Influence of niobium precipitates on the hydrogen-induced cracking resistance of X80 pipeline steel
-
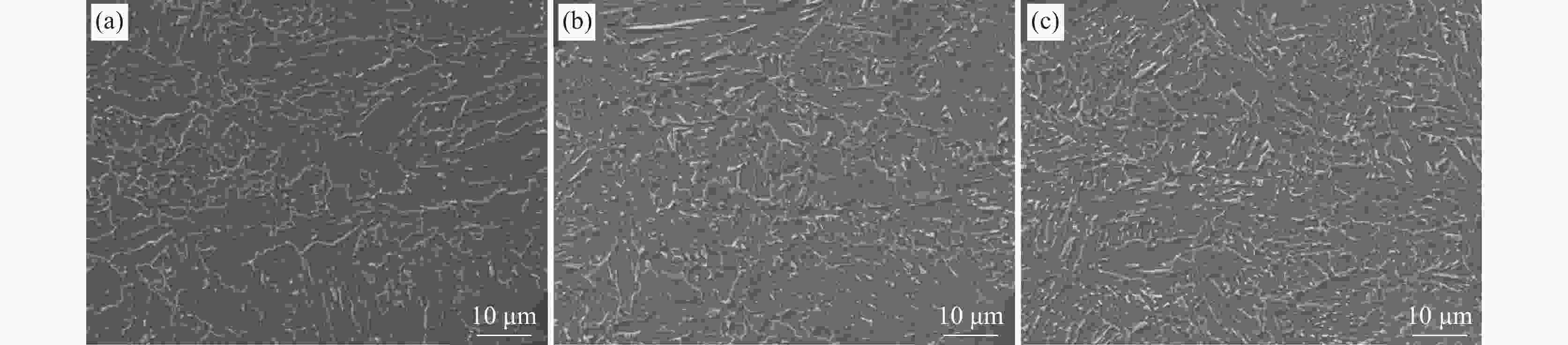
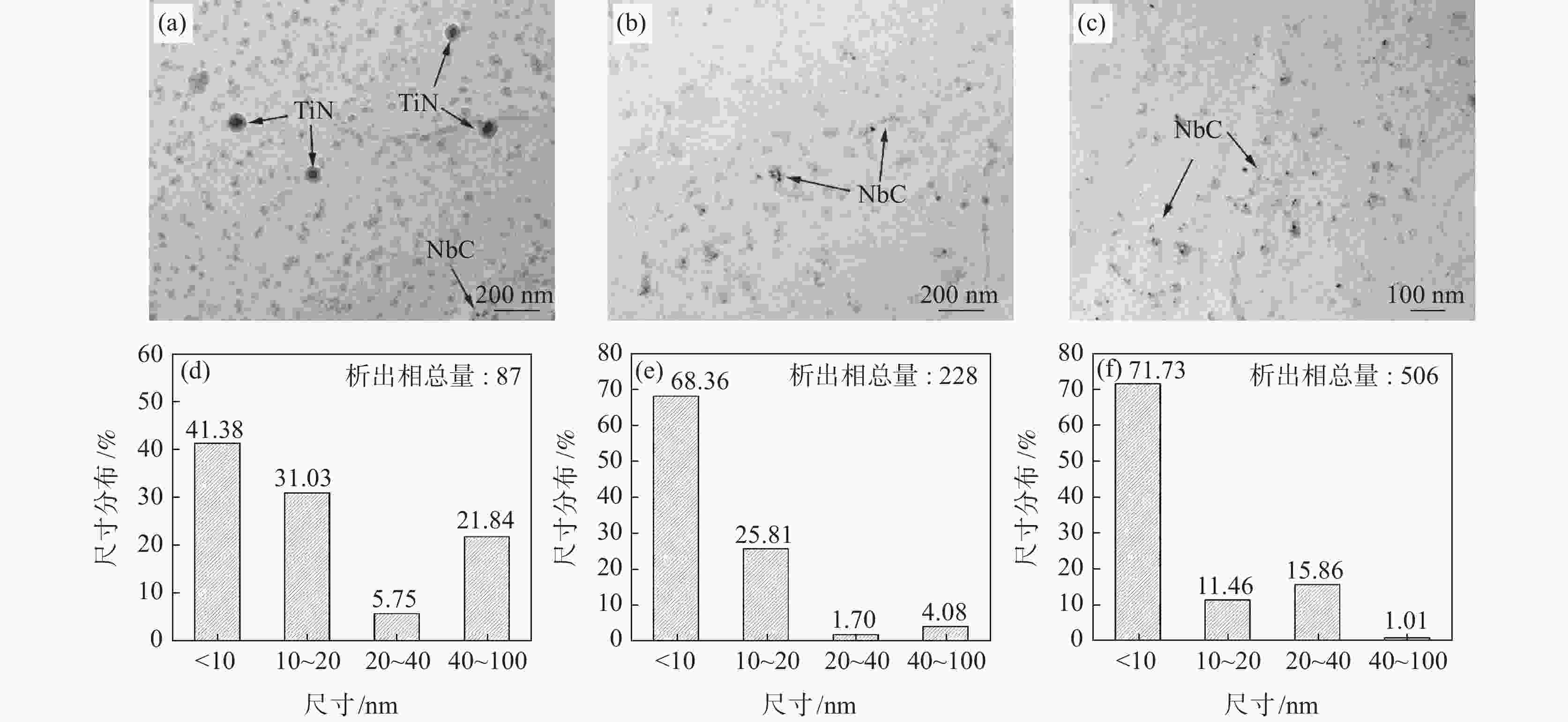
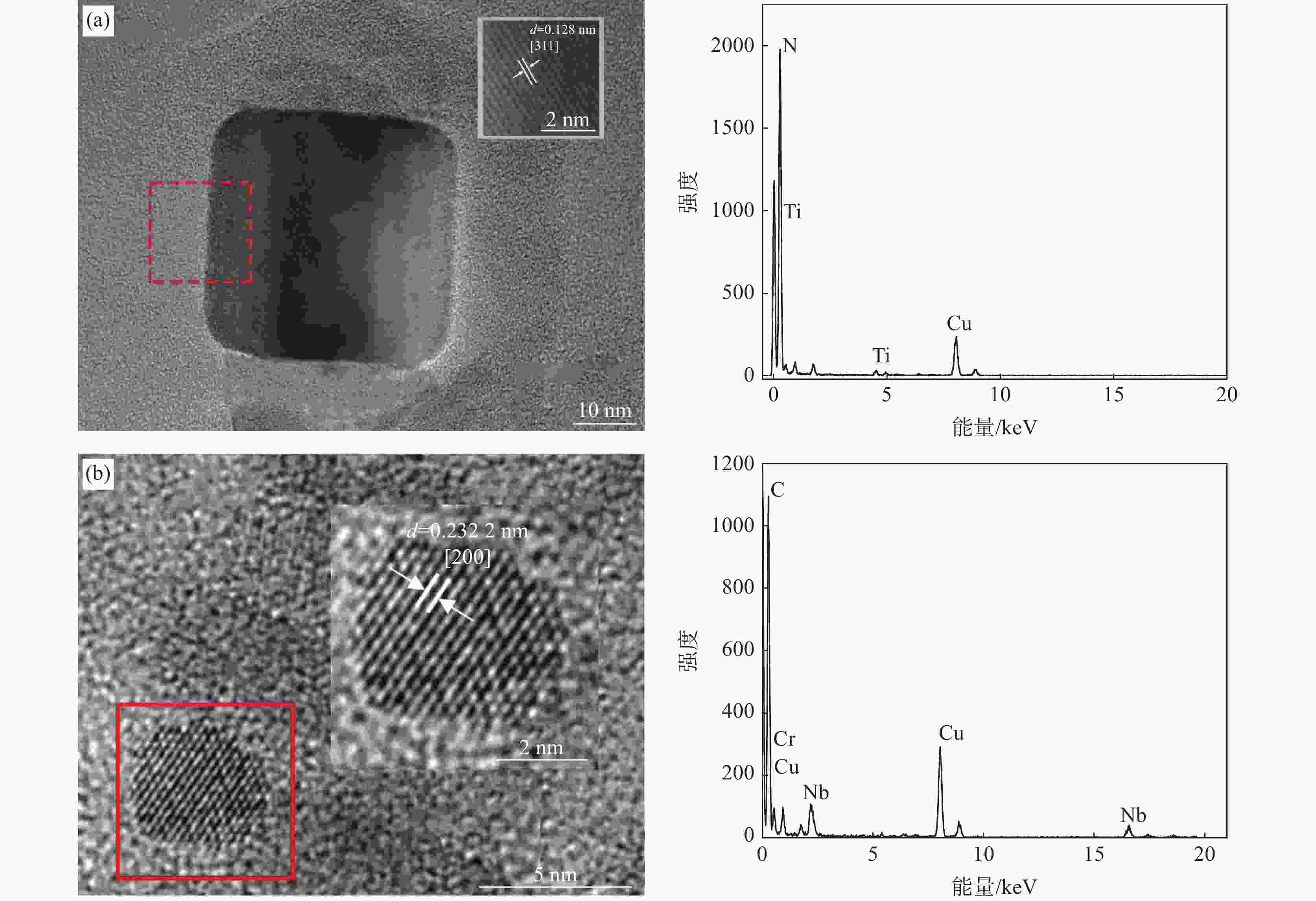
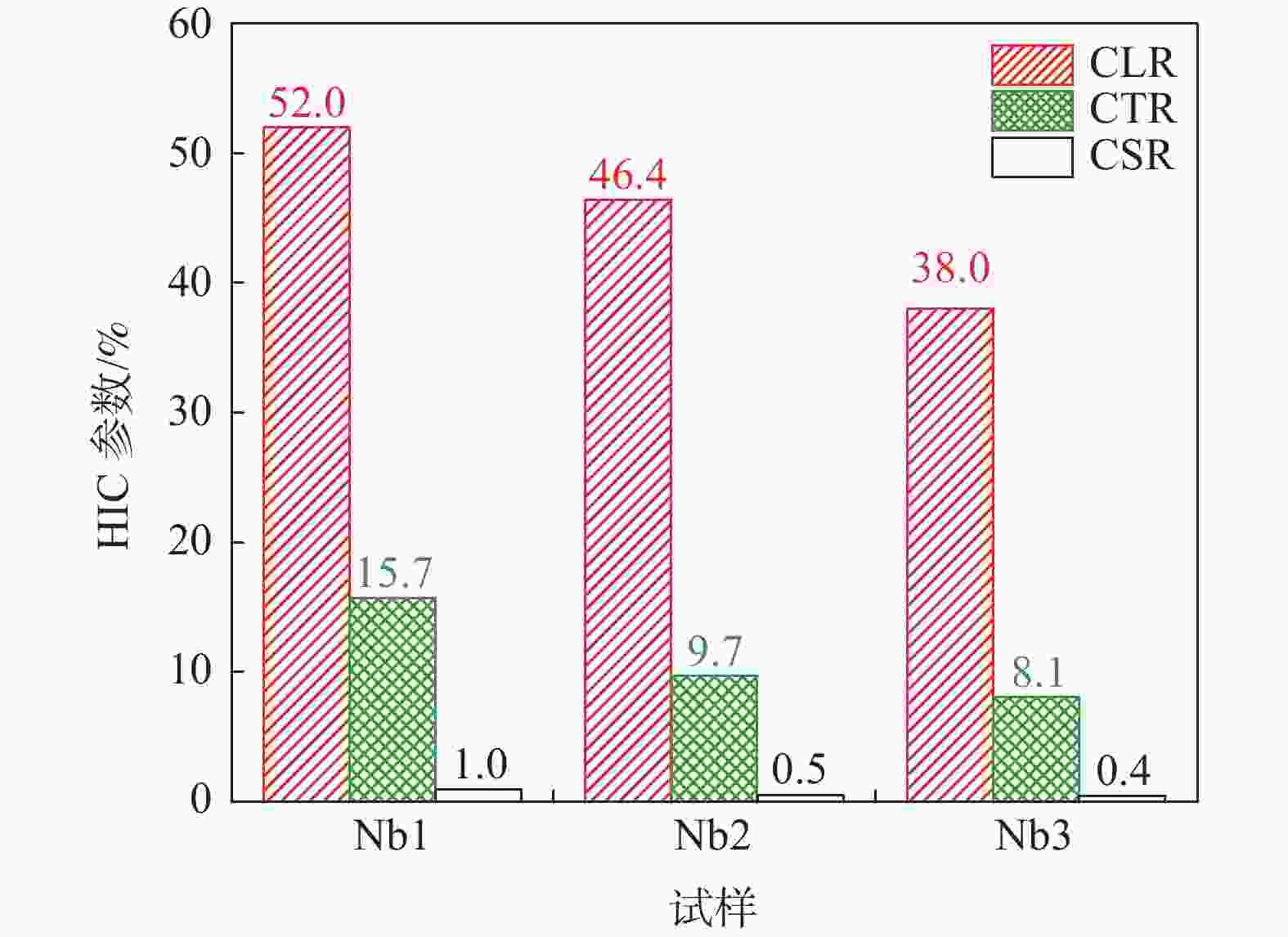
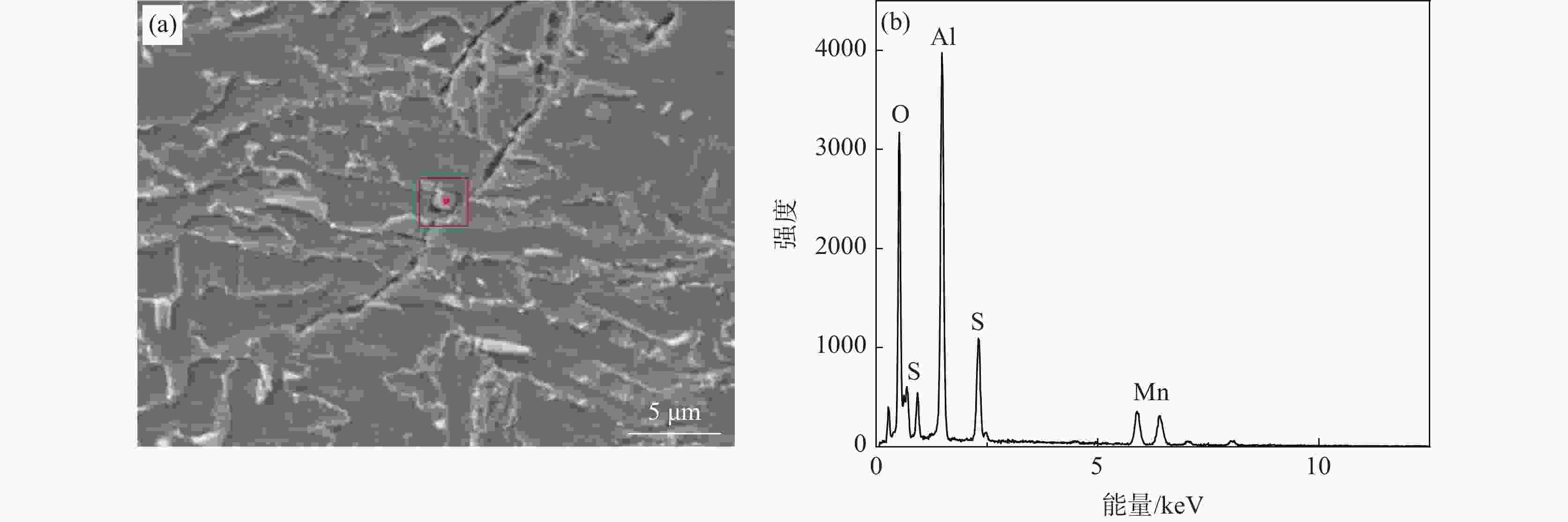
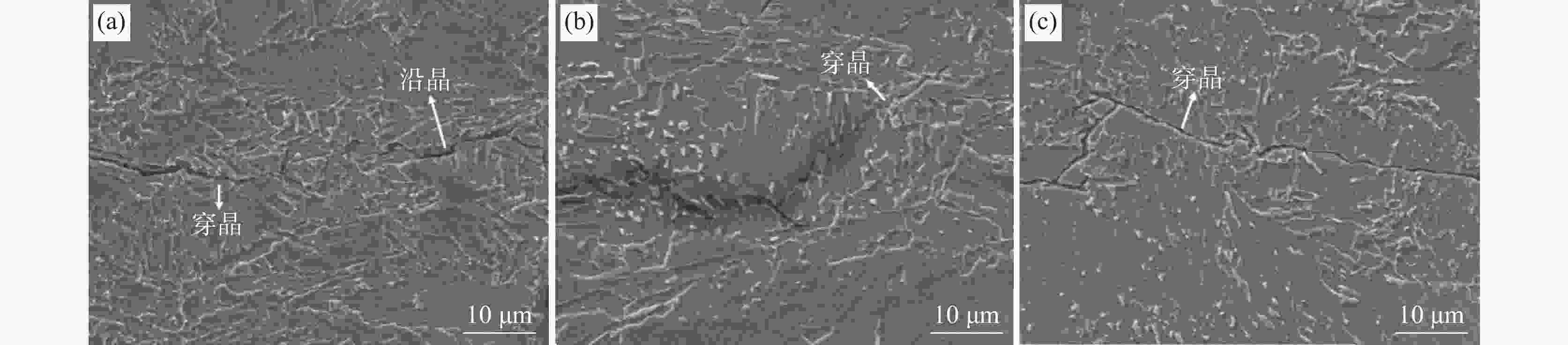
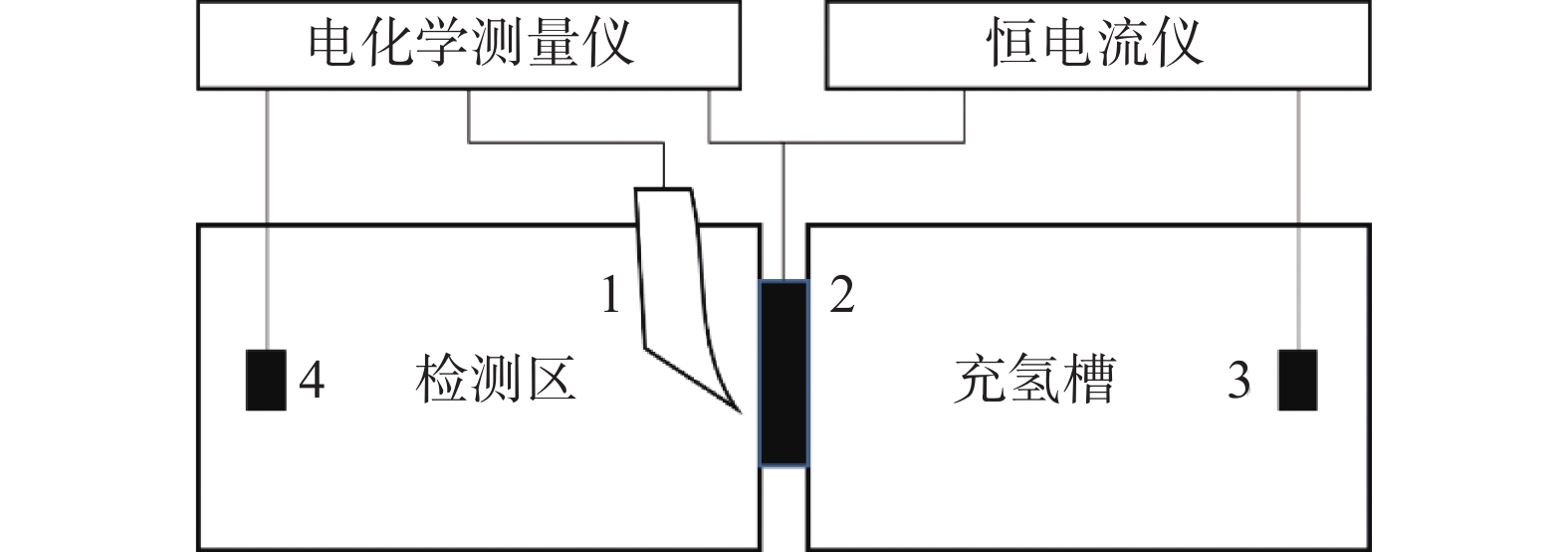
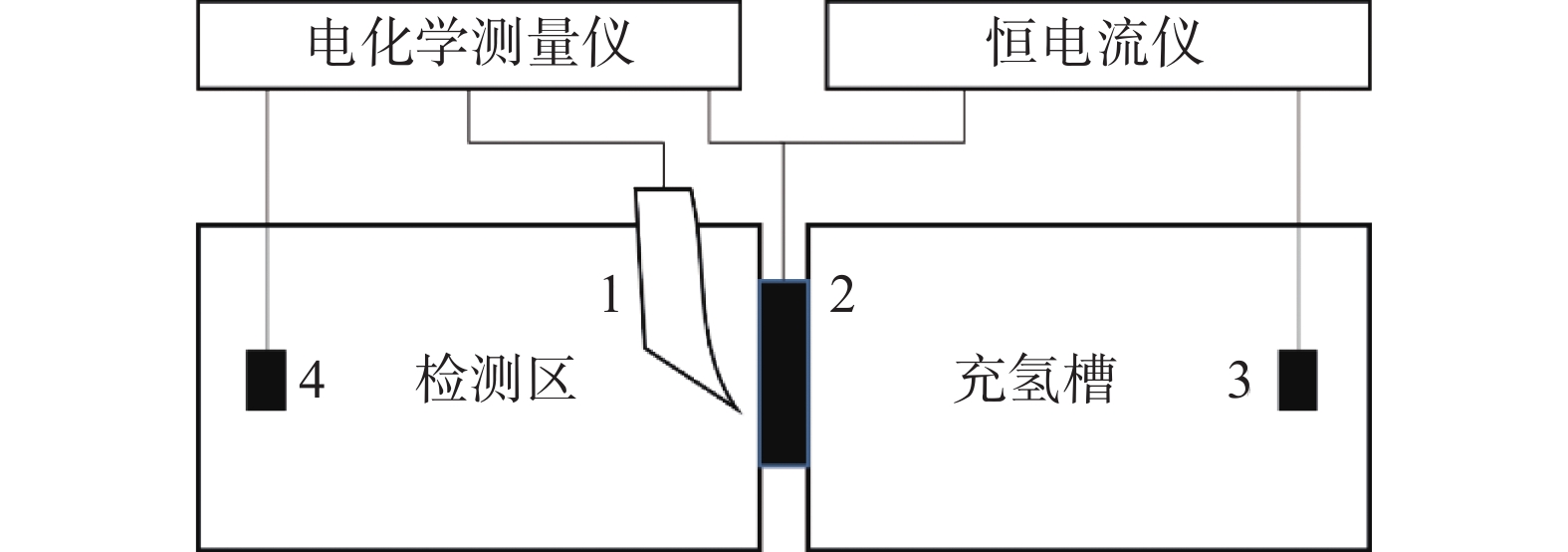
摘要: 研究了Nb含量对X80管线钢中析出相特征、氢扩散行为、抗氢致裂纹(HIC)性能的影响。结果表明:随着钢中Nb含量增加,在相同的统计面积下,钢中纳米级析出相数量由Nb1钢(含铌0.04%)中的87个增加到Nb3钢(含铌0.12%)中的506个,钢中NbC占比由64.82%增加到98.22%。氢原子在钢中的扩散系数由Nb1钢中的1.63×10−6 cm2/s降低到Nb3钢中的9.35×10−7 cm2/s。钢中裂纹的扩展模式由Nb1钢中沿晶、穿晶混合变为Nb2、Nb3钢中的以穿晶为主。纳米级NbC可作为氢陷阱捕获钢中可扩散氢原子,降低氢原子的聚集和钢中氢致裂纹的萌生。当钢中Nb含量为0.12%时,钢的抗HIC性能最好。Abstract: The effects of Nb content on the precipitated phase characteristics, hydrogen diffusion behavior and hydrogen-induced crack resistance (HIC) performance in X80 pipeline steel were studied. The results show that with the increase of Nb content in steel, the number of nanoscale precipitated phases in steel increases from 87 in Nb1 steel with niobium 0.04wt% to 506 in Nb3 steel with niobium 0.12wt%, and the proportion of NbC in steel increases from 64.82% to 98.22% under the same statistical area. The diffusion coefficient of hydrogen atoms in steel decreases from 1.63×10−6 cm2/s in Nb1 steel to 9.35×10−7 cm2/s in Nb3 steel. The propagation mode of cracks in steel has changed from the mixing of grain along and through grain in Nb1 steel to the main penetration in Nb2 and Nb3 steels. Nanoscale NbC particles can be used as hydrogen traps to fix diffusible hydrogen atoms in steel, then reduce the aggregation of hydrogen atoms and the initiation of hydrogen-induced cracks in steel. The experimental result indicates that 0.12wt%Nb steel achieves the best resistance to HIC.
-
Key words:
- X80 pipeline steel /
- niobium precipitation phase /
- hydrogen diffusion /
- HIC
-
表 1 试验钢化学成分
Table 1. The chemical compositions of experimental steels
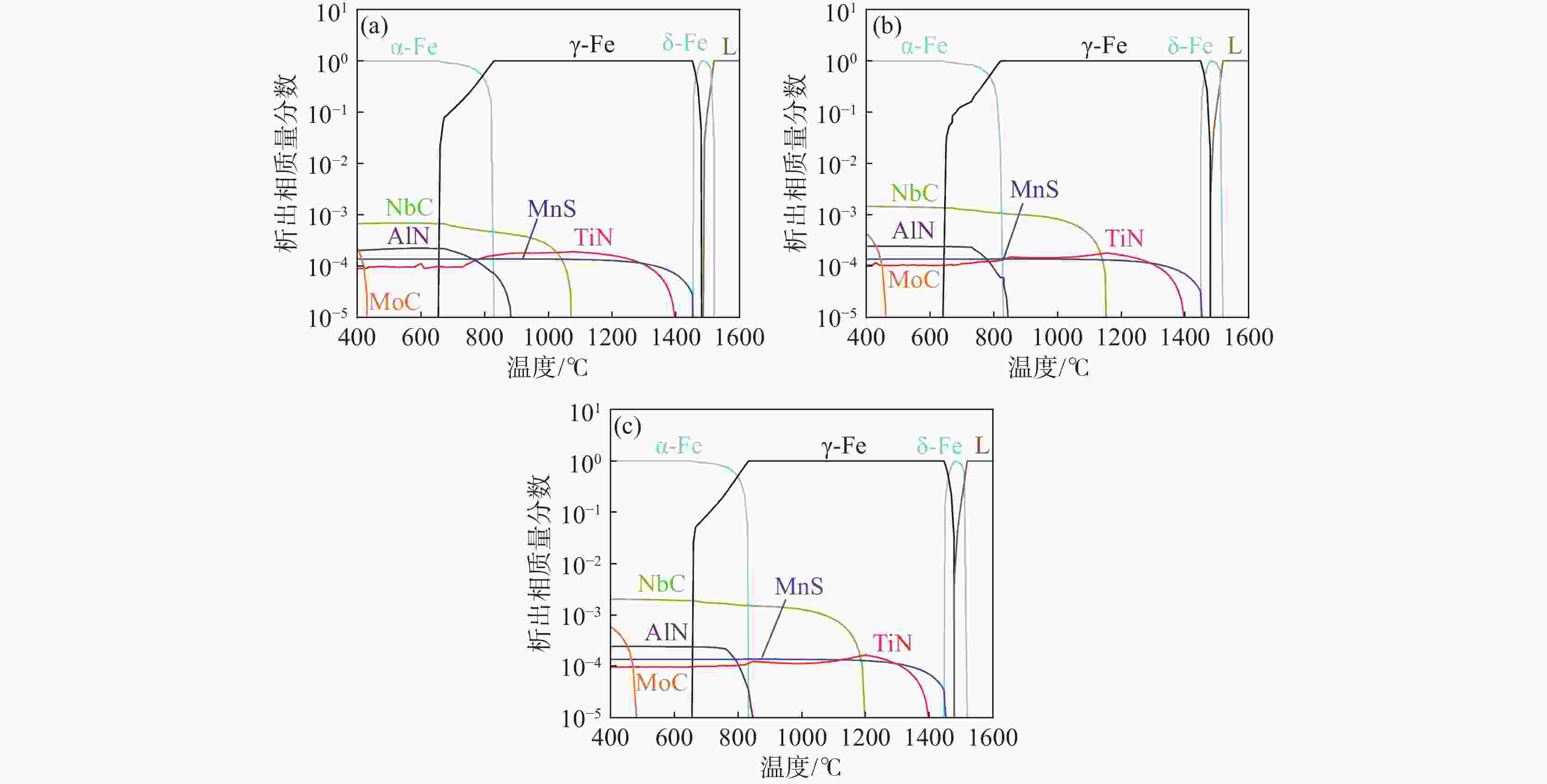
% 编号 C Si Mn S Mo Nb Ti Cr Ni Nb1 0.056 0.20 1.81 0.004 0.11 0.04 0.01 0.26 0.26 Nb2 0.056 0.20 1.82 0.005 0.11 0.08 0.01 0.26 0.25 Nb3 0.058 0.20 1.82 0.005 0.11 0.12 0.01 0.26 0.25 表 2 含铌钢中NbC平衡相的析出参数
Table 2. Precipitation parameters of the NbC equilibrium phase in niobium-containing steels
编号 析出温度/℃ 最大析出质量分数 Nb1 1070 6.89×10−4 Nb2 1150 1.3×10−3 Nb3 1200 2.0×10−3 表 3 试验钢中不同析出相占比和平均尺寸
Table 3. Proportions and average sizes of different precipitated phases in experimental steels
编号 TiN NbC 占比/% 平均尺寸/nm 占比/% 平均尺寸/nm Nb1 35.18 44.8 64.82 9.0 Nb2 4.82 58.8 95.18 10.4 Nb3 1.78 40.0 98.22 10.3 表 4 试验钢氢渗透参数
Table 4. Hydrogen permeation parameters of different experimental steels
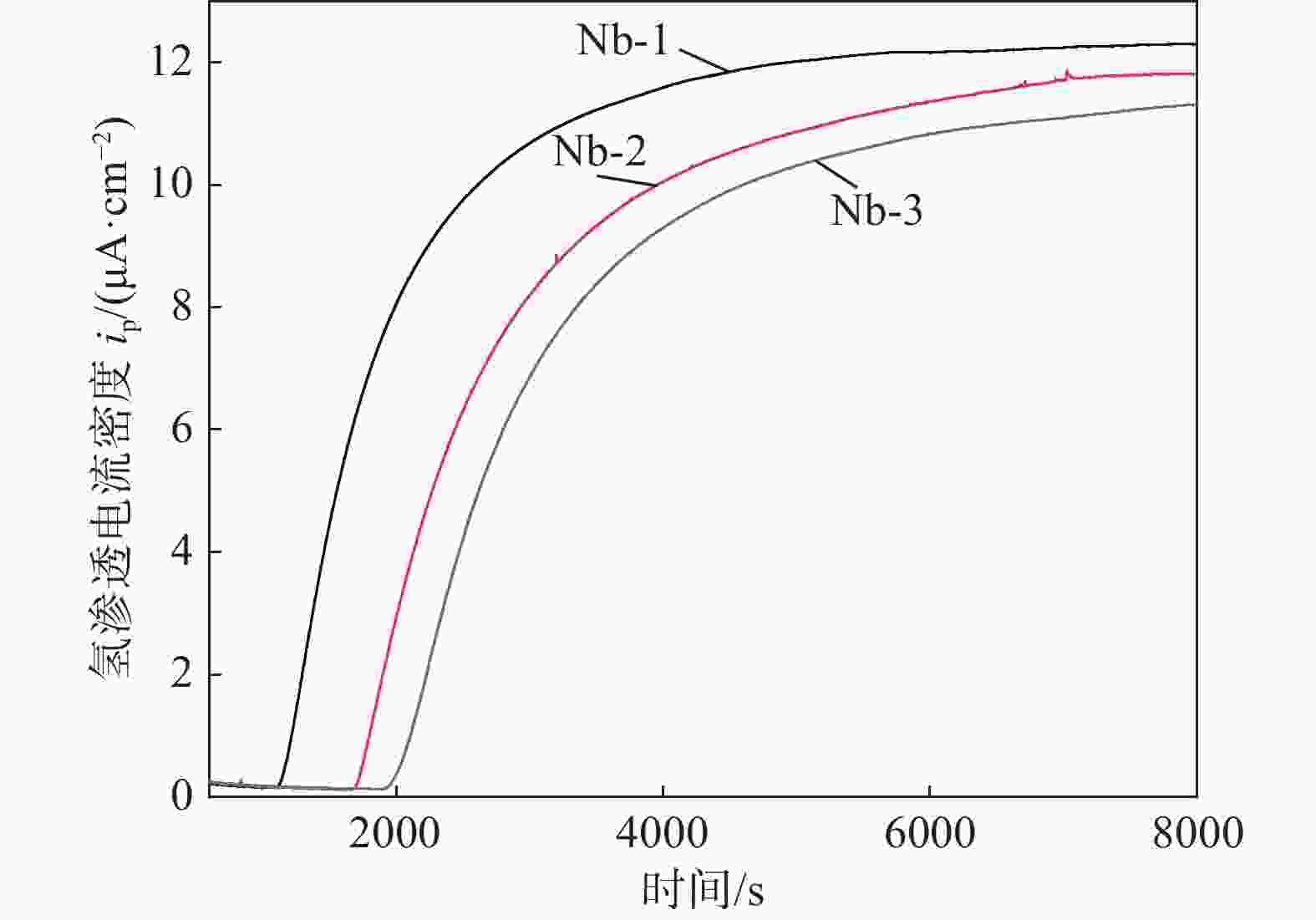
编号 L/mm I∞/μA tL/s J∞×10−10/(mol·cm−2·s−1) Dapp×10−6/(cm2·s−1) Capp×10−5/(mol·cm−3) NT×1020/cm−3 Nb1 1.14 21.5 1329 1.27 1.63 0.885 1.38 Nb2 1.14 20.7 2163 1.22 1.00 1.39 3.53 Nb3 1.18 20.0 2481 1.18 0.935 1.49 4.05 -
[1] GAO H L. Pipeline steel and pipeline steel pipe[M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 2012. (高惠临. 管线钢与管线钢管[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2012.GAO H L. Pipeline steel and pipeline steel pipe[M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 2012. [2] FENG H, CHI Q, JI L K, et al. Research and development of hydrogen embrittlement of pipeline steel[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2017, 29(3): 318-322. (封辉, 池强, 吉玲康, 等. 管线钢氢脆研究现状及进展[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2017, 29(3): 318-322. doi: 10.11903/1002.6495.2016.154FENG H, CHI Q, JI L K, et al. Research and development of hydrogen embrittlement of pipeline steel[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2017, 29(3): 318-322. doi: 10.11903/1002.6495.2016.154 [3] WANG X M, JIN P P, WANG A, et al. Research on corrosion and protection of petroleum and natural gas pipelines[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2023, 52(11): 1602-1605. (汪仙明, 靳培培, 王傲, 等. 石油天然气管道腐蚀与防护[J]. 辽宁化工, 2023, 52(11): 1602-1605.WANG X M, JIN P P, WANG A, et al. Research on corrosion and protection of petroleum and natural gas pipelines[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2023, 52(11): 1602-1605. [4] FAN Y W, WU M, CHEN X, et al. Research progress of hydrogen induced cracking for pipeline steel[J]. Thermal Working Technology, 2017, 46(4): 48-53. (范裕文, 吴明, 陈旭, 等. 管线钢氢致开裂研究现状[J]. 热加工工艺, 2017, 46(4): 48-53.FAN Y W, WU M, CHEN X, et al. Research progress of hydrogen induced cracking for pipeline steel[J]. Thermal Working Technology, 2017, 46(4): 48-53. [5] CHENG Y F, SUN Y H, ZHANG Y D. Development of hydrogen pipelines and hydrogen embrittlement challenges of pipeline steel[J]. Journal of Yangtze University, 2022, 19(1): 54-69. (程玉峰, 孙颖昊, 张引弟. 氢气管道发展与管线钢氢脆挑战[J]. 长江大学学报, 2022, 19(1): 54-69.CHENG Y F, SUN Y H, ZHANG Y D. Development of hydrogen pipelines and hydrogen embrittlement challenges of pipeline steel[J]. Journal of Yangtze University, 2022, 19(1): 54-69. [6] LI T Y, CHEN Y M, MA G Q, et al. Effect of microalloying by adding Nb and V on phase precipitation behaviors and strengths of high strength pipeline steels[J]. Angang Technology, 2023(6): 64-70, 83. (李天怡, 陈义冕, 马国强, 等. Nb、V微合金化对高强管线钢相析出及强度的影响[J]. 鞍钢技术, 2023(6): 64-70, 83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4613.2023.06.0011LI T Y, CHEN Y M, MA G Q, et al. Effect of microalloying by adding Nb and V on phase precipitation behaviors and strengths of high strength pipeline steels[J]. Angang Technology, 2023(6): 64-70, 83. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4613.2023.06.0011 [7] DU J W, MING H L, WANG J Q. Research status and progress of hydrogen embrittlement of hydrogen pi[elines[J]. Oil& Gas Storage and Transportation, 2023, 42(10): 1107-1117. (杜建伟, 明洪亮, 王俭秋. 输氢管道氢脆研究现状及进展[J]. 油气储运, 2023, 42(10): 1107-1117.DU J W, MING H L, WANG J Q. Research status and progress of hydrogen embrittlement of hydrogen pi[elines[J]. Oil& Gas Storage and Transportation, 2023, 42(10): 1107-1117. [8] DEPOVER T, VERBEKEN K. The effect of TiC on the hydrogen induced ductility loss and trapping behavior of Fe-C-Ti alloys[J]. Corrosion Science, 2016, 112: 308-326. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2016.07.013 [9] LI L F, SONG B, CHENG J, et al. Effects of vanadium precipitates on hydrogen trapping efficiency and hydrogen induced cracking resistance in X80 pipeline steel[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(36): 17353-17363. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.07.110 [10] WAN R C, YU M. Effects of Nb on austenite dynamic recovery and dynamic recrystallization of low-carbon steels[J]. Thermal Working Technology, 2015, 44(2): 115-117, 20. (万荣春, 于淼. 铌对低碳钢奥氏体的变形及动态回复再结晶的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2015, 44(2): 115-117, 20.WAN R C, YU M. Effects of Nb on austenite dynamic recovery and dynamic recrystallization of low-carbon steels[J]. Thermal Working Technology, 2015, 44(2): 115-117, 20. [11] ZHANG S Q, WAN J F, ZHAO Q Y, et al. Dual role of nanosized NbC precipitates in hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of lath martensitic steel[J]. Corrosion Science, 2020, 164: 108345. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2019.108345 [12] FAN Y Q, MA C W, LI S P, et al. Effect of Nb on the hydrogen-induced cracking of X80 pipeline steel[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2023, 2566(1): 012082. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2566/1/012082 [13] WANG H. Research on the effects of dispersion precipitates on hydrogen behavior in structural steels[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2023. (王恒. 弥散析出相对结构钢中氢行为影响机制的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2023.WANG H. Research on the effects of dispersion precipitates on hydrogen behavior in structural steels[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2023. [14] MA Y, SHI Y F, WANG H Y, et al. A first-principles study on the hydrogen trap characteristics of coherent nano-precipitates in α-Fe[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(51): 27941-27949. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.07.123 [15] GUO A M, MA M T, XU Z, et al. EVI with embrittlement[M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2023. (郭爱民, 马鸣图, 徐佐, 等. EVI与氢脆[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2023.GUO A M, MA M T, XU Z, et al. EVI with embrittlement[M]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2023. [16] RAMIREZ M F G, HERNÁNDEZ J W C, LADINO D H, et al. Effects of different cooling rates on the microstructure, crystallographic features, and hydrogen induced cracking of API X80 pipeline steel[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 14: 1848-1861. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.060 [17] GOU J X, XING X, CUI G, et al. Hydrogen-induced cracking in CGHAZ of welded X80 steel under tension load[J]. 2023, 13(7): 1307-1325. [18] MOHTADI-BONAB M A, SZPUNAR J A, RAZAVI-TOUSI S S. Hydrogen induced cracking susceptibility in different layers of a hot rolled X70 pipeline steel[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(31): 13831-13841. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.08.046 [19] XIE D G, WAN L, SHAN Z W. Hydrogen enhanced cracking via dynamic formation of grain boundary inside aluminium crystal[J]. Corrosion Science, 2021, 183: 109307. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109307 -




 下载:
下载: