Study on the selective separation of gallium and iron from vanadium converter sludge
-
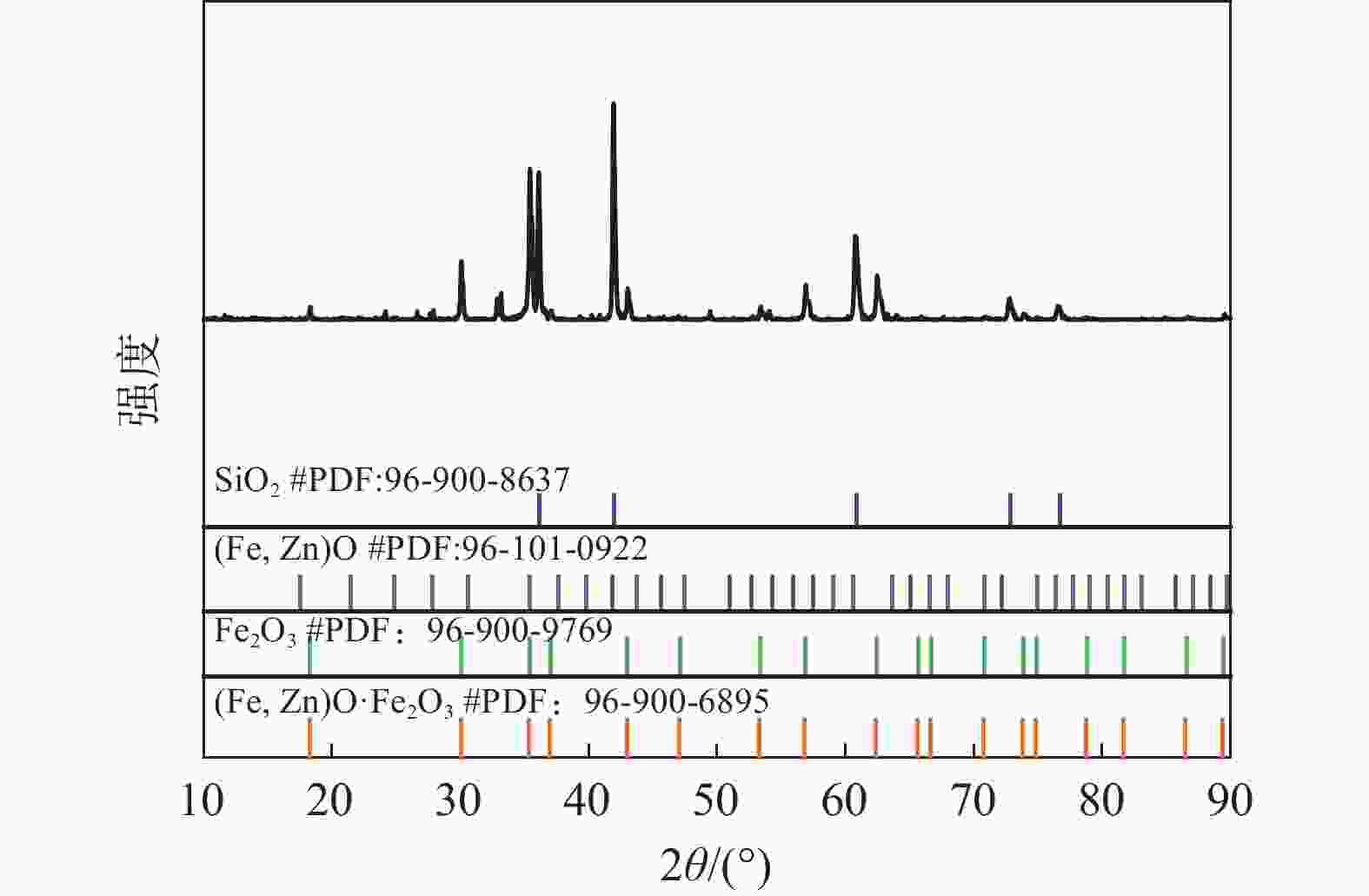
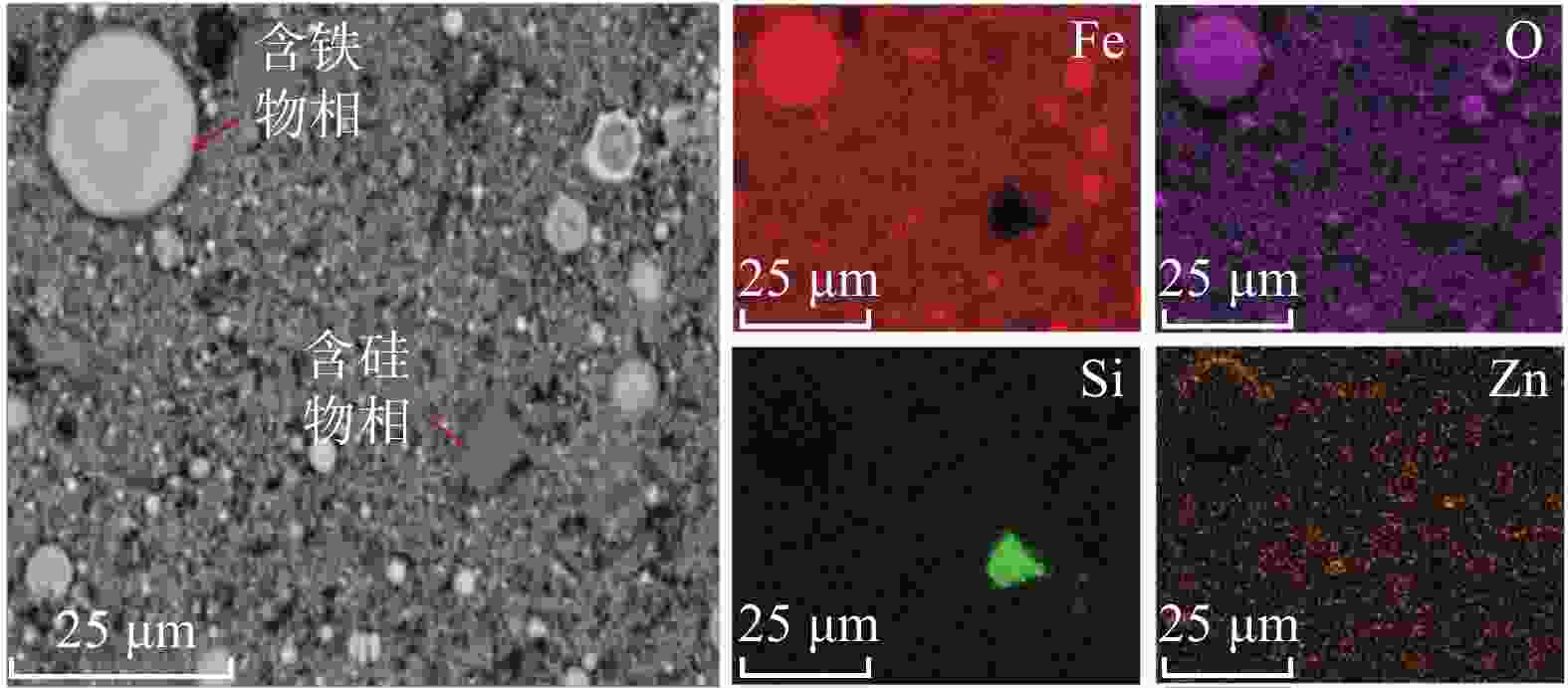
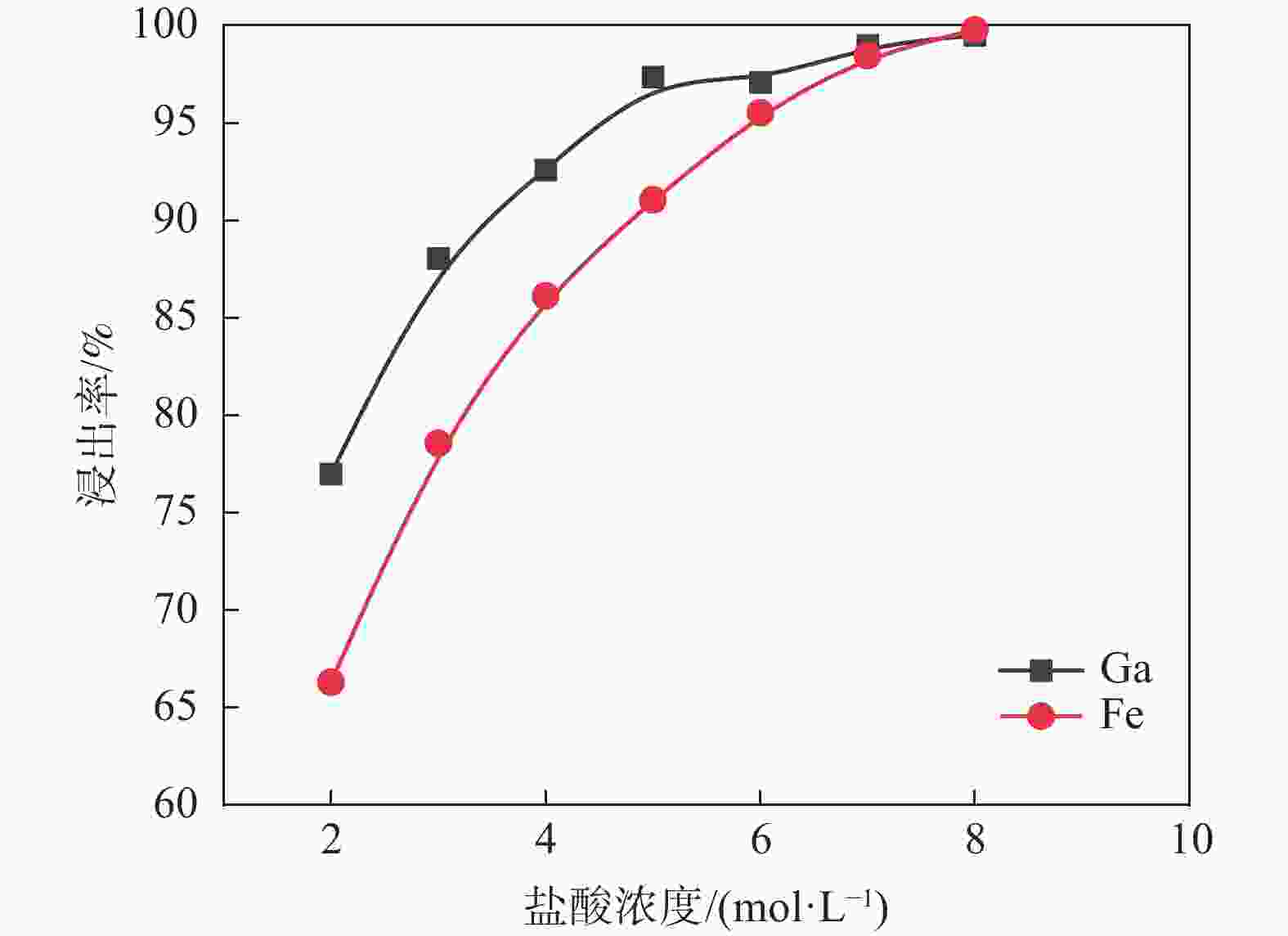
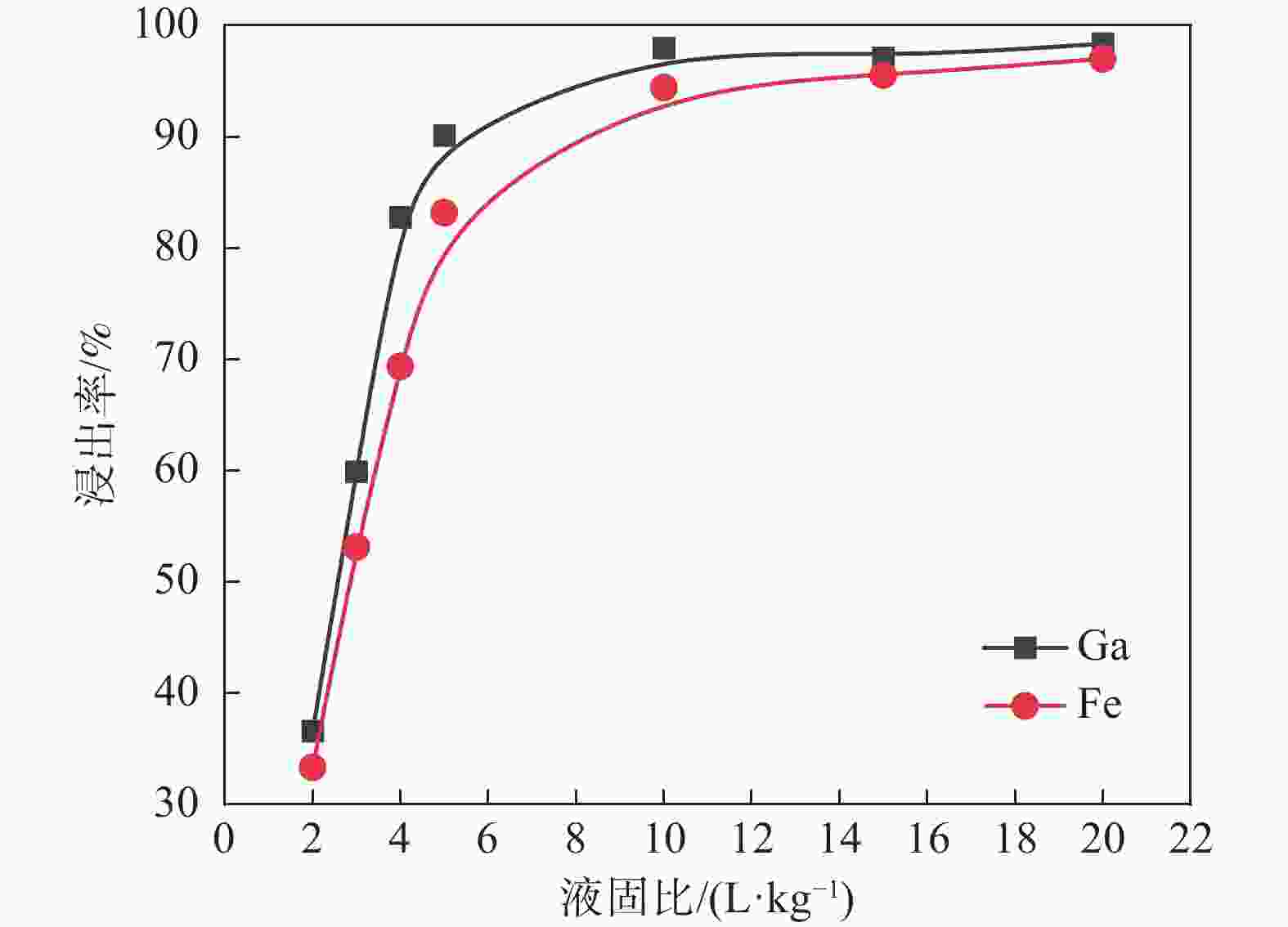
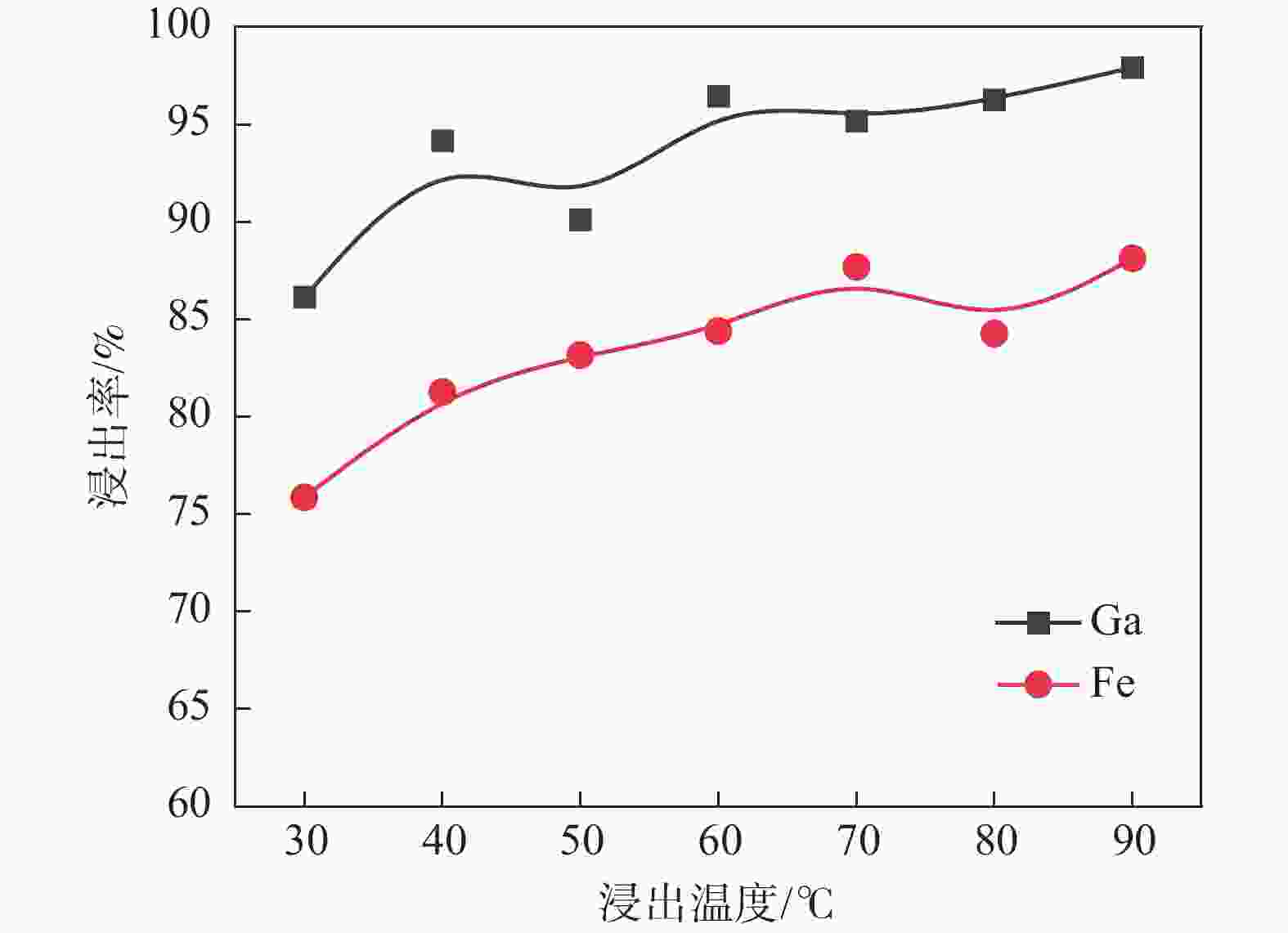
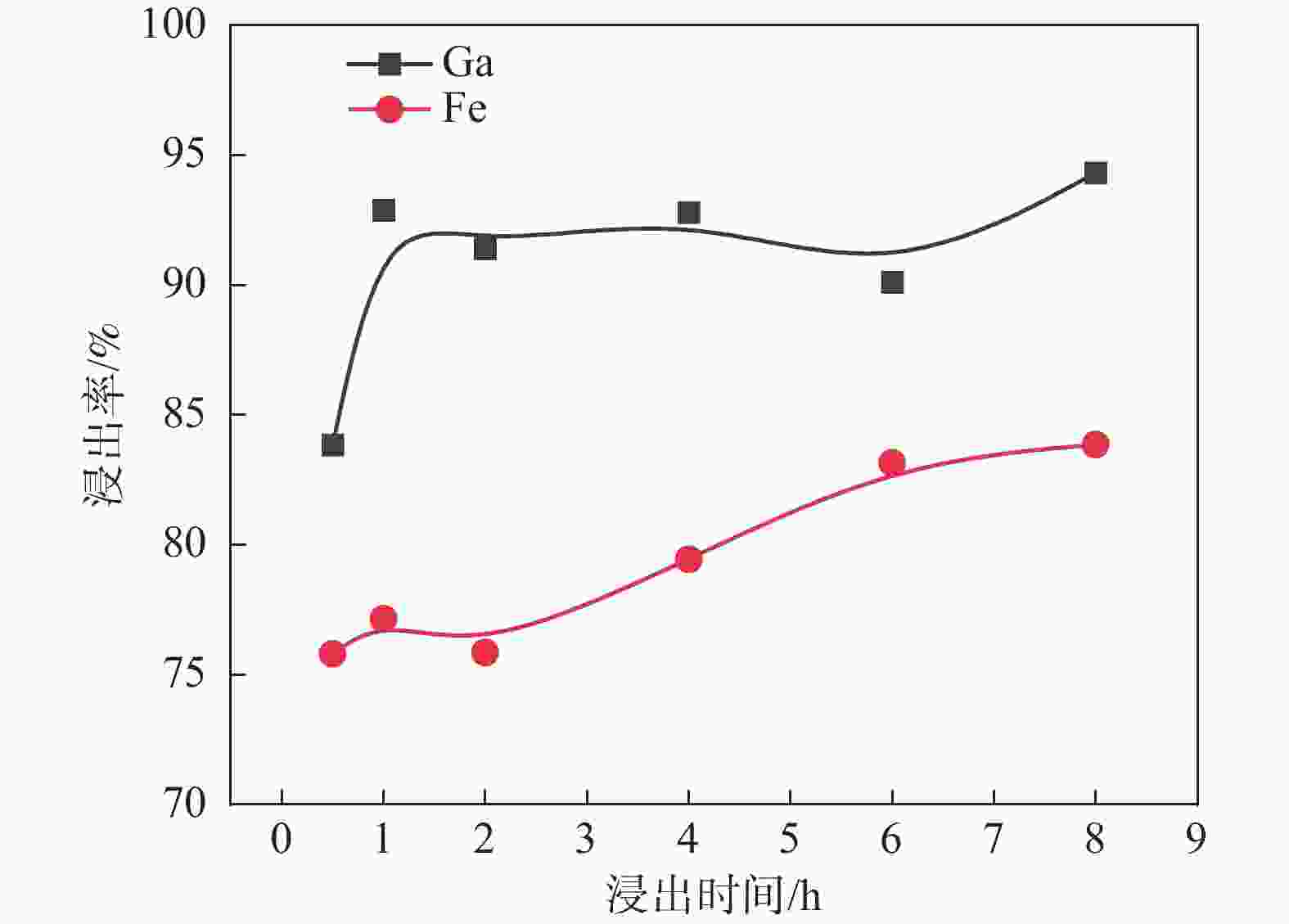
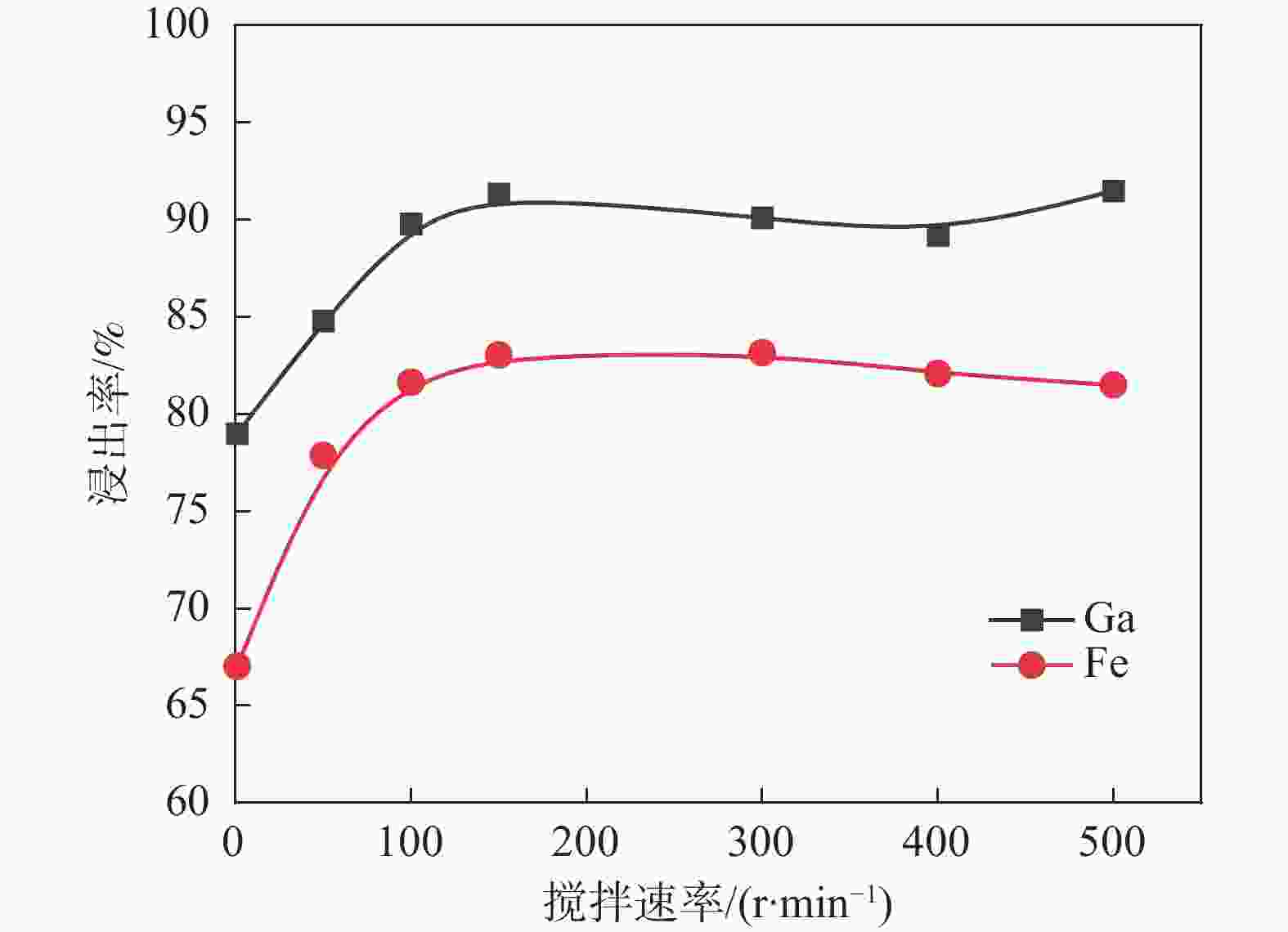
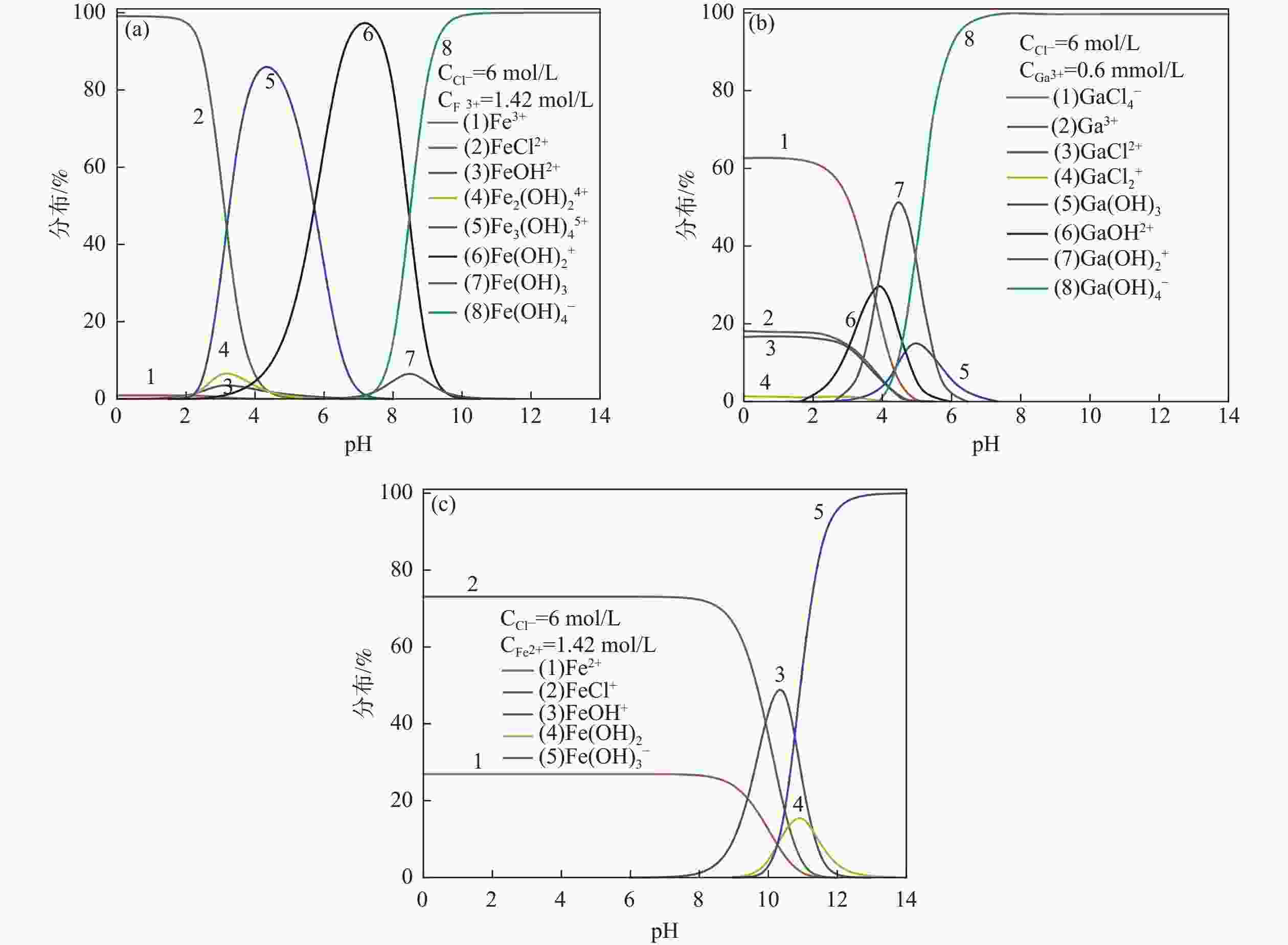
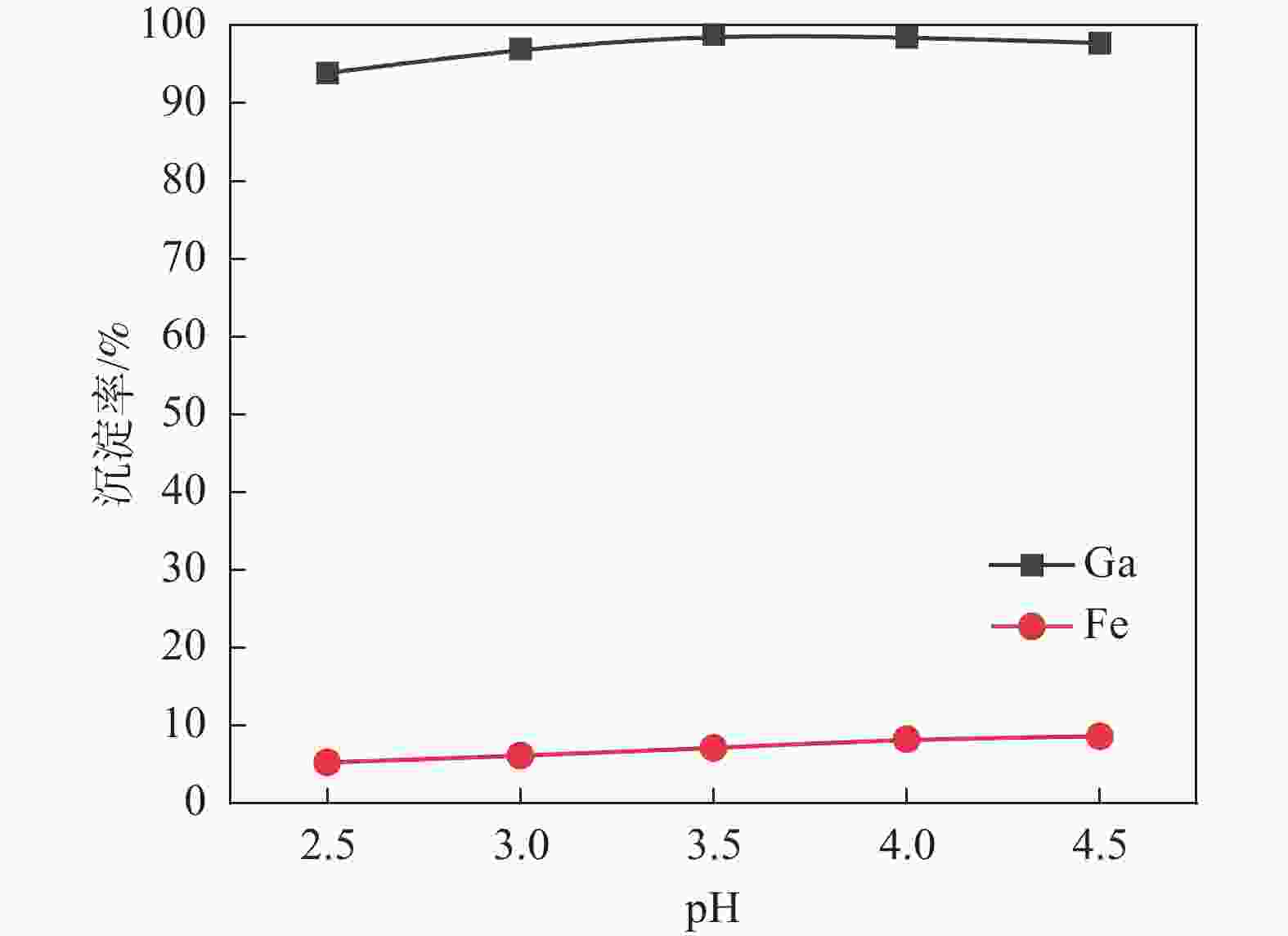
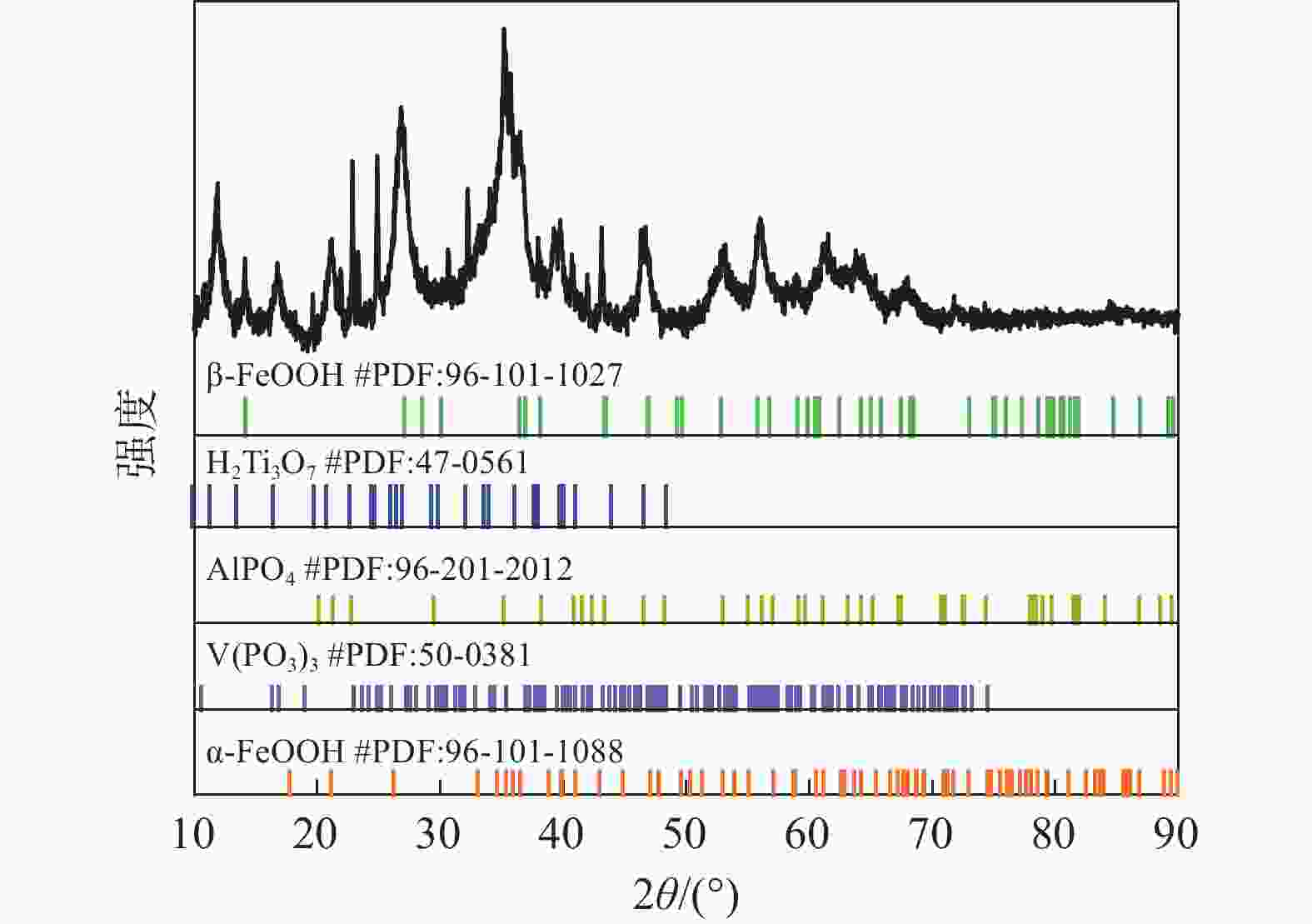
摘要: 采用酸浸法对冶炼流程中的提钒转炉污泥进行了镓的浸出试验,考察了镓在提钒转炉污泥中的赋存状态及多种因素对镓浸出率的影响,包括酸浓度、液固比、反应温度、反应时间和搅拌速率等。结果表明,镓离子主要赋存在氧化铁的晶格中,盐酸可作为有效浸出试剂破坏氧化铁的晶格,在盐酸浓度为5 mol/L,反应时间1 h,反应温度60 °C,液固比为5:1时镓的浸出率为90%。利用元素沉淀pH值的差异可有效分离镓和铁,进而得到富镓料,与提钒转炉污泥对比,富镓料中的镓富集24倍。该研究成果有望为实现钒钛磁铁矿中高附加值关键金属的提取提供技术支撑。Abstract: In this study, the leaching test of gallium from the vanadium extraction converter sludge in the smelting process was conducted using the acid leaching method. The occurrence state of gallium in the vanadium extraction converter sludge and the influence of various factors on the leaching rate of gallium were investigated, including acid concentration, liquid-solid ratio, reaction temperature, reaction time and stirring rate, etc. The results showed that gallium ions were mainly present in the lattice of iron oxide. Hydrochloric acid could be used as an effective leaching agent to break the lattice of iron oxide. Under a specific condition with the hydrochloric acid concentration of 5 mol/L, the reaction time of 1 h, the reaction temperature of 60 °C, and the liquid-solid ratio of 5:1, the leaching rate of gallium was 90%. The difference in pH values of elements can effectively separate gallium and iron, and thereby obtain a gallium-rich material. The gallium enrichment in the gallium-rich material was 24 times as high as the vanadium extraction converter sludge. This research result is expected to provide technical support for the extraction of high-value-added key metals from vanadium-titanium magnetite.
-
Key words:
- vanadium extraction converter sludge /
- gallium /
- acid leaching /
- separation
-
表 1 提钒转炉污泥成分分析结果
Table 1. Result of XRF analysis of vanadium extraction converter sludge
% Al Cr Ca Fe Mg Mn Ni P Pb Si Ti V Zn Ga* O 0.2 0.1 0.2 64.2 0.1 0.3 0.3 0.1 0.5 0.6 0.1 0.1 3.0 0.03 Bal. 注:*该元素含量为ICP检测结果。 表 2 提钒转炉污泥电子探针物相定量结果
Table 2. EPMA result of vanadium extraction converter sludge
% 物相 SiO2 Fe3O4 ZnO Ga 含硅物相 98.5 1.3 0.017 4 含铁物相 0.7 96.2 1.3 0.057 8 表 3 富镓料成分分析结果
Table 3. XRF analysis result of Ga-rich material
% Al Cr Ca Fe Mn Ni P Pb Si Ti V Zn Ga O 0.73 0.82 0.04 51.25 0.06 0.03 1.37 2.26 0.07 0.91 2.22 2.03 0.73 Bal. -
[1] KURTULDU F, MUTLU N, BOCCACCINI A R, et al. Gallium containing bioactive materials: A review of anticancer, antibacterial, and osteogenic properties[J]. Bioactive Materials, 2022, 17: 125-146. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.12.034 [2] KAUR D, GHOSH A, KUMAR M. A strategic review on gallium oxide based power electronics: Recent progress and future prospects[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2022, 33: 104244. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104244 [3] ZHAO Z, YANG Y X, et al. Recovery of gallium from Bayer liquor: A review [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2012. [4] LU F, XIAO T, LIN J, et al. Resources and extraction of gallium: A review[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017, 174. [5] QIN Z F, WANG S H, ZHANG S H, et al. Cross-linked amidoxime porous resin for selective gallium separation in Bayer solutions: Reaction mechanism and kinetic study[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 481: 14830. [6] Zhongshang Industry Research Institute. Analysis of the upstream, midstream and downstream markets of China's gallium industry chain in 2023 [EB/OL]. https://www.seccw.com/Document/detail/id/22188.html. (中商产业研究院. 2023年中国镓产业链上中下游市场分析[EB/OL]. https://www.seccw.com/Document/detail/id/22188.html .Zhongshang Industry Research Institute. Analysis of the upstream, midstream and downstream markets of China's gallium industry chain in 2023 [EB/OL]. https://www.seccw.com/Document/detail/id/22188.html. [7] SONG X Y, SHE Y W, LUAN Y, et al. Resources of Co, Ga and Sc of V-Ti magnetite deposits in the Panxi area within the Emeishan Large Igneous Provence and their integrated utilization potentials[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2024, 43(1): 218-231. (宋谢炎, 佘宇伟, 栾燕, 等. 峨眉大火成岩省攀西钒钛磁铁矿矿集区钴、镓、钪资源及综合利用潜力[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2024, 43(1): 218-231.SONG X Y, SHE Y W, LUAN Y, et al. Resources of Co, Ga and Sc of V-Ti magnetite deposits in the Panxi area within the Emeishan Large Igneous Provence and their integrated utilization potentials[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2024, 43(1): 218-231. [8] GAO L, SHI Z, YIN S B, et. al. Comparative study on the recovery of gallium from V-recovering tail slag[J]. Mining & Metallurgy, 2014, 23(3): 73-76. (高磊, 施哲, 阴树标, 等. 提钒尾渣镓回收方法研究[J]. 矿冶, 2014, 23(3): 73-76.GAO L, SHI Z, YIN S B, et. al. Comparative study on the recovery of gallium from V-recovering tail slag[J]. Mining & Metallurgy, 2014, 23(3): 73-76. [9] WANG N, SHI L, CHEN J, et al. Research on the occurrence state of gallium in fly ash and its comprehensive recovery and utilization[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2007, 27(z1): 396-397. (王宁, 石莉, 陈娟, 等. 粉煤灰中镓的赋存状态及综合回收利用研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2007, 27(z1): 396-397.WANG N, SHI L, CHEN J, et al. Research on the occurrence state of gallium in fly ash and its comprehensive recovery and utilization[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2007, 27(z1): 396-397. [10] LIU J Y. Research Progress of gallium in Panzhihua vanadium titano-magnetite ore[J]. Modern Mining, 2019(1): 102-105. (刘佳媛. 攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿中镓的研究进展[J]. 现代矿业, 2019(1): 102-105.LIU J Y. Research Progress of gallium in Panzhihua vanadium titano-magnetite ore[J]. Modern Mining, 2019(1): 102-105. [11] WEI J. Separation, Enrichment and determination of gallium in the tailings of Panzhihua vanadium-titanium magnetite [D]. Sichuan: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018. (魏娟. 攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿尾矿中镓的分离富集与测定[D]. 四川: 成都理工大学, 2018.WEI J. Separation, Enrichment and determination of gallium in the tailings of Panzhihua vanadium-titanium magnetite [D]. Sichuan: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018. [12] GUO H J, LIN J. Extraction of gallium from vanadium leaching residue by chlorination roasting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993, 14(4): 58-66. (郭汉杰, 林洁. 氯化焙烧提取浸钒渣中的镓[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1993, 14(4): 58-66.GUO H J, LIN J. Extraction of gallium from vanadium leaching residue by chlorination roasting[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993, 14(4): 58-66. [13] LI H, LI J J, WANG W J, et al. Experimental study on the leaching of gallium from vanadium leaching residue containing gallium[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993(4): 82-87. (李宏, 李景捷, 王万军, 等. 从含镓浸钒渣中浸出镓的试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1993(4): 82-87.LI H, LI J J, WANG W J, et al. Experimental study on the leaching of gallium from vanadium leaching residue containing gallium[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993(4): 82-87. [14] GUO H J, ZHOU R Z, LIN Z C, et al. Extracting gallium from vanadium leaching residue by smelting reduction-the smelting reduction process under carbon-unsaturated conditions[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993(4): 67-74. (郭汉杰, 周荣章, 林宗彩, 等. 用熔融还原的方法从浸钒渣中提镓-碳不饱和情况下的熔融还原过程[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1993(4): 67-74.GUO H J, ZHOU R Z, LIN Z C, et al. Extracting gallium from vanadium leaching residue by smelting reduction-the smelting reduction process under carbon-unsaturated conditions[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1993(4): 67-74. [15] CHEN S F. Research on the extraction of metallic gallium from the discarded vanadium pentoxide slag of Panzhihua iron and steel group[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1994(1): 49-52. (陈世芳. 攀钢V2O5弃渣中金属镓的提取研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1994(1): 49-52.CHEN S F. Research on the extraction of metallic gallium from the discarded vanadium pentoxide slag of Panzhihua iron and steel group[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1994(1): 49-52. [16] HOU J, WU E H, LI J. Current situation and progress of comprehensive utilization of vanadium extraction tailings[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(6): 103-108. (侯静, 吴恩辉, 李军. 提钒尾渣的综合利用研究现状及进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2017(6): 103-108.HOU J, WU E H, LI J. Current situation and progress of comprehensive utilization of vanadium extraction tailings[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2017(6): 103-108. -





 下载:
下载: