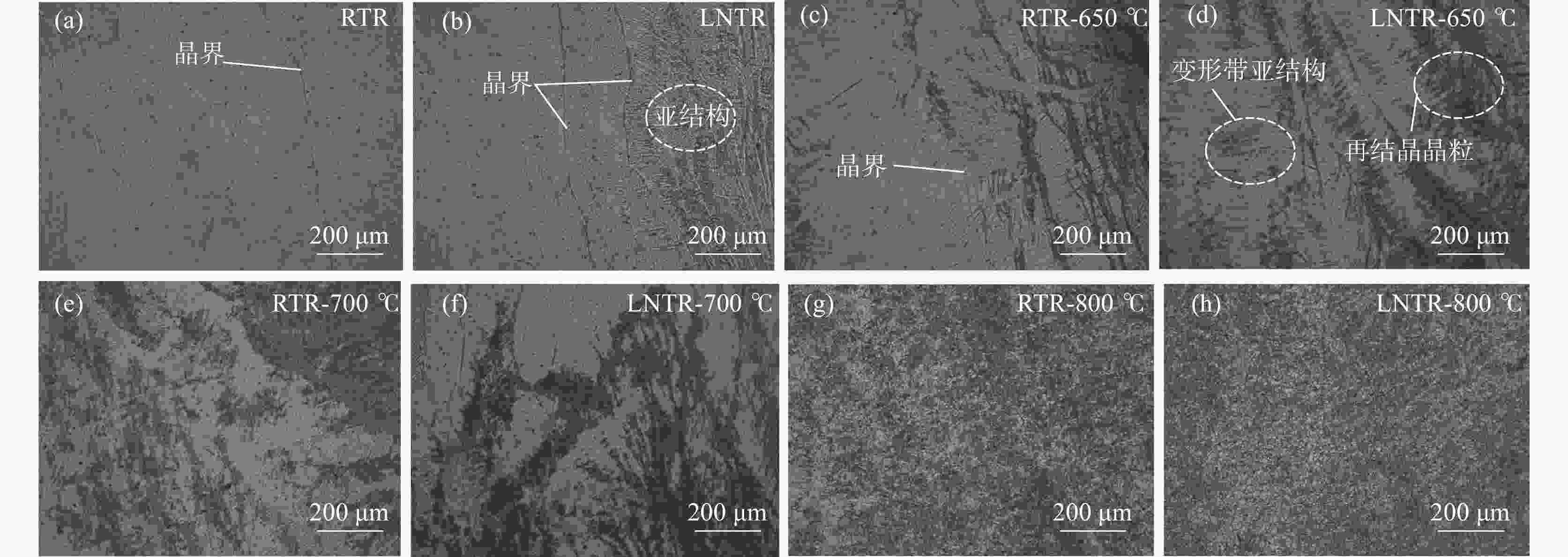
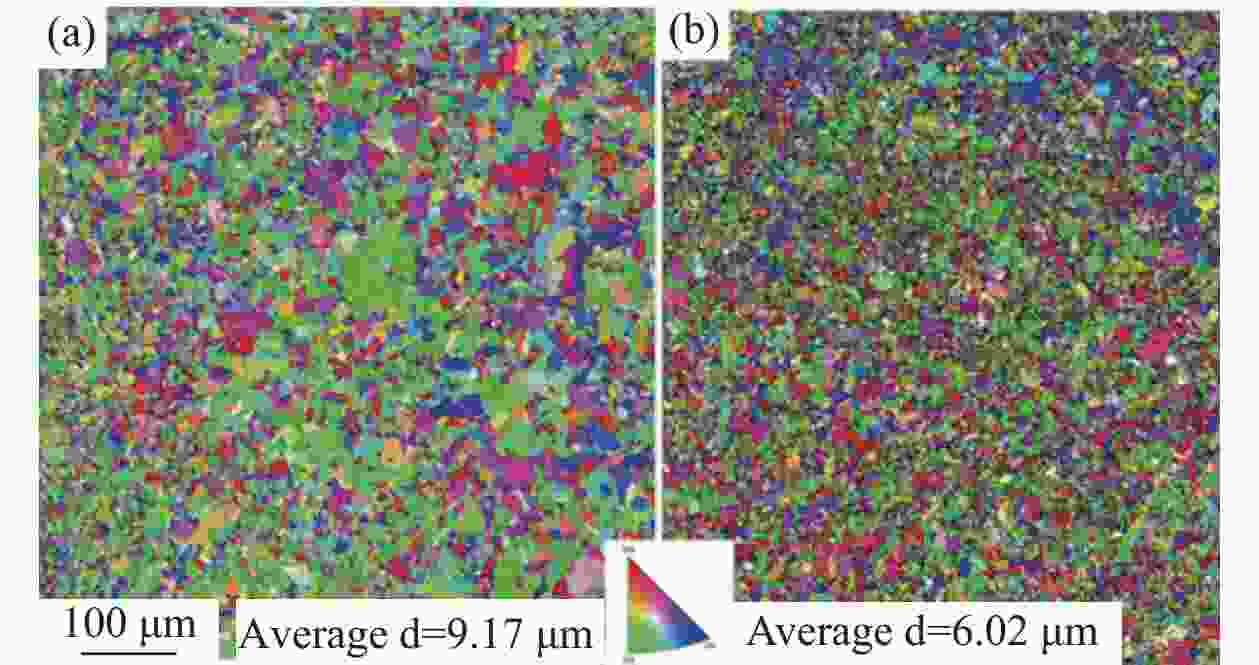
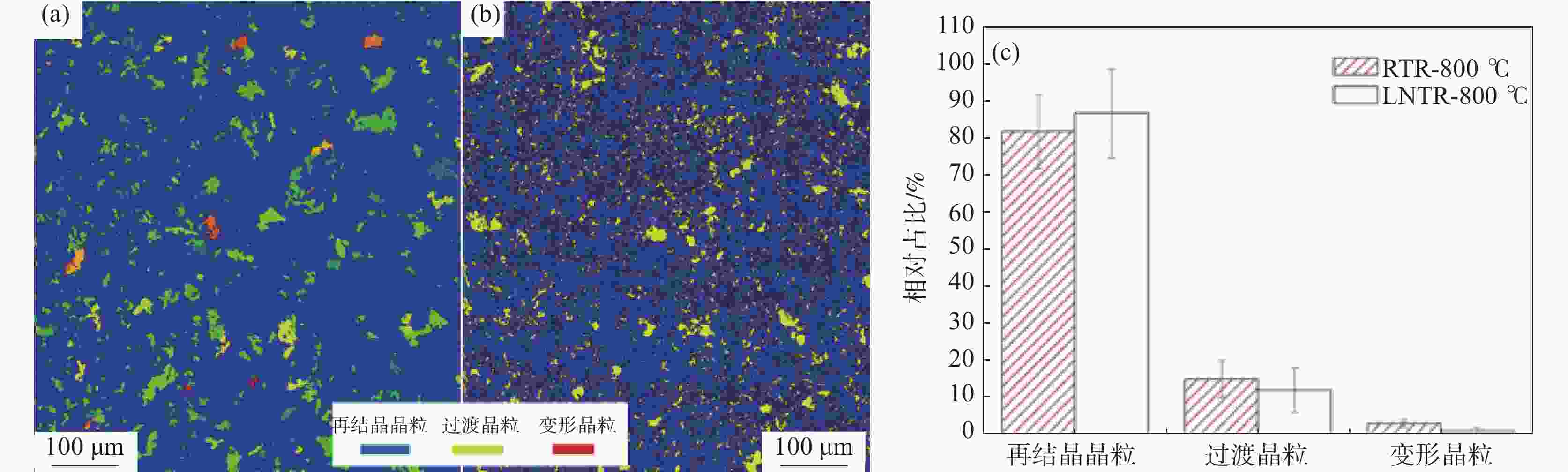
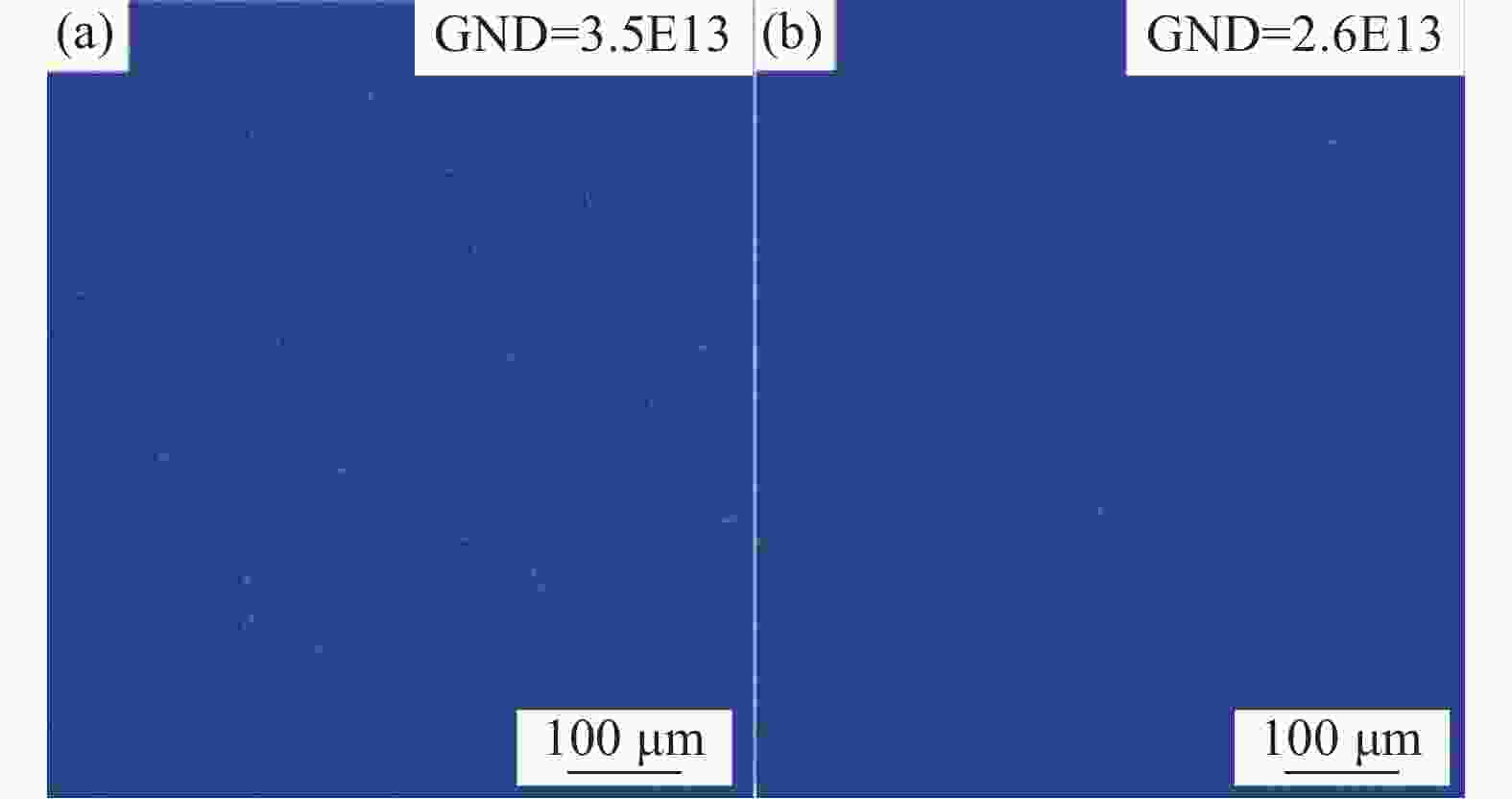
| [1] |
YEH J, CHEN S, LIN S. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004,6:299-303. doi: 10.1002/adem.200300567
|
| [2] |
CANTOR B, CHANG I T H, KNIGHT P. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004,375:213-218.
|
| [3] |
HSU Y J, CHIANG W C, WU J K. Corrosion behavior of FeCoNiCrCux high-entropy alloys in 3.5% sodium chloride solution[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2005,92(1):112-117. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2005.01.001
|
| [4] |
ZHANG W, LIAW P K, ZHANG Y. Science and technology in high-entropy alloys[J]. Science China Materials, 2018,61(1):2-22. doi: 10.1007/s40843-017-9195-8
|
| [5] |
GAO M C, YEH J W, LIAW P K, et al. High-entropy alloys[J]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016.
|
| [6] |
ZHANG Y. High-entropy materials[J]. Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd, 2019,2:215-232.
|
| [7] |
MIAHRA R S, HARIDAS R S, AGRAWAL P. High entropy alloys – tunability of deformation mechanisms through integration of compositional and microstructural domains[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2021,812:141085. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.141085
|
| [8] |
ZHANG Y, ZUO T T, TANG Z, et al. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2014,61:1-93. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.10.001
|
| [9] |
YEH J. Alloy design strategies and future trends in high-entropy alloys[J]. JOM, 2013,65(12):1759-1771. doi: 10.1007/s11837-013-0761-6
|
| [10] |
TSAI K Y, TSAI M H, YEH J W. Sluggish diffusion in Co–Cr–Fe–Mn–Ni high-entropy alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2013,61(13):4887-4897. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2013.04.058
|
| [11] |
SLONE C E, MIAO J, GEORGE E P, et al. Achieving ultra-high strength and ductility in equiatomic CrCoNi with partially recrystallized microstructures[J]. Acta Materialia, 2019,165:496-507. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.12.015
|
| [12] |
WU Z, BEI H, PHARR G M, et al. Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 81: 428.
|
| [13] |
SONG Li Y, WANG Y F, WANG M S, et al. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of CrCoNi medium entropy alloys in 1000 MPa grade[J]. Joural of Aeronautical Materials, 2020,40(4):62-70. (宋凌云, 王艳飞, 王明赛, 等. 1000 MPa级CrCoNi中熵合金的微观组织和力学行为[J]. 航空材料学报, 2020,40(4):62-70.SONG Li Y, WANG Y F, WANG M S, et al. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of CrCoNi medium entropy alloys in 1000 MPa grade[J]. Joural of Aeronautical Materials, 2020, 40(4): 62-70.
|
| [14] |
PRAVEEN S, BAE J W, ASGHARI Rad P, et al. Ultra-high tensile strength nanocrystalline CoCrNi equiatomic medium entropy alloy processed by high-pressure torsion[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018,735:394-397. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.08.079
|
| [15] |
SCHNEIDER M, GEORGE E P, MANESCAU T J, et al. Analysis of strengthening due to grain boundaries and annealing twin boundaries in the CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2020,124:155-169. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2019.08.009
|
| [16] |
LIANG Y, YANG X, MING K. et al. In situ observation of transmission and reflection of dislocations at twin boundary in CoCrNi alloys[J]. Science China Technological Sciences volume, 2021,64:407-413. doi: 10.1007/s11431-019-1517-8
|
| [17] |
LAPLANCHE G, KOSTKA A, REINHART C, et al. Reasons for the superior mechanical properties of medium-entropy CrCoNi compared to high-entropy CrMnFeCoNi[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017,128:292-303. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2017.02.036
|




 下载:
下载: