Effects of ageing treatment on the microstructures and tensile properties of maraging stainless steel
-
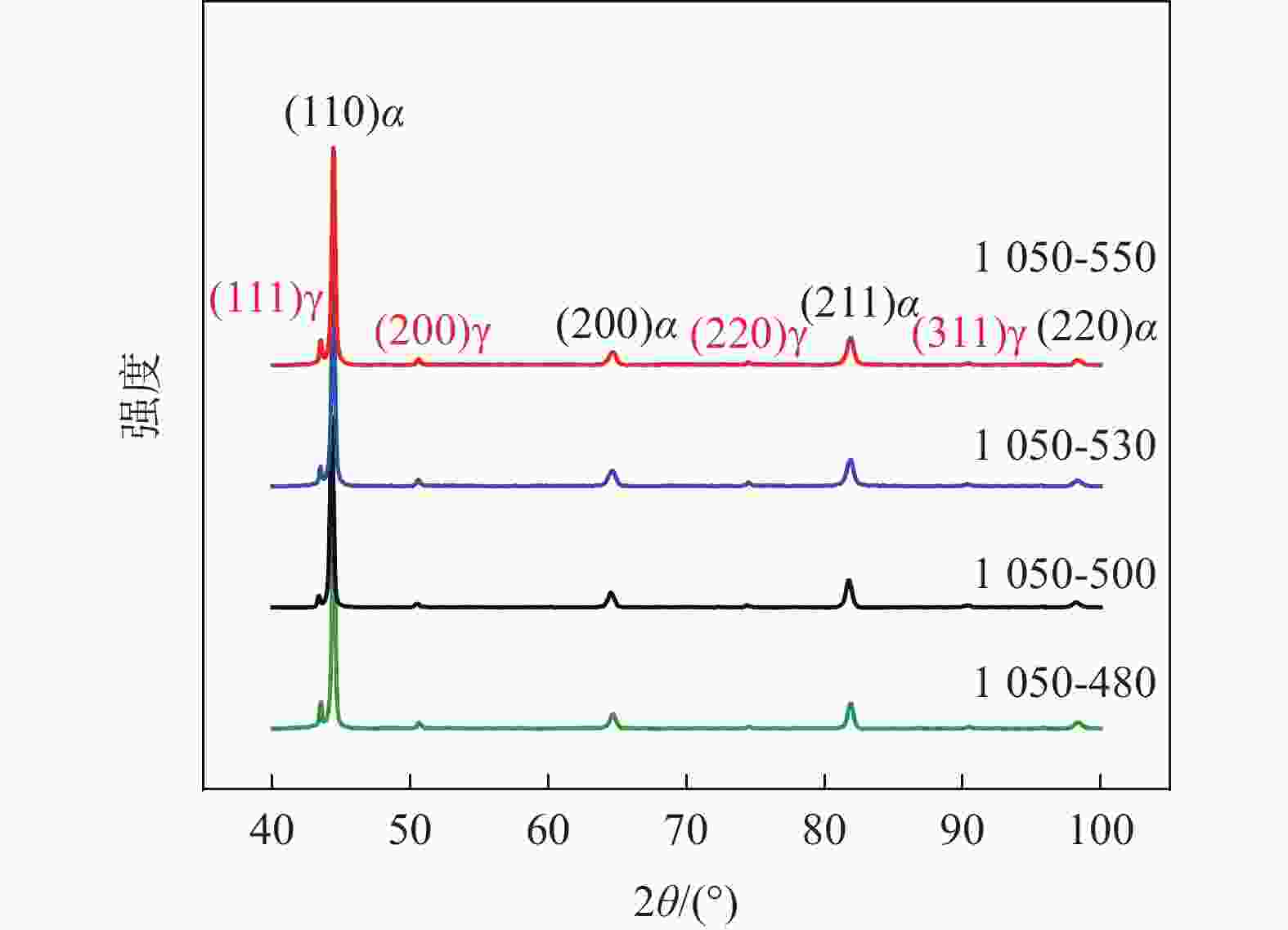
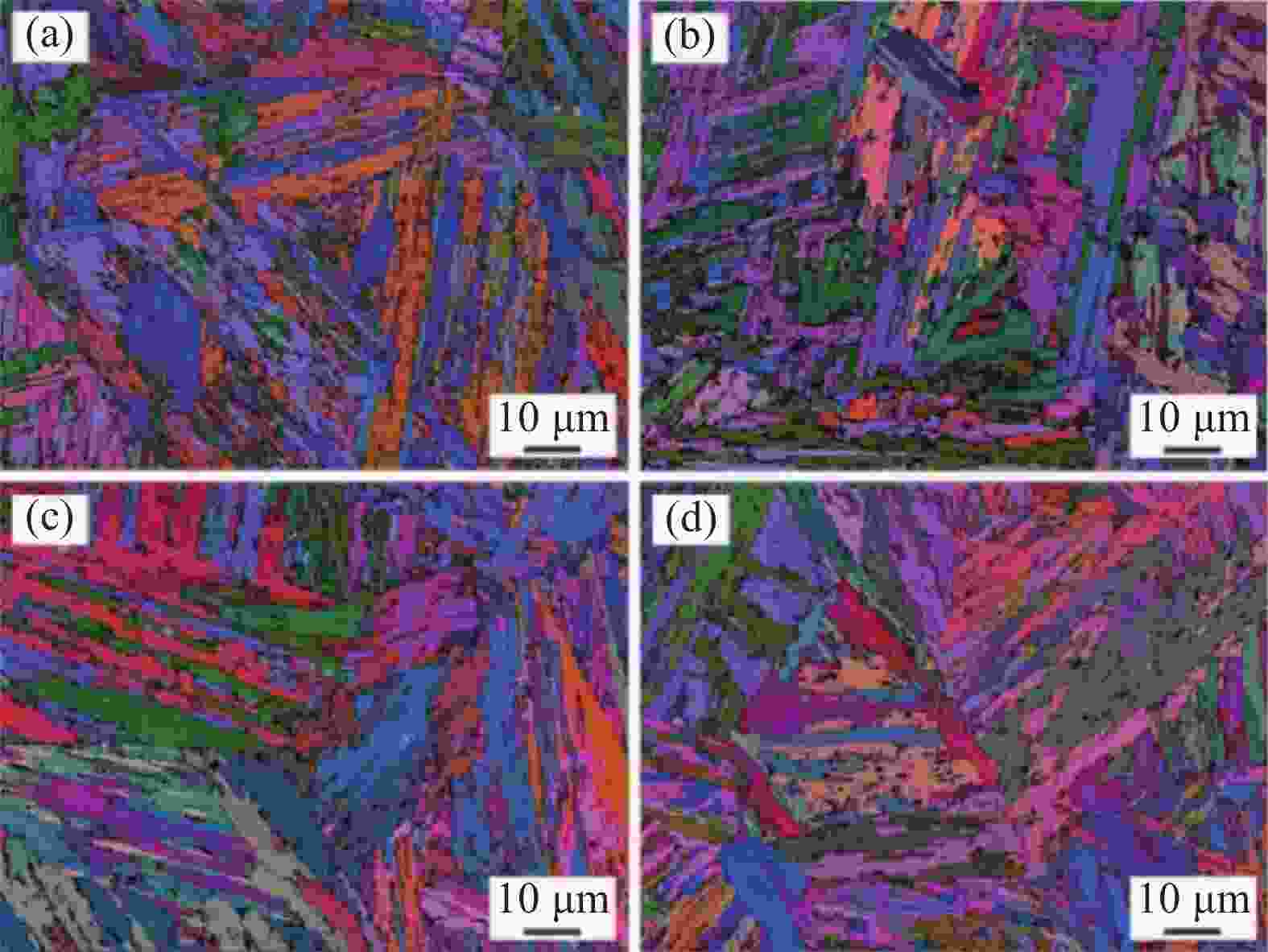
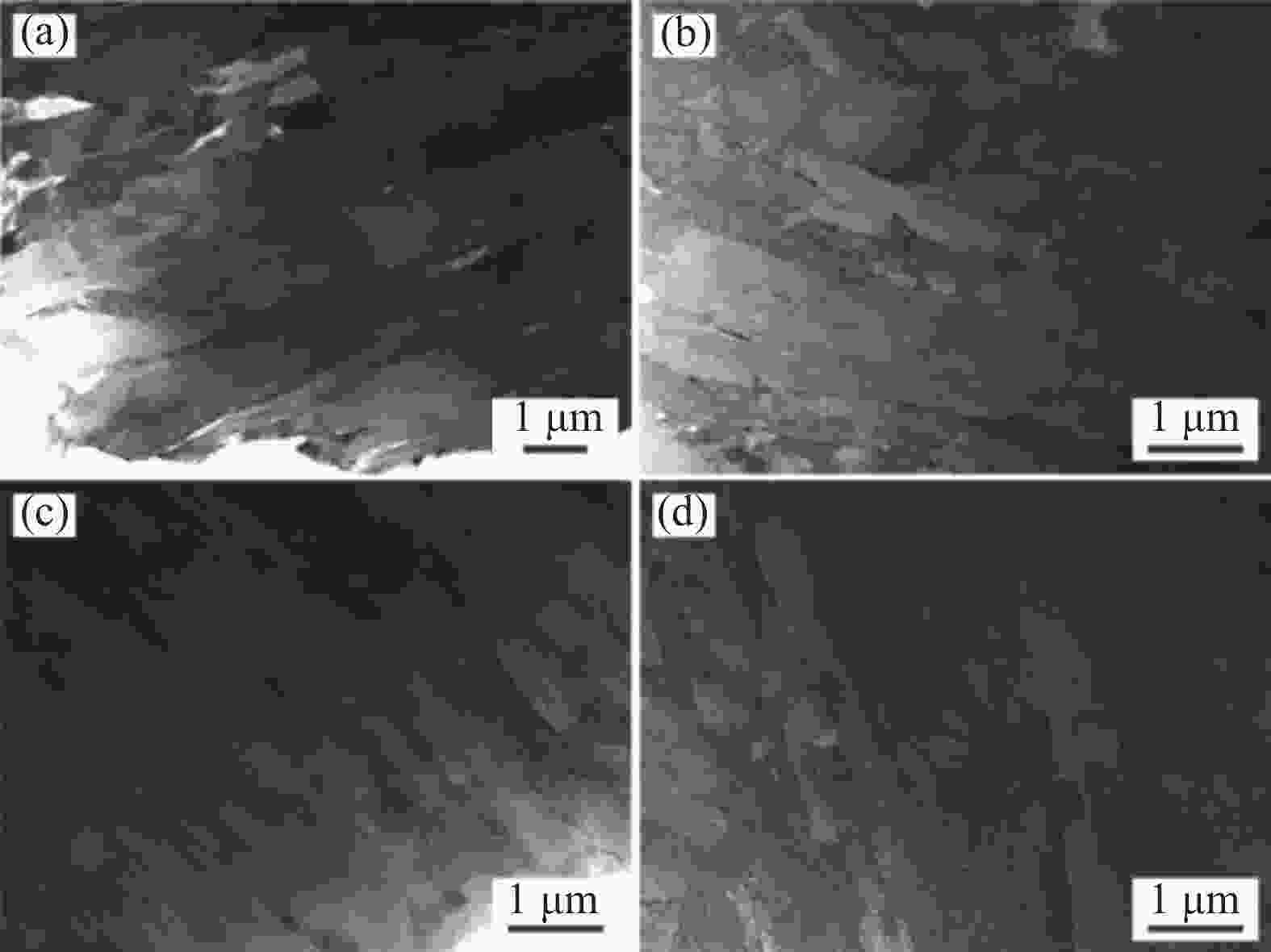
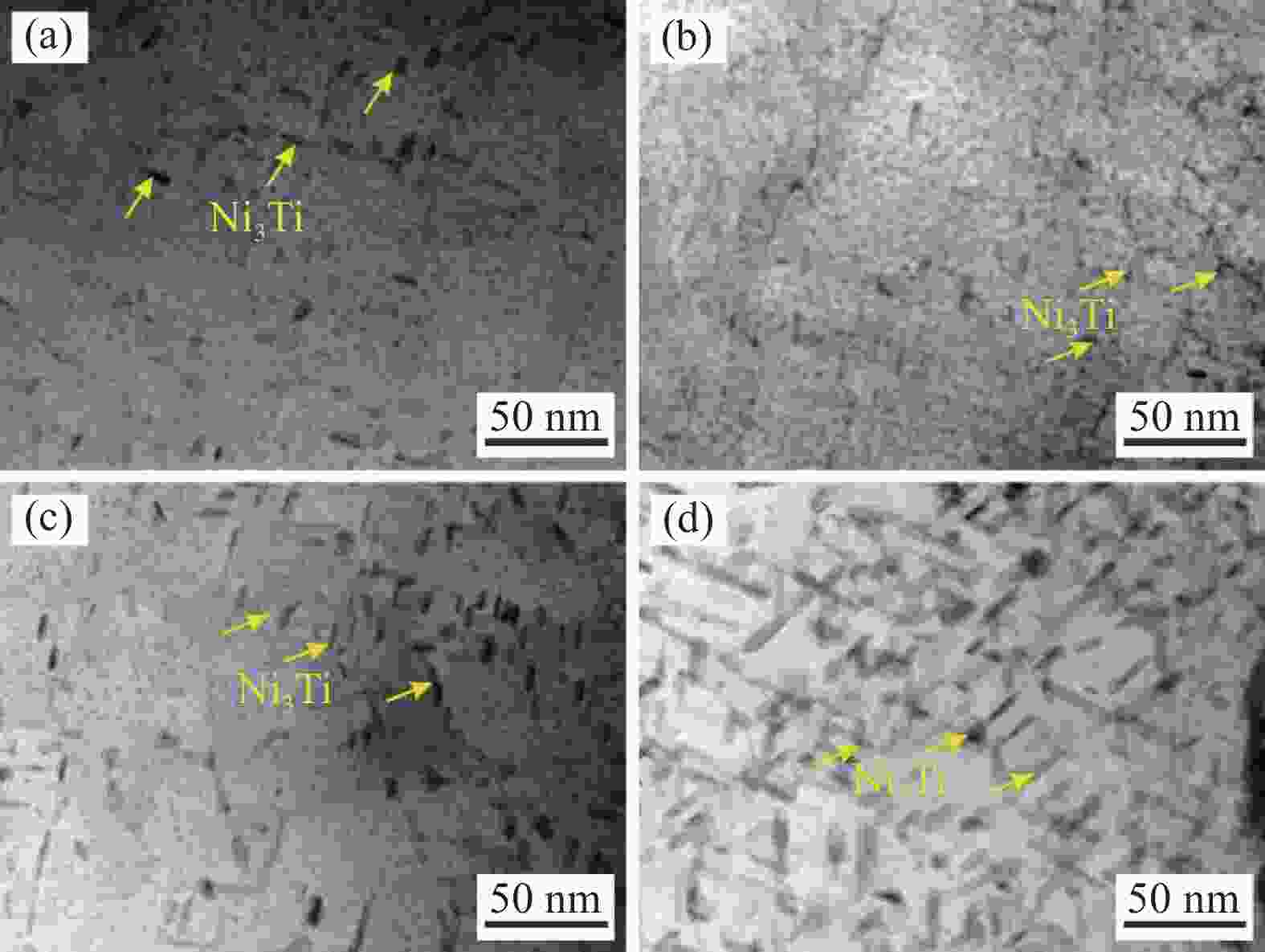
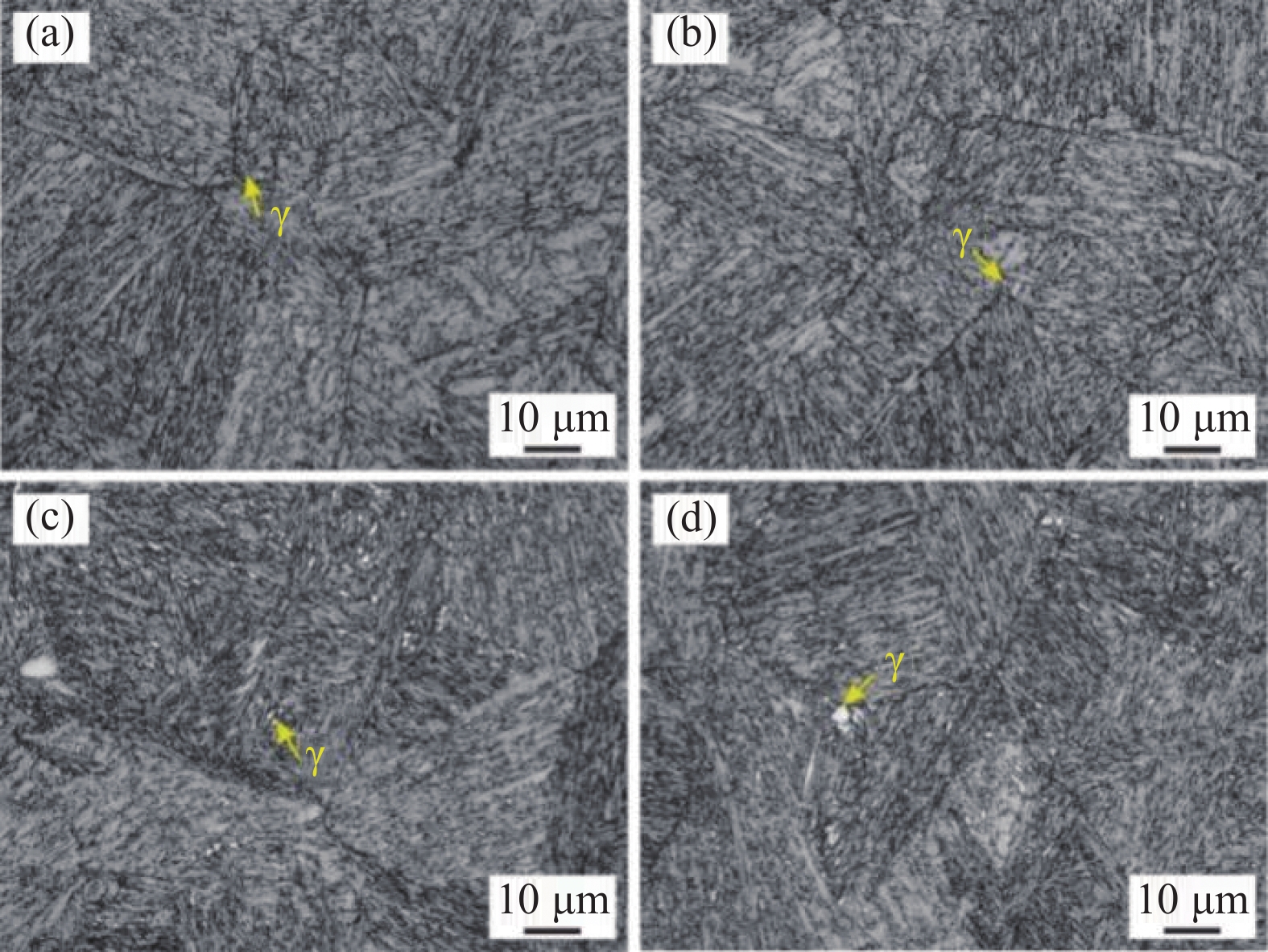
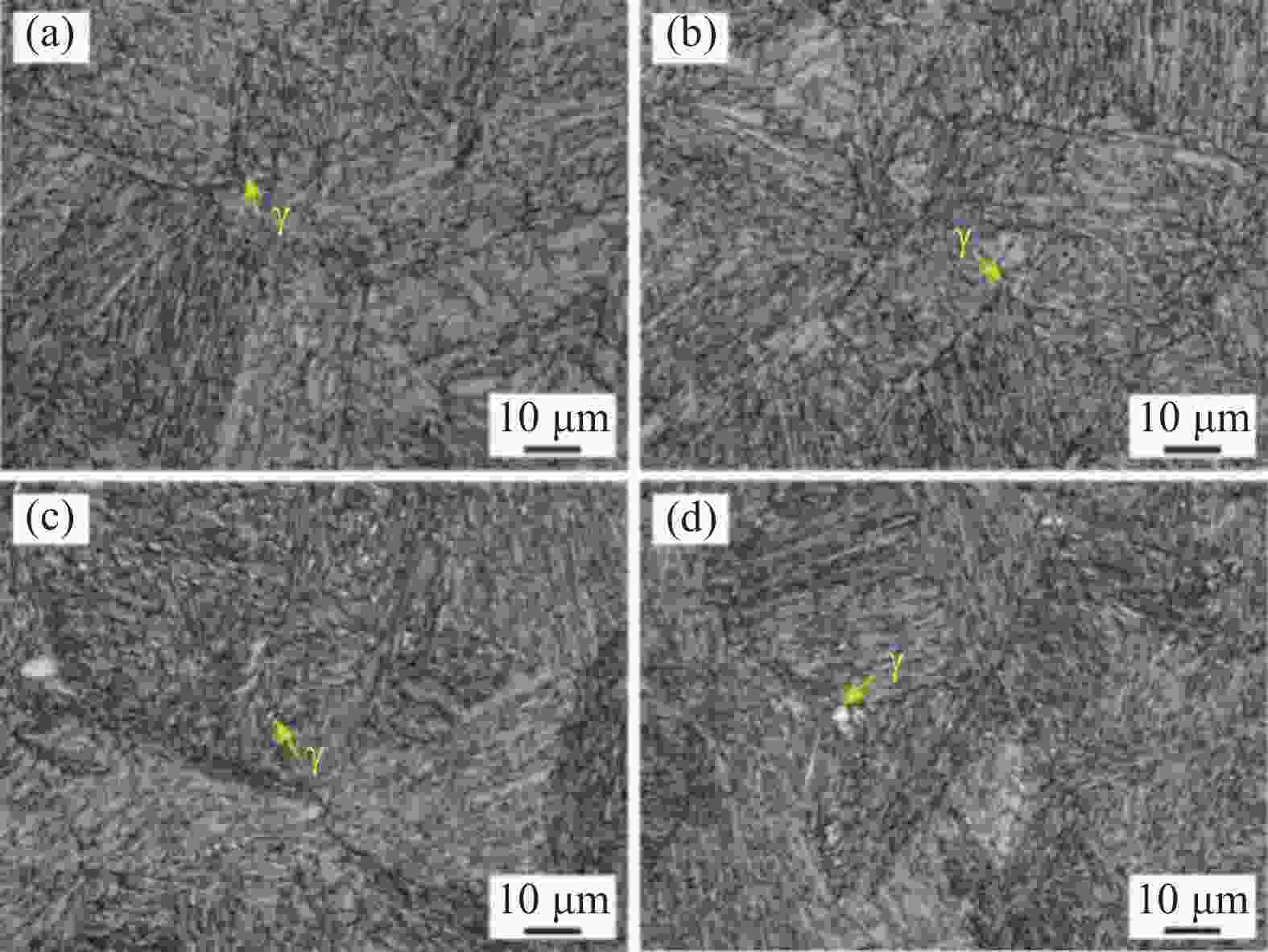
摘要: 采用金相显微镜、扫描电镜、透射电镜及拉伸试验机等研究了不同时效处理高钛马氏体时效不锈钢的微观组织与拉伸行为。结果表明,不同时效处理高钛马氏体时效不锈钢的组织为马氏体和少量奥氏体,在马氏体基体内存在大量纳米级Ni3Ti析出相;
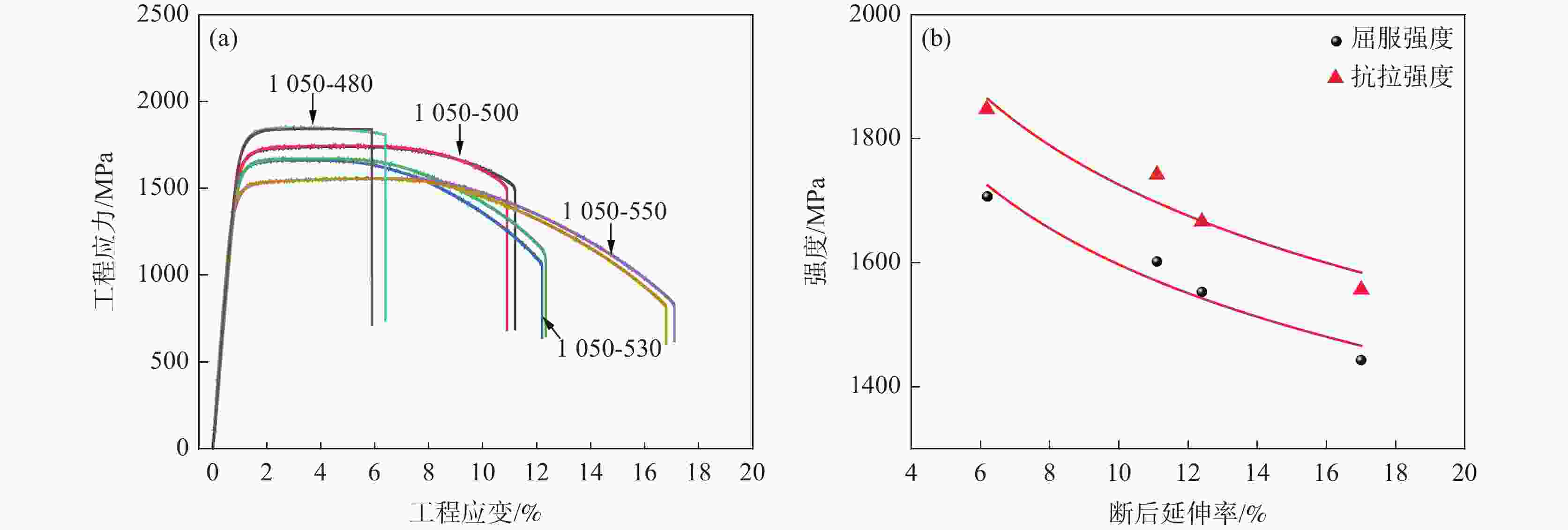
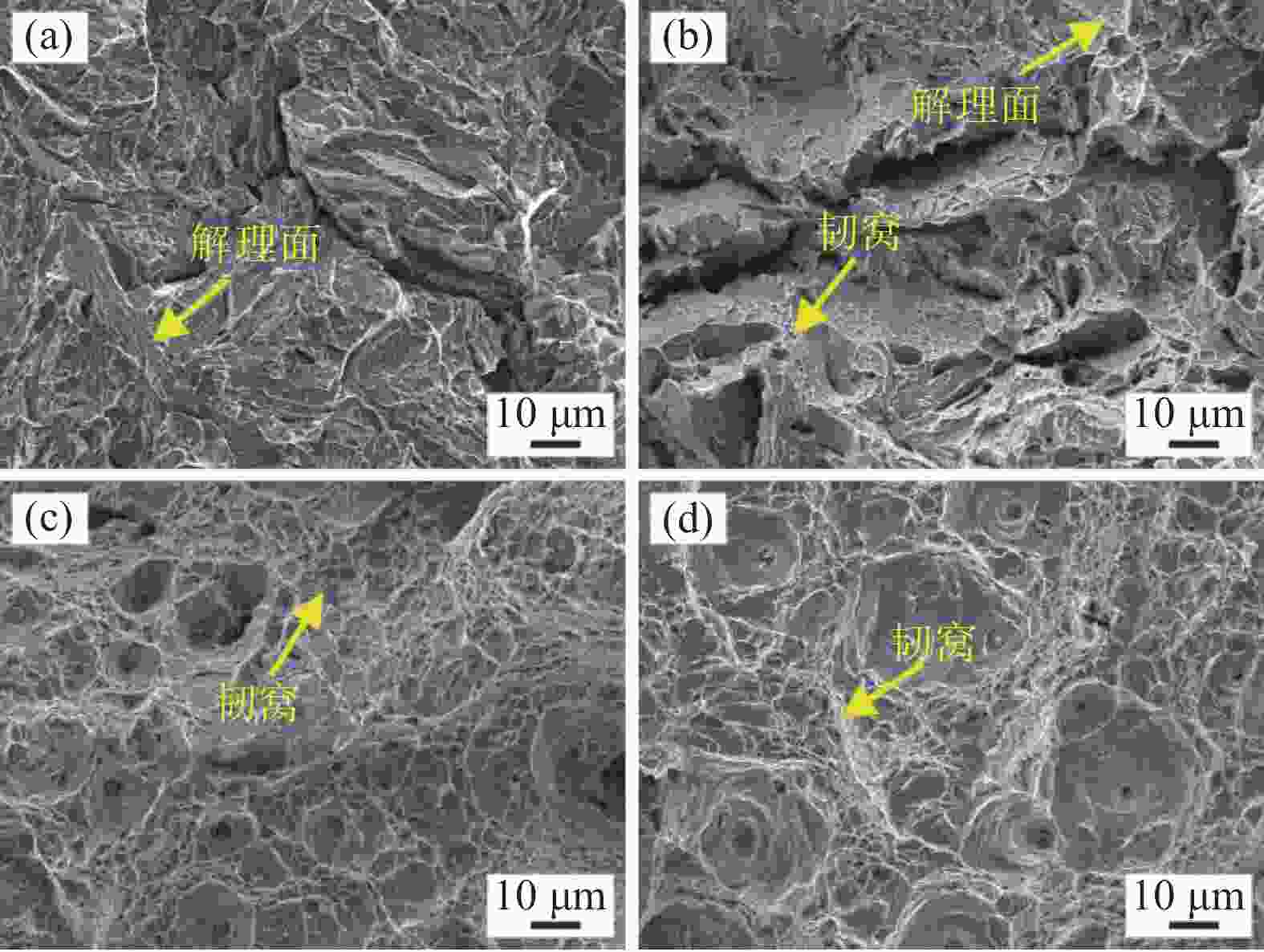
1050 -480、1050 -500、1050 -530和1050 -550样品中Ni3Ti析出相长度分别为11.5、7.9、15.9 nm和33.1 nm,宽度分别为2.8、2.8、4.3 nm和7.8 nm。随析出相尺寸的增大,析出相分布逐渐变得稀疏,高钛马氏体时效不锈钢拉伸强度逐渐降低,塑性逐渐增大,拉伸断裂特征从脆性解理断裂向韧性韧窝断裂转变。-
关键词:
- 高钛马氏体时效不锈钢 /
- 时效处理 /
- 微观组织 /
- 拉伸性能 /
- 断裂特征
Abstract: The microstructures and tensile behaviors of high-titanium maraging stainless steel under different ageing treatments were studied by means of metallurgical microscope, scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope and tensile testing machine. Microstructures observations shows high-titanium maraging stainless steel with different ageing treatments consist of martensite and a small amount of austenite, and there are a large number of nano-scaled Ni3Ti precipitates in the martensite matrix. The lengths of Ni3Ti precipitates in 1050-480, 1050-500, 1050-530 and 1050-550 samples are 11.5, 7.9, 15.9 and 33.1 nm, respectively, and their corresponding widths are 2.8, 2.8, 4.3 and 7.8 nm, respectively. As Ni3Ti precipitates size increases, their distribution gradually becomes sparse, consequently the tensile strength of high-titanium maraging stainless steel decreases and the plasticity improves, and the resulting tensile fracture characteristics change from brittle cleavage fracture to ductile dimple fracture. -
表 1 新型高钛马氏体时效不锈钢的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of the newly developed high-titanium martensitic aged stainless steel
% C Co Cr Mo Ni Ti O Ni 0.0022 ~0.0037 7.94~8.13 12.51~12.62 3.18~3.23 7.12~7.18 1.32~1.76 0.0005 ~0.0023 0.002~ 0.0044 表 2 马氏体板条束的平均尺寸
Table 2. The average size of martensite block bundles
样品名称 平均长度 /μm 平均宽度 /μm 长宽比 1050 -48018.3 2.9 6.3 1050 -50019.6 2.9 6.8 1050 -53017.1 3.8 4.5 1050 -55014.4 3.5 4.1 表 3 马氏体板条的平均尺寸
Table 3. The average size of martensite lath bundles
样品名称 平均宽度 /nm 1050 -480512.9 1050 -500433.0 1050 -530482.8 1050 -550363.1 表 4 棒状析出相Ni3Ti的平均尺寸
Table 4. The average size of rod-like precipitated phase Ni3Ti
样品名称 平均宽度 /nm 平均长度 /nm 1050 -4802.8 11.5 1050 -5002.8 7.9 1050 -5304.3 15.9 1050 -5507.8 33.1 表 5 不同时效处理高钛马氏体时效不锈钢的拉伸性能
Table 5. Tensile properties of high-titanium maraging stainless steel obtained with different ageing treatments
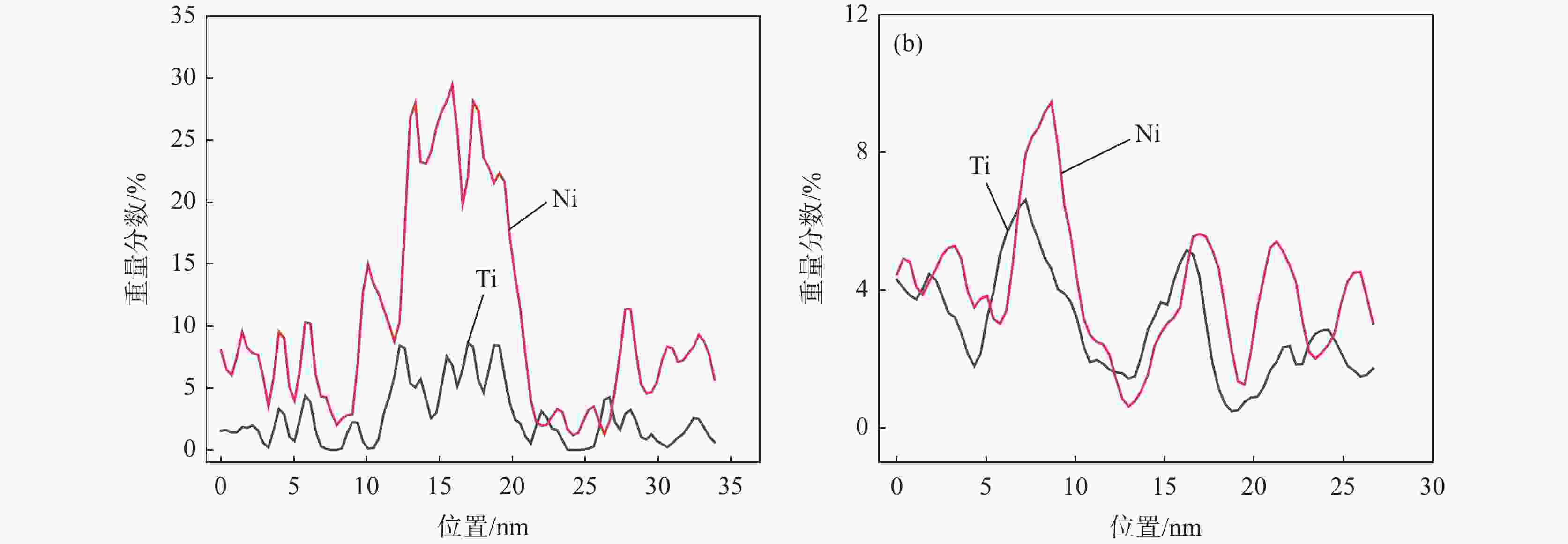
样品 屈服强
度/MPa抗拉强
度/MPa断后延
伸率/%断面收
缩率/%1050 -4801707 ±21 847±4 6.2±0.2 9.4±0.3 1050 -5001602 ±11743 ±311.1±0.2 25.0±3.9 1050 -5301553 ±41667 ±512.4±0.2 56.8±1.4 1050 -5501443 ±41556 ±217.0±0.2 67.6±0.5 -
[1] WANG B, NIU M C, WANG W, et al. Microstructure and strength-toughness of a Cu-contained maraging stainless steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2023,59(5):636-646. (王滨, 牛梦超, 王威, 等. 含Cu马氏体时效不锈钢的组织与强韧性[J]. 金属学报, 2023,59(5):636-646.WANG B, NIU M C, WANG W, et al. Microstructure and strength-toughness of a Cu-contained maraging stainless steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2023, 59(5): 636-646. [2] WANG W, YAN W, DUAN Q Q, et al. Study on fatigue property of a new 2.8 GPa grade maraging steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010,527(13-14):3057-3063. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.02.002 [3] YANG K, ZHU H W, YU L M, et al. Effect of aging time on microstructure and mechanical properties of PH13-8Mo stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2023,48(3):100-103. (杨凯, 朱宏伟, 于利民, 等. 时效时间对PH13-8Mo不锈钢组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2023,48(3):100-103.YANG K, ZHU H W, YU L M, et al. Effect of aging time on microstructure and mechanical properties of PH13-8Mo stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2023, 48(3): 100-103. [4] WANG X M, HE W W, WEI H D, et al. Effect of heat treatment process on microstructure and mechanical properties of 17-4PH stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2023,48(6):85-88. (王旭明, 何文武, 魏海东, 等. 热处理工艺对17-4PH不锈钢组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2023,48(6):85-88.WANG X M, HE W W, WEI H D, et al. Effect of heat treatment process on microstructure and mechanical properties of 17-4PH stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2023, 48(6): 85-88. [5] ZHAN Z H, ZHANG Y L, CHENG G G, et al. Study on smelting deoxidation process of 15-5PH stainless steel large forgings[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2021,33(8):752-758. (詹中华, 张延玲, 成国光, 等. 15-5PH不锈钢大型锻件冶炼脱氧工艺研究[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2021,33(8):752-758.ZHAN Z H, ZHANG Y L, CHENG G G, et al. Study on smelting deoxidation process of 15-5PH stainless steel large forgings[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2021, 33(8): 752-758. [6] CHEN J Y, YANG Z Y, SONG W S, et al. Effects of aging temperature on mechanical properties of Custom 465[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2008,20(12):31-34. (陈嘉砚, 杨卓越, 宋维顺, 等. 时效温度对Custom 465钢力学性能的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2008,20(12):31-34.CHEN J Y, YANG Z Y, SONG W S, et al. Effects of aging temperature on mechanical properties of Custom 465[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2008, 20(12): 31-34. [7] ZHANG S Y. Study on welding and heat treatment technology of Custom 455 precipitation hardening stainless steel[D]. Chengdou: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022. (张思远. Custom 455沉淀硬化不锈钢焊接及热处理工艺研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2022.ZHANG S Y. Study on welding and heat treatment technology of Custom 455 precipitation hardening stainless steel[D]. Chengdou: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2022. [8] ZHANG M, ZHU Q L. Heat treatment of 17-4PH stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2012,37(9):8-11. (张敏, 褚巧玲. 17-4PH不锈钢热处理工艺[J]. 金属热处理, 2012,37(9):8-11.ZHANG M, ZHU Q L. Heat treatment of 17-4PH stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2012, 37(9): 8-11. [9] WANG Q T. 00Cr13Ni7Co5Mo4W2 maraging stainless steel performance research[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2014. (王启廷. 00Cr13Ni7Co5Mo4W2马氏体时效不锈钢性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2014.WANG Q T. 00Cr13Ni7Co5Mo4W2 maraging stainless steel performance research[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Science and Technology, 2014. [10] WANG X J, SHEN Q, YAN J J, et al. Precipitation characterization of NiAl and Cu-rich phases in dual-phase region of precipitation strengthening steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014,50(11):1305-1310. (王晓姣, 沈琴, 严菊杰, 等. 沉淀强化钢中两相区NiAl相和富Cu相的析出特点[J]. 金属学报, 2014,50(11):1305-1310. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2014.00118WANG X J, SHEN Q, YAN J J, et al. Precipitation characterization of NiAl and Cu-rich phases in dual-phase region of precipitation strengthening steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014, 50(11): 1305-1310. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2014.00118 [11] ZHEN C X, MA Q P, LIN L, et al. Effect of aging treatment on microstructure and properties of 00Cr13Ni7Co5Mo4Ti stainless steel[J]. Jiangxi Building Materials, 2015(3):65. (甄彩霞, 马庆朋, 林兰, 等. 时效处理对00Cr13Ni7Co5Mo4Ti不锈钢组织与性能的影响[J]. 江西建材, 2015(3):65.ZHEN C X, MA Q P, LIN L, et al. Effect of aging treatment on microstructure and properties of 00Cr13Ni7Co5Mo4Ti stainless steel[J]. Jiangxi Building Materials, 2015(3): 65. [12] LI K X, ZOU D N, ZHANG W, et al. Effect of aging temperature on microstructure and properties of Co-Cu alloying maraging hardening stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2017,42(11):72-76. (李科欣, 邹德宁, 张威, 等. 时效温度对Co-Cu合金化马氏体时效硬化不锈钢组织性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2017,42(11):72-76.LI K X, ZOU D N, ZHANG W, et al. Effect of aging temperature on microstructure and properties of Co-Cu alloying maraging hardening stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2017, 42(11): 72-76. [13] DENG D W, CHEN R, TIAN X, et al. Influence of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of 17-4PH martensitic stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2013,38(4):32-36. (邓德伟, 陈蕊, 田鑫, 等. 热处理对17-4PH马氏体不锈钢显微组织及性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2013,38(4):32-36.DENG D W, CHEN R, TIAN X, et al. Influence of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of 17-4PH martensitic stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2013, 38(4): 32-36. [14] HOU H, QI L, ZHAO Y H. Effect of austenitizing temperature on the mechanical properties of high-strength maraging steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013,587:209-212. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.08.070 [15] LIU K, SHAN Y Y, YANG Z Y, et al. Effect of aging on microstructure and mechanical property of 1900 MPa grade maraging stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2007,23(3):312-318. [16] SINHA P P, SIVAKUMAR D, BABU N S, et al. Austenite reversion in 18 Ni Co-free maraging steel[J]. Steel Research, 1995,66(11):490-494. doi: 10.1002/srin.199501160 [17] PARDAL J M, TAVARES S S M, FONSECA M P C, et al. Study of the austenite quantification by X-ray diffraction in the 18Ni-Co-Mo-Ti maraging 300 steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2006,41(8):2301-2307. doi: 10.1007/s10853-006-7170-y [18] ZEMTSOVA N D, KABANOVA I G, ANUFRIEVA E I. Kinetics and the mechanism of the realization of the reverse alpha-gamma transformation in the metastable Fe-Ni-Ti alloys: II. Electron-microscopic examination of the alloy structure[J]. Physics of Metals and Metallography, 2008,105(1):19-35. doi: 10.1134/S0031918X08010031 [19] LUO H W, WANG X H, et al. Influence of refined hierarchical martensitic microstructures on yield strength and impact toughness of ultra-high strength stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2020,51:130-136. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.04.001 [20] SHEKHTER A, AARONSON H I, et al. Effect of aging and deformation on the microstructure and properties of Fe−Ni−Ti maraging steel[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 2004, 35A:973-983. [21] TIAN J L, LI Y C, WANG W, et al. Alloying element segregation effect in a multi-phase strengthened maraging stainless steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016,52(12):1517-1526. (田家龙, 李永灿, 王威, 等. 多相强化型马氏体时效不锈钢中的合金元素偏聚效应[J]. 金属学报, 2016,52(12):1517-1526.TIAN J L, LI Y C, WANG W, et al. Alloying element segregation effect in a multi-phase strengthened maraging stainless steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016,52(12): 1517-1526. [22] VISWANATHAN U K, DEY G K, SETHUMADHAVAN V. Effects of austenite reversion during overageing on the mechanical properties of 18 Ni (350) maraging steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 398(1-2): 367-372. [23] REIS D G A, REIS P A D, ABDALLA J A, et al. High-temperature creep resistance and effects on the austenite reversion and precipitation of 18 Ni (300) maraging steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2015,107:350-357. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2015.08.002 [24] WANG M M, WEI C Y, GUO G S, et al. Research progress on strengthening, toughening, and fatigue properties of ultra-high strength martensitic-based steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2023, 4(3):17-27. (王明明, 魏晨阳, 郭广顺, 等. 超高强度马氏体基钢强韧化及疲劳性能研究进展[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2023, 4(3):17-27.WANG M M, WEI C Y, GUO G S, et al. Research progress on strengthening, toughening, and fatigue properties of ultra-high strength martensitic-based steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2023, 4(3): 17-27. [25] VISWANATHAN U K, DEY G K, ASUNDI M K. Precipitation hardening in 350 grade maraging steel[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1993, 24(11):2429-2442. doi: 10.1007/BF02646522 [26] WANG B, ZHANG P, DUAN Q Q, et al. Optimizing the fatigue strength of 18Ni maraging steel through ageing treatment[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017,707:674-688. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.09.107 -




 下载:
下载: