ANN-Driven modeling of high-temperature flow behavior in P650 for nonmagnetic drilling collars
-
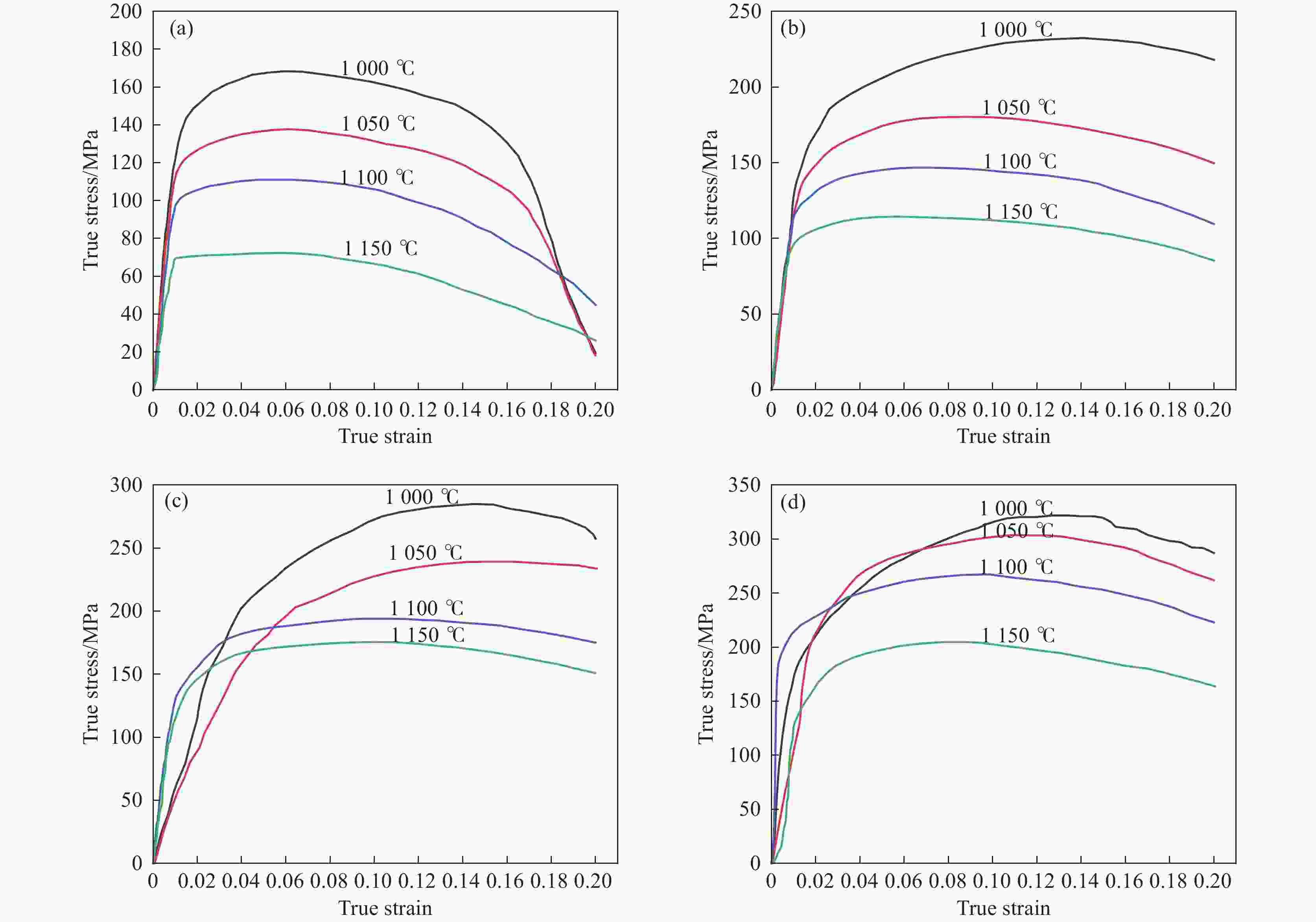
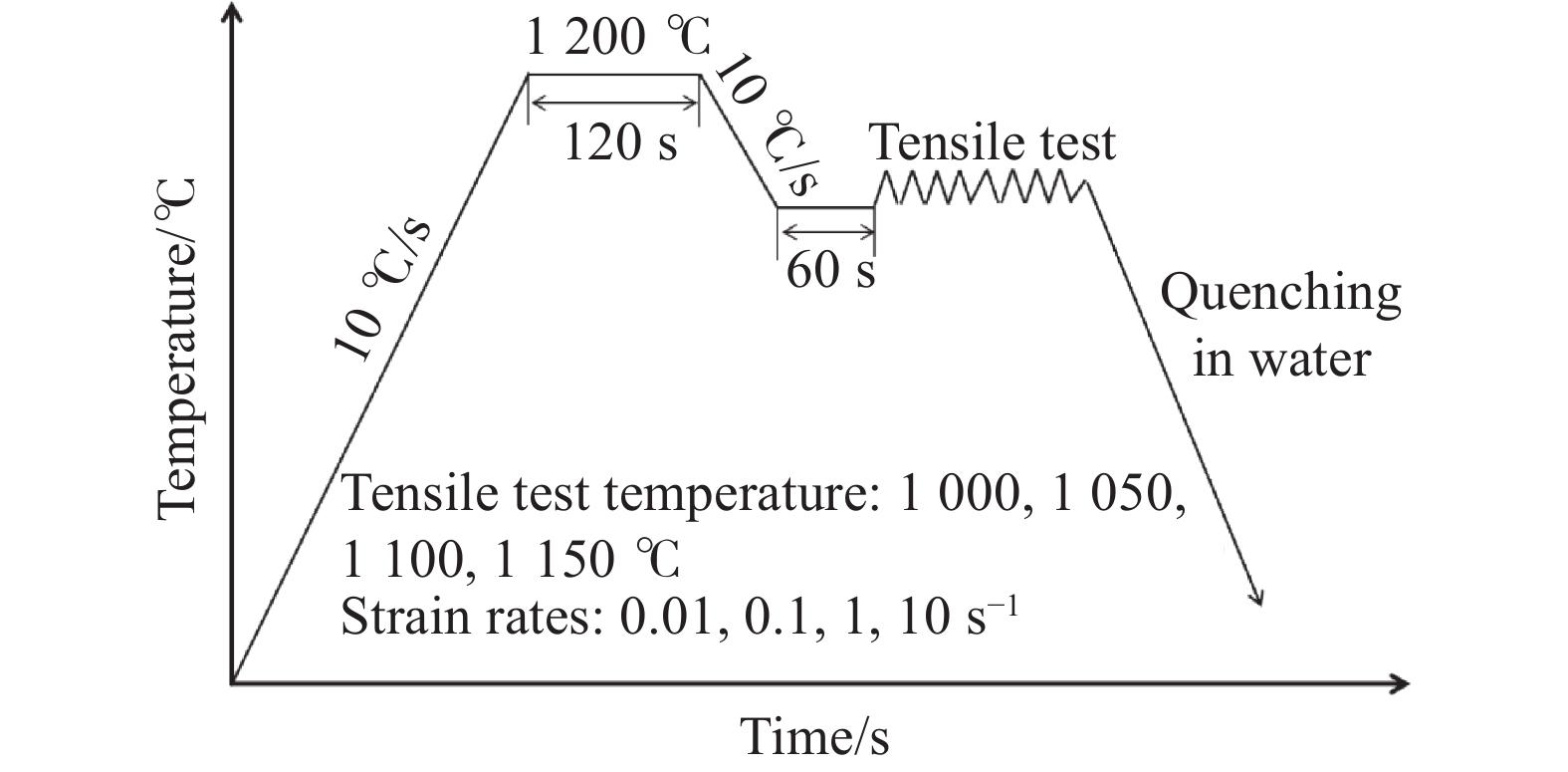
摘要: 通过Gleeble-3500热模拟试验机对P650高氮钢进行
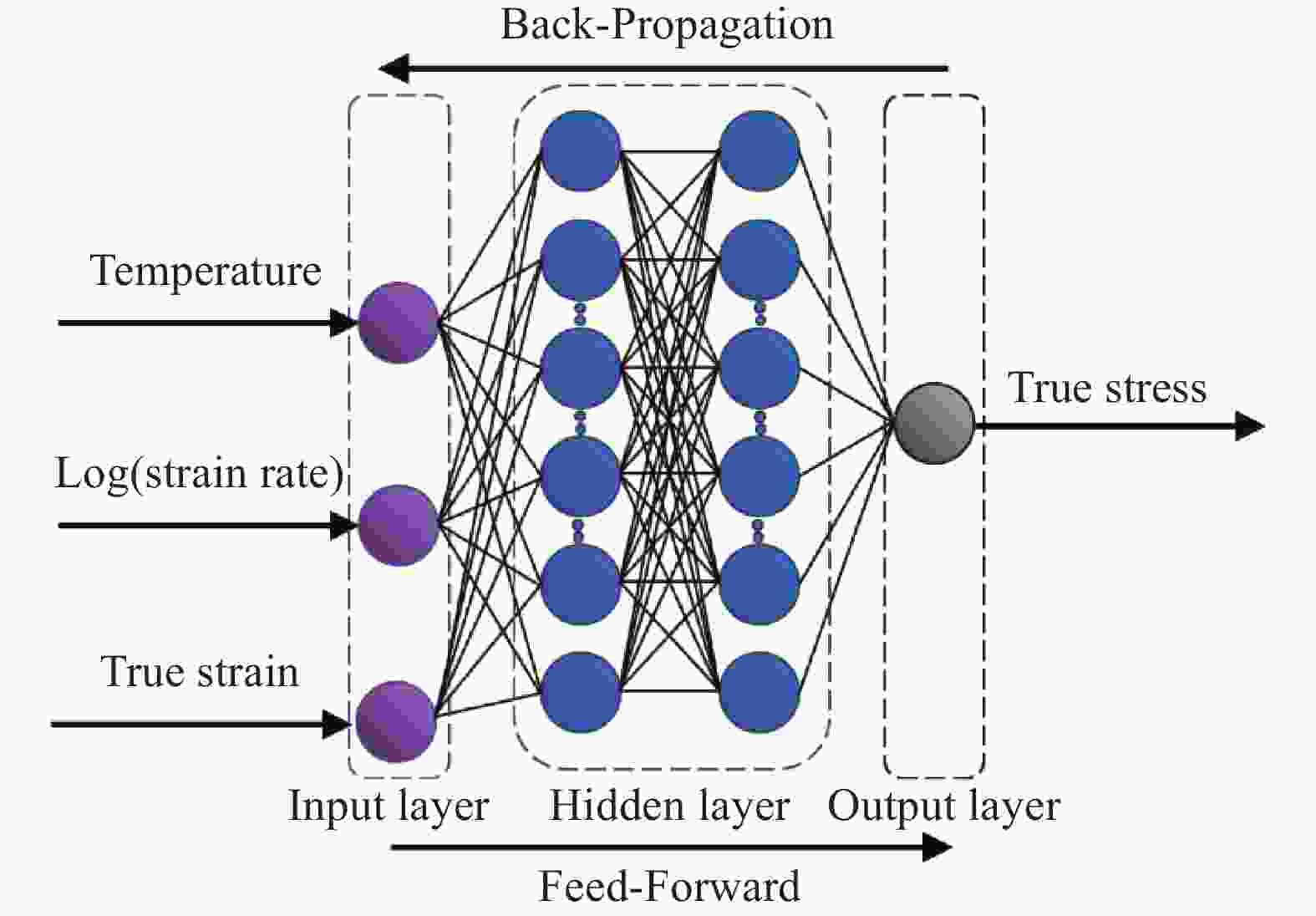
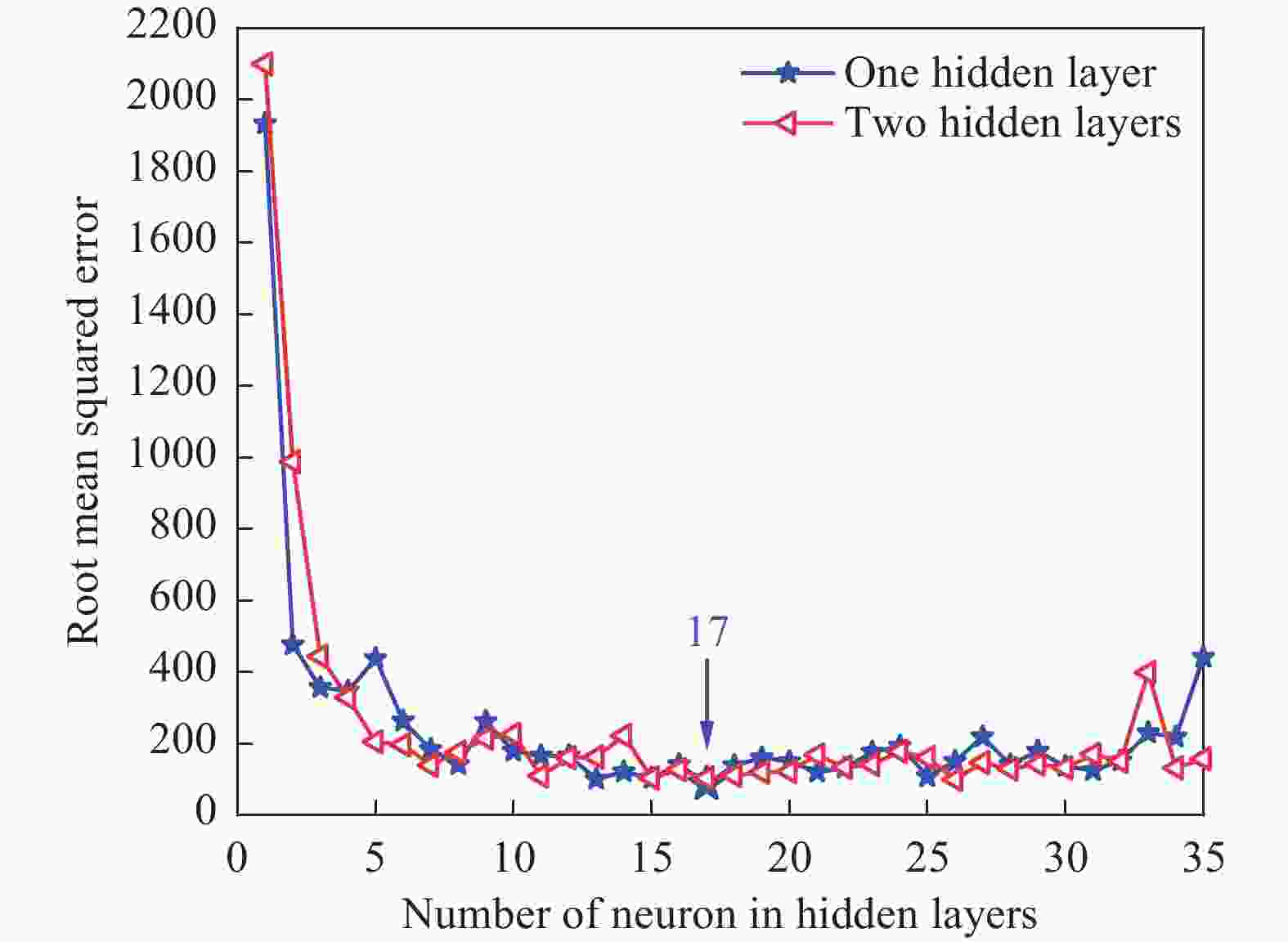
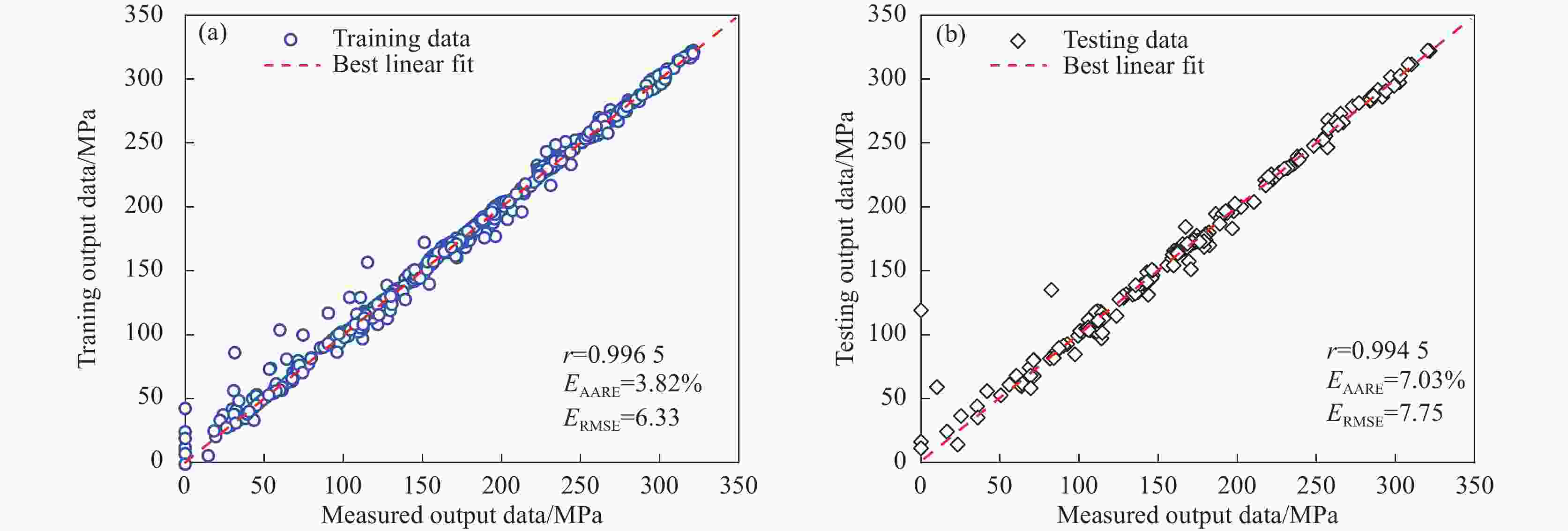
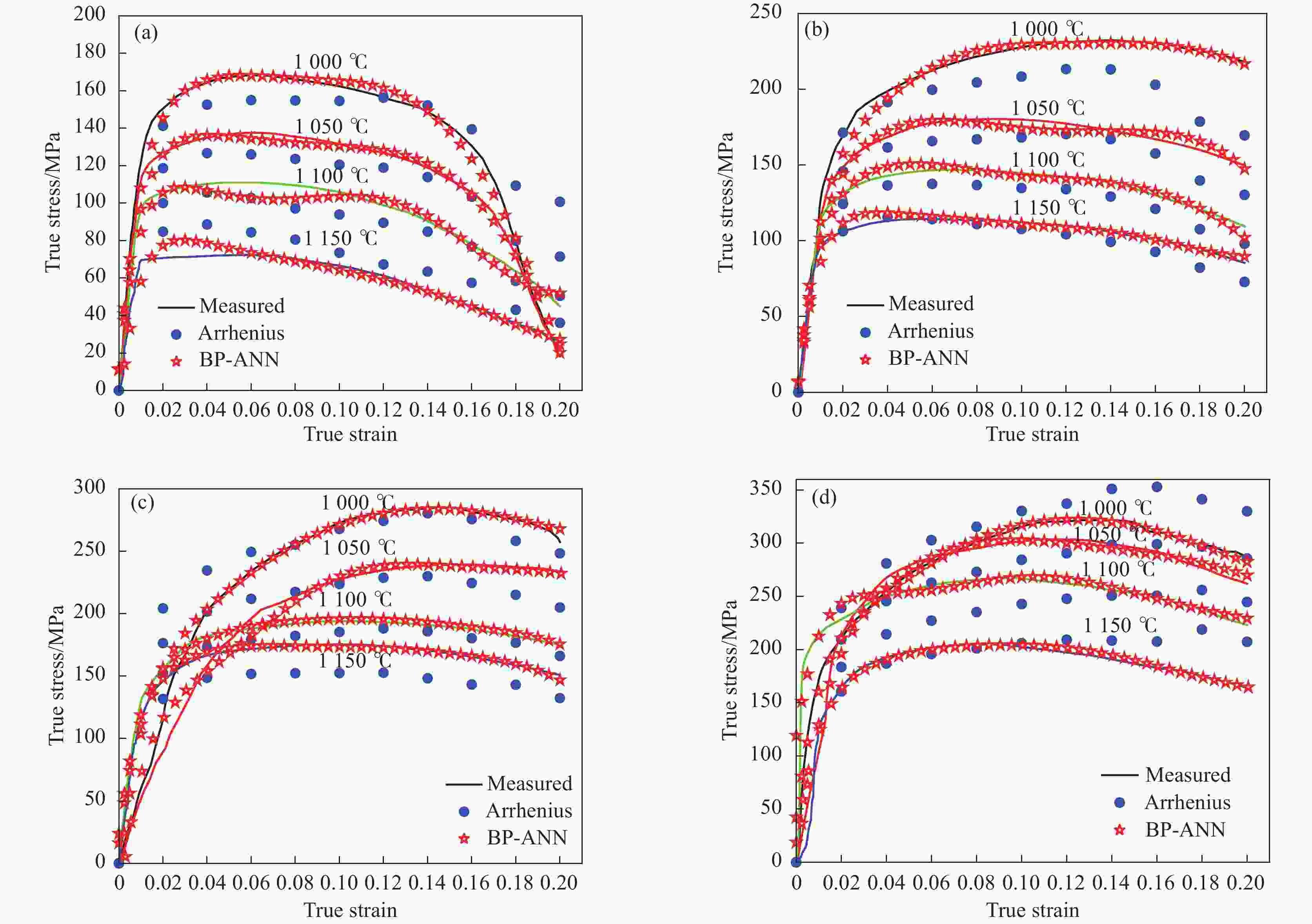
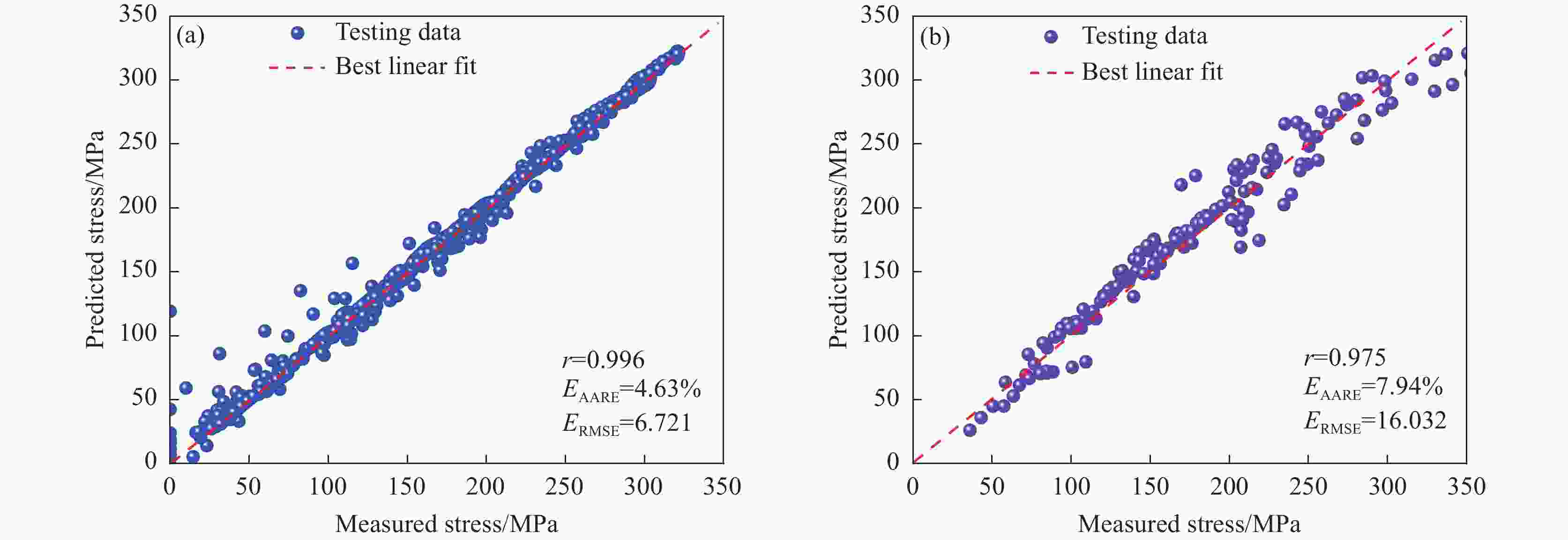
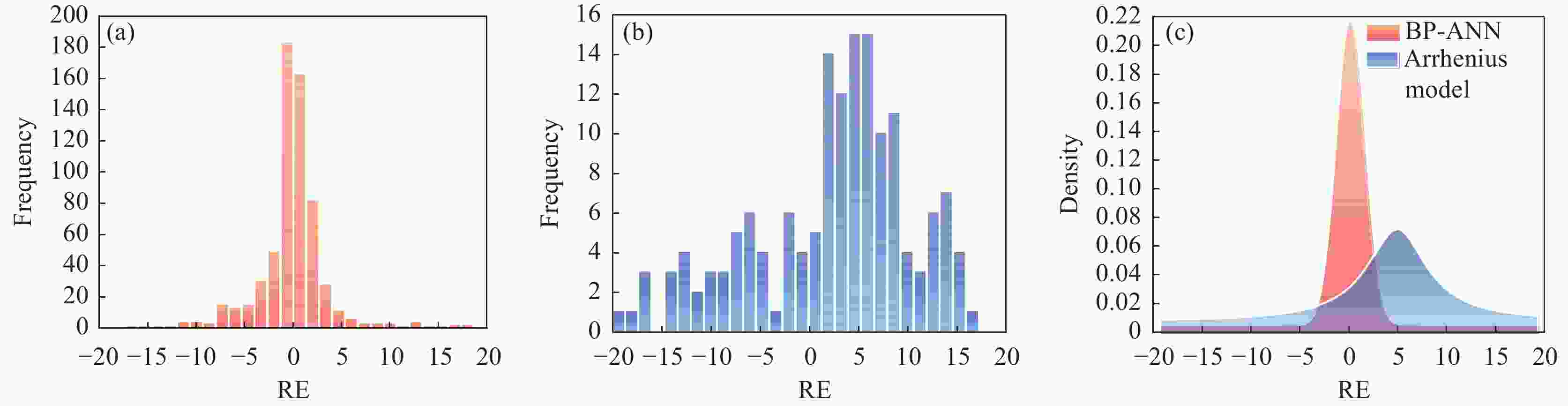
1000 ~1150 ℃、应变速率0.01~10 s−1条件下的高温拉伸试验,获取流变应力-应变曲线。基于试验数据,分别构建应变补偿Arrhenius本构模型与人工神经网络(ANN)模型,并采用平均绝对相对误差、均方根误差和相关系数系统评价模型预测性能。结果表明,ANN模型通过单隐藏层拓扑结构(含17个神经元)实现了温度、应变速率及应变与流变应力的高精度非线性映射。其预测结果与试验值高度吻合(r=0.996,EAARE=4.63%,ERMSE=6.721 MPa),显著优于传统Arrhenius模型(r=0.975,EAARE=7.94%,ERMSE=16.032 MPa)。研究表明人工神经网络能够有效捕捉复杂热变形行为的本构关系特征,为建立高精度流变应力预测模型及材料加工工艺优化提供了改进策略。Abstract: High-temperature tensile tests on P650 high-nitrogen steel had been conducted under1000 -1150 ℃ and strain rates of 0.01-10 s−1, using a Gleeble-3500 thermomechanical simulator. Based on the obtained stress-strain data, a strain-compensated Arrhenius constitutive model and an artificial neural network (ANN) model were developed, with prediction accuracy evaluated by average absolute relative error, root mean square error, and correlation coefficient. Results demonstrated that the prediction by ANN model with a single hidden layer (17 neurons) achieved high-precision nonlinear mapping between input parameters (temperature, strain rate, strain) and flow stress. Besides, the ANN predictions exhibited good agreement with experimental data (r=0.996, EAARE=4.63%, ERMSE=6.721 MPa) compared to the Arrhenius model (r=0.975, EAARE=7.94%, ERMSE=16.032 MPa). This study reveals that artificial neural networks can effectively capture constitutive relationship characteristics of complex thermal deformation behaviors, providing an improved strategy for establishing high-accuracy flow stress prediction models and optimizing material processing technologies. -
表 1 P650钢的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of the P650 steel
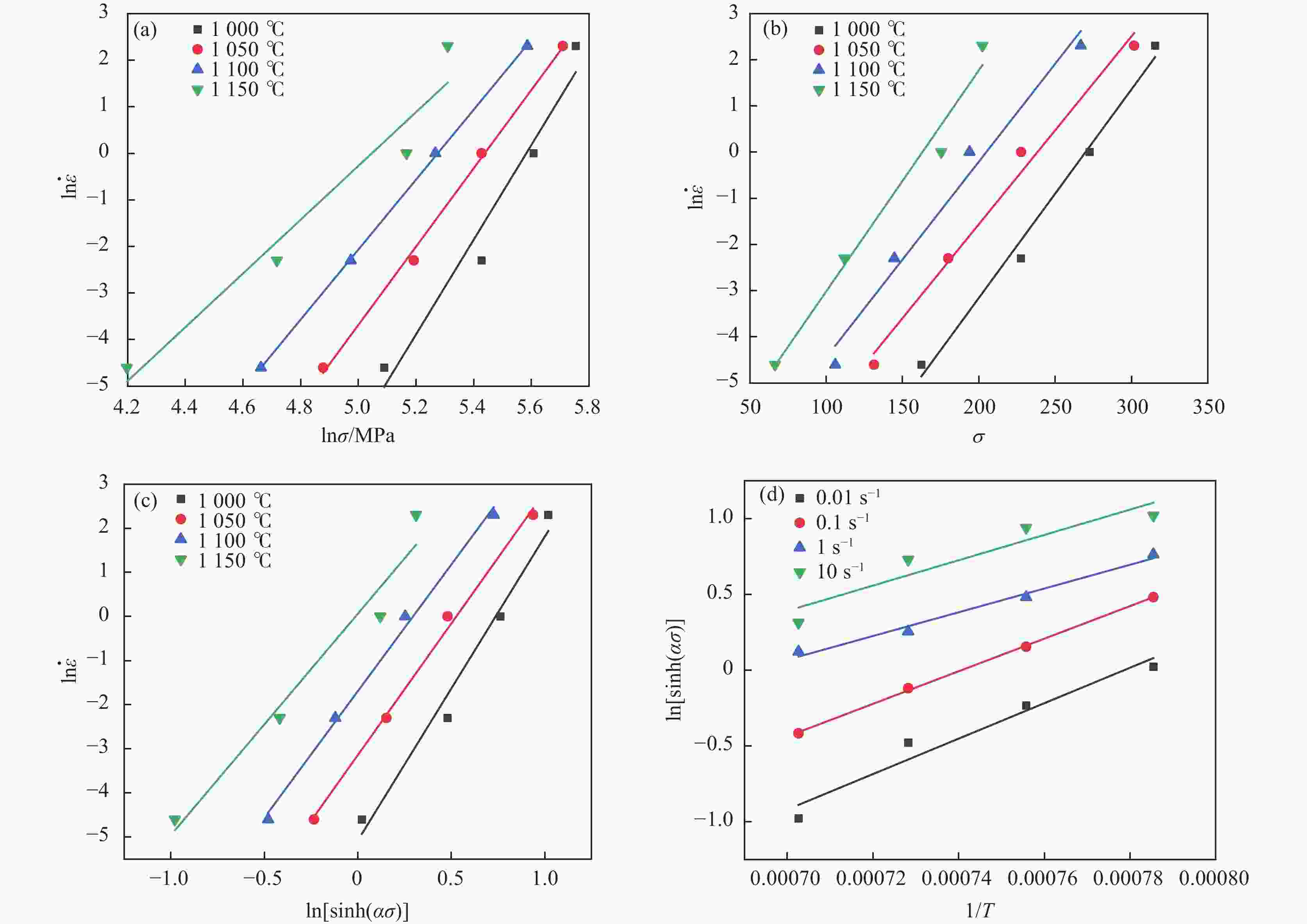
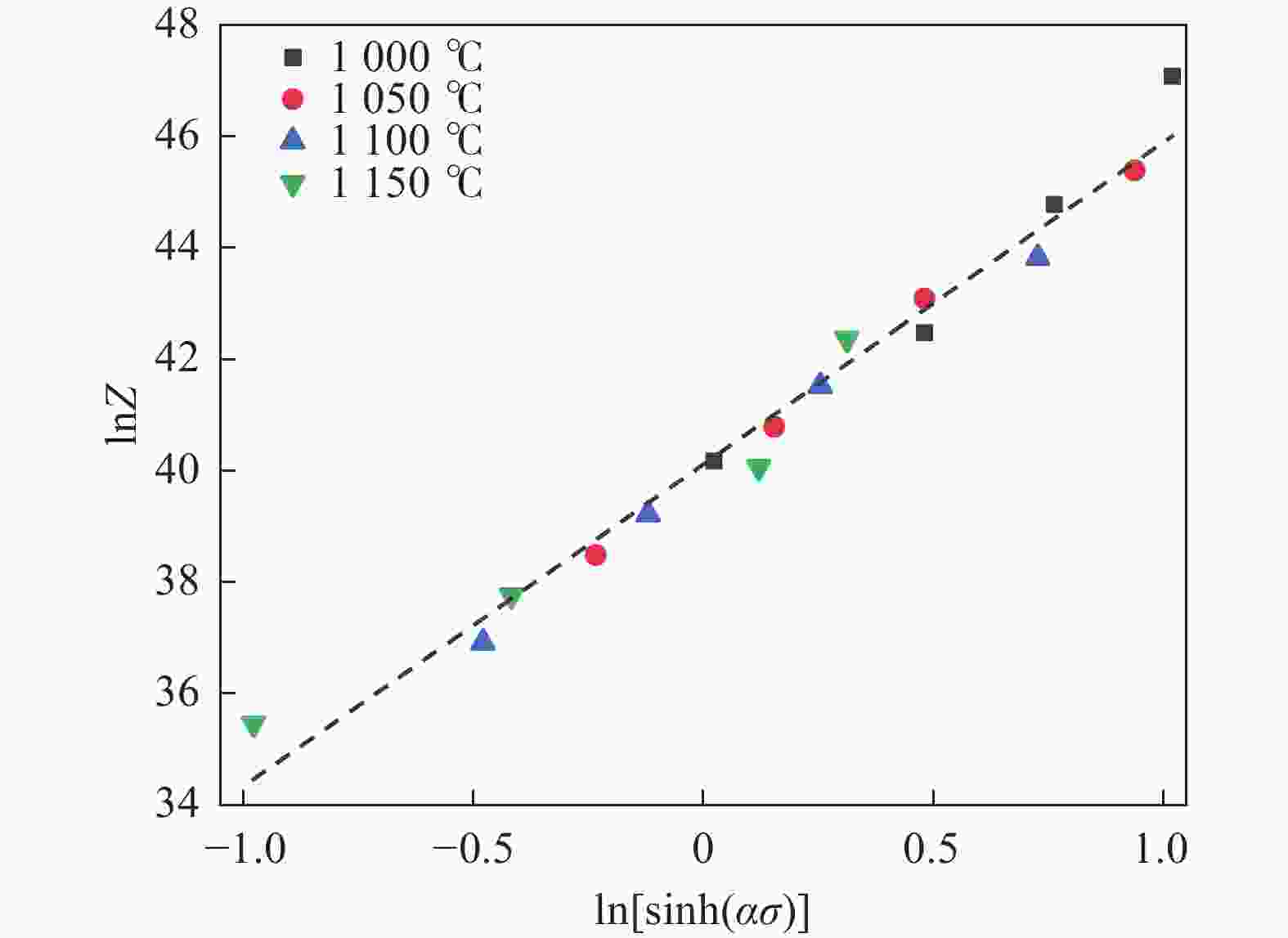
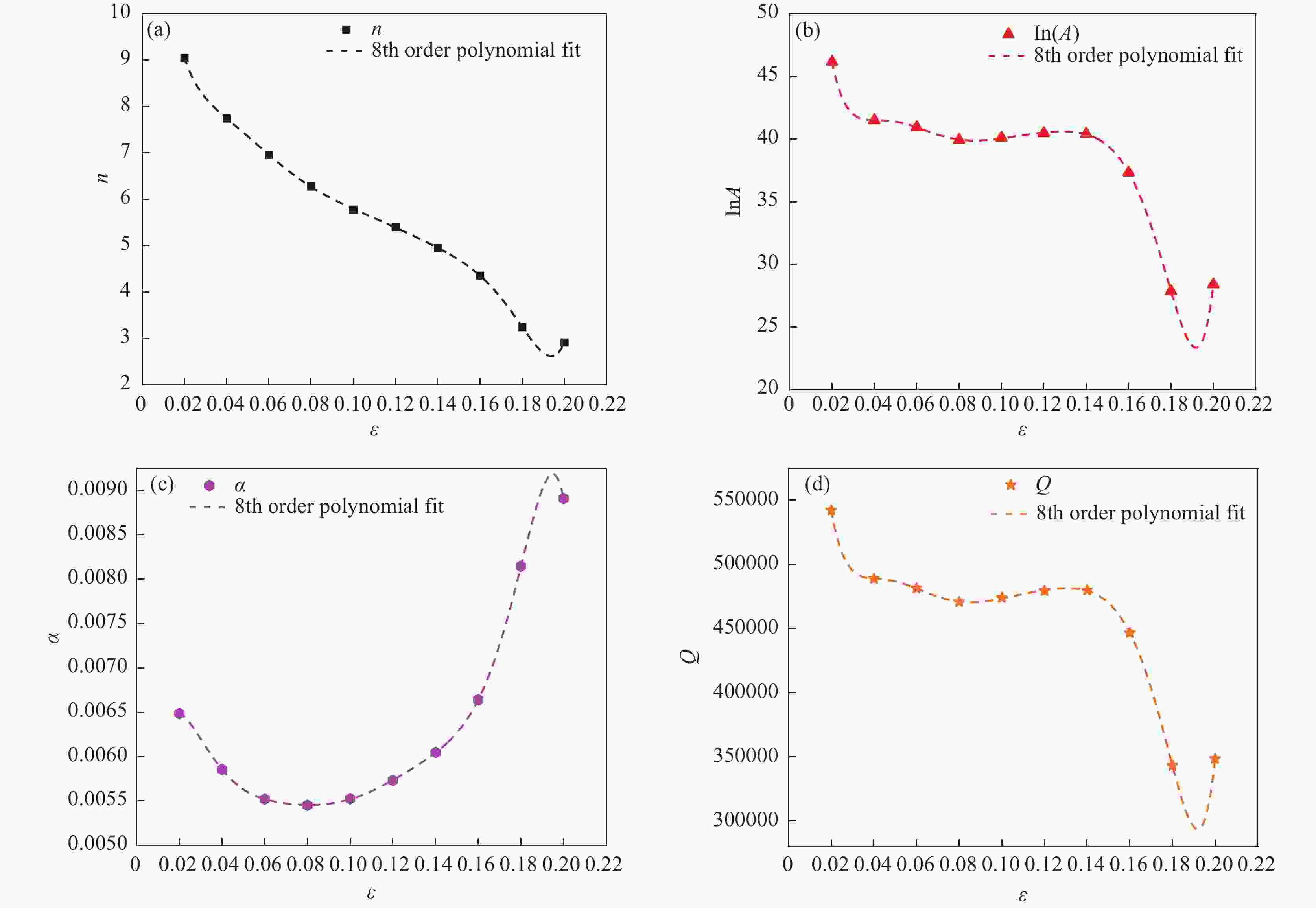
% C Mn Si Ni Cr Mo Al P H O N S Ca Mg Fe 0.03 20.2 0.66 3.96 18.02 1.93 0.026 0.014 0.00034 0.0006 0.665 0.0005 0.006 < 0.0005 Bal. 表 2 α, n, $Q$and lnA的多项式系数
Table 2. Polynomial coefficients for α, n, Q and lnA
Stain n lnA α $Q$/(kJ·mol−1) 0.02 9.04702 46.1746 0.006487 542190.911 0.04 7.74126 41.50792 0.005855 488845.541 0.06 6.95528 40.94971 0.005522 481427.444 0.08 6.27618 39.92596 0.005454 470686.347 0.1 5.77992 40.11359 0.005525 474033.633 0.12 5.40157 40.46626 0.005732 479360.231 0.14 4.94388 40.41974 0.006049 479873.334 0.16 4.35556 37.32439 0.006641 446595.561 0.18 3.24416 27.87121 0.008147 343149.771 0.2 2.91547 28.40286 0.008911 348449.722 -
[1] ZHANG S X, CUI Y, QU H P, et al. Precipitation mechanical of 0Cr19Mn21Ni2N austenitic stainless steel for non-magnetic drill collar during isothermal aging at 800 ℃[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2016, 41(9): 52-56. (张世霄, 崔岩, 屈华鹏, 等. 无磁钻铤用0Cr19Mn21Ni2N奥氏体不锈800 ℃等温时效析出机制[J]. 金属热处理, 2016, 41(9): 52-56.ZHANG S X, CUI Y, QU H P, et al. Precipitation mechanical of 0Cr19Mn21Ni2N austenitic stainless steel for non-magnetic drill collar during isothermal aging at 800 ℃[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2016, 41(9): 52-56. [2] CORDEA J N, SHETH H V, JASPER J C. Development of an improved austenitic drilling collar alloy[J]. Material Performance, 1987(23): 50-54. [3] ZHANG S X. Research on processing technology of high nitrogen austenitic stainless steels for offshore oil gas drilling application[D]. Tangshan: North China University of Science and Technology, 2016. (张世霄. 海洋油气钻采高氮奥氏体不锈钢加工工艺研究[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2016.ZHANG S X. Research on processing technology of high nitrogen austenitic stainless steels for offshore oil gas drilling application[D]. Tangshan: North China University of Science and Technology, 2016. [4] AO Y, ZHOU C D. Thermal deformation behavior of P550 austenitic stainless steel[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2016, 38(5): 22-26. (敖影, 周灿栋. 0Cr19Mn21Ni2N奥氏体不锈钢的热变形行为研究[J]. 上海金属, 2016, 38(5): 22-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2016.05.005AO Y, ZHOU C D. Thermal deformation behavior of P550 austenitic stainless steel[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2016, 38(5): 22-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2016.05.005 [5] QU H P, LANG Y P, CHEN H T. Research and development on high nitrogen stainless steels used for non-magnetic drilling collar[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2014, 43(24): 14-17. (屈华鹏, 郎宇平, 陈海涛. 无磁钻铤用高氮不锈钢的研究和发展[J]. 热加工工艺, 2014, 43(24): 14-17.QU H P, LANG Y P, CHEN H T. Research and development on high nitrogen stainless steels used for non-magnetic drilling collar[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2014, 43(24): 14-17. [6] LÜ S L, LUO F Q, ZHOU J, et al. Fracture reason analysis on drill collar[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis, 2009, 45(5): 309-311. (吕栓录, 骆发前, 周杰, 等. 钻铤断裂原因分析[J]. 理化检验, 2009, 45(5): 309-311.LÜ S L, LUO F Q, ZHOU J, et al. Fracture reason analysis on drill collar[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis, 2009, 45(5): 309-311. [7] LÜ S L, ZHANG H, XU F, et al. Gause analysis of oil drill collar fracture[J]. Material for Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 36(6): 80-82. (吕栓录, 张宏, 许峰, 等. 石油钻铤断裂原因分析[J]. 机械工程材料, 2010, 36(6): 80-82.LÜ S L, ZHANG H, XU F, et al. Gause analysis of oil drill collar fracture[J]. Material for Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 36(6): 80-82. [8] SHI F, CUI W F, WANG L J, et al. Advance in the research of high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steels[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2006, 28(5): 45-50. (石锋, 崔文芳, 王立军, 等. 高氮奥氏体不锈钢研究进展[J]. 上海金属, 2006, 28(5): 45-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2006.05.011SHI F, CUI W F, WANG L J, et al. Advance in the research of high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steels[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2006, 28(5): 45-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2006.05.011 [9] WANG Y H, ZHENG H B, SONG L X, et al. High temperature plastic deformation behavior of 0Cr19Mn21Ni2N high nitrogen steel for nonmagnetic drilling collar[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2022, 47(1): 113-119. (王英虎, 郑淮北, 宋令玺, 等. 无磁钻铤用0Cr19Mn21Ni2N高氮钢的高温塑性变形行为[J]. 金属热处理, 2022, 47(1): 113-119.WANG Y H, ZHENG H B, SONG L X, et al. High temperature plastic deformation behavior of 0Cr19Mn21Ni2N high nitrogen steel for nonmagnetic drilling collar[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2022, 47(1): 113-119. [10] LI Y F, WANG Z H, ZHANG L Y, et al. Arrhenius-type constitutive model and dynamic recrystallization behavior of V-5Cr-5Ti alloy during hot compression[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(6): 1889-1900. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63796-7 [11] GAO X J, LIU X, LUO J, et al. Arrhenius constitutive model for hot deformation of DP1180 steel[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2024, 16(11): 108-116. (高兴健, 刘鑫, 罗健, 等. DP1180 钢的热变形Arrhenius本构模型[J]. 精密成形工程, 2024, 16(11): 108-116.GAO X J, LIU X, LUO J, et al. Arrhenius constitutive model for hot deformation of DP1180 steel[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2024, 16(11): 108-116. [12] XU L W, LI H B, JIANG Z H, et al. Hot deformation behavior of P550 steels for nonmagnetic drilling collars[J]. Steel Research International, 2020, 91(8): 1-11. [13] GUO W. Study on thermal deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of P550 high nitrogen austenitic stainless steel[J]. Materials Research Express, 2023, 10(6). [14] REDDY N S, LEE Y H, KIM J H, et al. High temperature deformation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with and equiaxed microstructure: a neural networks analysis[J]. Met Mater Int, 2008, 14(2): 213-221. doi: 10.3365/met.mat.2008.04.213 [15] AHMADI H, ASHTIANI H R R, HEIDARI M, A comparative study of phenomenological, physically-based and artificial neural network models to predict the hot flow behavior of API 5CT-L80 steel[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2020, 25, 101528. [16] JI G L, LI F G, LI Q H, et al. Prediction of the hot deformation behavior for Aermet100 steel using an artificial neural network[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2010, 48(7): 626-632. [17] YANG J C, GAO F B, REN J L. Research on plastic deformation behavior of 00Cr17Mn6Ni5N at high temperature[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2014, 43(16): 102-104. (杨吉春, 高福彬, 任金亮. 00Cr17Mn6Ni5N的高温塑性变形行为研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2014, 43(16): 102-104.YANG J C, GAO F B, REN J L. Research on plastic deformation behavior of 00Cr17Mn6Ni5N at high temperature[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2014, 43(16): 102-104. [18] YU X P, DONG H B. Numerical simulation of austenite recrystallization process in 40Cr steel[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2015, 35(1): 26-29. (余新平, 董洪波. 40Cr钢奥氏体动态再结晶过程数值模拟[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2015, 35(1): 26-29.YU X P, DONG H B. Numerical simulation of austenite recrystallization process in 40Cr steel[J]. Special Casting & Nonferrous Alloys, 2015, 35(1): 26-29. [19] WEI H L, PAN H B, ZHOU H W. Physical and apparent arrhenius constitutive models of a Nb–Ti microalloyed C–Mn–Al high strength steel: A comparative study[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2022, 75(2): 327-336. doi: 10.1007/s12666-021-02414-3 [20] ZENER C, HOLLOMON J H. Effect of strain rate upon plastic flow of steel[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1944, 15(1): 22-32. doi: 10.1063/1.1707363 [21] LONG S, XIA Y, WANG P, et al. Constitutive modelling, dynamic globularization behavior and processing map for Ti-6Cr-5Mo-5V-4Al alloy during hot deformation[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 796(5): 65-76. -




 下载:
下载: