Research on the microstructure and properties of titanium alloy weld metal by laser-arc hybrid welding with different filler wires
-
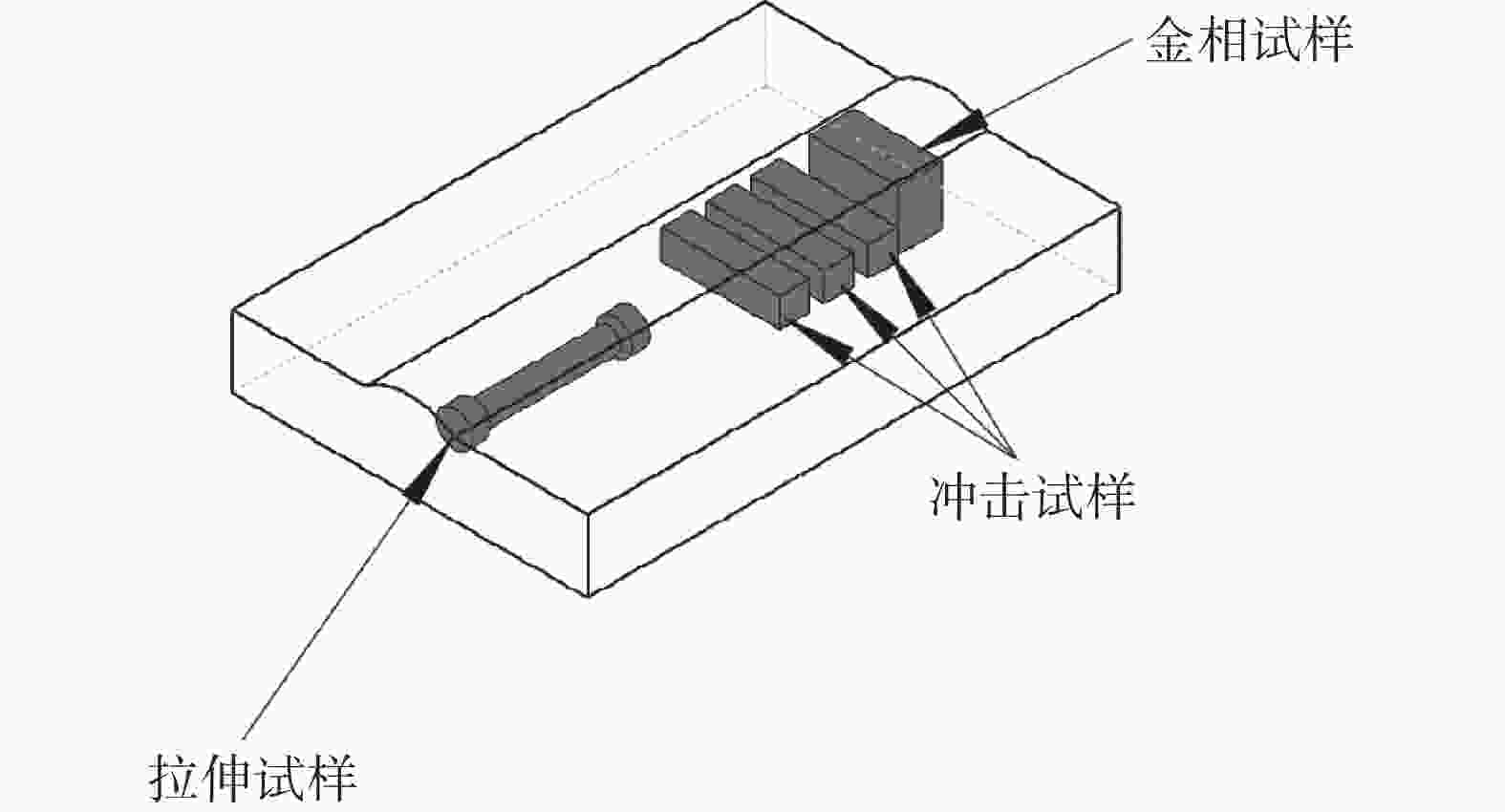
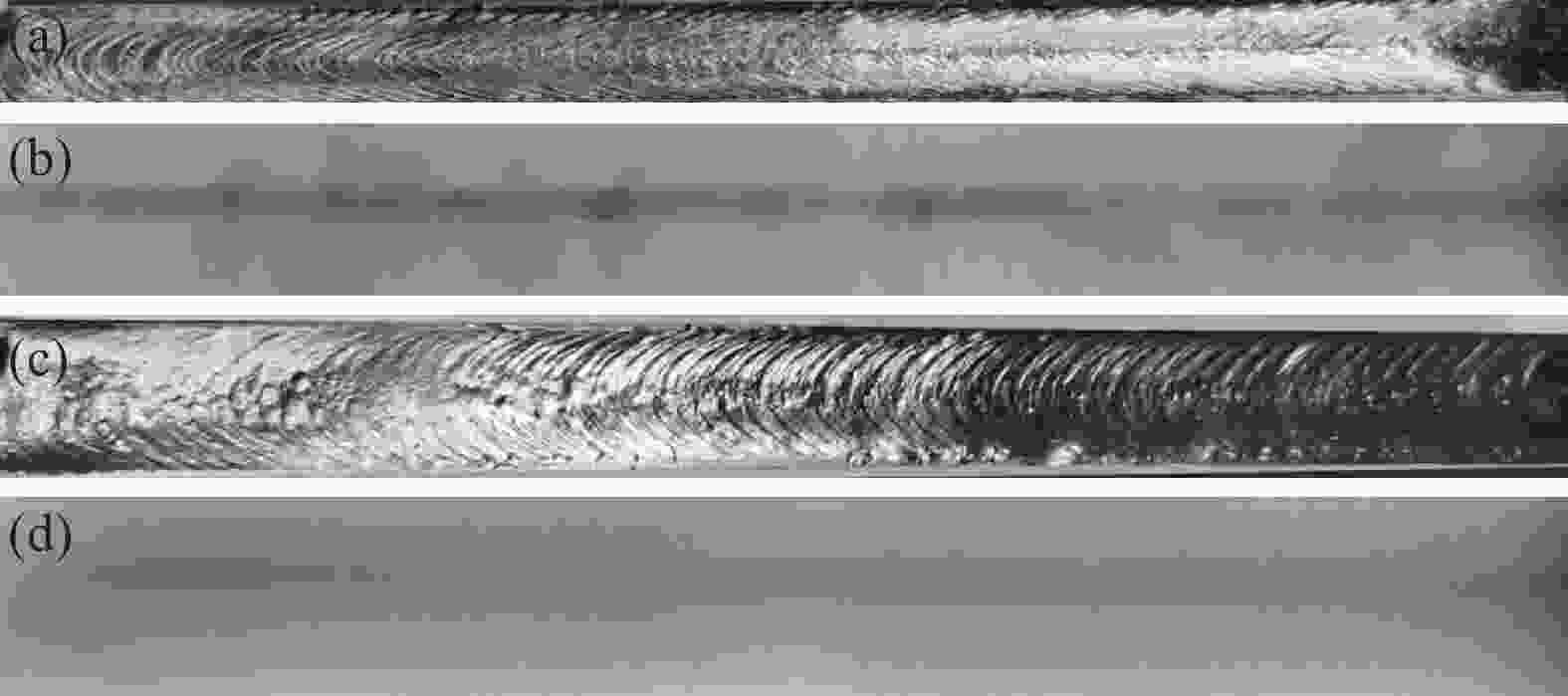
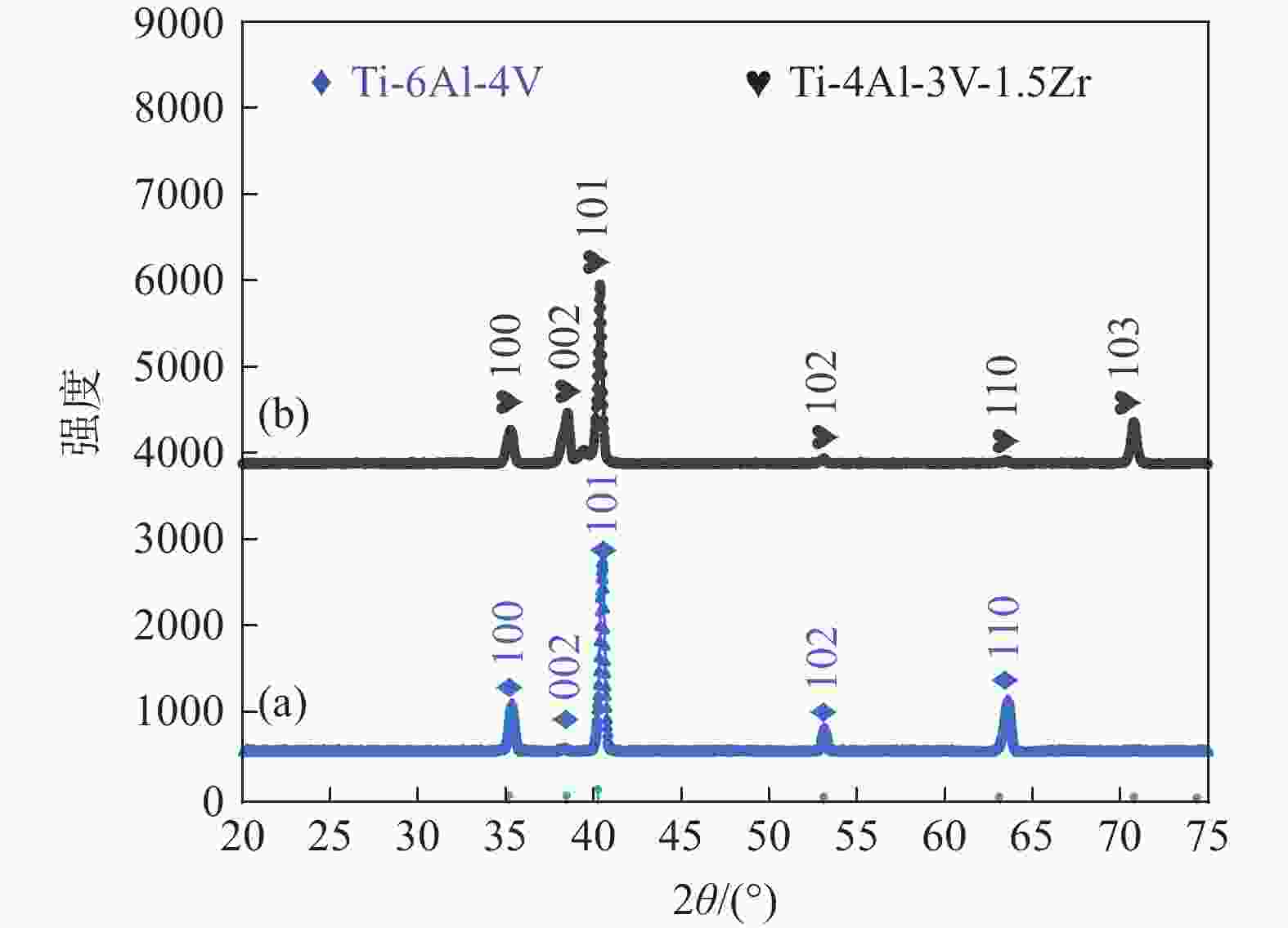
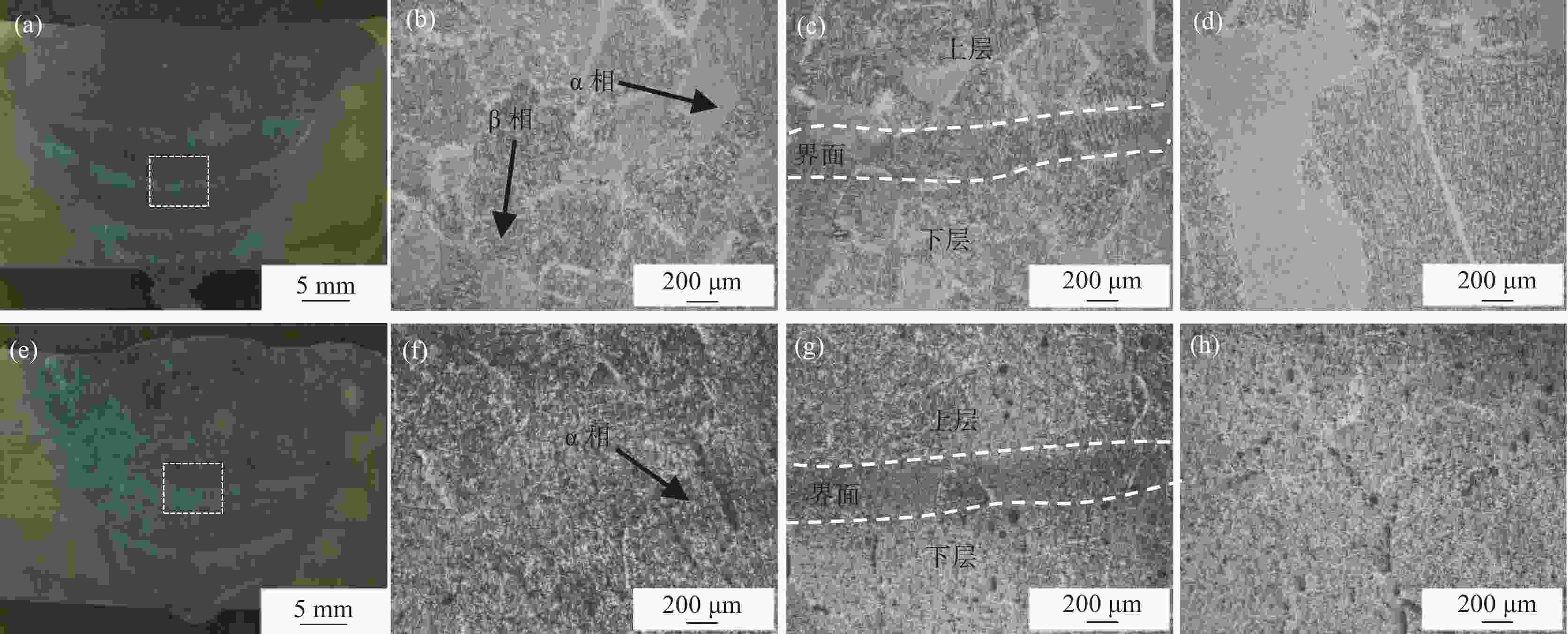
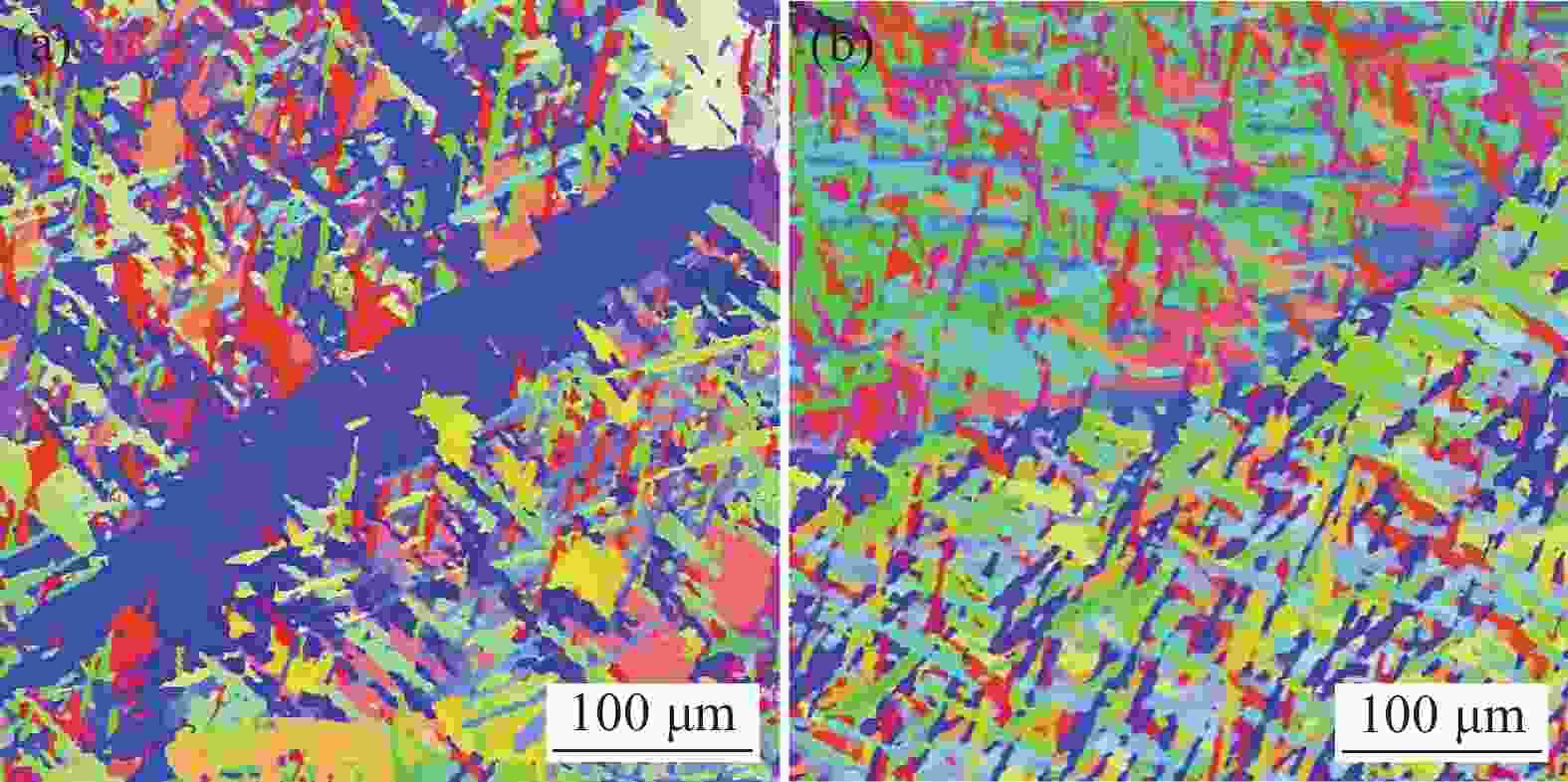
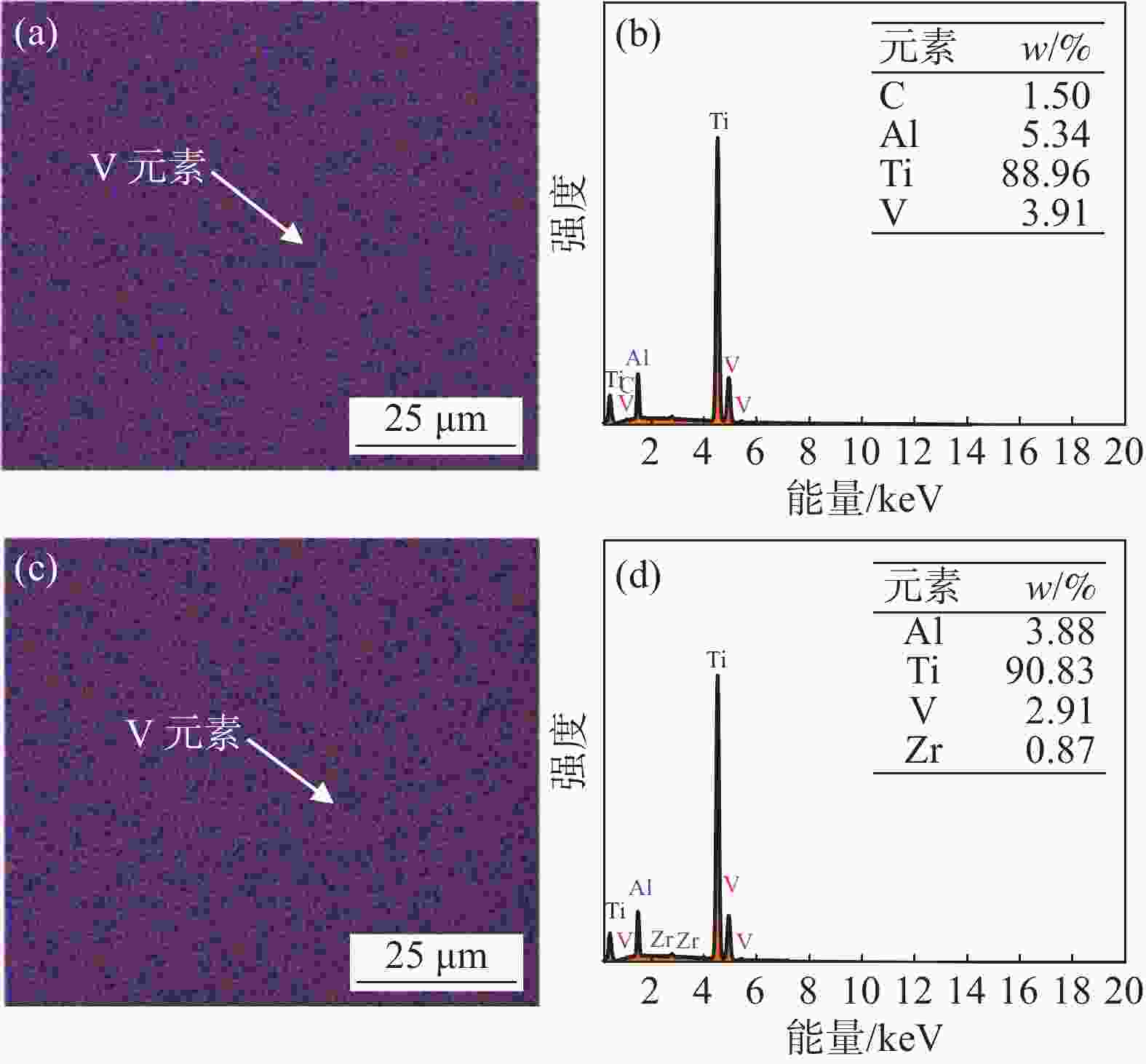
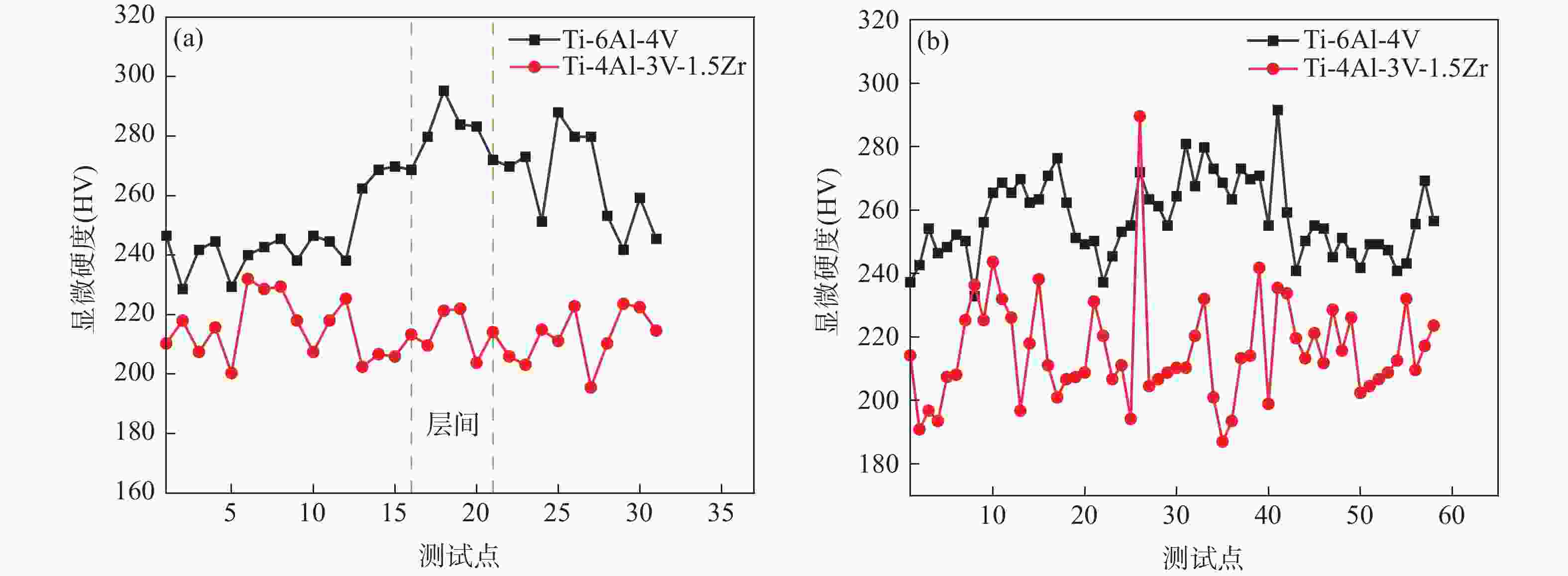
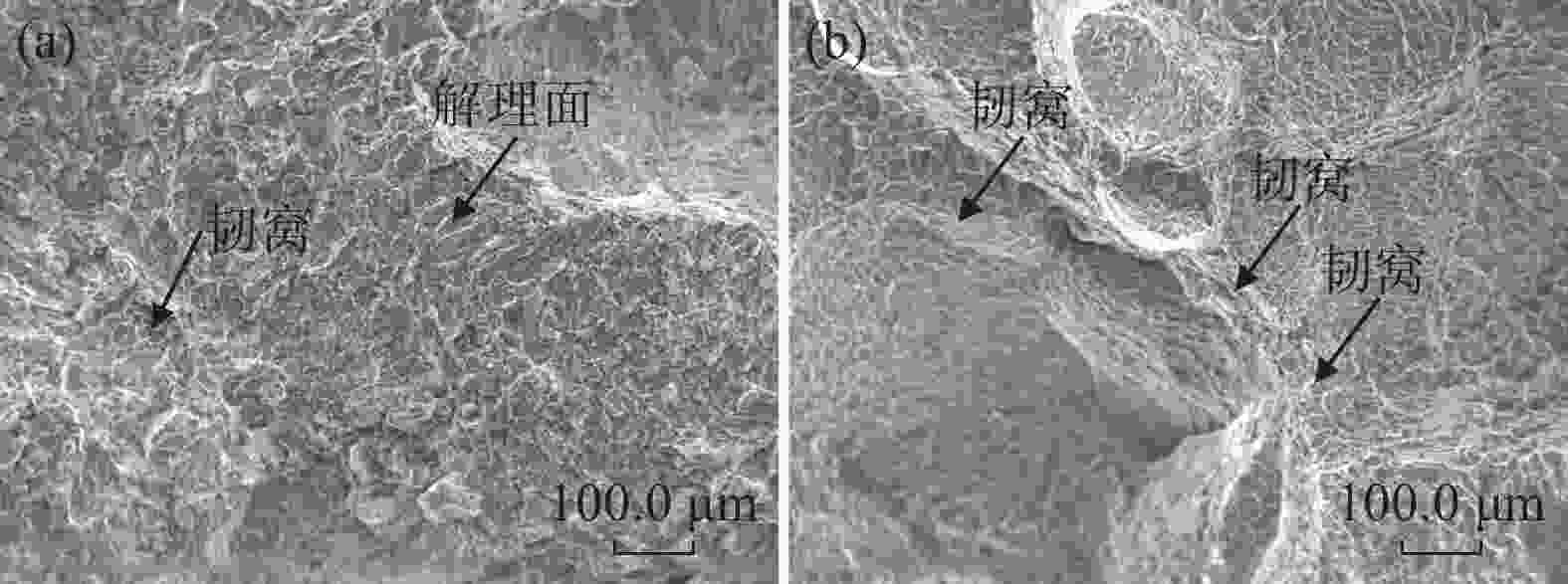
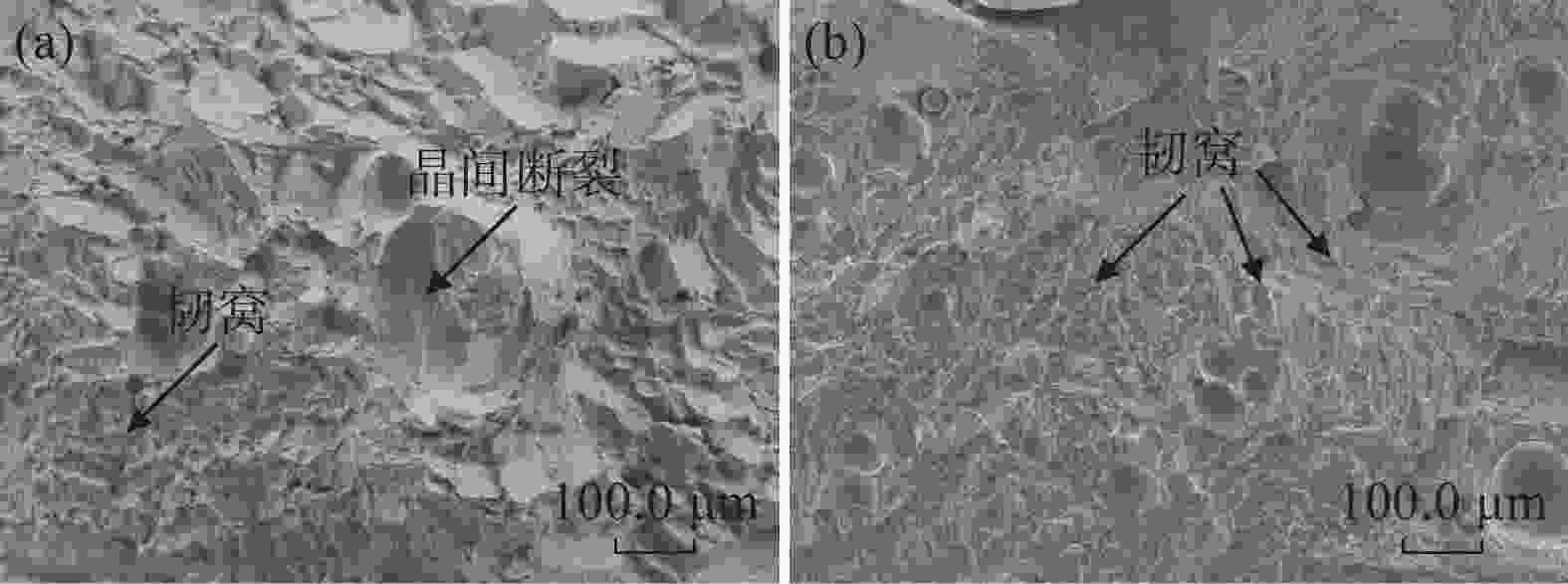
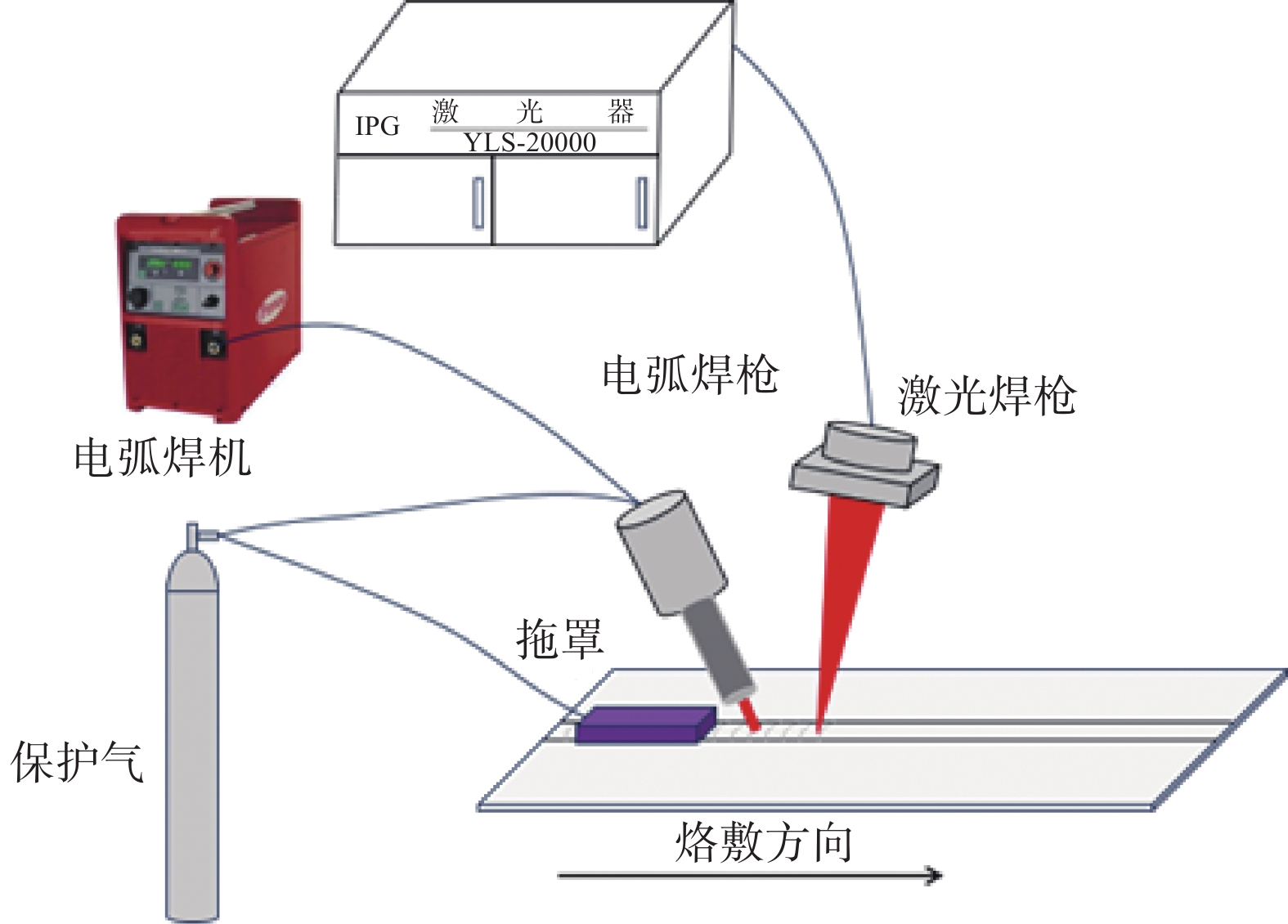
摘要: 为探明激光−电弧复合焊接中钛合金焊丝熔敷金属组织性能的演变,分别以Ti-6Al-4V和Ti-4Al-3V-1.5Zr焊丝为焊材,利用摆动激光-MIG复合焊接工艺制备钛合金焊丝熔敷金属,采用X射线探伤、OM、SEM和EBSD分析熔敷金属的缺陷、组织、物相成分、晶粒尺寸和断口形貌。采用拉伸试验机、冲击试验机及维氏硬度仪测试熔敷金属的强度、冲击功和硬度。结果表明:摆动激光-MIG复合焊接钛合金熔敷金属内部无明显气孔和裂纹;Ti-6Al-4V焊丝熔敷金属由针叶状α相和网篮状β相组成,晶粒较小,平均晶粒尺寸约7.96 µm,硬度(HV0.2)、抗拉强度和冲击吸收功分别为257、
1057 MPa和41.7 J;Ti-4Al-3V-1.5Zr焊丝熔敷金属主要由片层状α相构成,晶粒较大,平均晶粒尺寸为8.96 µm,硬度和抗拉强度较低,而冲击吸收功较大,冲击吸收功49.6 J。这与摆动激光复合焊熔敷工艺、Ti-6Al-4V中V元素的第二相强化和晶粒细化作用密切相关。-
关键词:
- 钛合金焊丝 /
- 摆动激光−电弧复合焊 /
- 熔敷金属 /
- 微观组织 /
- 力学性能
Abstract: To elucidate the evolution mechanism of the microstructure and properties of the titanium alloy during the welding process, deposited metal was prepared by oscillating laser-MIG hybrid welding with Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-4Al-3V-1.5Zr welding wires. Titanium alloy welding metal was characterized by X-ray detection, OM, SEM and EBSD to examine defects, tissue, phase composition, grain size, and fracture morphology. The tensile testing machine, impact testing machine and Vickers hardness instrument were employed to evaluate the strength, impact force, and hardness of the deposited metal. The results indicate that there are no obvious pores and cracks in the oscillating laser-arc hybrid welding titanium alloy. The deposited metal from Ti-6Al-4V wire consists of needle-like α phase and mesh-like β phase, with fine crystal grains averaging approximately 7.96 µm in size. The hardness (HV0.2), tensile strength, and impact absorption energy were measured at 257,1057 MPa and 41.7 J, respectively. In contract, the deposited metal from Ti-4Al-3V-1.5Zr wire is primarily composed of lamellar α phase, with larger grains averaging 8.96 µm. And this deposited metal exhibits lower hardness and tensile strength but relatively higher impact absorption energy of 49.6 J. These differences are attributed to the melting process of oscillating laser welding, the second-phase enhancement and grain refinement induced by vanadium Ti-6Al-4V. -
表 1 Ti-6Al-4V和Ti-4Al-3V-1.5Zr焊丝化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of Ti-6Al-4V and Ti-4Al-3V-1.5Zr wires
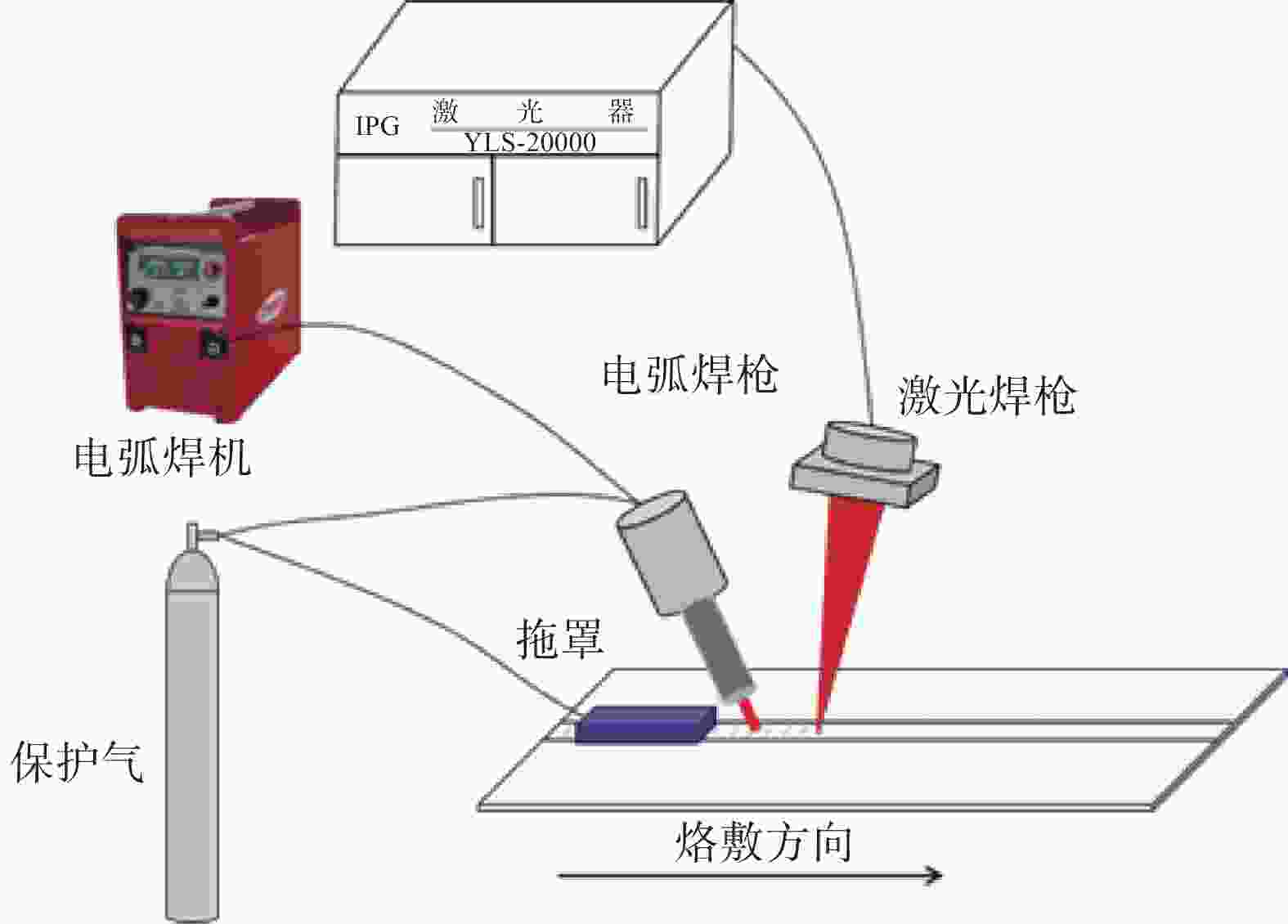
% 材料 Al V Fe O C N H Si Zr Ti Ti-6Al-4V 6.15 4.15 0.025 0.11 0.036 0.006 0.001 余量 Ti-4Al-3V-1.5Zr 3.75 2.36 0.09 0.15 0.028 0.025 0.002 0.06 1.13 余量 表 2 摆动激光-MIG复合熔敷参数
Table 2. Parameters of oscillating laser-MIG hybrid welding
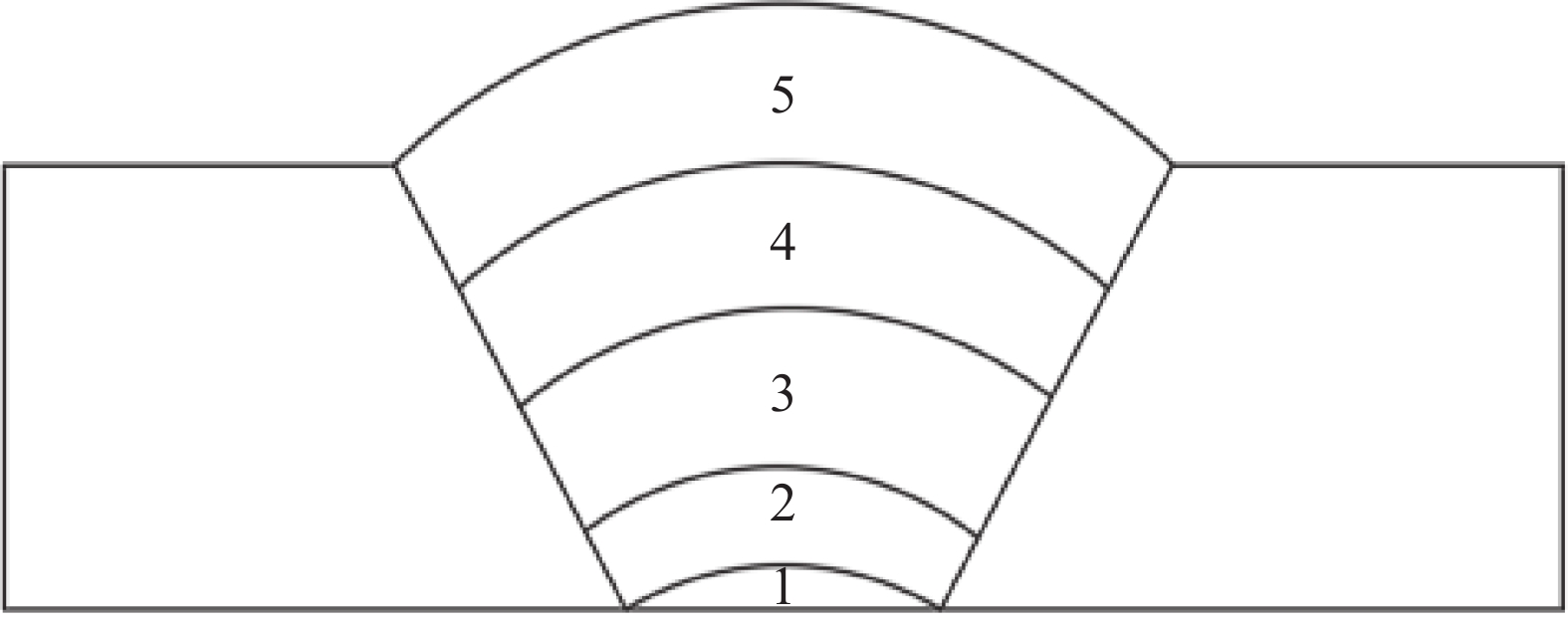
层数 激光功率/kW 激光摆动频率/Hz 激光摆动幅度/mm 熔敷速度/(m·min−1) 光丝间距/mm 电弧电流/A 机器人摆动幅度/mm 1~5 2 300 1 0.2~0.4 2 180~220 4~10 表 3 各区域平均晶粒尺寸
Table 3. Average grain size of each region
μm 材料 下层晶粒尺寸 层间晶粒尺寸 上层晶粒尺寸 Ti-6Al-4V 9.35 6.984 7.55 Ti-4Al-3V-1.5Zr 9.649 8.4 8.84 表 4 抗拉强度和断后伸长率
Table 4. Tensile strength and elongation
材料 抗拉强度 Rm/MPa 断后伸长率 A/% Ti-6Al-4V 1057 9.5 Ti-4Al-3V-1.5Zr 896 13.3 表 5 熔敷金属吸收功
Table 5. Impact absorption energy of the deposited metal
材料 吸收功/J 平均值/J Ti-6Al-4V 40.9, 41.8, 42.4 41.7 Ti-4Al-3V-1.5Zr 48.9,50.2,49.7 49.6 -
[1] GAO Y N, ZHANG S, LIU J, et al. Joining process, microstructure and properties of ultra-thin plate TA1/304 dissimilar metals[J/OL]. Welding & Joining, 1-7[2024-10-05]. (郜雅楠, 张帅, 刘杰, 等. 超薄板TA1/304异种金属连接工艺、组织及性能[J/OL]. 焊接, 1-7[2024-10-05].GAO Y N, ZHANG S, LIU J, et al. Joining process, microstructure and properties of ultra-thin plate TA1/304 dissimilar metals[J/OL]. Welding & Joining, 1-7[2024-10-05]. [2] YADAV P, SAXENA K K. Effect of heat-treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti alloys: an overview[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020, 26: 2546-2557. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.541 [3] LIU G Q, FENG C J, XIN L, et al. Preparation and microstructure of diffused Ti-Al-Si coatings on Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J/OL]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 1-18[2024-10-05]. (刘国强, 冯长杰, 辛丽, 等. 钛合金表面Ti-Al-Si扩散涂层的制备和显微结构[J/OL]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 1-18[2024-10-05].LIU G Q, FENG C J, XIN L, et al. Preparation and microstructure of diffused Ti-Al-Si coatings on Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J/OL]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 1-18[2024-10-05]. [4] MOTYKA M. Martensite formation and decomposition during traditional and AM processing of two phase titanium alloys—An overview[J]. Metals, 2021, 11(3): 481. doi: 10.3390/met11030481 [5] LIU Q M, ZHANG Z H, LIU S F, et al. Application and development of titanium alloy in aerospace and military hardware[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2015, 27(3): 1-4. (刘全明, 张朝晖, 刘世锋, 等. 钛合金在航空航天及武器装备领域的应用与发展[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2015, 27(3): 1-4.LIU Q M, ZHANG Z H, LIU S F, et al. Application and development of titanium alloy in aerospace and military hardware[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2015, 27(3): 1-4. [6] LING Z Y. Research on titanium alloy sheets and bending properties under the compound energy-field with temperature, ultrasonic vibration and speed[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Aerospace University, 2022. (凌志远. 温度/超声/速度复合能场下钛合金板材及弯曲性能研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳航空航天大学, 2022.LING Z Y. Research on titanium alloy sheets and bending properties under the compound energy-field with temperature, ultrasonic vibration and speed[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Aerospace University, 2022. [7] DU J, WEI Z Y, WANG X, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental research of fused deposition for forming large-size thin-walled parts[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2016(8): 86-89, 93. (杜军, 魏正英, 王鑫, 等. 大型薄壁件熔融成形数值计算与工艺实验研究[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2016(8): 86-89, 93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2016.08.023DU J, WEI Z Y, WANG X, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental research of fused deposition for forming large-size thin-walled parts[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2016(8): 86-89, 93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2016.08.023 [8] WANG Y. Induction re-melt deposit welding for aluminum cladding to copper[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2012. (汪云. 铜基体表面感应熔敷铝基材料[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2012.WANG Y. Induction re-melt deposit welding for aluminum cladding to copper[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology, 2012. [9] CHEN W. Microstructure and mechanical property control of CMT arc additive manufacturing TC4 titanium alloy[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2019. (陈伟. CMT电弧增材制造TC4钛合金组织及力学性能调控[D]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2019.CHEN W. Microstructure and mechanical property control of CMT arc additive manufacturing TC4 titanium alloy[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2019. [10] HU J, TAO M P, TANG J Y. Study on forming process and heat treatment behavior of 3D print TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017, 46(16): 220-224. (胡婧, 陶梅平, 唐金颖. 3D打印TC4钛合金的成形工艺与热处理行为研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2017, 46(16): 220-224.HU J, TAO M P, TANG J Y. Study on forming process and heat treatment behavior of 3D print TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017, 46(16): 220-224. [11] GONCALO P, FILOMENO M, STEWART W. Laser stabilization of GMAW additive manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V components[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 272: 1-8. [12] YAO Y L, FENG N Q. Automatic identification of robot weld defect image based on artificial neural network[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2023(6): 268-271, 276. (姚迎乐, 冯乃勤. 人工神经网络的机器人焊缝缺陷图像自动辨识[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2023(6): 268-271, 276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2023.06.056YAO Y L, FENG N Q. Automatic identification of robot weld defect image based on artificial neural network[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2023(6): 268-271, 276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2023.06.056 [13] GAO P F, FAN J K, ZHANG J, et al. The influence of interlayer temperature on microstructure and properties of high nitrogen steel fabricated by arc additive manufacturing[J/OL]. Acta Armamentari, 1-12[2024-07-10]. (高鹏飞, 范霁康, 张建, 等. 层间温度对高氮钢电弧增材组织与性能的影响[J/OL]. 兵工学报, 1-12[2024-07-10].GAO P F, FAN J K, ZHANG J, et al. The influence of interlayer temperature on microstructure and properties of high nitrogen steel fabricated by arc additive manufacturing[J/OL]. Acta Armamentari, 1-12[2024-07-10]. [14] LUAN Z F, DI X J, LI C N, et al. Effect of Al and Mg elements on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the fused metal[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(12): 20-26. (栾宗锋, 邸新杰, 利成宁, 等. Al和Mg元素对吉帕级熔敷金属组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(12): 20-26. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20211201001LUAN Z F, DI X J, LI C N, et al. Effect of Al and Mg elements on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the fused metal[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(12): 20-26. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20211201001 [15] YAO X Z, LI H J, YANG Z W, et al. Tailoring the microstructure and mechanical properties of wire arc additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloy by trace TiC powder addition[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2024, 45(6): 12-19. (姚兴中, 李会军, 杨振文, 等. 微量TiC粉末合金化改善电弧增材制造Ti-6Al-4V合金的组织和性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2024, 45(6): 12-19. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230422001YAO X Z, LI H J, YANG Z W, et al. Tailoring the microstructure and mechanical properties of wire arc additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V alloy by trace TiC powder addition[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2024, 45(6): 12-19. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230422001 [16] ZHANG Z Q, LI H Q, HE S W, et al. Study on microstructure characterization by laser and CMT-P arc hybrid additive components[J]. Materials Protection, 2023, 56(10): 74-82. (张志强, 李涵茜, 贺世伟, 等. 激光与CMT-P电弧复合增材构件的微观组织特征研究[J]. 材料保护, 2023, 56(10): 74-82.ZHANG Z Q, LI H Q, HE S W, et al. Study on microstructure characterization by laser and CMT-P arc hybrid additive components[J]. Materials Protection, 2023, 56(10): 74-82. -




 下载:
下载: