Study on the effects of high-frequency induction heated sintering and hot isostatic pressing sintering on microstructure and properties of powder metallurgy high-speed steel
-
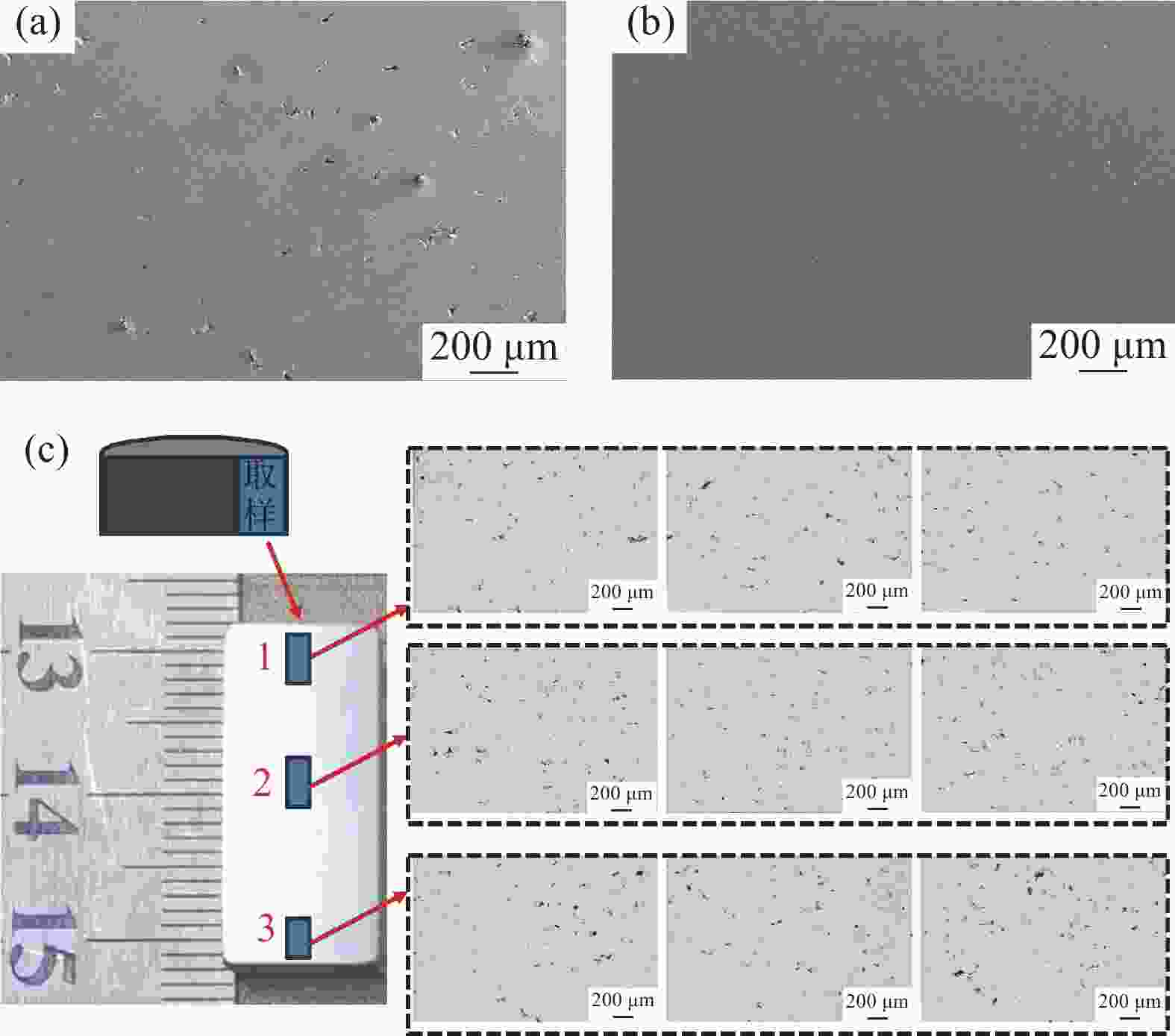
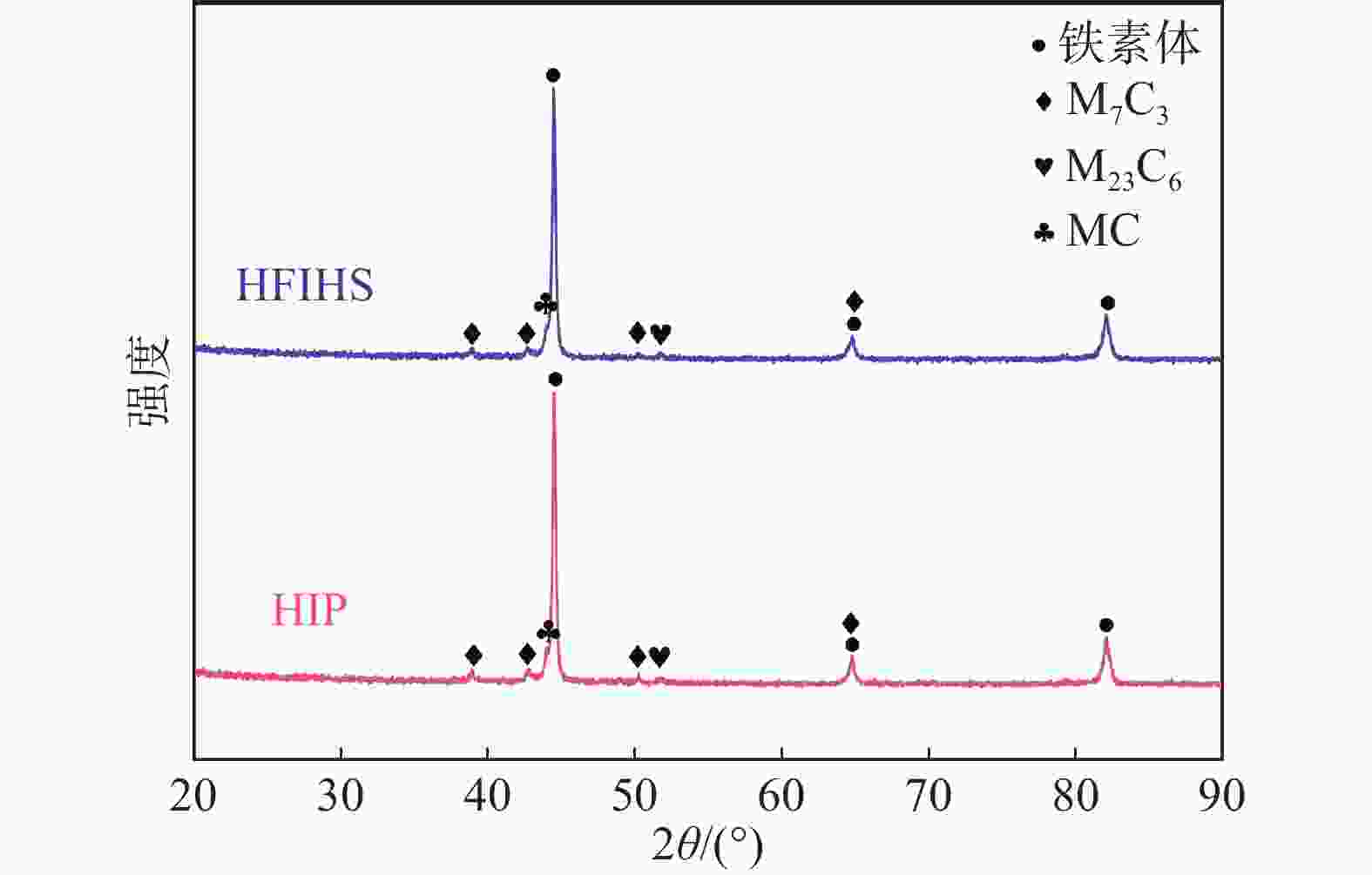
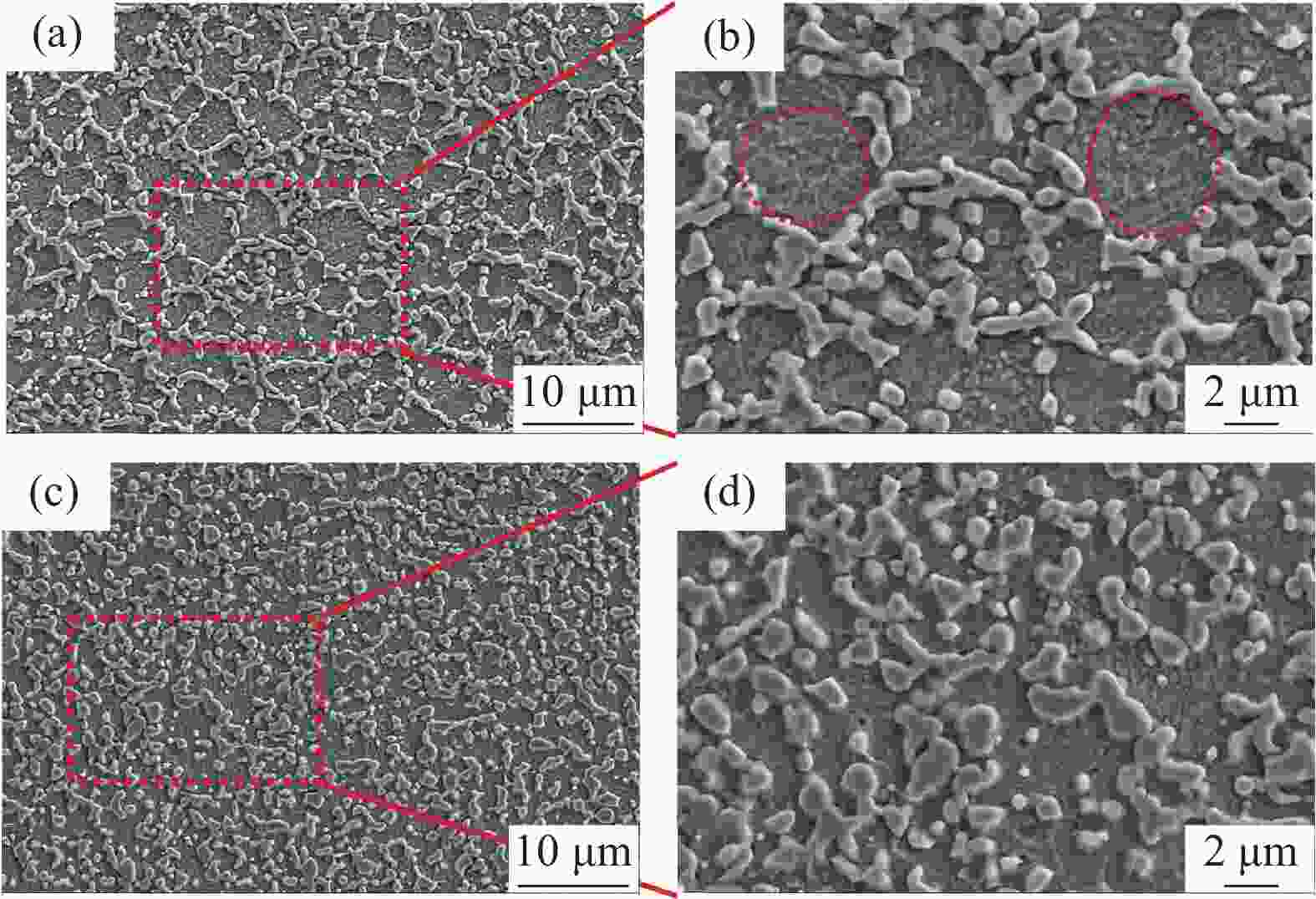
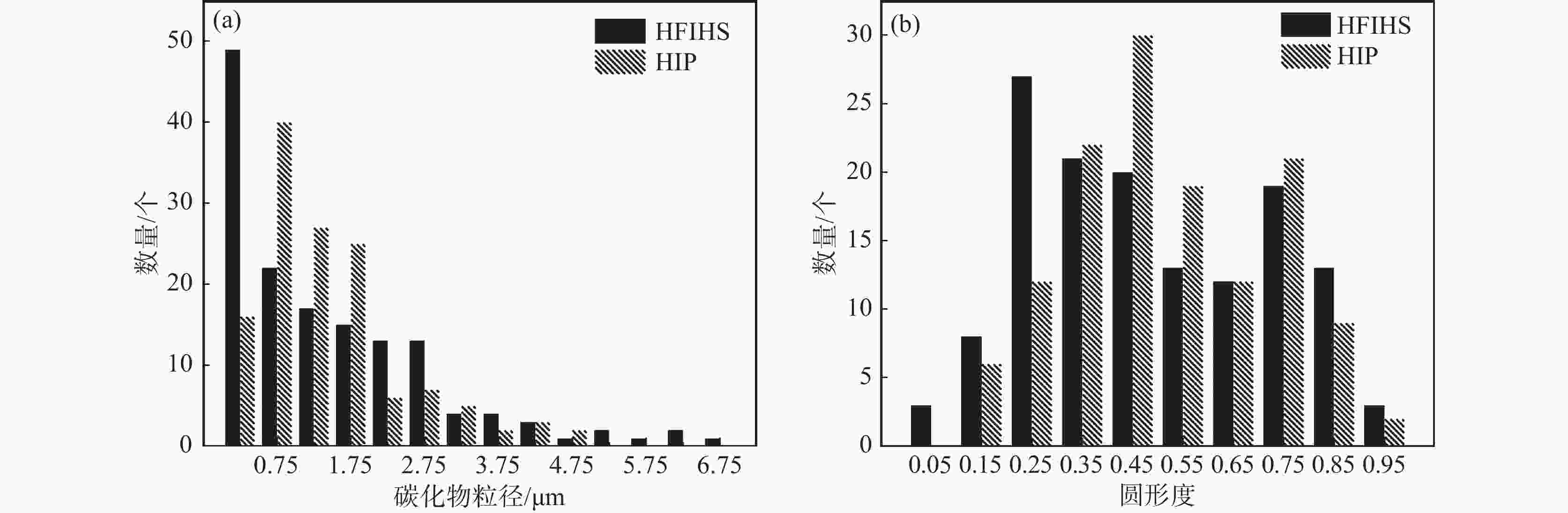
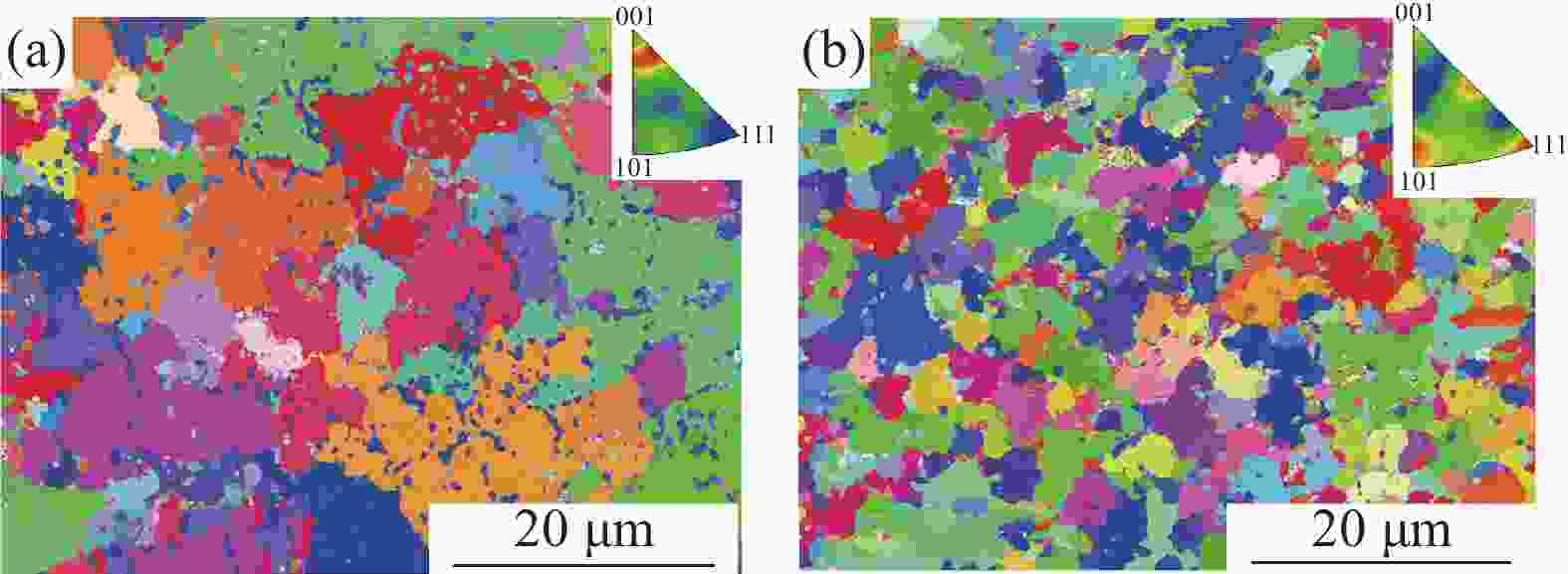
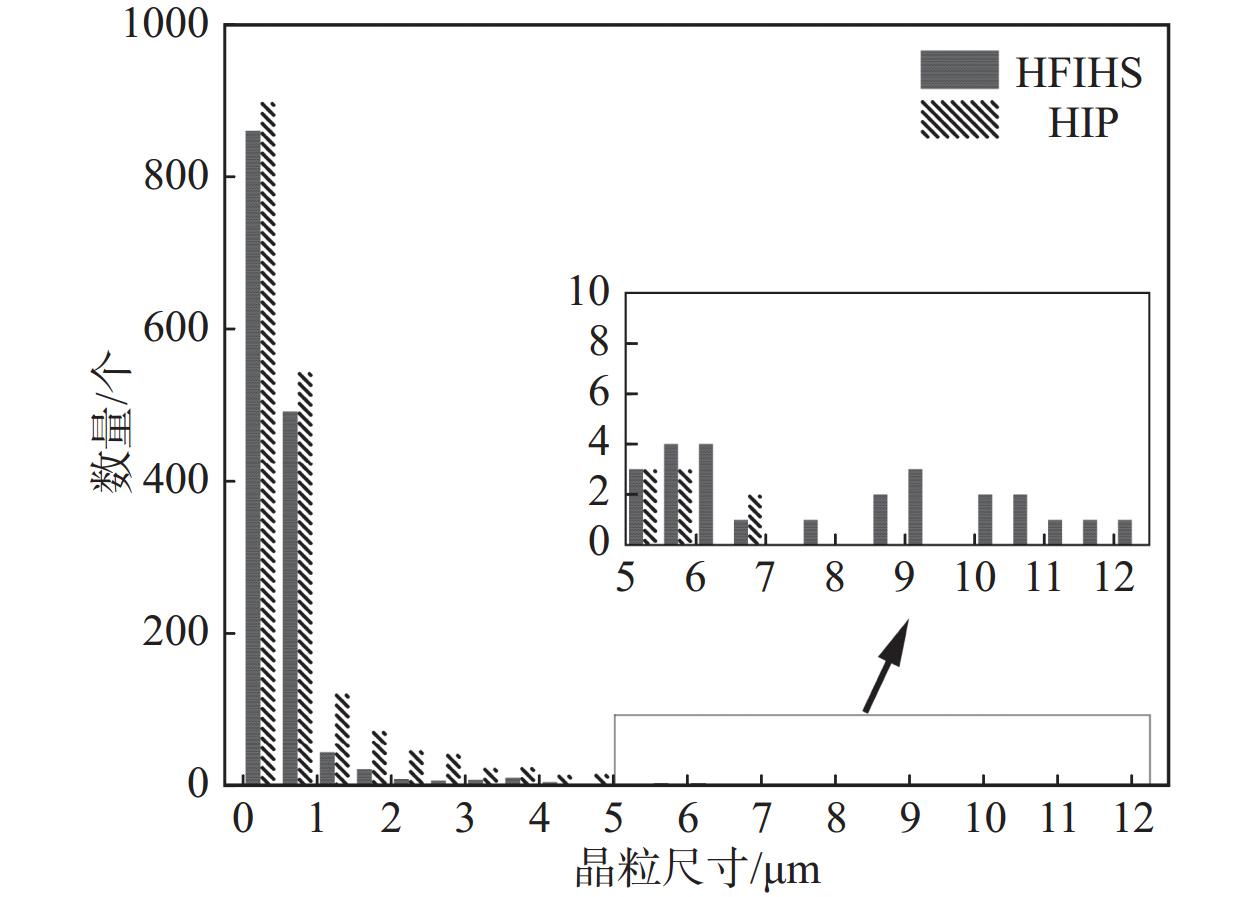
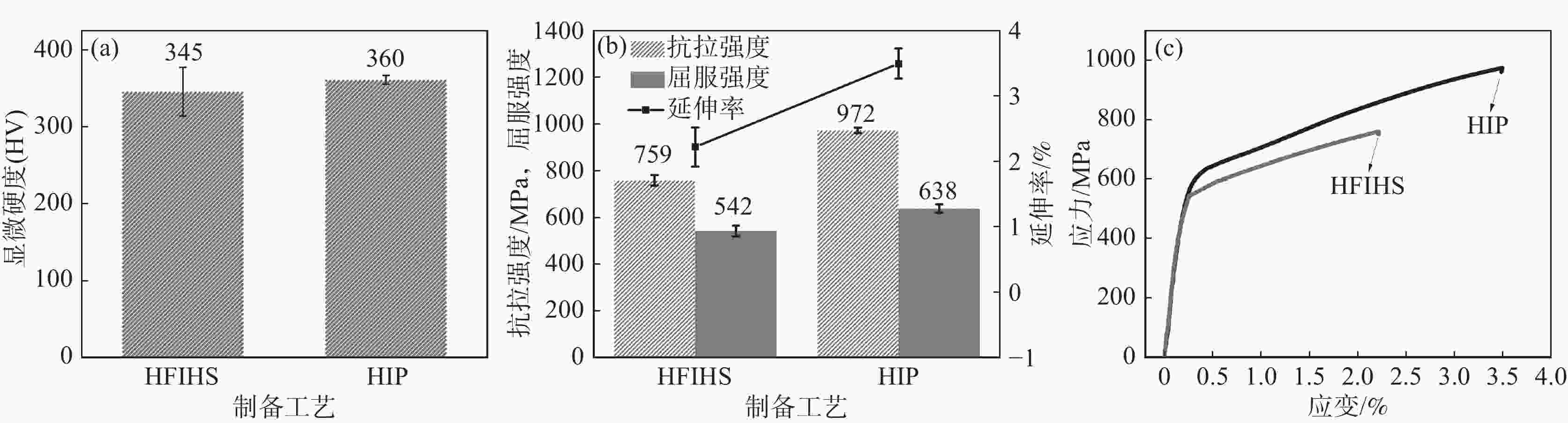
摘要: 以国产气雾化高速钢粉末为原料,通过高频感应加热烧结和热等静压烧结两种工艺制备粉末高速钢,研究了不同工艺对材料致密化、微观组织和力学性能的影响。结果表明,高频感应加热烧结工艺在短时低压下可制备出致密度接近95%的粉末高速钢,虽略低于热等静压工艺,但生产效率更高;在微观组织上,两种工艺制备的粉末高速钢表现出显著差异:高频感应加热烧结粉末高速钢由铁素体基体与大量类网状碳化物组成,热等静压烧结粉末高速钢则由铁素体基体与大量均匀分布的条块状碳化物组成。虽然高频感应加热烧结粉末高速钢的显微硬度、屈服强度、抗拉强度与延伸率略低于热等静压烧结样品,但性能仍相近。高频感应加热烧结工艺能够在短时间和低成本条件下制备出性能优异的粉末高速钢产品,特别适用于对成本和生产周期有较高要求的工业领域。Abstract: The effects of high frequency induction heated sintering (HFIHS) and hot isostatic pressing (HIP) processes on the densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of prepared powder metallurgy high speed steel (PM-HSS) were studied. The results show that the HFIHS process can be used to prepare PM-HSS with a density of nearly 95% under short-time and low-pressure conditions, which is slightly lower than that prepared by HIP. In terms of microstructure, the PM-HSS produced by these two processes show significant differences: The sample prepared by HFIHS is composed of ferrite matrix and a large number of reticular carbides, while the other produced by HIP is composed of ferrite matrix and a large number of homogenously distributed strip carbides. Although the micro-hardness, yield strength, tensile strength and elongation of the high speed steel sintered by HFIHS process were lower than those of the HIPed sample, the performance is still similar. This finding indicates that the HFIHS process can be used to prepare PM-HSS products with excellent performance in a short time and at low cost, thus it is especially suitable for industrial fields with high requirements for cost and production cycle.
-
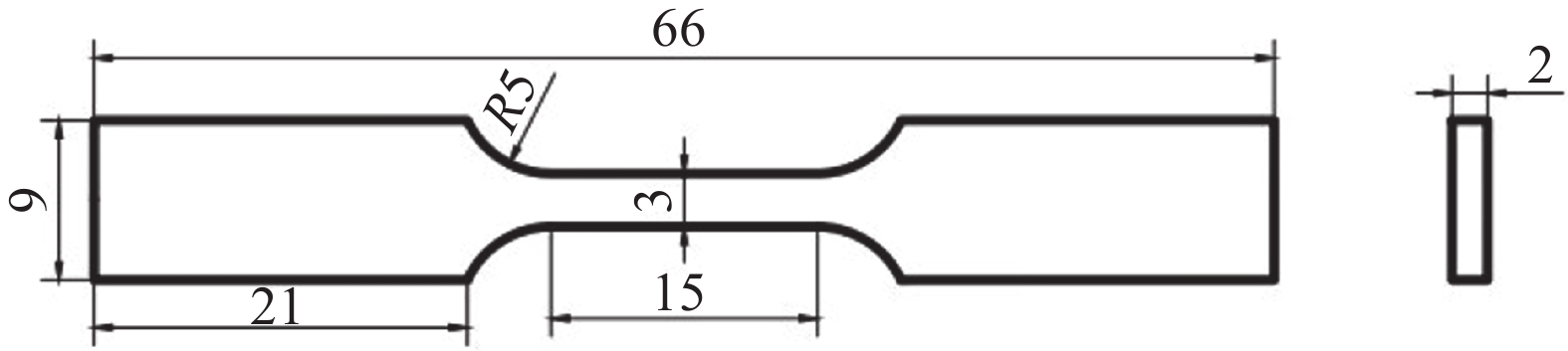
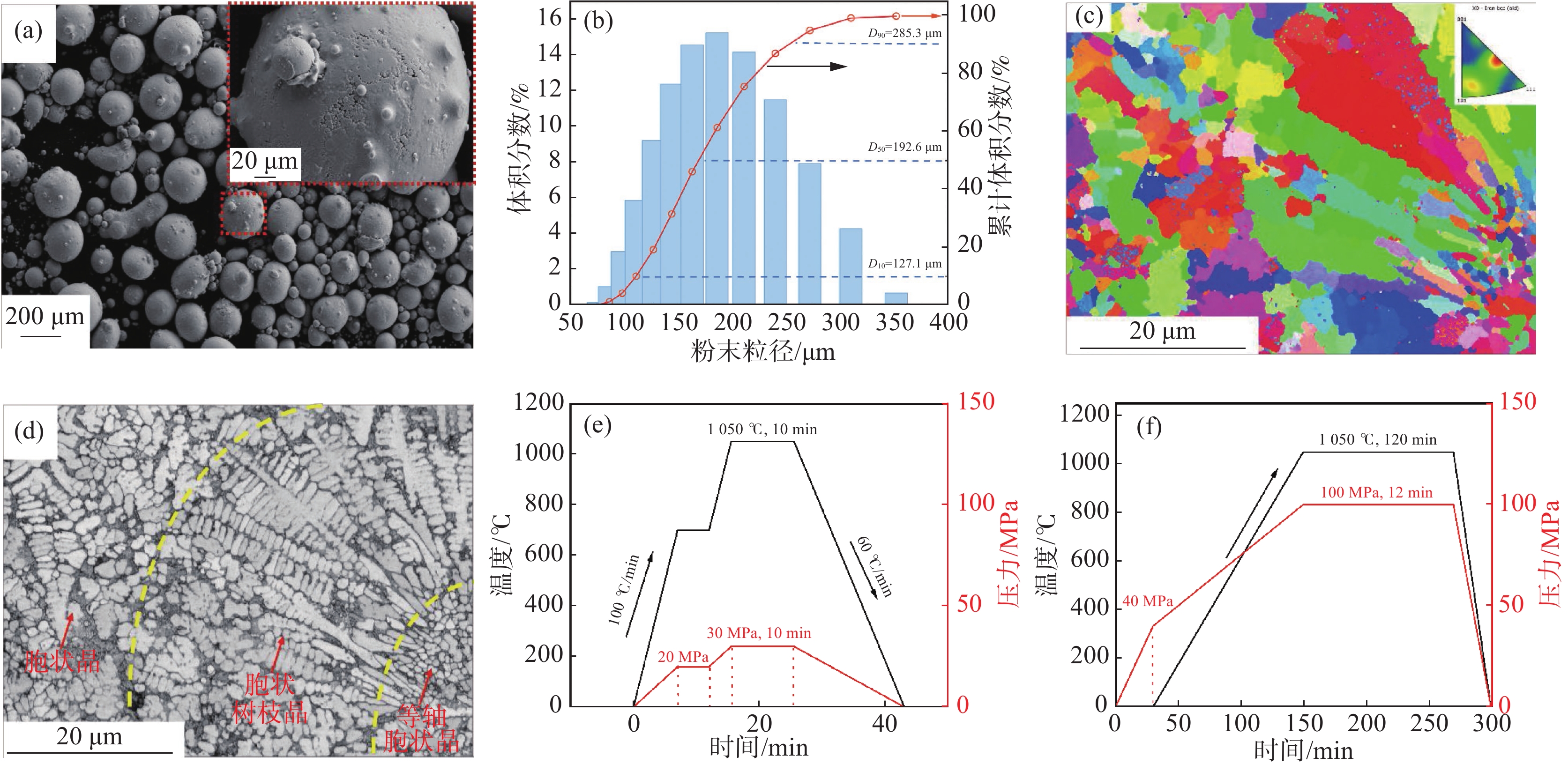
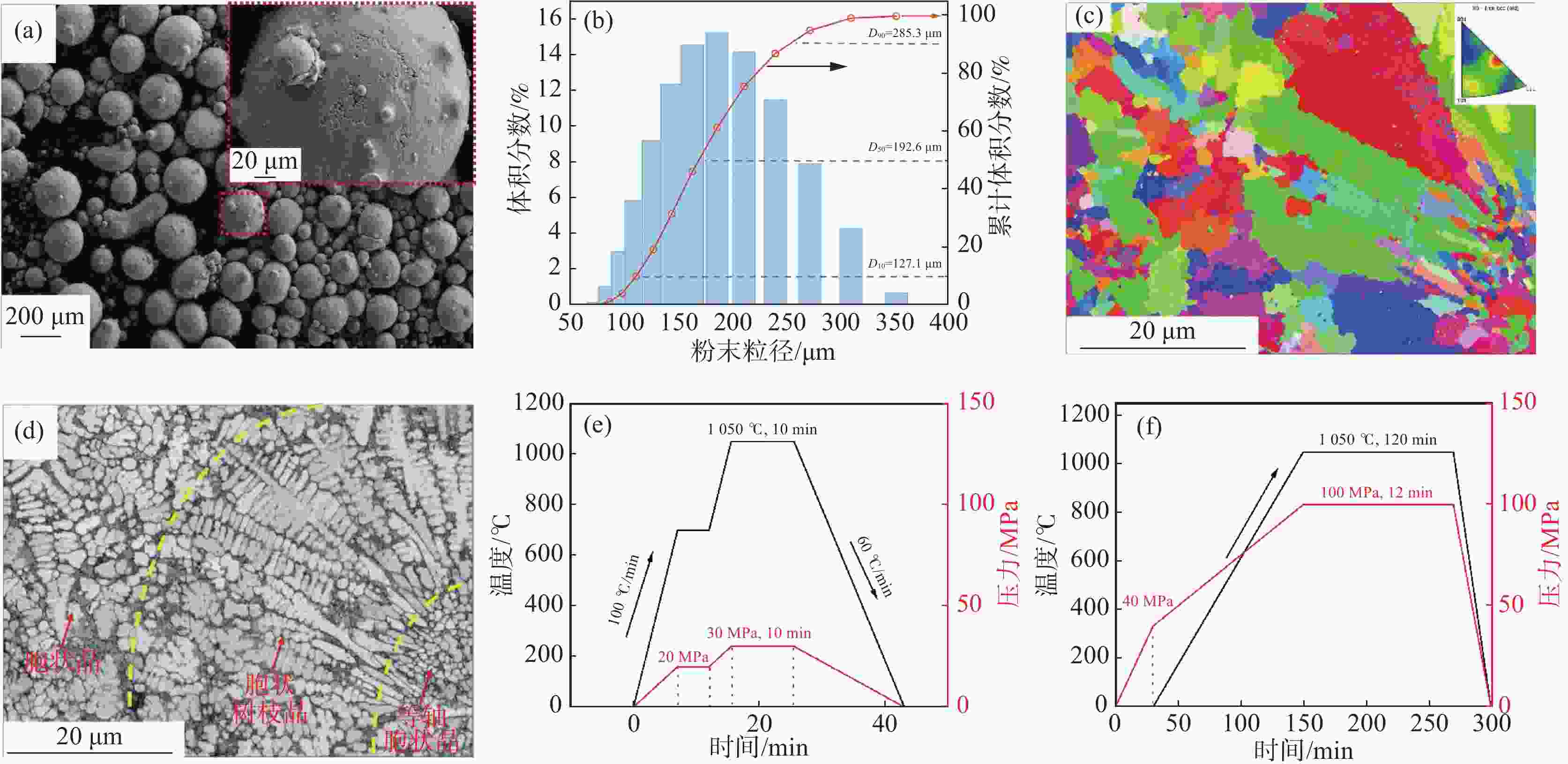
图 1 (a)粉末SEM形貌;(b)粉末粒径分布;(c)粉末EBSD晶粒取向分布;(d)粉末EBSD质量;(e)高频感应加热烧结工艺;(f)热等静压工艺
Figure 1. (a) SEM diagram of powder morphology; (b) Powder particle size distribution graph; (c) Grain orientation distribution diagram of powder EBSD; (d) Powder EBSD quality diagram; (e) High frequency induction heated sintering process diagram; (f) HIP process diagram
表 1 高速钢粉末化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of high-speed steel powder
% C Cr V Mo Si W Mn N Fe 1.97 19.7 4.0 0.97 0.7 0.6 0.3 0.21 余量 -
[1] YU Y, XU S H, LIAO J. Progress on manufacture of powder metallurgy HSS/tool steels and development on their applications(Ⅰ)[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2024, 34(1): 1-10. (于洋, 徐圣航, 廖俊. 粉末冶金工模具钢的生产技术及应用研究进展(上)[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2024, 34(1): 1-10.YU Y, XU S H, LIAO J. Progress on manufacture of powder metallurgy HSS/tool steels and development on their applications(Ⅰ)[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2024, 34(1): 1-10. [2] YU Y, XU S H, LIAO J. Progress on manufacture of powder metallurgy HSS/tool steels and development on their applications(Ⅱ)[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2024, 34(2): 1-10. (于洋, 徐圣航, 廖俊. 粉末冶金工模具钢的生产技术及应用研究进展(下)[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2024, 34(2): 1-10.YU Y, XU S H, LIAO J. Progress on manufacture of powder metallurgy HSS/tool steels and development on their applications(Ⅱ)[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2024, 34(2): 1-10. [3] XU G L, HUANG P, SUN X, et al. Research status and development trend of high-speed-steel’s preparation and heat treatment process[J]. Materials China, 2020, 39(1): 70-77. (徐桂丽, 黄鹏, 孙溪, 等. 高速钢制备和热处理工艺的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 中国材料进展, 2020, 39(1): 70-77. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.201811007XU G L, HUANG P, SUN X, et al. Research status and development trend of high-speed-steel’s preparation and heat treatment process[J]. Materials China, 2020, 39(1): 70-77. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.201811007 [4] WU L Z. Developments and challenges of China high-speed steel industry over last decade[M]// Advanced Steels. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2011. [5] WANG J J. Brief introduction to the present situation of atomization powder technology in China[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2016, 26(5): 1-4. (王建军. 中国雾化制粉技术现状简介[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2016, 26(5): 1-4.WANG J J. Brief introduction to the present situation of atomization powder technology in China[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry, 2016, 26(5): 1-4. [6] DOBRZAŃSKI L A, MATULA G, VÁREZ A, et al. Fabrication methods and heat treatment conditions effect on tribological properties of high speed steels[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2004, 157: 324-330. [7] OUYANG Q, YU Y L, HUANG Y P, et al. Properties of the PM M3∶2 high speed steel in different sintering atmospheres[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2016, 34(5): 351-355. (欧阳齐, 于永亮, 黄雍平, 等. 不同烧结气氛下M3∶2粉末高速钢的性能研究[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(5): 351-355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.05.006OUYANG Q, YU Y L, HUANG Y P, et al. Properties of the PM M3∶2 high speed steel in different sintering atmospheres[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2016, 34(5): 351-355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.05.006 [8] GIMENEZ S, ZUBIZARRETA C, TRABADELO V, et al. Sintering behaviour and microstructure development of T42 powder metallurgy high speed steel under different processing conditions[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 480(1-2): 130-137. [9] QIU Y, LIN Y J, ZHANG Q Y, et al. Study on tool steels with ultrahigh carbon and ultrahigh chromium prepared by vacuum hot-pressing[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2021, 39(4): 297-303. (邱悦, 林耀军, 张覃轶, 等. 真空热压超高碳超高铬模具钢研究[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2021, 39(4): 297-303.QIU Y, LIN Y J, ZHANG Q Y, et al. Study on tool steels with ultrahigh carbon and ultrahigh chromium prepared by vacuum hot-pressing[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2021, 39(4): 297-303. [10] KIM H C, OH D Y, JIANG G J, et al. Synthesis of WC and dense WC-5 vol.% Co hard materials by high-frequency induction heated combustion[J]. Materials Science and Engineering a-Structural Materials Properties Microstructure and Processing, 2004, 368(1-2): 10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2003.08.105 [11] KIM B R, WOO K D, DOH J M, et al. Mechanical properties and rapid consolidation of binderless nanostructured tantalum carbide[J]. Ceramics International, 2009, 35(8): 3395-3400. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2009.06.012 [12] KIM H C, KIM D K, WOO K D, et al. Consolidation of binderless WC-TiC by high frequency induction heating sintering[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2008, 26(1): 48-54. [13] KIM H C, SHON I J, JEONG I K, et al. Rapid sintering of ultra fine WC and WC-Co hard materials by high-frequency induction heated sintering and their mechanical properties[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2007, 13(1): 39-45. doi: 10.1007/BF03027821 [14] KIM H C, SHON I J , YOON J K, et al. One step synthesis and densification of ultra-fine WC by high-frequency induction combustion [J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2006, 24(3): 202-209. [15] KIM H C, YOON J K, DOH J M, et al. Rapid sintering process and mechanical properties of binderless ultra fine tungsten carbide[J]. Materials Science and Engineering a-Structural Materials Properties Microstructure and Processing, 2006, 435: 717-724. [16] KIM H C, SHON I J, YOON J K, et al. Rapid sintering of ultrafine WC-Ni cermets[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 2006, 24(6): 427-431. [17] KIM H C, SHON I J, MUNIR Z A. Rapid sintering of ultra-fine WC-10% Co by high-frequency induction heating[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2005, 40(11): 2849-2854. doi: 10.1007/s10853-005-2422-9 [18] KIM H C, OH D Y, SHON I J. Sintering of nanophase WC–15vol.% Co hard metals by rapid sintering process[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2004, 22(4-5): 197-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2004.06.006 [19] CAO R, SHEN Y, ZHOU Z Z, et al. Effect of different cooling rates on microstructure and hardness of M390 powder metallurgy high-speed steel[J]. Transactions of Metal Heat Treatment, 2022, 43(4): 116-123. (曹睿, 沈漪, 周珍珍, 等. 不同冷却速度对M390粉末冶金高速钢组织与硬度的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2022, 43(4): 116-123.CAO R, SHEN Y, ZHOU Z Z, et al. Effect of different cooling rates on microstructure and hardness of M390 powder metallurgy high-speed steel[J]. Transactions of Metal Heat Treatment, 2022, 43(4): 116-123. [20] HU Y, NIU Z G, LI K J, et al. Composition optimization and heat treatment study of carbide strengthened novel invar alloys[J]. Materials Research and Applications, 2024, 18(2): 292-298. (胡瑜, 牛振国, 栗克建, 等. 碳化物增强新型因瓦合金的成分优化及热处理工艺研究[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2024, 18(2): 292-298.HU Y, NIU Z G, LI K J, et al. Composition optimization and heat treatment study of carbide strengthened novel invar alloys[J]. Materials Research and Applications, 2024, 18(2): 292-298. [21] YANG Y, YANG H K, HE Q, et al. The effect of aging treatment on the mechanical and impact properties of solid soluted Fe-Mn-Al-C lightweight high manganese steel[J]. Materials Research and Applications, 2023, 17(2): 303-309. (杨壹, 杨浩坤, 何强, 等. 时效热处理对Fe-Mn-Al-C轻质高锰钢拉伸和冲击性能的影响[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2023, 17(2): 303-309.YANG Y, YANG H K, HE Q, et al. The effect of aging treatment on the mechanical and impact properties of solid soluted Fe-Mn-Al-C lightweight high manganese steel[J]. Materials Research and Applications, 2023, 17(2): 303-309. -




 下载:
下载: