Research on droplet transfer in MIG welding based on high-speed photography and FLUENT
-
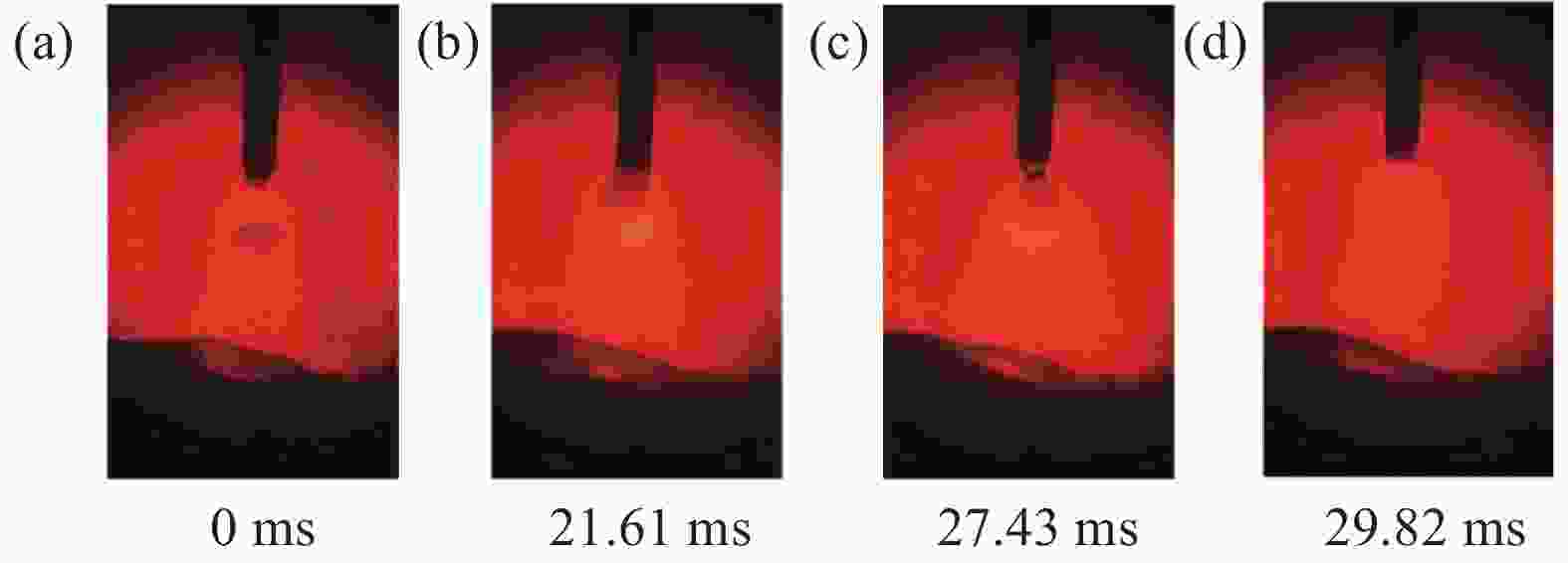
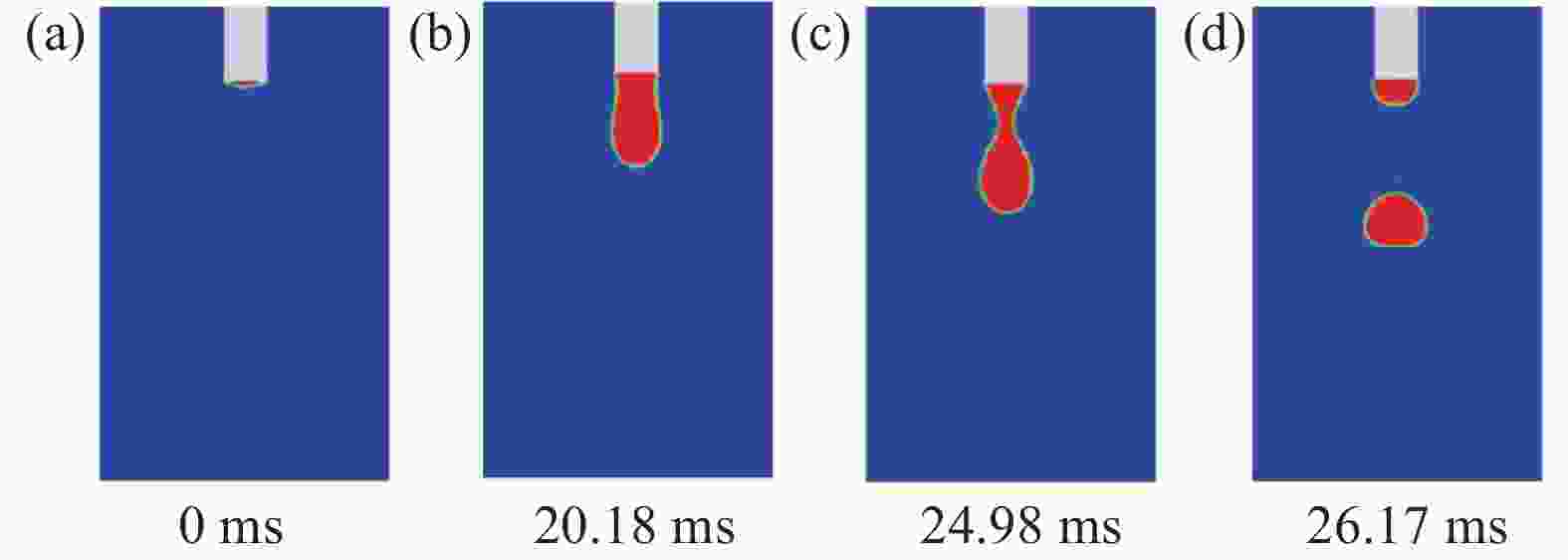
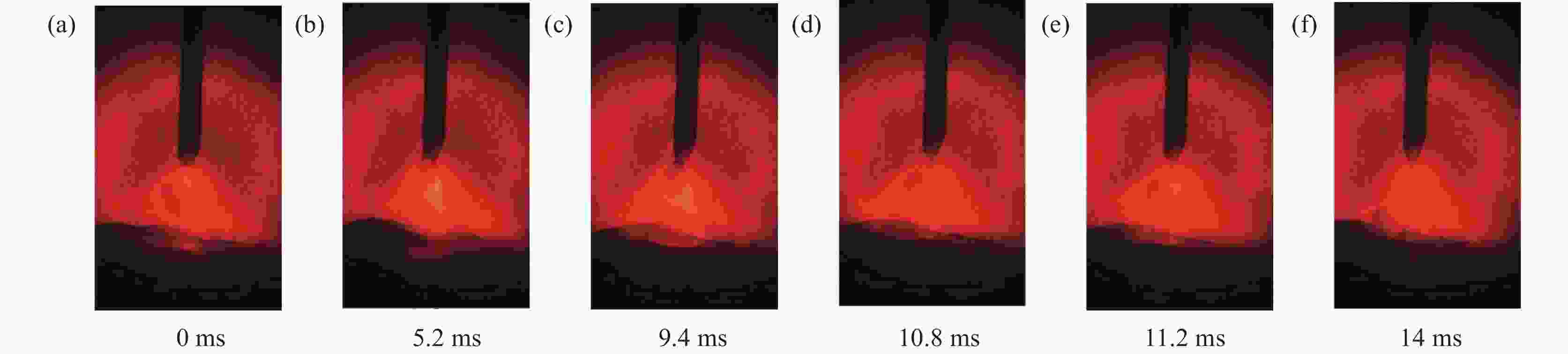
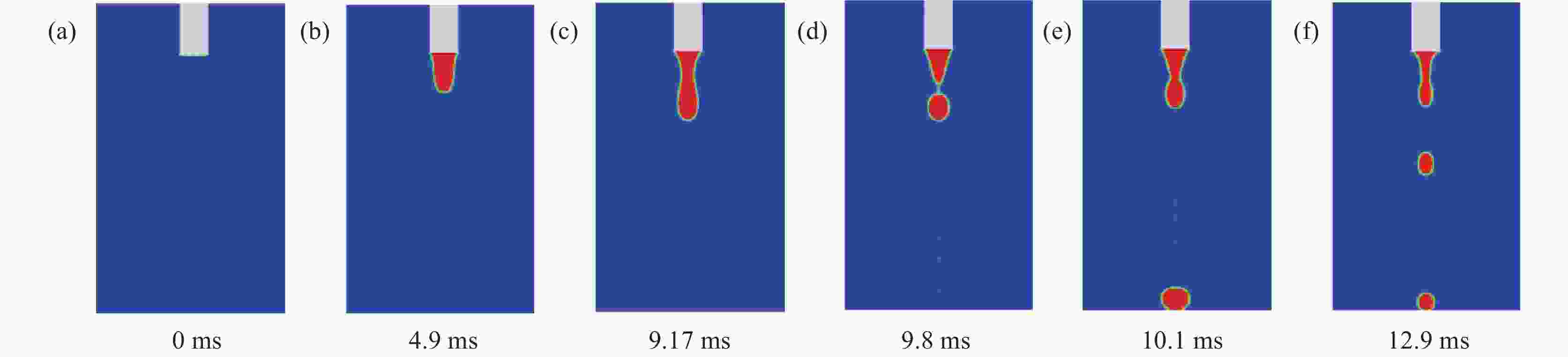
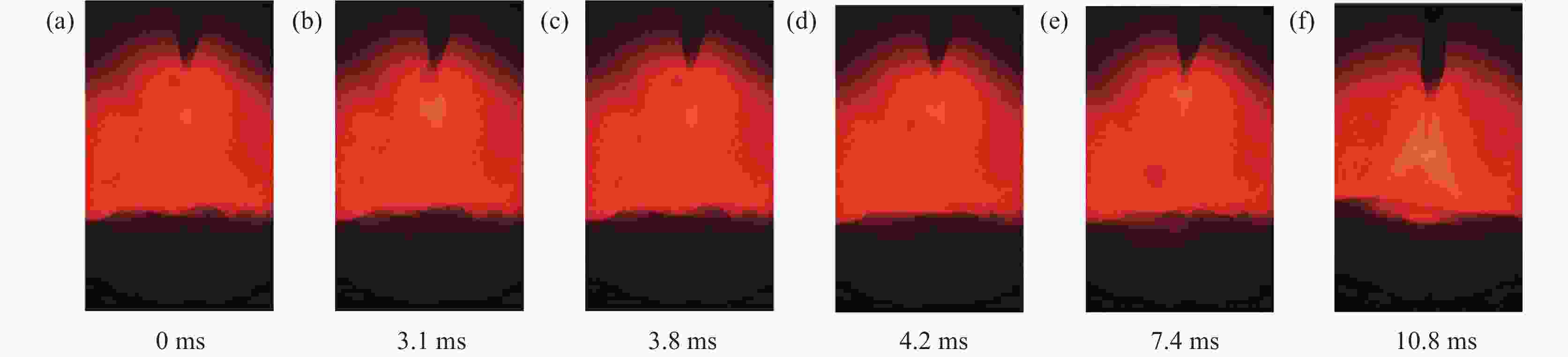
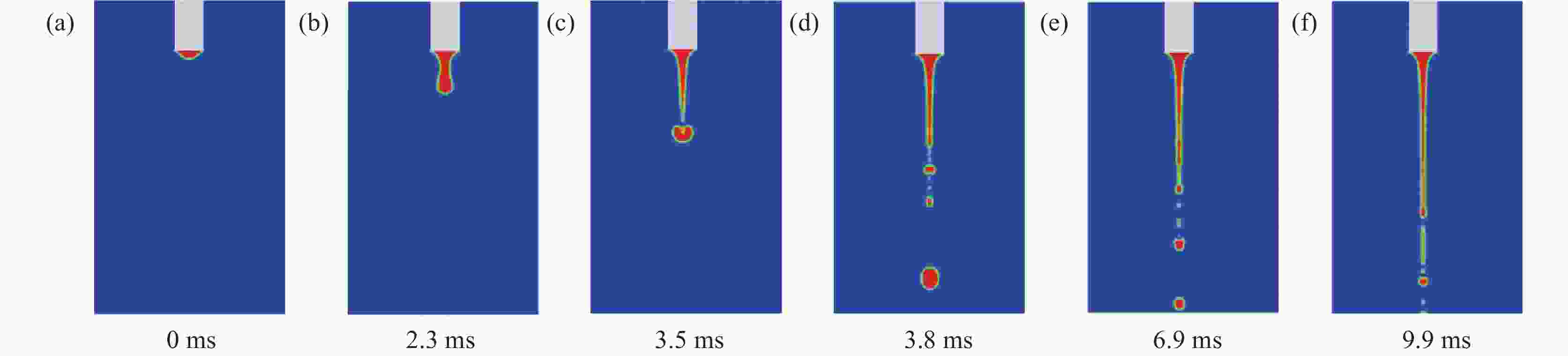
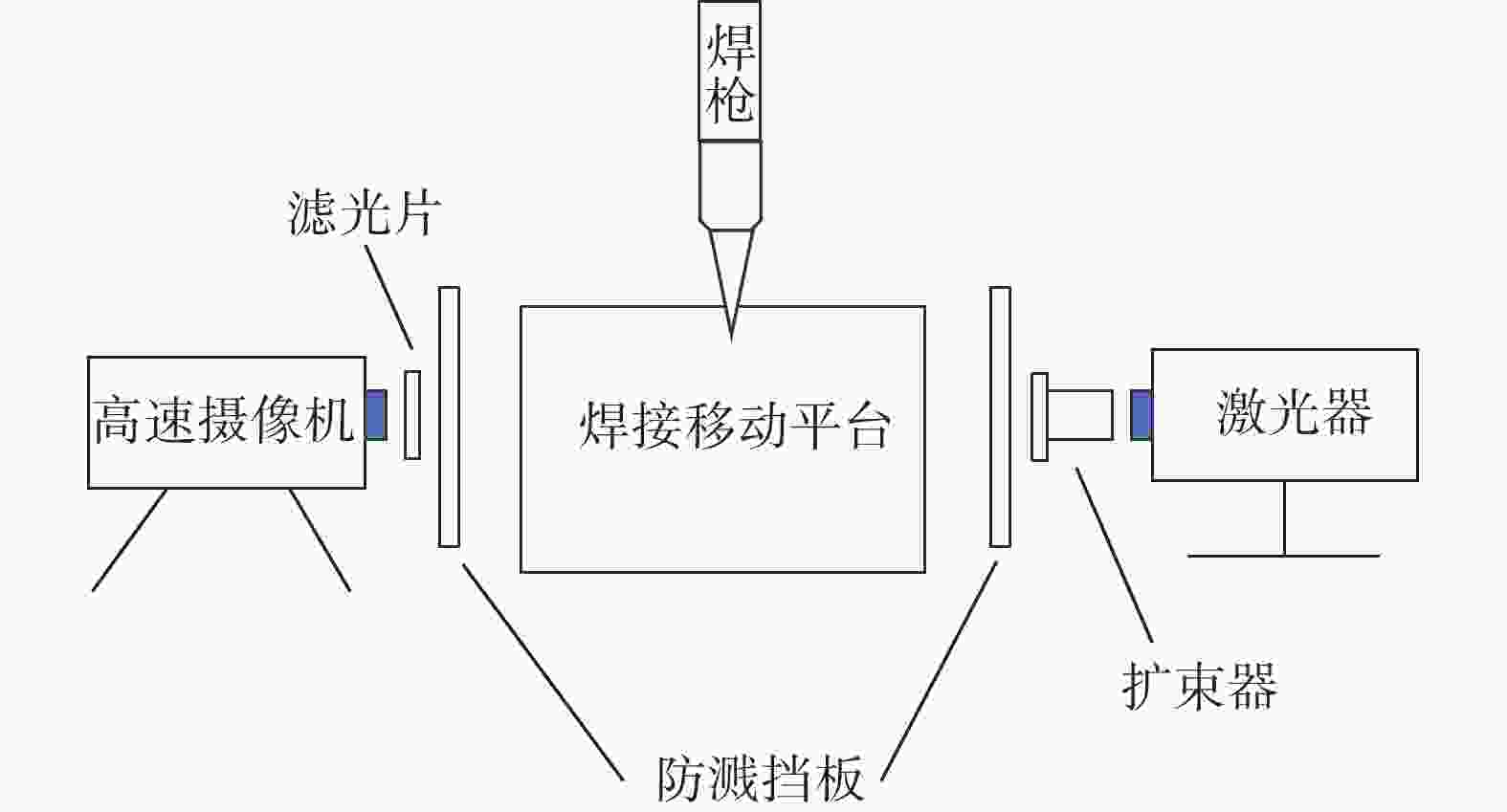
摘要: 针对304L不锈钢MIG焊接过程中的熔滴过渡现象,运用FLUENT软件进行数值模拟,借助高速摄影系统进行拍摄,对焊接电流分别为150、180 A和 260 A时的熔滴过渡形态特征和频率进行分析。研究结果显示,随着焊接电流的增大,熔滴所受电磁收缩力和等离子流力逐渐占据主导地位;随着熔滴温度逐渐升高,表面张力随之变小,使得熔滴从焊丝末端分离所需的重力减小,导致熔滴直径逐渐变小,过渡频率逐渐加快,依次呈现出大滴过渡、射滴过渡和射流过渡。通过对比三组焊接电流的高速摄影和数值模拟结果,二者在过渡周期、特征时间和熔滴尺寸等方面的试验值与模拟值相似度均分别超过87%、90%、91%,表明所采用的数值模拟模型具有较高的可靠性。Abstract: In order to study the droplet transfer behaviors during the MIG welding process of 304L stainless steel, a FLUENT numerical simulation software and high-speed photography system had been utilized to analyze the characteristics and frequency of droplet transfer at currents of 150, 180 A, and 260 A, respectively. The results show that the electromagnetic constriction force and the plasma drag force acting on the droplet both become dominant gradually with the increasing of welding current. As the droplet temperature rises gradually, the surface tension acting on the droplet decreases accordingly, which reduces the required gravity of the droplet to separate from the end of the welding wire. Consequently, the droplet diameter decreases and the transfer frequency increases gradually, presenting the modes of globular transfer, projected transfer and spray transfer in turn. Through the comparison between the high-speed video pictures and numerical simulation results of the three groups of welding currents, the similarity of experimental and the simulated values containing transfer period, characteristic time and droplet size exceeds 87%, 90%, and 91% respectively, indicating that the numerical simulation model adopted in this study has a relatively high reliability.
-
Key words:
- MIG welding /
- droplet transfer /
- numerical simulation /
- high-speed photography /
- FLUENT software /
- 304L stainless steel
-
表 1 选材化学成分表
Table 1. Chemical compositions of selected materials
% 材质 C Mn Si S P Ni Cr Fe 试板 ≤0.080 ≤2.00 ≤1.00 ≤0.030 ≤0.045 8.00 ~ 10.50 18.00 ~ 20.00 余量 焊丝 0.025 1.90 0.75 0.015 0.014 10.50 18.00 余量 表 2 304L不锈钢的数值模拟物性参数
Table 2. Physical property parameters of 304L stainless steel for numerical simulation
钢液熔点
Tm/℃钢液密度
ρ/(kg·m−3)钢液动力粘性
µ/(Pa·s)钢液比热容
C/(J·kg−1·℃−1)磁导率
µ0/(H·m−1)电导率
σ/(S·m−1)表面张力系数
γ/(N·m−1)重力加速度
g/(m·s−2)1.45×103 8×103 2×10−3 1.5 ×102 4π×10−7 7.7×10−5 1.2 9.8 表 3 氩气的数值模拟物性参数
Table 3. Physical property parameters of argon for numerical simulation
密度/
(kg·m−3)粘度/
(Pa·s)导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)比热容/
(kJ·kg−1·K−1)1.784 2.02 ×10−5 0.01795 0.52 -
[1] FU S Q. Numerical simulation study on arc shape and droplet transfer behavior in ultrasonic-assisted MIG welding[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2024. (付水淇. 超声波辅助MIG焊接电弧形态与熔滴过渡行为的数值模拟研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2024.FU S Q. Numerical simulation study on arc shape and droplet transfer behavior in ultrasonic-assisted MIG welding[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2024. [2] ZHU M, SHI Y, WANG G L, et al. Metal transfer behaviors in consumable double-electrode GMAW process[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(12): 50-54. (朱明, 石玗, 王桂龙, 等. 双丝旁路耦合电弧GMAW熔滴过渡特性分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2013, 49(12): 50-54. doi: 10.3901/JME.2013.12.050ZHU M, SHI Y, WANG G L, et al. Metal transfer behaviors in consumable double-electrode GMAW process[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 49(12): 50-54. doi: 10.3901/JME.2013.12.050 [3] ALLUM, C J. Metal transfer in arc welding as a varicose instability. I. Varicose instabilities in a current-carrying liquid cylinder with surface charge[J]. Journal of Physics D Applied Physics, 2000, 18(7): 1431-1446. [4] CAO M G. Study of the effect of droplet oscillation momentum on the surface forming quality of Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2023. (曹美光. 熔滴振荡动量对电弧增材制造表面成形质量影响的研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学, 2023.CAO M G. Study of the effect of droplet oscillation momentum on the surface forming quality of Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2023. [5] HERTEL M, SPILLE-KOHOFF A, FUSSEL U. et al. Numerical simulation of droplet detachment in pulsed gas-metal arc welding including the influence of metal vapour[J]. Journal of Physics D Applied Physics, 2013, 46(22): 4003-4014. [6] FAN H G, KOVACEVIC R. Droplet formation, detachment, and impingement on the molten pool in gas metal arc welding[J]. Metallurgical& Materials Transactions B, 1999, 30(4): 791-801. [7] LIU W Q, SHAN Y G, YUAN Z. Simulation of droplet transfer process in GMAW[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2016, 45(21): 215-219. (刘维球, 单彦广, 袁张. GMAW焊接熔滴过渡过程的模拟研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2016, 45(21): 215-219.LIU W Q, SHAN Y G, YUAN Z. Simulation of droplet transfer process in GMAW[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2016, 45(21): 215-219. [8] LI K, CHEN F H, ZHU Y J, et al. Simulation and experiment study on droplet transfer of MIG welding for Low-carbon steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2020, 49(7): 149-152,156. (李科, 陈峰华, 朱彦军, 等. 低碳钢MIG焊熔滴过渡的模拟与试验研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2020, 49(7): 149-152,156.LI K, CHEN F H, ZHU Y J, et al. Simulation and experiment study on droplet transfer of MIG welding for Low-carbon steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2020, 49(7): 149-152,156. [9] WANG R C, WANG H, LI H J, et al. Research on numerical simulation of weld pool behavior in pulsed MIG[J]. New Technology& New Process, 2023(8): 47-53. (王瑞超, 王皓, 李会军, 等. 脉冲MIG焊熔池行为的数值模拟研究[J]. 新技术新工艺, 2023(8): 47-53.WANG R C, WANG H, LI H J, et al. Research on numerical simulation of weld pool behavior in pulsed MIG[J]. New Technology& New Process, 2023(8): 47-53. [10] John D. Anderson. Computational fluid dynamics: the basics and its applications[M]. Beijing: China MachinePress, 2009.40. (约翰D. 安德森, 计算流体力学基础及其应用[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2009.40.John D. Anderson. Computational fluid dynamics: the basics and its applications[M]. Beijing: China MachinePress, 2009.40. [11] LIU W Q, LI Q, LIU F D, et al. Research on the electromagnetic constriction force of droplet transfer in laser-arc hybrid welding [J]. Applied Laser, 2016, 36(2): 188-192. (刘万强, 李彦清, 刘凤德, 等. 激光-电弧复合焊熔滴过渡的电磁收缩力研究[J]. 应用激光, 2016, 36(2): 188-192.LIU W Q, LI Q, LIU F D, et al. Research on the electromagnetic constriction force of droplet transfer in laser-arc hybrid welding [J]. Applied Laser, 2016, 36(2): 188-192. [12] ZHAO X Y. Numerical analysis of arc-droplet pool behavior in TIG-MIG hybrid welding[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2022. (赵昕宇. TIG-MIG复合焊电弧-溶滴-溶池数值分析[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2022.ZHAO X Y. Numerical analysis of arc-droplet pool behavior in TIG-MIG hybrid welding[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2022. [13] ZHOU S J, DUAN R, SU Z, et al. Numerical simulation of weld pool formation driven by surface tension in laser welding of austenitic stainless steel sheet[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2024, 54(6): 87-93. (周世杰, 段瑞, 苏哲, 等. 奥氏体不锈钢薄板激光焊表面张力驱动熔池形成的数值模拟分析[J]. 电焊机, 2024, 54(6): 87-93. doi: 10.7512/j.issn.1001-2303.2024.06.14ZHOU S J, DUAN R, SU Z, et al. Numerical simulation of weld pool formation driven by surface tension in laser welding of austenitic stainless steel sheet[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2024, 54(6): 87-93. doi: 10.7512/j.issn.1001-2303.2024.06.14 -




 下载:
下载: