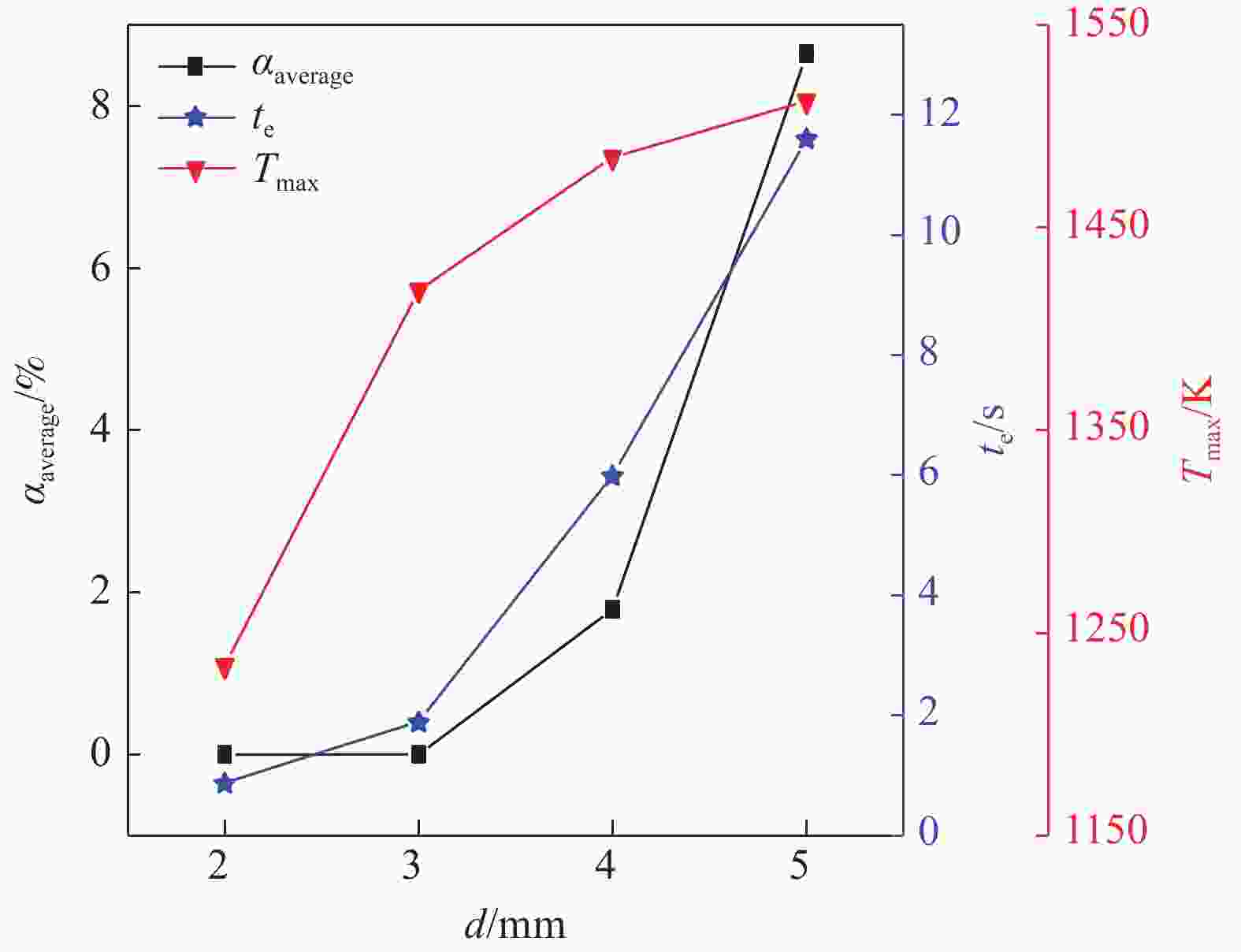
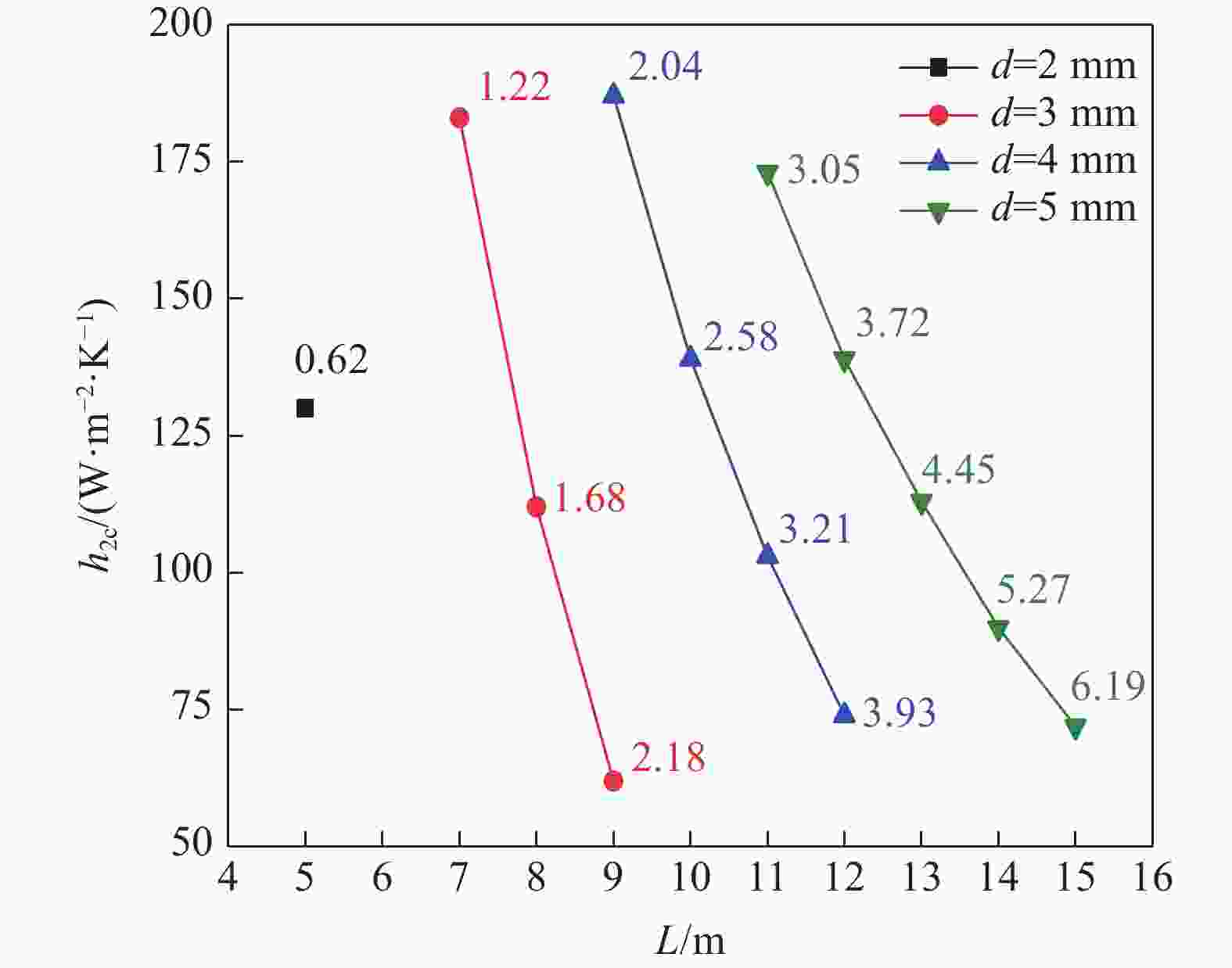
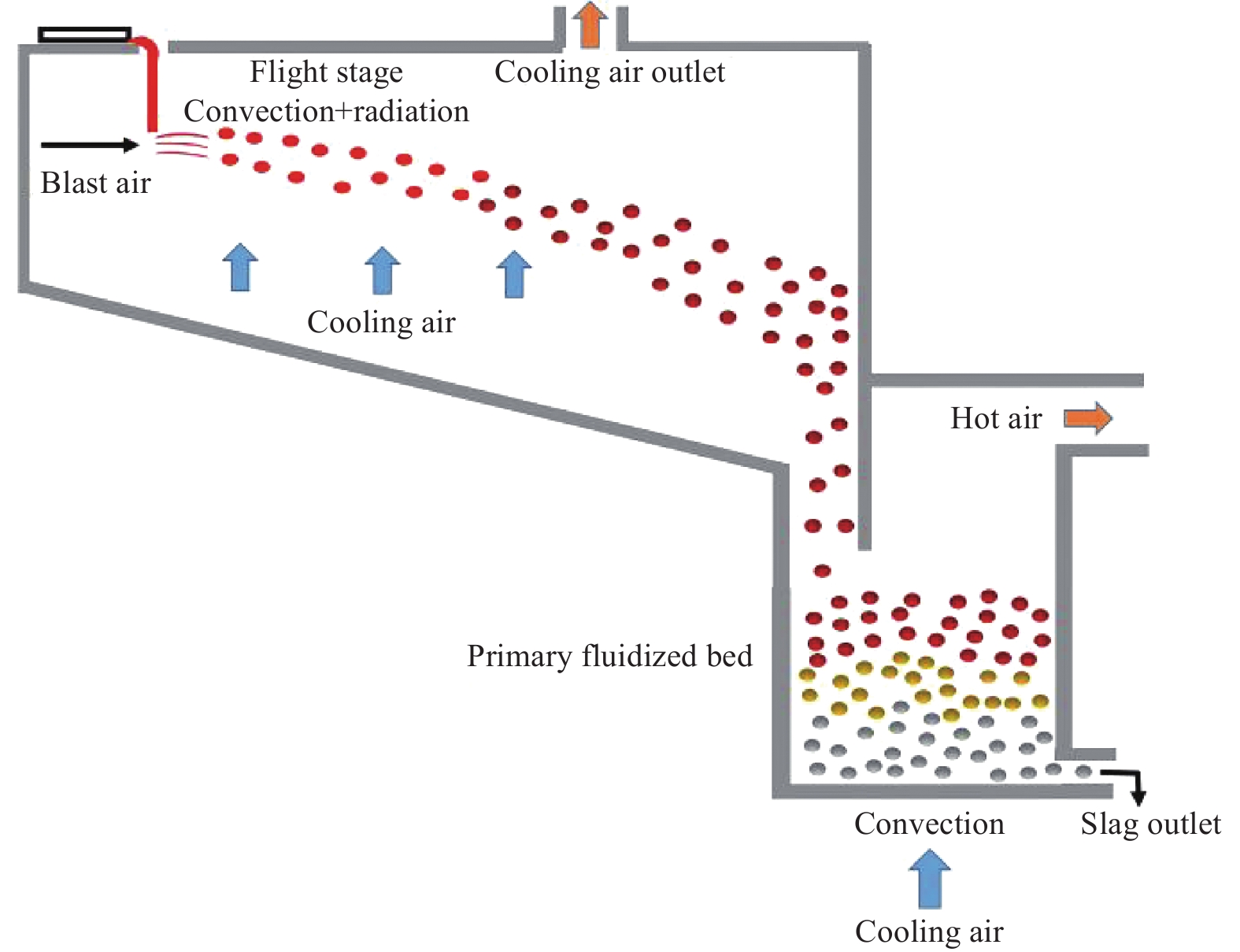
| [1] |
SI W H, ZHANG Y Q. Current status and development trend of waste heat recovery technology for high-temperature slag[J]. Yizhong Technology, 2025(1): 1-4. (姒伟华, 张元奇. 高温熔渣余热回收技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 一重技术, 2025(1): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3355.2025.01.001SI W H, ZHANG Y Q. Current status and development trend of waste heat recovery technology for high-temperature slag[J]. Yizhong Technology, 2025(1): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3355.2025.01.001
|
| [2] |
DING B, LIAO Q, ZHU X, et al. Deep insight into phase transition and crystallization of high temperature molten slag during cooling: A review[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 184: 116260. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.116260
|
| [3] |
ZHANG X, WANG S, WU Z, et al. Optimizing heat transfer and solidification crystallization in dry granulation of blast furnace slag[J]. Powder Technology, 2024, 447: 120202. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2024.120202
|
| [4] |
KUMAR S S, SINGH A R, KARTIK S. Utilizing ground granulated blast furnace slag during carbon sequestration in concrete[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2025, 37(2): 12-27.
|
| [5] |
LIU J X, QIN Q, YU Q B. The effect of size distribution of slag particles obtained in dry granulation on blast furnace slag cement strength[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 362(C): 32-36.
|
| [6] |
KAVEH T M, MOHAMMADI E, MEHRNAHAD H. Durability of steel slag as railway ballast under freezing–thawing and salt crystallization weathering[J]. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management, 2025, 27(3): 1-14.
|
| [7] |
SUN R J, KANG Y, SHAO C, et al. Numerical simulation on intensified cooling and solidification process of gas-quenched blast furnace slag beads[J]. China Metallurgy, 2024, 34(9): 34-44. (孙瑞靖, 康月, 邵宸, 等. 气淬高炉渣珠强化冷却凝固过程数值仿真[J]. 中国冶金, 2024, 34(9): 34-44.SUN R J, KANG Y, SHAO C, et al. Numerical simulation on intensified cooling and solidification process of gas-quenched blast furnace slag beads[J]. China Metallurgy, 2024, 34(9): 34-44.
|
| [8] |
LI X H, WANG X S, LIU Z L, et al. New direction for comprehensive utilization of high-titanium blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2009, 30(3): 10-16. (李兴华, 王雪松, 刘知路, 等. 高钛高炉渣综合利用新方向[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2009, 30(3): 10-16. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2009.03.002LI X H, WANG X S, LIU Z L, et al. New direction for comprehensive utilization of high-titanium blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2009, 30(3): 10-16. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2009.03.002
|
| [9] |
FANG W Y, WANG H, ZHU X, et al. Heat transfer characteristics of molten slag in rotary cup granulation process[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020, 55(8): 151-159. (方维扬, 王宏, 朱恂, 等. 转杯粒化工艺高温熔渣换热数值模拟[J]. 钢铁, 2020, 55(8): 151-159.FANG W Y, WANG H, ZHU X, et al. Heat transfer characteristics of molten slag in rotary cup granulation process[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020, 55(8): 151-159.
|
| [10] |
SUN G T. Study on mechanical centrifugal granulation characteristics of blast furnace slag[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2020. (孙广彤. 高炉熔渣机械离心粒化特性研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2020.SUN G T. Study on mechanical centrifugal granulation characteristics of blast furnace slag[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2020.
|
| [11] |
SHAO C, KANG Y, XING H W, et al. Experimental and simulation on the granulation process of blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2024, 45(1): 104-114. (邵宸, 康月, 邢宏伟, 等. 高炉熔渣粒化工艺试验及其数值仿真研究分析[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2024, 45(1): 104-114. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2024.01.016SHAO C, KANG Y, XING H W, et al. Experimental and simulation on the granulation process of blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2024, 45(1): 104-114. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2024.01.016
|
| [12] |
CHANG Q M, CHENG Y K, LI X W, et al. Modeling and simulation study on dry centrifugal granulation of blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014, 35(1): 69-73. (常庆明, 程永楷, 李先旺, 等. 高炉渣干式离心粒化的建模仿真研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2014, 35(1): 69-73. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.01.014CHANG Q M, CHENG Y K, LI X W, et al. Modeling and simulation study on dry centrifugal granulation of blast furnace slag[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2014, 35(1): 69-73. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2014.01.014
|
| [13] |
LI X H. Study on mechanism of gas-liquid atomization and solidification heat transfer characteristics of blast furnace slag [D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2025. (刘晓宏. 高炉熔渣气雾粒化机理及凝固换热特性研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2025.LI X H. Study on mechanism of gas-liquid atomization and solidification heat transfer characteristics of blast furnace slag [D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2025.
|
| [14] |
WANG Z B, LIU Y, ZHANG Y Z, et al. Experimental study on heat recovery of blast furnace slag by gas quenching granulation[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018, 39(4): 93-98. (王子兵, 刘跃, 张玉柱, 等. 高炉熔渣气淬粒化热量回收试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018, 39(4): 93-98. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.04.016WANG Z B, LIU Y, ZHANG Y Z, et al. Experimental study on heat recovery of blast furnace slag by gas quenching granulation[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018, 39(4): 93-98. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2018.04.016
|
| [15] |
LIU X Y, ZHU X, LIAO Q, et al. Theoretic analysis on transient solidification behaviors of a molten blast furnace slag particle[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(S1): 285-291. (刘小英, 朱恂, 廖强, 等. 高温熔融高炉渣颗粒相变冷却特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(S1): 285-291.LIU X Y, ZHU X, LIAO Q, et al. Theoretic analysis on transient solidification behaviors of a molten blast furnace slag particle[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(S1): 285-291.
|
| [16] |
QIU Y J, ZHU X, WANG H, et al. Three-dimensional simulation of solidification and heat transfer for air-cooling molten blast furnace slag droplet[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(S1): 340-345. (邱勇军, 朱恂, 王宏, 等. 熔渣颗粒空冷相变换热的三维数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(S1): 340-345.QIU Y J, ZHU X, WANG H, et al. Three-dimensional simulation of solidification and heat transfer for air-cooling molten blast furnace slag droplet[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(S1): 340-345.
|
| [17] |
WANG H, DING B, LIU X Y, et al. Solidification behaviors of a molten blast furnace slag droplet cooled by air[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 127: 915-924. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.07.215
|
| [18] |
DING B, WANG H, ZHU X, et al. Crystallization behaviors of blast furnace (BF) slag in a phase-change cooling process[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(4): 3331-3339.
|
| [19] |
DING B, ZHU X, WANG H, et al. Numerical investigation on phase change cooling and crystallization of a molten blast furnace slag droplet[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 118: 471-479. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.10.108
|
| [20] |
GAO J, FENG Y H, FENG D L, et al. Solidification with crystallization behavior of molten blast furnace slag particle during the cooling process[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 146: 118888. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.118888
|
| [21] |
GAO J, FENG Y H, FENG D L, et al. The effects of interactions between multiple blast furnace slag particles on crystallization characteristics[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 185: 122374. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2021.122374
|
| [22] |
FAN F H, MIN Z, YANG S L, et al. Numerical study of fluid dynamics and heat transfer property of dual fluidized bed gasifier[J]. Energy, 2021, 234: 74-83.
|
| [23] |
WANG B, QIU J Y, GUO Q H, et al. Numerical simulations of solidification characteristics of molten slag droplets in radiant syngas coolers for entrained-flow coal gasification[J]. ACS omega, 2021, 6(31): 20388-20397. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02406
|
| [24] |
YANG P, MA C, MA G, et al. Waste heat recovery of blast furnace slag in moving bed: Influencing of structural parameters and operating parameters[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2024, 107: 109421. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2024.109421
|




 下载:
下载: