Study on performance of Machine-Learning-Based prediction model for slab reheating furnaces
-
摘要: 基于国内某钢铁厂1 450 mm热连轧加热炉生产线采集的
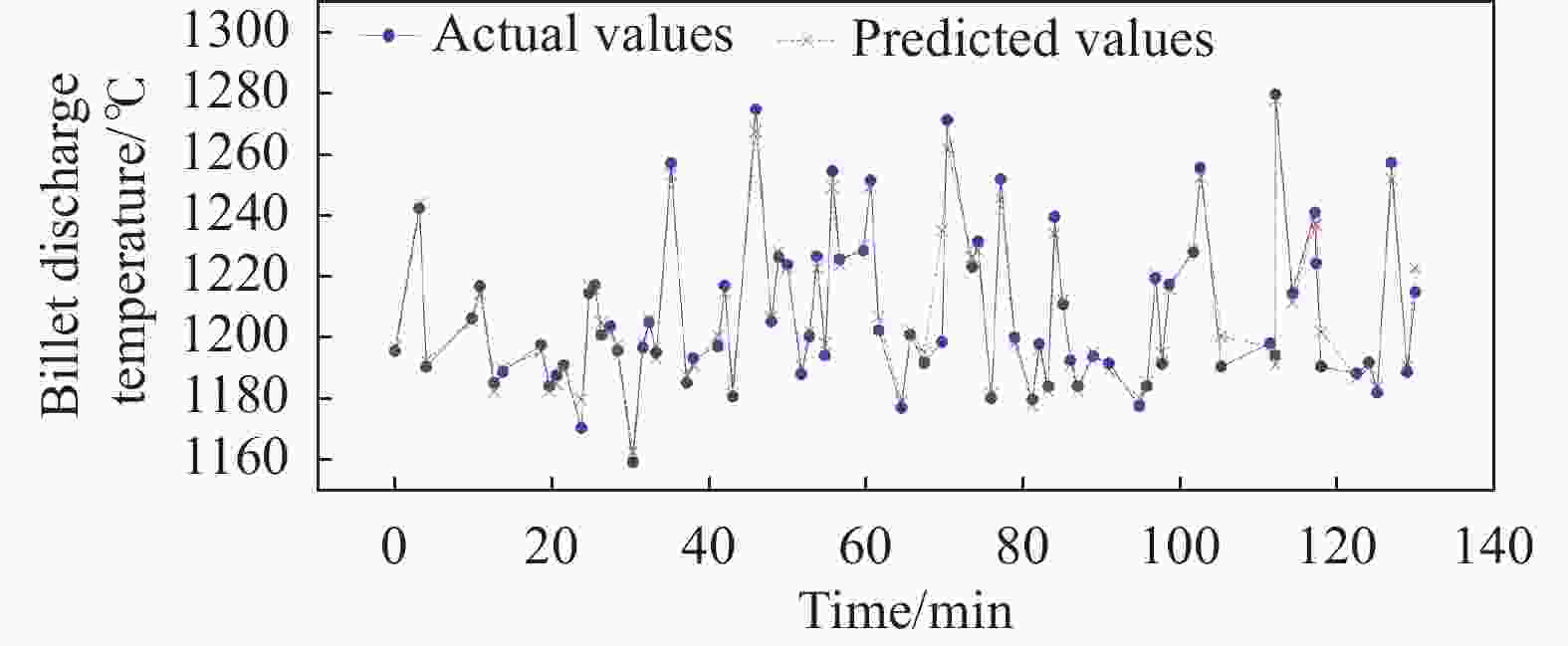
8297 组数据,建立了四组不同输入变量的XGBoost和LSTM模型,对出炉钢温、单耗和烧损进行了预测和比较分析。结果表明,LSTM模型在出炉钢温和烧损的预测中表现出色,决定系数R2均超过0.95,预测精度和稳定性均较高;而XGBoost模型在单耗预测方面表现优异,决定系数达0.94以上变化趋势稳定。通过对比分析得出,LSTM在出炉钢温和烧损的预测中具有更高的可靠性,而XGBoost在单耗预测上精度更高。研究还显示,LSTM因门控机制擅长捕捉时序依赖(如钢温、烧损),而XGBoost通过特征组合优化对静态参数(如单耗)更敏感。将两种模型联合建模构建LSTM-XGBoost联合模型,分别处理时序特征与静态特征,应用于加热炉工艺控制,可进一步提升出炉钢温、单耗和烧损的预测精度,为钢铁行业加热工艺的优化控制和资源的高效利用提供了理论支持与数据依据。Abstract: Based on8297 data samples from a1450 mm hot-strip mill reheating furnace in a Chinese steel plant, XGBoost and LSTM models using four sets of input variables had been developed and used to predict furnace discharge temperature, energy consumption of per ton steel, and oxidation burn rate. It was found out that the LSTM model performed well in predicting furnace discharge temperature and oxidation burn rate, with coefficients of determination (R2) exceeding 0.95. The XGBoost model was superior in predicting energy consumption, achieving R2 values above 0.94 and stable prediction trends. Comparative analysis indicated that LSTM was more reliable for predicting time-dependent parameters (such as discharge temperature and oxidation burn), while XGBoost provided higher accuracy for static parameters (such as energy consumption). Further investigation revealed that LSTM effectively captures time-related patterns due to its gated mechanism. In contrast, XGBoost performed better on static features due to its ability to optimize feature combinations. Based on these findings, a hybrid LSTM-XGBoost model was proposed. In this combined model, LSTM deals with time-series data, and XGBoost processes static data. Applying the combined model to furnace control can further improve prediction accuracy. This study provides theoretical guidance and data support for optimizing reheating furnace operations and enhancing resource efficiency in the steel industry.-
Key words:
- hot strip rolling /
- reheating furnace /
- machine learning /
- heating-process optimization
-
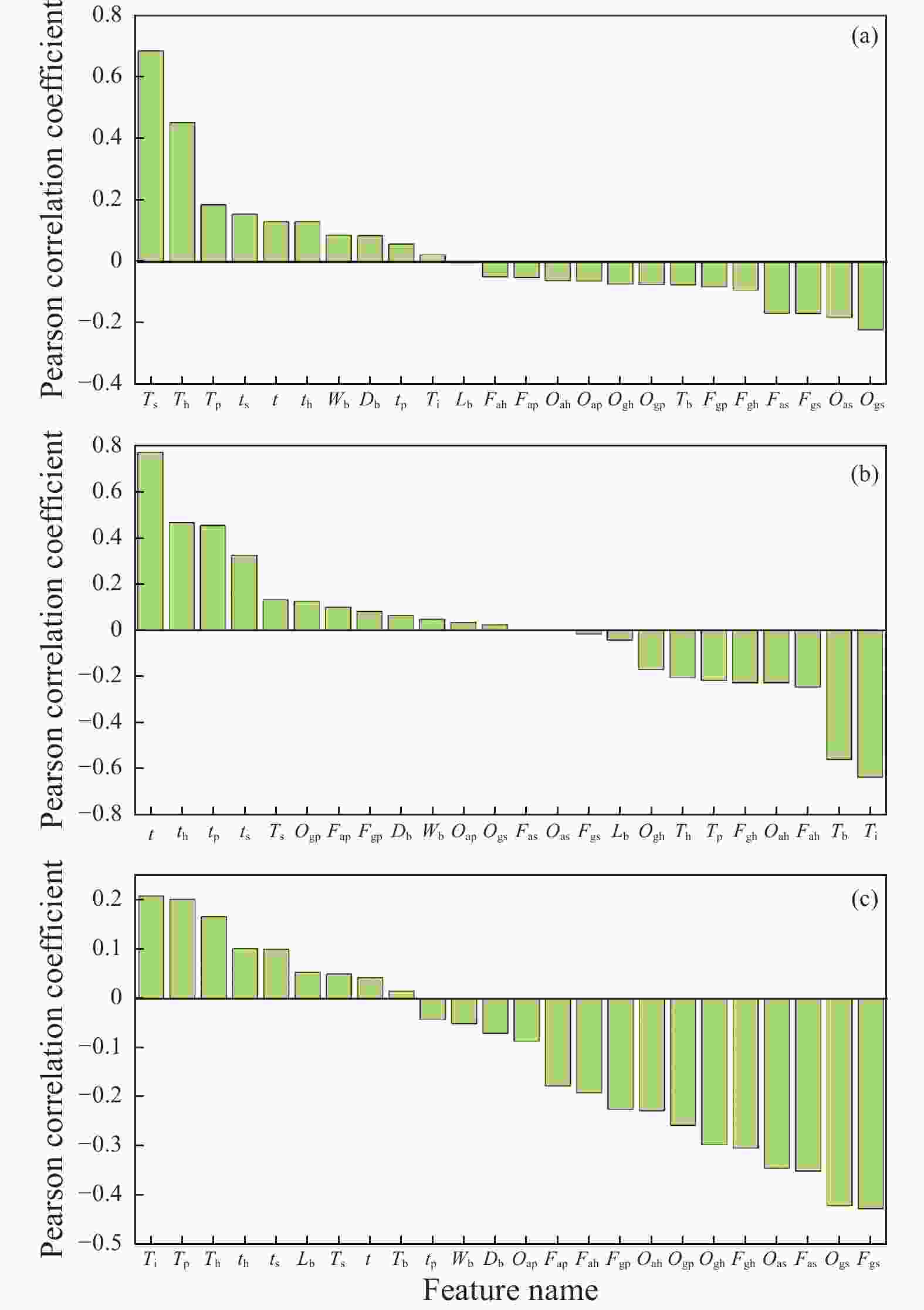
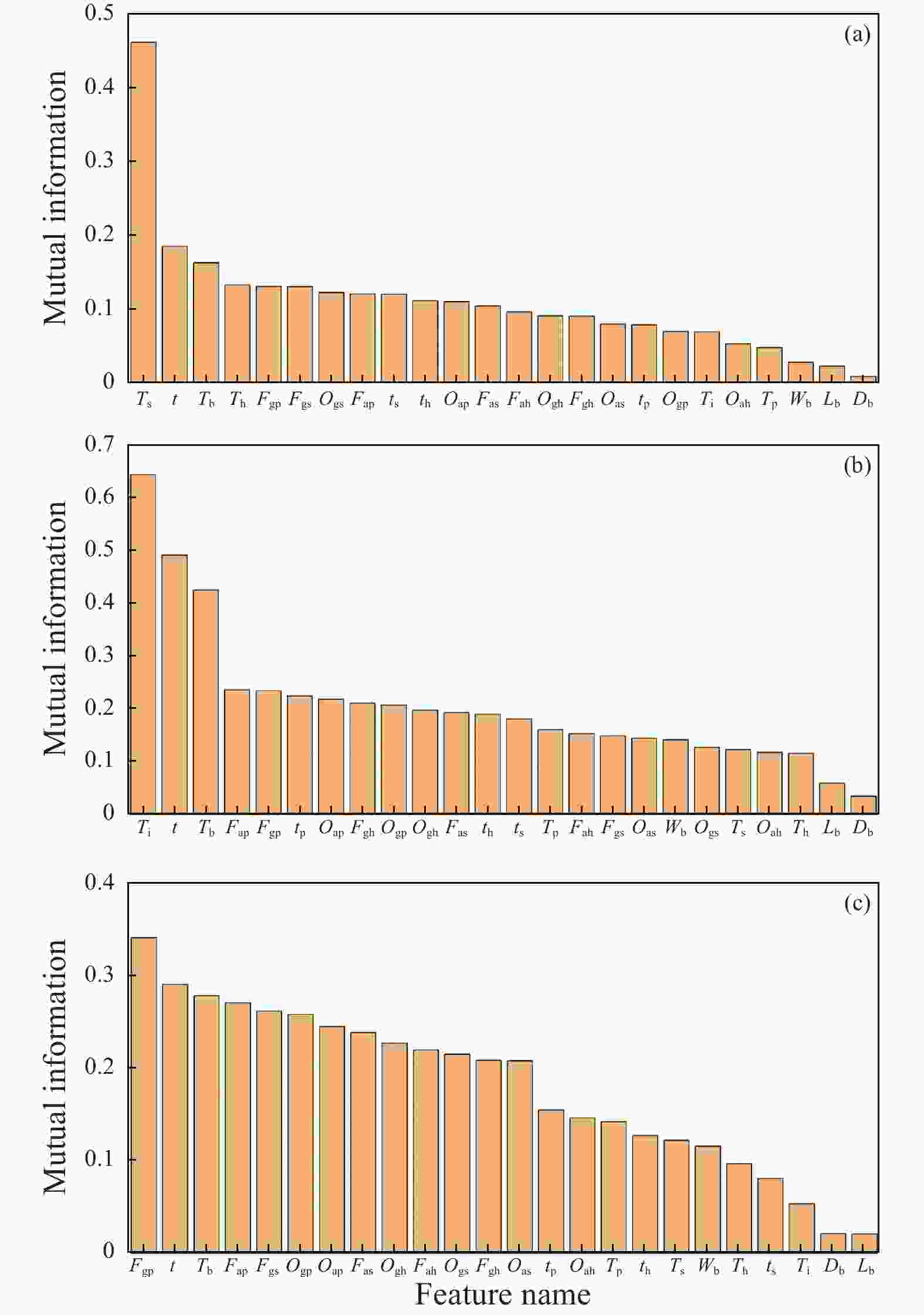
表 1 机器学习模型的输入与输出特征参数
Table 1. Input and output feature parameters of the machine-learning models
Condition Input features Output features 1 Db,Lb,Ti,tp、th、ts、t、Ogp、Ogh、Ogs Td、Ei、Bo 2 Db,Lb,Ti、t、Ogp、Ogh、Ogs 3 Db,Lb,Ti,tp、th、ts、t、Tp、Th、Ts 4 Db,Lb,Ti、t、Tp、Th、Ts 表 2 模型超参数调优配置
Table 2. Hyperparameter tuning configurations for the models
Model Hyperparameter Search scope Optimal value XGBoost Tree depth [3, 5, 7, 10] 7 Learning rate [0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2] 0.1 Subsample [0.6, 0.8, 1.0] 0.8 L1 regularization coefficient [0, 0.1, 0.5] 0.1 LSTM Number of hidden
layer units[32, 64, 128] 64 Time steps [5, 10, 15] 10 Dropout [0.1, 0.2, 0.3] 0.2 Optimizer [Adam, RMSprop, SGD] Adam 表 3 XGBoost模型预测能力评价指标
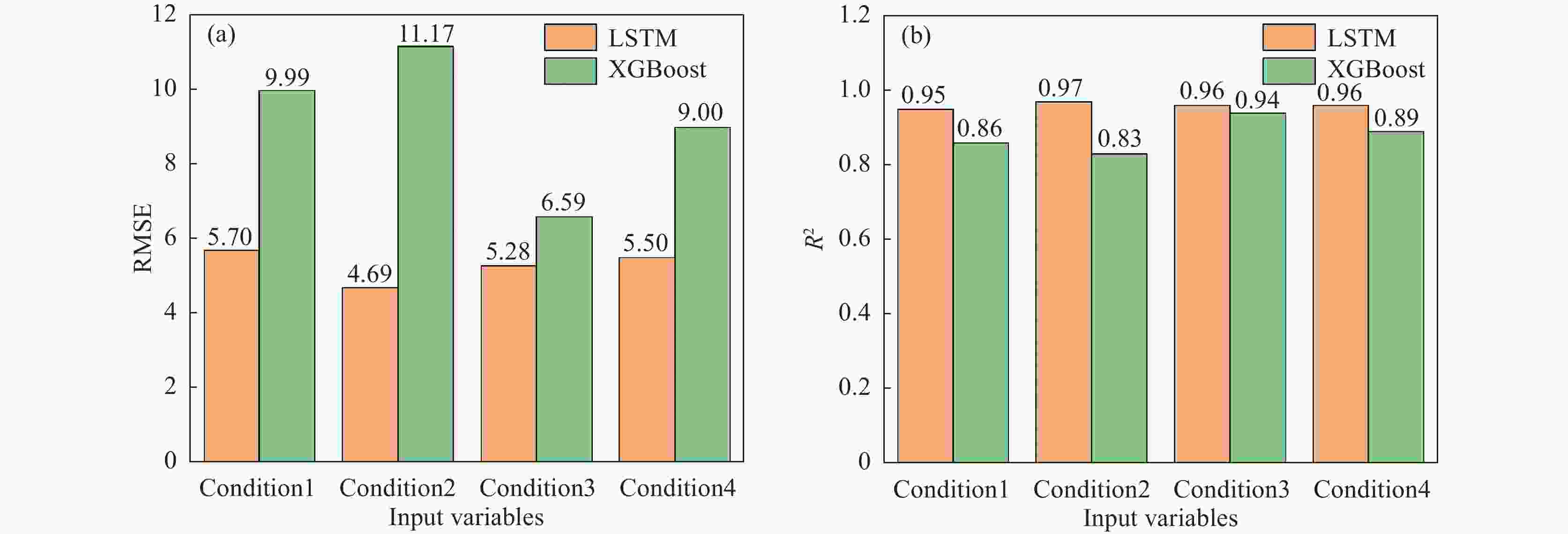
Table 3. Evaluation metrics for the predictive capability of the XGBoost model
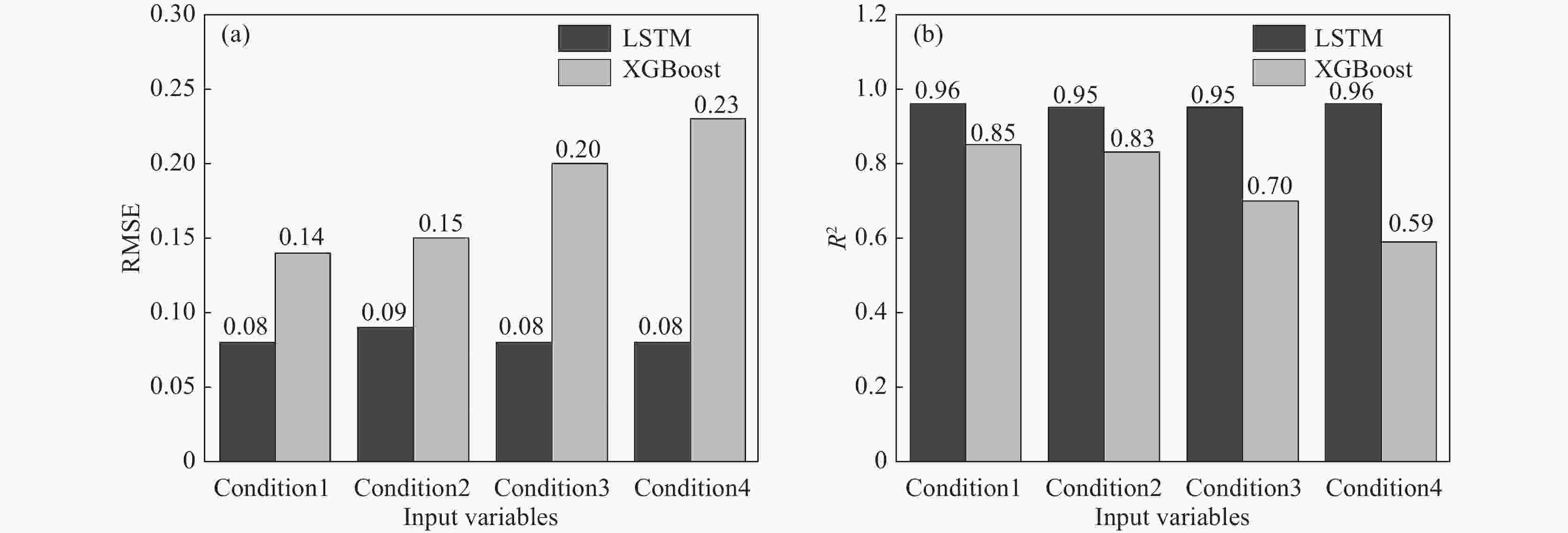
No. RMSE R2 Td Ei Bo Td Ei Bo 1 9.99 0.054 0.141 0.86 0.95 0.85 2 11.17 0.054 0.15 0.83 0.95 0.83 3 6.59 0.06 0.197 0.94 0.94 0.70 4 9.0 0.063 0.231 0.89 0.94 0.59 表 4 LSTM模型预测能力评价指标
Table 4. Evaluation metrics for the predictive capability of the LSTM model
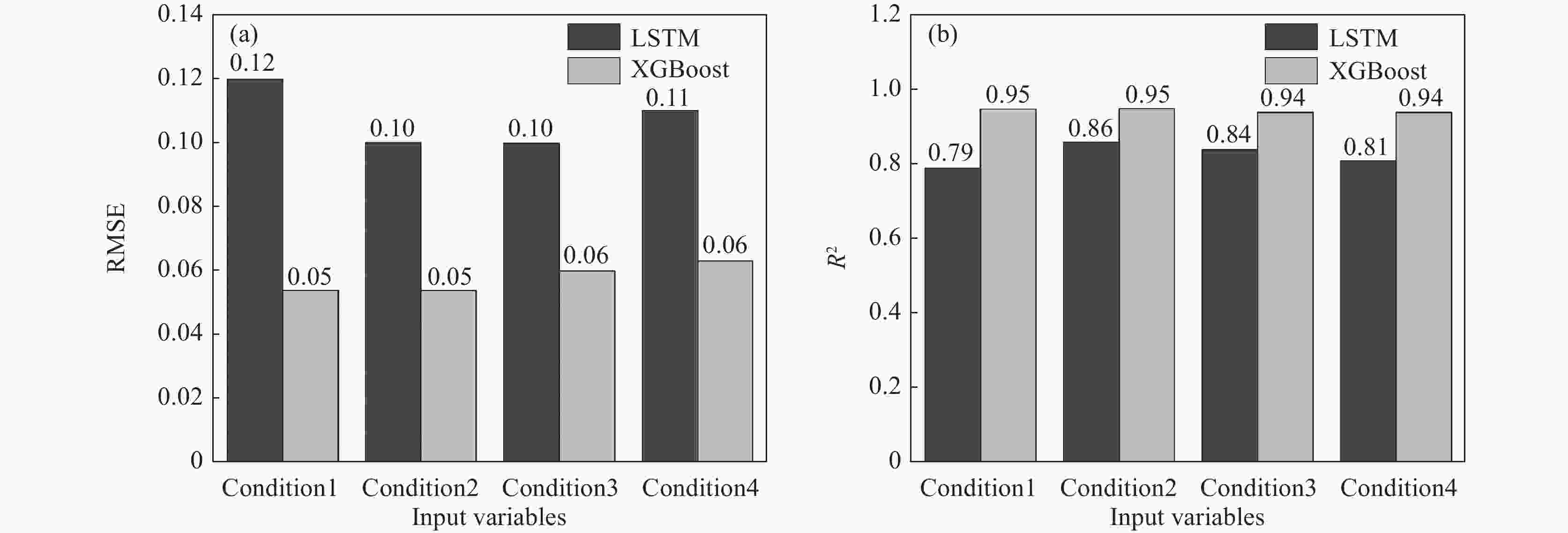
No. RMSE R2 Td Ei Bo Td Ei Bo 1 5.7 0.12 0.08 0.95 0.79 0.96 2 4.69 0.10 0.09 0.97 0.86 0.95 3 5.28 0.10 0.08 0.96 0.84 0.95 4 5.50 0.11 0.08 0.96 0.81 0.96 -
[1] LU B, TANG K, CHEN D, et al. A novel approach for lean energy operation based on energy apportionment model in reheating furnace[J]. Energy, 2019, 182: 1239-1249. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.06.076 [2] LIAO Y X, SHE J H, WU M, et al. Integrated hybrid-PSO and fuzzy-NN decoupling control for temperature of reheating furnace[J]. IEEE transactions on industrial electronics, 2009, 56(7): 2704-2714. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2019753 [3] WEI E Z, PENG Y H. Status and prospect of control technology for slab reheatingfurnace(A)[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2010, 34(3): 5-9. (卫恩泽, 彭燕华. 板坯加热炉控制技术现状及发展(上)[J]. 冶金自动化, 2010, 34(3): 5-9.WEI E Z, PENG Y H. Status and prospect of control technology for slab reheatingfurnace(A)[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2010, 34(3): 5-9. [4] ZHANG Q G, LI S Y, CHEN L Q. "Black Box" test and application of mathematical model for walking beam slab reheating furnace[J]. Industrial Furnace, 2012, 34(3): 5-7. (张强国, 李仕一, 陈亮全. 步进梁式板坯加热炉数学模型的“黑匣子”测试与应用[J]. 工业炉, 2012, 34(3): 5-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6988.2012.03.002ZHANG Q G, LI S Y, CHEN L Q. "Black Box" test and application of mathematical model for walking beam slab reheating furnace[J]. Industrial Furnace, 2012, 34(3): 5-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6988.2012.03.002 [5] YANG X J, DUAN Y, HE S F, et al. Prediction of slab unit energy consumption in steel rollingheating furnace based on all influencing factors[J]. Energy for Metallurgical Industry, 2024, 43(3): 14-18. (杨筱静, 段毅, 何胜方, 等. 基于全影响因素的轧钢加热炉板坯单耗预测[J]. 冶金能源, 2024, 43(3): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1617.2024.03.003YANG X J, DUAN Y, HE S F, et al. Prediction of slab unit energy consumption in steel rollingheating furnace based on all influencing factors[J]. Energy for Metallurgical Industry, 2024, 43(3): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1617.2024.03.003 [6] ZHAI N, ZHOU X. Temperature prediction of heating furnace based on deep transfer learning[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(17): 4676. doi: 10.3390/s20174676 [7] CHEN Y W, CHAI T Y. Modelling and prediction for steel billet temperature of heating furnace[J]. International Journal of Advanced Mechatronic Systems, 2010, 2(5-6): 342-349. [8] ZHOU J X, ZHENG R C, HOU H Y, et al. lmproved pelican algorithm for optimizing LSTM basedtemperature prediction of reheating furnace billets[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2023, 42(5): 174-179. (周建新, 郑日成, 侯宏瑶, 等. 改进鹈鹕算法优化LSTM的加热炉钢坯温度预测[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2023, 42(5): 174-179.ZHOU J X, ZHENG R C, HOU H Y, et al. lmproved pelican algorithm for optimizing LSTM basedtemperature prediction of reheating furnace billets[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2023, 42(5): 174-179. [9] SUN J, YU M H. Temperature neural network prediction model of billet in rollingheating furnace[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 40(9): 5. (孙洁, 于孟晗. 轧钢加热炉钢坯温度神经网络预测模型[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2021, 40(9): 5.SUN J, YU M H. Temperature neural network prediction model of billet in rollingheating furnace[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 40(9): 5. [10] YU H, GONG J, WANG G, et al. A hybrid model for billet tapping temperature prediction and optimization in reheating furnace[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 19(8): 8703-8712. [11] SHI Q, TANG J, CHU M S. Key issues and progress of industrial big data-based intelligent blast furnace ironmaking technology[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2023, 30(9): 1651-1666. doi: 10.1007/s12613-023-2636-3 [12] RESHEF D N, RESHEF Y A, FINUCANE H K, et al. Detecting novel associations in large data sets[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6062): 1518-1524. doi: 10.1126/science.1205438 [13] RAMRAJ S, UZIR N, SUNIL R, et al. Experimenting XGBoost algorithm for prediction and classification of different datasets[J]. International Journal of Control Theory and Applications, 2016, 9(40): 651-662. [14] XIE C L. Wind-induced acceleration prediction of cable-stayed bridges based on LST model[D]. Guang Zhou: Guangzhou University, 2023. (谢诚朗. 基于LSTM模型的斜拉桥风致加速度预测[D]. 广州: 广州大学, 2023.XIE C L. Wind-induced acceleration prediction of cable-stayed bridges based on LST model[D]. Guang Zhou: Guangzhou University, 2023. -




 下载:
下载: