Numerical simulation of vacuum arc remelting process of nickel base superalloy
-
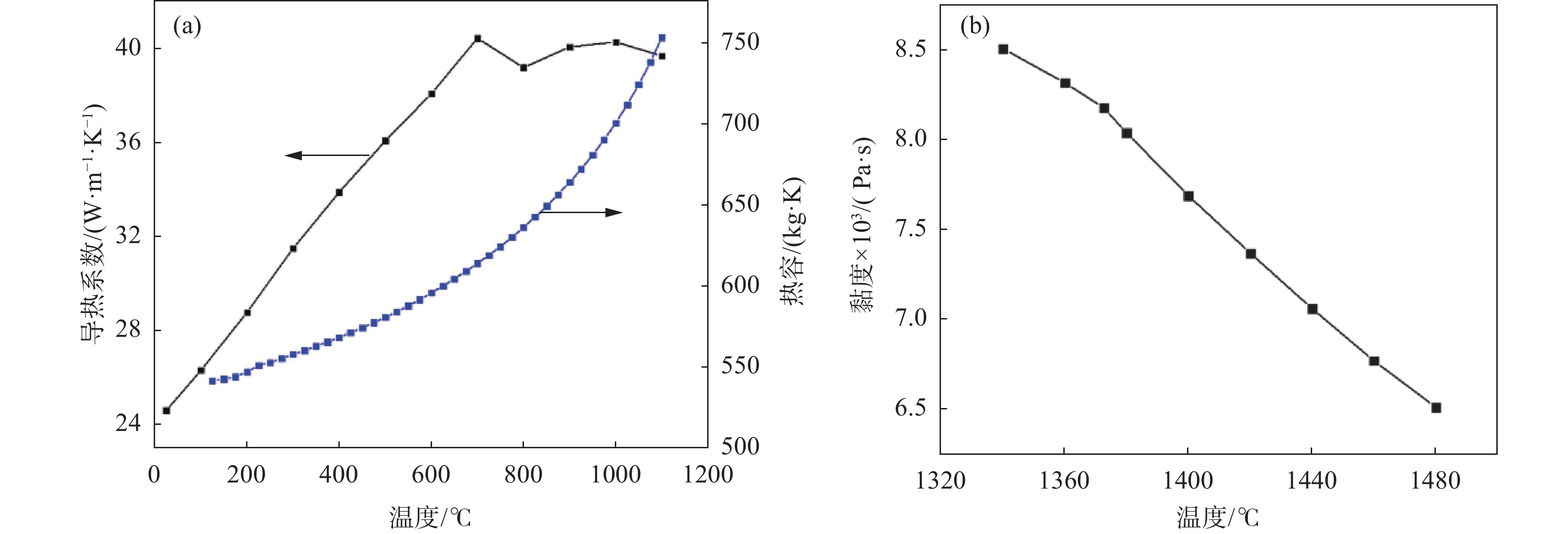
摘要: 利用Meltflow-VAR软件对镍基高温合金真空自耗过程进行了数值模拟研究,模拟分析了真空自耗冶炼过程不同阶段电磁分布、熔池流动传热、形态尺寸演化特征,探究了整个冶炼过程黑斑缺陷形成倾向大小及原因,同时研究了氦气压力对熔池流动传热、形态尺寸及黑斑缺陷形成的影响规律。结果表明,真空自耗冶炼过程中,电势主要位于铸锭上表面心部,而磁感应强度主要位于铸锭上表面边部,金属熔池流动主要受到热浮力的驱动。分布在铸锭表面及内部的电场强度、电流密度、洛伦兹力以及金属熔池尺寸、熔池流动强度等参数在起弧阶段逐渐增大,在稳态阶段逐渐保持稳定,而在热封顶阶段逐渐减小。整个冶炼过程,随着铸锭在纵向方向的生长,底部结晶器底板的冷却效果减弱,热封顶氦气压力减小,低熔速保温时间较长会导致铸锭上部热封顶附近位置容易出现黑斑缺陷。增大氦气压力能减小熔池尺寸,减轻铸锭偏析,但持续增大氦气压力改善铸锭偏析缺陷的效果会逐渐变得不显著。最后将试验解剖的与模拟预测的自耗锭熔池深度进行对比,验证了所建数学模型的合理性。Abstract: In this paper, the numerical simulation on vacuum arc remelting process of nickel base superalloy with respect to electromagnetic distribution, flow and heat transfer behavior of molten pool, as well as the morphology and size at different stages of the vacuum arc remelting process had been carried out by using a Meltflow-VAR software. Moreover, the formation tendency and reasons for the freckle defects throughout the smelting process had been investigated. At the same time, the influence of helium pressure on the flow and heat transfer behavior of molten pool, the morphology and size of molten pool, and the freckle formation was studied. The results show that the potential is mainly located in the center of the surface of the ingot, while the magnetic induction intensity is mainly located at the edge of the surface of the ingot, as well as the flow of the molten pool is mainly driven by thermal buoyancy. In addition, the electric field strength, current density, Lorentz force as well as the size and flow intensity of the molten pool that distributed on the surface and inside of the ingot, gradually increase at the ignition process of vacuum arc, and remain stable during the steady-state stage, then gradually decrease during the hot tap stage. During the entire smelting process, the freckle defect easily forms near the top of the hot seal on the upper part of the ingot because the cooling effect of the bottom plate of the crystallizer is weak, the helium pressure at the top of the hot seal decreases and the holding time at low melting rates is long as the ingot grows in the longitudinal direction. Increasing helium pressure can reduce the size of the molten pool and alleviate ingot segregation, but the effect of improving ingot segregation defects will gradually become less significant as continuously increasing helium pressure. Finally, the comparison of molten pool depth observed by experimental dissection and simulation is conducted, which verifies the rationality of the established mathematical model.
-
Key words:
- nickel base superalloy /
- vacuum arc remelting /
- numerical simulation /
- physical mechanism /
- freckle /
- helium pressure
-
表 1 镍合金的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of nickel alloys %
Cr W Mo Al Ti Ni 18.5 4.5 4.5 1.2 2.2 余量 表 2 模拟采用的主要工艺参数
Table 2. The main process parameters used in the simulation
电极直径/mm 结晶器尺寸/mm 熔速/(kg$ \cdot $min−1) 氦气压力/Pa 395 508 3.4 200~800 -
[1] GUO J T. Materials science and engineering for superalloy (Superalloy materials and engineering applications)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. (郭建亭. 高温合金材料学(高温合金材料与工程应用) [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.GUO J T. Materials science and engineering for superalloy (Superalloy materials and engineering applications)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. [2] GENG L, NA Y S, PARK N K. Oxidation behavior of alloy 718 at a high temperature[J]. Materials & Design, 2007, 28(3): 978-981. [3] JIANG S C, ZHANG J, HE Y H, et al. Microstructure evolution and processing maps of GH4169 during deformation[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021, 42(2): 161-166. (蒋世川, 张健, 何云华, 等. GH4169 合金高温变形显微组织演变及热加工图[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021, 42(2): 161-166.JIANG S C, ZHANG J, HE Y H, et al. Microstructure evolution and processing maps of GH4169 during deformation[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021, 42(2): 161-166. [4] ZHONG Z Y, ZHUANG J Y. Development of several important problems on producing technologies of wrought superalloy[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2003(z1): 9. (仲增墉, 庄景云. 变形高温合金生产工艺中几个重要问题的研究和进展[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2003(z1): 9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.2003.z1.001ZHONG Z Y, ZHUANG J Y. Development of several important problems on producing technologies of wrought superalloy[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2003(z1): 9. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.2003.z1.001 [5] WANG Z X. Microstrcture and property controlling of IN718 alloy bar by triple melting [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2019. (王资兴. 三联冶炼工艺制备IN718合金棒材组织与性能控制[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2019.WANG Z X. Microstrcture and property controlling of IN718 alloy bar by triple melting [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2019. [6] SANKAR M, PRASAD V V S, BALIGIDAD R G, et al. Effect of vacuum arc remelting and processing parameters on structure and properties of high purity niobium[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2015, 50: 120-125. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2014.12.001 [7] NING J, WANG A , BI Z X, et al. Optimization of vacuum arc remelting process for M54 ultra-high strength steel based on simulation[J] Special Steel, 2023, 44(5): 60-68. (宁静, 王敖, 毕正绪, 等. 基于仿真的M54超高强度钢真空自耗重熔工艺优化[J]. 特殊钢, 2023, 44(5): 60-68.NING J, WANG A , BI Z X, et al. Optimization of vacuum arc remelting process for M54 ultra-high strength steel based on simulation[J] Special Steel, 2023, 44(5): 60-68. [8] DAI P. Effects of different helium cooling conditions on the structures of GH4169 alloy vacuum arc remelting ingots[J]. Baosteel Technical Research, 2020, 14(4): 40-46. [9] HUANG Z. Study on solidification segregation and homogenization of C700R1-1 nickle-base heat resistant alloy[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2023. (黄震. C700R-1镍基耐热合金凝固偏析与均匀化研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2023.HUANG Z. Study on solidification segregation and homogenization of C700R1-1 nickle-base heat resistant alloy[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2023. [10] WANG X, WARD R M, JACBS M H, et al. Effect of variation in process parameters on the formation of freckle in inconel 718 by vacuum arc remelting[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2008, 39: 2981-2989. doi: 10.1007/s11661-008-9638-7 [11] QU J L, YANG S F, CHEN Z Y, et al. Research progress in numerical simulation of vacuum arc remelting process[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020, 30(1): 1-9. (曲敬龙, 杨树峰, 陈正阳, 等. 真空自耗冶炼过程数值仿真研究进展[J]. 中国冶金, 2020, 30(1): 1-9.QU J L, YANG S F, CHEN Z Y, et al. Research progress in numerical simulation of vacuum arc remelting process[J]. China Metallurgy, 2020, 30(1): 1-9. [12] WANG Y D, ZHANG L F, ZHANG J, et al. Numerical simulation of macrosegregation in vacuum arc remelting process[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2021, 33(8): 718-725. (王亚栋, 张立峰, 张健, 等. 真空自耗熔炼过程宏观偏析的数值模拟[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2021, 33(8): 718-725.WANG Y D, ZHANG L F, ZHANG J, et al. Numerical simulation of macrosegregation in vacuum arc remelting process[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2021, 33(8): 718-725. [13] BERTRAM L A, ADSCZIK C B, EVANS D G, et al. Quantitative simulations of a superalloy VAR ingot at the macroscale[C]//Proceedings of the 1997 International Symposium on Liquid Metal Processing and Casting, A. Mitchell and P. Auburtin, eds., (Am. Vac. Soc. , 1997). 1997: 110-132. [14] HOSAMANI L G, Experimental and theoretical heat transfer studies in vacuum arc remelting[D]. Portland: Oregon Health & Science University, 1988. [15] YUAN L, DJAMBAZOV G, LEE P D, et al. Multiscale modeling of the vacuum arc remelting process for the prediction on microstructure formation[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics B, 2009, 23(06n07): 1584-1590. doi: 10.1142/S0217979209061305 [16] BÖTTGER B, SCHMITZ G J, WAHLERS F J, et al. New freckle criterion for technical remelting processes[J]. High Temperatures-High Pressures, 2013, 42(2): 115-136. [17] MOTLEY J, KELKAR K. Masurement of the spatio-temporal distribution of arcs during vacuum arc remelting and their implications on VAR solicitation defects[C]. Proceedings of the Liquid Metals Processing & Casting Conference. 2019. -





 下载:
下载: