Study on the parameters of sodium roasting process of titanium slag from Chaoyang area
-
摘要: 利用钠化焙烧工艺对朝阳地区钛渣进行提质处理,对高温下熔融碳酸钠与钛渣反应的控制环节和活化能进行分析计算,对焙烧过程的工艺参数,如焙烧温度、时间以及碱渣比的影响效果进行研究。动力学分析表明,焙烧过程的控制性环节为反应物在固体产物层中的内扩散,反应活化能为50.13 kJ/mol。吉布斯自由能随温度变化情况表明在温度高于900 ℃时反应基本均可发生;转化率随时间变化情况表明在1 h后反应基本完成。通过分析各参数对焙烧过程的影响效果,最终确定焙烧温度900 ℃,碳酸钠与钛渣质量比值1.0,焙烧时间1.5 h为兼具了除杂效果和经济性的最佳工艺参数 。Abstract: The paper used a sodium roasting process to improve the quality of titanium slag from Chaoyang area. The controlling steps of the process were analyzed and the activation energy of the reactions between molten sodium carbonate and titanium slag were calculated. The effects of process parameters such as roasting temperature, time, and alkali to slag ratio were also discussed. Kinetic analysis shows that the controlling step of the process is the internal diffusion of reactants through the solid product layer, with a reaction activation energy of 50.13 kJ/mol. The change in Gibbs free energy with temperature indicates that the reactions can occur mostly at temperatures above 900 °C, and the change in conversion rate over time indicates that the reactions are essentially completed after 1 hour. According to the analysis of the effects of various parameters on the roasting process, the optimal process parameters for both impurity removal and cost-effectiveness are determined to be roasting at 900 °C, a sodium carbonate to titanium slag mass ratio of 1.0, and a roasting time of 1.5 hours.
-
Key words:
- titanium slag /
- solid waste utilization /
- sodium roasting /
- reaction kinetics /
- synthetic rutile
-
表 1 朝阳地区钛渣化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of titanium slag from Chaoyang area
% TiO2 SiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 TFe FeO Mn V 36.77 13.65 3.67 4.42 11.97 8.82 6.73 0.56 2.31 表 2 酸洗预处理后钛渣主要化学成分
Table 2. Chemical composition of acid-leached titanium slag
% TiO2 CaO MgO SiO2 Al2O3 70.95 0.047 6.07 2.22 4.91 表 3 不同温度下的反应速率常数
Table 3. Reaction rate constant at various temperatures
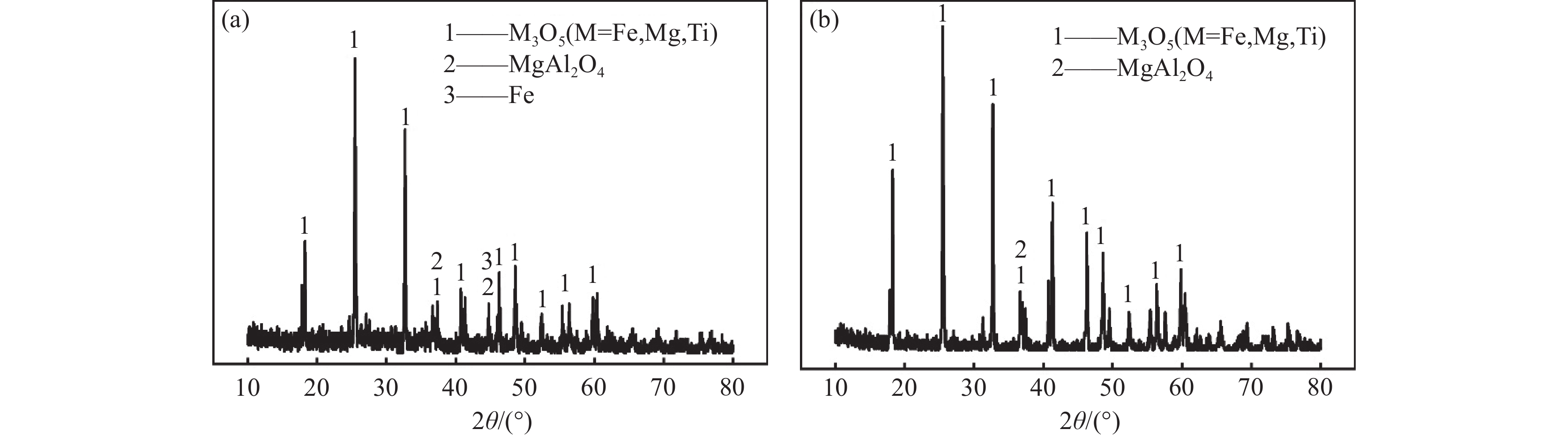
T/℃ T/K (1000 /T)/K−1kd lnkd 875 1148 0.8711 0.02200 − 3.8167 900 1173 0.8525 0.02420 − 3.7214 925 1198 0.8347 0.02736 − 3.5987 950 1223 0.8177 0.03021 − 3.4996 表 4 图14(a)中焙烧产物不同区域EDS分析结果
Table 4. EDS analysis of different regions of roasted sample in figure 14(a)
% 图14(a)中点位 O Na Mg Al Si Ti Fe Total 1 42.87 14.83 4.11 1.73 2.09 34.37 100.00 2 40.90 17.12 12.13 8.82 15.37 5.65 100.00 3 21.13 10.87 1.92 0.13 65.95 100.00 4 36.79 11.69 8.67 0.98 0.30 35.46 6.12 100.00 表 5 焙烧产物结果分析
Table 5. The results analysis of roasted product
组分 质量分数/% 回收率K/% 去除率αi/% TiO2 65.91 92.3439 CaO 0.10 98.5963 MgO 5.72 33.3309 SiO2 0.81 96.9429 Al2O3 1.04 95.5240 -
[1] LÜ J W, YU Z X, LI J L, et al. Resource characteristics and exploitation prospect of vanadium titano magnetite in Chaoyang, Liaoning province[J]. Non-Ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2023, 39(3): 9-11. (吕佳卫, 于泽新, 李玖龙, 等. 辽宁朝阳钒钛磁铁矿资源特点及开发利用前景[J]. 有色矿冶, 2023, 39(3): 9-11.LÜ J W, YU Z X, LI J L, et al. Resource characteristics and exploitation prospect of vanadium titano magnetite in Chaoyang, Liaoning province[J]. Non-Ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2023, 39(3): 9-11. [2] HAN J Q, ZHANG J, ZHANG J H, et al. Recovery of Fe, V and Ti in modified Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2022, 32(1): 333-344. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(22)65798-4 [3] ZHANG Y M, YI L Y, WANG L N, et al. A novel process for the recovery of iron, titanium and vanadium from vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite: sodium modification-direct reduction coupled process[J]. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials, 2017, 24(5): 504-511. doi: 10.1007/s12613-017-1431-4 [4] SHI J J, QIU Y C, YU B, et al. Titanium extraction from titania-bearing blast furnace slag: A review[J]. The Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, 2022, 74(2): 654-667. doi: 10.1007/s11837-021-05040-y [5] LIU X J, CHEN D S, CHU J L, et al. Recovery of titanium and vanadium from titanium-vanadium slag obtained by direct reduction of titanomagnetite concentrates[J]. Rare Metals, 2022, 41(5): 1688-1696. doi: 10.1007/s12598-015-0532-3 [6] JING J F, GUO Y F, CHEN F, et al. A novel sequential leaching process for titanium slag to increase TiO2 grade to prepare boiling chlorinated charges[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2023, 217. [7] SUI Q Q, DOU Z H, ZHANG T A, et al. Study on the one-step acid conversion of the alkali conversion product of high titanium slag to prepare TiO2 of high purity[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2022, 211. [8] XUE T Y, WANG L N, QI T, et al. Decomposition kinetics of titanium slag in sodium hydroxide system[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2009, 95(1-2): 22-27. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2008.04.004 [9] ZHANG L, ZHANG L N, WANG M Y, et al. Recovery of titanium compounds from molten Ti-bearing blast furnace slag under the dynamic oxidation condition[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2007, 20(7): 684-693. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2007.01.003 [10] ZHENG F Q, GUO Y F, LIU S S, et al. Removal of magnesium and calcium from electric furnace titanium slag by H3PO4 oxidation roasting-leaching process[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(2): 356-366. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64669-2 [11] FAN H L, WANG R X, XU Z F, et al. Migration and enrichment behaviors of Ca and Mg elements during cooling and crystallization of boron-bearing titanium slag melt[J]. Crystals, 2021, 11(8): 888. doi: 10.3390/cryst11080888 [12] LIU S S, GUO Y F, QIU G Z, et al. Preparation of Ti-rich material from titanium slag by activation roasting followed by acid leaching[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(4): 1174-1178. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62580-7 [13] ABDELGALIL M S, EL-BARAWY K, YANG G, et al. The recovery of TiO2 from ilmenite ore by ammonium sulfate roasting–leaching process[J]. Processes, 2023, 11(9): 2570-2587. doi: 10.3390/pr11092570 [14] MA J, LI W, FU G Q, et al. Effect of TiO2 on the phase transformation and microstructure evolution of Ti-containing melting slag in the alkali fusion process[J]. Jom, 2024, 76(6): 3021-3027. doi: 10.1007/s11837-024-06558-7 [15] CHEN J, JIANG Q, LI K Q, et al. The productive preparation of synthetic rutile from titanium slag via an improved microwave heating and acid-alkali joint leaching approach[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification, 2022, 172, 108773. [16] CHEN J, PENG J H, HE A X, et al. Investigation on the decomposition of titanium slag using sodium carbonate for preparing rutile TiO2[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 290, 126626. [17] MA J, LI W, FU G Q, et al. Effect of roasting characteristics on the alkali fusion behavior and mechanism of melting titanium slag[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2022, 8(3): 1381-1391. doi: 10.1007/s40831-022-00580-2 [18] CHEN J, GUO S H, OMRAN M, et al. Microwave-assisted preparation of nanocluster rutile TiO2 from titanium slag by NaOH-KOH mixture activation[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2022, 33(5): 103549. [19] Fan H L. Fundamental research on modification of molten titanium slag from electric furnace and removal of calcium and magnesium impurities[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2019. (范鹤林. 熔融电炉钛渣改性及钙镁杂质去除的基础研究[D].重庆: 重庆大学, 2019.Fan H L. Fundamental research on modification of molten titanium slag from electric furnace and removal of calcium and magnesium impurities[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2019. [20] CHEN W, LIU B G, DING J, et al. Mechanism and kinetics study on sulfuric acid leaching of titanium from NaOH roasting ilmenite[J]. Jom, 2024, 76(9): 5365-5375. doi: 10.1007/s11837-024-06746-5 [21] DE O A L B, DA S G D S, DE A P F, et al. Optimization of alkaline roasting to enable acid leaching of titanium from anatase ores[J]. Journal of Sustainable Metallurgy, 2023, 9(1): 183-193. doi: 10.1007/s40831-022-00637-2 [22] DONG H G, JIANG T, GUO Y F, et al. Upgrading a Ti-slag by a roast-leach process[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012, 113-114: 119-121. [23] LIU J. Research on UGS slag production process[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2013. (刘娟. UGS渣生产工艺研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2013.LIU J. Research on UGS slag production process[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2013. [24] KANG J X, GAO L, ZHANG M Y, et al. Synthesis of rutile TiO2 powder by microwave-enhanced roasting followed by hydrochloric acid leaching[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2020, 31(3): 1140-1147. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2019.12.042 -





 下载:
下载: