Microstructure tailoring and fatigue crack resistance in precipitation-strengthened TB9 titanium alloy
-
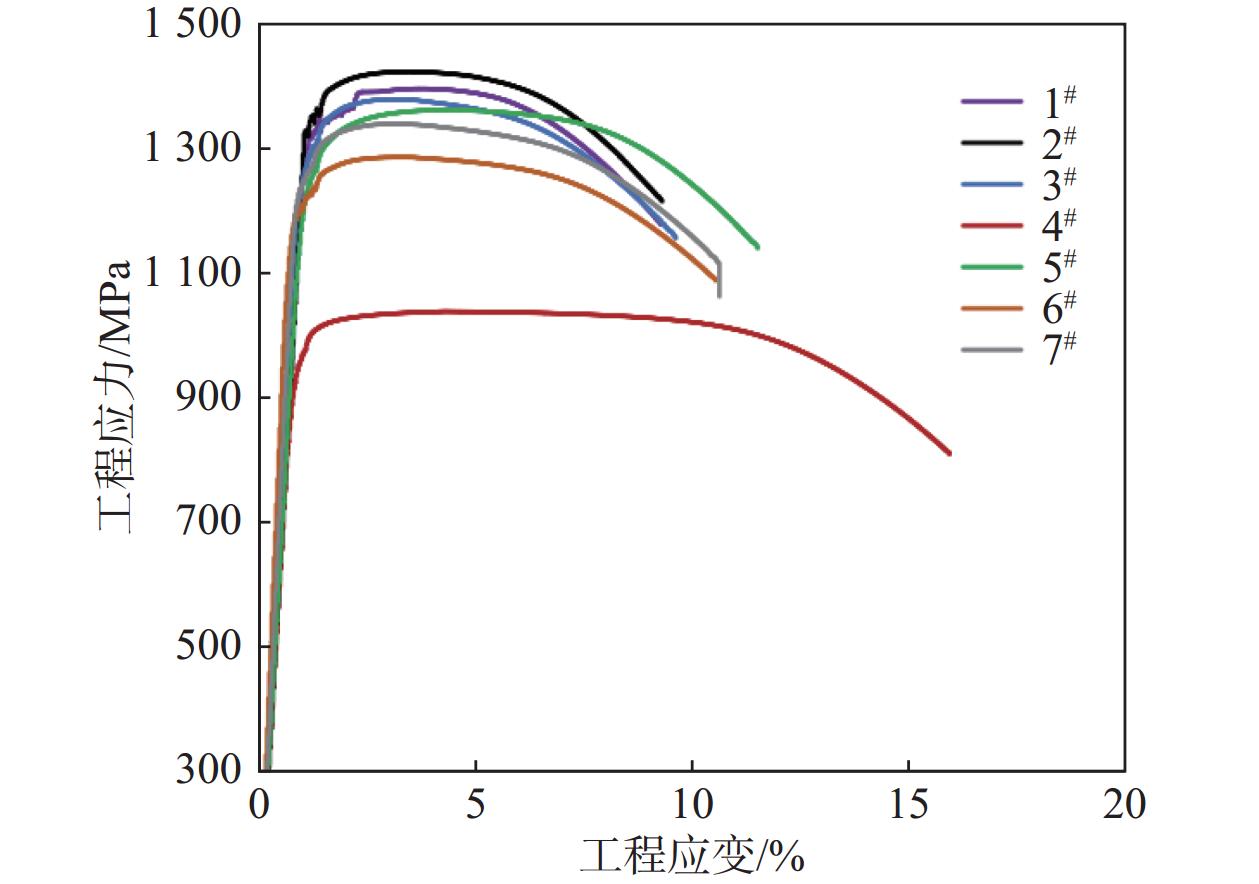
摘要: 研究了不同热处理制度对TB9(Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr)钛合金alpha(α)相和力学性能的影响。结果表明,当固溶温度从800 ℃上升至810 ℃,后续采用相同时效工艺时,虽然beta(β)晶粒尺寸略微长大,但其抗拉强度显著降低。采用相同固溶工艺时,500 ℃时效8 h出现了无α相析出区域,随着时效时间的延长,α析出相分布特点由非均匀逐渐转变为弥散分布,抗拉强度在时效16 h出现峰值。根据微观组织演变规律,采用800 ℃-0.5 h, 自然空气冷却(AC)+500 ℃-16 h, AC与810 ℃-0.5 h, AC+520 ℃-8 h, AC两种热处理制度时,获得相似微观组织,但前者的拉伸和疲劳性能明显优于后者。虽然两种合金的疲劳裂纹扩展机制均表现为粗糙度诱导裂纹闭合效应,但是通过对疲劳数据进行归一化处理,其结果进一步证实了α相尺寸和分布均匀性对力学性能影响显著。Abstract: The effect of microstructure on mechanical properties in TB9 (Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr) titanium alloy subject to different heat-treatment processes had been investigated. The results show when the solid solution temperature increases from 800 ℃to 810 ℃, and β grain size in the obtained alloyed after complete heat treatment slightly increases, while tensile strength decreases significantly. When the solid solution process remains same, the occurrence of precipitates free zones can be observed within β grain after aging at 500 ℃ for 8 h. The distribution of α precipitates becomes homogeneous with prolonged aging time, and there is a peak-value of tensile strength at aging temperature of 500 ℃ for 16 h. Based on the microstructure observations, both heat treatment processes of 800 ℃-0.5 h, AC+500 ℃-16 h, AC and 810 ℃-0.5 h, AC+520 ℃-8 h, generate comparable microstructures, while the former process can achieve superior tensile and fatigue properties. Although roughness-induced crack closure effect is main fatigue crack resistance behavior in both alloys after different heat treatment processed, fatigue data normalized by tensile strength verifies that the size and distribution of α precipitates impact mechanical properties significantly.
-
Key words:
- TB9 alloy /
- precipitation strengthening /
- fatigue properties /
- tensile strength /
- dislocation
-
表 1 TB9合金化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of TB9 titanium alloy
% Ti Al V Cr Mo Zr Fe O N H Bal. 3.34 7.92 5.90 3.96 4.10 0.059 0.126 0.013 0.00026 表 2 TB9合金热处理制度
Table 2. Heat treatment processes for TB9 titanium alloy
序号 固溶处理 时效处理 温度/℃ 时间/h 方式 温度/℃ 时间/h 方式 1# 800 0.5 AC 500 8 AC 2# 500 16 AC 3# 500 20 AC 4# 600 8 AC 5# 810 0.5 AC 500 8 AC 6# 520 8 AC 7# 830 0.5 AC 500 8 AC AC:自然空气冷却 -
[1] GAO W J. Impact of cold drawing deformation and aging on microstructure and mechanical property of TB9 titanium alloy[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2020(12): 154-155. (高文静. 变形量和时效对TB9钛合金丝材组织和性能影响[J]. 世界有色金属, 2020(12): 154-155.GAO W J. Impact of cold drawing deformation and aging on microstructure and mechanical property of TB9 titanium alloy[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2020(12): 154-155. [2] LI L, LUO B L, YANG H J, et al. Impact of solution and aging treatment on the properties of TB9 alloy and its spring[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2012, 29(5): 30-32. (李雷, 罗斌莉, 杨宏进, 等. 固溶时效处理对TB9钛合金棒材组织与性能及其弹簧弹性的影响[J]. 钛工业进展, 2012, 29(5): 30-32.LI L, LUO B L, YANG H J, et al. Impact of solution and aging treatment on the properties of TB9 alloy and its spring[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2012, 29(5): 30-32. [3] WANG J, HUANG L J, JIN W. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties and microstructure of TB9 alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(S1): 129-133. (王健, 黄鎏杰, 金伟. 热处理对TB9合金力学性能及显微组织的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(S1): 129-133.WANG J, HUANG L J, JIN W. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties and microstructure of TB9 alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(S1): 129-133. [4] HU M, QIU J K, LEI X F, et al. Precipitation behavior of secondary α phase and mechanical properties of high strength TB9 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2024, 44(2): 159-168. (胡明, 邱建科, 雷晓飞, 等. 高强TB9钛合金次生α相析出行为及力学性能[J]. 航空材料学报, 2024, 44(2): 159-168.HU M, QIU J K, LEI X F, et al. Precipitation behavior of secondary α phase and mechanical properties of high strength TB9 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2024, 44(2): 159-168. [5] HAN W S, ZHU B H, LI J F, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of Ti-38644 titanium alloy bar[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2022, 47(10): 185-190. (韩伟松, 朱宝辉, 李建锋, 等. 热处理对Ti-38644钛合金棒材组织和性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2022, 47(10): 185-190.HAN W S, ZHU B H, LI J F, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of Ti-38644 titanium alloy bar[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2022, 47(10): 185-190. [6] WANG X M, ZHANG S Q, YUAN Z Y, et al. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties of Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2017, 31(6): 409-414. (王雪萌, 张思倩, 袁子尧, 等. 时效处理对Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr合金力学性能的影响[J]. 材料研究学报, 2017, 31(6): 409-414.WANG X M, ZHANG S Q, YUAN Z Y, et al. Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties of Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2017, 31(6): 409-414. [7] SCHMIDT P, EL-CHAIKH A, CHRIST H. Effect of duplex aging on the initiation and propagation of fatigue cracks in the solute-rich metastable β titanium alloy Ti 38-644[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42: 2652-2667. doi: 10.1007/s11661-011-0662-7 [8] DONG E T, TENG A J, GENG N T, et al. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of TB9 alloy bar and wire in the production process[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2024, 39(4): 56-65. (董恩涛, 滕艾均, 耿乃涛, 等. TB9钛合金棒线材制备过程中微观组织和力学性能演变[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2024, 39(4): 56-65.DONG E T, TENG A J, GENG N T, et al. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of TB9 alloy bar and wire in the production process[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2024, 39(4): 56-65. [9] SHANG Q H, GUO J M, WANG G D, et al. Effects of solution and aging treatment on microstrucure and mechanical properties of TB9 titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2023, 52(14): 147-149. (尚庆慧, 郭金明, 王国栋, 等. 固溶和时效处理对TB9钛合金显微组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2023, 52(14): 147-149.SHANG Q H, GUO J M, WANG G D, et al. Effects of solution and aging treatment on microstrucure and mechanical properties of TB9 titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2023, 52(14): 147-149. [10] LI S J, HU F C, MA L Y, et al. Effect of aging treatment on microstructure and properties of solution treated and cold-drawn TB9 titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2024, 49(9): 251-254. (李世键, 胡福常, 马蓼奕, 等. 时效处理对固溶冷拉态TB9钛合金组织与性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2024, 49(9): 251-254.LI S J, HU F C, MA L Y, et al. Effect of aging treatment on microstructure and properties of solution treated and cold-drawn TB9 titanium alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2024, 49(9): 251-254. [11] CUI W, GUO A. Microstructures and properties of biomedical TiNbZrFe β-titanium alloy under aging conditions[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2009, 527(1-2): 258-262. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2009.08.057 [12] KOYAMA M, ZHANG Z, WANG M, et al. Bone-like crack resistance in hierarchical metastable nanolaminate steels[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6329): 1055-1057. doi: 10.1126/science.aal2766 [13] ZHANG Z, KOYAMA M, WANG M, et al. Fatigue resistance of laminated and non-laminated TRIP-maraging steels: Crack roughness vs tensile strength[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2019, 50(3): 1142-1145. doi: 10.1007/s11661-018-5081-6 [14] DONG R, ZHANG X, KOU H, et al. Texture evolution associated with the preferential recrystallization during annealing process in a hot-rolled near β titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 12: 63-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.02.062 [15] WILLIAMS J C. Titanium and titanium alloys: scientific and technological aspects volume 3[M]. Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. [16] HUANG J, WANG Z, ZHOU J. Cyclic deformation response of β-annealed Ti-5Al-5V-5Mo-3Cr alloy under compressive loading conditions[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42: 2868-2880. doi: 10.1007/s11661-011-0705-0 [17] BUCHINGER L, CHENG A S, STANZL S, et al. The cyclic stress—strain response and dislocation structures of Cu 16 at. %Al alloy III: Single crystals fatigued at low strain amplitudes[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1986, 80(2): 155-167. doi: 10.1016/0025-5416(86)90194-1 [18] KRUPP U, FLOER W, LEI J, et al. Mechanisms of short-fatigue-crack initiation and propagation in a β-Ti alloy[J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 2002, 82(17-18): 3321-3332. [19] GAO T, XUE H, SUN Z, et al. Investigation of crack initiation mechanism of a precipitation hardened TC11 titanium alloy under very high cycle fatigue loading[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2020, 776: 138989. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.138989 [20] ODA Y, FURUYA Y, NOGUCHI H, et al. AFM and SEM observation on mechanism of fatigue crack growth in an Fe-Si single crystal[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2002, 113(3): 213-231. doi: 10.1023/A:1014211617958 [21] PIPPAN R, STROBL G, KREUZER H, et al. Asymmetric crack wake plasticity–a reason for roughness induced crack closure[J]. Acta materialia, 2004, 52(15): 4493-4502. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2004.06.014 [22] ELBER W. The significance of fatigue crack closure[M]//ASTM International, 1971. -





 下载:
下载: