Study on the motion and heat transfer behavior of semi-steel droplet during centrifugal granulation-water curtain cooling process
-
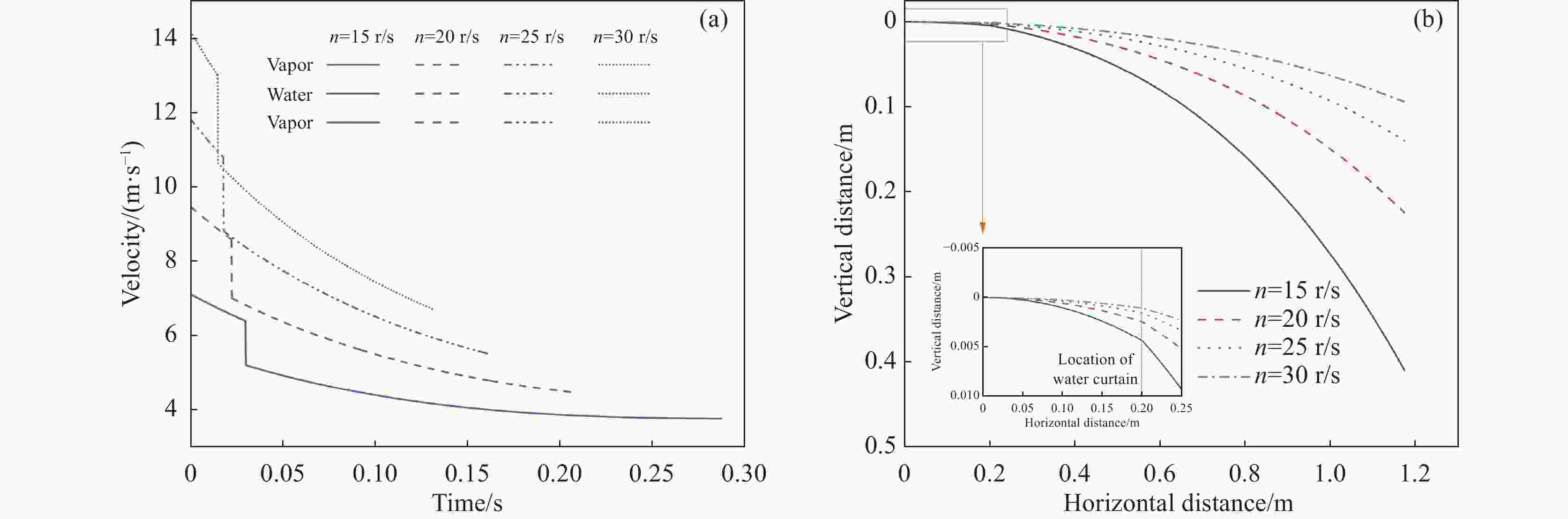
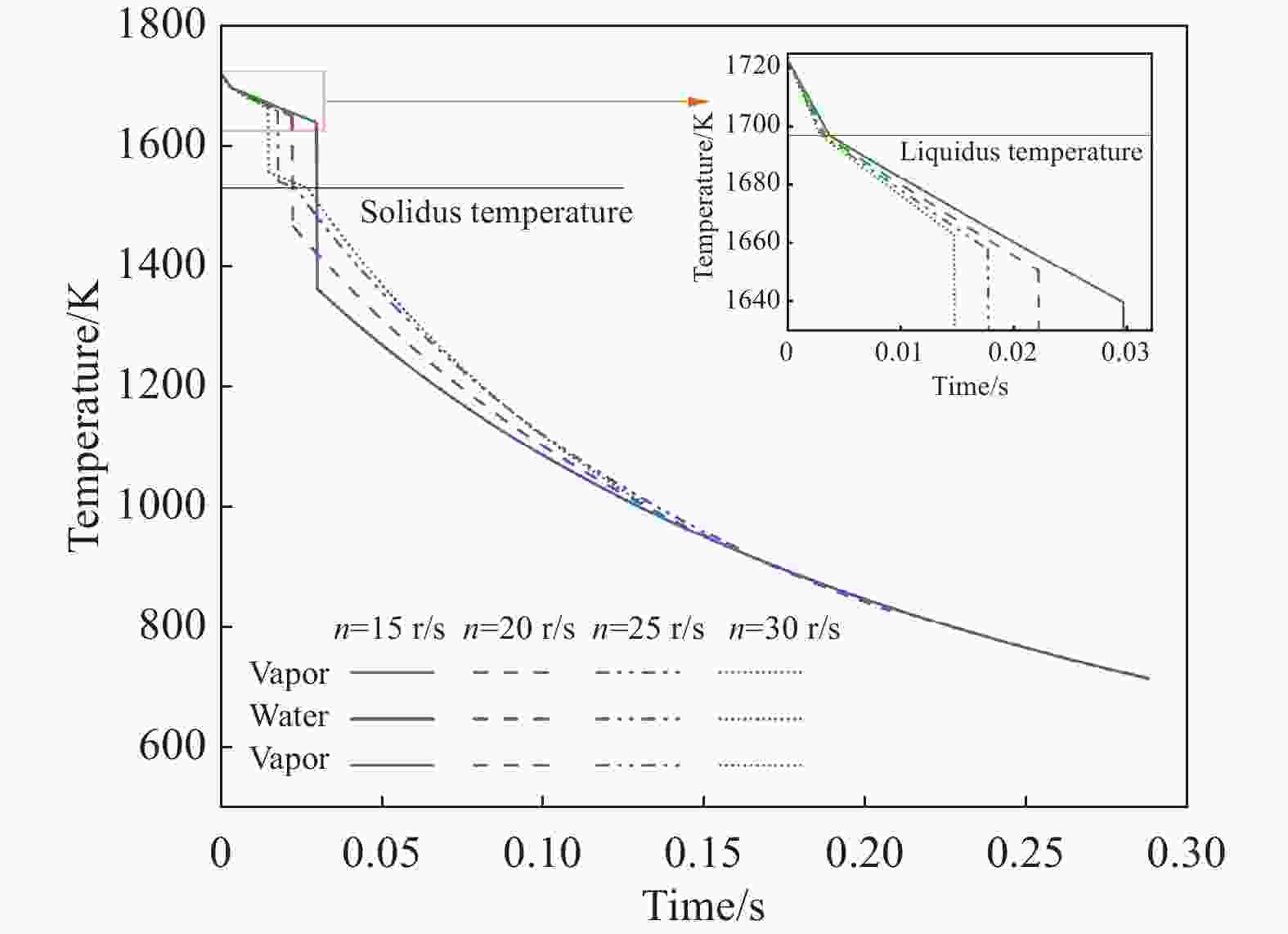
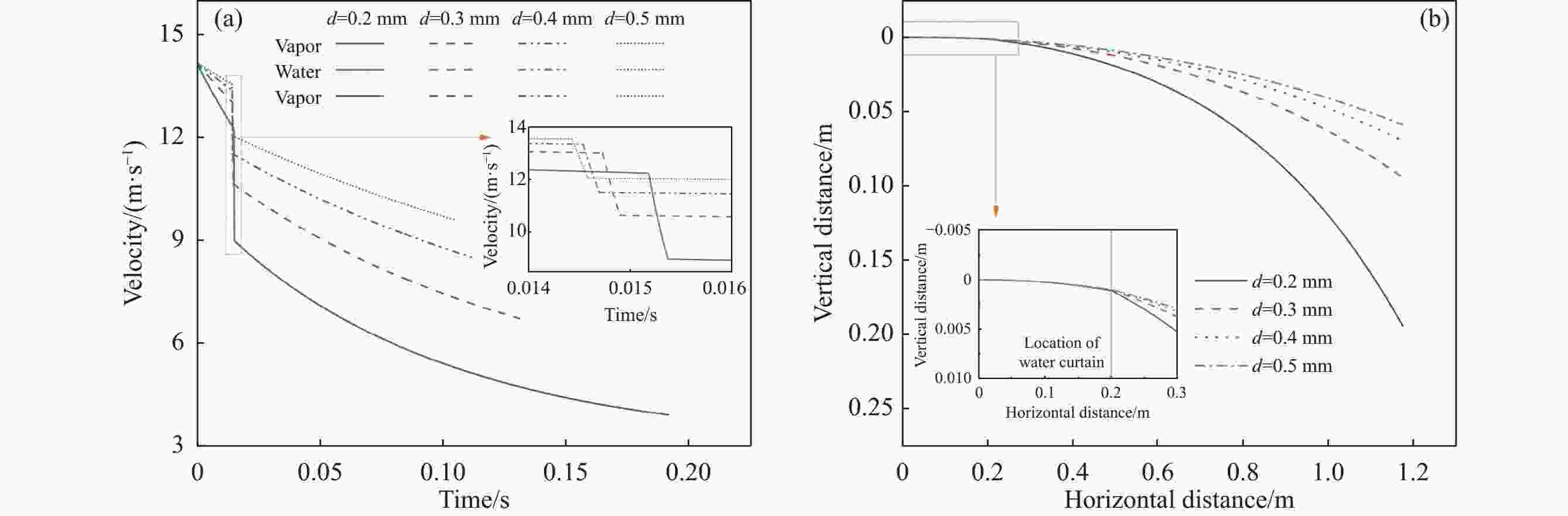
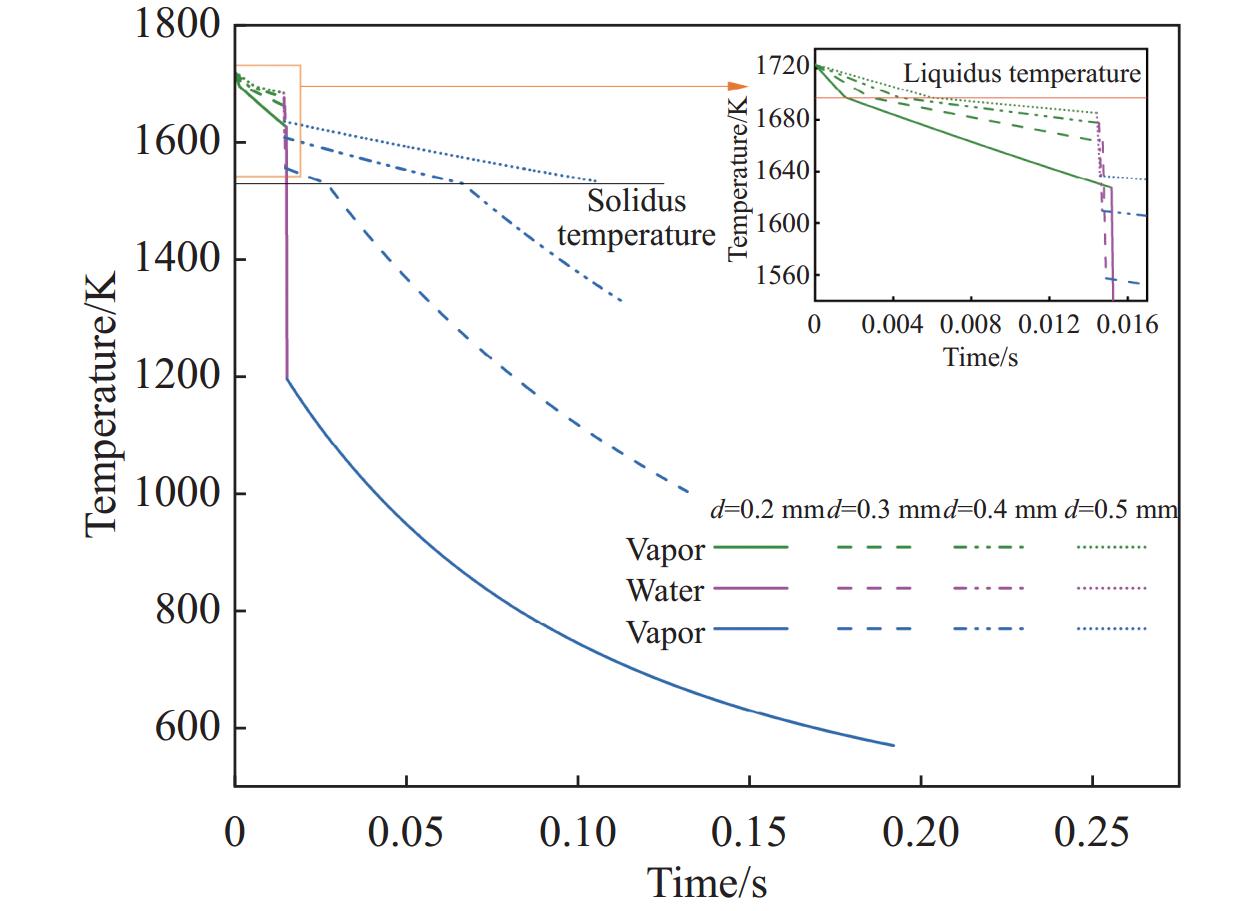
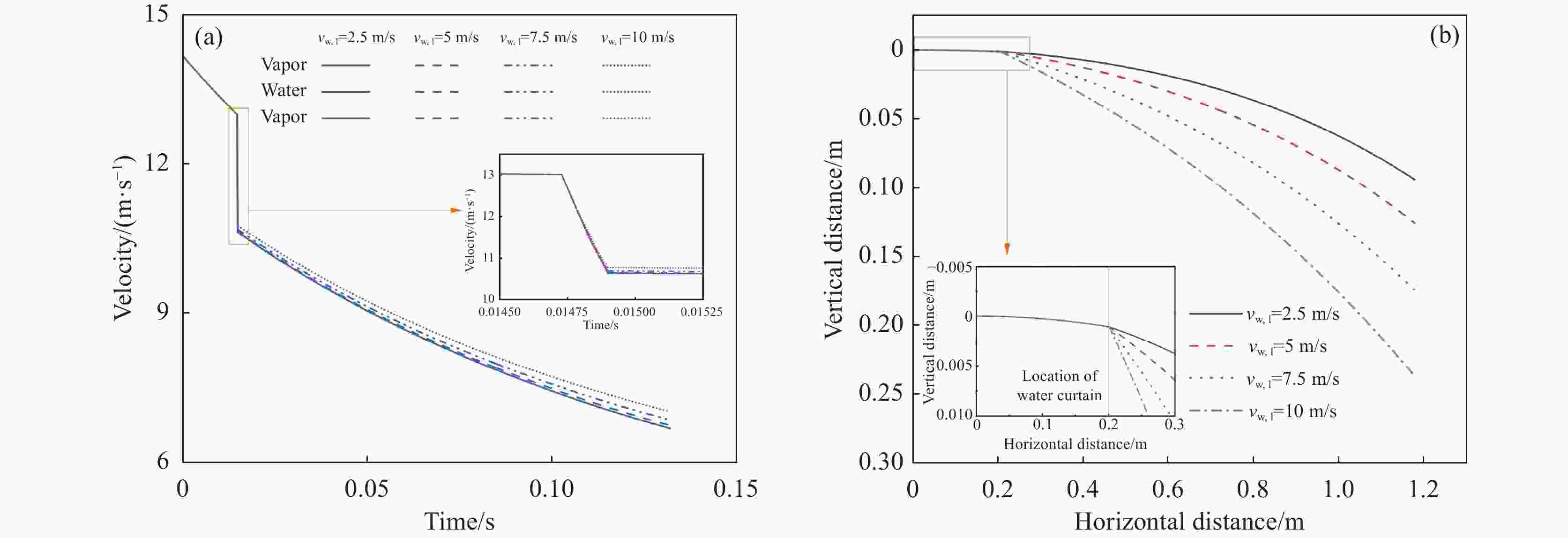
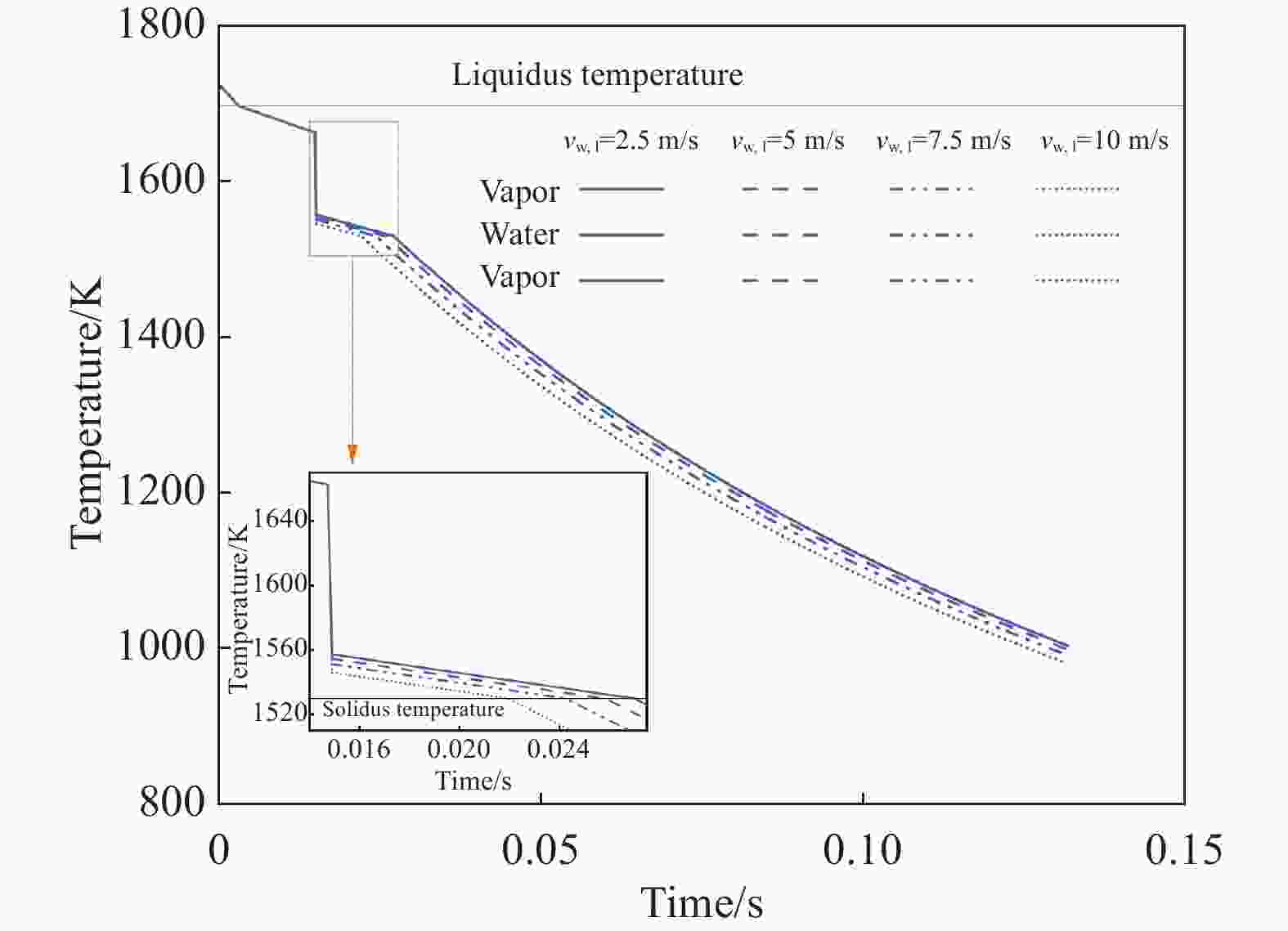
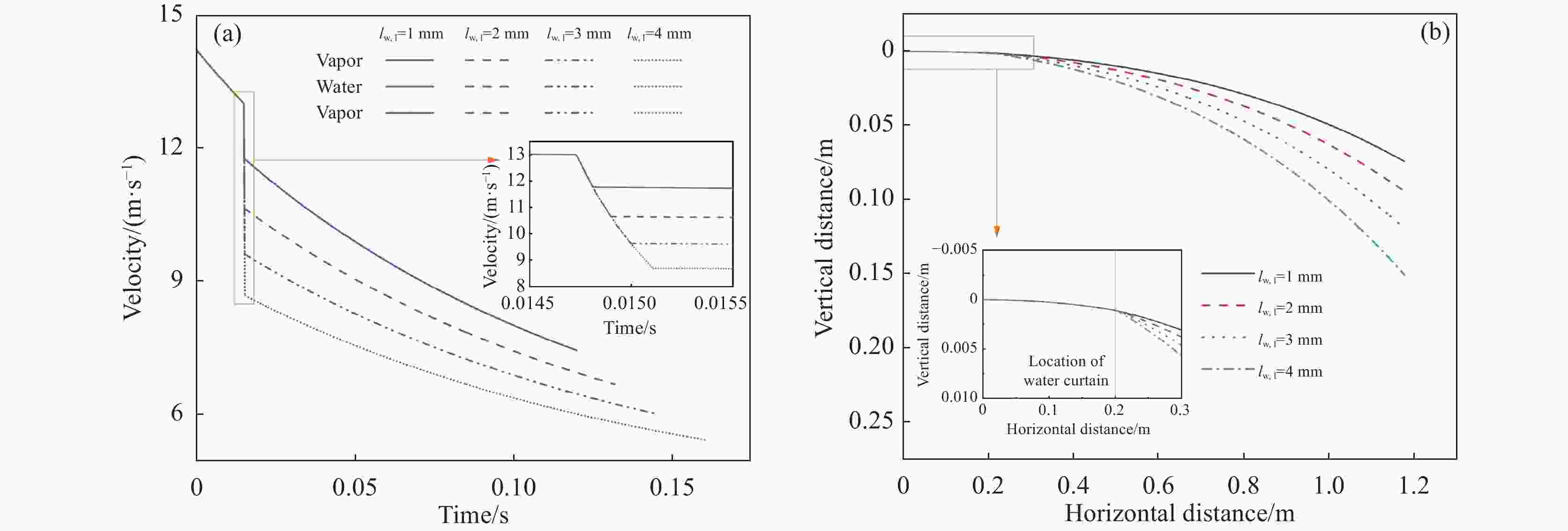
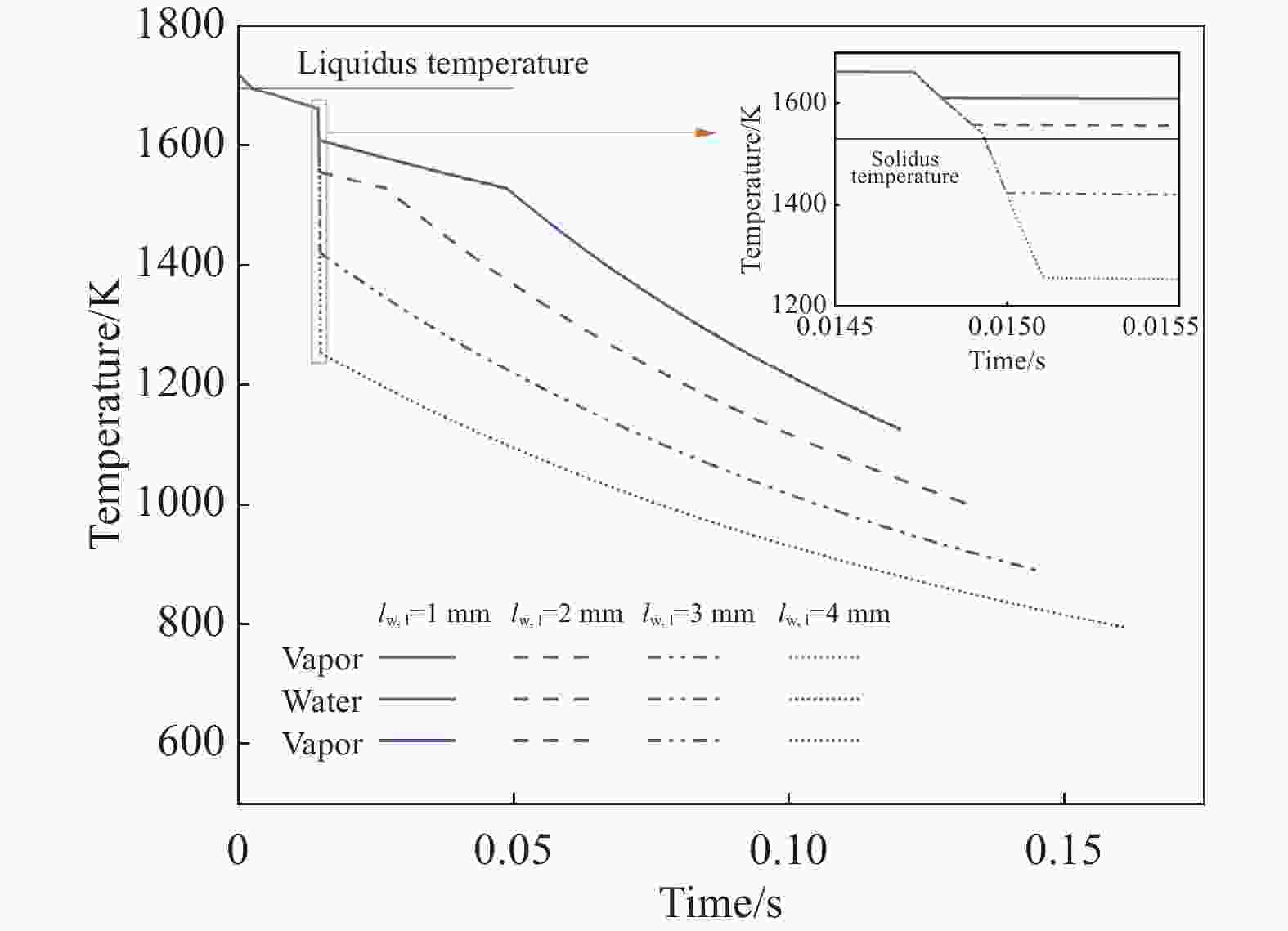
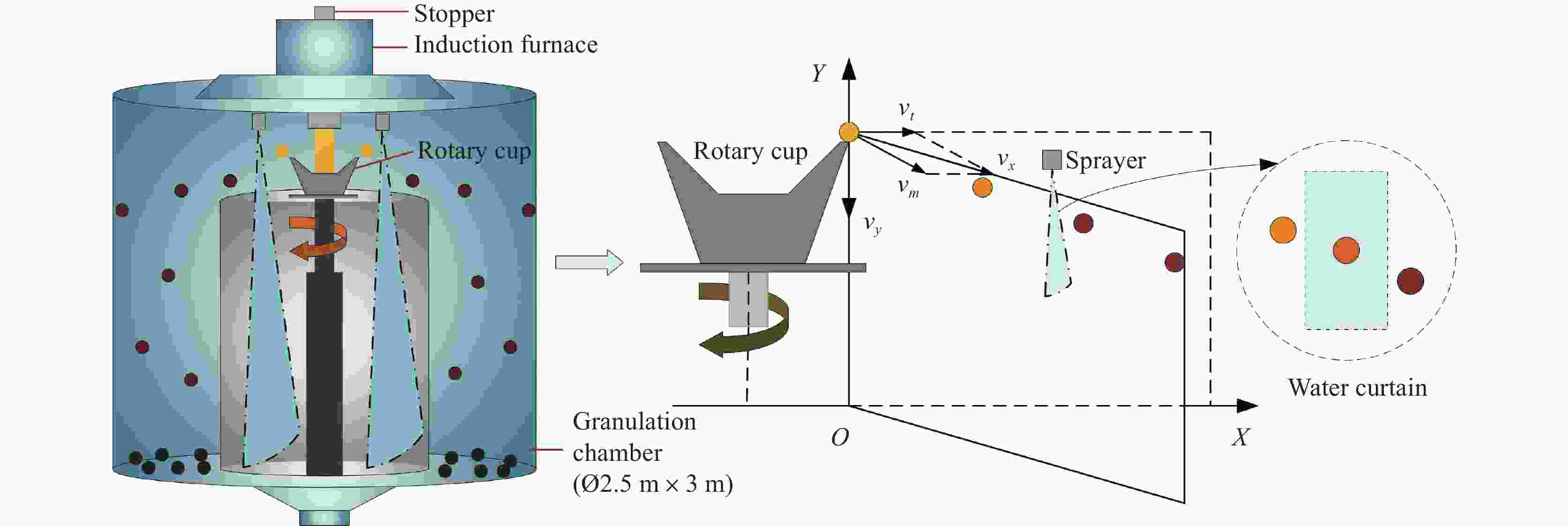
摘要: 离心粒化-水幕冷却过程中半钢熔滴依次与蒸汽、水幕、蒸汽进行热量交换,研究熔滴的运动换热行为对于粒化装置和水幕工艺设计具有重要意义。建立了熔滴飞行动力学模型和换热模型,通过模拟计算分析了转杯转速、熔滴粒径、水幕流速和水幕厚度等因素对熔滴飞行轨迹和温度影响。研究结果表明,熔滴到达装置侧壁时在垂直方向的飞行距离随着转杯转速、熔滴粒径的增大以及水幕流速、水幕厚度的减小而减小。其中转杯转速对熔滴飞行轨迹的影响较大,当转速由15 r/s增大至30 r/s时,熔滴在垂直方向的飞行距离由0.410 m减至0.094 m。熔滴到达装置侧壁时的温度随着转杯转速、熔滴粒径的增大以及水幕流速、水幕厚度的减小而增大。其中水幕厚度对熔滴的温度影响较大,当厚度由1 mm增大至4 mm时,颗粒温度由
1127.41 K降至796.29 K。Abstract: During the centrifugal granulation-water curtain cooling process, the sequential heat exchange occurs between the molten semi-steel droplet and vapor, followed by their interaction with the water curtain and vapor. Studying the motion and heat transfer behavior of these droplets is crucial for the design of granulation equipment and water curtain processes. A flight dynamics model and a heat transfer model were established to analyze the effects of rotary speed, droplet size, water curtain velocity, and water curtain thickness on droplet trajectory and temperature through simulation calculations. The results indicate that the vertical distance of the droplet upon reaching the sidewall of the device decreases with increasing cup rotation speed, droplet size, and decreasing water curtain flow rate and thickness. Among them, the rotary speed has a greater impact on the flight trajectory of the droplets. When the rotation speed increases from 15 r/s to 30 r/s, the vertical flight distance of the droplet decreases from 0.410 m to 0.094 m. Additionally, the temperature of the droplet upon reaching the sidewall of the device increases with increasing cup rotation speed, droplet size, and decreasing water curtain velocity and thickness. When the water curtain thickness increases from 1 mm to 4 mm, the droplet temperature decreases from1127.41 K to 796.29 K. -
表 1 模拟计算方案
Table 1. Details of the simulation conditions
n/(r·s−1) d/mm vw,l/(m·s−1) lw,l/mm 15, 20, 25, 30 0.3 2.5 2 30 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5 2.5 2 30 0.3 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 2 30 0.3 2.5 1, 2, 3, 4 表 2 模拟计算相关参数
Table 2. Relevant parameters for simulation calculation
Density/(kg·m−3) Viscosity×105/( Pa·s) Prandtl number Thermal conductivity/(W·m−1·K−1) Specific heat/(J·kg−1·K−1) ρ ρw,g ρw,l μ μw,g μw,l Prw,g Prw,l λw,l λw,g Cl Cs 7750 2.548 998.2 250 1.39 10.05 1.08 7.02 0.599 0.0298 800 678 Temperature/K D/m a/(°) ε Q/(m3·s) δ/(W·m−2·K−4) ΔHm/(J·kg−1) T0 Tw,g Tw,l Tl Ts 1723 423 293 1697 1530 0.15 45 0.8 1.3×10−5 5.67×10−8 268000 -
[1] LUO L G, PANG J M, LI X, et al. Separation of iron and titanium by reduction grinding separation process of vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Iron and Steel, 2024, 59(8): 13-18. (罗林根, 庞建明, 李新, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿还原-磨选工艺分离铁钛试验[J]. 钢铁, 2024, 59(8): 13-18.LUO L G, PANG J M, LI X, et al. Separation of iron and titanium by reduction grinding separation process of vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Iron and Steel, 2024, 59(8): 13-18. [2] WANG H B, LI J, ZHANG G H. Efficient recovery of ilmenite from vanadium bearing titanomagnetite in Panxi area[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(3): 23-29. (王洪彬, 李金, 张国华. 攀西钒钛磁铁矿中钛铁矿高效回收工艺研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020, 41(3): 23-29. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.03.003WANG H B, LI J, ZHANG G H. Efficient recovery of ilmenite from vanadium bearing titanomagnetite in Panxi area[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(3): 23-29. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.03.003 [3] WU D P, WANG X B, ZHAO L Y. Research and practice on optimization of grinding and classification process of low-grade vanadium titanomagnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(5): 117-122. (吴登平, 王祥波, 赵刘阳. 低品位钒钛磁铁矿磨矿分级工艺优化研究与实践[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022, 43(5): 117-122.WU D P, WANG X B, ZHAO L Y. Research and practice on optimization of grinding and classification process of low-grade vanadium titanomagnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(5): 117-122. [4] LUO J H. Thoughts and countermeasures on the development of Panzhihua vanadium and titanium industry[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(6): 9-16. (罗金华. 攀枝花钒钛产业发展思考及对策建议[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023, 44(6): 9-16.LUO J H. Thoughts and countermeasures on the development of Panzhihua vanadium and titanium industry[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(6): 9-16. [5] ZHANG F. Current situation and development orientation of utilization for semisteel produced in smelting of titanium slag at PZH steel[J]. Sichuan Metallurgy, 2020, 42(4): 12-19. (张峰. 攀钢钛渣副产半钢利用现状及发展方向[J]. 四川冶金, 2020, 42(4): 12-19.ZHANG F. Current situation and development orientation of utilization for semisteel produced in smelting of titanium slag at PZH steel[J]. Sichuan Metallurgy, 2020, 42(4): 12-19. [6] LIAO R H. Study of carburisation and desulfuration for semisteel produced in smelting of titanium slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2003, 24(3): 11-16. (廖荣华. 钛渣副产半钢脱硫增碳试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2003, 24(3): 11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7638.2003.03.003LIAO R H. Study of carburisation and desulfuration for semisteel produced in smelting of titanium slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2003, 24(3): 11-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7638.2003.03.003 [7] HUANG Q Y, HE W C, LÜ X W. Preparation of iron powders with semi-steel by rotary cup atomizer[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2020, 32(7): 563-570. (黄青云, 贺文超, 吕学伟. 电炉半钢转杯离心粒化制备铁粉工艺[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2020, 32(7): 563-570.HUANG Q Y, HE W C, LÜ X W. Preparation of iron powders with semi-steel by rotary cup atomizer[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2020, 32(7): 563-570. [8] LIU S M, ZHAO J. Develoment and prospect of iron and steel powder in China[C]// 2007 CSM Annual Meeting Proceedings. Beijing: Chinese Society for Metals, 2007. (刘世民, 赵晶. 我国钢铁粉末的发展与展望[C]//2007中国钢铁年会. 北京: 中国金属学会, 2007.LIU S M, ZHAO J. Develoment and prospect of iron and steel powder in China[C]// 2007 CSM Annual Meeting Proceedings. Beijing: Chinese Society for Metals, 2007. [9] LIU Y, NIU S, LI F, et al. Preparation of amorphous Fe-based magnetic powder by water atomization[J]. Powder Technology. 2011, 213(1-3): 36-40. [10] LIU J Q, DONG Y N, WANG P, et al. Simulation and experiment investigations on fabrication of Fe-based amorphous powders by a novel atomization process equipped with assisted gas nozzles[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2022, 30(6): 1142-1155. [11] MIZUOCHI T, AKIYAMA T, SHIMADA T, et al. Feasibility of rotary cup atomizer for slag granulation[J]. ISIJ International, 2001, 41(12): 1423-1428. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.41.1423 [12] XIE J W, ZHAO Y Y, DUNKLEY J J. Effects of processing conditions on powder particle size and morphology in centrifugal atomisation of tin[J]. Powder Metallurgy, 2013, 47(2): 168-172. [13] LIU J X, YU Q B, DUAN W J, et al. Experimental investigation on ligament formation for molten slag granulation[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering Design Processes Equipment Economics, 2014, 73(1): 888-893. [14] PLOOKPHOL T, WISUTMETHANGOON S, GONSRANG S. Influence of process parameters on SAC305 lead-free solder powder produced by centrifugal atomization[J]. Powder Technology, 2011, 214(3): 506-512. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2011.09.015 [15] LIU J X, YU Q B, GUO Q. Experimental investigation of liquid disintegration by rotary cups[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 73(1): 44-50. [16] ZHU X, ZHANG H, TAN Y, et al. Analogue experimental study on centrifugal-air blast granulation for molten slag[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 88: 157-164. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.11.077 [17] LIU J X, YU Q B, LI P, et al. Cold experiments on ligament formation for blast furnace slag granulation[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2012, 40: 351-357. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2012.01.063 [18] HE W C, LÜ X W, PAN F F, et al. Novel preparation process of iron powders with semisteel by rotary cup atomizer[J]. Powder Technology, 2019, 356: 1087-1096. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.09.009 [19] LI H P, TSAKIROPOULOS P. Droplet dynamic and solidification progress during rotating disk centrifugal atomization[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(5): 793-99. (李会平, P. Tsakiropoulos. 旋转盘离心雾化熔滴飞行动力学与凝固进程[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(5): 793-99.LI H P, TSAKIROPOULOS P. Droplet dynamic and solidification progress during rotating disk centrifugal atomization[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2006, 16(5): 793-99. [20] QIN Y L, LÜ X W, BAI C G, et al. Mechanism of dry molten slag granulation using a rotating multi-nozzle cup atomizer[J]. Steel research international, 2014, 85(1): 44-52. doi: 10.1002/srin.201300007 [21] WANG H, DING B, LIU X Y, et al. Solidification behaviors of a molten blast furnace slag droplet cooled by air[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 127: 915-24. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.07.215 [22] ZHU X, DING B, WANG H, et al. Numerical study on solidification behaviors of a molten slag droplet in the centrifugal granulation and heat recovery system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 130: 1033-1043. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.080 [23] LEE E S, AHN S. Solidification progress and heat transfer analysis of gas-atomized alloy droplets during spray forming[J]. Acta Metallurgica Et Materialia, 1994, 42(9): 3231-3243. doi: 10.1016/0956-7151(94)90421-9 [24] ZHAO Y Y. Analysis of flow development in centrifugal atomization: Part I. Film thickness of a fully spreading melt[J]. Modelling & Simulation in Materials Science & Engineering, 2004, 12(12): 959-971. [25] HE W C, LÜ X W, PAN F F, et al. Granulation of ferrosilicon alloy by rotary multi-nozzles cup atomizer: Granulation behavior and model formation[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2019, 30(5): 895-902. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2019.02.003 [26] LI H C, LAN Y F, ZHANG B L. Numerical simulation of solidification and heat-transferring process of continuous casting round billet[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2008, 37(9): 35-40. [27] HE W C, LÜ X W, PAN F F, et al. Preparation of iron powders using rotary cup atomizer with water curtain[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 364: 300-309. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.01.046 -




 下载:
下载: