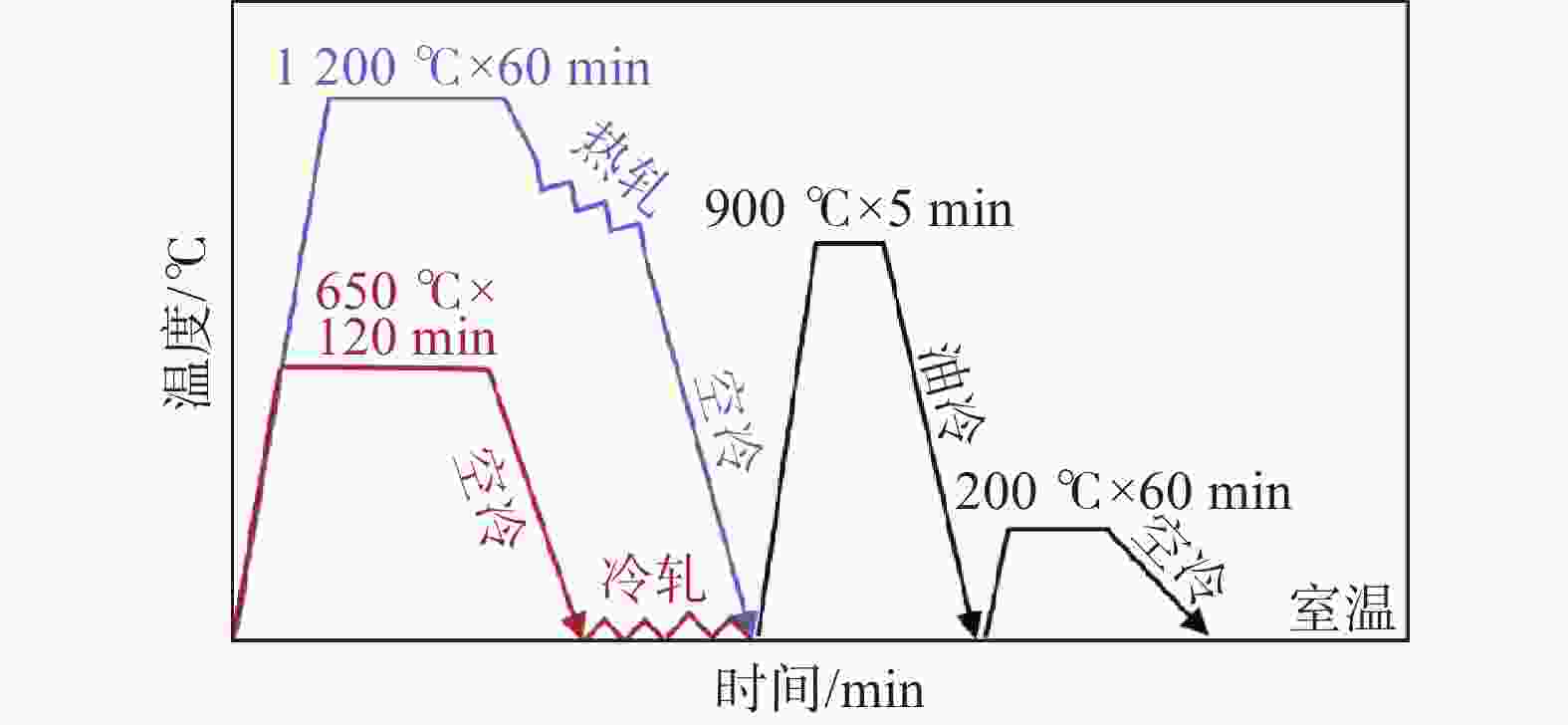
2300 MPa grade vanadium-containing low alloyed steel: ultrafine microstructure preparation and performance
-
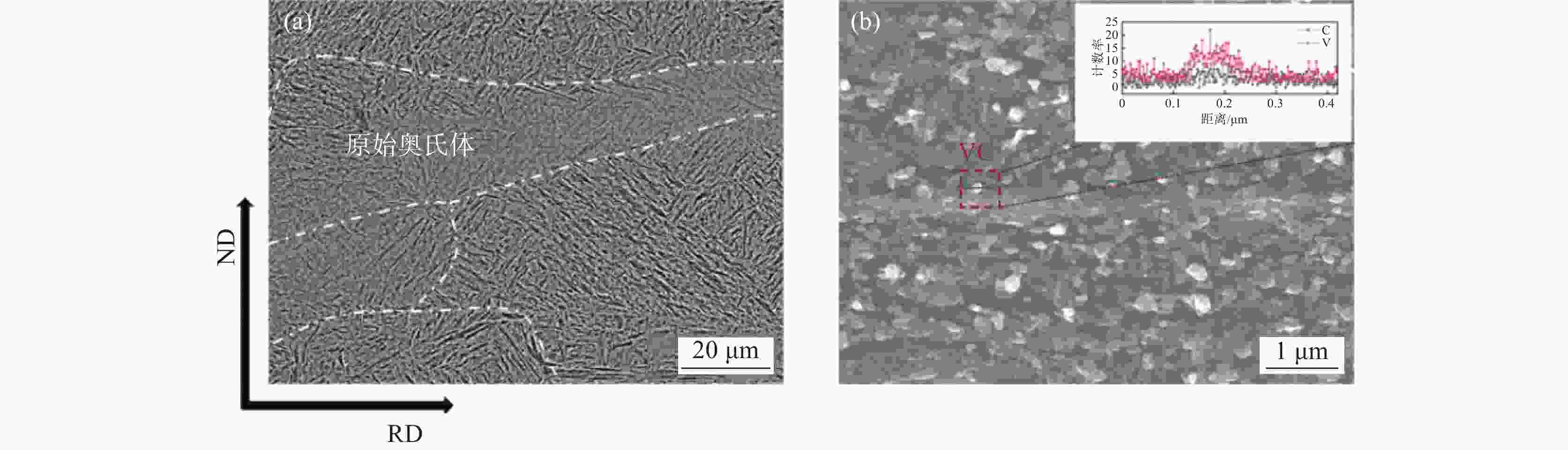
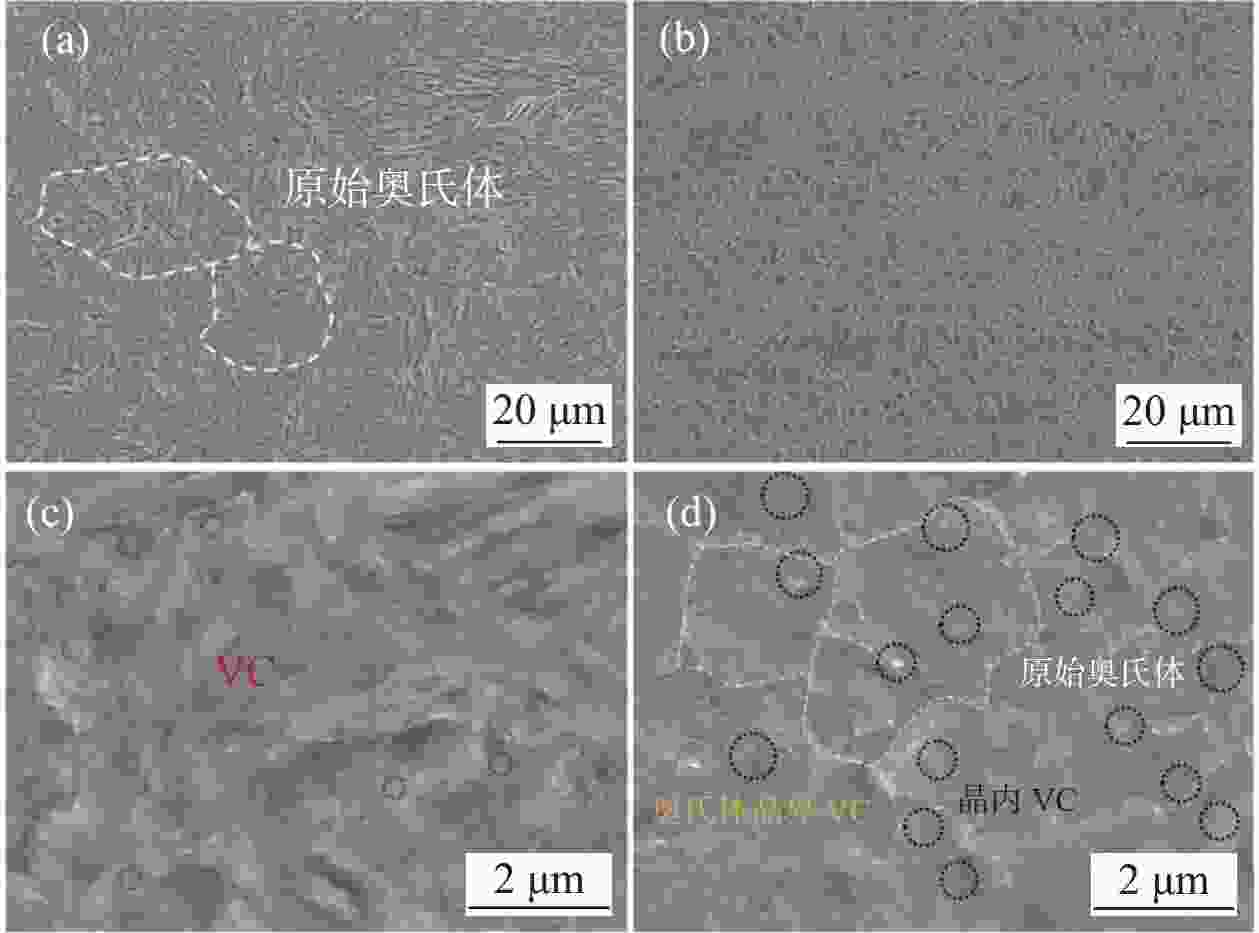
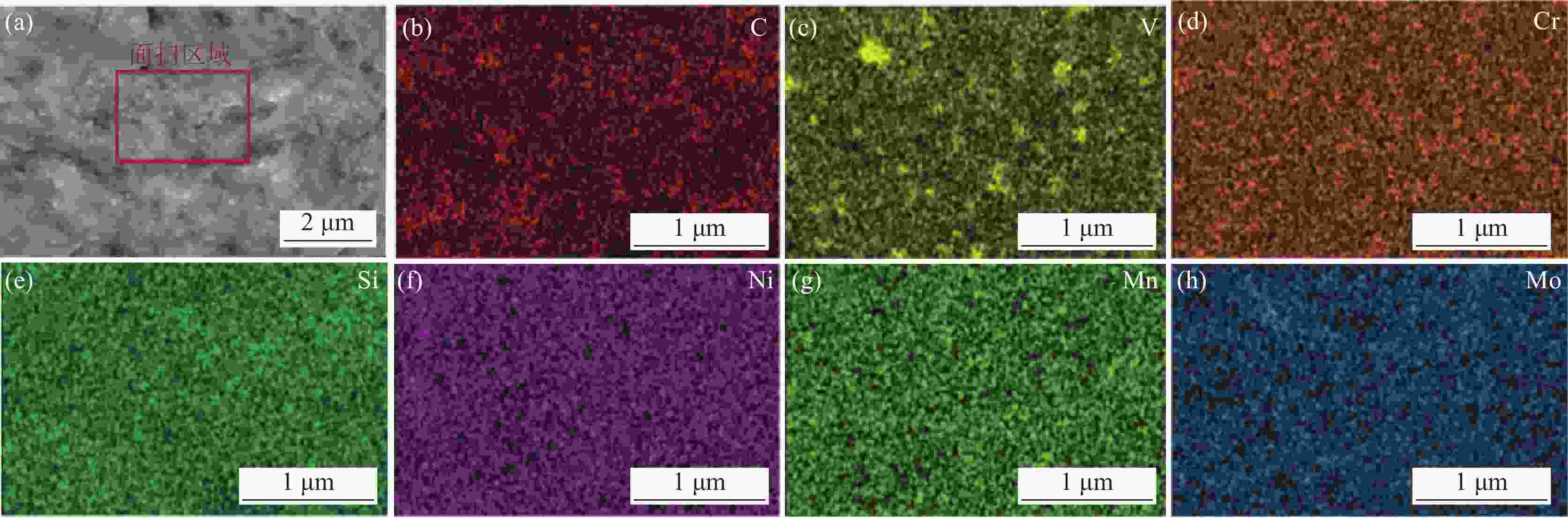
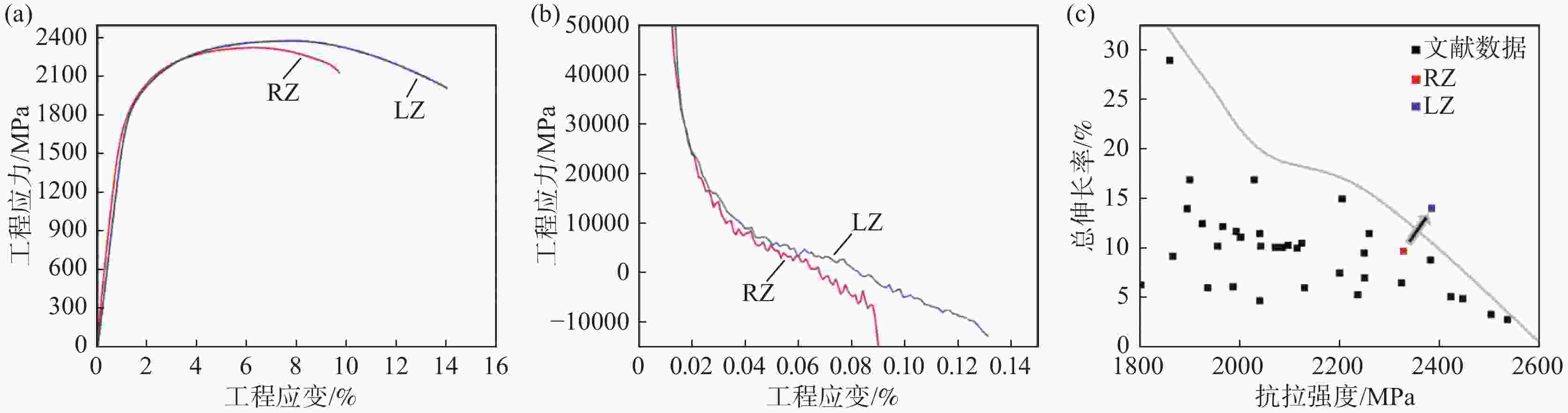
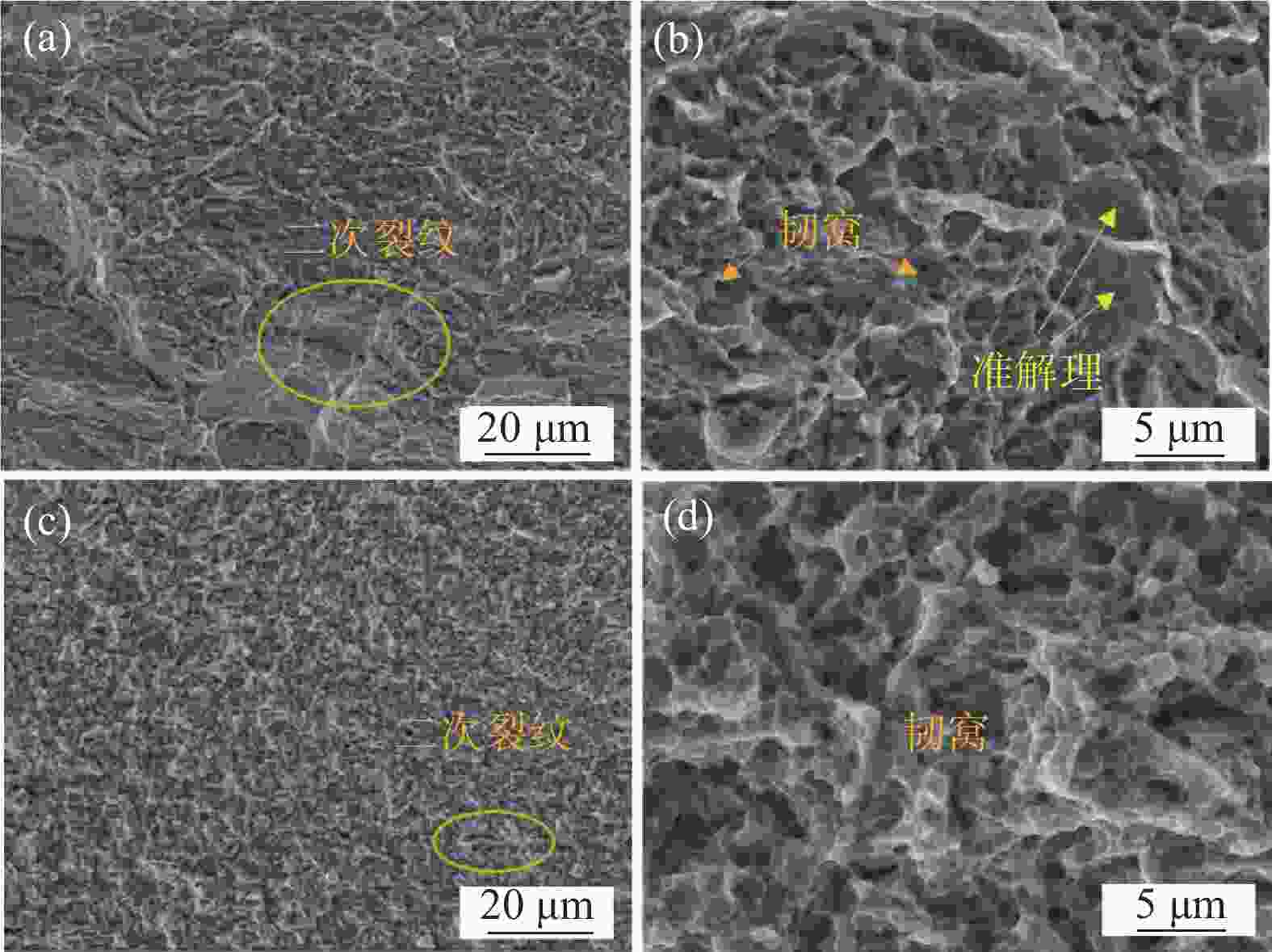
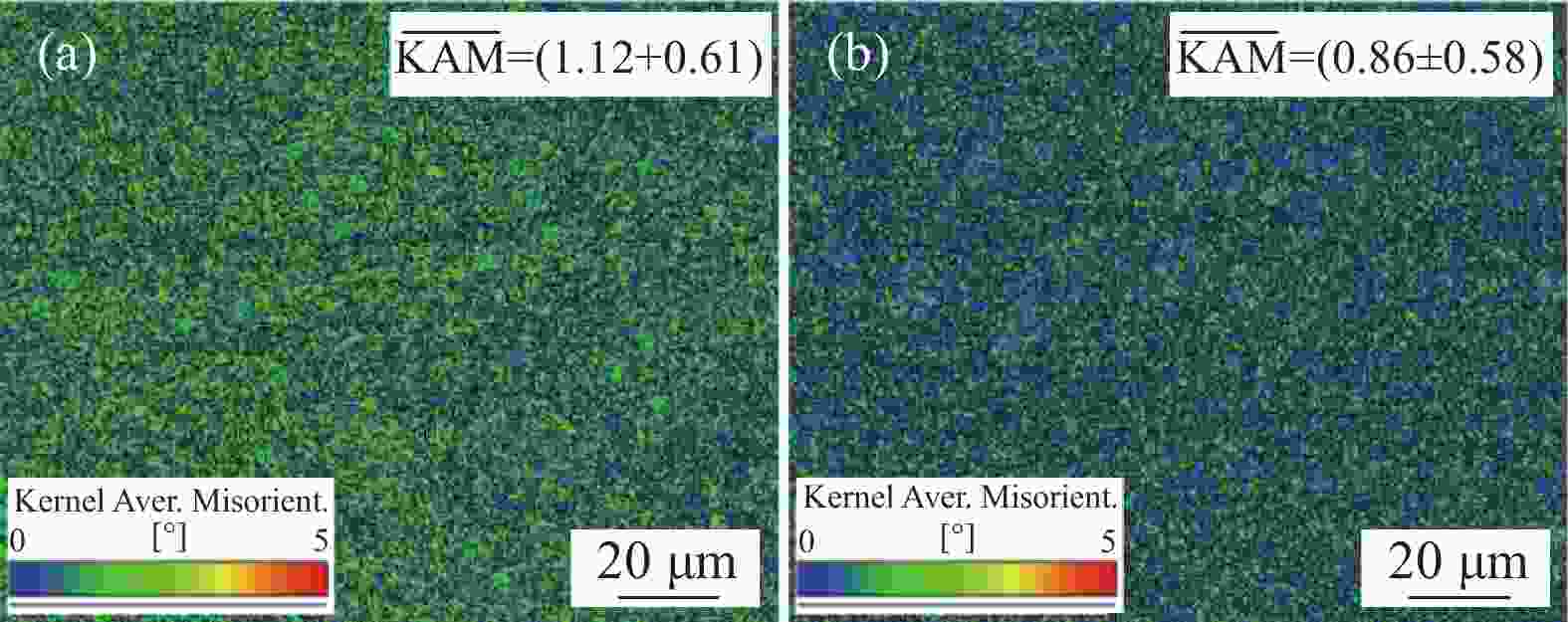
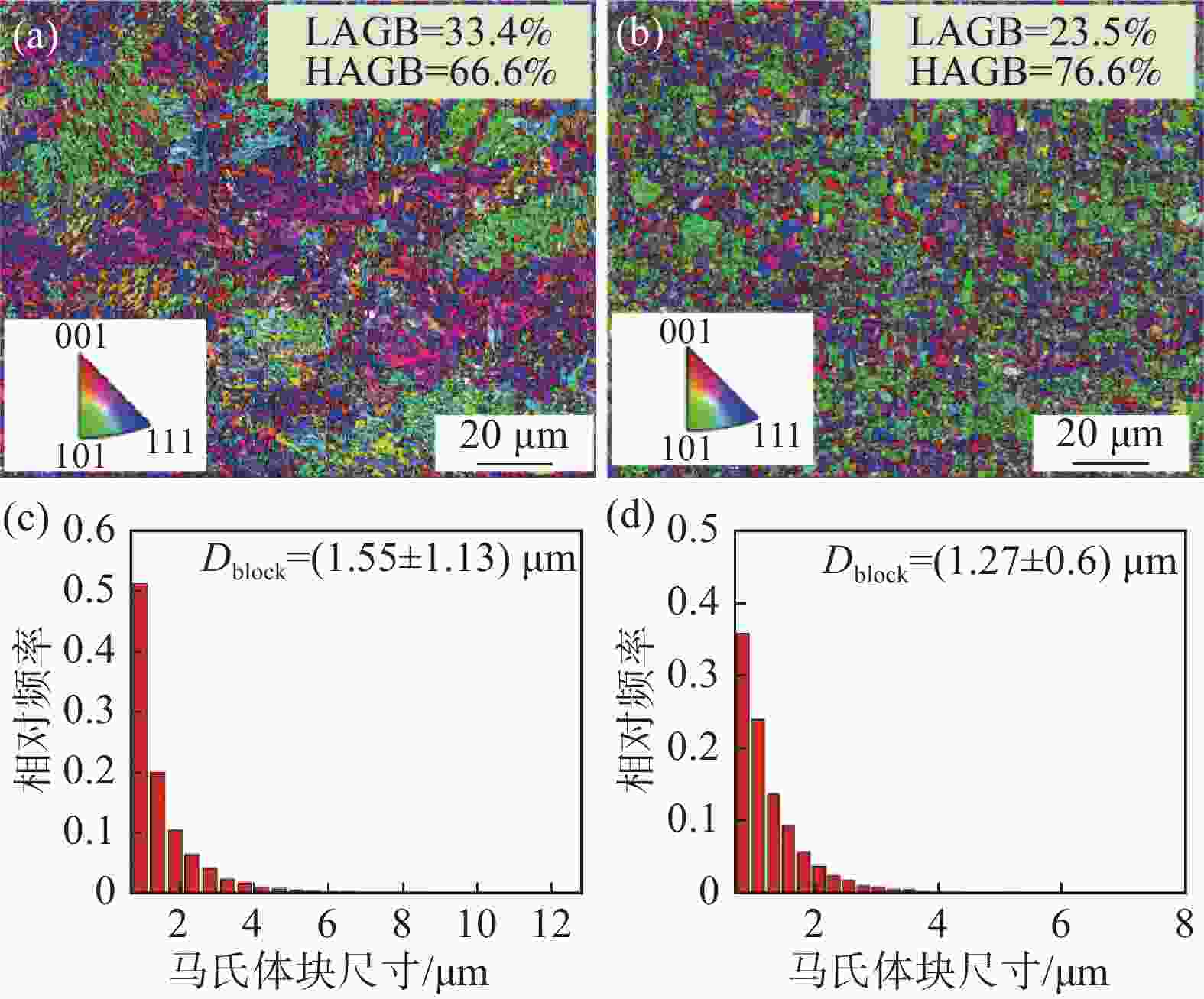
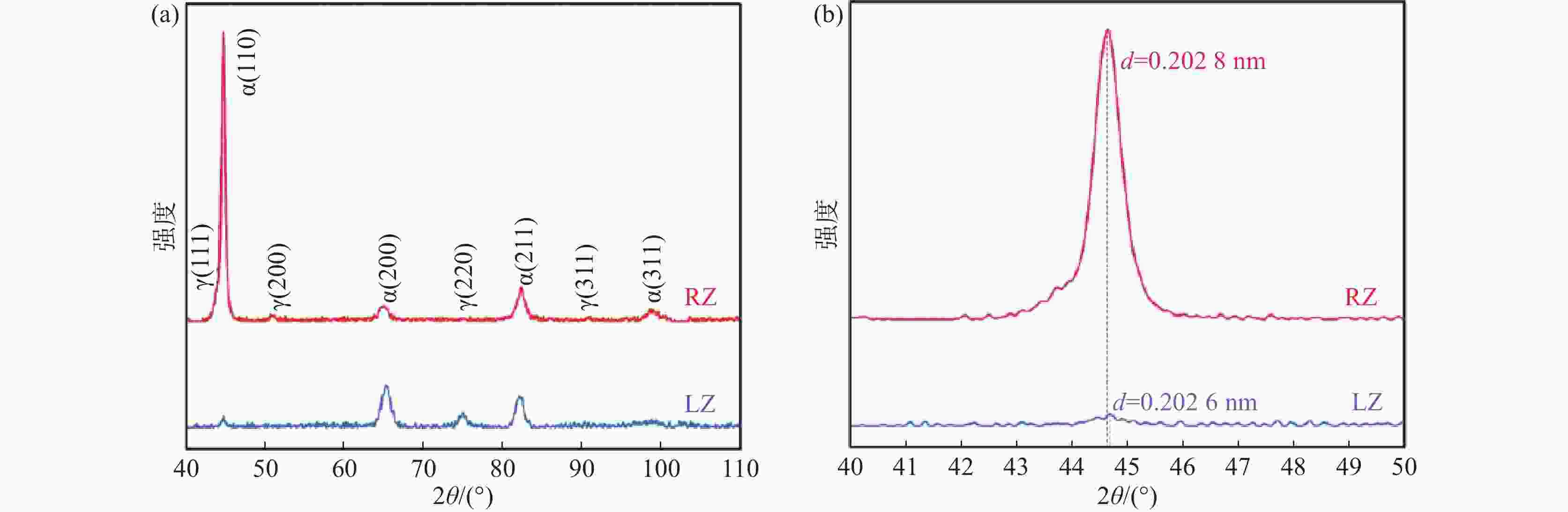
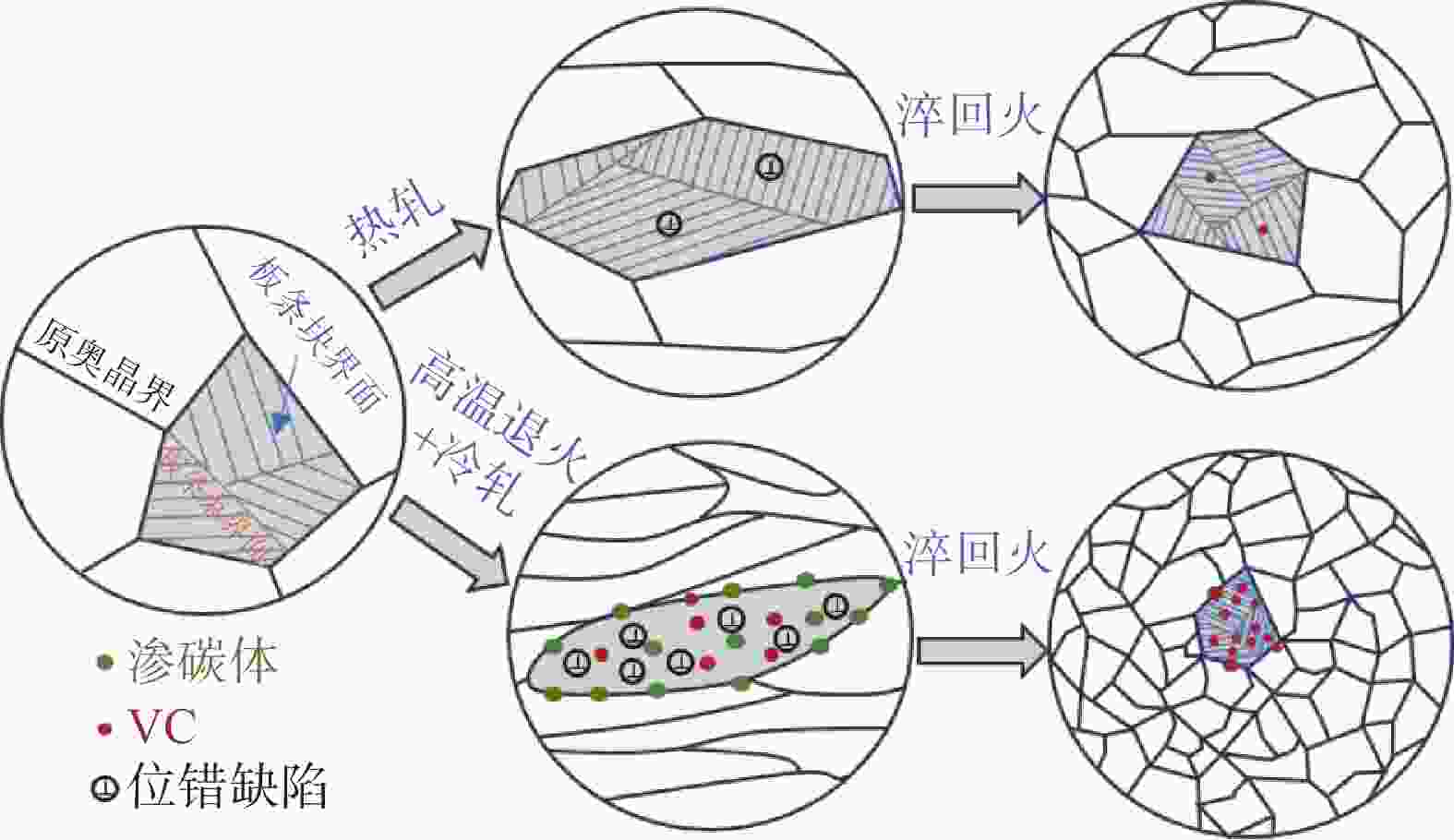
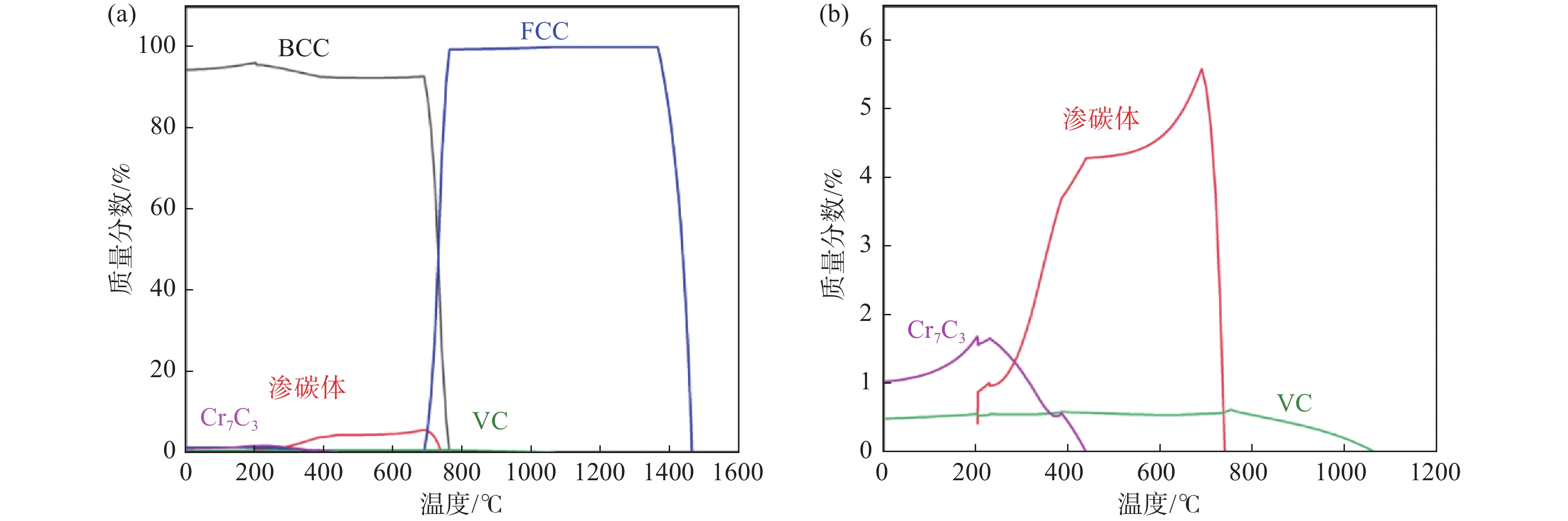
摘要: 通过常规热轧和高温退火+冷轧制备了两种不同的初始组织,研究了初始组织对奥氏体化淬火后微观组织和力学性能的影响规律。结果表明,常规热轧样品淬火组织较为粗大,而高温退火+冷轧由于在淬火前引入了更多的晶界、更高密度的渗碳体、VC和位错缺陷,实现了淬火组织的显著细化。热轧样品和冷轧样品均可以实现较高的强度和塑性匹配,但冷轧样品由于更为细化的组织,其强度和塑性更为优异。冷轧样品可以在实现
2384 MPa超高抗拉强度的同时获得14.0%的超高总伸长率,强塑积可达到33.4 GPa·%。Abstract: For a conventional low alloyed steel, two different initial microstructures were achieved by conventional hot rolling and high-temperature annealing followed by cold rolling. The effects of the initial microstructures on the microstructure and mechanical properties after austenitization and quenching were investigated. The results indicate that the quenched microstructure of the conventional hot-rolled sample is relatively coarse, while the high-temperature annealing followed by cold rolling, which introduces more grain boundaries, a higher density of cementite, VC, and dislocation defects before quenching, can significantly refine the quenched microstructure. Both hot-rolled and cold-rolled samples achieve a high strength-ductility balance, but the cold-rolled sample, with its more refined microstructure, exhibits superior strength and ductility. The cold-rolled sample achieves ultra-high tensile strength of2384 MPa and extraordinary total elongation of 14.0%, with product of strength and elongation reaching 33.4 GPa·%. -
表 1 试验钢的成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of experimental steel
% C Si Mn Ni Cr Mo V Fe 0.53 1.44 0.44 1.79 0.84 0.51 0.30 Bal. 表 2 试验钢的力学性能
Table 2. Mechanical properties of experimental steel
样品 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 均匀伸长率/% 总伸长率/% 强塑积/(GPa·%) RZ 1757 2329 6.1 9.7 22.6 LZ 1823 2384 8.2 14.0 33.4 -
[1] LIU S, CHEN H Q, CAO M, et al. Study on microstructure evolution and austenitizing process of 1800 MPa grade ultra-high strength hot stamping steels[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023,44(6):133-138. (刘爽, 陈慧琴, 曹苗, 等. 1800MPa级超高强热成形钢组织性能演变及奥氏体化工艺制度研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023,44(6):133-138. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2023.06.019LIU S, CHEN H Q, CAO M, et al. Study on microstructure evolution and austenitizing process of 1800 MPa grade ultra-high strength hot stamping steels[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(6): 133-138. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2023.06.019 [2] QIN S, LIU Y, HAO Q, et al. The mechanism of high ductility for novel high-carbon quenching-partitioning-tempering martensitic steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2015,46(9):4047-4055. doi: 10.1007/s11661-015-3021-2 [3] SUN J, GUO S, ZHAO S, et al. Improving strength of cold-drawn wire by martensitic transformation in a 0.65wt% C low-alloy steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020,790(14):139719. [4] HUANG M X, HE B B. Alloy design by dislocation engineering[J]. Journal of materials science & technology, 2018,34(3):417-420. [5] SAEGLITZ M, KRAUSS G. Deformation, fracture, and mechanical properties of low-temperature-tempered martensite in SAE 43xx steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 1997,28(2):377-387. doi: 10.1007/s11661-997-0139-x [6] LIU F, CHEN K, KANG C, et al. Effects of V-Nb microalloying on the microstructure and properties of spring steel under different quenching-tempering times[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022,19:779-793. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.05.043 [7] HIDALGO J, SANTOFIMIA M J. Effect of prior austenite grain size refinement by thermal cycling on the microstructural features of as-quenched lath martensite[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2016,47(11):5288-5301. doi: 10.1007/s11661-016-3525-4 [8] WANG Y, SUN J, JIANG T, et al. A low-alloy high-carbon martensite steel with 2.6 GPa tensile strength and good ductility[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018,158:247-256. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.07.060 [9] WANG M L, CHANG H. Effects of initial microstructure on creep properties of Mg-8Gd-2Y-0.5Zr alloys[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2022,42(6):65-71. (王美玲, 常海. 初始组织对Mg-8Gd-2Y-0.5Zr合金蠕变性能的影响[J]. 航空材料学报, 2022,42(6):65-71. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2020.000172WANG M L, CHANG H. Effects of initial microstructure on creep properties of Mg-8Gd-2Y-0.5Zr alloys[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2022, 42(6): 65-71. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2020.000172 [10] LIU Z, YANG Z, WANG X, et al. Enhanced strength-ductility synergy in a new 2.2 GPa grade ultra-high strength stainless steel with balanced fracture toughness: Elucidating the role of duplex aging treatment[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022,928:167135. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.167135 [11] KIM B, BOUCARD E, SOURMAIL T, et al. The influence of silicon in tempered martensite: Understanding the microstructure-properties relationship in 0.5-0.6 wt. % C steels[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014,68:169-178. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2014.01.039 [12] LIU T, CAO Z, WANG H, et al. A new 2.4 GPa extra-high strength steel with good ductility and high toughness designed by synergistic strengthening of nano-particles and high-density dislocations[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2020,178:285-289. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2019.11.045 [13] LIU F, LIN X, SONG M, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser solid formed 300M steel[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015,621:35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.09.111 [14] YANG B, HE Q, WANG H, et al. Achieving an extra-high-strength yet ductile steel by synergistic effects of TRIP and maraging[J]. Materials Research Letters, 2023,11(7):578-585. doi: 10.1080/21663831.2023.2194910 [15] CHENG Z, LIU J, LIU G, et al. Enhancement of strength-ductility trade-off in a 2000 MPa grade press-hardened steel via refined martensite with stable high-density cementite[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023,27:664-680. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.09.295 [16] CHEN K, JIANG Z, LIU F, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties by retained austenite in medium-carbon Si-rich microalloyed steel treated by quenching-tempering, austempering and austempering-tempering processes[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020,790:139742. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.139742 [17] WANG J, WANG S, LI W, et al. Ultrastrong and ductile additively-manufactured medium-carbon steel via modulating austenite stability[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2024,239:115780. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2023.115780 [18] WANG S, XI X, ZHAO Y, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of an ultrahigh-strength and ductile medium-carbon high-silicon spring steel[J]. Steel Research International, 2023,94(1):2200149. doi: 10.1002/srin.202200149 [19] SUNIL S, KAPOOR R, SARKAR S K, et al. Ultra-high strength steel made from AISI 304L using a novel thermo-mechanical processing technique[J]. Acta Materialia, 2021,221:117379. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117379 [20] WANG J, EL-FALLAH G M A M, WANG Z, et al. Strength improvement over 2 GPa and austenite grain ultra-refinement in a low carbon martensite steel achieved by ultra-rapid heating and quenching[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2023,884:145538. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2023.145538 [21] YANG G, SUN X, LI Z, et al. Effects of vanadium on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a high strength low alloy martensite steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2013,50:102-107. [22] SUN J, LIU Y, ZHU Y, et al. Super-strong dislocation-structured high-carbon martensite steel[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017,7(1):6596. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06971-w [23] Gao B, WANG L, LIU Y, et al. Achieving ultrahigh strength by tuning the hierarchical structure of low-carbon martensitic steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2023,881:145370. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2023.145370 [24] ZHAO L, QIAN L, ZHOU Q, et al. The combining effects of ausforming and below-Ms or above-Ms austempering on the transformation kinetics, microstructure and mechanical properties of low-carbon bainitic steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2019,183:108123. -




 下载:
下载: