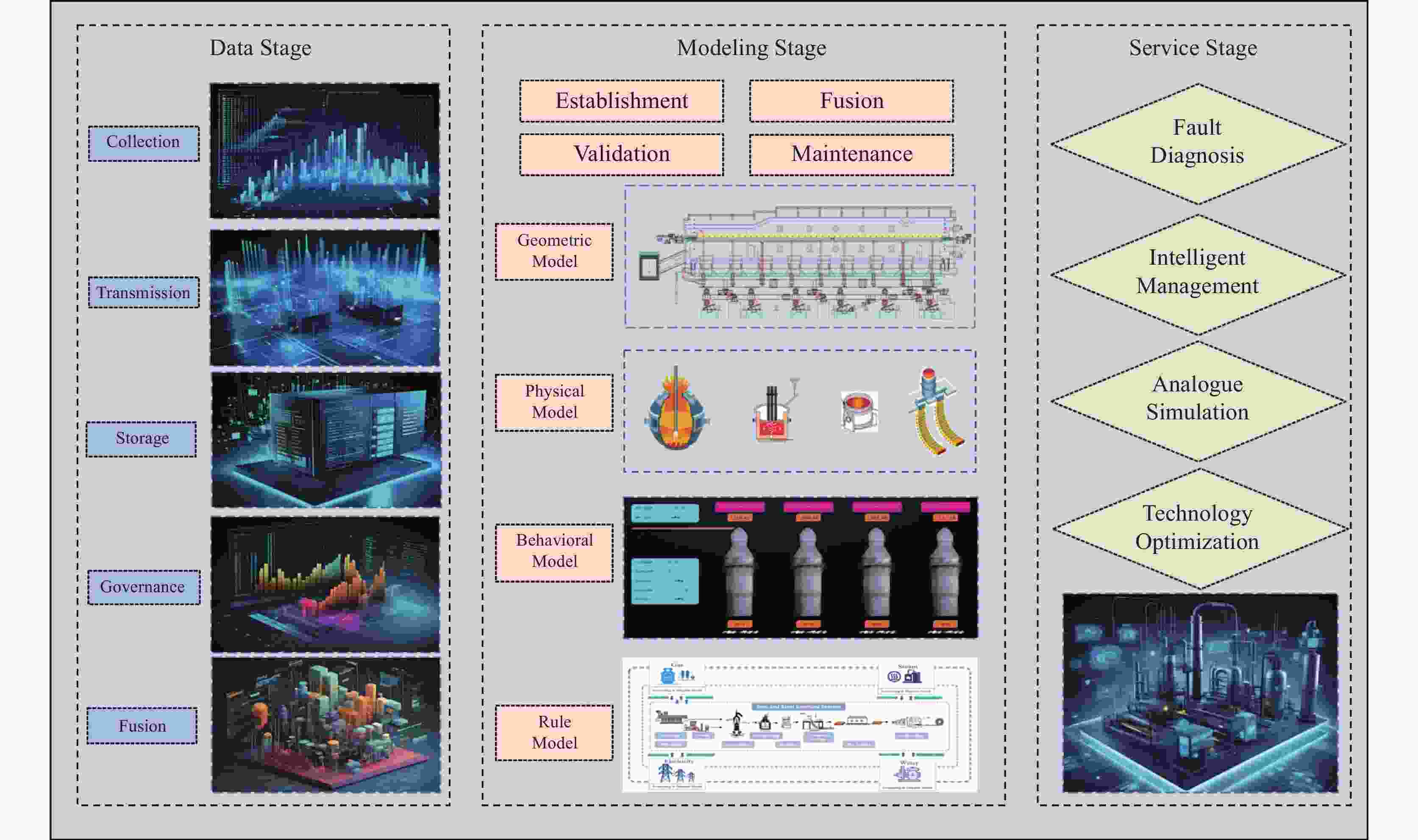
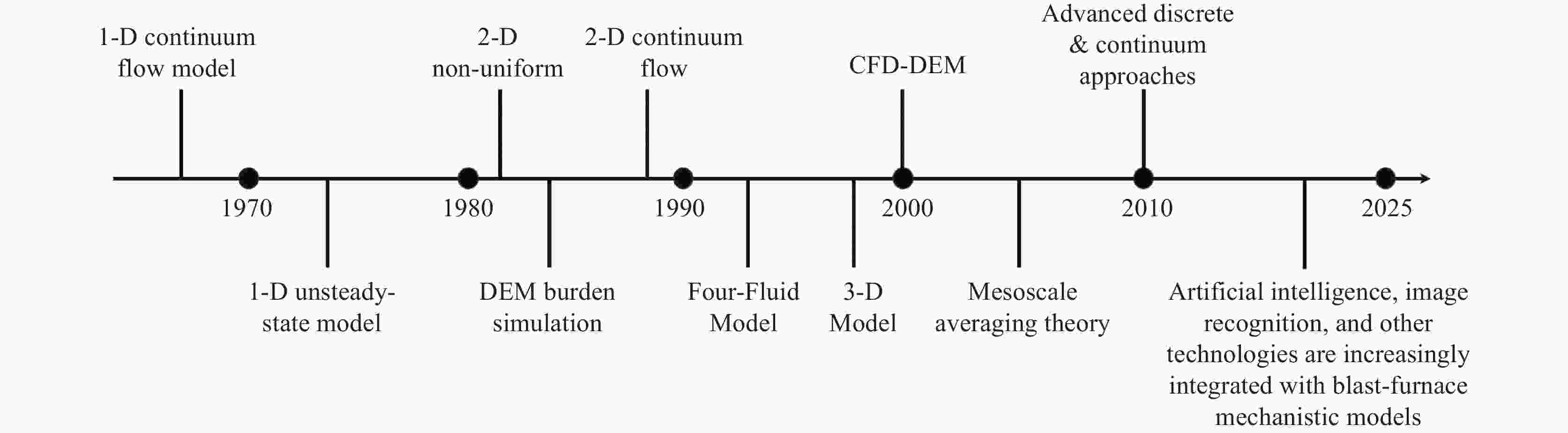
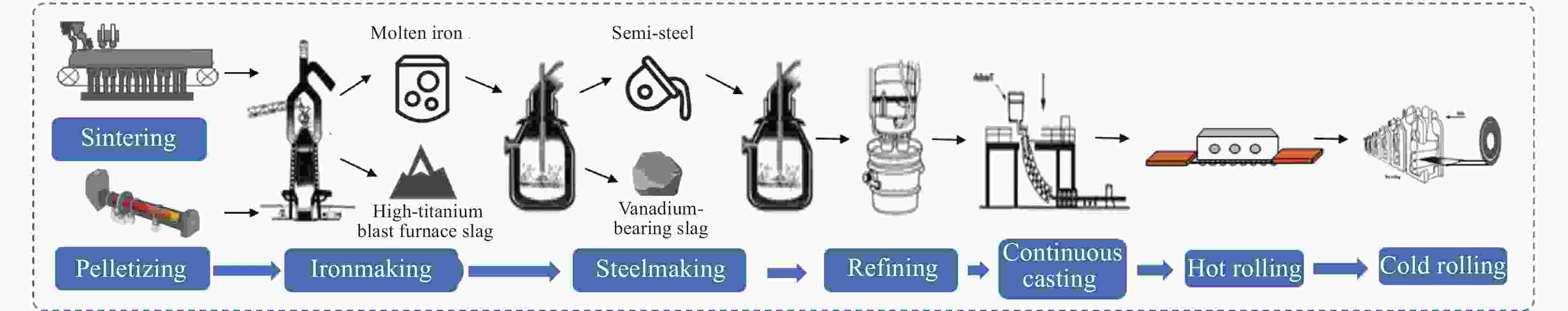
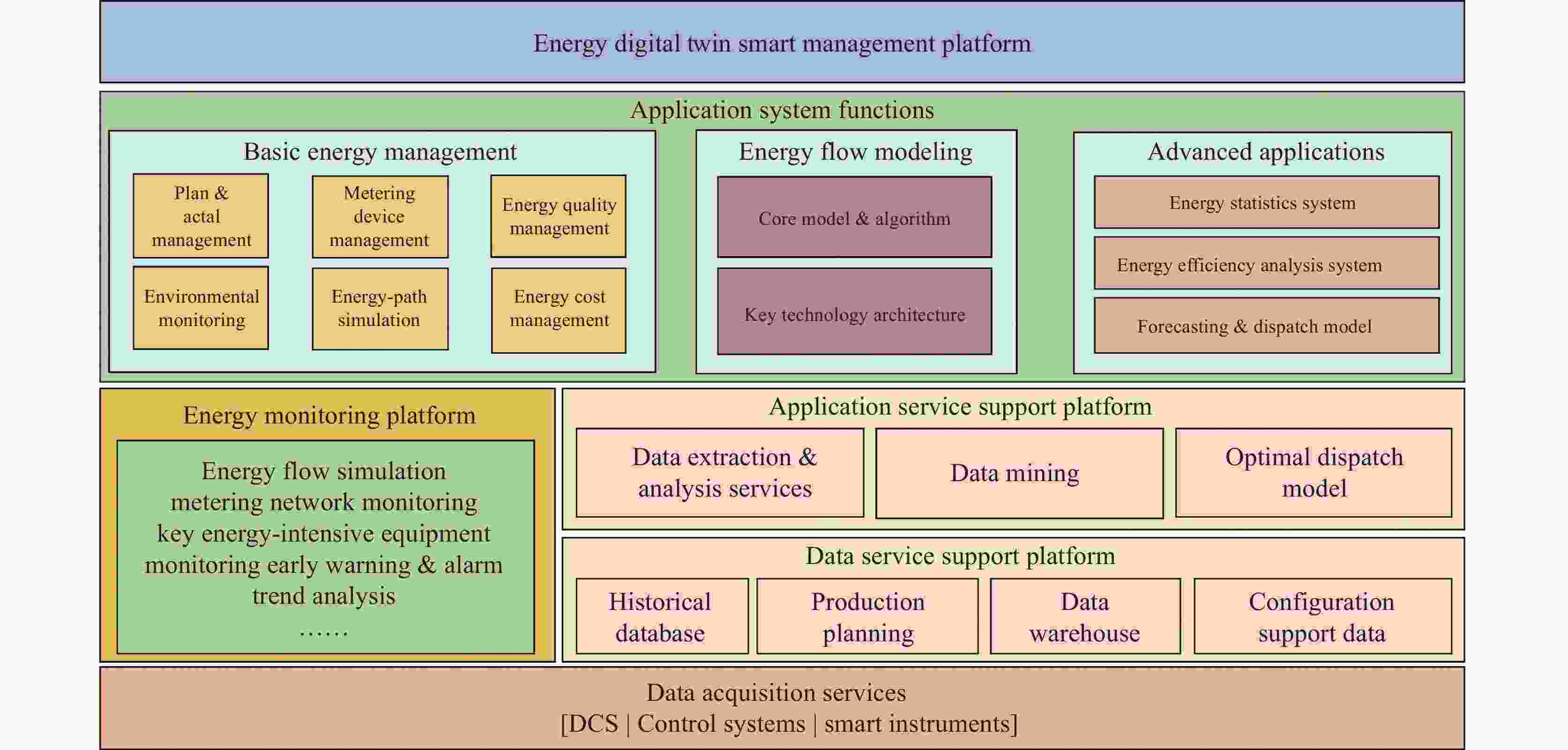
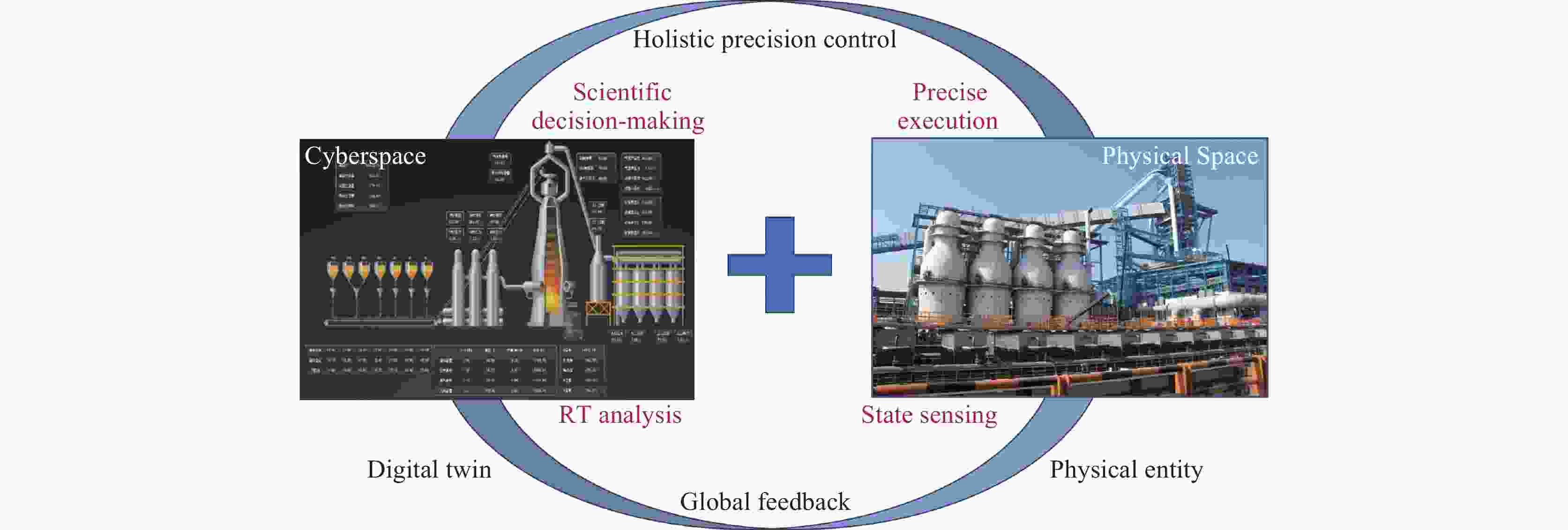
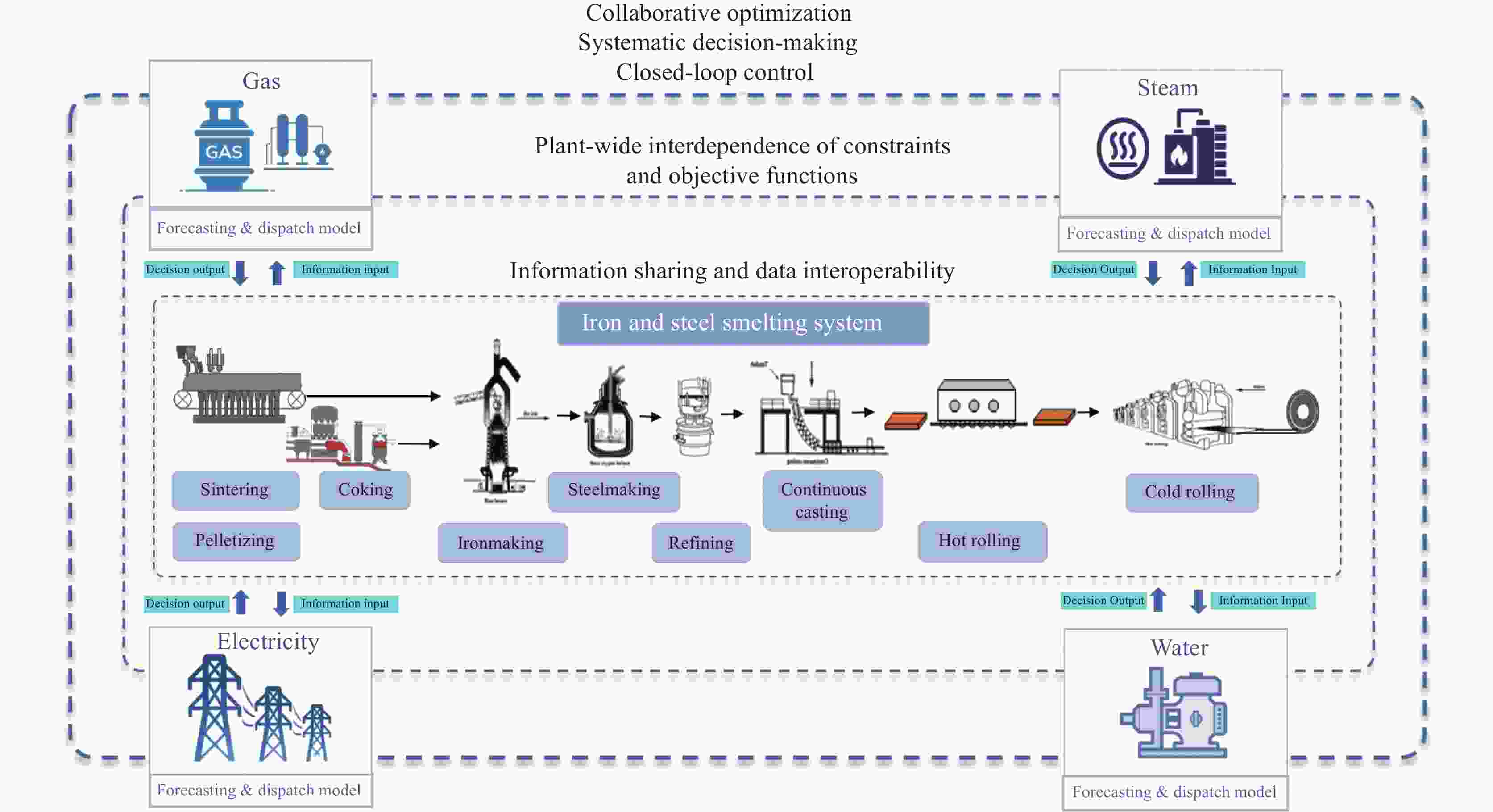
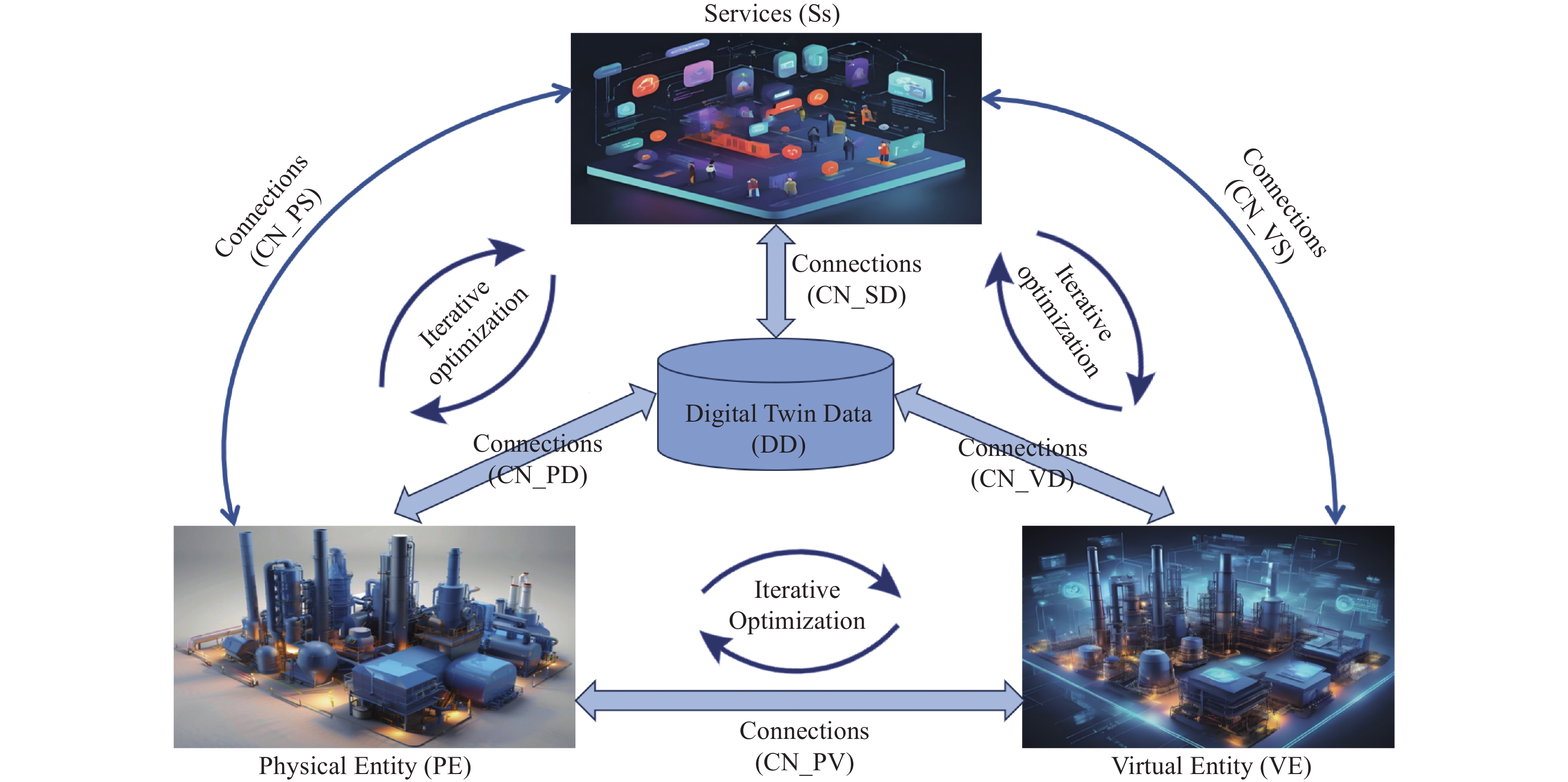
Development and prospect of digital twin technology in vanadium-titanium ore-based iron and steel production process
-
摘要: 钒钛磁铁矿作为战略性资源,其高效冶炼对我国钢铁工业至关重要。钒钛磁铁矿冶炼过程中面临矿中钛元素回收率低、工艺流程智能化程度欠缺、高炉冶炼技术优化难度高、综合能源智慧管理欠缺等问题,影响其产品升级和产能提高。数字孪生技术通过构建虚实融合的智能系统,可助力实现钒钛矿钢铁生产全流程的工艺优化、设备研发和智能控制。目前,相关研究尚处于探索阶段,研究成果较少且缺乏系统性。为此,介绍了数字孪生的内涵与发展历史,系统梳理了数字孪生在钒钛矿钢铁生产流程中的研究热点,总结了相关研究结果与工程实践,展望了数字孪生技术未来的发展趋势,为后续研究人员提供研究思路,以促进数字孪生技术应用,提升我国特色钒钛资源利用与钢铁智能制造水平。Abstract: Vanadium-titanium magnetite, as a strategic resource, its efficient smelting is of vital importance to China's steel industry. During the smelting process of vanadium-titanium magnetite, problems such as low recovery rate of titanium in the ore, insufficient intelligence of the process flow, high difficulty in optimizing blast furnace smelting technology, and lack of comprehensive energy intelligent management are faced, which affect its product upgrading and capacity improvement. Digital twin technology can help achieve process optimization, equipment research and development, and intelligent control throughout the entire production process of vanadium-titanium ore steel by building an intelligent system that integrates the virtual and the real. At present, the relevant research is still in the exploratory stage, with few research achievements and a lack of systematicness. For this purpose, the connotation and development history of digital twins were introduced. The research hotspots of digital twins in the production process of vanadium-titanium ore steel were systematically sorted out. The relevant research results and engineering practices were summarized, and the future development trends of digital twin technology were prospected, providing research ideas for subsequent researchers to promote the application of digital twin technology and enhance the utilization of characteristic vanadium-titanium resources and the intelligent manufacturing level of steel in China.
-
表 1 钢厂多源异构数据来源对比
Table 1. Comparison of multi-source heterogeneous data sources in steel mills
Feature dimension PLC data DCS Data SCADA Data Others Data sources Production-line controllers Distributed control systems Supervisory layer MES/ERP, lab testing Data types Boolean, integer Float, analog Mixed types Structured tables,
unstructured imagesData frequency Milliseconds Seconds-minutes Seconds-hours Minutes-days Typical uses Equipment interlocking
& fault diagnosisProcess parameter optimization Plant-wide visualization,
alarming, reportingQuality traceability
& schedulingData storage Local cache
(circular buffer)Real-time database Relational database Data warehouse/hadoop Communication protocols Modbus, profibus OPC UA, foundation fieldbus OPC DA, TCP/IP HTTP/REST, MQTT Heterogeneity challenges Inconsistent protocols Large volume & time-
series processingMulti-system interface
compatibilityDifficult fusion of structured
& unstructured dataApplication examples
in steel industryRolling-mill E-stop
signals, motor speedDynamic adjustment of BF
hot-metal compositionEnergy dashboard, overall
equipment effectivenessSteel surface-defect
image recognition -
[1] National Bureau of Statistics of China. Statistical communiqué of the People's Republic of China on the 2024 national economic and social development[R/OL]. (2025-02-28) [2025-08-02]. https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202502/t20250228_1958817.html. (国家统计局. 中华人民共和国2024年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[R/OL]. (2025-02-28) [2025-08-02]. https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202502/t20250228_1958817.html.National Bureau of Statistics of China. Statistical communiqué of the People's Republic of China on the 2024 national economic and social development[R/OL]. (2025-02-28) [2025-08-02]. https://www.stats.gov.cn/sj/zxfb/202502/t20250228_1958817.html. [2] World Steel Association. 2024 World Steel in Figures[R/OL]. (2024) [2025-08-03]. https://worldsteel.org/zh-hans/data/world-steel-in-figures/world-steel-in-figures-2024/. (世界钢铁协会. 2024年世界钢铁统计数据[R/OL]. (2024) [2025-08-03]. https://worldsteel.org/zh-hans/data/world-steel-in-figures/world-steel-in-figures-2024/.World Steel Association. 2024 World Steel in Figures[R/OL]. (2024) [2025-08-03]. https://worldsteel.org/zh-hans/data/world-steel-in-figures/world-steel-in-figures-2024/. [3] WANG Y H. Study on reduction mechanism of vanadium oxides in process of smelting V-Ti-magnetite in blast furnace[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2010. (王永红. 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿钒还原机理研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2010.WANG Y H. Study on reduction mechanism of vanadium oxides in process of smelting V-Ti-magnetite in blast furnace[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2010. [4] DU H G. Principle of blast furnace smelting of vanadium-titanium magnetite[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996. (杜鹤桂. 高炉冶炼钒钛磁铁矿原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996.DU H G. Principle of blast furnace smelting of vanadium-titanium magnetite[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996. [5] LI Y Y. Fundamental studies on the pre-concentration and separation of titanium from Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2024. (李有余. 含钛高炉渣中钛预富集分离相关的基础研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2024.LI Y Y. Fundamental studies on the pre-concentration and separation of titanium from Ti-bearing blast furnace slag[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2024. [6] HAN T. Investigation on metallization reduction - electromagnetic separation of vanadium-titanium magnetite in western Liaoning[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2022. (韩通. 辽西钒钛磁铁矿金属化还原−电磁选分研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2022.HAN T. Investigation on metallization reduction - electromagnetic separation of vanadium-titanium magnetite in western Liaoning[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2022. [7] GRIEVES M. Virtually perfect: driving innovative and lean products through product lifecycle management[M]. Florida: Space Coast Press, 2011. [8] SHAFTO M, CONROY M, DOYLE R, et al. Draft modeling, simulation, information technology & processing roadmap[J]. Technology Area, 2010, 11: 1-32. [9] GLAESSGEN E H, STARGEL D S. The digital twin paradigm for future NASA and U. S. air force vehicles[C]. 53rd AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference, Reston, VA: AIAA, 2012. [10] GRIEVES M. Digital twin: Manufacturing excellence through virtual factory replication[R]. 2014. [11] TAO F, LIU W R, ZHANG M, et al. Five-dimension digital twin model and its ten applications[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2019, 25(1): 1-18. (陶飞, 刘蔚然, 张萌, 等. 数字孪生五维模型及十大领域应用[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2019, 25(1): 1-18.TAO F, LIU W R, ZHANG M, et al. Five-dimension digital twin model and its ten applications[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2019, 25(1): 1-18. [12] LUO R P, SHENG B Y, HUANG Y Z, et al. Key technologies and development trends of digital twin-based production system simulation software[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2023, 29(6): 1965-1982. (罗瑞平, 盛步云, 黄宇哲, 等. 基于数字孪生的生产系统仿真软件关键技术与发展趋势[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2023, 29(6): 1965-1982.LUO R P, SHENG B Y, HUANG Y Z, et al. Key technologies and development trends of digital twin-based production system simulation software[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2023, 29(6): 1965-1982. [13] LIN C D, ZHOU T C, ZHANG Y, et al. Research and application of 3D digital twin virtual factory platform for copper smelter[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2021, 45(4): 12-19. (林成东, 周天驰, 张沅, 等. 铜冶炼厂三维数字孪生417虚拟工厂平台研究与应用[J]. 冶金自动化2021, 45(4): 12-19.LIN C D, ZHOU T C, ZHANG Y, et al. Research and application of 3D digital twin virtual factory platform for copper smelter[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2021, 45(4): 12-19. [14] WEN T P, YU J K, JIN E D, et al. A novel electrochemical sensor for phosphorus determination in the high phosphorus liquid iron[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(3): 3530-3536. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.090 [15] Kang J H, Jung S Y. Sensor for the prognostics and health management of multiple impinging jet nozzles[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 2022: 1563–1573. [16] HUSSAIN T, HONG J, SEOK J. A hybrid deep learning and machine learning-based approach to classify defects in hot rolled steel strips for smart manufacturing[J]. Computers, Materials & Continua, 2024, 80(2): 2099-2119. [17] LI Y R, YANG C J, ZHANG H W, et al. Discussion on key technologies of digital twin in process industry[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(3): 501-514. (李彦瑞, 杨春节, 张瀚文, 等. 流程工业数字孪生关键技术探讨[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(3): 501-514.LI Y R, YANG C J, ZHANG H W, et al. Discussion on key technologies of digital twin in process industry[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(3): 501-514. [18] BELLO L L, STEINER W. A perspective on IEEE time-sensitive networking for industrial communication and automation systems[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(6): 1094-1120. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2905334 [19] REIS M J C S, SERÔDIO C. Edge AI for real-time anomaly detection in smart homes[J]. Future Internet, 2025, 17(4): 179. doi: 10.3390/fi17040179 [20] LI H Y, LI X, LIU X J, et al. Industrial internet platforms: Applications in BF ironmaking[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2022, 49(9): 905-916. [21] LIU S H, SUN W Q, LI W D, et al. Prediction of blast furnace gas generation based on data quality improvement strategy[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2023, 30(5): 864-874. doi: 10.1007/s42243-023-00944-2 [22] CAO Q S, BEDEN S, BECKMANN A. A core reference ontology for steelmaking process knowledge modelling and information management[J]. Computers in Industry, 2022, 135: 103574. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2021.103574 [23] XU Y H, YANG C J, LOU S W, et al. Analysis and summary of digital twin in iron and steel industry[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2023, 47(1): 10-23. (许永泓, 杨春节, 楼嗣威, 等. 钢铁行业数字孪生研究现状分析和综述[J]. 冶金自动化, 2023, 47(1): 10-23.XU Y H, YANG C J, LOU S W, et al. Analysis and summary of digital twin in iron and steel industry[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2023, 47(1): 10-23. [24] ZHANG H S, JIANG B Z. Modeling and simulation system of digital factory based on Unity3D[J]. Journal of Henan Science and Technology, 2020, 39(29): 71-74. (张宏帅, 姜宝柱. 基于Unity3D的数字化工厂建模仿真系统[J]. 河南科技, 2020, 39(29): 71-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5168.2020.29.028ZHANG H S, JIANG B Z. Modeling and simulation system of digital factory based on Unity3D[J]. Journal of Henan Science and Technology, 2020, 39(29): 71-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5168.2020.29.028 [25] YILDIZ E, MØLLER C, BILBERG A. Virtual factory: Digital twin based integrated factory simulations[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2020, 96: 216-221. [26] BAMBAUER F, WIRTZ S, SCHERER V, et al. Transient DEM-CFD simulation of solid and fluid flow in a three dimensional blast furnace model[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 334: 53-64. [27] AGIUS D, MAMUN A A, SIMPSON C A, et al. Predictive crystal plasticity finite element model of fatigue-dwells[J], Computational Materials Science, 2020, 183: 109823. [28] LIU C, WANG S, ZHOU W, et al. Research of integrated scheduling method of steelmaking-continuous casting-hot rolling[J]. Manufacturing Automation, 2015, 37(9): 81-83, 86. (刘超, 王森, 周维, 等. 炼钢-连铸-热轧一体化生产计划排程方法研究[J]. 制造业自动化, 2015, 37(9): 81-83, 86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0134.2015.09.022LIU C, WANG S, ZHOU W, et al. Research of integrated scheduling method of steelmaking-continuous casting-hot rolling[J]. Manufacturing Automation, 2015, 37(9): 81-83, 86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0134.2015.09.022 [29] ZHANG T, ZHOU F, J. ZHAO J, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for secondary energy scheduling in steel industry[C]. 2020 2nd International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence (AI), Shenyang, China, 2020: 1-5. [30] LIU S H, SUN W Q. Knowledge- and data-driven prediction of blast furnace gas generation and consumption in iron and steel sites[J]. Applied Energy, 2025, 399: 125819. [31] LIN Z W, ZHANG Y Z, CHEN C H, et al. Multi-process digital twin closed-loop machining through shape-feature state update and error propagation knowledge graph[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2025, 65: 103403. doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2025.103403 [32] ZHANG K N, TSANG Y P, LEE C K M, et al. Integrating large language models with explainable fuzzy inference systems for trusty steel defect detection[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2025, 192: 29-35. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2025.03.017 [33] SUN W Q, WANG Z H, WANG Q. Hybrid event-, mechanism- and data-driven prediction of blast furnace gas generation[J]. Energy, 2020, 199: 117497. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.117497 [34] ZHANG X, WANG J C, ZHANG B B, et al. Research on data-driven continuous casting billet quality prediction modeling approach[C]. 2024 4th International Conference on Electronic Information Engineering and Computer Communication (EIECC), Wuhan, China, 2024: 1429-1433. [35] ZAPPULLA M L S, CHO S, KORIC S, et al. Multiphysics modeling of continuous casting of stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020, 278: 116469. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116469 [36] MELOUK S H, FREEMAN N K, MILLER D, et al. Simulation optimization-based decision support tool for steel manufacturing[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2013, 141(1): 269-276. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2012.08.001 [37] FANG X Q, LIU S H, SUN W Q. Hydraulic modelling and scheduling scheme of blast furnace gas pipeline network[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2023, 44(1): 69-75. (房晓晴, 刘书含, 孙文强. 高炉煤气管网水力建模及调度策略[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(1): 69-75. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2023.01.010FANG X Q, LIU S H, SUN W Q. Hydraulic modelling and scheduling scheme of blast furnace gas pipeline network[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2023, 44(1): 69-75. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2023.01.010 [38] HONG T Y, CHEN C A, CHIEN C F. Towards sustainable production with resource efficiency: An empirical study of steelmaking continuous casting scheduling[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2024, 209: 107806. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2024.107806 [39] Industry and Information Technology Department of Hunan Province. The implementation plan for the construction of new materials pilot platform (Base) in Hunan Province[Z]. Raw Materials Industry Division, Industry and Information Technology Department of Hunan Province [2023] No. 22, (2023-01-17) [2025-08-02]. http://gxt.hunan.gov.cn/gxt/xxgk_71033/zcfg/gfxwj/202401/t20240118_32628741.html. (湖南省工业和信息化厅. 湖南省新材料中试平台(基地)建设实施方案[Z]. 湘工信原材料[2023]22号, (2023-01-17) [2025-08-02]. http://gxt.hunan.gov.cn/gxt/xxgk_71033/zcfg/gfxwj/202401/t20240118_32628741.html.Industry and Information Technology Department of Hunan Province. The implementation plan for the construction of new materials pilot platform (Base) in Hunan Province[Z]. Raw Materials Industry Division, Industry and Information Technology Department of Hunan Province [2023] No. 22, (2023-01-17) [2025-08-02]. http://gxt.hunan.gov.cn/gxt/xxgk_71033/zcfg/gfxwj/202401/t20240118_32628741.html. [40] DONG X S, RAO J T, ZHENG K. Simulation of operation inner profile of blast furnace with smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2024, 45(3): 121-130, 154. (董晓森, 饶家庭, 郑魁. 冶炼钒钛矿高炉操作炉型计算模拟研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2024, 45(3): 121-130, 154. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2024.03.017DONG X S, RAO J T, ZHENG K. Simulation of operation inner profile of blast furnace with smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2024, 45(3): 121-130, 154. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2024.03.017 [41] YANG Q. The static model of oxygen converter devanadium[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2002. (杨旗. 转炉提钒静态模型研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2002.YANG Q. The static model of oxygen converter devanadium[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2002. [42] GAO Z B. Research and application of intelligent production control technology of converter based on digital twin[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2024. (高志滨. 基于数字孪生的转炉智能生产控制技术研究与应用[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2024.GAO Z B. Research and application of intelligent production control technology of converter based on digital twin[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2024. [43] GAO S Z, XUE Y J. Construction practice of digital factory in iron and steel enterprises[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2022, 46(4): 38-45. (高士中, 薛颖健. 钢铁企业数字化工厂建设实践[J]. 冶金自动化, 2022, 46(4): 38-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7059.2022.04.005GAO S Z, XUE Y J. Construction practice of digital factory in iron and steel enterprises[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2022, 46(4): 38-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7059.2022.04.005 [44] MA L Y. Research on the impact of digital transformation on the international competitiveness of steel industry enterprises[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics, 2025. (马丽云. 数字化转型对钢铁行业企业国际竞争力的影响研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州财经大学, 2025.MA L Y. Research on the impact of digital transformation on the international competitiveness of steel industry enterprises[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics, 2025. [45] ZHANG Q, LIU S, XU H Y, et al. Development and practice of smart energy management and control system in iron and steel works[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019, 54(10): 125-133. (张琦, 刘帅, 徐化岩, 等. 钢铁企业智慧能源管控系统开发与实践[J]. 钢铁, 2019, 54(10): 125-133.ZHANG Q, LIU S, XU H Y, et al. Development and practice of smart energy management and control system in iron and steel works[J]. Iron and Steel, 2019, 54(10): 125-133. [46] LIU X M, LU M, LIU X, et al. Prediction of coal demand of pellet rotary kilns[J]. Energy for Metallurgical Industry, 2024, 43(2): 30-35. (刘新民, 路明, 刘旭, 等. 球团回转窑煤粉供入量预测[J]. 冶金能源, 2024, 43(2): 30-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1617.2024.02.007LIU X M, LU M, LIU X, et al. Prediction of coal demand of pellet rotary kilns[J]. Energy for Metallurgical Industry, 2024, 43(2): 30-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1617.2024.02.007 [47] BAI P. Prediction technique research on blast furnace gas in iron and steel enterprise[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Technology, 2016. (白鹏. 钢铁企业高炉煤气预测技术研究[D]. 天津: 天津理工大学, 2016.BAI P. Prediction technique research on blast furnace gas in iron and steel enterprise[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Technology, 2016. [48] LIU S H, SUN W Q, SHI X X, et al. Prediction of gas consumption of a hot blast stove group based on BP neutral network[J]. Chinese Metallurgy, 2022, 32(2): 77-83. (刘书含, 孙文强, 石晓星, 等. 基于BP神经网络的热风炉群煤气消耗量预测[J]. 中国冶金, 2022, 32(2): 77-83.LIU S H, SUN W Q, SHI X X, et al. Prediction of gas consumption of a hot blast stove group based on BP neutral network[J]. Chinese Metallurgy, 2022, 32(2): 77-83. [49] LIU S H, SUN W Q, FAN T J, et al. A hybrid event-driven and data-driven method for predicting the gas consumption of reheating furnaces[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2021, 20(4): 304-309. (刘书含, 孙文强, 范天骄, 等. 事件和数据融合的加热炉煤气消耗量预测方法[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2021, 20(4): 304-309.LIU S H, SUN W Q, FAN T J, et al. A hybrid event-driven and data-driven method for predicting the gas consumption of reheating furnaces[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2021, 20(4): 304-309. [50] KIM J H, YI H S, HAN C. A Novel MILP Model for Plantwide Multiperiod Optimization of Byproduct Gas Supply System in the Iron- and Steel-Making Process[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2003, 19(8): 1015-1025. [51] ZHAO L, ZHANG D K. Construction and application of JISCO digital twin platform visualization intelligent system in pipeline network control process[J]. China Steel, 2025(2): 22-25. (赵亮, 张得科. 酒钢数字孪生平台可视化智能系统在管网管控过程中的建设与应用[J]. 中国钢铁业, 2025(2): 22-25.ZHAO L, ZHANG D K. Construction and application of JISCO digital twin platform visualization intelligent system in pipeline network control process[J]. China Steel, 2025(2): 22-25. [52] LIU X M, SUN W Q, CHEN T T, et al. Energy and environmental performance of iron and steel industry in real-time demand response: A case of hot rolling process[J]. Applied Energy, 2025, 389: 125717. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2025.125717 [53] CAI J J, SUN W Q, YUE Q, et al. Energy consumption and efficiency analysis, and CO2 emission assessment of typical iron and steel production routes[J]. Iron and Steel, 2025, 60(7): 59-70. (蔡九菊, 孙文强, 岳强, 等. 典型钢铁流程能耗能效分析及其碳排放评价[J]. 钢铁, 2025, 60(7): 59-70.CAI J J, SUN W Q, YUE Q, et al. Energy consumption and efficiency analysis, and CO2 emission assessment of typical iron and steel production routes[J]. Iron and Steel, 2025, 60(7): 59-70. -




 下载:
下载: