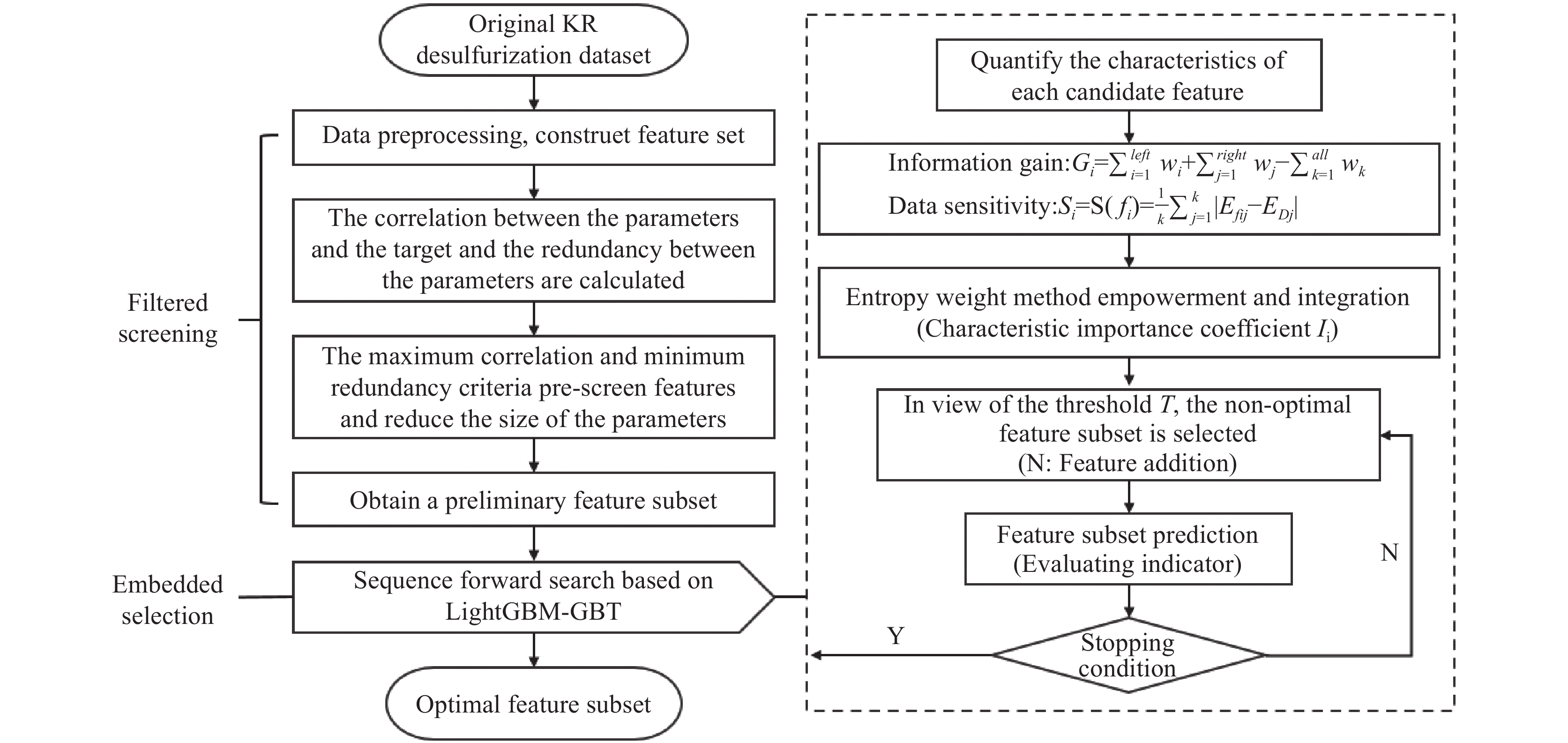
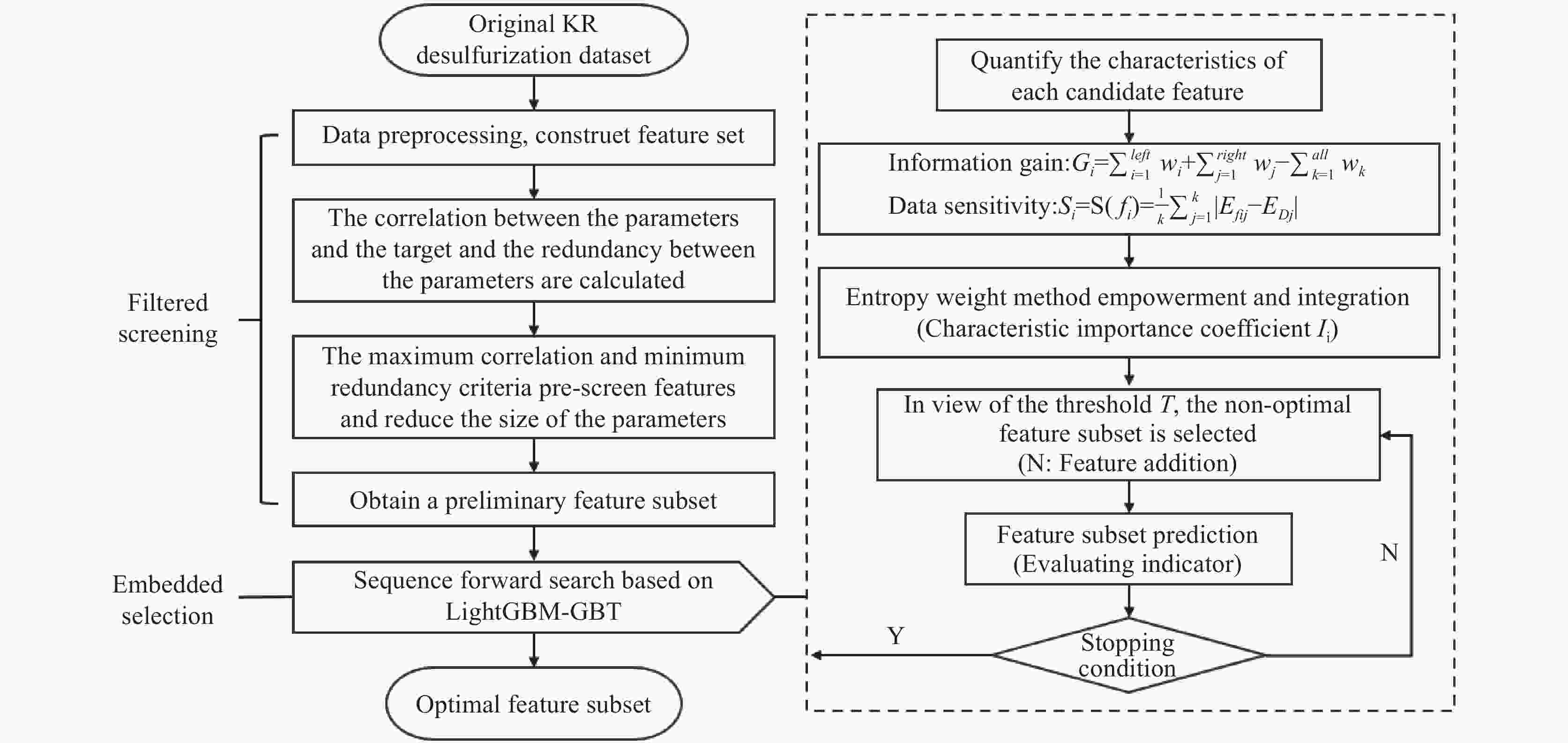
A feature selection method for desulfurizer addition prediction based on importance measure
-
摘要: 针对铁水KR脱硫生产工序中参数维度高、特征冗余性强以及目标变量与特征间相关性较弱的问题,提出了一种基于重要性度量的集成式特征选择方法IMFS(Feature selection based on importance measure)。在过滤式预筛选阶段,通过最大互信息系数(MIC)度量各参数与目标变量的关联性以及各参数之间冗余性,并根据最大相关、最小冗余准则缩小候选参数规模;在嵌入式精选阶段,引入LightGBM算法作为量化信息贡献度与数据敏感度的依托模型,采用熵权法对双重度量结果进行赋权融合;最后,根据特征重要性系数,结合GBT序列向前搜索策略优化特征子集。试验结果表明,IMFS相较于其他方法,在消除冗余特征和提升预测准确性方面具有显著优势,并且能够有效平衡特征数量与预测精度。Abstract: Aiming at the problems of high parameter dimension, strong feature redundancy and weak correlation between target variables and features in hot metal KR desulfurization production process, an integrated feature selection method IMFS (Feature selection based on importance measure) based on importance measure is proposed. In the filtering pre-screening stage, the maximal mutual information coefficient ( MIC ) is used to measure the correlation between each parameter and the target variable, as well as the redundancy among each parameter, and the scale of candidate parameters is reduced according to the maximum relevance and minimal redundancy criteria. In the embedded selection stage, the LightGBM algorithm is introduced as the supporting model for quantifying information contribution and data sensitivity, and the entropy weight method is used to weight and fuse the dual measurement results. Finally, according to the feature importance coefficient, the feature subset is optimized by combining the GBT sequential forward search strategy. The experimental results show that compared with other methods, IMFS has significant advantages in eliminating redundant features and improving prediction accuracy, and can effectively balance the number of features and prediction accuracy.
-
Key words:
- desulfurizer addition /
- feature selection /
- importance coefficient /
- double metric /
- search strategy
-
表 1 序列向前搜索过程
Table 1. Sequence forward search process
Iteration times Current subset Evaluation number
$ ({a}_{0} > {a}_{1} > {a}_{2} > {a}_{3}) $Optimal subset 1 Satisfy characteristic$ {f}_{i} $ $ {a}_{3} $ $ {f}_{1}{f}_{2} $ 2 $ {f}_{1}{f}_{2}{f}_{3} $ $ {a}_{2} $ $ {f}_{1}{f}_{2}{f}_{4} $ $ {f}_{1}{f}_{2}{f}_{4} $ $ {a}_{0} $ $ {f}_{1}{f}_{2}{f}_{5} $ $ {a}_{1} $ 3 $ {f}_{1}{f}_{2}{f}_{3}{f}_{4} $ $ {a}_{2} $ $ Stop\left({f}_{1}{f}_{2}{f}_{4}\right) $ $ {f}_{1}{f}_{2}{f}_{4}{f}_{5} $ $ {a}_{1} $ 表 2 某钢厂脱硫工艺数据实例
Table 2. An example of desulfurization process data in a steel plant
Number Steel grade Class Group Mixing
speed/(r·min−1)… Process
duration/min1 M2A4-2 2 1 68 … 34 2 SPHC(MD) 2 4 75 … 33 3 B(H) 1 4 70 … 25 … … … … … … … 6650 H2B1-1 B 1 1 65 … 29 … … … … … … … 12670 B(H1) 2 4 74 … 31 表 3 部分工艺参数统计分析
Table 3. Analysis of statistical indexes of some process parameters
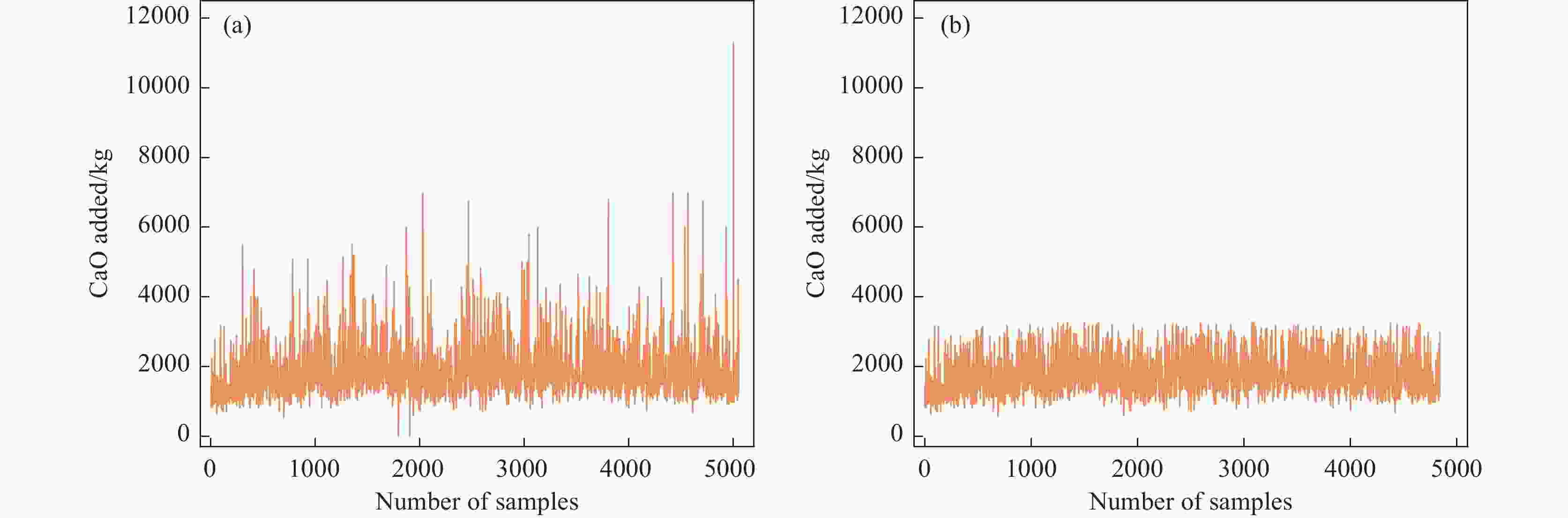
Statistics Temperature/℃ S content/% Si content/% Mixing speed/(r·min−1) Depth/mm CaO added/kg Metal quality/kg Before Range 1211 ~1471 0.005~0.540 0.030~1.600 5~110 4200 ~5040 5~ 11305 135700 ~401800 Median 1362 0.036 0.386 74 4590 1690.5 254600 Average 1360 0.041 0.403 71.8 4587 1858.7 253758 Standard 32.3 0.022 0.161 9.1 214 724.8 11840.6 After Range 1281 ~1443 0.005~0.070 0.057~0.752 49~95 4200 ~5040 550~ 3272 227300 ~278200 Median 1363 0.036 0.387 74 4591 1661 254800 Average 1362 0.037 0.395 71.9 4588 1751.6 254068 Standard 29.8 0.012 0.126 8.9 214 493.8 9810.7 表 4 特征敏感性评估表
Table 4. Feature sensitivity assessment
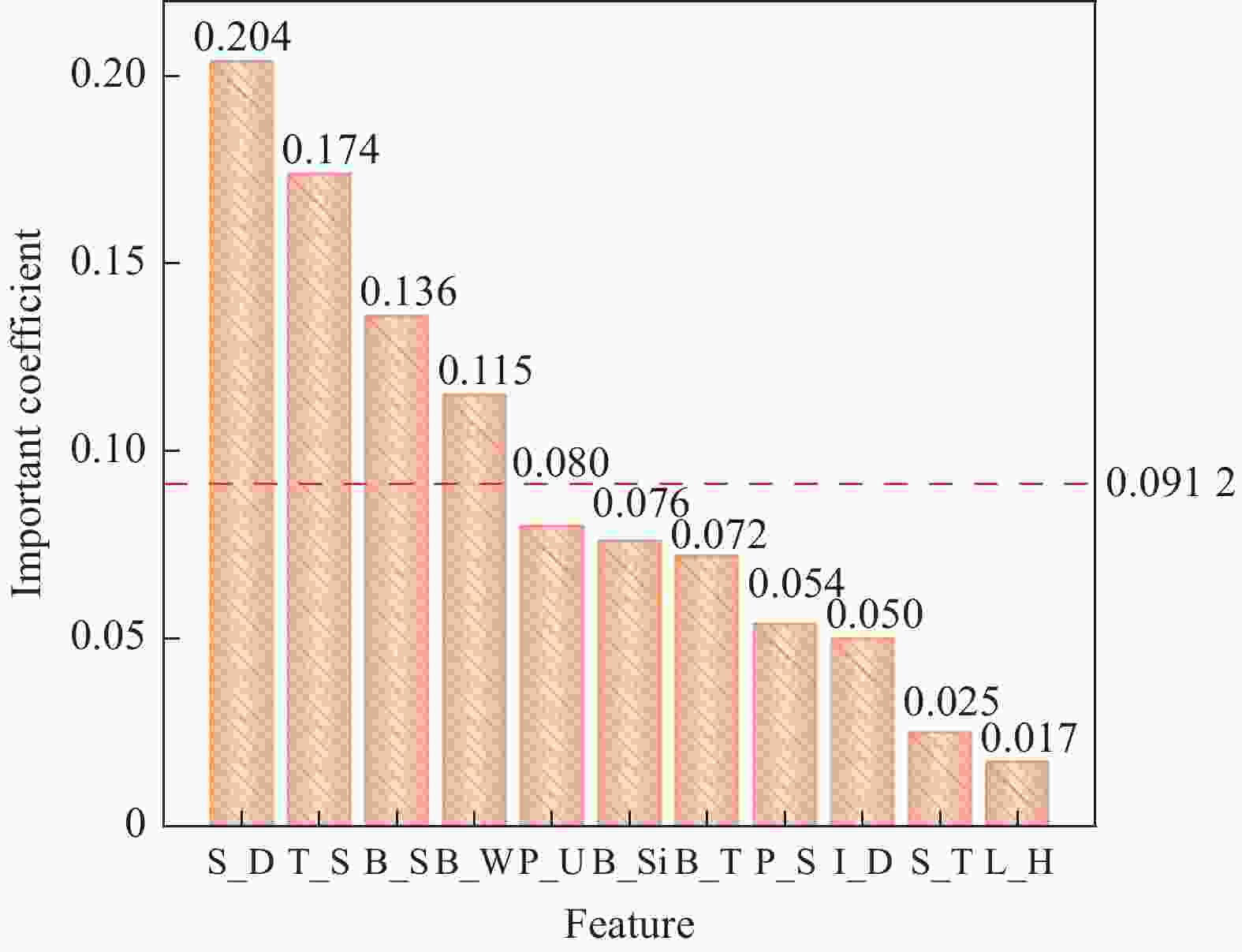
Feature $ {S}_{i} $ Feature $ {S}_{i} $ Feature $ {S}_{i} $ B_T 5.07 S_T 1.84 B_W 7.66 B_S 6.75 P_S 3.41 T_S 15.45 B_Si 6.07 I_D 4.38 S_D 9.04 P_U 4.19 L_H 1.10 表 5 特征子集评价表
Table 5. Feature subset evaluation
Optimal composition R2 RMSE MAE S_D、T_S、B_S、B_W 0.8990 162.1303 114.7563 S_D、T_S、B_S、B_W、P_U 0.9075 159.5028 111.7163 S_D、T_S、B_S、B_W、P_U、B_Si 0.9075 155.1069 109.3095 S_D、T_S、B_S、B_W、P_U、B_Si、
B_T0.9107 152.4032 107.4982 S_D、T_S、B_S、B_W、P_U、B_Si、
B_T、I_D0.9073 155.3352 109.3237 S_D、T_S、B_S、B_W、P_U、B_Si、
B_T、I_D、P_S0.8973 163.4473 114.9965 S_D、T_S、B_S、B_W、P_U、B_Si、
B_T、I_D、P_S、L_H0.9022 155.1182 108.8067 S_D、T_S、B_S、B_W、P_U、B_Si、
B_T、I_D、P_S、L_H、S_T0.8978 163.0450 115.7291 表 6 不同特征选择方法所选特征
Table 6. Features selected by different feature selection methods
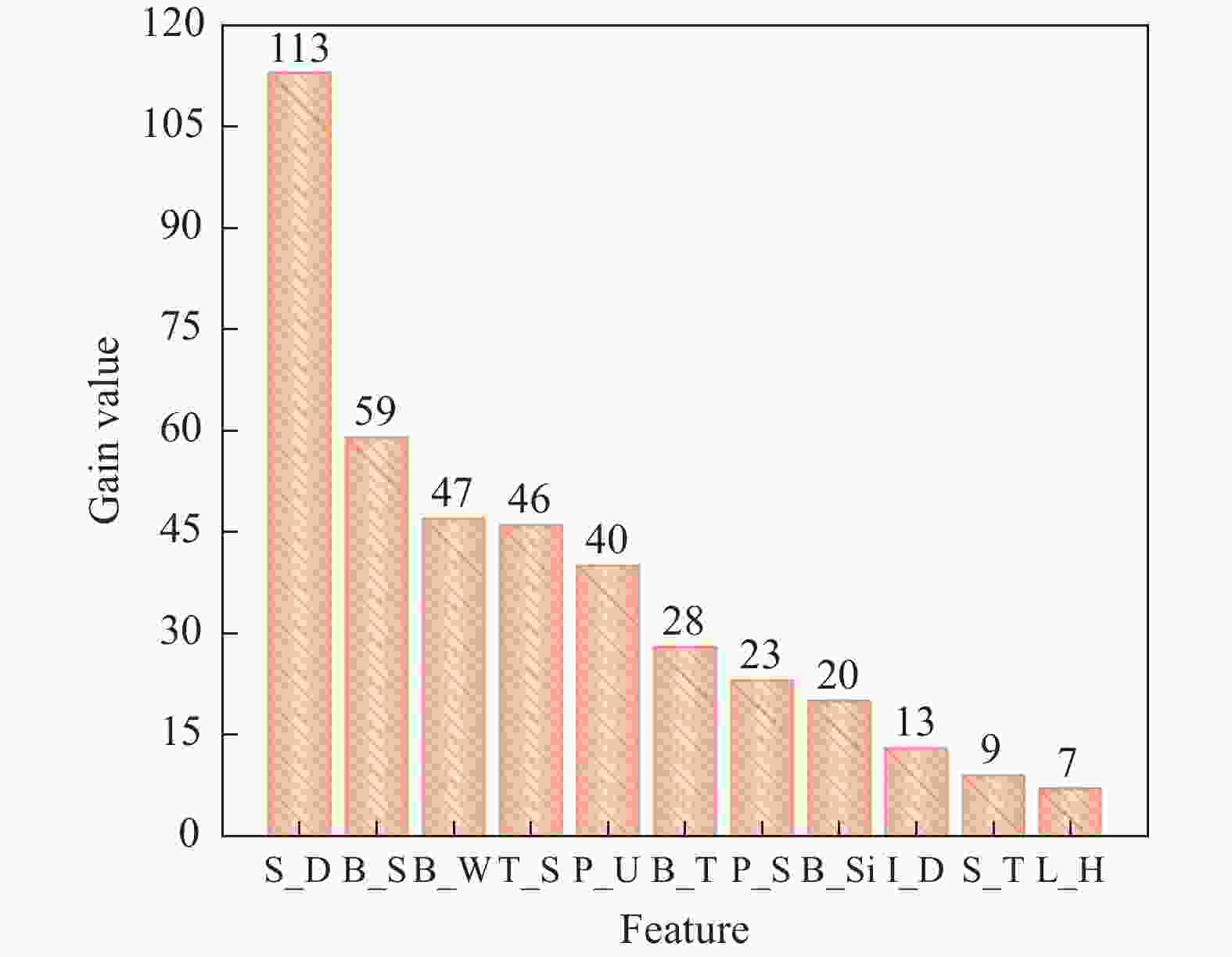
Method Feature subset Pearson S_D、B_S、T_S、L_H Spearman B_T、B_S、B_Si、T_S、B_W、L_H MIC B_S、B_W、B_Si、B_T、T_S、L_H、P_U LightGBM S_D、B_S、B_W、T_S、P_U、B_T、P_S、B_Si、I_D IMFS S_D、T_S、B_S、B_W、P_U、B_Si、B_T 表 7 模型超参数设置
Table 7. Super parameter setting of the model
KNN DNN RF XGBoost SVR K Batch_size Lr Epochs N_estimators Max_depth N_estimators Lr Kernel Degree Coef0 5 32 0.01 320 100 10 100 0.1 poly 3 1.0 表 8 传统特征选择方法对脱硫剂加入量预测的评价结果
Table 8. Evaluation results of the traditional feature selection method for the prediction of desulfurizer addition
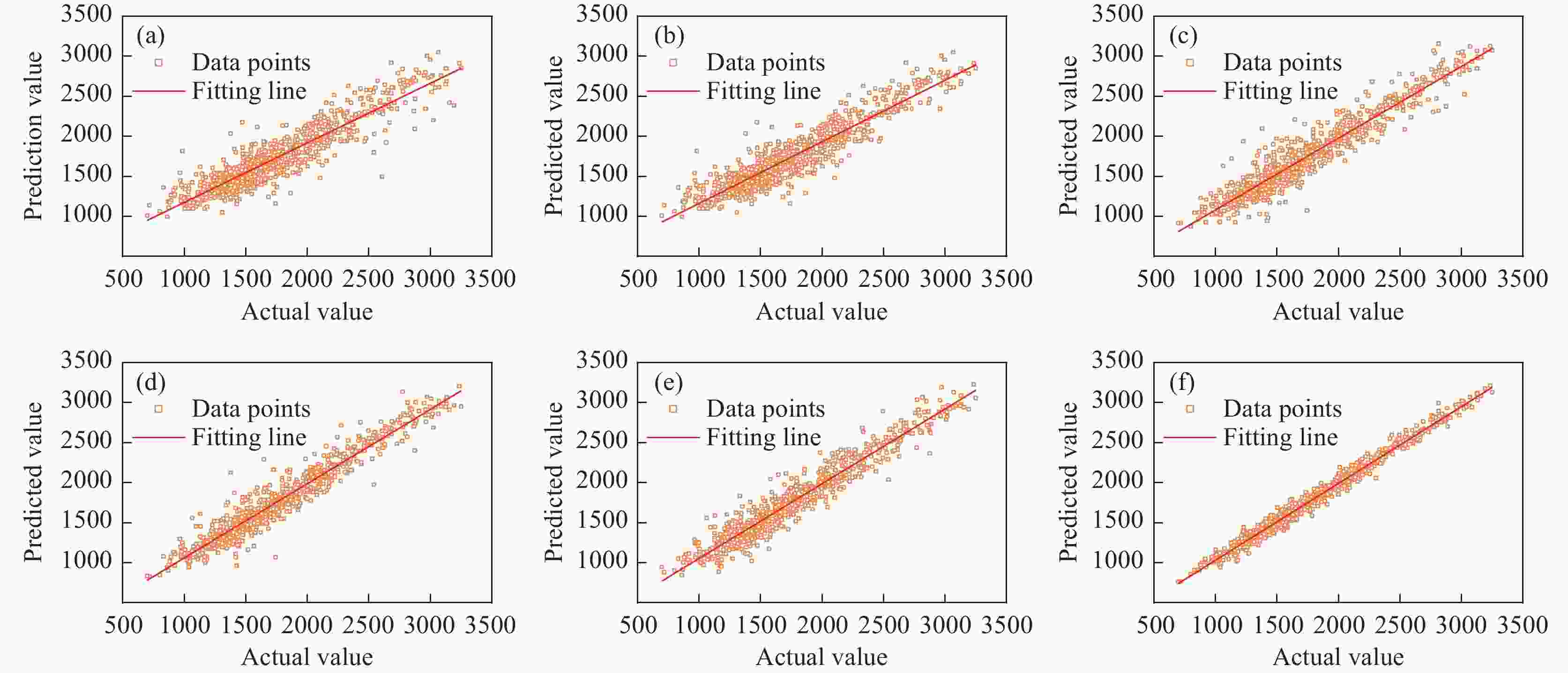
Method Model R2 RMSE MAE t/s Pearson KNN 0.869 187.48 156.66 0.085 DNN 0.879 185.39 150.68 0.086 RF 0.893 163.96 133.29 1.378 XGBoost 0.884 175.86 148.28 0.133 SVR 0.881 177.17 149.36 2.128 Spearman KNN 0.865 191.24 160.53 0.012 DNN 0.881 183.4 147.92 0.097 RF 0.891 167.37 133.52 1.554 XGBoost 0.889 170.77 139.25 0.152 SVR 0.883 174.76 146.34 2.374 MIC KNN 0.856 203.51 174.35 0.013 DNN 0.894 167.73 134.07 0.103 RF 0.893 164.48 132.12 1.815 XGBoost 0.883 184.24 148.37 0.143 SVR 0.889 169.77 138.53 2.43 LightGBM KNN 0.873 182.01 153.25 0.018 DNN 0.897 163.55 131.82 0.113 RF 0.896 161.26 130.64 2.092 XGBoost 0.894 162.73 130.88 0.15 SVR 0.899 156.17 127.35 2.384 IMFS KNN 0.884 167.97 146.44 0.013 DNN 0.908 152.58 118.41 0.103 RF 0.912 144.65 113.86 1.754 XGBoost 0.913 142.79 112.34 0.145 SVR 0.897 158.96 126.48 2.843 All features KNN 0.729 330.98 298.47 0.216 DNN 0.773 287.17 254.38 0.137 RF 0.770 290.71 257.17 2.482 XGBoost 0.765 297.22 263.29 0.178 SVR 0.787 271.56 239.36 3.895 表 9 深度学习特征提取方法的预测性能
Table 9. Prediction performance of deep learning feature extraction methods
Algorithm Optimizer Batch size Lr Epochs R2 RMSE MAE ANN Adam 64 0.01 500 0.84 203.64 129.60 GRNN 1.0 0.82 215.77 156.01 1D-CNN Adam 32 0.005 800 0.86 182.80 133.32 -
[1] GAO J, CUI L, WANG W, et al. Prediction of sulfur content during steel refining process based on machine learning methods[J]. Steel Research International, 2024, 96(3): 2400662-2400662. [2] GONG H J, LIANG X T, ZHOU Z C, et al. Application of rotary injection desulfurization technology in hot metal pretreatment[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(1): 173-178. (龚洪君, 梁新腾, 周遵传, 等. 旋转喷吹脱硫技术在铁水预处理上的应用研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020, 41(1): 173-178. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.01.030GONG H J, LIANG X T, ZHOU Z C, et al. Application of rotary injection desulfurization technology in hot metal pretreatment[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(1): 173-178. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.01.030 [3] ADHIWIGUNA IBGS, KARAGÜLMEZ G, KESKIN O, et al. Investigation on applicability of lime as desulfurization agent for molten cast iron[J]. Steel Research International, 2025, 96(1): 2400416. [4] ZHENG Y, ZUO K L. Prediction model of desulfurizer consumption based on BP neural network and regression[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017, 38(4): 130-134. (郑毅, 左康林. 基于BP神经网络和回归的脱硫粉剂预报模型[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2017, 38(4): 130-134. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.04.023ZHENG Y, ZUO K L. Prediction model of desulfurizer consumption based on BP neural network and regression[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2017, 38(4): 130-134. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2017.04.023 [5] LIU Z X, DU J Q, LUO J G, et al. Review on stability feature selection[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2025, 61(7): 81-95. (刘梓萱, 杜建强, 罗计根, 等. 稳定性特征选择研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2025, 61(7): 81-95. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2406-0410LIU Z X, DU J Q, LUO J G, et al. Review on stability feature selection[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2025, 61(7): 81-95. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2406-0410 [6] WANG N, LI X F, NIE L D, et al. High-precision vehicle energy consumption prediction using mutual information feature selection[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2024, 52(S1): 39-45. (王宁, 李秀峰, 聂辽栋, 等. 基于MI特征选择的车辆能耗高精度预测方法[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(S1): 39-45. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.24794WANG N, LI X F, NIE L D, et al. High-precision vehicle energy consumption prediction using mutual information feature selection[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2024, 52(S1): 39-45. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.24794 [7] YAN X M, CHEN C, WANG N, et al. Prediction of desulfurization rate during LF refining process based on random search and AdaBoost model[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2023, 22(5): 430-436, 443. (严旭梅, 陈超, 王楠, 等. 基于随机搜索算法和AdaBoost模型预测LF精炼过程脱硫率[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2023, 22(5): 430-436, 443.YAN X M, CHEN C, WANG N, et al. Prediction of desulfurization rate during LF refining process based on random search and AdaBoost model[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2023, 22(5): 430-436, 443. [8] FANG Y F, DAN B B, WU J W, et al. Method for predicting desulfurizer dosage based on ensemble learning[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2024, 47(5): 361-367. (方一飞, 但斌斌, 吴经纬, 等. 基于集成学习的脱硫剂加入量预测方法[J]. 武汉科技大学学报, 2024, 47(5): 361-367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3644.2024.05.006FANG Y F, DAN B B, WU J W, et al. Method for predicting desulfurizer dosage based on ensemble learning[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2024, 47(5): 361-367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3644.2024.05.006 [9] XU M, LEI H, HE J Y, et al. Predicting the endpoint steel temperature of RH refining using improved XGBoost[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2023, 22(5): 437-443. (徐猛, 雷洪, 何江一, 等. 利用改进XGBoost预测RH精炼终点钢水温度[J]. 材料与冶金学报, 2023, 22(5): 437-443.XU M, LEI H, HE J Y, et al. Predicting the endpoint steel temperature of RH refining using improved XGBoost[J]. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2023, 22(5): 437-443. [10] GU T Y, GUO J S, LI Z X, et al. Detecting associations based on the multi-variable maximum information coefficient[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 54912-54922. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3070925 [11] JU Y, SUN G Y, CHEN Q H, et al. A model combining convolutional neural network and LightGBM algorithm for ultra-short-term wind power forecasting[J]. IEEE Access, 2019: 28309-28318. [12] LI Y Z, DAI W, ZHANG W F. Bearing fault feature selection method based on weighted multidimensional feature fusion[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 19008-19025. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2967537 [13] ZHANG S G, ZHOU T, SUN L, et al. v-Support vector regression model based on Gauss-Laplace mixture noise characteristic for wind speed prediction[J]. Entropy, 2019, 21(11): 1056. -




 下载:
下载: