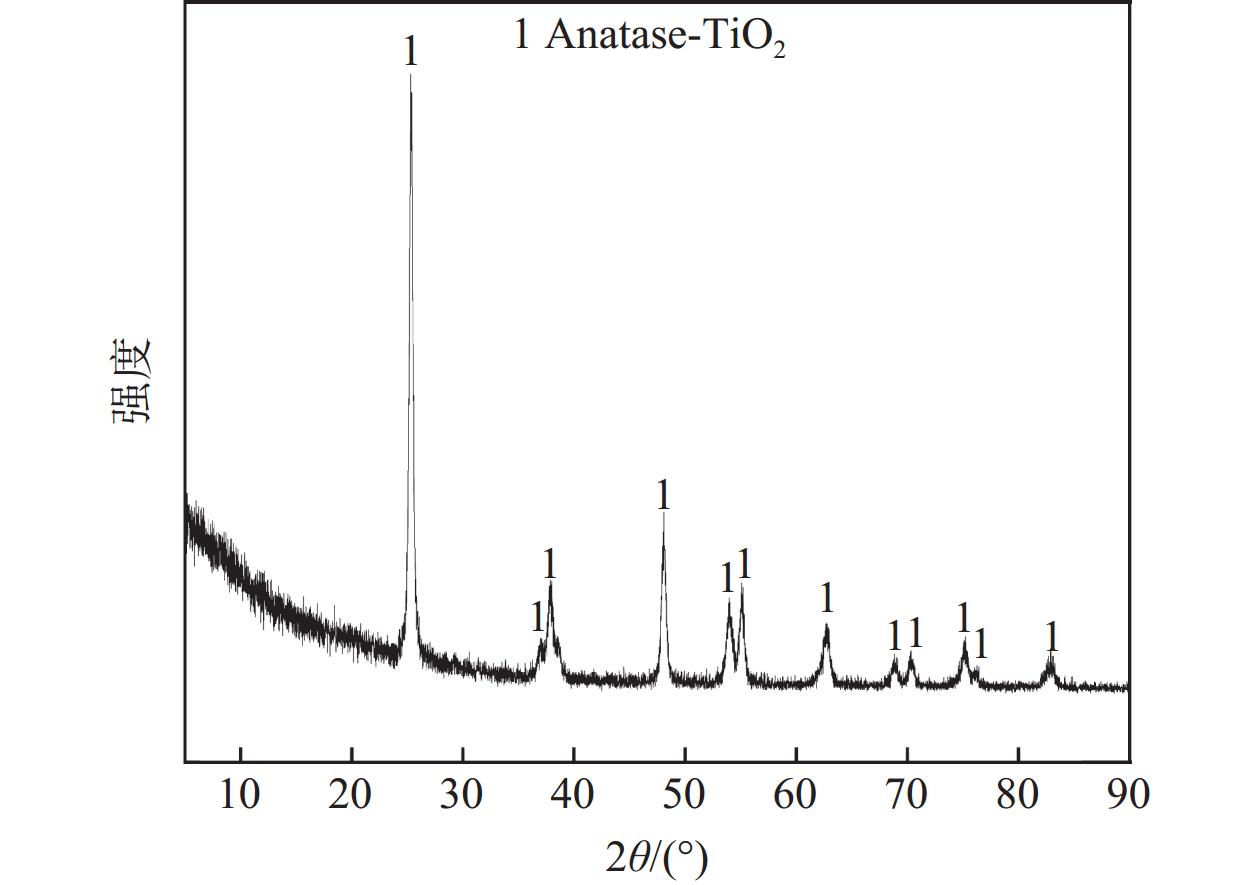
Study on selective separation of V, Mo, W from Ti in spent SCR denitrification catalyst
-
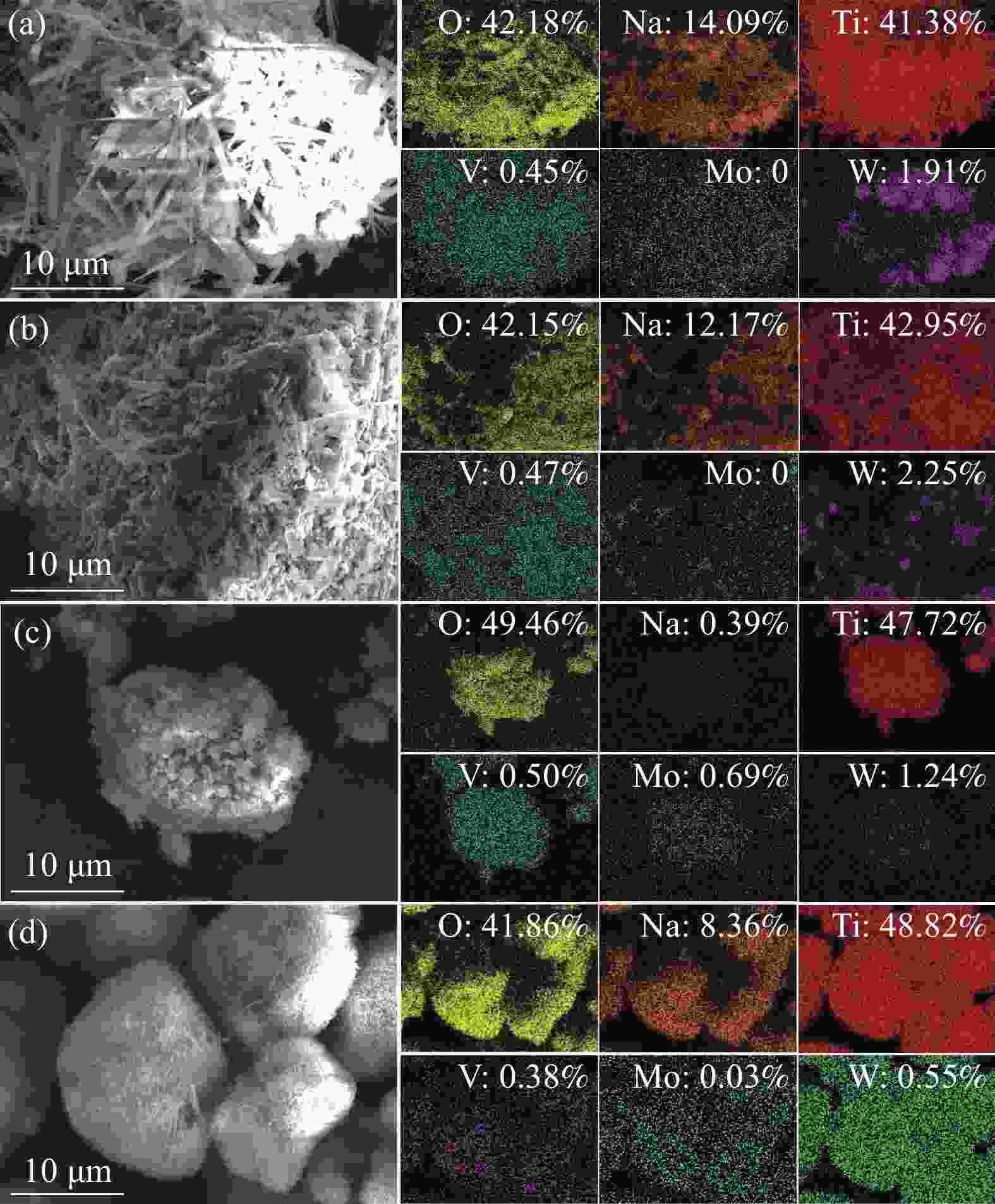
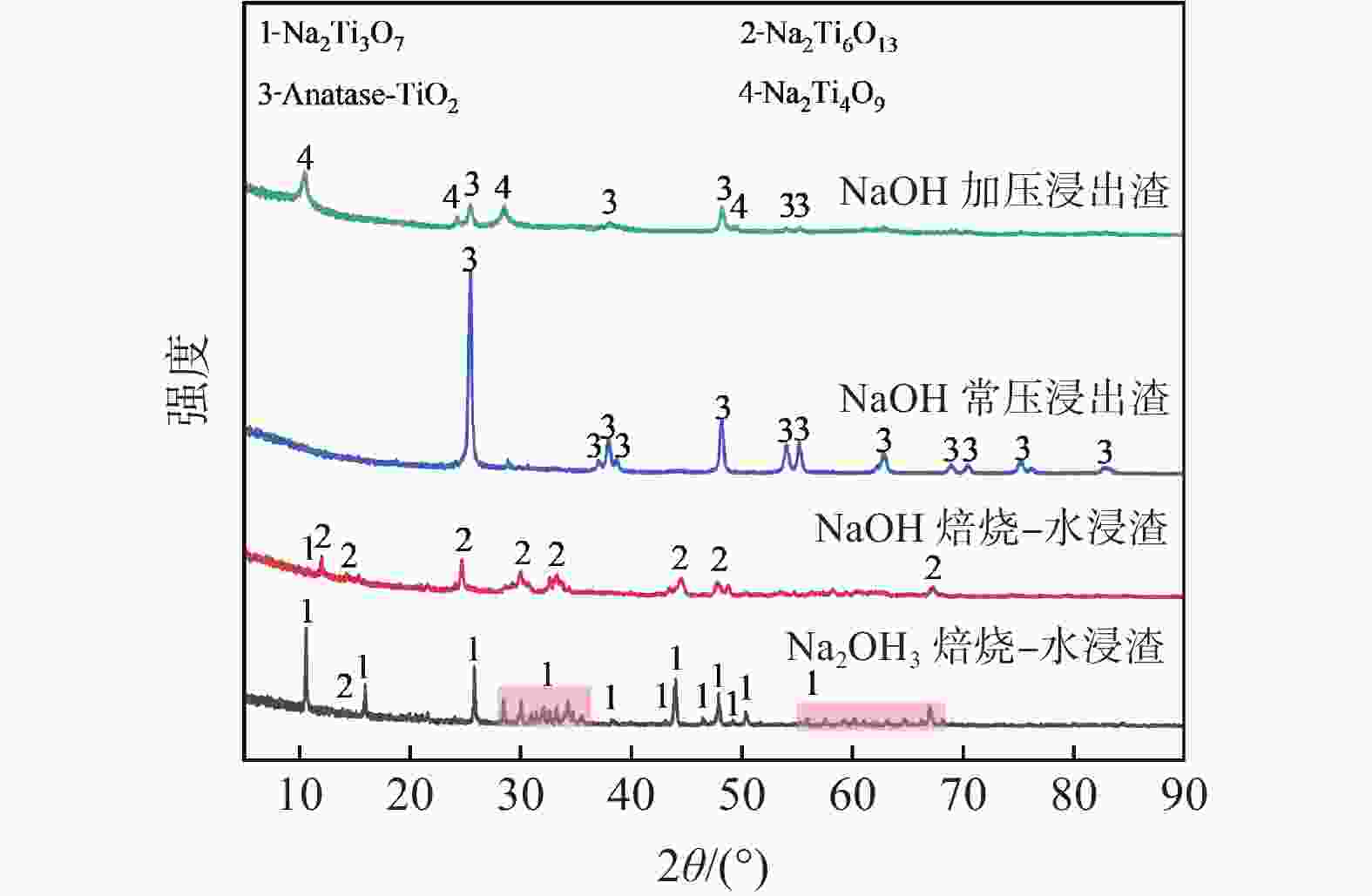
摘要: 废钒钛系SCR脱硝催化剂是一种含有V、Mo、W、Ti等有价金属的危险废物,实现其无害化处理和资源化利用具有重要意义。分别采用Na2CO3焙烧-水浸、NaOH焙烧-水浸、NaOH常压浸出、NaOH加压浸出等工艺处理废V2O5-MoO3-WO3/TiO2四元SCR脱硝催化剂,实现了钒、钼、钨等活性组分与钛的选择性分离。通过研究焙烧参数和浸出参数对钒、钼、钨浸出率及浸出渣物相的影响,确定了NaOH焙烧-水浸工艺为废V2O5-MoO3-WO3/TiO2四元SCR脱硝催化剂的优选处理工艺。在优选条件下,经过NaOH焙烧-水浸后,V、Mo、W的浸出率分别为97.29%、99.33%和87.57%,并获得了主要物相为六钛酸钠(Na2Ti6O13)的浸出渣。Abstract: Spent V-Ti based SCR denitrification catalyst is a hazardous waste containing valuable metals such as V, Mo, W and Ti. It is of great significance to realize its harmless treatment and resource utilization. This study adopted processes such as Na2CO3 roasting-water leaching, NaOH roasting-water leaching, NaOH atmospheric pressure leaching, and NaOH pressurized leaching to treat spent V2O5-MoO3-WO3/TiO2 quaternary SCR denitration catalyst respectively, achieving the selective separation of active components such as vanadium, molybdenum, and tungsten from titanium. By studying the influences of roasting parameters and leaching parameters on the leaching efficiencies of vanadium, molybdenum, and tungsten, as well as the phases of the leaching residues, the NaOH roasting-water leaching process was determined as the optimal treatment process for the spent V2O5-MoO3-WO3/TiO2 quaternary SCR denitration catalyst. Under the optimized conditions, after NaOH roasting-water leaching, the leaching efficiencies of V, Mo and W reached 97.29%, 99.33% and 87.57%, respectively, and the leaching residue with sodium hexatitanate (Na2Ti6O13) as the main phase was obtained.
-
Key words:
- spent SCR catalyst /
- sodium roasting-water leaching /
- Na2CO3 /
- NaOH /
- selective separation
-
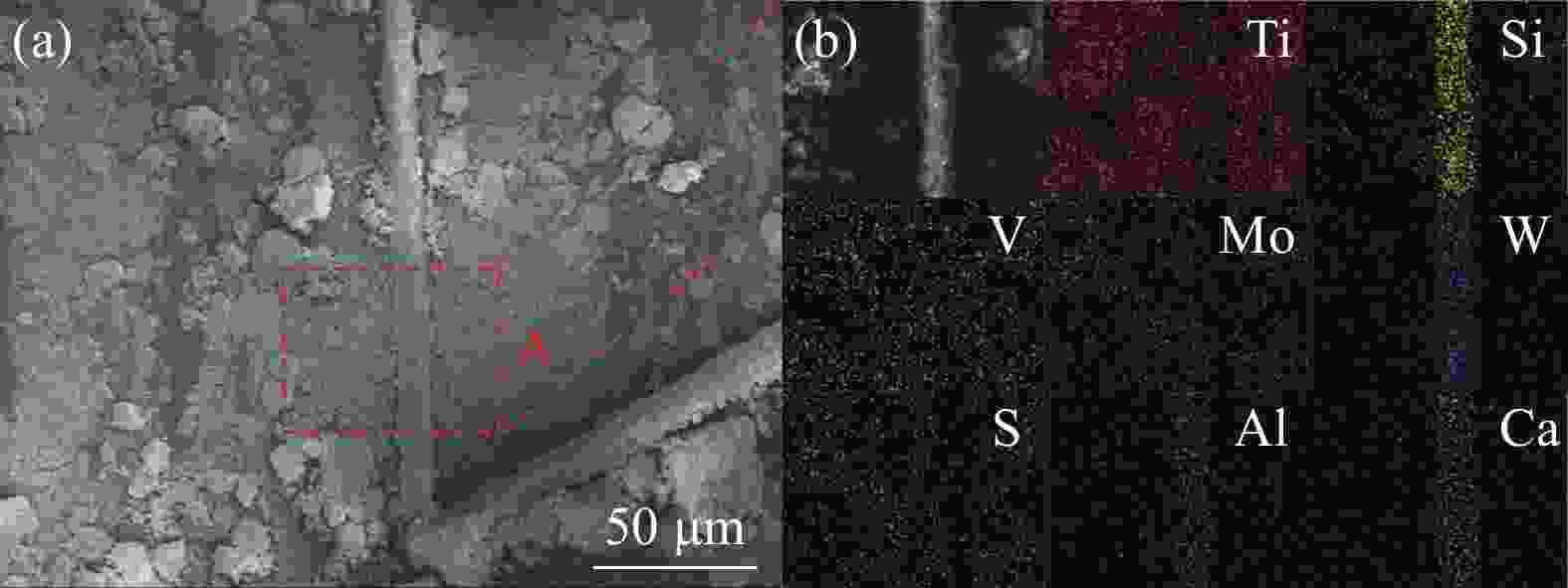
表 1 废SCR催化剂化学组成
Table 1. Chemical composition of spent SCR catalyst
% Ti V Mo W Si Ca Al S C O 其他 43.15 1.25 0.93 1.04 1.12 0.79 0.28 1.63 3.09 43.75 2.97 表 2 四种分离工艺的优选条件及浸出率总结
Table 2. Summary of optimized conditions and leaching efficiencies for four separation processes
工艺 优选条件 浸出率/% 质量比 T/℃ t/min L/S CNaOH/
(mol·L−1)V Mo W Na2CO3
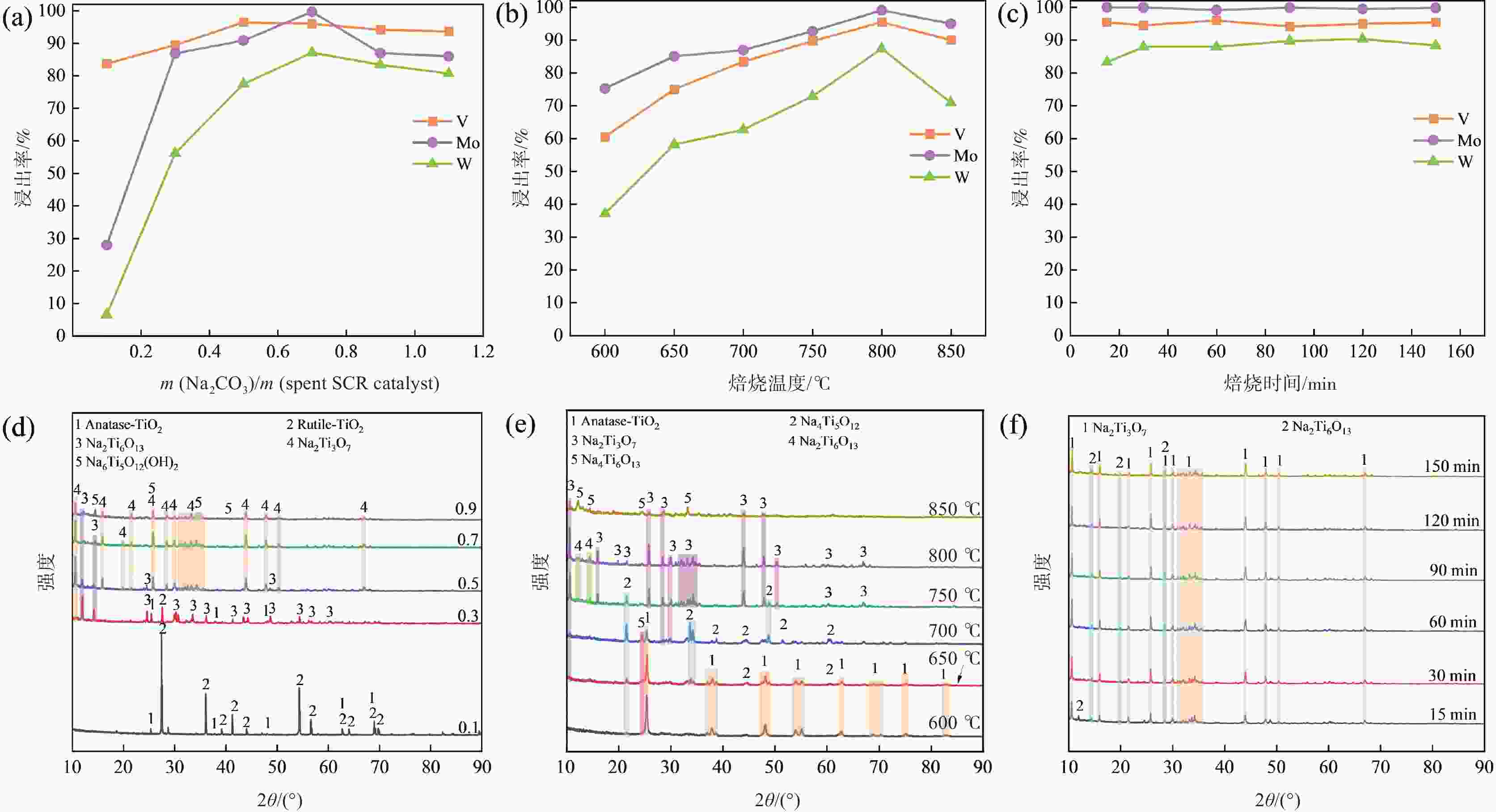
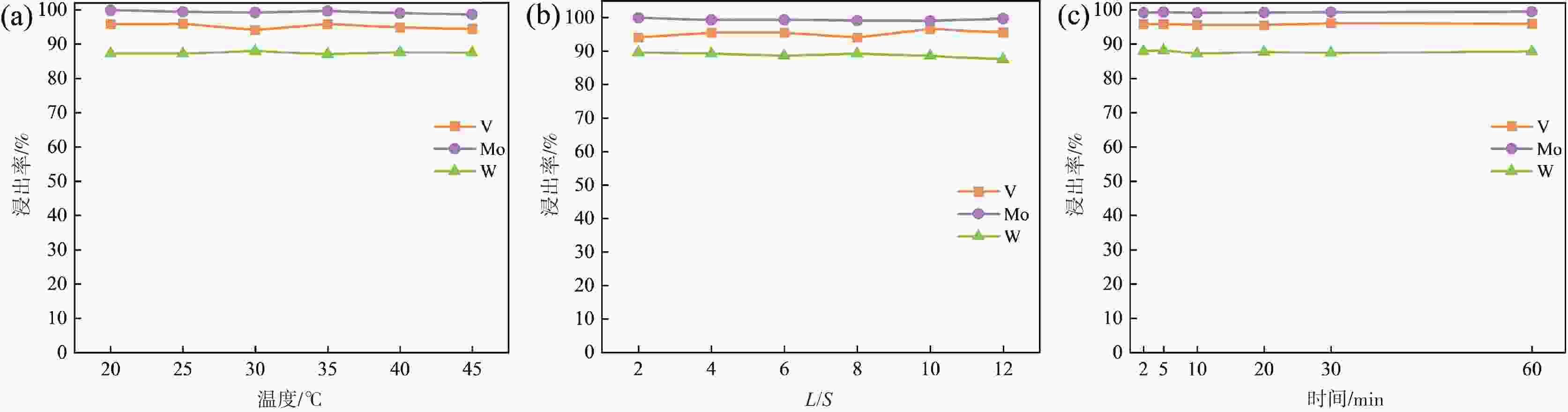
焙烧-水浸焙烧 0.7 800 30 95.82 99.15 87.91 浸出 20 2 4:1 NaOH
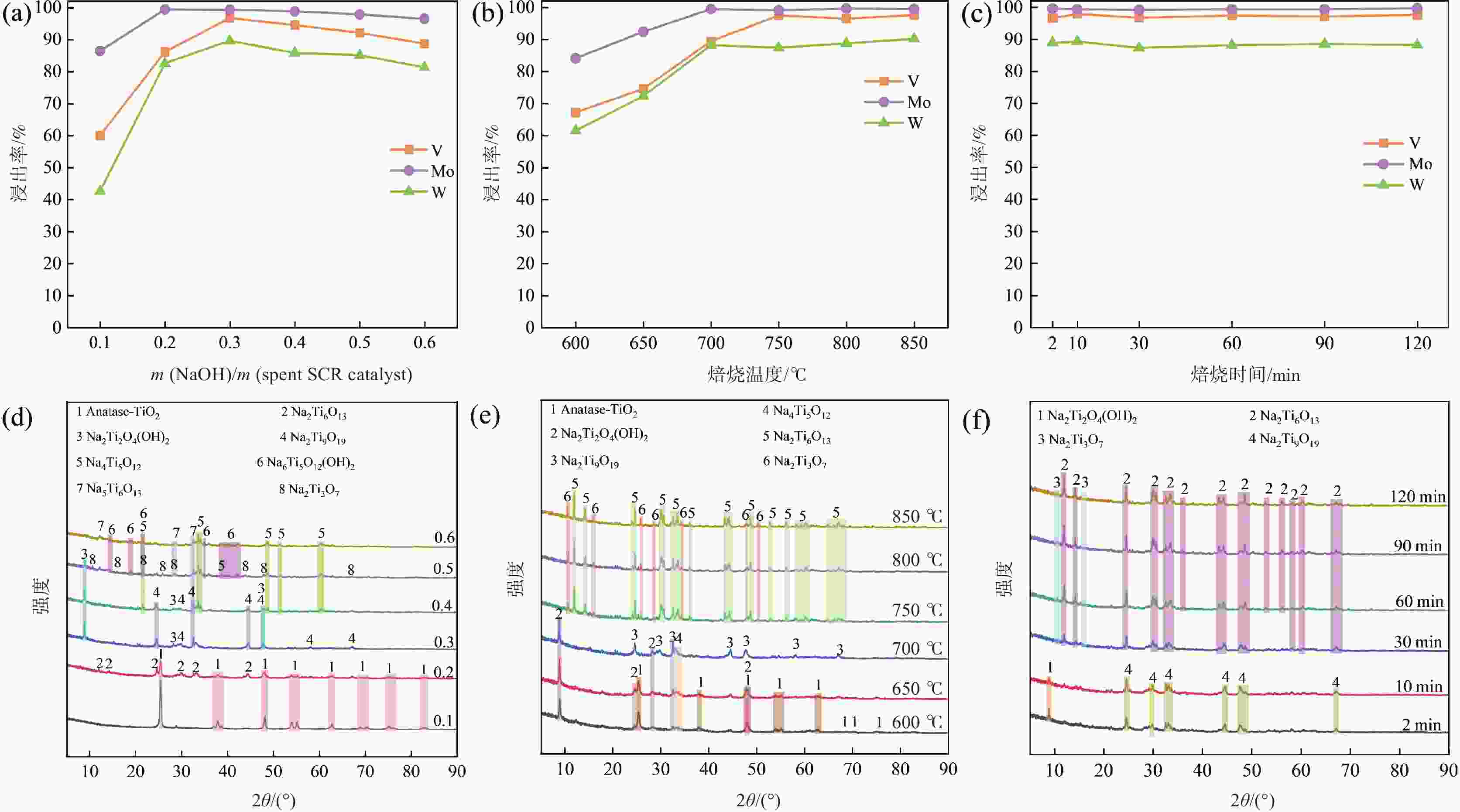
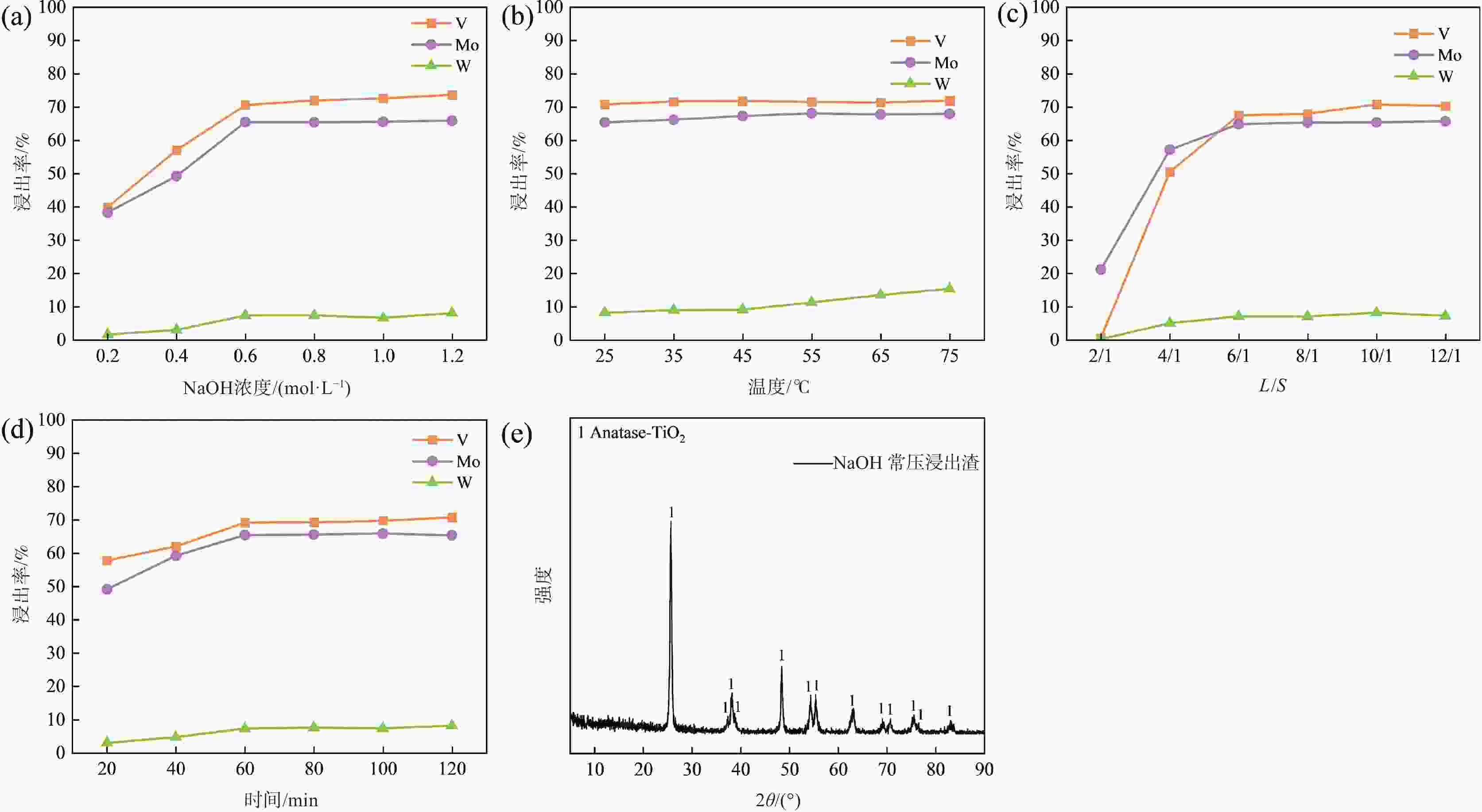
焙烧-水浸焙烧 0.3 750 30 97.29 99.33 87.57 浸出 25 6 3:1 NaOH
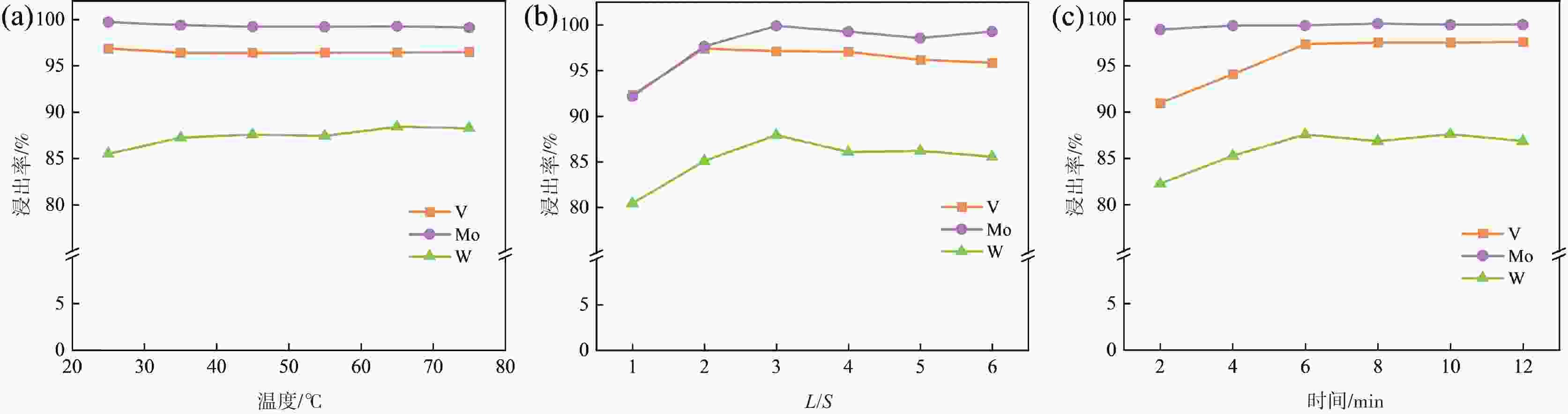
常压浸出浸出 25 60 6:1 0.6 69.16 65.44 7.09 NaOH
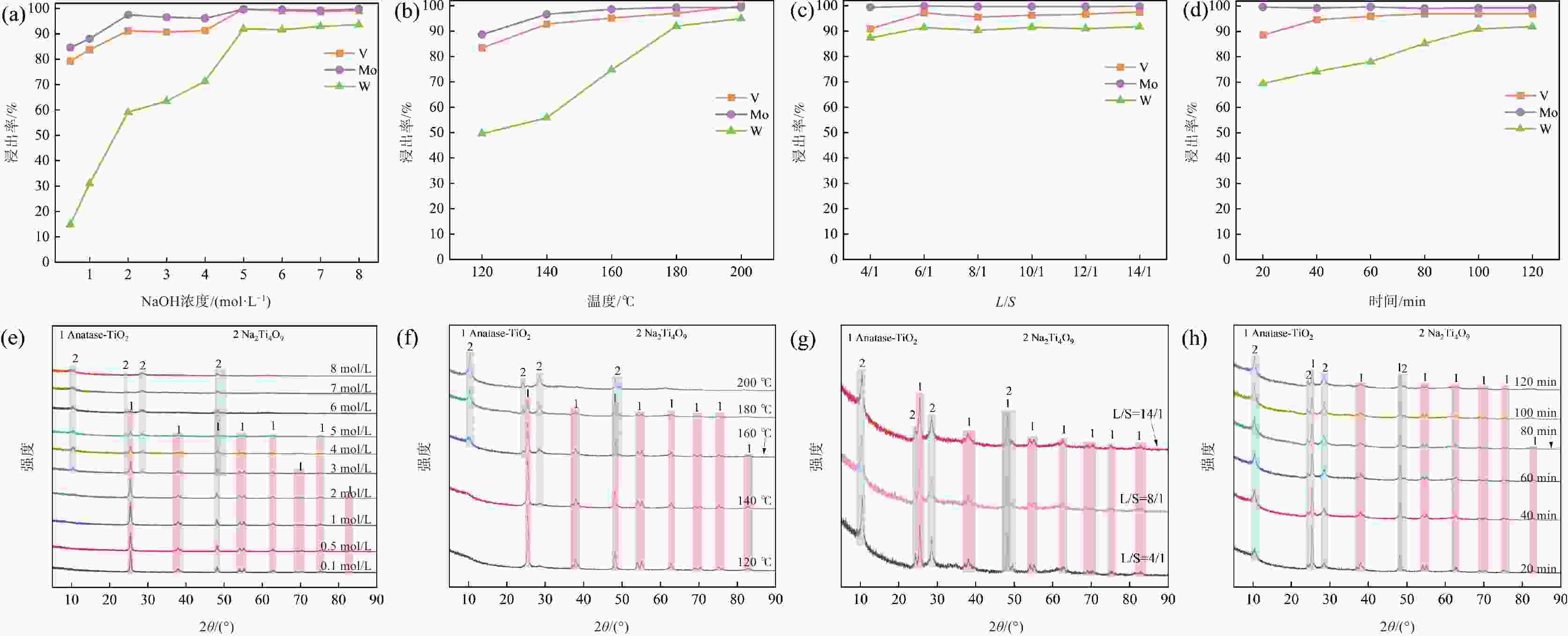
加压浸出浸出 180 100 6:1 5 96.97 99.25 90.93 表 3 NaOH焙烧-水浸工艺获得的浸出液元素浓度
Table 3. Element concentration of leaching solution obtained by the NaOH roasting-water leaching process
g/L V Mo W Al P Ti Si S Na Ca 3.39 2.72 2.63 1.27 0.32 0.08 3.72 4.34 表 4 NaOH焙烧-水浸获得的浸出渣的化学组成
Table 4. Chemical composition of leaching residue obtained by the NaOH roasting-water leaching process
% TiO2 Na2O SiO2 CaO Al2O3 V2O5 MoO3 WO3 P SO3 69.53 21.87 3.43 1.59 0.94 0.12 0.17 0.26 0.04 0.67 -
[1] WEI Y, LI D, QIAO J, et al. Recovery of spent SCR denitration catalyst: A review and recent advances[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(3): 110104. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.110104 [2] RAKSHA S. Selective catalytic reduction catalyst (SCR Catalyst) market size [2031]. Growth market reports, 2025. Report ID: CM-566. [3] GAO Y, LUAN T, LÜ T, et al. Performance of V2O5-WO3-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2013, 21(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1016/S1004-9541(13)60434-6 [4] WEN C, GUO Y, YAN K, et al. Variations in the physicochemical properties of spent honeycomb V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalysts from PC and CFB boilers SCR denitration systems[J]. Fuel, 2023, 347: 128384. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.128384 [5] MA L, XI X, CHEN J, et al. Comprehensive recovery of W, V, and Ti from spent selective reduction catalysts[J]. Rare Metals, 2023, 42(10): 3518-3531. doi: 10.1007/s12598-023-02321-0 [6] FERELLA F. A review on management and recycling of spent selective catalytic reduction catalysts[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 246: 118990. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118990 [7] GAO J, LU W, LI Y, et al. Organic acid-mediated leaching kinetics study and selective extraction of Mo, V, and Ni from spent catalysts[J]. Waste Management, 2024, 187: 198-206. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2024.07.022 [8] ZHANG Q, WU Y, LI L, et al. Sustainable approach for spent V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalysts management: Selective recovery of heavy metal vanadium and production of value-added WO3–TiO2 photocatalysts[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(9): 12502-12510. [9] SHI Z, DING Y, REN J, et al. Oxidation leaching of NiMoV alloy enriched from spent hydrogenation catalysts and solvent extraction of Mo and V[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(1): 111714. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2023.111714 [10] SU Q, MIAO J, LI H, et al. Optimizing vanadium and tungsten leaching with lowered silicon from spent SCR catalyst by pre-mixing treatment[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2018, 181: 230-239. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2018.10.003 [11] MA Z, LIU Y, ZHOU J, et al. Recovery of vanadium and molybdenum from spent petrochemical catalyst by Microwave-assisted leaching[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy, and Materials, 2019, 26(1): 33-40. doi: 10.1007/s12613-019-1707-y [12] CHOI I H, MOON G, LEE J Y, et al. Extraction of tungsten and vanadium from spent selective catalytic reduction catalyst for stationary application by pressure leaching process[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 197: 163-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.196 [13] CHOI I H, MOON G, LEE J Y, et al. Alkali fusion using sodium carbonate for extraction of vanadium and tungsten for the preparation of synthetic sodium titanate from spent SCR catalyst[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 12316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48767-0 [14] WANG B, YANG Q. Optimization of roasting parameters for recovery of vanadium and tungsten from spent SCR catalyst with composite roasting[J]. Processes, 2021, 9(11): 1923. doi: 10.3390/pr9111923 [15] HUANG S, LIU J, ZHANG C, et al. Extraction of molybdenum from spent HDS catalyst by two-stage roasting followed by water leaching[J]. JOM, 2019, 71(12): 4681-4686. doi: 10.1007/s11837-019-03741-z [16] LIETTI L, NOVA I, RAMIS G, et al. Characterization and reactivity of V2O5–MoO3/TiO2 De-NOx SCR catalysts[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 1999, 187(2): 419-435. doi: 10.1006/jcat.1999.2603 [17] Teng Y T. Recovery of waste SCR denitration catalyst resource components[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2020. (滕玉婷. 废弃SCR脱硝催化剂资源化成分回收[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2020.Teng Y T. Recovery of waste SCR denitration catalyst resource components[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2020. -




 下载:
下载: