The influence of second-phase particles on austenite grain growth behavior in Nb-Ti microalloyed steel
-
摘要: 对Nb-Ti微合金化钢在
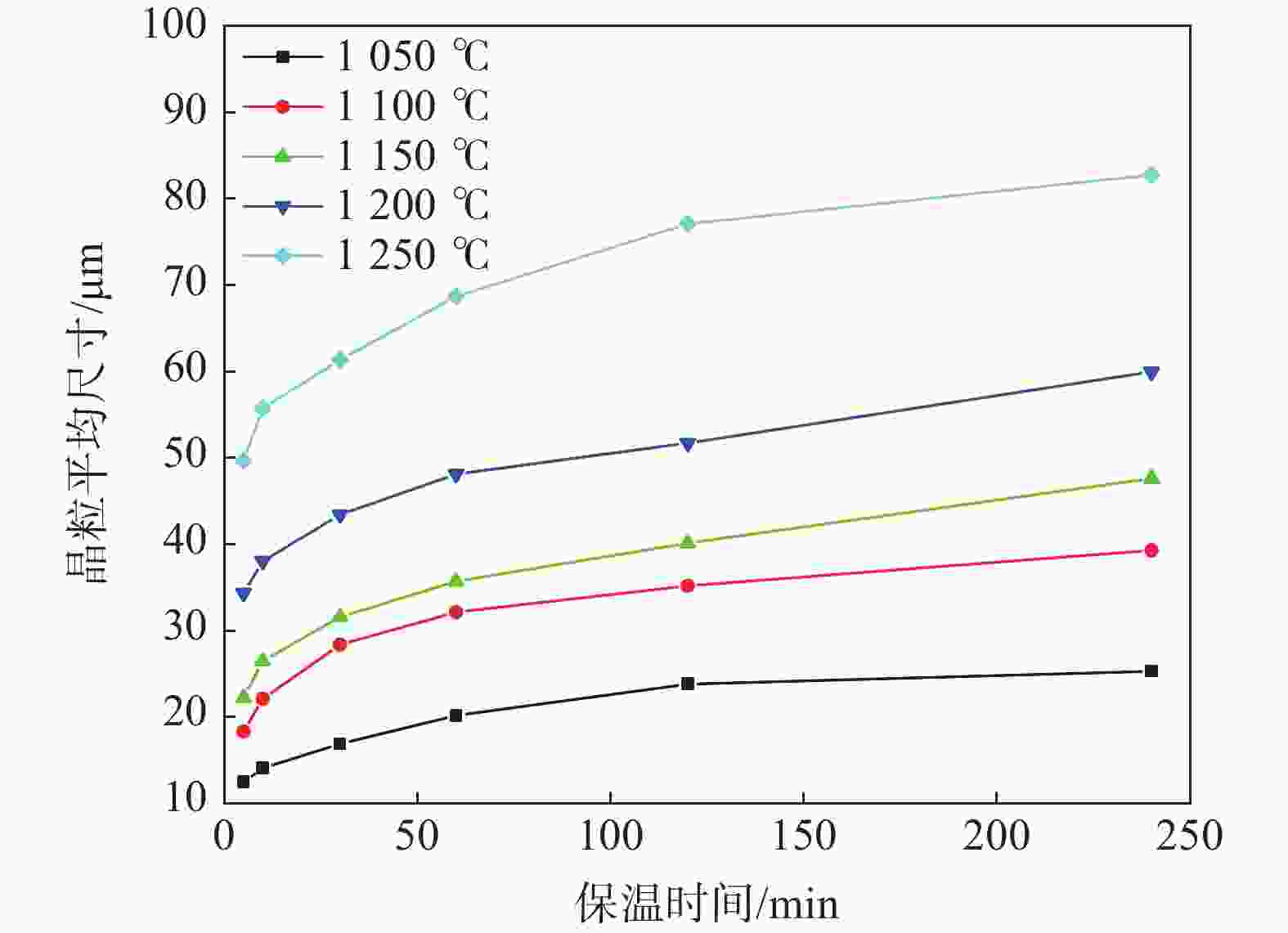
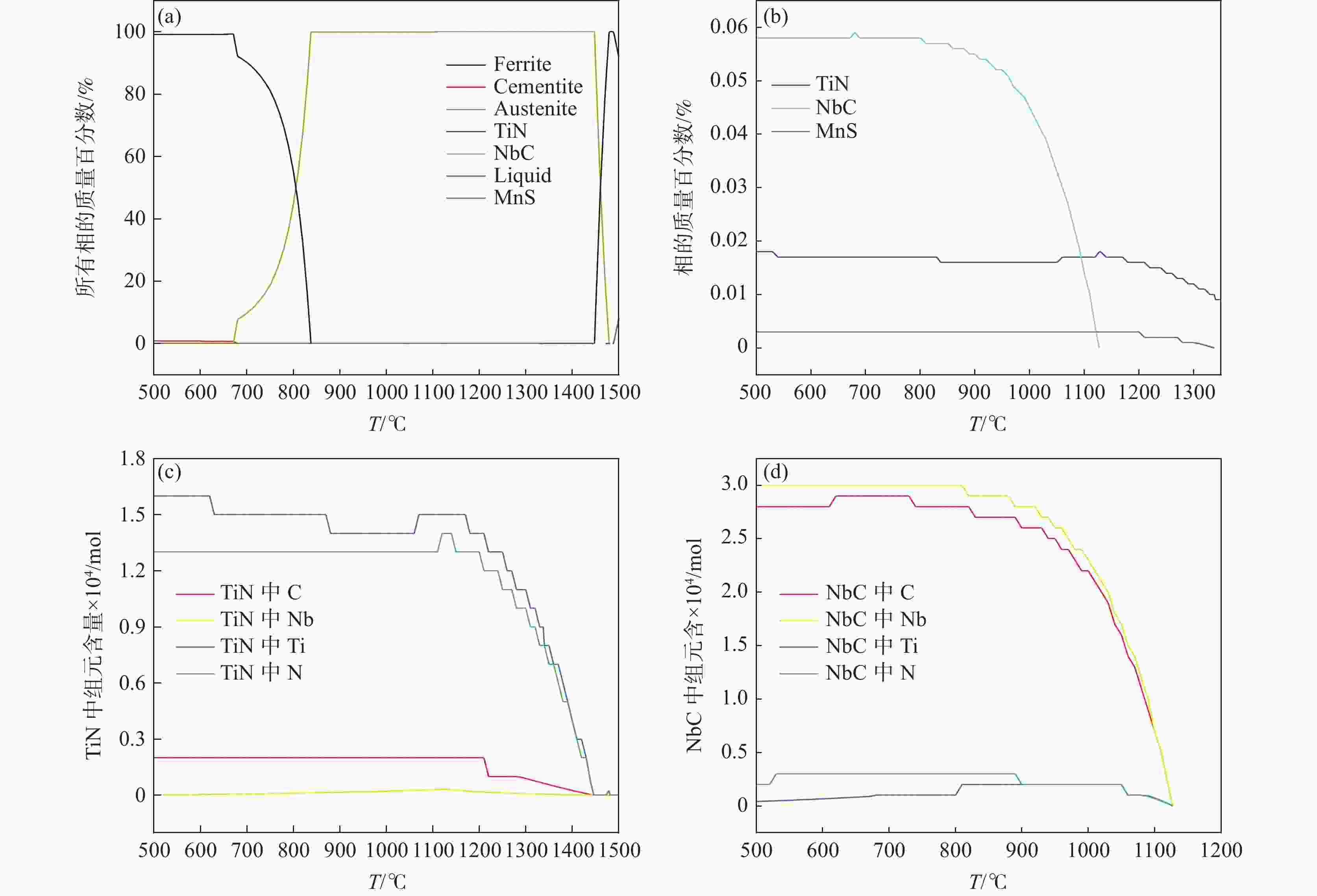
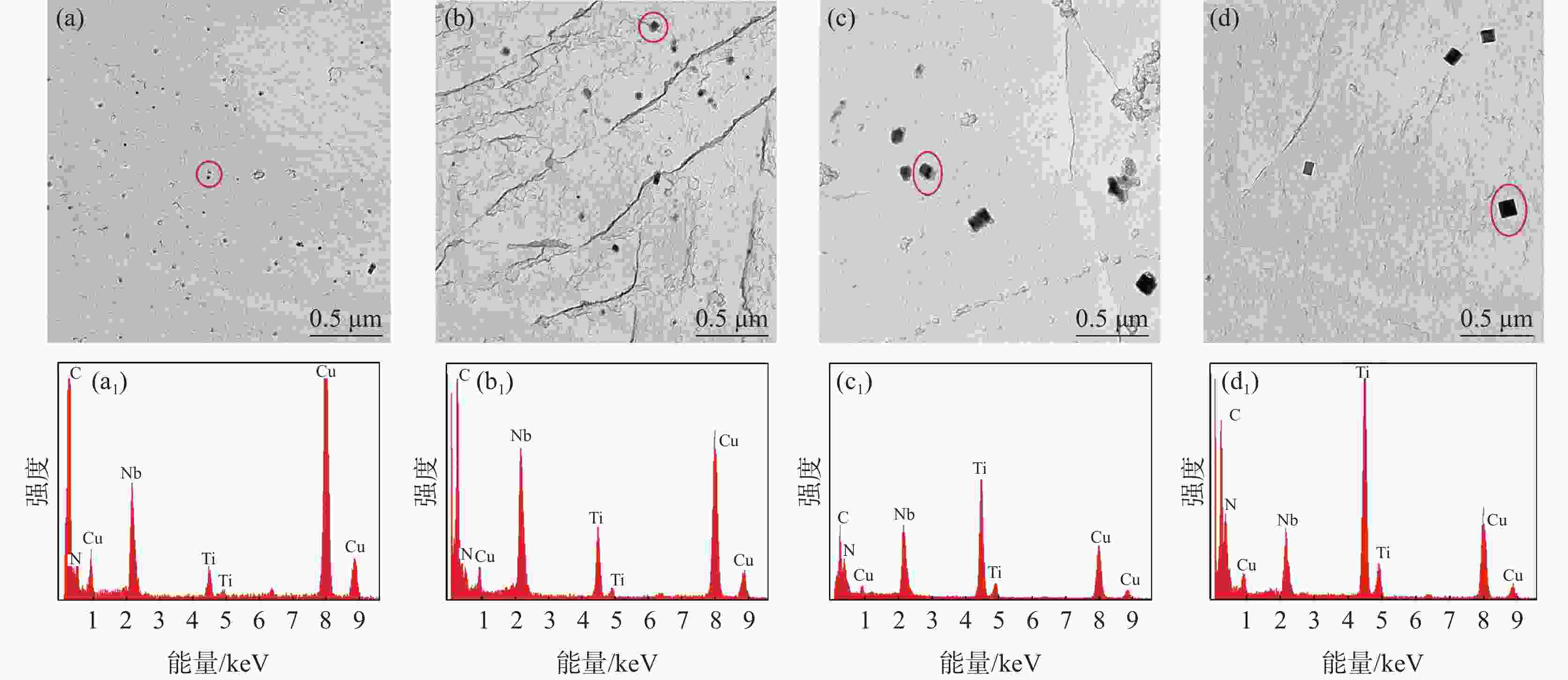
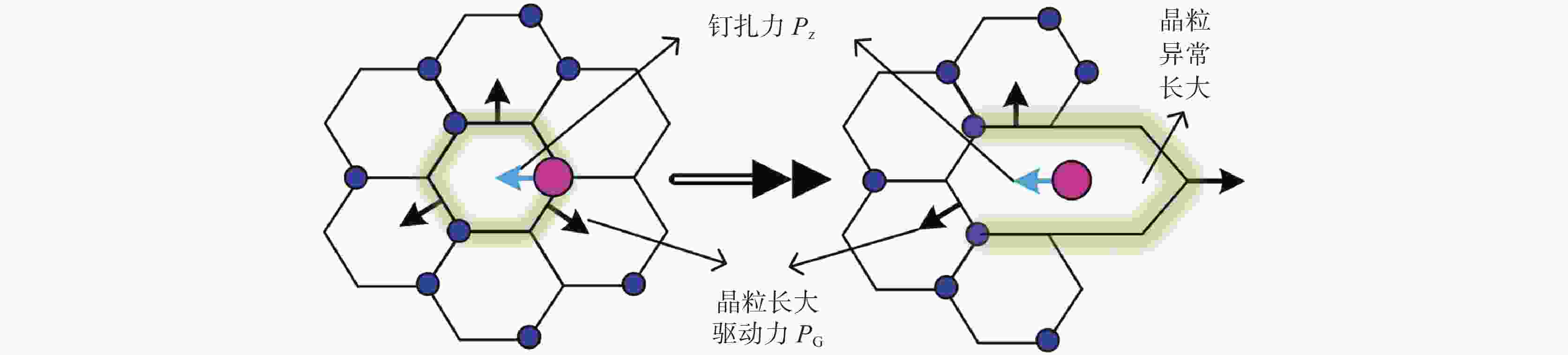
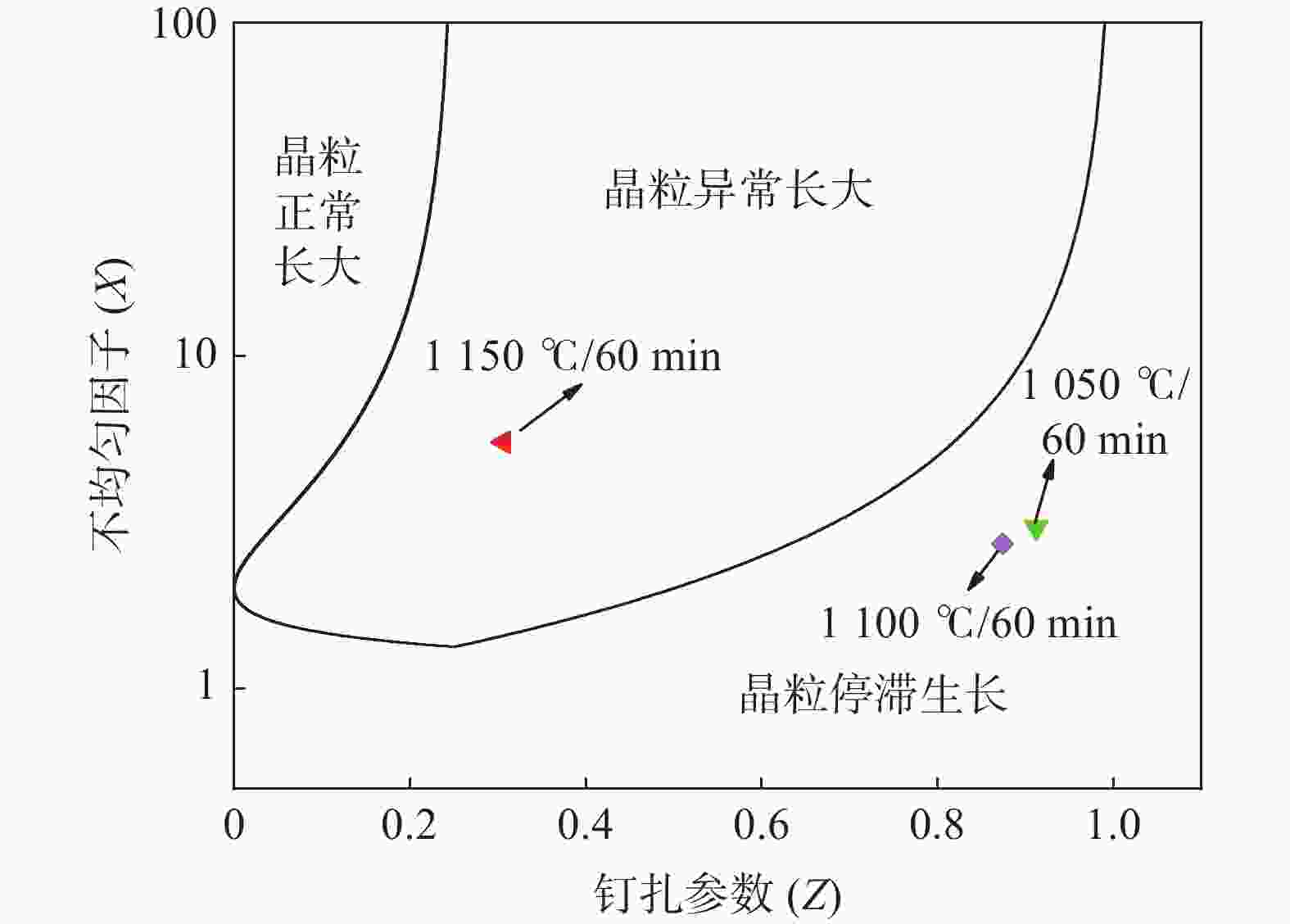
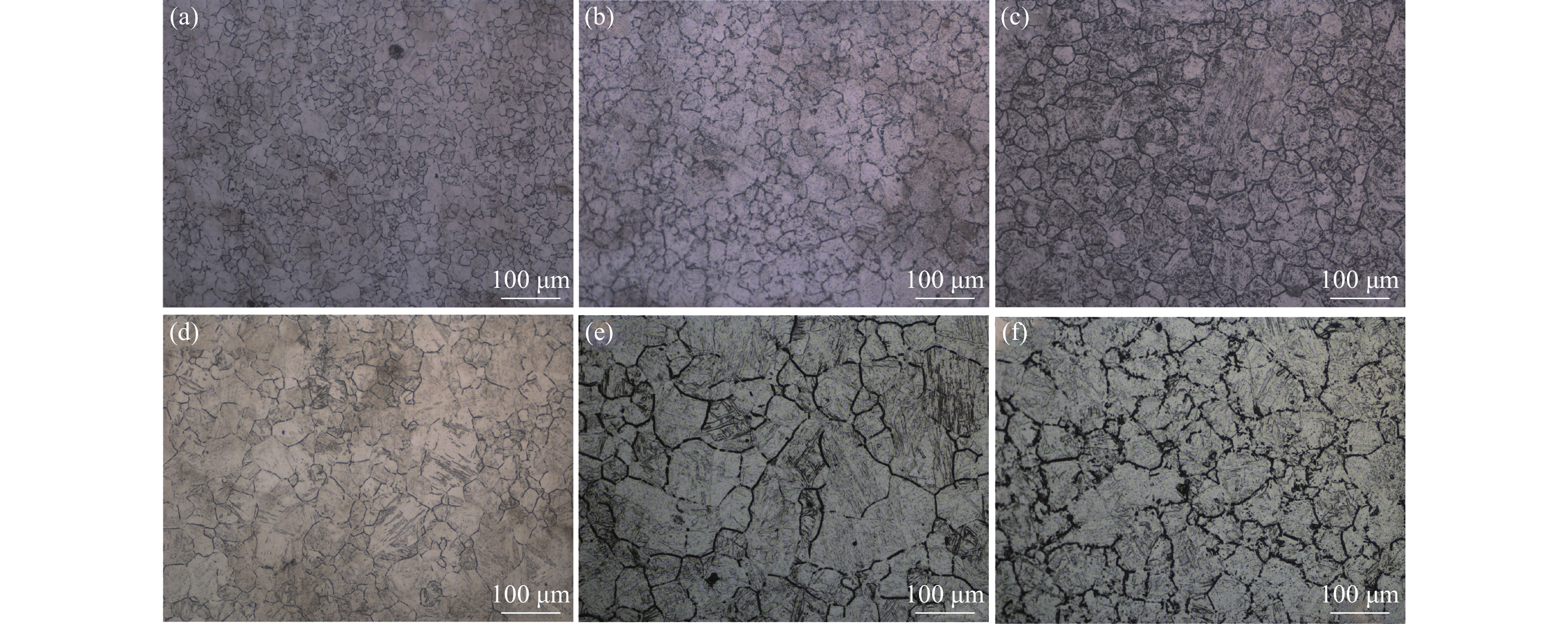
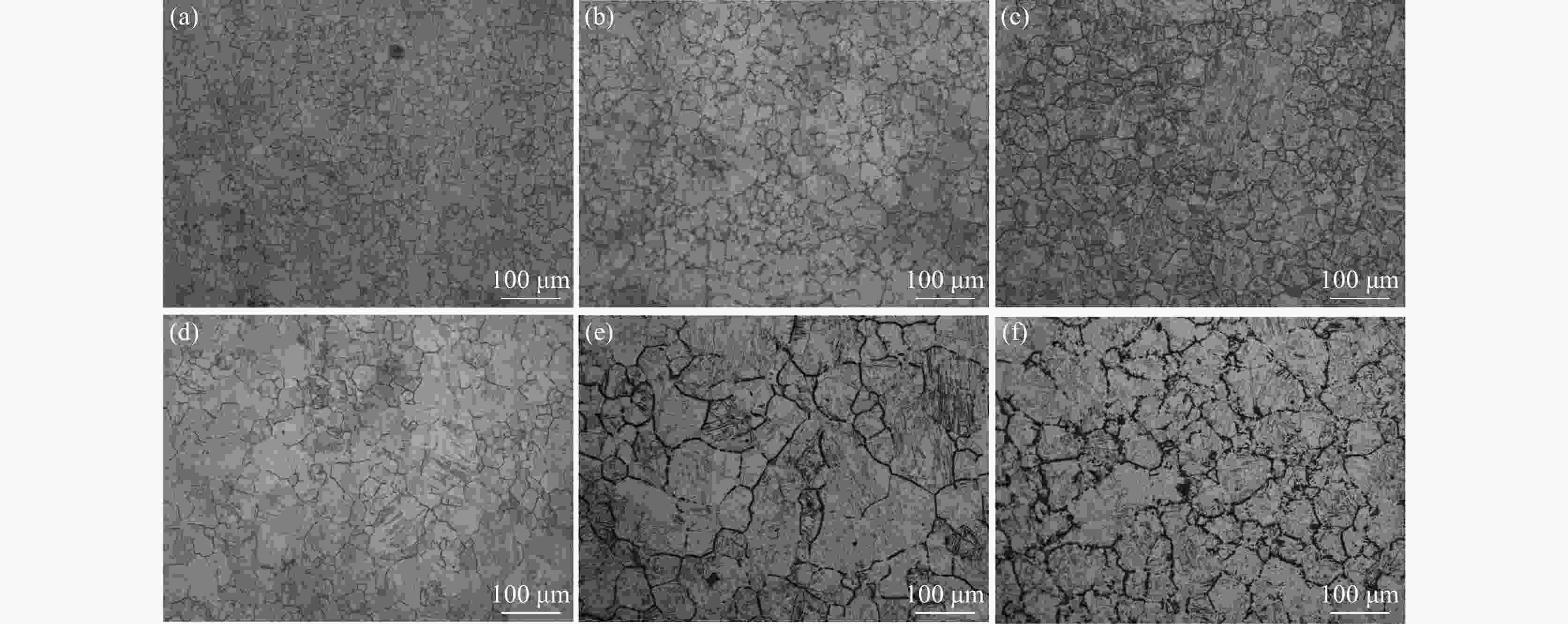
1050 ~1250 ℃条件下分别进行5~240 min等温奥氏体化的热处理试验,研究其奥氏体晶粒长大行为,利用Thermo-calc及TEM对不同加热工艺下的第二相粒子进行分析,通过HUMPHREYS理论对晶粒长大方式进行了预测。结果表明:随着奥氏体化温度的升高,NbC粒子中的Nb/Ti质量比逐渐减小,1050 ~1100 ℃保温1 h时晶粒尺寸细小均匀,温度升高至1150 ℃时发生晶粒异常长大现象,1250 ℃加热时晶粒尺寸粗化明显,各工艺下晶粒的实际长大方式与HUMPHREYS模型预测相同。综合考虑加热过程中奥氏体晶粒尺寸及微合金元素的溶解与析出规律,试验钢的最佳加热温度为1200 ℃左右。-
关键词:
- Nb-Ti微合金钢 /
- 奥氏体晶粒尺寸 /
- 晶粒长大动力学 /
- 第二相 /
- HUMPHREYS模型
Abstract: The heat treatment experiments were conducted on Nb-Ti microalloyed steel at 1050-1250 ℃ for 5-240 minutes to study the austenite grain growth behaviour. Thermo-calc and TEM were used to analyze the precipitation particles under different heating processes, and the grain growth mode was predicted using the HUMPHREYS' theory. The results showed that as the austenitization temperature increased, the mass ratio of Nb/Ti in the NbC particles gradually decreased. The grain size was small and uniform when the temperature was kept at1050 -1100 ℃ for 1 hour. As the temperature increased to1150 ℃, abnormal grain growth occurred. When heated at1250 ℃, the grain size coarsened significantly. The actual grain growth mode under each process was the same as predicted by the HUMPHREYS' model. Considering the austenite grain size and the dissolution and precipitation patterns of microalloyed elements during the heating process, the optimal heating temperature for the experimental steel is around1200 ℃. -
表 1 试样化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of test material
% C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Mo Nb Ti Al Fe 0.059 0.21 1.60 0.0076 0.0012 $\leqslant $0.6 0.050 0.014 0.033 余量 表 2 奥氏体晶粒在不同温度下的长大规律
Table 2. Growth rule of austenite grains at different temperatures
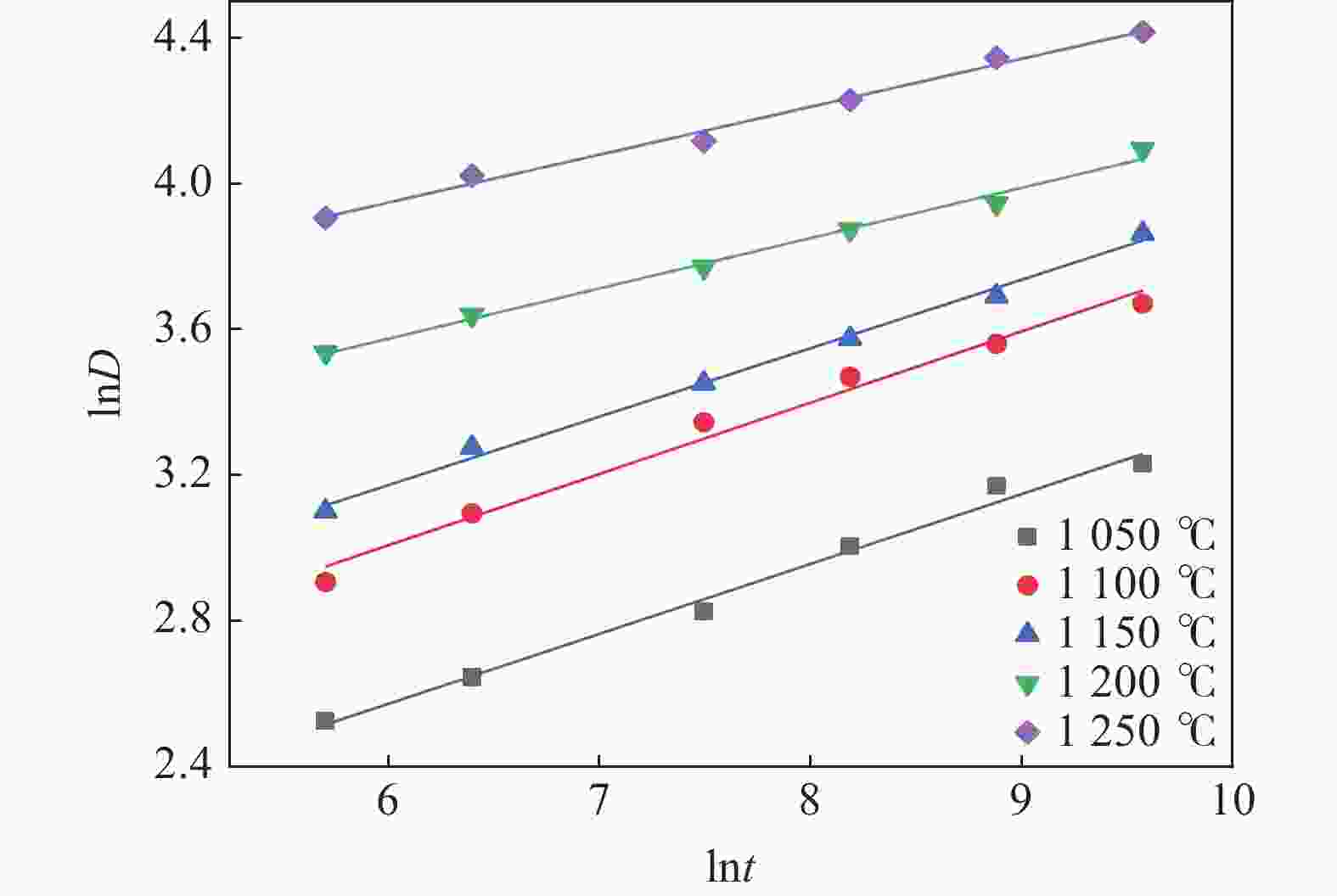
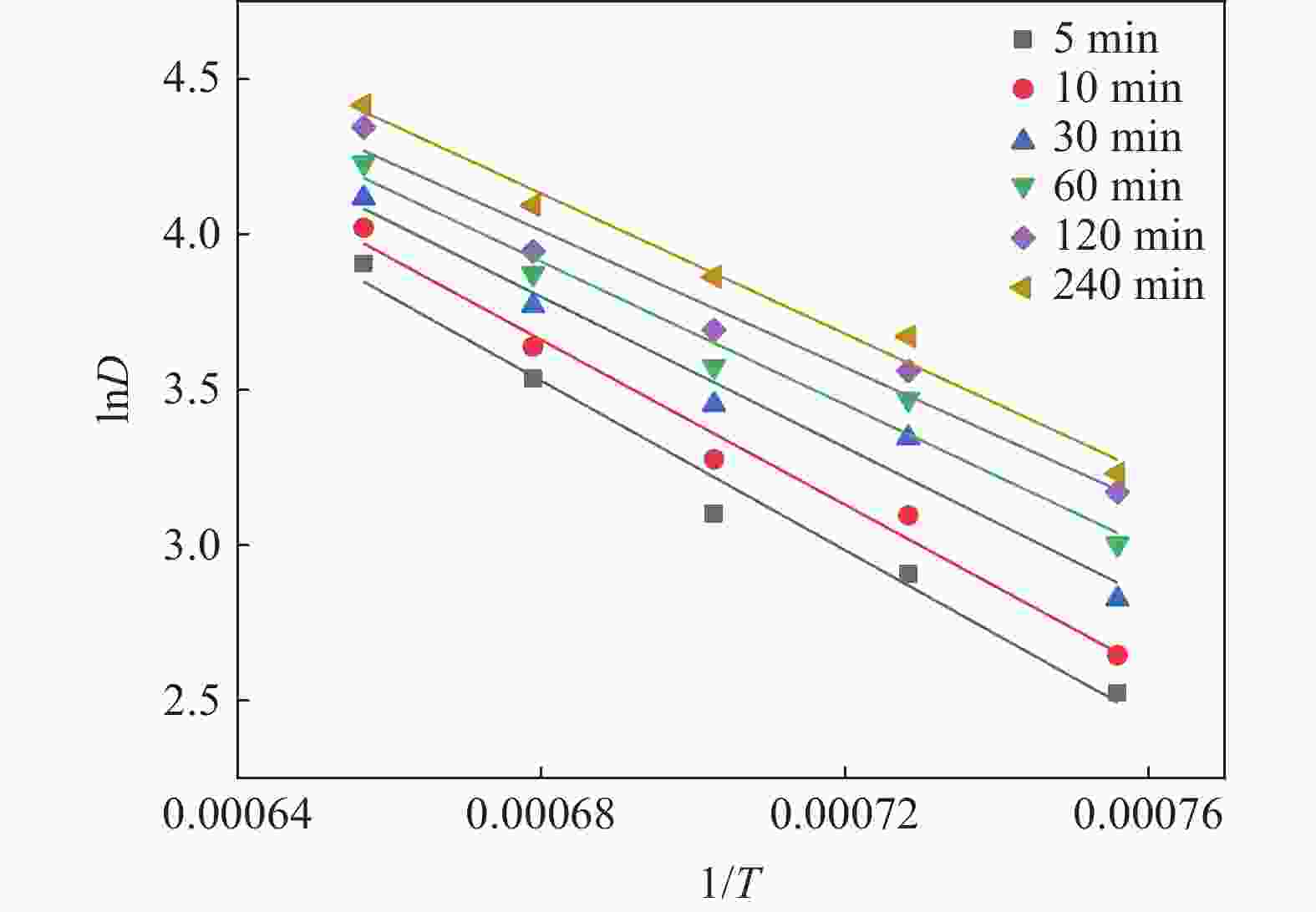
温度/℃ n K 温度/℃ n K 1050 0.19189 4.14076 1200 0.13806 15.57769 1100 0.19568 6.25400 1250 0.1315 23.54515 1150 0.18785 7.73186 表 3 Nb/Ti质量比随温度变化关系
Table 3. The relationship between Nb/Ti mass ratio and temperature
温度/℃ Nb/Ti质量比 温度/℃ Nb/Ti质量比 1050 7.73 1150 1.36 1100 4.85 1200 0.58 表 4 HUMPHREYS模型中的参数
Table 4. Parameters in the HUMPHREYS model
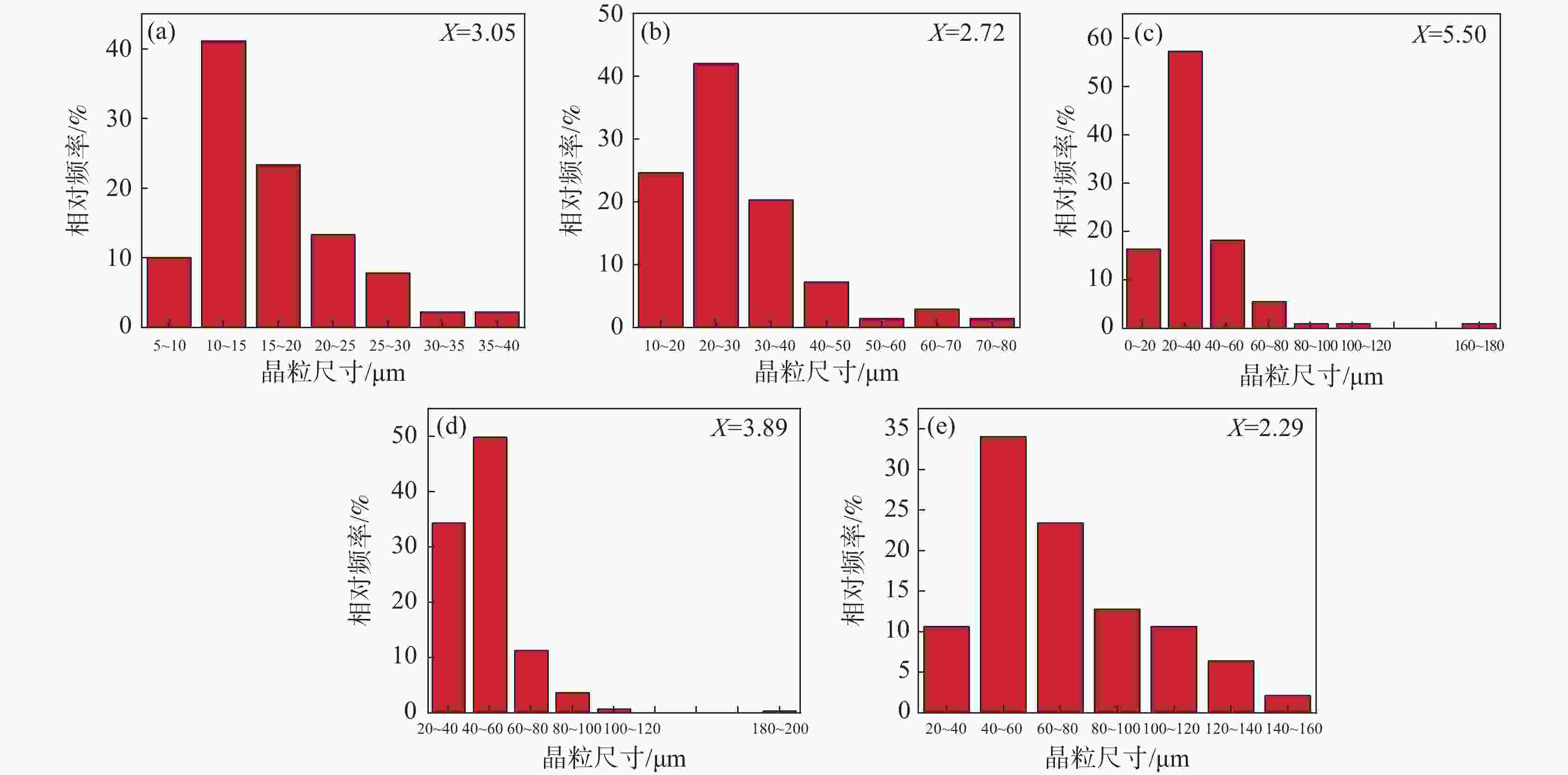
加热温度/℃ 保温时间/min 不均匀因子 平均晶粒直径/μm 析出相直径/nm 1050 30 3.05 20.16 18.56 1100 30 2.72 32.13 23.16 1150 30 5.5 35.69 36.69 1200 30 3.89 48.13 68.83 1250 30 2.29 63.61 0 -
[1] FERNANDEZ J, ILLESCAS S, GUILEMANY J M. Effect of microalloying elements on the austenitic grain growth in a low carbon HSLA steel[J]. Materials Letters, 2007, 61(11/12): 2389-2392. [2] ZHANG Z W. Research progress on high-strength low-alloy steel (HSLA)[J]. Materials China, 2016, 35(2): 141-151. (张中武. 高强度低合金钢(HSLA)的研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2016, 35(2): 141-151.ZHANG Z W. Research progress on high-strength low-alloy steel (HSLA)[J]. Materials China, 2016, 35(2): 141-151. [3] MAALEKIAN M, RADIS R, MILITZER M, et al. In situ measurement and modelling of austenite grain growth in a Ti/Nb microalloyed steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(3): 1015-1026. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2011.11.016 [4] LIU X, DU Q L, LI X. Effect of heating process on austenitic grain growth of Nb-Ti microalloys steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2019, 54(9): 116-120. (刘祥, 杜群力, 李新. 加热工艺对Nb-Ti微合金钢奥氏体晶粒长大的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2019, 54(9): 116-120.LIU X, DU Q L, LI X. Effect of heating process on austenitic grain growth of Nb-Ti microalloys steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2019, 54(9): 116-120. [5] YU S, TAO Z, DU L X. Study on the kinetics of austenite grain growth in medium manganese steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2020, 49(6): 121-123. (于帅, 陶振, 杜林秀. 中锰钢的奥氏体晶粒长大动力学研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2020, 49(6): 121-123.YU S, TAO Z, DU L X. Study on the kinetics of austenite grain growth in medium manganese steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2020, 49(6): 121-123. [6] XUE L, ZHANG L W, DING H C, et al. Comparison of austenite grain growth behavior between 20CrMnTi steel and 20 steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2023, 48(10): 45-49. (薛莉, 张立文, 丁浩晨, 等. 20CrMnTi钢和20钢奥氏体晶粒长大行为对比[J]. 金属热处理, 2023, 48(10): 45-49.XUE L, ZHANG L W, DING H C, et al. Comparison of austenite grain growth behavior between 20CrMnTi steel and 20 steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2023, 48(10): 45-49. [7] DING Z M, FANG J F, LIANG B, et al. Dynamics of austenite grain growth in V-Nb-(Ti) microalloyed steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2013, 34(S1): 88-92. (丁志敏, 方建飞, 梁博, 等. V-Nb-(Ti)微合金化钢奥氏体晶粒长大的动力学[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2013, 34(S1): 88-92.DING Z M, FANG J F, LIANG B, et al. Dynamics of austenite grain growth in V-Nb-(Ti) microalloyed steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2013, 34(S1): 88-92. [8] LIANG W, WU R, HU J, et al. Effect of heating process on Nb-Ti microalloys in high strength steel[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2019, 50(9): 2063-2073. (梁文, 吴润, 胡俊, 等. 加热工艺对Nb-Ti微合金化高强钢的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 50(9): 2063-2073.LIANG W, WU R, HU J, et al. Effect of heating process on Nb-Ti microalloys in high strength steel[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2019, 50(9): 2063-2073. [9] HUI Y J, YU Y, WANG C, et al. Austenitic grain coarsening behavior of titanium microalloyed hot-rolled high-strength steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2014, 35(12): 140-145. (惠亚军, 于洋, 王畅, 等. 钛微合金化热轧高强钢奥氏体晶粒粗化行为[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2014, 35(12): 140-145.HUI Y J, YU Y, WANG C, et al. Austenitic grain coarsening behavior of titanium microalloyed hot-rolled high-strength steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2014, 35(12): 140-145. [10] YANG X L. The effect of heating temperature on solid solution and grain growth of second phase particles in pipeline steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2002, 23 (2): 11-15. (杨秀亮. 加热温度对管线钢第二相粒子固溶及晶粒长大的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2002, 23( 2) : 11-15.YANG X L. The effect of heating temperature on solid solution and grain growth of second phase particles in pipeline steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2002, 23 (2): 11-15. [11] RAZZAK MA, PEREZ M, SOURMAIL T. A simple model for abnormal grain growth[J]. ISIJ INTERNATIONAL, 2012, 52(12): 2278-2282. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.52.2278 [12] NES E, RYUM N, HUNDERI O. On the Zener drag[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1985, 33(1): 11-22. doi: 10.1016/0001-6160(85)90214-7 [13] GLADMAN T. On the theory of the effect of precipitate particles on grain growth in metals[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1966, 294(1438): 298-309. [14] HUMPHREYS F J. A unified theory of recovery, recrystallization and grain growth, based on the stability and growth of cellular microstructures-Ⅱ. The effect of secondphaseparticles[J]. Acta Materialia, 1997, 45(12): 5031-5039. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(97)00173-0 [15] JANA S, MISHRA R S, BAUMANN J A, et al. Effect of process parameters on abnormal grain growth during friction stir processing of a cast Al alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 528(1): 189-199. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.08.049 [16] FERRY M, HAMILTON N E, HUMPHREYS F J. Continuous and discontinuous grain coarsening in a fine-grained particle-containing Al-Sc alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53(4): 1097-1109. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2004.11.006 [17] CHEN K, GAAN W, OKMAOTO K, et al. The mechanism of grain coarsening in friction stir-welded AA5083 after heat treatment[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2011, 42(2): 488-507. doi: 10.1007/s11661-010-0426-9 [18] BECK P A, KREMER J C, DEMER L J, et al. Grain growth in high-purity aluminium and in an aluminum-magnesium alloy[J]. Trans AIME, 1948, 175: 372-394. [19] ZHANG, S S, LI M Q, LIU Y G, et al. The growth behavior of austenite grain in the heating process of 300M steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011, 528: 4967-4972. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.02.089 [20] CHEN M A, WU C S, YANG M, et al. Response of second phase particles in Ti-V-Nb microalloyed steel during weld thermal cycling[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2004, 40(2): 148-154. (陈茂爱, 武传松, 杨敏, 等. Ti-V-Nb微合金钢第二相粒子在焊接热循环过程中的变化规律[J]. 金属学报, 2004, 40(2): 148-154.CHEN M A, WU C S, YANG M, et al. Response of second phase particles in Ti-V-Nb microalloyed steel during weld thermal cycling[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2004, 40(2): 148-154. [21] FENG R, LI S L, LI Z S, et al. Characteristic of diphase precipitate of Nb-V-Ti microalloyed steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2013, 34(2): 37-41. (冯锐, 李胜利, 李贞顺, 等. Nb-V-Ti微合金钢复合析出相的特征[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2013, 34(2): 37-41.FENG R, LI S L, LI Z S, et al. Characteristic of diphase precipitate of Nb-V-Ti microalloyed steel[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2013, 34(2): 37-41. [22] LUO A A, KUBIC R C, TARTAGLIA J M. Microstructure and fatigue properties of hydroformed aluminum alloys 6063 and 5754[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 2003, 34: 2549-2557. [23] TSUJI N, OKUNO S, MATSUURA T. Mechanical properties as a function of grain size in ultrafine grained aluminum and iron fabricated by ARB and annealing process[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2003(Pt.3): 426/432. [24] ANDERSEN I, GRONG O, RYUM N. Analytical modelling of grain growth in metals and alloys in the presence of growing and dissolving precipitates—II. Abnormal grain growth[J]. Acta Metallurgica Et Materialia, 1995, 43(7): 2689-2700. doi: 10.1016/0956-7151(94)00489-5 -




 下载:
下载: