Influence of alkali metal oxides on the melt structure and viscosity properties of CaO-Al2O3 based mold flux
-
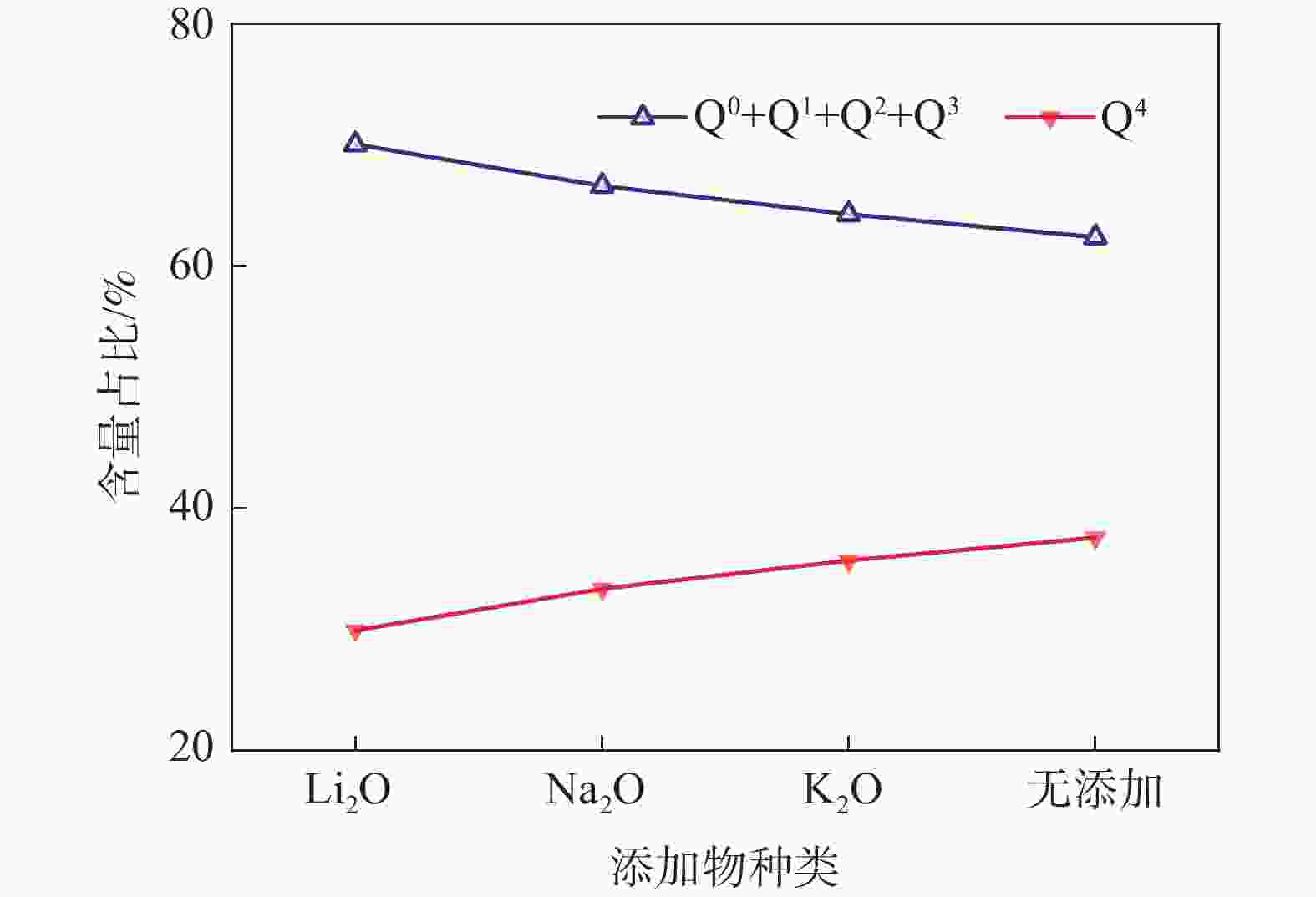
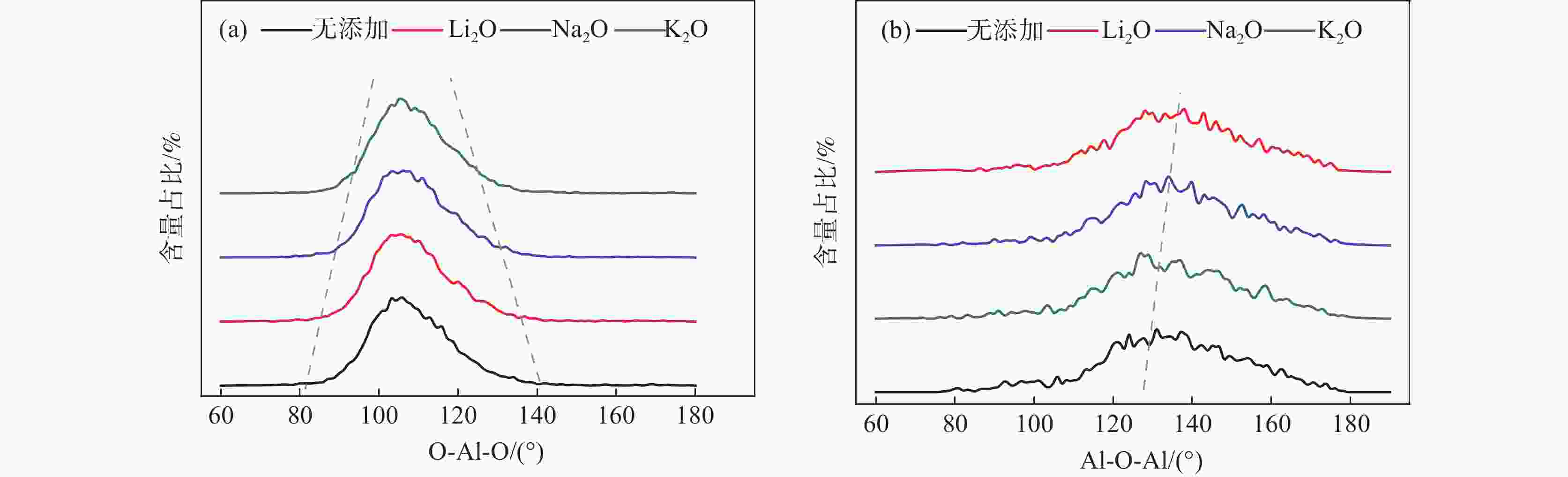
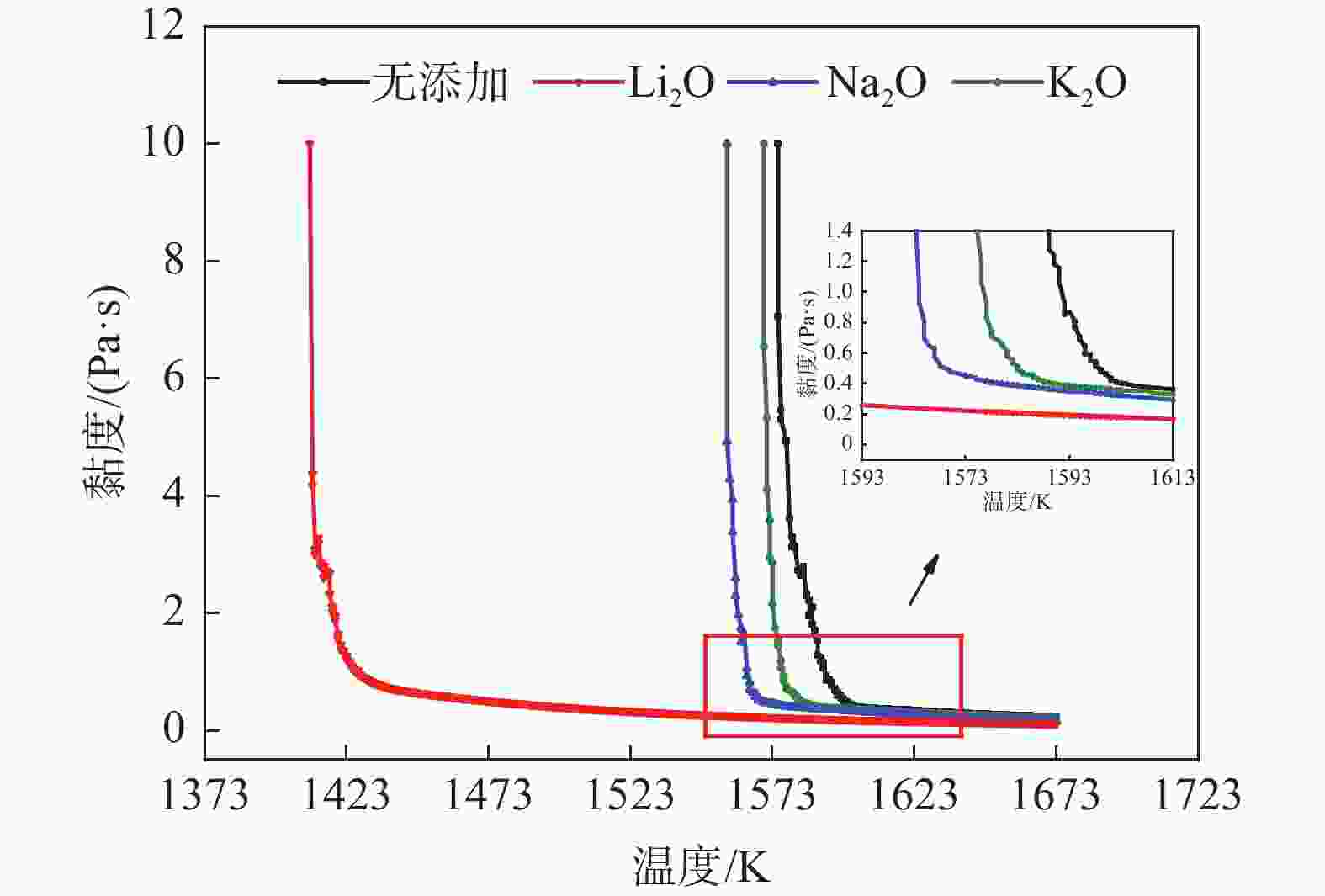
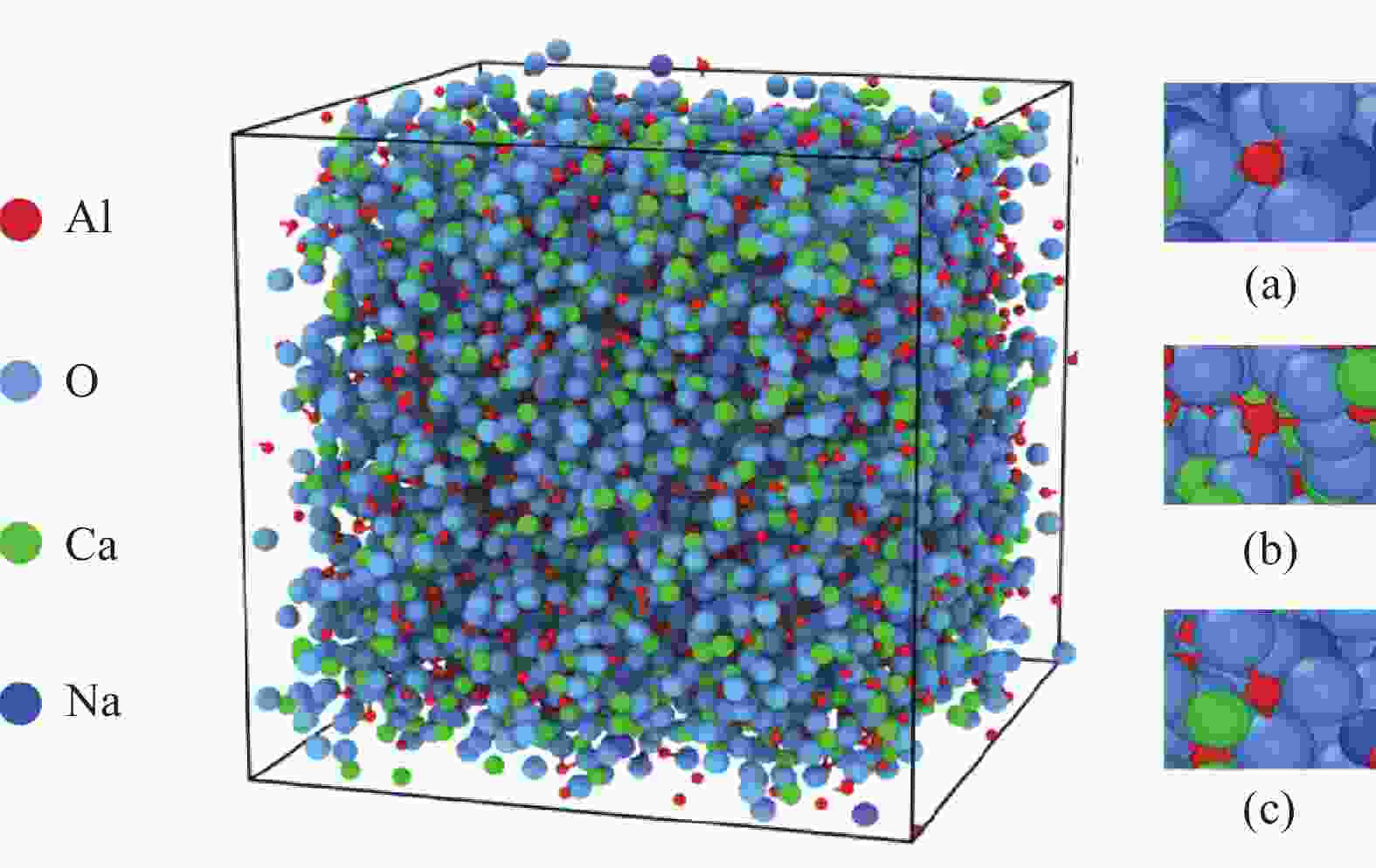
摘要: 低反应性CaO-Al2O3基保护渣可以大幅降低高铝钢连铸过程中的渣-钢反应强度,但此类保护渣黏度较大,结晶性能较强,易在结晶器弯月面处产生较大渣圈,造成铸坯缺陷。采用分子动力学模拟方法结合黏度测试试验,解析同为碱金属氧化物的Li2O、Na2O和K2O对CaO-Al2O3基保护渣熔体结构和黏性特性影响的异同,结果表明,碱金属氧化物对[AlO4]5−四面体进行电荷补偿遵循Li2O<Na2O<K2O的顺序,对铝酸盐网络结构的解聚能力遵循Li2O>Na2O>K2O的顺序。Abstract: Low reactivity CaO-Al2O3 based mold flux can significantly reduce the intensity of slag-steel reaction in the continuous casting process of high-alumina steel. But the viscosity of this kind of mold flux is larger and the crystallization performance is stronger, which is easy to produce larger slag rims at the mold meniscus and cause casting defects. In this paper, the molecular dynamics simulation method combined with viscosity test experiment was used to analyze the similarities and differences of the effects of Li2O, Na2O and K2O, which are alkali metal oxides, on the melt structure and viscosity properties of CaO-Al2O3 based mold flux. The results show that the charge compensation of [AlO4]5− tetrahedra by alkali metal oxides follows the order of Li2O<Na2O<K2O, and the depolymerization ability of aluminate network structure follows the order of Li2O>Na2O>K2O.
-
Key words:
- mold flux /
- aluminates /
- alkali metals /
- melt structure /
- viscosity
-
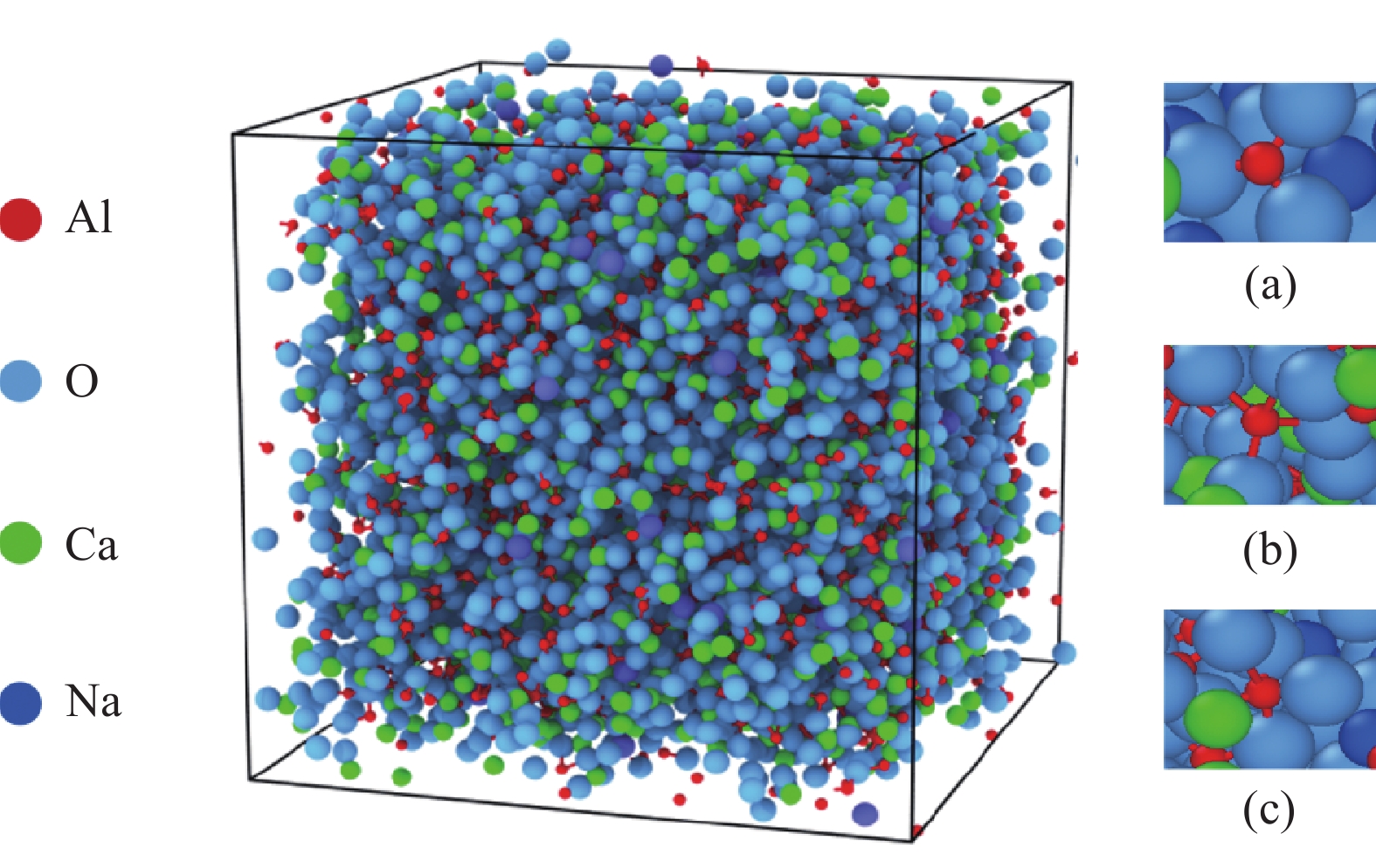
表 1 配加不同碱金属氧化物(Li2O、Na2O、K2O)体系的分子动力学模拟体系组成
Table 1. Composition of molecular dynamics simulation system with different alkali metal oxides (Li2O, Na2O, K2O) systems
质量分数/% 粒子数量/个 密度/(g·cm−3) CaO Al2O3 Li2O Na2O K2O CaO Al2O3 Li2O Na2O K2O 总数 1 50 50 2107 1157 9999 2.77 2 48 48 4 1 920 1055 295 10000 2.70 3 48 48 4 2 009 1104 154 10000 2.72 4 48 48 4 2 042 1122 102 10000 2.74 表 2 分子动力学模拟中采用的Buckingham势参数[21-23]
Table 2. Buckingham potential parameters used in molecular dynamics simulations
粒子对 Aij/eV ρij/nm Cij×106/(eV·nm6) Li-O 37795.00 0.0165 4.34 Na-O 282278.80 0.016 8.67 K-O 2149947.00 0.0165 13.00 Ca-O 717827.00 0.0165 8.67 Al-O 86057.58 0.0165 0.00 O-O 1497049.00 0.017 17.34 表 3 黏度测试用保护渣化学成分
Table 3. Chemical compositions of mold flux for viscosity test
% CaO Al2O3 Li2O Na2O K2O CaF2 B2O3 1 40 40 10 10 2 38 38 4 10 10 3 38 38 4 10 10 4 38 38 4 10 10 -
[1] WANG Q, QIU S T, ZHAO P, et al. Status of research on mold flux for high aluminum steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2012, 28(1): 74-78. (王强, 仇圣桃, 赵沛, 等. 高铝钢连铸保护渣的研究现状[J]. 炼钢, 2012, 28(1): 74-78.WANG Q, QIU S T, ZHAO P, et al. Status of research on mold flux for high aluminum steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2012, 28(1): 74-78. [2] WANG H, TANG P, WEN G H, et al. Research on the non-reactive mold powder for high aluminium steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2010, 31(3): 20-24. (王欢, 唐萍, 文光华, 等. 高铝钢非反应性连铸保护渣的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2010, 31(3): 20-24. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2010.03.005WANG H, TANG P, WEN G H, et al. Research on the non-reactive mold powder for high aluminium steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2010, 31(3): 20-24. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2010.03.005 [3] YUTAKA Y, YASUHIRO K, TOSHIHIKO E, et al. Powder for surface coating of molten metal in continuous casting[P]. JPS6356019B2 [P/OL]. 1988-11-07. [4] ZHU Z M, ZHANG C, CAI D X, et al. A kind of continuous casting mold flux for high aluminum steel and its manufacturing method: CN200710042540.6[P]. 2010-05-19. (朱祖民, 张晨, 蔡得祥, 等. 一种高铝钢用连铸保护渣及其制造方法: CN200710042540.6[P]. 2010-05-19.ZHU Z M, ZHANG C, CAI D X, et al. A kind of continuous casting mold flux for high aluminum steel and its manufacturing method: CN200710042540.6[P]. 2010-05-19. [5] WANG H, TANG P, WEN G H, et al. Effect of Na2O on crystallization behavior and heat transfer of high Al steel mould fluxes[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2011, 38(5): 369-373. doi: 10.1179/1743281211Y.0000000011 [6] STŔEET S. Production of high-aluminum steel slabs[J]. Iron and Steel Technology, 2008, 7: 38-49. [7] BLAZEK K, YIN H, SKOCZYLAS G, et al. Development and evaluation of lime aluminum-based mold powders for casting high-aluminum TRIP steel grades[J]. AIST Transactions, 2011, 8: 232-240. [8] HE S P, LIU Y D, LI Q H, et al. Research progress of mold fluxes for high-Al steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2024, 59(5): 1-11. (何生平, 刘亚东, 李权辉, 等. 高铝钢连铸保护渣研究进展[J]. 钢铁, 2024, 59(5): 1-11.HE S P, LIU Y D, LI Q H, et al. Research progress of mold fluxes for high-Al steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2024, 59(5): 1-11. [9] ZHANG C, CAI D X. Investigation on development of low-Li2O mold fluxes used for high aluminum steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2017, 33(3): 51-55. (张晨, 蔡得祥. 高铝钢用低Li2O保护渣的开发研究[J]. 炼钢, 2017, 33(3): 51-55.ZHANG C, CAI D X. Investigation on development of low-Li2O mold fluxes used for high aluminum steel[J]. Steelmaking, 2017, 33(3): 51-55. [10] PAN W J, LI M, ZHU L L, et al. Effect of Na2O on properties of ultra-high basicity continuous casting mold fluxes[J]. Iron and Steel, 2022, 57(1): 93-101. (潘伟杰, 李民, 朱礼龙, 等. Na2O对超高碱度连铸保护渣性能的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2022, 57(1): 93-101.PAN W J, LI M, ZHU L L, et al. Effect of Na2O on properties of ultra-high basicity continuous casting mold fluxes[J]. Iron and Steel, 2022, 57(1): 93-101. [11] SEO M S, SOHN I. Substitutional effect of Na2O with K2O on the viscosity and structure of CaO-SiO2-CaF2‐based mold flux systems[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2019, 102(10): 6275-6283. doi: 10.1111/jace.16456 [12] LI C, QI J, LIU C J, et al. Effect of fluxing agent on the properties of CaO-Al2O3 based mold flux[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021, 42(4): 124-130. (李晨, 亓捷, 刘承军, 等. 助熔剂对CaO-Al2O3基保护渣理化性能的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021, 42(4): 124-130. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.04.021LI C, QI J, LIU C J, et al. Effect of fluxing agent on the properties of CaO-Al2O3 based mold flux[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021, 42(4): 124-130. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.04.021 [13] KIM G H, SOHN I. Influence of Li2O on the viscous behavior of CaO-Al2O3-12 mass% Na2O-12 mass% CaF2 based slags[J]. ISIJ International, 2012, 52(1): 68-73. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.52.68 [14] ZHANG X B, LIU C J, JIANG M F. Molecular dynamics simulations of melt structure properties of CaO-Al2O3-Na2O slag[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2021, 52(4): 2604-2611. doi: 10.1007/s11663-021-02184-9 [15] ZHANG G H, CHOU K C. Measuring and modeling viscosity of CaO-Al2O3-SiO2(-K2O) melt[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2012, 43: 841-848. doi: 10.1007/s11663-012-9668-9 [16] ZHANG X B, LIU C J, JIANG M F. Effect of fluorine on melt structure for CaO-SiO2-CaF2 and CaO-Al2O3-CaF2 by molecular dynamics simulations[J]. ISIJ International, 2020, 60(10): 2176-2182. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2020-002 [17] ZHANG X B, LIU C J, JIANG M F. Effect of Na ions on melt structure and viscosity of CaO-SiO2-Na2O by molecular dynamics simulations[J]. ISIJ International, 2021, 61(5): 1389-1395. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2020-635 [18] JEREBTSOV D, MIKHAILOV G. Phase diagram of CaO-Al2O3 system[J]. Ceramics International, 2001, 27(1): 25-28. doi: 10.1016/S0272-8842(00)00037-7 [19] WU T, HE S P, LIANG Y, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of the structure and properties for the CaO-SiO2 and CaO-Al2O3 systems[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2015, 411: 145-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2014.12.030 [20] NOSÉ S. A molecular dynamics method for simulations in the canonical ensemble[J]. Molecular Physics, 1984, 52(2): 255-268. doi: 10.1080/00268978400101201 [21] SAETOVA N, RASKOVALOV A, ANTONOV B, et al. Structural features of Li2O-V2O5-B2O3 glasses: Experiment and molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2020, 545: 120253. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2020.120253 [22] BELASHCHENKO D K, SKVORTSOV L V. Molecular dynamics study of CaO–Al2O3 melts[J]. Inorganic Materials, 2001, 37: 476-481. doi: 10.1023/A:1017576717112 [23] WU T, WANG Q, YAO T, et al. Molecular dynamics simulations of the structural properties of Al2O3-based binary systems[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2016, 435: 17-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2015.12.025 [24] CORMIER L, NEUVILLE D R, CALAS G. Structure and properties of low-silica calcium aluminosilicate glasses[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2000, 274(1-3): 110-114. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3093(00)00209-X [25] HANNON A C, PARKER J M. The structure of aluminate glasses by neutron diffraction[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2000, 274(1-3): 102-109. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3093(00)00208-8 [26] KARLSSON C, ZANGHELLINI E, SWENSON J, et al. Structure of mixed alkali/alkaline-earth silicate glasses from neutron diffraction and vibrational spectroscopy[J]. Physical Review B, 2005, 72(6): 064206. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.064206 [27] LI K, KHANNA R, BOUHADJA M, et al. A molecular dynamic simulation on the factors influencing the fluidity of molten coke ash during alkalization with K2O and Na2O[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 313: 1184-1193. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.11.011 [28] JIA B, LI M, YAN X, et al. Structure investigation of CaO-SiO2-Al2O3-Li2O by molecular dynamics simulation and Raman spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2019, 526: 119695. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2019.119695 [29] WU T, YANG W, ZHANG C, et al. Microstructural analysis by molecular dynamics simulation of aluminate ternary slag with alkaline oxide[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2021, 570: 121044. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2021.121044 [30] MCMILLAN P, PIRIOU B. The structures and vibrational spectra of crystals and glasses in the silica-alumina system[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1982, 53(3): 279-298. doi: 10.1016/0022-3093(82)90086-2 [31] MYSEN B O, VIRGO D, SCARFE C. Relations between the anionic structure and viscosity of silicate melts; a Raman spectroscopic study[J]. American Mineralogist, 1980, 65: 690-710. -




 下载:
下载: