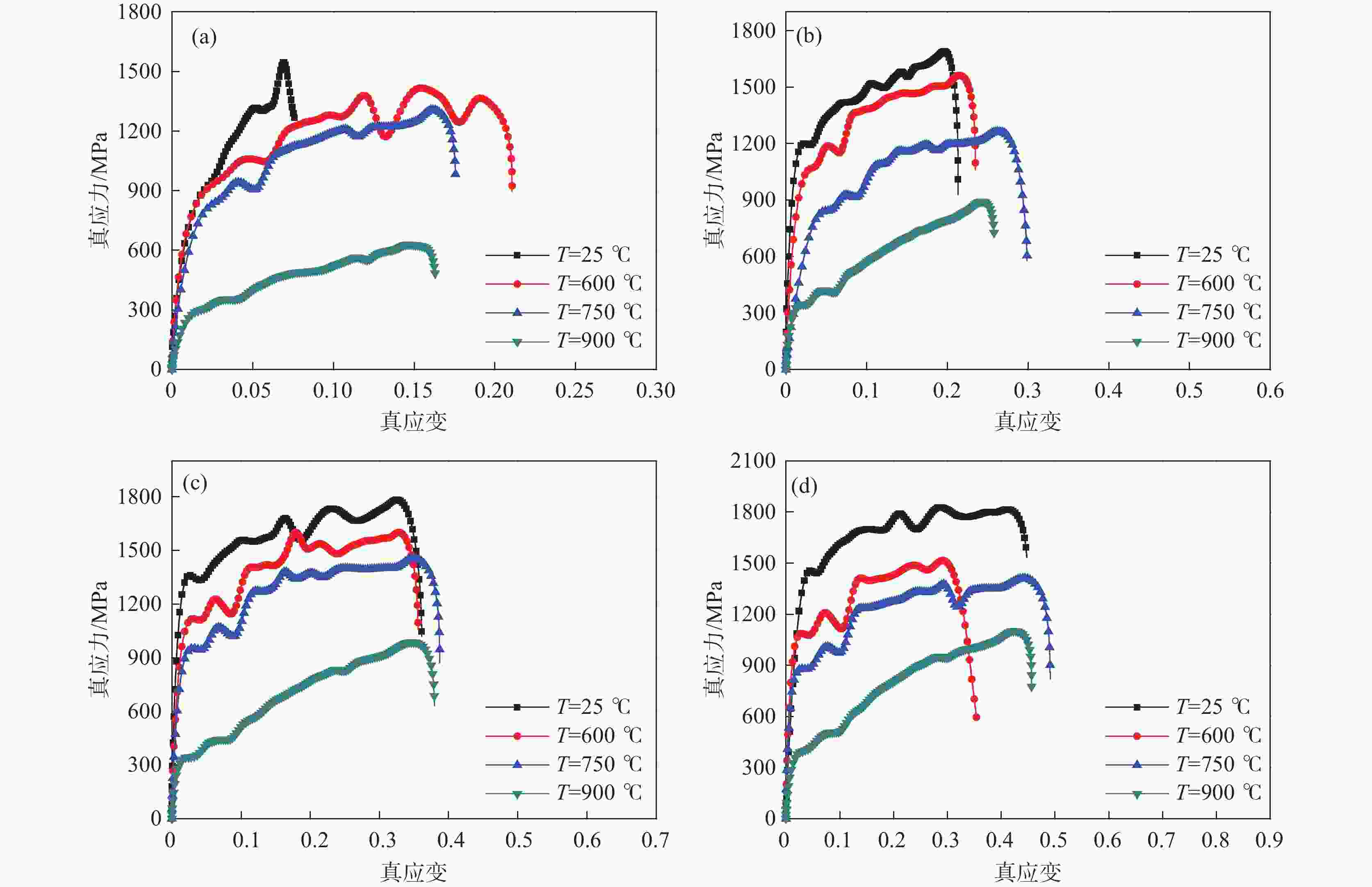
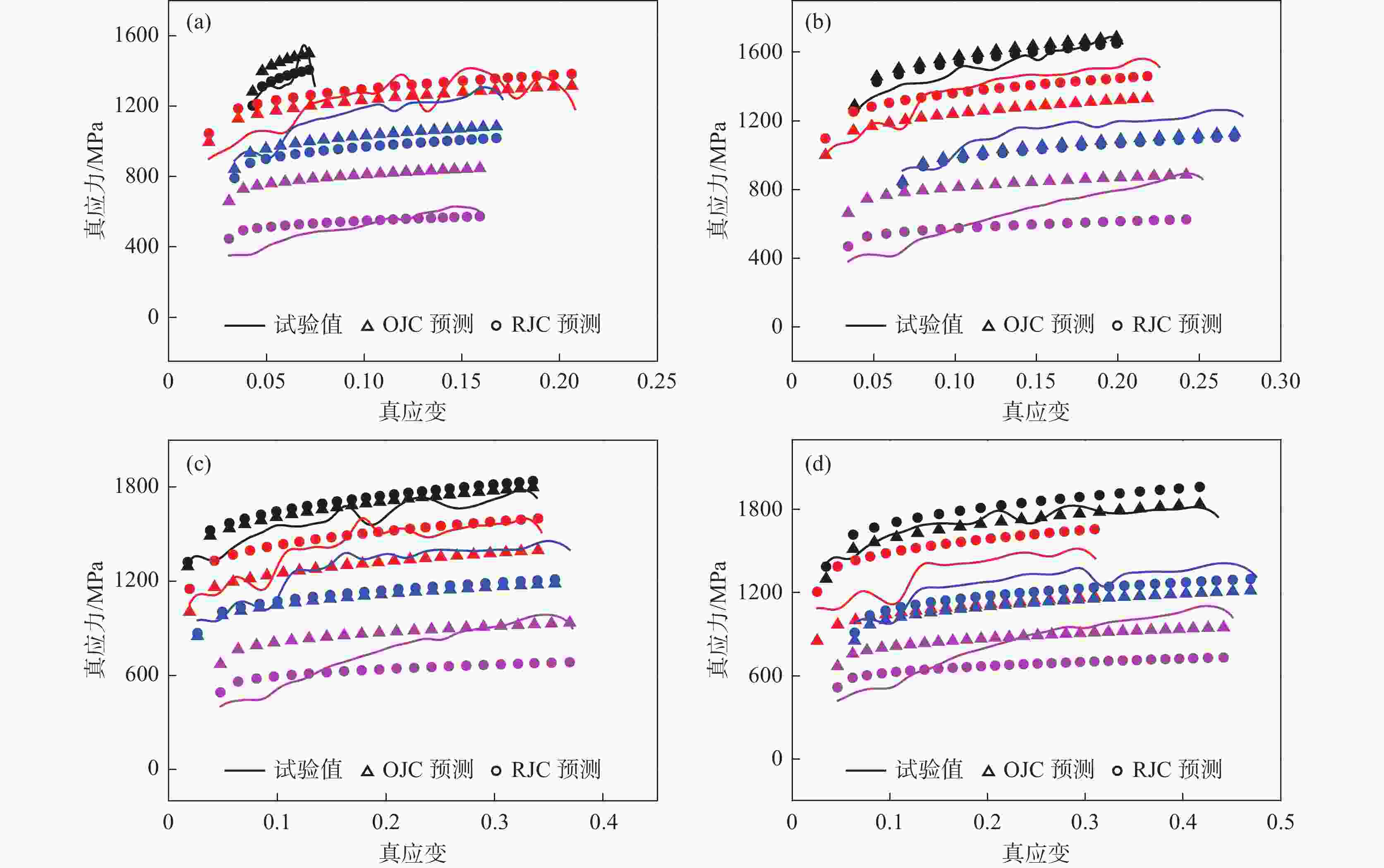
图 8 两种本构模型的真应力预测和试验值比较
黑色:25℃;红色:600℃;蓝色:750℃;紫色:900℃(a)$ \dot{\varepsilon}=1\ 500\text{ }\text{s}^{-1} $ ; (b) $ \dot{\varepsilon}=2\ 500\text{ }\text{s}^{-1} $;(c) $ \dot{\varepsilon}=3\ 500\text{ }\text{s}^{-1} $ ; (d) $ \dot{\varepsilon}=4\ 500\text{ }\text{s}^{-1} $
Figure 8. Comparison of true stress predictions and experimental values for two constitutive models
表 1 25、600、750、900 ℃下GH4169合金材料不同应变率时的屈服强度
Table 1. Yield strength of GH4169 alloy at different strain rates at 25, 600, 750 and 900 ℃
温度/℃ 应变率/s−1 屈服强
度/MPa塑性流动
段应变失效
应变失效应
力/MPa25 1500 1221.30 0.0747 0.0761 1263.98 2500 1240.02 0.2028 0.2130 931.75 3500 1305.97 0.3390 0.3611 1020.32 4500 1404.72 0.4357 0.4475 1535.05 600 1500 900.83 0.2079 0.2106 898.18 2500 1000.46 0.2254 0.2345 1062.14 3500 1054.44 0.3434 0.3557 1058.25 4500 1085.02 0.3101 0.3541 595.29 750 1500 891.21 0.1709 0.1756 974.66 2500 910.31 0.2765 0.2987 579.53 3500 950.69 0.3693 0.3868 872.06 4500 979.47 0.4749 0.4910 820.53 900 1500 350.86 0.1605 0.1632 458.72 2500 380.28 0.2519 0.2578 708.53 3500 401.32 0.3718 0.3793 632.80 4500 420.20 0.4506 0.4560 766.36 表 2 不同应变率下加工硬化参数(25、600、750、900 ℃下)
Table 2. Work hardening parameters at different strain rates for temperatures of 25, 600, 750, and 900 ℃
温度/℃ k n 1500 s−12500 s−13500 s−14500 s−11500 s−12500 s−13500 s−14500 s−125 3289 1327 1098 862 0.78 0.61 0.70 0.61 600 1655 1920 1386 2536 0.67 0.70 0.71 1.20 750 2430 2131 2207 1153 0.84 0.99 1.05 0.84 900 4622 2188 1 918 1769 1.24 0.93 0.94 0.88 表 3 GH4169合金传动J-C本构模型参数C的值
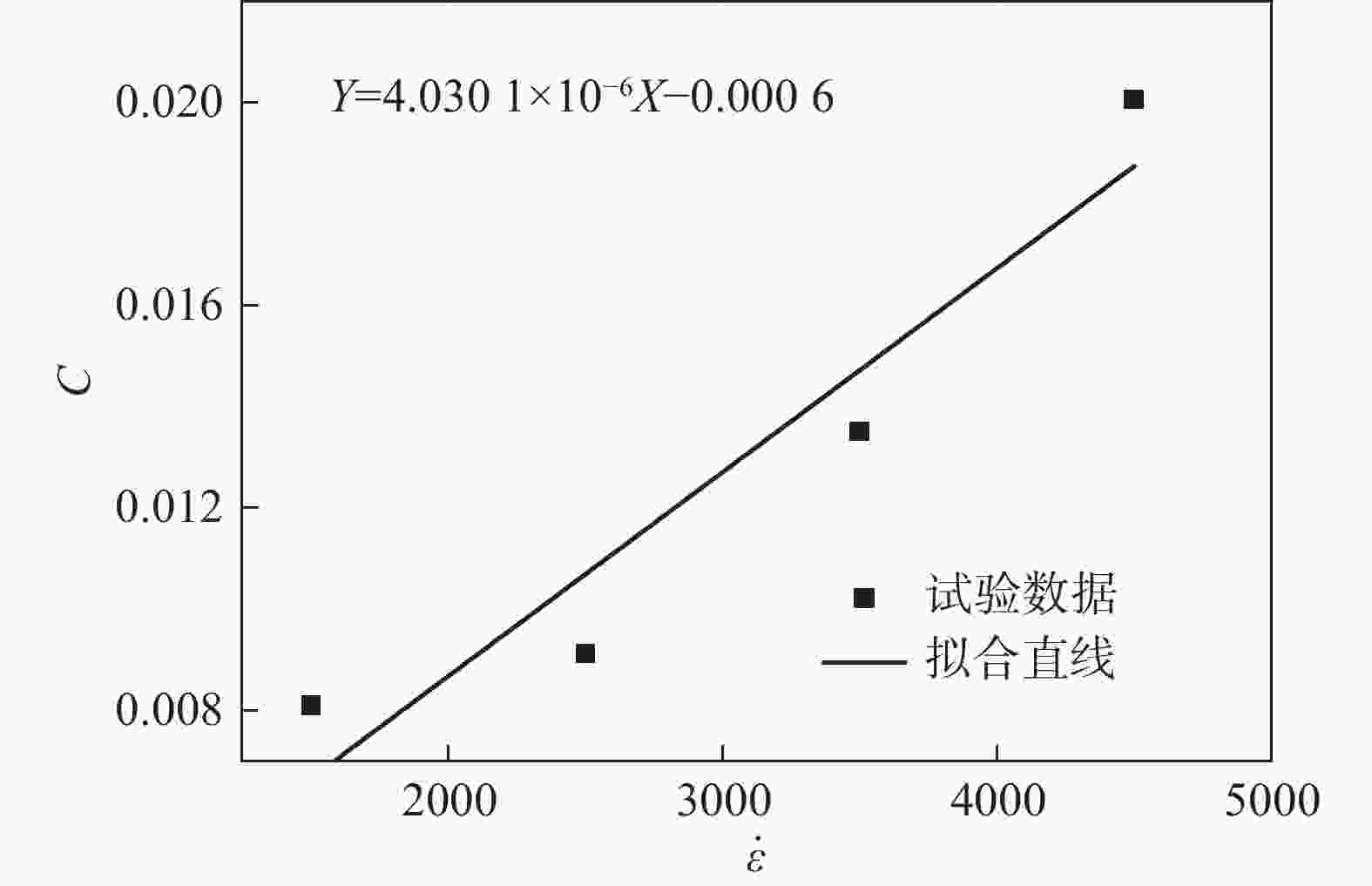
Table 3. Values of parameter C of the J-C constitutive model of GH4169 alloy transmission
$ T $/℃ 应变率$ \dot \varepsilon $/s−1 屈服强度$ \sigma $/MPa 参数$ C $值 参数$ C $平均值 25 1500 1175.10 0.0081 0.0127 2500 1305.08 0.0091 3500 1471.96 0.0135 4500 1618.27 0.0201 表 4 GH4169合金传动J-C本构模型参数m的值
Table 4. Values of parameter m of the J-C constitutive model of GH4169 alloy transmission
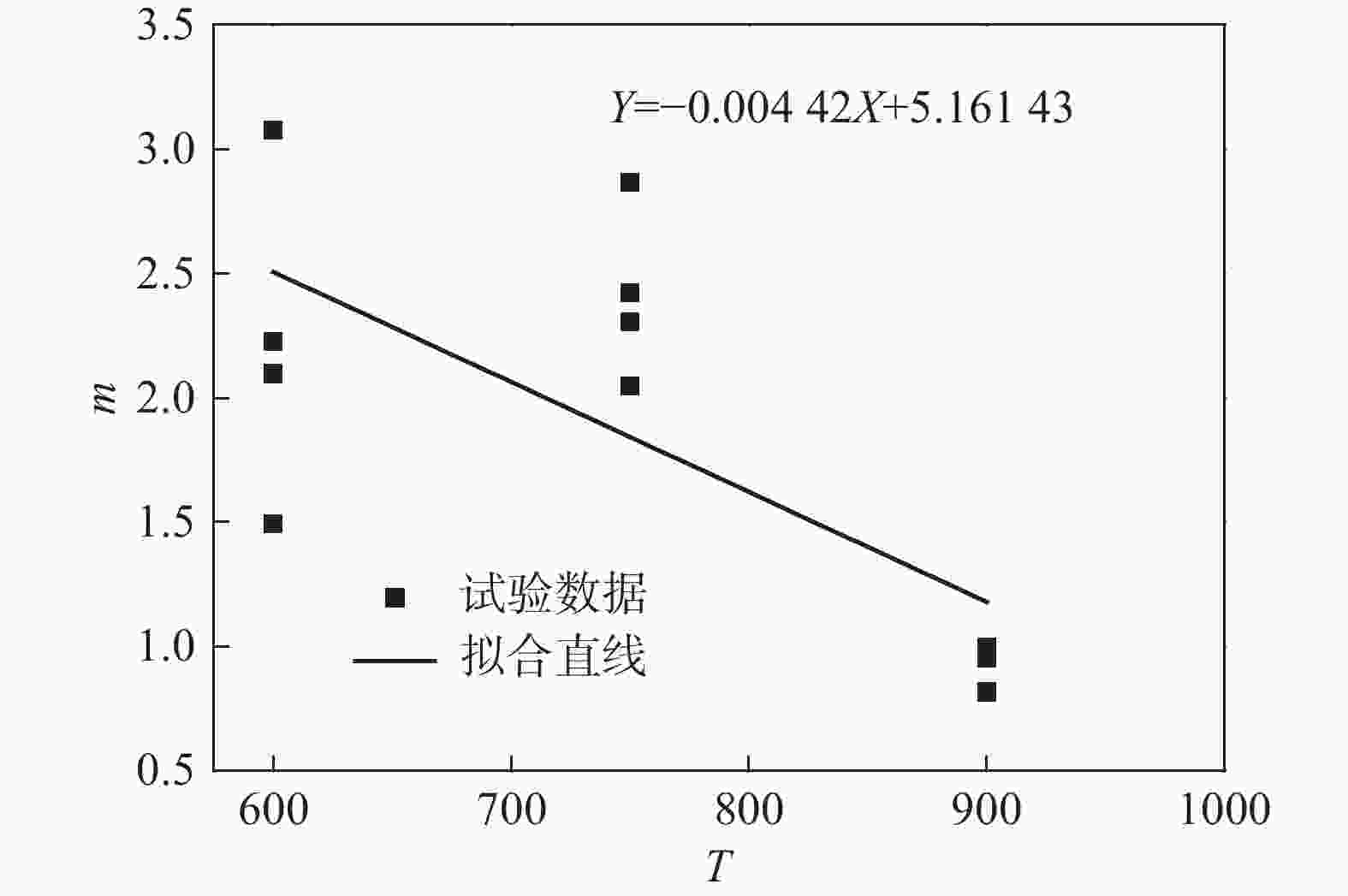
应变率$ \dot \varepsilon $/s−1 温度$ T $/℃ 屈服应力$ \sigma $/MPa 参数$ m $值 参数$ m $平均值 1500 600 900.83 1.4931 1.8429 750 891.21 2.0468 900 350.86 0.8153 2500 600 1054.43 2.0961 750 950.69 2.3037 900 401.32 0.9510 3500 600 1187.94 3.0772 750 1048.92 2.8663 900 355.53 0.8192 4500 600 1085.02 2.2265 750 979.47 2.4221 900 420.20 0.9978 表 5 GH4169合金的修正J-C本构模型参数值
Table 5. Parameters of modified J-C constitutive model for GH4169 alloy
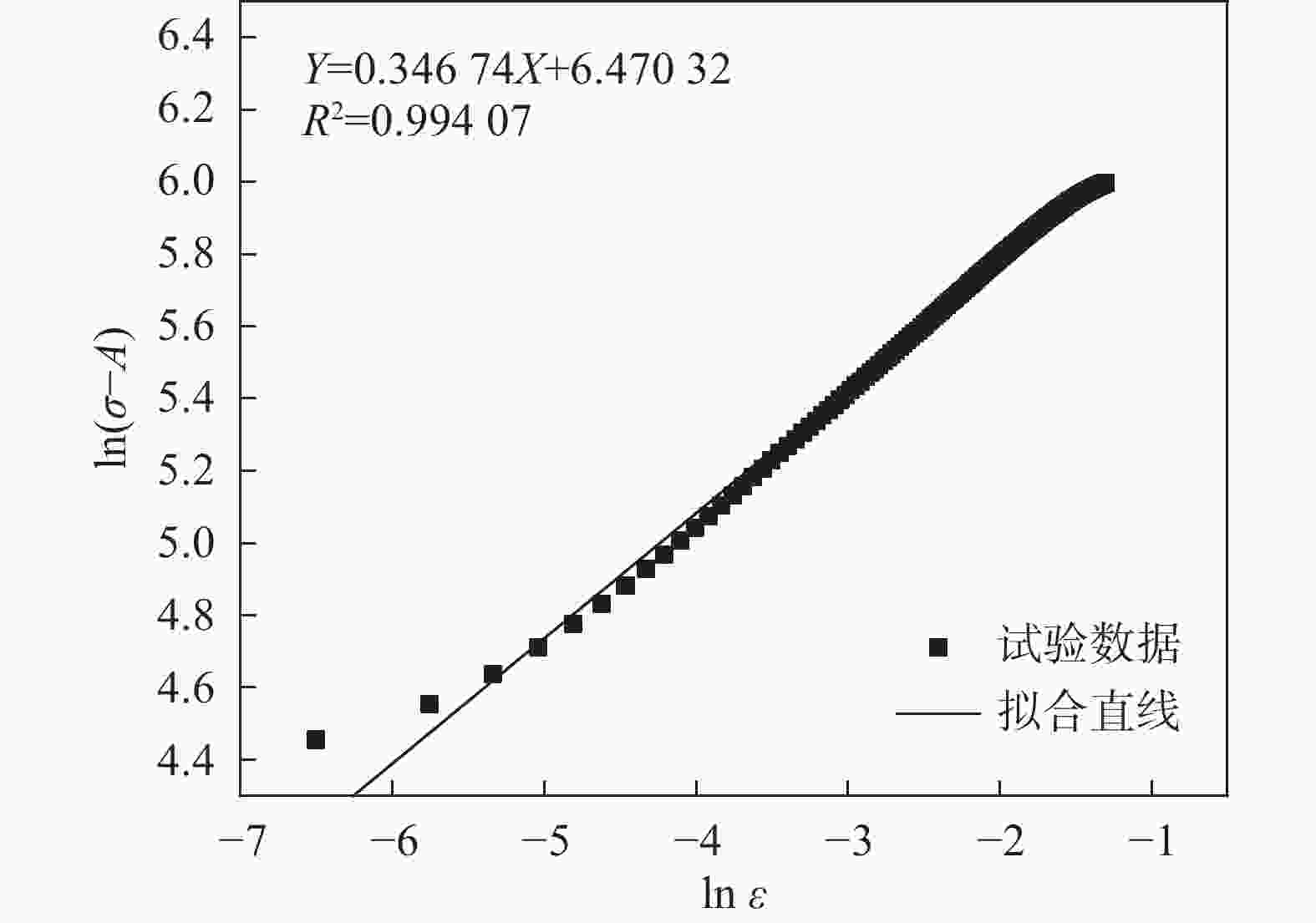
$ A $/MPa $ B $/MPa $ n $ $ {C_1} $ $ {C_2} $ $ {m_1} $ $ {m_2} $ 1113.84 645.69 0.34674 − 0.0006 4.0301 ×10−65.16143 − 0.00442 -
[1] WU H, KONG X W, LUO P. Constitutive equation for high-temperature deformation of GH4169 alloy[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2020(8):163-167. (吴昊, 孔祥伟, 罗平. GH4169合金高温变形过程本构方程[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2020(8):163-167.WU H, KONG X W, LUO P. Constitutive equation for high-temperature deformation of GH4169 alloy[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2020(8): 163-167. [2] LIU X, YAN H S, KONG Z K, et al. Dynamic mechanical behavior and constitutive relationship of superalloy GH4169[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2019,43(1):75-81. (刘晓, 闫欢松, 孔祖开, 等. GH4169高温合金的动态力学行为及其本构关系[J]. 机械工程材料, 2019,43(1):75-81. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl201901016LIU X, YAN H S, KONG Z K, et al. Dynamic mechanical behavior and constitutive relationship of superalloy GH4169[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 43(1): 75-81. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl201901016 [3] WANG T, CHEN G D, JU J T. Experimental study of constitutive relationship of superalloy GH4169 under high strain rates[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013,34(4):946-953. (王涛, 陈国定, 巨江涛. GH4169高温合金高应变率本构关系试验研究[J]. 航空学报, 2013,34(4):946-953. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2013.0155WANG T, CHEN G D, JU J T. Experimental study of constitutive relationship of superalloy GH4169 under high strain rates[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013, 34(4): 946-953. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2013.0155 [4] HU W. Experiment and simulation of dynamic mechanical properties of GH4169 alloy under high strain rate impact loading based on SHPB[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University of Technology, 2021. (胡伟. 基于SHPB高应变率冲击加载下的GH4169合金动态力学性能实验与仿真[D]. 重庆: 重庆理工大学, 2021.HU W. Experiment and simulation of dynamic mechanical properties of GH4169 alloy under high strain rate impact loading based on SHPB[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University of Technology, 2021. [5] WANG X Y. Study on cutting performance evaluation and constitutive model of superalloy GH4169[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2016. (王相宇. 高温合金GH4169的切削加工性评价方法和本构模型研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2016.WANG X Y. Study on cutting performance evaluation and constitutive model of superalloy GH4169[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2016. [6] ZHANG B, YUE L, CHEN H F, et al. Hot deformation behavior of as-cast GH4169 alloy and comparison of three constitutive models[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2021,50(1):212-222. (张兵, 岳磊, 陈韩锋, 等. 铸态GH4169合金热变形行为及三种本构模型对比[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2021,50(1):212-222.ZHANG B, YUE L, CHEN H F, et al. Hot deformation behavior of as-cast GH4169 alloy and comparison of three constitutive models[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2021, 50(1): 212-222. [7] GU Y C. Study on the constitutive model of GH4169 alloy under high temperature and high strain rate based on genetic algorithm and neural network[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University of Technology, 2022. (古愉川. 基于遗传算法与神经网络的高温高应变率下GH4169本构模型研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆理工大学, 2022.GU Y C. Study on the constitutive model of GH4169 alloy under high temperature and high strain rate based on genetic algorithm and neural network[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University of Technology, 2022. [8] ZOU P. Research on dynamic constitutive model at high temperatures and high speed impact performance of GH4169[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018. (邹品. GH4169高温动态本构模型与高速冲击性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2018.ZOU P. Research on dynamic constitutive model at high temperatures and high speed impact performance of GH4169[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018. [9] REN Y H, CHENG Z, WANG L X, et al. Constitutive equation for hot deformation and hot processing map of wrought GH4169 superalloy[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2023,15(5):148-155. (任永海, 程治, 王龙祥, 等. 锻态GH4169合金热变形本构方程及热加工图[J]. 精密成形工程, 2023,15(5):148-155.REN Y H, CHENG Z, WANG L X, et al. Constitutive equation for hot deformation and hot processing map of wrought GH4169 superalloy[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2023, 15(5): 148-155. [10] WANG W. Hot deformation behaviour and recrystallization model of GH4169 nickel base superalloy[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2020,44(9):87-91,98. (王稳. GH4169镍基高温合金的热变形行为与再结晶模型[J]. 机械工程材料, 2020,44(9):87-91,98.WANG W. Hot deformation behaviour and recrystallization model of GH4169 nickel base superalloy[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 44(9): 87-91,98. [11] LUO P. Dynamic recrystallization simulation of GH4169 alloy during thermal deformation[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2014. (罗平. GH4169合金热变形动态再结晶模拟[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2014.LUO P. Dynamic recrystallization simulation of GH4169 alloy during thermal deformation[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2014. [12] CHEN G, WANG Q Q, DU H J. Experimental study on dynamic mechanical properties of S500MC steel[J]. Railway Quality Control, 2019,47(5):27-30. (陈刚, 王青权, 杜洪军. S500MC钢动态力学性能试验研究[J]. 铁道技术监督, 2019,47(5):27-30.CHEN G, WANG Q Q, DU H J. Experimental study on dynamic mechanical properties of S500MC steel[J]. Railway Quality Control, 2019, 47(5): 27-30. [13] ZHANG R J. Study on dynamic mechanical behaviors of GH4169 nickel based superalloy[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016. (张锐杰. GH4169镍基高温合金动态力学性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京理工大学, 2016.ZHANG R J. Study on dynamic mechanical behaviors of GH4169 nickel based superalloy[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016. [14] HAN R R. Research on deforming properties of superalloy GH4169[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2014. (韩蕊蕊. GH4169高温合金的成型性能研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2013.HAN R R. Research on deforming properties of superalloy GH4169[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2014. [15] BAO W P, ZHAO Y Z, LI C M, et al. Experimental research on the dynamic constitutive relation of pure iron at elevated temperatures and high strain rates[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010,46(4):74-79. (包卫平, 赵昱臻, 李春明, 等. 纯铁高温高应变率下的动态本构关系试验研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2010,46(4):74-79. doi: 10.3901/JME.2010.04.074BAO W P, ZHAO Y Z, LI C M, et al. Experimental research on the dynamic constitutive relation of pure iron at elevated temperatures and high strain rates[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 46(4): 74-79. doi: 10.3901/JME.2010.04.074 [16] MA B, LI P, LIANG Q. Comparison on high temperature flow behavior of HNi55-7-4-2 alloy predicted by modified JC model and BP-ANN algorithm[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2021,45(1):92-99. (马斌, 李平, 梁强. 基于修正JC模型和BP-ANN算法预测HNi55-7-4-2合金高温流变行为的对比[J]. 机械工程材料, 2021,45(1):92-99.MA B, LI P, LIANG Q. Comparison on high temperature flow behavior of HNi55-7-4-2 alloy predicted by modified JC model and BP-ANN algorithm[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 45(1): 92-99. [17] KHAN A S, HUANG S. Experimental and theoretical study of mechanical behavior of 1100 aluminum in the strain rate range 10−5−104s−1[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 1992,8:397-424. doi: 10.1016/0749-6419(92)90057-J [18] JOHNSONG R, COOK W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures[C]//Proc. 7Int. Symp. Ballistics, 1983: 541-547. [19] JOHNSONG R, HOEGFELDTJM, LINDHOLM U S, et al. Response of various metals o large torsional strains over a large range of strain rates. part 1: ductile metals[J]. Trans. ASME, J. Eng. Mat. Tech. , 1983, 105: 42-47. [20] GUO P C, LI J, CAO S F, et al. Deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of an AM80 magnesium alloy at large strain rate range[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(3): 586-595. (郭鹏程, 李健, 曹淑芬, 等. 大应变率范围内AM80镁合金的变形行为及组织演变[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 38(3): 586-595.GUO P C, LI J, CAO S F, et al. Deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of an AM80 magnesium alloy at large strain rate range[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2018, 38(3): 586-595. [21] QIAN X Y, PENG X B, SONG Y T, et al. Dynamic constitutive relationship of CuCrZr alloy based on Johnson-Cook model[J]. Nuclear Materials and Energy, 2020,24(8):100768-100774. [22] ZHANG J L, ZHANG Y M, LUO W C, et al. Establishment of a constitutive model of aviation stainless steel 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb considering the coupling effects of strain, strain rate and temperature[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023,44(6):149-159. (张继林, 张又铭, 罗文翠, 等. 考虑应变、应变率和温度耦合作用下航空不锈钢0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb本构模型的建立[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023,44(6):149-159.ZHANG J L, ZHANG Y M, LUO W C, et al. Establishment of a constitutive model of aviation stainless steel 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb considering the coupling effects of strain, strain rate and temperature[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(6): 149-159. [23] XU T P, WANG L L, LU W X. The thermo-viscoplasticity and adiabatic shear deformation for a titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V under high strain rates[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1987(1):1-8. (徐天平, 王礼立, 卢维娴. 高应变率下钛合金Ti-6Al-4V的热-粘塑性特性和绝热剪切变形[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 1987(1):1-8.XU T P, WANG L L, LU W X. The thermo-viscoplasticity and adiabatic shear deformation for a titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V under high strain rates[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 1987(1): 1-8. [24] NIU D X, ZHAO C, LI D X, et al. Constitutive modeling of the flow stress behavior for the hot deformation of Cu-15Ni-8Sn alloys[J]. Frontiers in Materials, 2022,7(12):577867. [25] LI Z H, HUANG L, BAN Y J, et al. Research on flow stress and constitutive equation for GH4698 alloy[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2024,49(3):207-218. (李中豪, 黄亮, 班宜杰, 等. GH4698 合金流动应力及本构方程研究[J]. 锻压技术, 2024,49(3):207-218.LI Z H, HUANG L, BAN Y J, et al. Research on flow stress and constitutive equation for GH4698 alloy[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2024, 49(3): 207-218. [26] SU N, CHEN M H, XIE L S, et al. Dynamic mechanical characteristics and constitutive model of TC2 Ti-alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2021,35(3):201-208. (苏楠, 陈明和, 谢兰生, 等. TC2钛合金的动态力学特征及其本构模型[J]. 材料研究学报, 2021,35(3):201-208.SU N, CHEN M H, XIE L S, et al. Dynamic mechanical characteristics and constitutive model of TC2 Ti-alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2021, 35(3): 201-208. [27] JIA H S, LUO W C, ZHANG J L, et al. Study on dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of 022Cr18Ni14Mo2 stainless steel under impact load[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(2):178-185. (贾海深, 罗文翠, 张继林, 等. 冲击载荷下022Cr18Ni14Mo2不锈钢动态力学特性及其本构模型研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(2):178-185. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.02.027JIA H S, LUO W C, ZHANG J L, et al. Study on dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive model of 022Cr18Ni14Mo2 stainless steel under impact load[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(2): 178-185. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.02.027 [28] ZHAO L D, ZHANG Y M, ZHANG J L, et al. Research on prediction accuracy of the flow stress of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel based on machine learning[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44 (4): 196-204. (赵礼栋, 张又铭, 张继林, 等. 基于机器学习的0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb不锈钢流变应力预测研究 [J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023, 44 (4): 196-204.ZHAO L D, ZHANG Y M, ZHANG J L, et al. Research on prediction accuracy of the flow stress of 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb stainless steel based on machine learning[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44 (4): 196-204. -




 下载:
下载: