Study on the microstructure and properties of the swing laser-MIG composite welding joint of TC4B titanium alloy
-
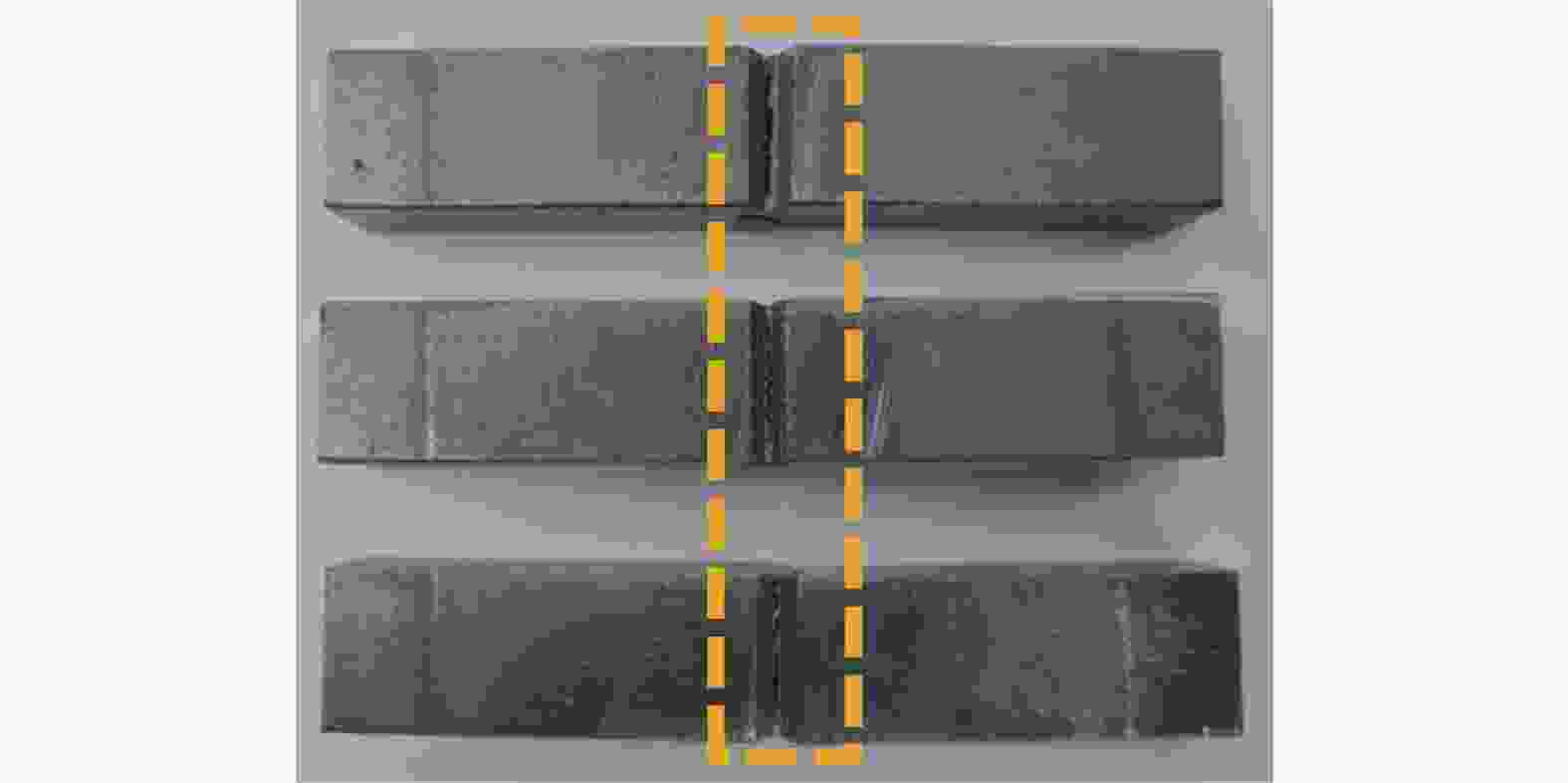
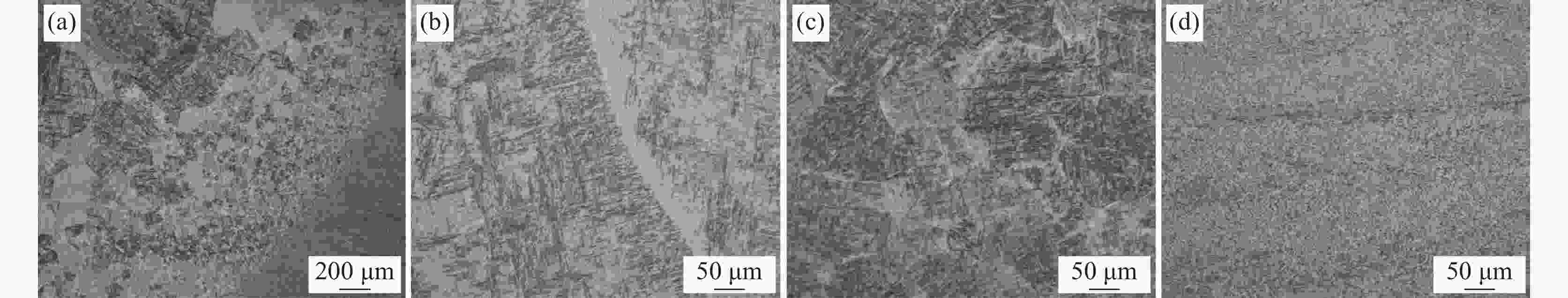
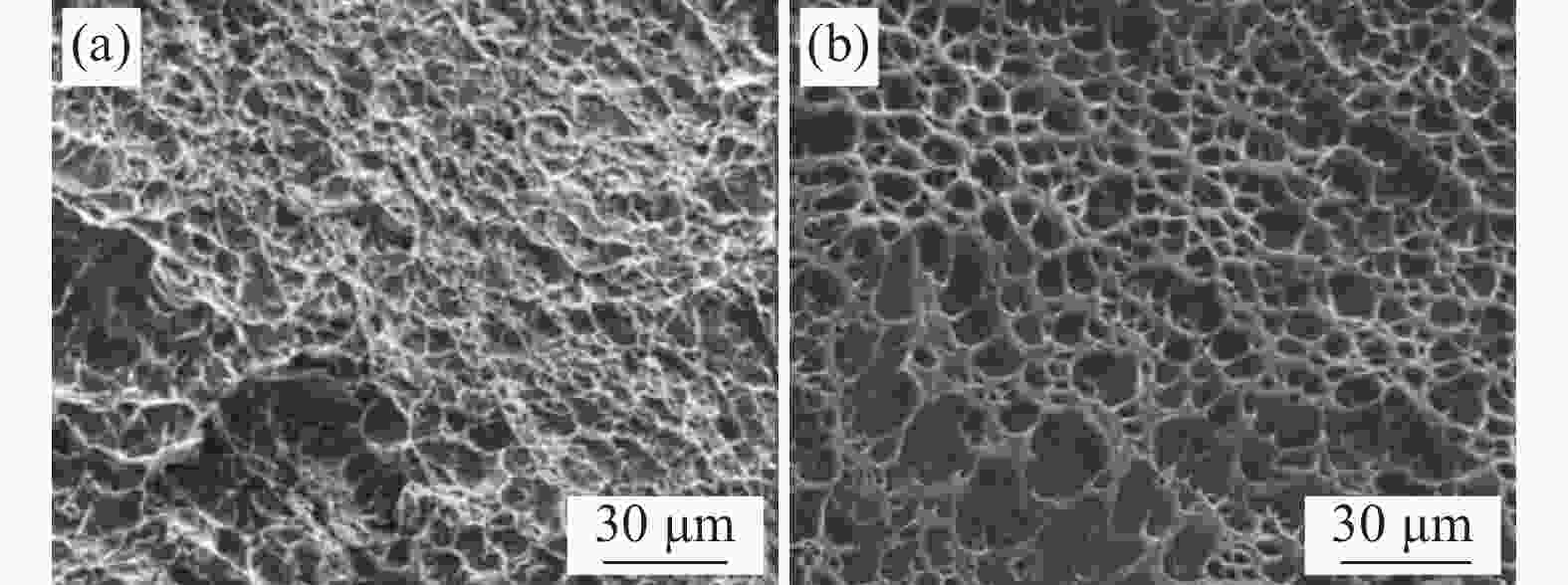
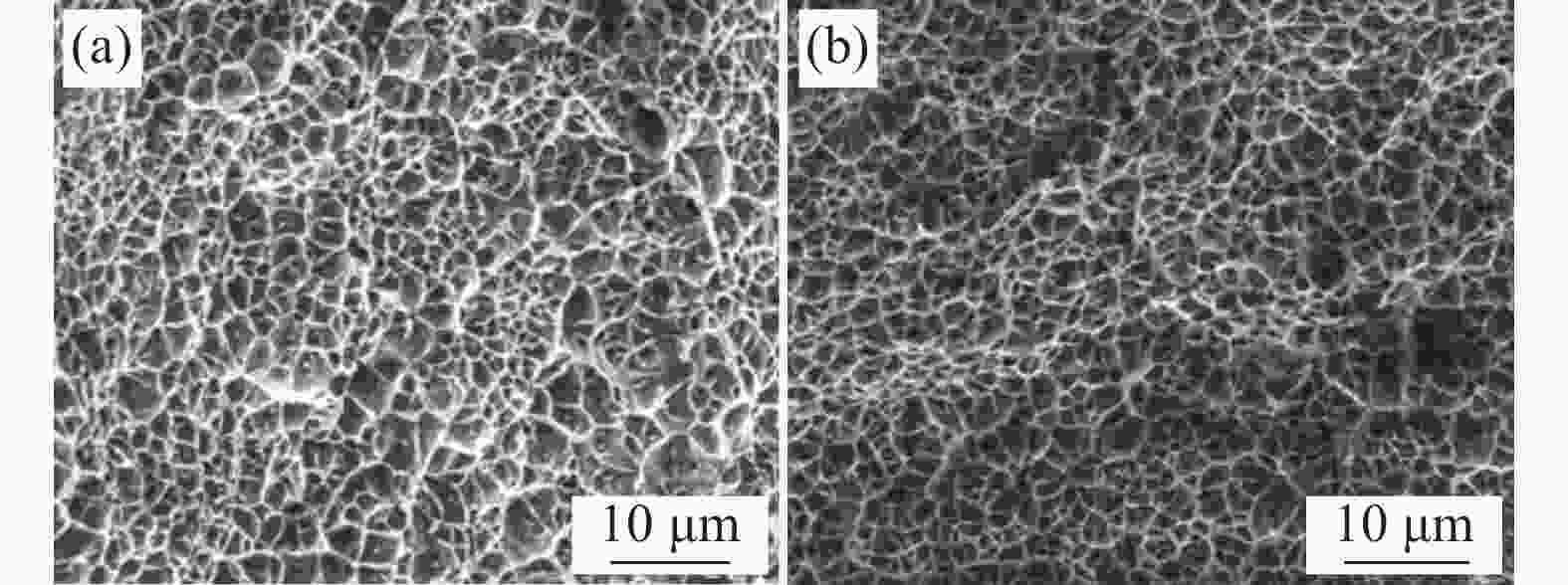
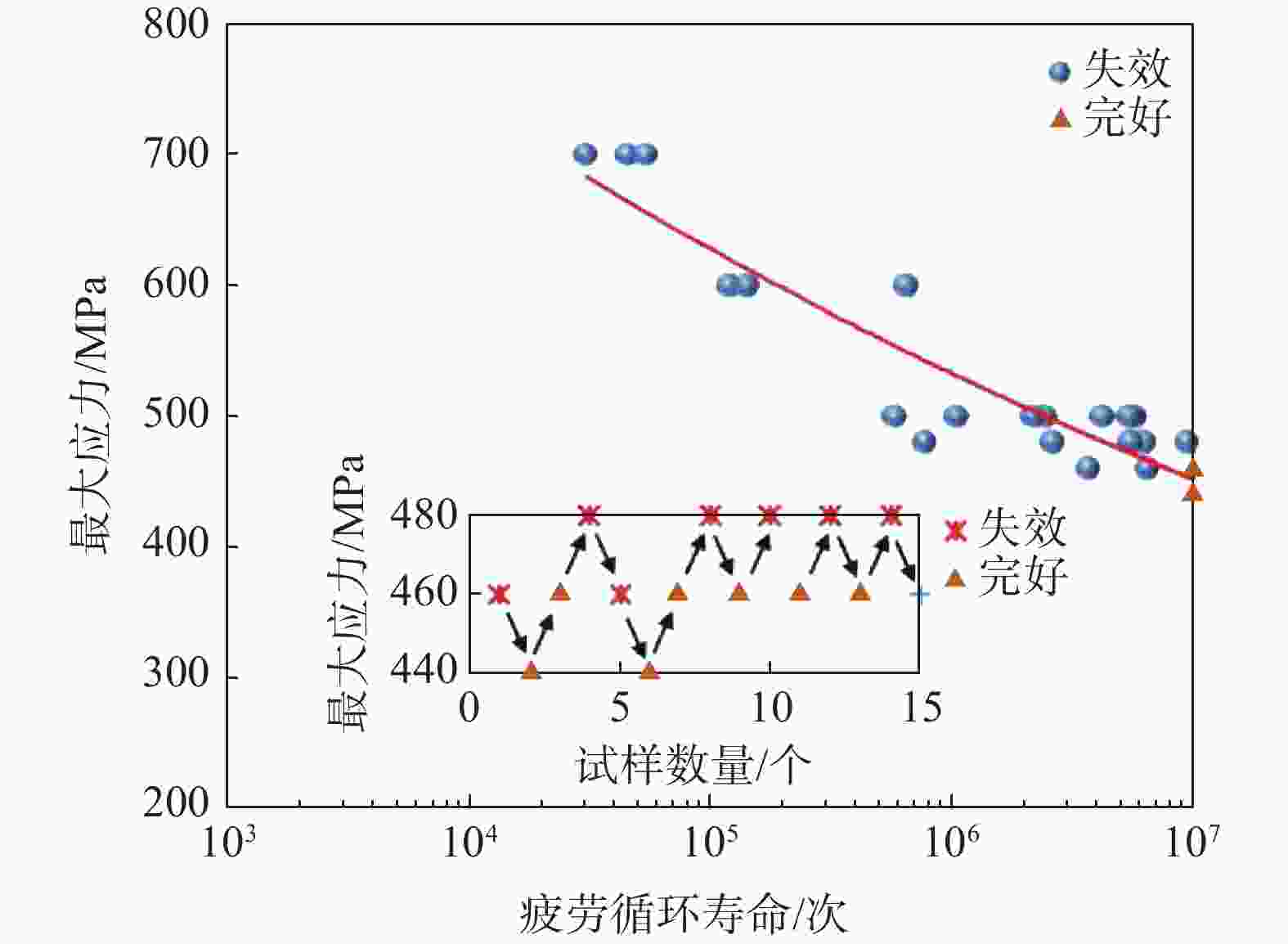
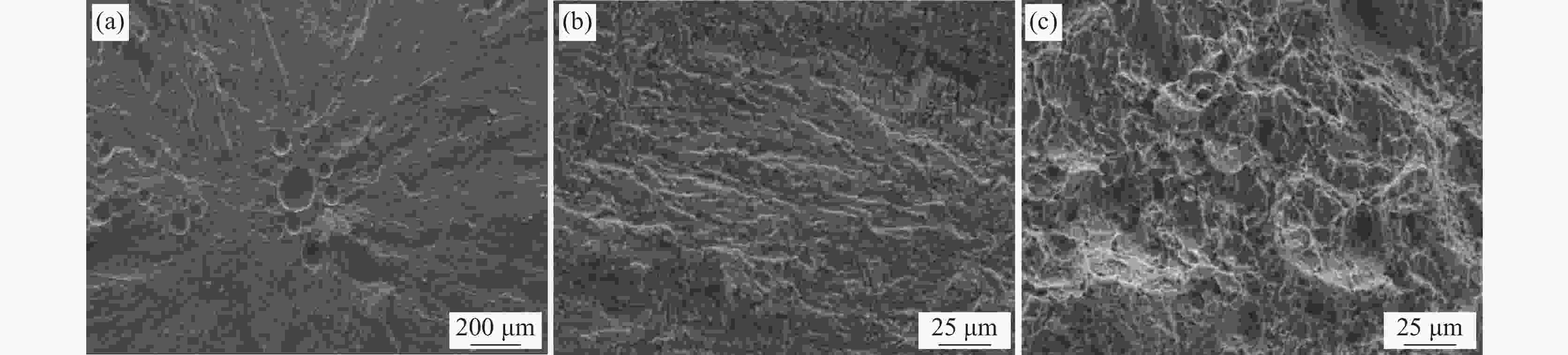
摘要: 采用摆动激光-MIG复合焊焊接20 mm厚TC4B钛合金板,研究焊接接头的显微组织,对比有无摆动对焊接接头抗拉强度以及冲击性能的影响,分析焊接接头的疲劳性能。结果表明:焊接热影响区分为粗晶区和细晶区,粗晶区高温区域停留时间较长,α相可以完全转变为高温β相,冷却开始β相向α′相转变,形成马氏体组织;细晶区加热温度不足以使α相完全转变为高温β相,冷却开始β相向α′相的转变不彻底,最终形成α相和α′相。摆动焊接接头抗拉强度为985 MPa,冲击功为42.6 J。摆动焊接接头的极限疲劳强度为464 MPa,疲劳裂纹起源于内部气孔,疲劳裂纹扩展区主要为韧性疲劳裂纹,瞬断区有大量的韧窝出现。
-
关键词:
- 钛合金 /
- 摆动激光-MIG复合焊接 /
- 显微组织 /
- 疲劳性能
Abstract: The microstructure of the welded joints was studied for the 20 mm thick TC4B titanium alloy plate welded by the swing laser-MIG hybrid welding. The effects of swing on the tensile strength and impact properties of the welded joints were compared and the fatigue properties of the welded joints were analyzed. The results show that the thermal influence of welding is divided into the coarse-grained and fine-grained regions. The high-temperature area of the coarse-grained region has a long residence time, the α phase can be completely transformed into the high-temperature β phase, the β phase transform into the α' phase at the beginning of cooling, forming a martensitic structure; the heating temperature of the fine-grained region is not high enough to completely transform the α phase into the high-temperature β phase, and the transition from the β phase to the α' phase at the beginning of cooling is incomplete, resulting the formation of α and α' phases. The tensile strength of the swing welded joint is 985 MPa, and the impact energy is 42.6 J. The ultimate fatigue strength of the swing welded joint is 464 MPa, and the fatigue cracks originate from internal pores, and the fatigue crack propagation zone is mainly ductile fatigue cracks, and a large number of dimples appear in the instantaneous fracture zone.-
Key words:
- titanium alloy /
- swing laser-MIG hybrid welding /
- microstructure /
- fatigue properties
-
表 1 母材化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of base metal
% 材料 Ti Al V O Fe C N H TC4B 余量 6.2 3.6 0.20 0.30 0.08 0.05 0.015 表 2 焊丝化学成分
Table 2. Chemical composition of welding wire
% 材料 Ti Al V O Fe C N Si TC4 余量 6.64 4.33 0.06 0.066 0.083 0.015 0.02 表 3 焊接工艺参数
Table 3. Welding process parameters
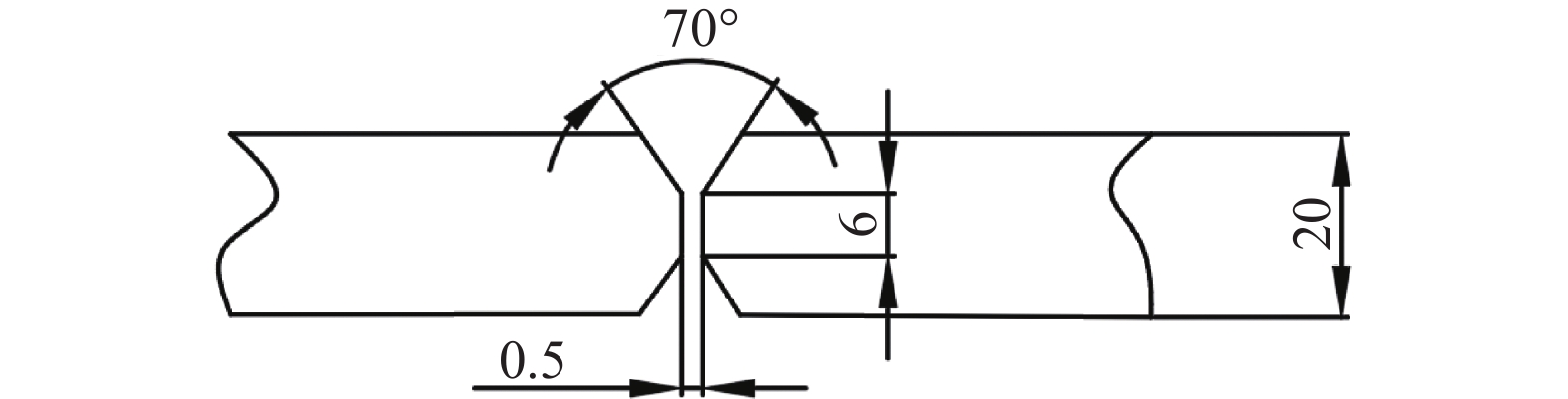
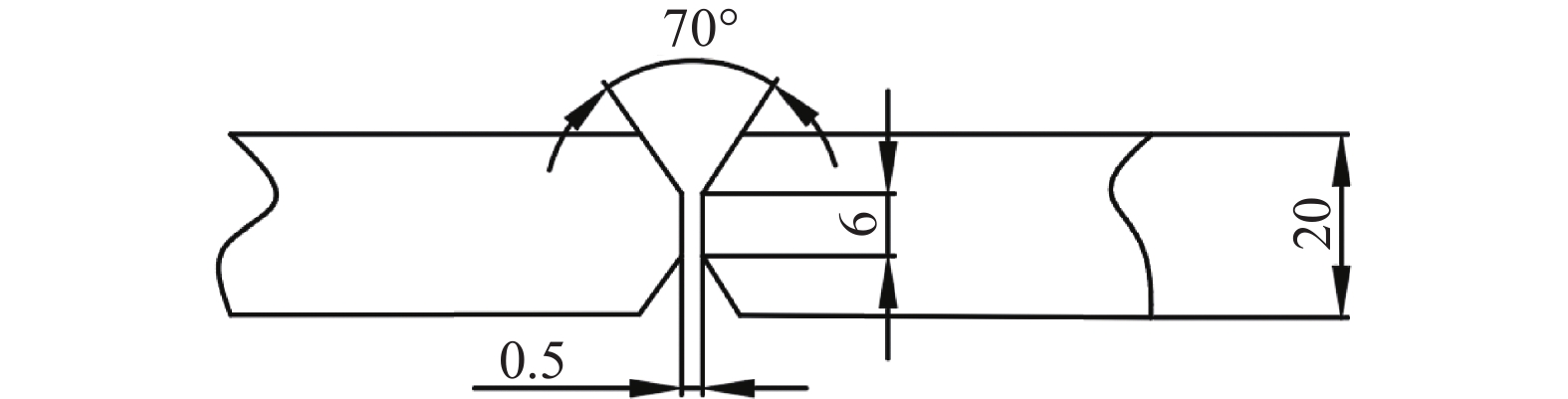
道序 激光功率/kW 激光摆动幅度/mm 激光摆动频率/Hz 焊接电流/A 焊接速度/(m·min−1) 干伸长/mm 打底(正) 5 0.5 300 140 1 20 填充(背) 2 200 0.6 20 填充(正) 2 200 0.6 20 表 4 拉伸试验结果
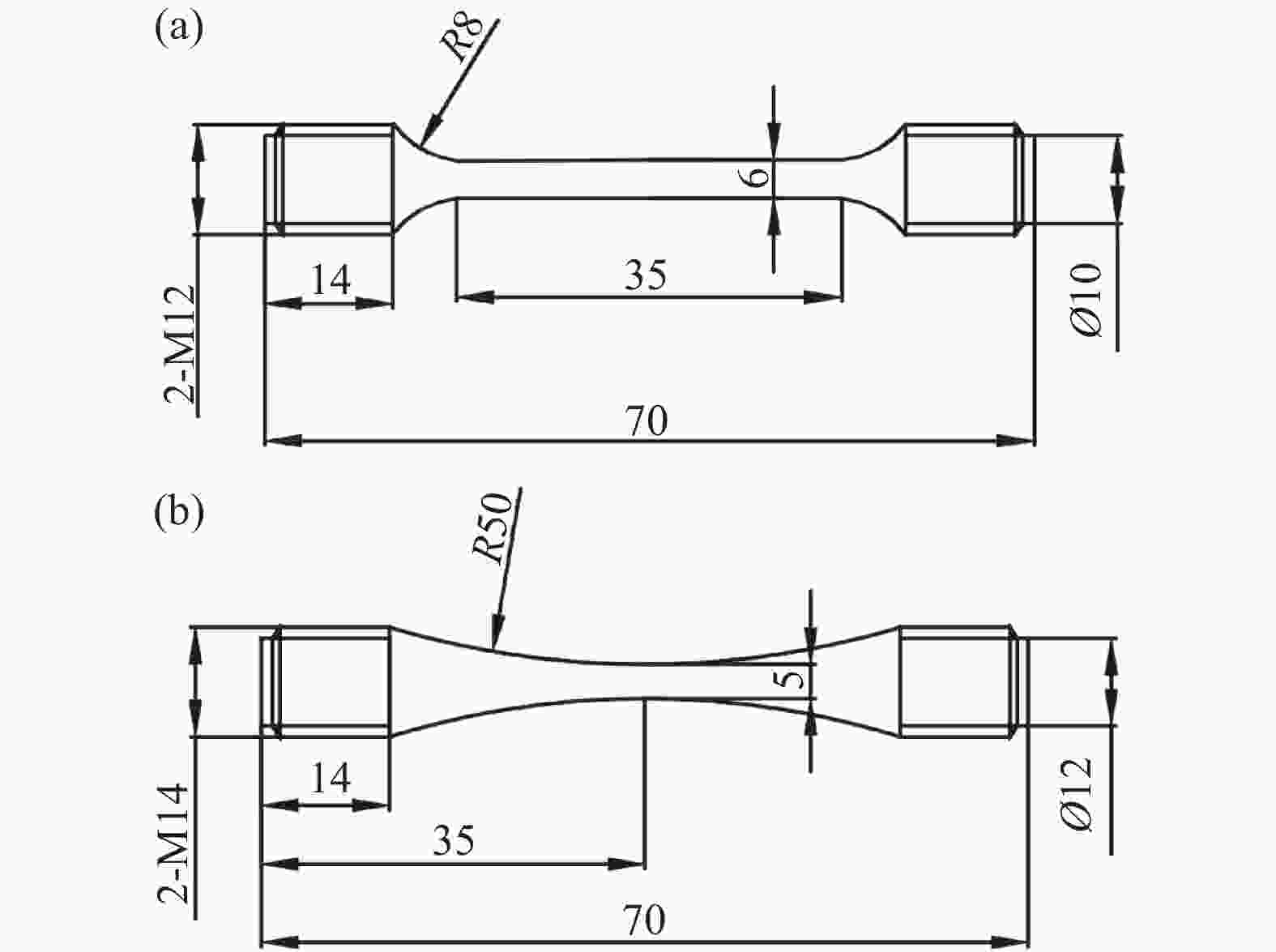
Table 4. Tensile test results
焊接方式 编号 抗拉强度/MPa 延伸率/% 无摆动 1-1 976 11 无摆动 1-2 978 10.5 无摆动 1-3 978 9 加摆动 2-1 989 10.5 加摆动 2-2 987 12.0 加摆动 2-3 980 11.5 表 5 冲击试验结果
Table 5. Impact test results
名称 编号 冲击功/J 实测值 平均值 无摆动 1-1 37 38 无摆动 1-2 39 无摆动 1-3 38 加摆动 2-1 41 42.6 加摆动 2-2 42 加摆动 2-3 45 表 6 疲劳试验测试结果
Table 6. Fatigue test results
编号 应力水平/MPa 寿命次数N/次 失效位置 1 700 53900 焊缝 2 600 648100 焊缝 3 500 5787700 焊缝 4 480 9472000 焊缝 5 460 10000000 完好 6 440 10000000 完好 -
[1] ZHANG L, LI Q B, DAI Y, et al. Study on fatigue damage behavior of TC4 titanium alloy monofilament MIG joint[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(2): 62-67. (张龙, 李清波, 戴宇, 等. TC4钛合金单丝MIG接头疲劳损伤行为研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022, 43(2): 62-67. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.02.010ZHANG L, LI Q B, DAI Y, et al. Study on fatigue damage behavior of TC4 titanium alloy monofilament MIG joint[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(2): 62-67. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.02.010 [2] REN L N, ZHANG Q B, LEI X W, et al. Effect of laser heat input on microstructure and fatigue behavior of TC17 titanium alloy laser welded joint[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2024, 53(7): 1836-1844. [3] CONG J H, GAO J Y, ZHOU S, et al. Effect of ultrasonic rolling on the fatigue performance of laser-welded TC4 titanium alloy joints[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2024, 247(1): 87-105. [4] LI L B, GU X M, SUN S L, et al. Effects of welding residual stresses on the vibration fatigue life of a ship’s shock absorption support[J]. Ocean Eng, 2018, 170: 237-245. [5] AKMAN E, DEMIR A, CANEL T, et al. Laser welding of Ti6Al4V titanium alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(8): 3705-3713. [6] SU R, LI H Z, WANG S Y, et al. Study on fatigue properties with composite waveform and variable amplitude of TC21 titanium alloy pulsed laser-arc hybrid welded joints[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2024, 165: 108797. [7] HU X A , ZHAO J, TENG X F, et al. Fatigue resistance improvement on double-sided welded joints of a titanium alloy treated by laser shock peening[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2022, 31(12): 10304-10313. [8] WU M S, DUAN X Y, LI L M, et al. Excitation of arc ultrasound and its characteristics[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Natural Science Edition), 1999(6): 111-113. (吴敏生, 段向阳, 李路明, 等. 电弧超声的激发及其特性研究[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 1999(6): 111-113.WU M S, DUAN X Y, LI L M, et al. Excitation of arc ultrasound and its characteristics[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Natural Science Edition), 1999(6): 111-113. [9] ZHU Z T, ZHU Q C, LI Y X, et al. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted A7N01 aluminum alloy laser-MIG composite welding structure and mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Welding Science, 2016, 37(6): 80-84, 132-133. (朱宗涛, 祝全超, 李远星, 等. 超声振动辅助A7N01铝合金激光-MIG复合焊接组织及力学性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2016, 37(6): 80-84, 132-133.ZHU Z T, ZHU Q C, LI Y X, et al. Ultrasonic vibration-assisted A7N01 aluminum alloy laser-MIG composite welding structure and mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Welding Science, 2016, 37(6): 80-84, 132-133. [10] LIU X H, NI J Q, LIU Y M. Study on fatigue properties of TA15 titanium alloy sheet laser-TIG composite welding joint[J]. Thermal Working Technology, 2019, 48(3): 15-18, 23. (刘晓寒, 倪家强, 刘艳梅. TA15钛合金薄板激光-TIG复合焊接头疲劳性能研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2019, 48(3): 15-18, 23.LIU X H, NI J Q, LIU Y M. Study on fatigue properties of TA15 titanium alloy sheet laser-TIG composite welding joint[J]. Thermal Working Technology, 2019, 48(3): 15-18, 23. -




 下载:
下载: