Analysis of slag sticking layer and research on sticking mechanism of RH insertion tube
-
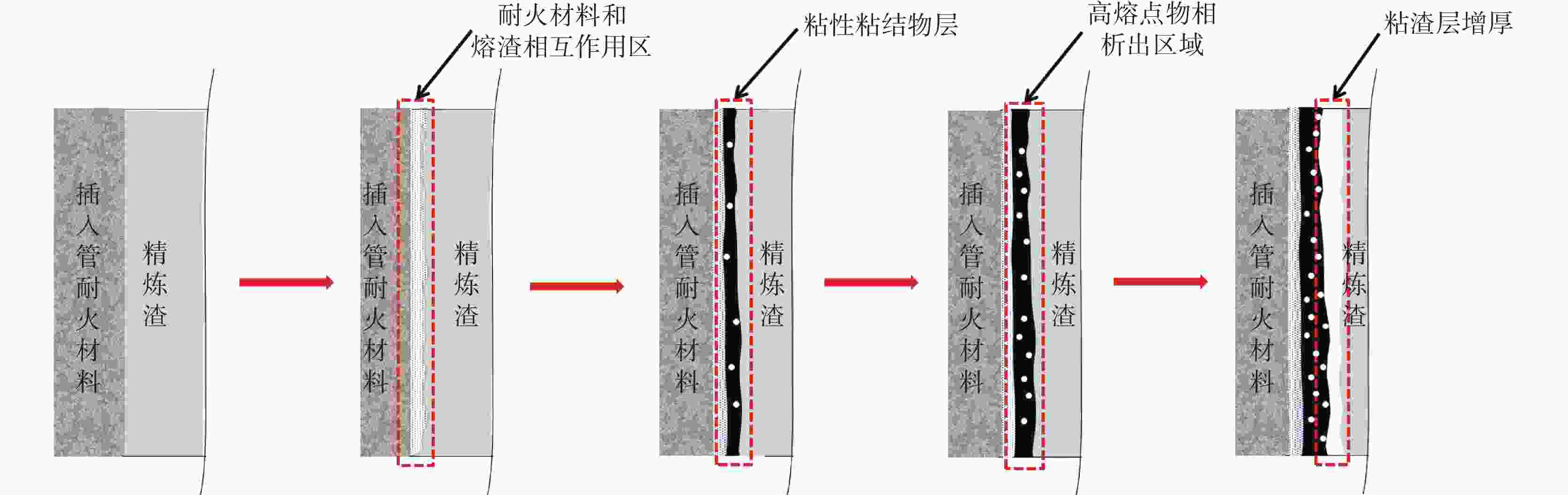
摘要: 针对重轨钢RH精炼过程中出现的RH插入管粘渣问题,对RH插入管表面粘结物进行现场取样,分析了其化学成分及物相组成特征,结合RH插入管外层浇注料与熔渣的相互作用以及熔渣冷凝析出的热力学分析,探讨了重轨钢精炼过程中RH插入管的粘渣机理。研究表明:RH插入管表面粘结物主要由Al2O3、 CaO、 SiO2和MgO等成分组成,形成的镁铝尖晶石(MgO·Al2O3)、镁橄榄石(2MgO·SiO2)以及铝硅酸钙(2CaO·Al2O3·SiO2)等高熔点物相是插入管粘渣的重要原因。插入管的粘渣机理可描述为:在插入管使用期间,由于温度交替变化,其表面持续发生熔渣的“粘性粘结”和“析出性粘结”使得插入管粘渣层不断增厚而难以自行脱落,导致RH插入管的严重粘渣。Abstract: In order to address the problem of slag sticking on RH insertion tube during the RH refining process of heavy rail steel, on-site sampling was carried out for the adhered substances on the surface of the RH insertion tube, and the chemical composition and phase composition characteristics were analyzed. The mechanism of slag sticking on the RH insertion tube during the refining process of heavy rail steel was explored by combining with the interaction between the outer layer castable of the RH insertion tube and the slag, as well as thermodynamic analysis of the slag condensation and precipitation. The study shows that the adhered substances on the surface of the RH insertion tube are mainly composed of Al2O3, CaO, SiO2 and MgO, and the formation of high-melting-point phases such as magnesium-aluminum spinel (MgO·Al2O3), magnesium-olivine (2MgO·SiO2), and calcium aluminum-silicate (2CaO·Al2O3·SiO2) is an important reason for the slag adhesion on the insertion tube. The slagging mechanism of the insertion tube can be described as follows: during the use of the insertion tube, due to the alternating temperature changes, the “viscous adhesion” and “precipitation adhesion” continuously occur on the surface of the slag, which makes the insertion tube slag layer thicken and difficult to fall off by itself, leading to the severe slagging of the RH insertion tube.
-
Key words:
- RH insertion tube /
- bonding material /
- slagging mechanism
-
表 1 精炼渣中主要的化学成分及其碱度
Table 1. Main chemical composition of the refining slag and its basicity
化学成分/% 碱度 CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MgO FeO MnO F 50~56 25~30 8~11 3~7 0.2~1.2 0.1~0.5 1.0~6.0 1.8~2.3 表 2 粘结物的化学成分
Table 2. Chemical compositions of adhesives
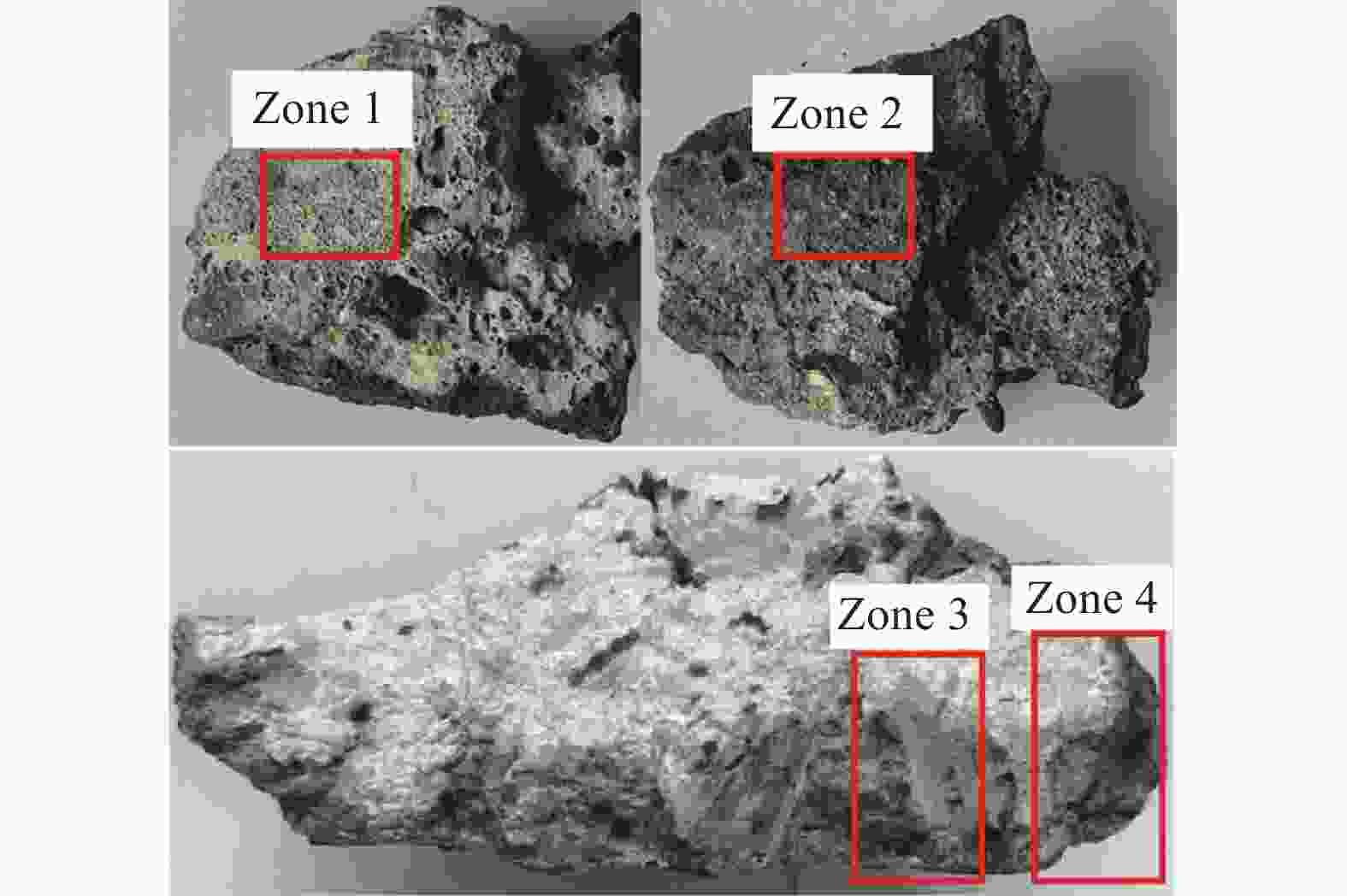
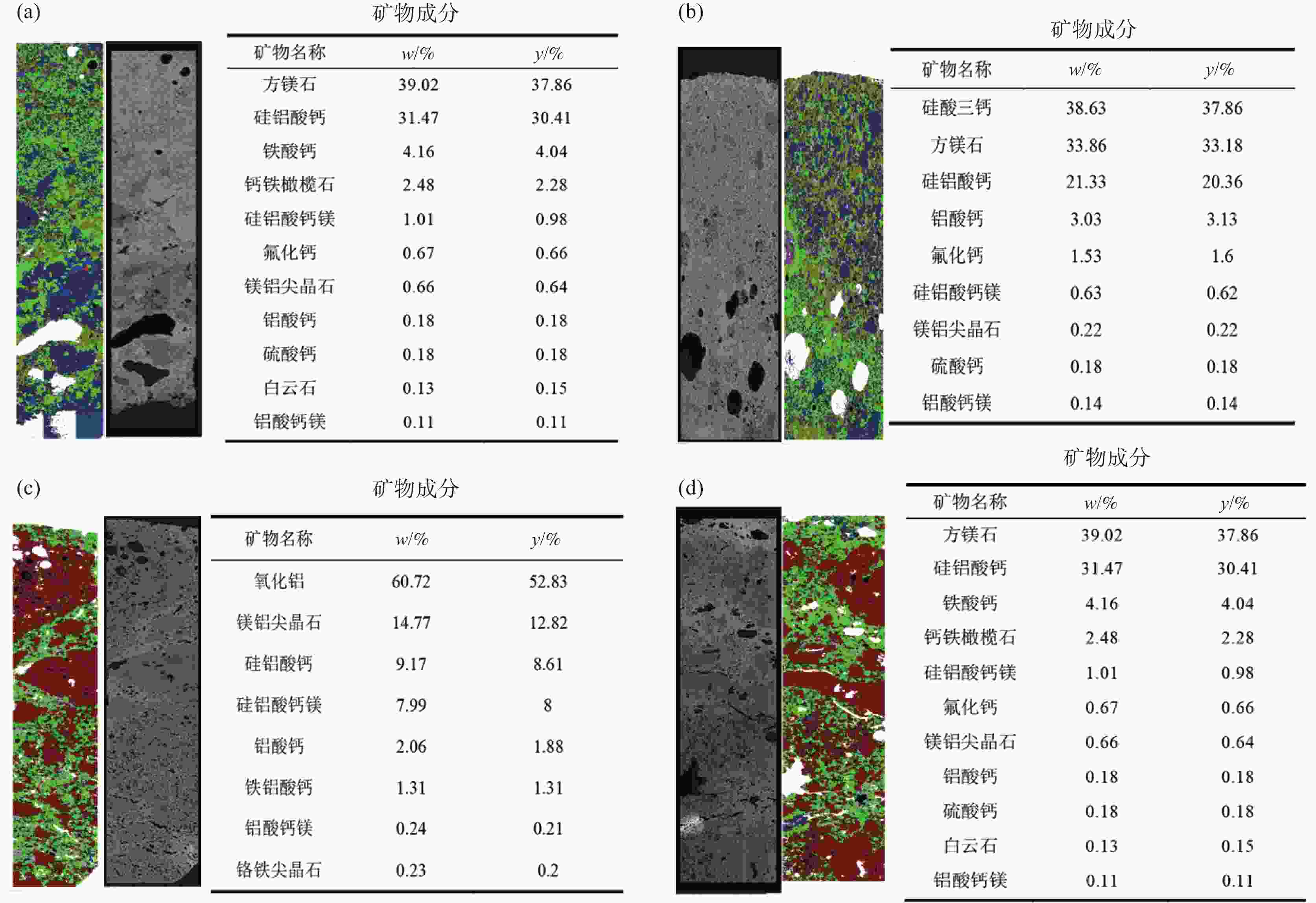
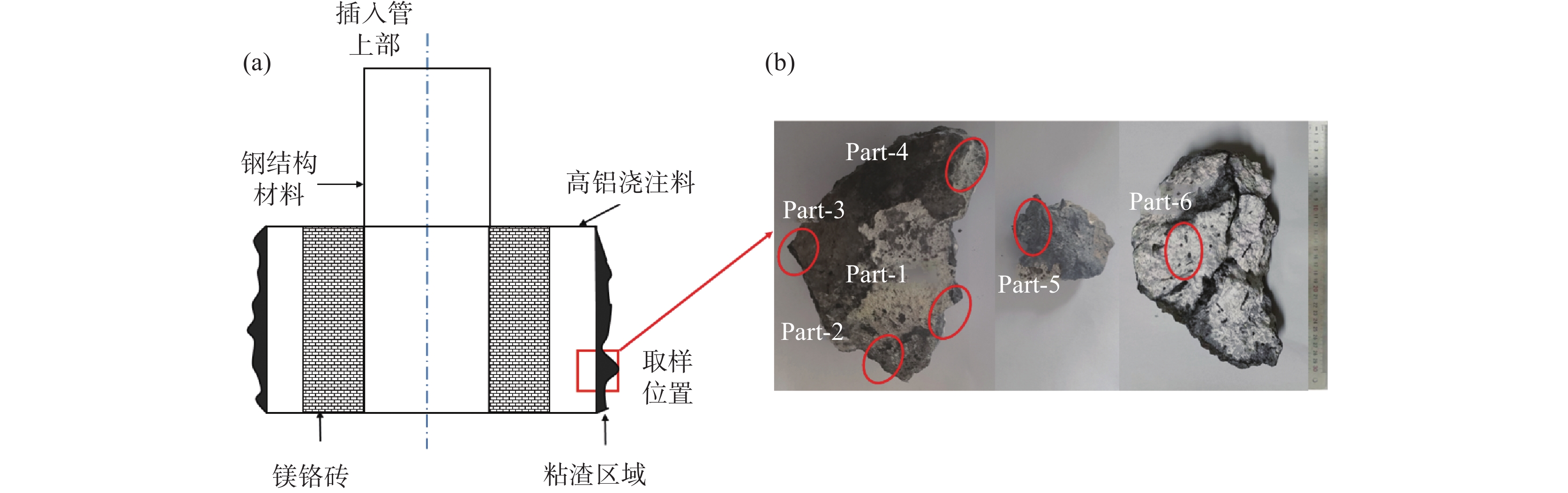
% 编号 CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MgO Fe2O3 MnO Na2O P2O5 TiO2 S V2O5 Cr2O3 F Part-1 14.93 17.85 3.76 57.31 1.02 0.10 0.27 0.29 0.19 0.84 0.01 0.09 3.34 Part-2 10.84 11.36 64.30 8.61 1.46 0.11 0.73 0.16 0.11 0.26 0.01 0.51 1.57 Part-3 11.00 10.18 68.59 5.98 0.80 0.06 0.58 0.16 0.13 0.23 0.01 0.10 2.19 Part-4 19.80 15.36 47.21 11.64 1.96 0.23 0.52 0.15 0.18 0.47 0.01 0.11 2.36 Part-5 17.88 18.79 5.69 51.69 0.85 0.11 0.27 0.25 0.20 0.80 0.00 0.02 3.44 Part-6 0.52 6.34 82.49 9.98 0.3 0.012 0.28 0.014 0.008 0.003 0.053 表 3 图5(a)中EDS点扫描结果
Table 3. EDS points scan results in Fig.5 (a)
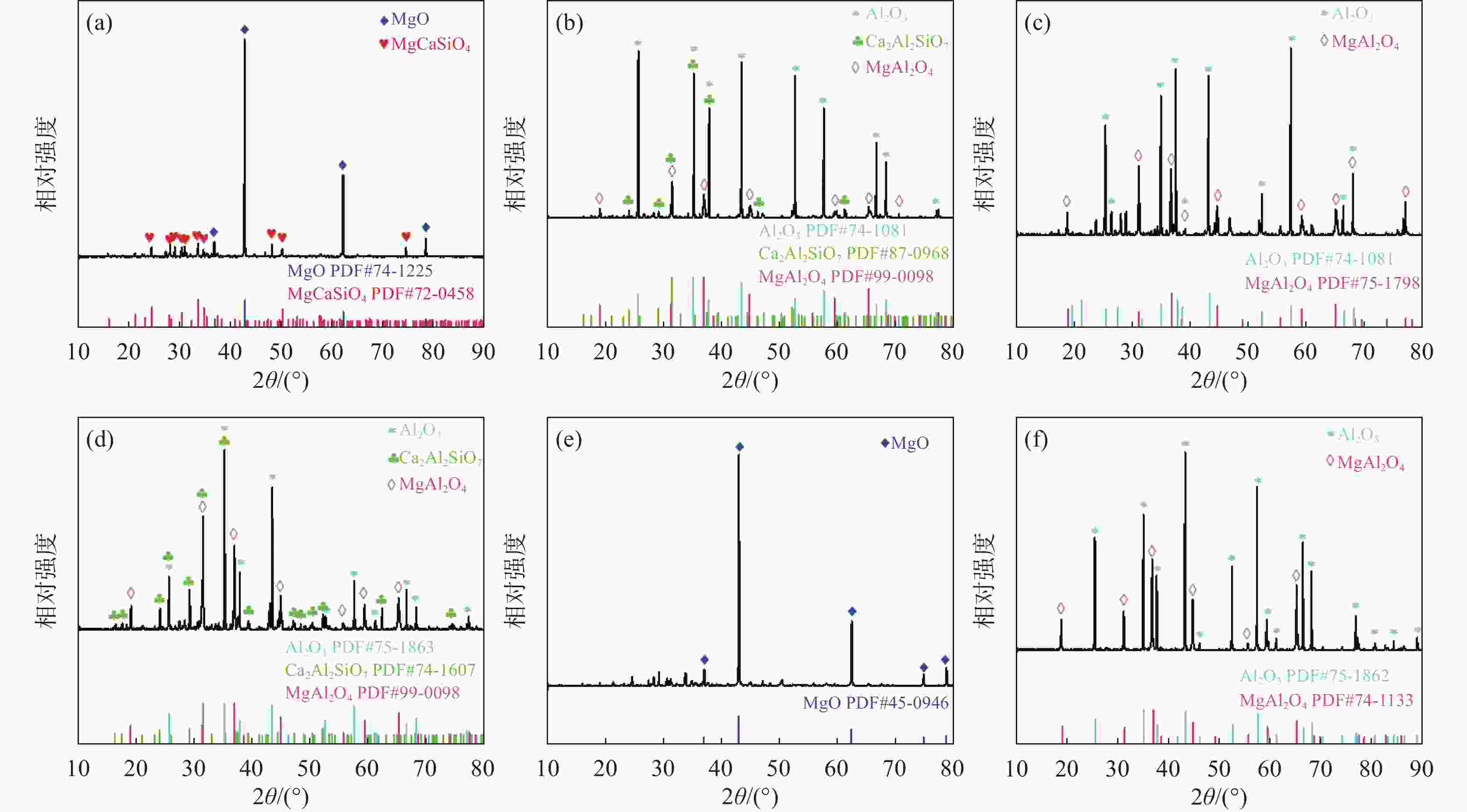
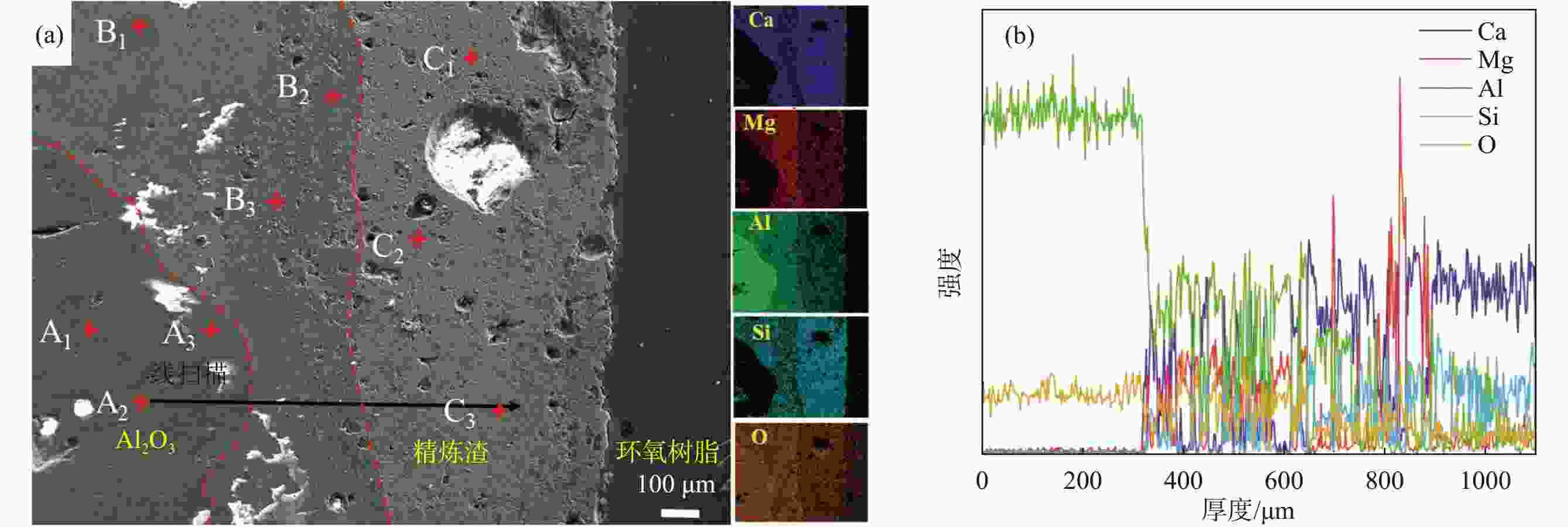
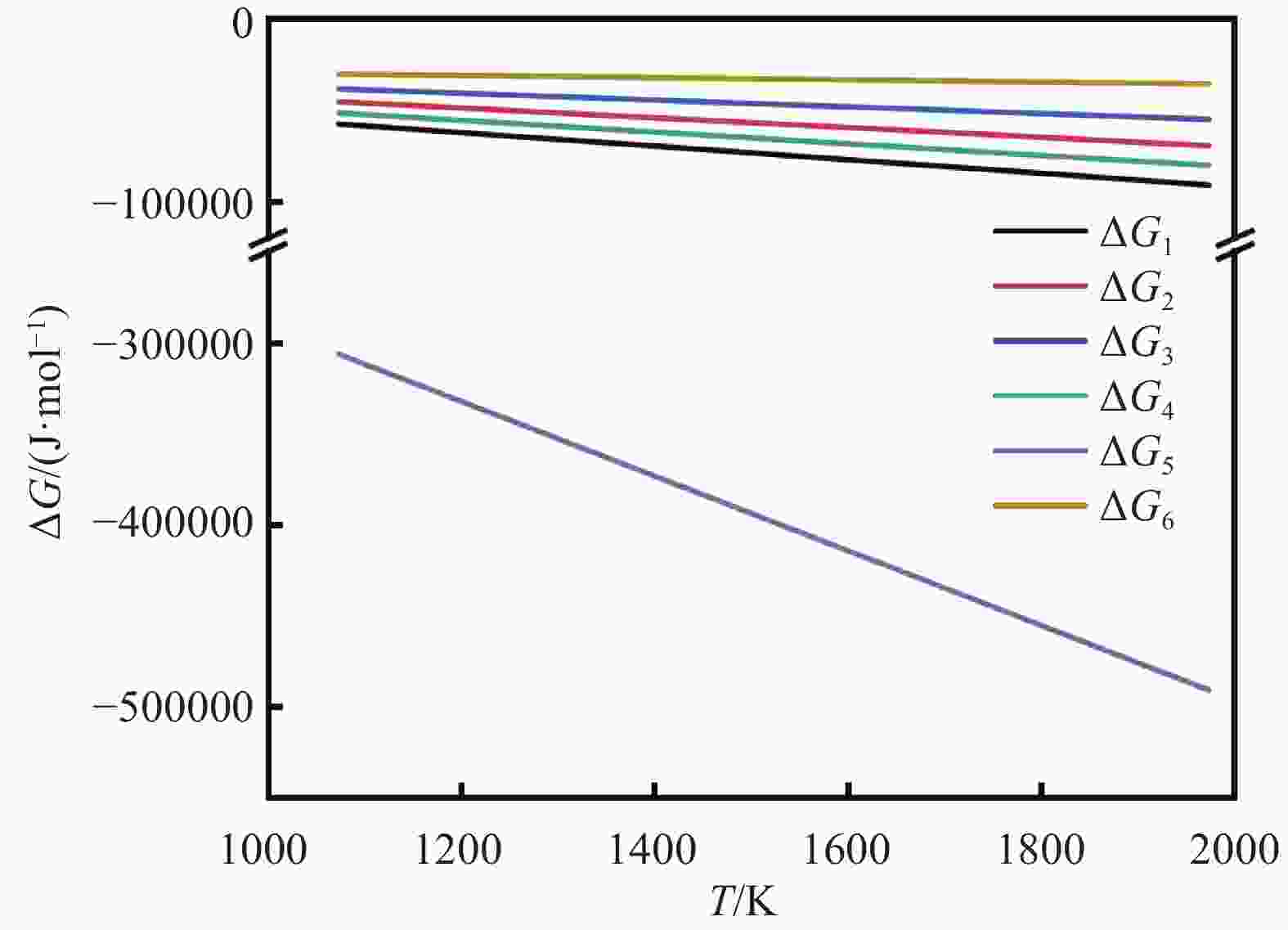
检测点 y/% 可能的物相 O Al Ca Si Mg F Na A1 63.99 36.01 Al2O3 A2 61.43 38.57 Al2O3 A3 69.92 30.08 Al2O3 B1 67.65 32.35 Al2O3 B2 66.21 19.56 3.55 1.09 9.59 MgO·Al2O3; 2CaO·SiO2 B3 70.04 8.97 9.94 3.09 4.32 2.73 0.9 MgO·Al2O3; 2CaO·SiO2; xCaO·yAl2O3; 3CaO·2SiO2·CaF2 C1 58.24 0.35 20.92 10.07 2.91 7.51 MgO·Al2O3; 2CaO·SiO2; 3CaO·2SiO2·CaF2 C2 61.03 17.99 16.07 4.29 0.61 MgO·Al2O3; 2CaO·SiO2; xCaO·yAl2O3 C3 71.19 1.03 14.24 5.86 3.61 4.07 MgO·Al2O3; 2CaO·SiO2; 3CaO·2SiO2·CaF2 -
[1] ZHAN D P, JIANG Z H, RUI S S, et al. Review of metallurgical multifunction of RH vacuum refining technology[J]. Baosteel Technology, 1999(4): 60-63. (战东平, 姜周华, 芮树森, 等. RH真空精炼技术冶金功能综述[J]. 宝钢技术, 1999(4): 60-63.ZHAN D P, JIANG Z H, RUI S S, et al. Review of metallurgical multifunction of RH vacuum refining technology[J]. Baosteel Technology, 1999(4): 60-63. [2] ZHAO S Z, GU H Z, HUANG A, et al. Physical properties and corrosion resistance of magnesia-calcium hexaaluminate refractories to molten steel[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(2): 3041-3048. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.09.288 [3] HOU X, DING D, XIAO G, et al. Corrosion mechanism of magnesia-chrome refractory bricks with FetO-SiO2-Cr2O3 copper converter slag[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(10): 15395-15401. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.01.124 [4] XU X F, ZHU T B, LI Y W, et al. Effect of particle grading on fracture behavior and thermal shock resistance of MgO–C refractories[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2022, 42(2): 672-681. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.10.037 [5] YAO J F. Slag buildup in ladle and countermeasures[J]. Iron and Steel, 2002, 37(2): 70-72. (姚金甫. 国内外钢包的粘渣及其对策[J]. 钢铁, 2002, 37(2): 70-72. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2002.02.019YAO J F. Slag buildup in ladle and countermeasures[J]. Iron and Steel, 2002, 37(2): 70-72. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2002.02.019 [6] LU C Y, CHEN M, SUN Z Q, et al. Study on corrosion mechanism of RH immersion tube castable[J]. China Sciencepaper Online, 2009, 4(11): 834-837. (陆彩云, 陈敏, 孙中强, 等. RH浸渍管浇注料侵蚀机理的研究[J]. 中国科技论文在线, 2009, 4(11): 834-837.LU C Y, CHEN M, SUN Z Q, et al. Study on corrosion mechanism of RH immersion tube castable[J]. China Sciencepaper Online, 2009, 4(11): 834-837. [7] QIU W D, WANG Y Q, MOU J N. The reason and measure for slag-adhesion and over wight of 300 t ladle in Baosteel[J]. Refractories, 1999, 33(4): 208-210. (邱文冬, 王燕群, 牟济宁. 宝钢300 t钢包粘渣的原因及对策[J]. 耐火材料, 1999, 33(4): 208-210.QIU W D, WANG Y Q, MOU J N. The reason and measure for slag-adhesion and over wight of 300 t ladle in Baosteel[J]. Refractories, 1999, 33(4): 208-210. [8] WANG H M, LI G R, XU M X, et al. Effect of additives on viscosity of LATS refining ladle slag[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2006, 6(2): 227-230. (王宏明, 李桂荣, 徐明喜, 等. 改质剂对LATS精炼钢包渣粘度的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2006, 6(2): 227-230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2006.02.015WANG H M, LI G R, XU M X, et al. Effect of additives on viscosity of LATS refining ladle slag[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2006, 6(2): 227-230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2006.02.015 [9] TOMBA MARTINEZ A G, LUZ A P, BRAULIO M A L, et al. Al2O3-based binders for corrosion resistance optimization of Al2O3-MgAl2O4 and Al2O3MgO refractory castables[J]. Casting Technology, 2015, 41(8): 9947-9956. [10] LIU Z, DENG C, YU C, et al. Molten salt synthesis and characterization of SiC whiskers containing coating on graphite for application in Al2O3-SiCC castables[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 777: 26-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.107 [11] BRAULIO MAL, MORBIOLI GG, PANDOLFELLI VC. Advanced boron-containing Al2O3-MgO refractory castables[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2011, 94(10): 3467-3472. doi: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2011.04608.x [12] LI G R. Effect of strong basic oxide (Li2O, Na2O, K2O and BaO) on property of CaO-based flux[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2003, 10(3): 6-9. [13] WANG H M, LI G R, DING Z T. Effect of additives on melting point of LATS refining ladle slag[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2007, 14(2): 25-29. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(07)60022-3 [14] WEI J W, MIAO Z, LI Y Y, et al. Chemical attack of Al2O3-MgAl2O4 refractory castables in the non-slag-tapping side of refining ladle[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(12): 16832-16838. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.02.236 [15] LIU F, ZOU C D, ZHAO J Q, et al. Causes and solutions for the formation of slag in RH impregnated pipes[J]. Modern Transportation and Metallurgical Materials, 2020, 48(4): 51-54. (刘飞, 邹长东, 赵家七, 等. RH浸渍管粘渣形成原因及解决办法[J]. 现代冶金, 2020, 48(4): 51-54.LIU F, ZOU C D, ZHAO J Q, et al. Causes and solutions for the formation of slag in RH impregnated pipes[J]. Modern Transportation and Metallurgical Materials, 2020, 48(4): 51-54. [16] WU F, XU L H, GU H Z, et al. Development and application of ladle nonsticking slag used as sprayed material[J]. Steelmaking, 2000, 16(3): 24-26. (吴峰, 许伦华, 顾华志, 等. 钢包不粘渣喷涂料的研制与应用[J]. 炼钢, 2000, 16(3): 24-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1043.2000.03.006WU F, XU L H, GU H Z, et al. Development and application of ladle nonsticking slag used as sprayed material[J]. Steelmaking, 2000, 16(3): 24-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1043.2000.03.006 [17] LI J Z, WU Y B, ZHANG H L, et al. Analysis of the microstructure of ladle slag building-up[J]. Steelmaking, 2008, 24(5): 37-39. (李继铮, 吴远兵, 张洪雷, 等. 钢包粘结物的显微结构分析[J]. 炼钢, 2008, 24(5): 37-39.LI J Z, WU Y B, ZHANG H L, et al. Analysis of the microstructure of ladle slag building-up[J]. Steelmaking, 2008, 24(5): 37-39. [18] JIN Y. Study the mechanism of slag building-up in RH immersion tube and additives[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2008. (金杨. RH浸渍管黏渣机理及减轻黏渣用改性剂研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2008.JIN Y. Study the mechanism of slag building-up in RH immersion tube and additives[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2008. [19] LIANG X P, JIN Y, WANG Y, et al. Reason and measure for slag buildup on RH immerge tube of Panzhihua steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2009, 44(8): 52-55. (梁小平, 金杨, 王雨, 等. 攀钢RH浸渍管粘渣原因分析与对策[J]. 钢铁, 2009, 44(8): 52-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2009.08.012LIANG X P, JIN Y, WANG Y, et al. Reason and measure for slag buildup on RH immerge tube of Panzhihua steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2009, 44(8): 52-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2009.08.012 [20] TANG H L, SUN X H, HONG J G. Analysis on the cause of ladle slag bonding and counter-measures[J]. Steelmaking, 2009, 25(4): 24-30. (唐洪乐, 孙晓辉, 洪建国. 钢包粘渣原因分析及措施[J]. 炼钢, 2009, 25(4): 24-30.TANG H L, SUN X H, HONG J G. Analysis on the cause of ladle slag bonding and counter-measures[J]. Steelmaking, 2009, 25(4): 24-30. [21] CHEN S L, LI Y, SHOU Y H, et al. Reason analysis for slag bonding in Anyang steel 25t ladle[J]. Henan Metallurgy, 2006, 14(B09): 149-151. (陈树林, 李勇, 寿业红, 等. 安钢25t钢包粘渣原因分析[J]. 河南冶金, 2006, 14(B09): 149-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3129.2006.z2.050CHEN S L, LI Y, SHOU Y H, et al. Reason analysis for slag bonding in Anyang steel 25t ladle[J]. Henan Metallurgy, 2006, 14(B09): 149-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3129.2006.z2.050 [22] LI X, LIANG X P, WANG Y, et al. Influences of flow and temperature fields on slag sticking of immersion tube during RH refining process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009, 9(S1): 308-311. (李欣, 梁小平, 王雨, 等. RH精炼中钢液温度场与流场对浸渍管粘渣的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2009, 9(S1): 308-311. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2009.z1.068LI X, LIANG X P, WANG Y, et al. Influences of flow and temperature fields on slag sticking of immersion tube during RH refining process[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2009, 9(S1): 308-311. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2009.z1.068 [23] ZHOU Y Z, ZOU C D. Optimization and application of 100 t ladle refining slag system[J]. Steelmaking, 2018, 34(4): 5. (周彦召, 邹长东. 100 t钢包精炼渣系优化选择及应用[J]. 炼钢, 2018, 34(4): 5.ZHOU Y Z, ZOU C D. Optimization and application of 100 t ladle refining slag system[J]. Steelmaking, 2018, 34(4): 5. [24] YE D L. Practical handbook of thermodynamic data of inorganic[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002. (叶大伦. 实用无机物热力学数据手册[M]. 冶金工业出版社, 2002.YE D L. Practical handbook of thermodynamic data of inorganic[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002. [25] LI Z G, YE F B, ZHANG Y. Effects of calcium aluminate cement on properties of corundum castables[J]. Refractories, 2007, 41(5): 336-340. (李志刚, 叶方保, 张宇. 铝酸钙水泥对刚玉基浇注料性能的影响[J]. 耐火材料, 2007, 41(5): 336-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1935.2007.05.004LI Z G, YE F B, ZHANG Y. Effects of calcium aluminate cement on properties of corundum castables[J]. Refractories, 2007, 41(5): 336-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1935.2007.05.004 [26] CHEN Z Y. Chemical thermodynamics and refractories[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2005. (陈肇友. 化学热力学与耐火材料[M]. 冶金工业出版社. 2005.CHEN Z Y. Chemical thermodynamics and refractories[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2005. -




 下载:
下载: