Study on the effect of rolling process on the deformation resistance of low carbon micro-Nb steel and its model
-
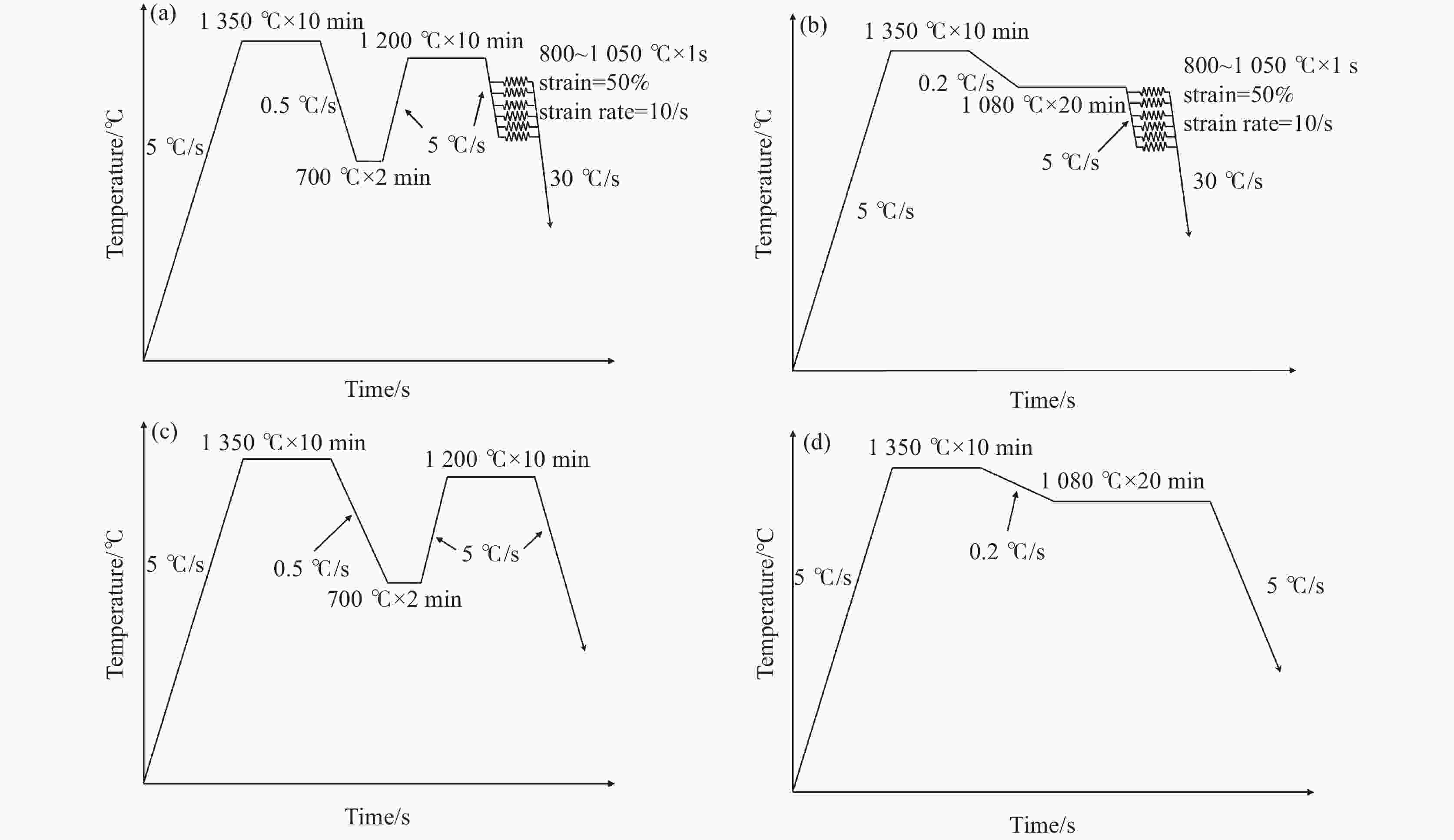
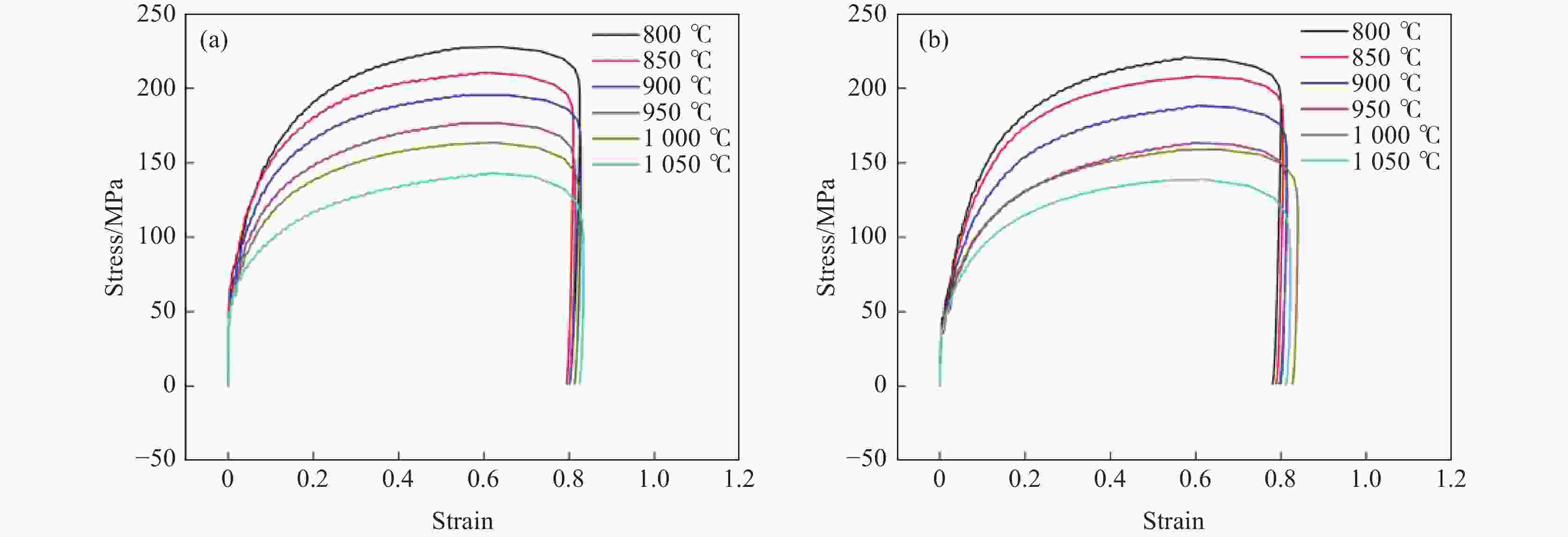
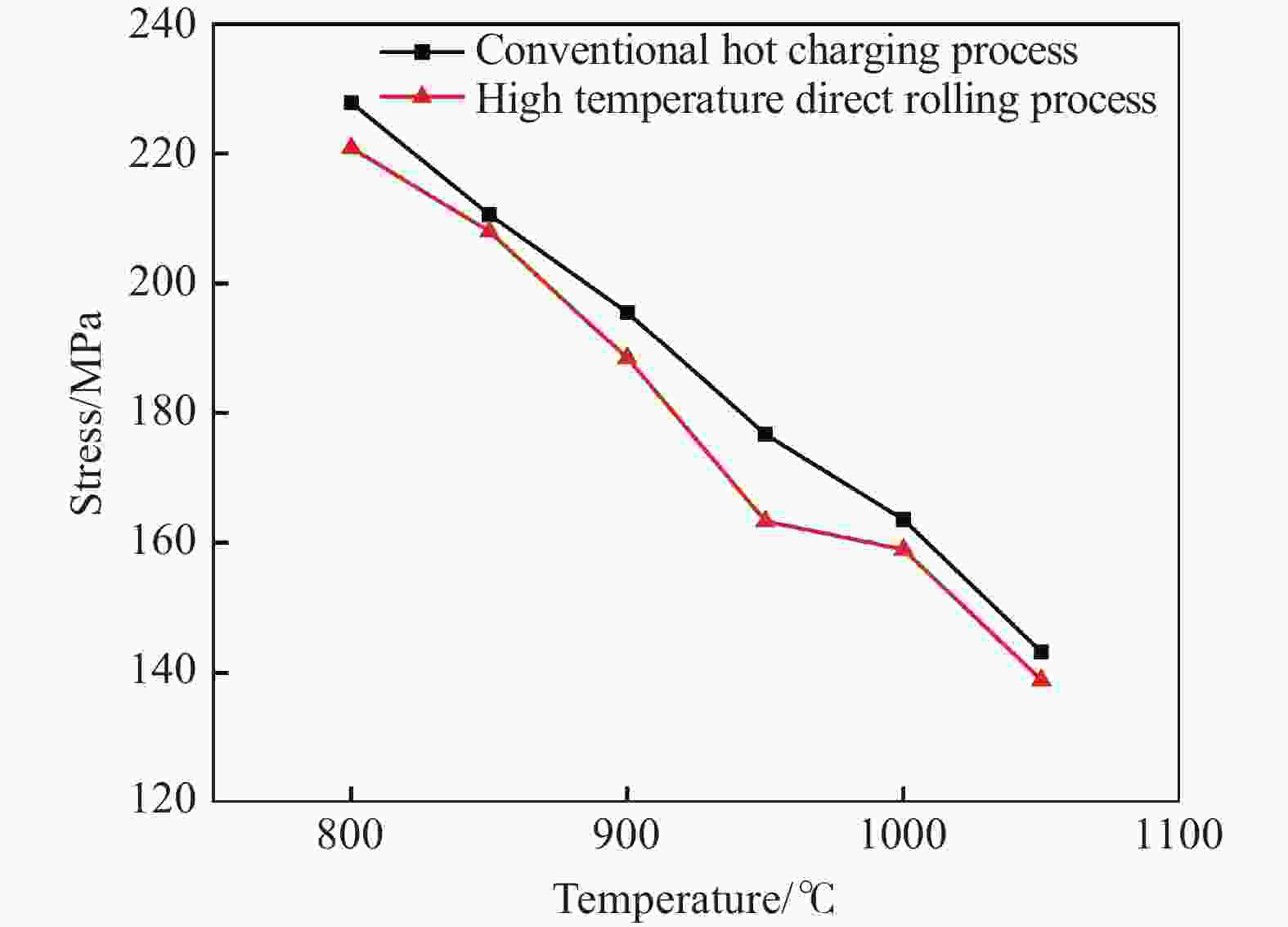
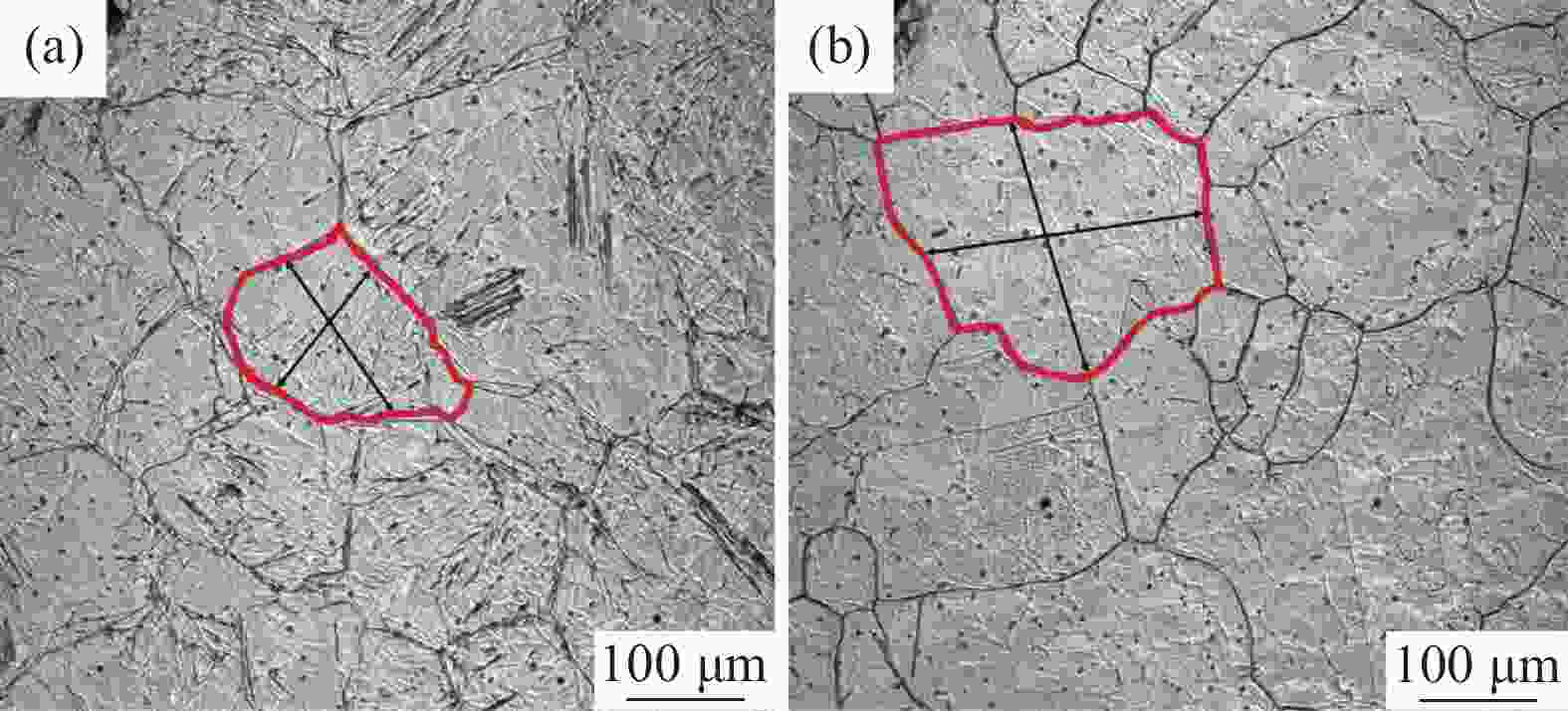
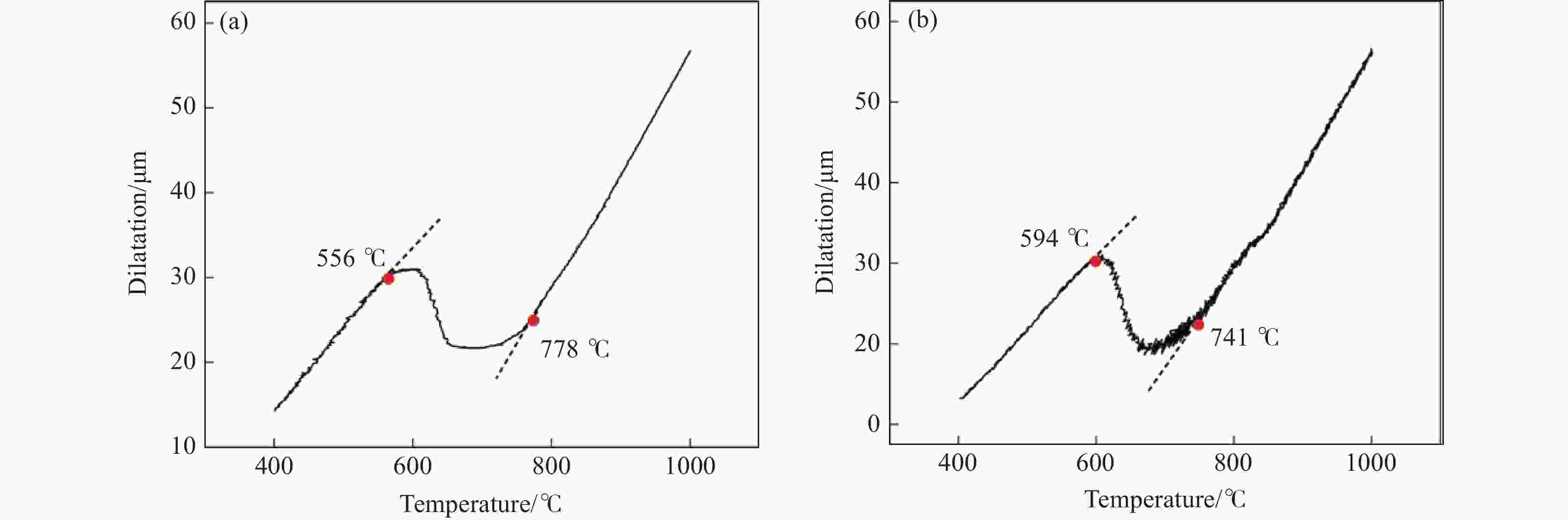
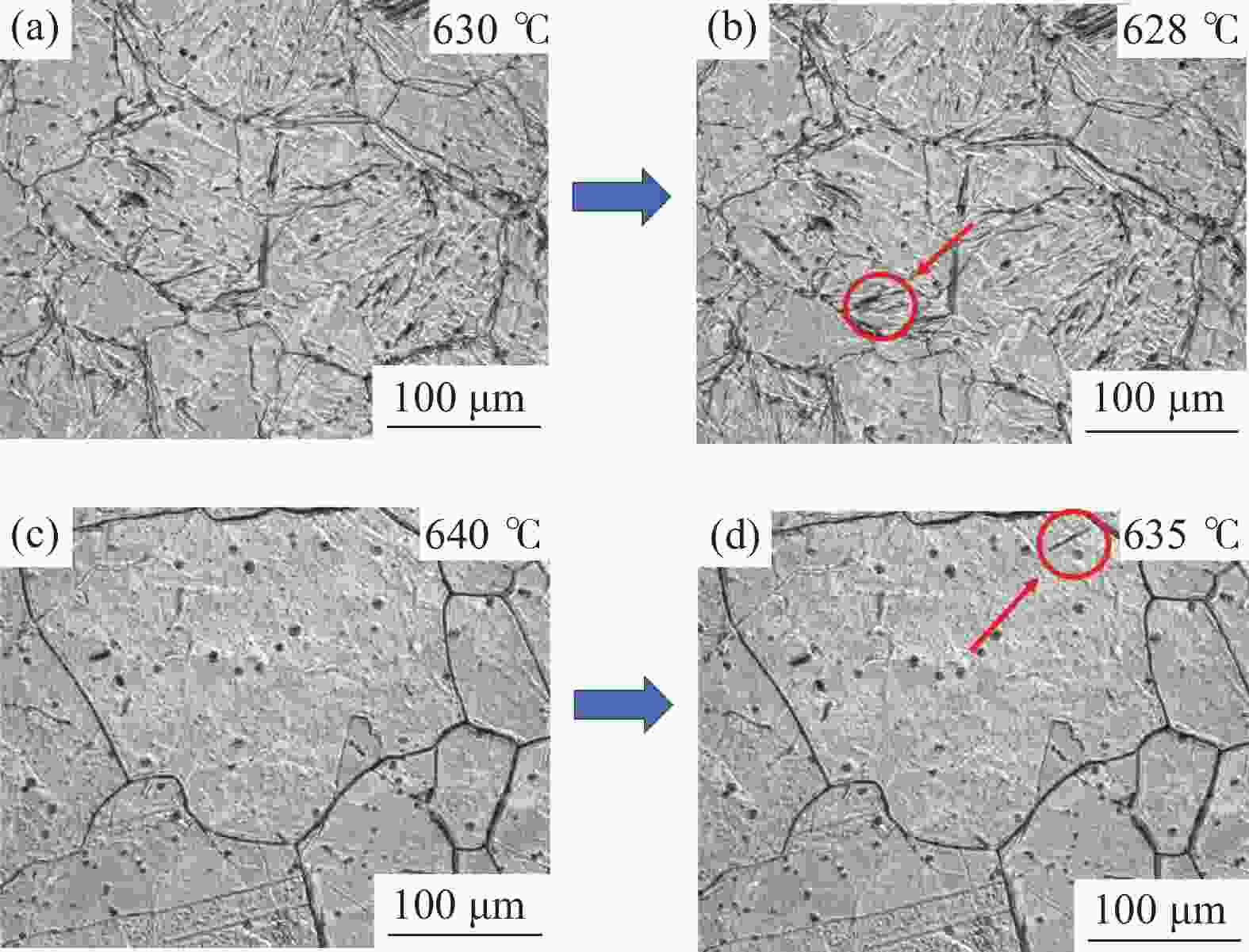
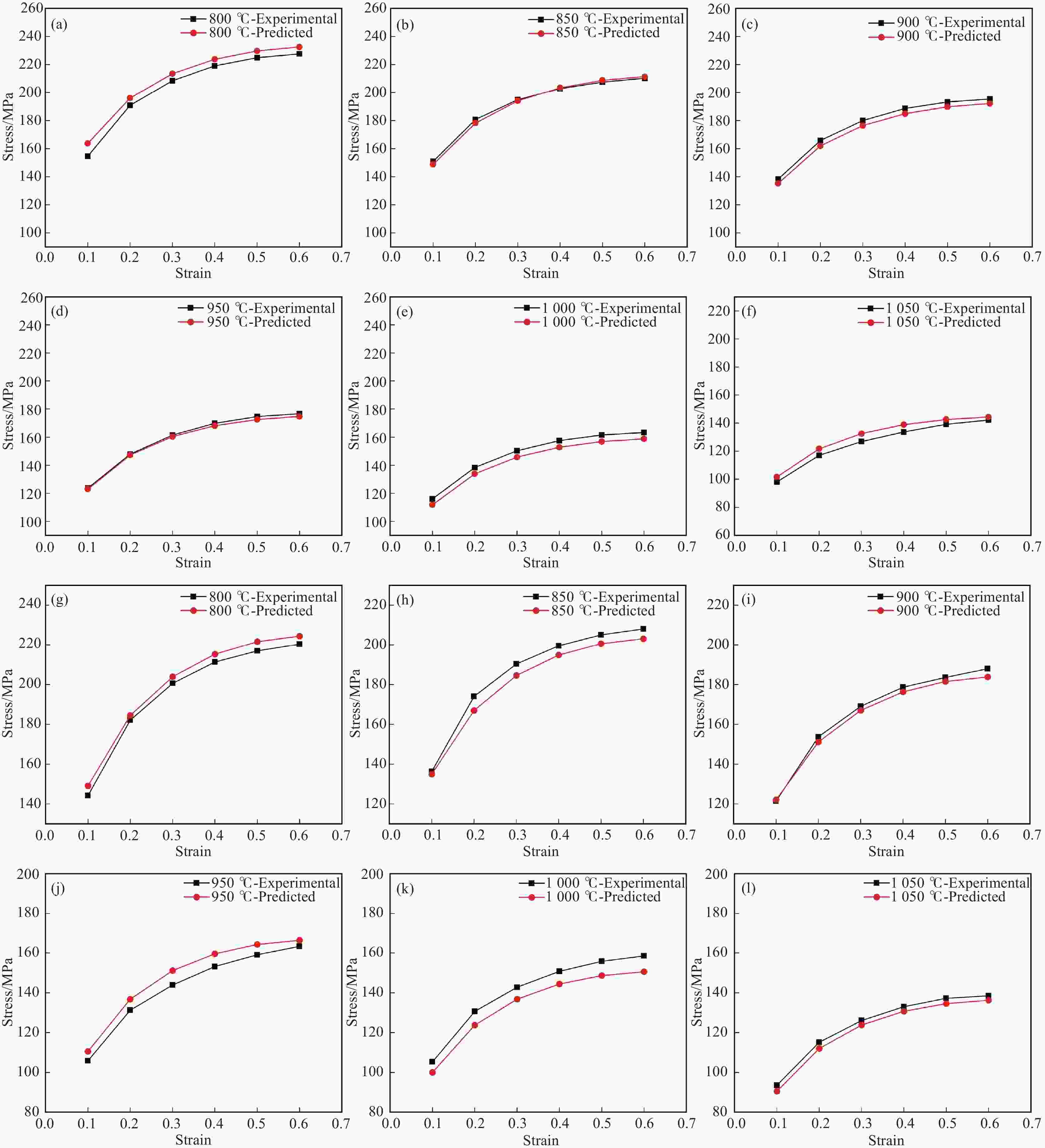
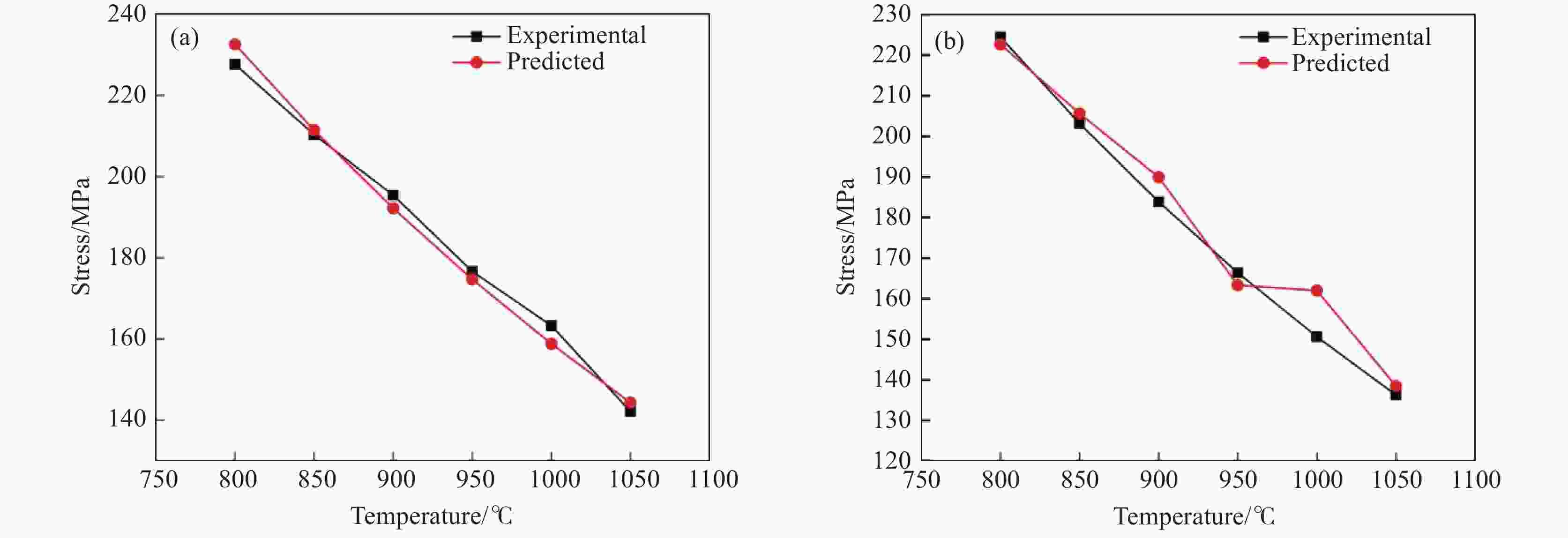
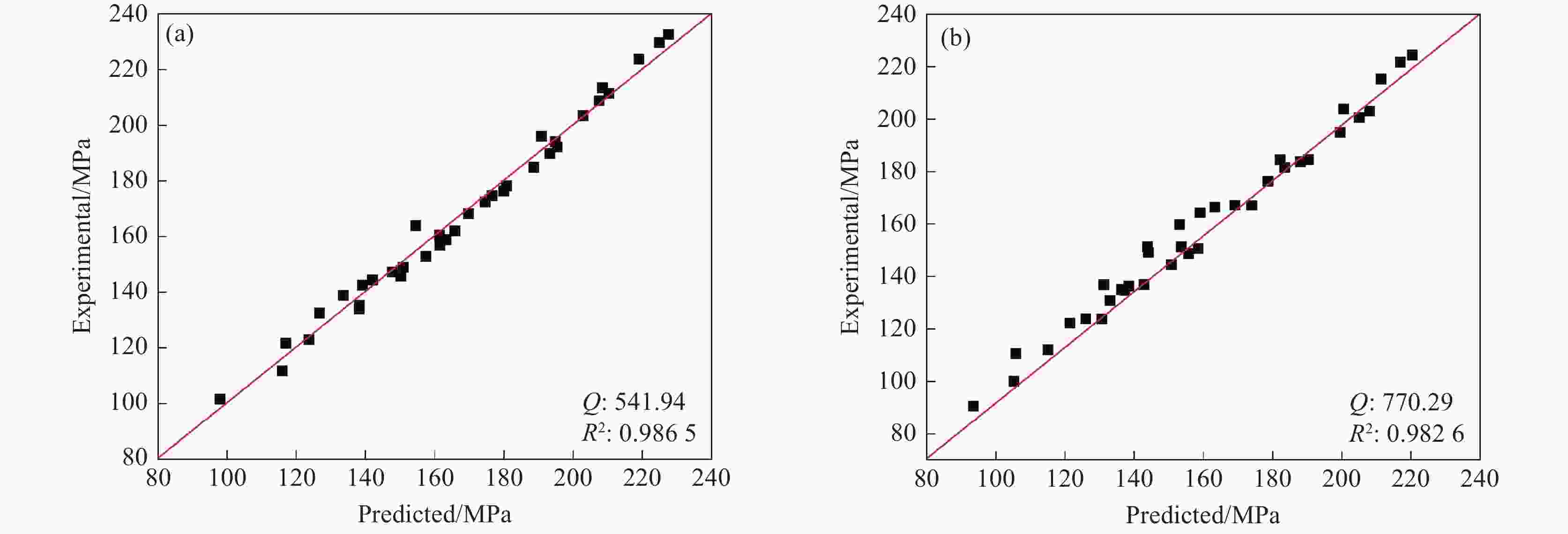
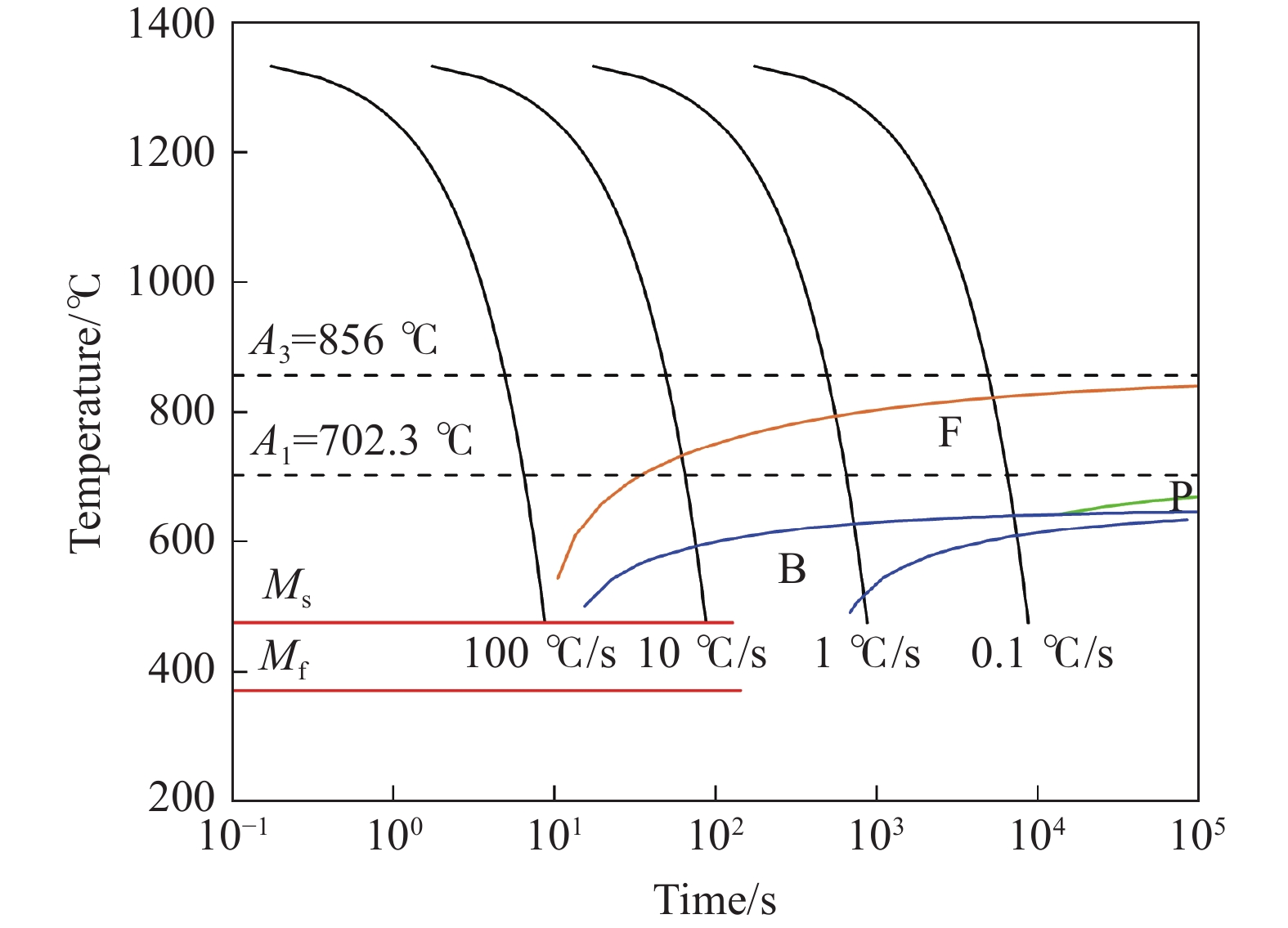
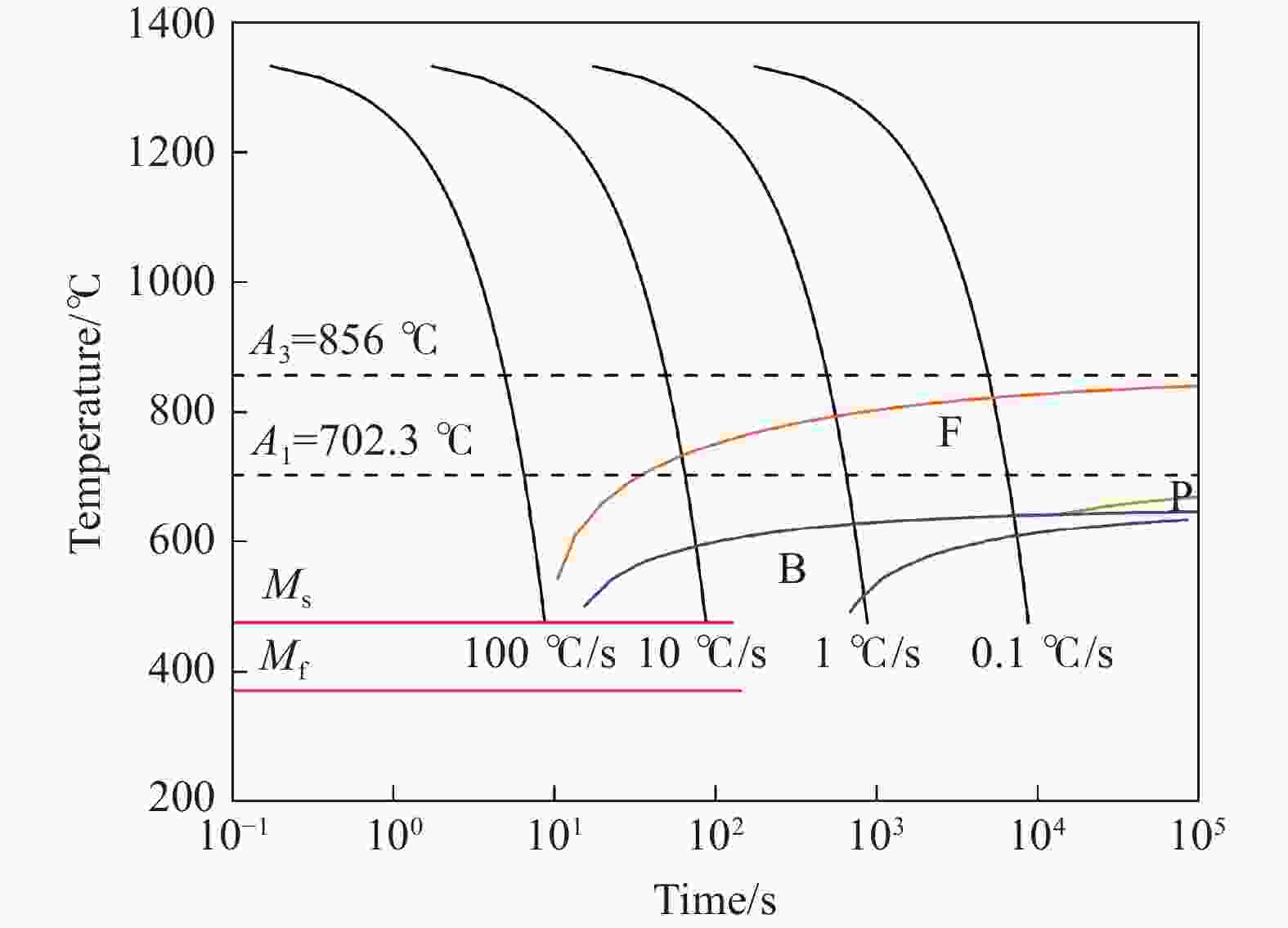
摘要: 金属变形时的变形抗力受到多种因素的影响,其中变形温度、变形工艺以及应变诱导相变均会对变形抗力造成影响。以低碳微Nb钢为对象,在Gleeble-3500热模拟试验机上进行热压缩试验,同时在高温激光共聚焦显微镜上辅助观察常规热装和高温直轧两种工艺下的高温原位形貌。结果表明,随着变形温度从800 ℃上升到
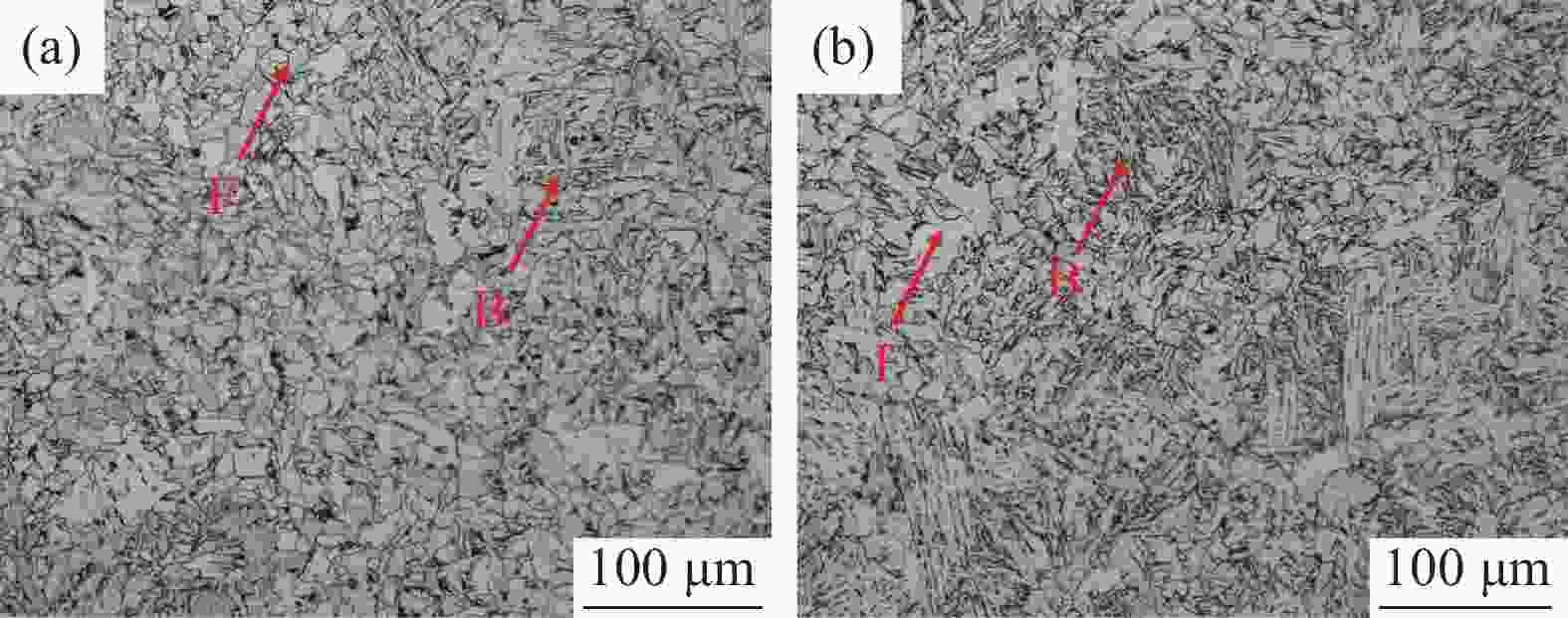
1050 ℃,高温直轧工艺下的最大变形抗力从220.9 MPa降低到138.9 MPa,而常规热装工艺下的最大变形抗力从227.9 MPa降低到143.8 MPa。这主要是因为随着温度的升高,热激活能逐渐加强,位错运动更加容易,使得变形抗力降低。此外,在相同温度变形时,常规热装工艺的变形抗力大于高温直轧工艺,这是由于常规热装工艺下的原始奥氏体晶粒尺寸(98.7 μm)小于高温直轧工艺(107.0 μm)。常规热装工艺在再次加热前的降温过程中会发生铁素体相变,再加热后重新奥氏体化,使得新生成的奥氏体晶粒要小于原始奥氏体晶粒,故常规热装工艺下晶粒尺寸小,细晶强化作用更强,导致变形抗力的增加。与此同时,对不同轧制工艺下变形抗力试验数据利用管克智、周纪华变形抗力模型进行拟合修正,建立了试验钢在高温变形时的变形抗力预测模型,常规热装工艺模型和高温直轧工艺模型的决定系数R2分别达到了0.9865 和0.9826 ,表明模型的预测结果与试验结果拟合程度较高。Abstract: The deformation resistance of metals during deformation is influenced by various factors. Among them, the deformation temperature, deformation process, and strain-induced phase transformation all have an impact on the deformation resistance. This article focuses on low carbon micro-Nb steel and conducts thermal compression experiments using a Gleeble-3500 thermal simulation testing machine. Simultaneously, the in-situ high-temperature morphology under conventional hot charging and high-temperature direct rolling was observed by high-temperature laser confocal microscope. The results show that as the deformation temperature increases from 800 ℃ to 1050 ℃, the maximum deformation resistance during high-temperature direct rolling decreases from 220.9 MPa to 138.9 MPa, while the maximum deformation resistance under the conventional hot charging process decreases from 227.9 MPa to 143.8 MPa. It is mainly because when the deformation temperature gradually increases, the thermal activation energy is enhanced, and the movement of dislocation becomes easier, which leads to a decrease in the deformation resistance. In addition, when the deformation temperature is the same, the deformation resistance of the conventional hot charging process is larger than that of the high-temperature direct rolling process. It is due to the original austenite grain size under the conventional hot charging process (98.7 μm) is smaller than that under the high-temperature direct rolling process (107.0 μm). During the cooling process before reheating in the conventional hot charging process, a ferrite phase transformation occurs, and austenitization occurs again after reheating, making the newly formed austenite grains smaller than the original austenite grains. Therefore, the smaller original austenite grain size under the conventional hot charging process leads to the stronger fine-grain strengthening effect, resulting in greater deformation resistance. Additionally, the experimental data of deformation resistance under different rolling processes were fitted and corrected by using the deformation resistance models proposed by Guan Kezhi and Zhou Jihua, and a deformation resistance prediction model for the tested steel during high-temperature deformation was established. The coefficient of determination R2 of the models for the conventional hot charging process and the high-temperature direct rolling process reaches0.9865 and0.9826 respectively, indicating a high fitting accuracy between the model's predictions and the experimental results. -
表 1 试验钢坯的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of the experimental steel
% C Si Mn P S Cu Ni 0.075 0.018 0.853 0.013 0.004 0.017 0.007 Cr Mo V Nb Ti N 0.022 0.002 0.001 0.014 0.012 0.003 表 2 不同变形温度下参数A的值
Table 2. The value of parameter A at different deformation temperatures
T/℃ A 700 ℃热装 高温直轧 800 0.33193 0.33987 850 0.34675 0.28606 900 0.35958 0.17181 950 0.3532 0.00061 1000 − 0.00038752 − 0.01603 1050 − 0.16117 − 0.14308 -
[1] BAN H Y, ZHOU G H, YU H Q, et al. Mechanical properties and modelling of superior high-performance steel at elevated temperatures[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2021, 176: 106407. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2020.106407 [2] YANG W J. Eeffect of tensile rate on tensile test results of 05Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb Steel[J]. Heat Treatment, 2024, 39(2): 15-18, 22. (杨旺久. 拉伸速率对05Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb钢拉伸试验结果的影响[J]. 热处理, 2024, 39(2): 15-18, 22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1690.2024.02.003YANG W J. Eeffect of tensile rate on tensile test results of 05Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb Steel[J]. Heat Treatment, 2024, 39(2): 15-18, 22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1690.2024.02.003 [3] WANG G D. Status and prospects of research and development of key common technologies for high-quality heavy and medium plate production[J]. Steel Rolling, 019, 36(1): 1-8, 30. (王国栋. 高质量中厚板生产关键共性技术研发现状和前景[J]. 轧钢, 2019, 36(01): 1-8, 30.WANG G D. Status and prospects of research and development of key common technologies for high-quality heavy and medium plate production[J]. Steel Rolling, 019, 36(1): 1-8, 30. [4] CHEN G X, LU X Y, YAN J, et al. High-temperature deformation behavior of M50 steel[J]. Metals, 2022, 12(4): 541. doi: 10.3390/met12040541 [5] SONG S Y, TIAN J Y, FAN L, et al. Study on dynamic and static CCT curves of steel Q460 for high performance building structures[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2021, 44(6): 406-414. (宋思颖, 田俊羽, 樊雷, 等. 高性能建筑结构用钢Q460的动态和静态CCT曲线研究[J]. 武汉科技大学学报, 2021, 44(6): 406-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3644.2021.06.002SONG S Y, TIAN J Y, FAN L, et al. Study on dynamic and static CCT curves of steel Q460 for high performance building structures[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2021, 44(6): 406-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3644.2021.06.002 [6] ZOU J H, TIAN J Y, LI X, et al. Study on dynamic CCT curve and cooling technology of steel containing low carbon niobium building structure[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2024, 47(5): 329-338. (邹佳辉, 田俊羽, 李显, 等. 低碳含铌建筑结构用钢动态CCT曲线及冷却工艺研究[J]. 武汉科技大学学报, 2024, 47(5): 329-338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3644.2024.05.002ZOU J H, TIAN J Y, LI X, et al. Study on dynamic CCT curve and cooling technology of steel containing low carbon niobium building structure[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2024, 47(5): 329-338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3644.2024.05.002 [7] ZHANG X P P, WU X D, ZHOU S R. Dynamic recrystallization and subdynamic recrystallization behavior of 18CrNiMo7-6 gear steel and their dynamic models[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2024, 48(11): 29-36. (张肖佩佩, 吴晓东, 周少荣. 18CrNiMo7-6齿轮钢的动态再结晶和亚动态再结晶行为及其动力学模型[J]. 机械工程材料, 2024, 48(11): 29-36. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl230552ZHANG X P P, WU X D, ZHOU S R. Dynamic recrystallization and subdynamic recrystallization behavior of 18CrNiMo7-6 gear steel and their dynamic models[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering, 2024, 48(11): 29-36. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl230552 [8] CHEN L H, LI C R, WEI J J. Effect of thermal deformation and Nb element action on the organization and performance of steel[J]. Materials Research Express, 2022, 9(5): 056518. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ac703b [9] SUN J H, GU H, ZHANG J, et al. Ti6Al4V-0.72H on the establishment of flow behavior and the analysis of hot processing maps[J]. Crystals, 2024, 14(4): 345. doi: 10.3390/cryst14040345 [10] SHEN W F, ZHANG C, ZHANG L W, et al. Experimental study on the hot deformation characterization of low-carbon Nb-V-Ti microalloyed steel[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2018, 27: 4616-4624. doi: 10.1007/s11665-018-3594-1 [11] SUN J Q, DAI H, ZHANG Y C. Research on mathematical model of thermal deformation resistance of X80 pipeline steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2011, 32(3): 1612-1616. [12] LIU J, MAO B X, DUANMU Y C, et al. An investigation on deformation resistance modeling for AH36 hull structural steel[J]. Modern Transportation and Metallurgical Materials, 2025, 5(1): 68-75, 84. (刘健, 毛柄勋, 端木怡超, 等. AH36船板钢变形抗力模型研究[J]. 现代交通与冶金材料, 2025, 5(1): 68-75, 84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-017X.2025.01.011LIU J, MAO B X, DUANMU Y C, et al. An investigation on deformation resistance modeling for AH36 hull structural steel[J]. Modern Transportation and Metallurgical Materials, 2025, 5(1): 68-75, 84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-017X.2025.01.011 [13] YIN B L, SAHAL A, CUI X Y, et al. Prediction model of deformation resistance of strip steel during hot continous rolling process[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2024, 31(10): 159-166. (尹宝良, SAHAL A, 崔熙颖, 等. 热连轧过程大梁钢变形抗力预报模型[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2024, 31(10): 159-166.YIN B L, SAHAL A, CUI X Y, et al. Prediction model of deformation resistance of strip steel during hot continous rolling process[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2024, 31(10): 159-166. [14] LI C, CHEN C Y, HUANG K, et al. Hot deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of Al-7.92Zn-1.64Mg-2.00Cu Alloy[J]. Metals, 2024, 14(2): 176. doi: 10.3390/met14020176 [15] LIU K Z, HUANG L, SU Y, et al. Hot deformation behavior and comparison of three rheological stress models on AerMet100 ultra-high strength steel[J]. Forging and Stamping Technology, 2024, 49(10): 209-220. (刘可卓, 黄亮, 苏阳, 等. AerMet100超高强钢热变形行为及3种流变应力模型对比[J]. 锻压技术, 2024, 49(10): 209-220.LIU K Z, HUANG L, SU Y, et al. Hot deformation behavior and comparison of three rheological stress models on AerMet100 ultra-high strength steel[J]. Forging and Stamping Technology, 2024, 49(10): 209-220. [16] FENG Y L, LI J, AI L Q, et al. Deformation resistance of Fe-Mn-V-N alloy under different deformation processes[J]. Rare Metals, 2017, 36: 833-839. doi: 10.1007/s12598-015-0678-z [17] ZHAO H T, PALMIERE E J. Influence of cooling rate on the grain-refining effect of austenite deformation in a HSLA steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2019, 158: 109990. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2019.109990 [18] ZHAO H T, PALMIERE E J. Effect of austenite grain size on acicular ferrite transformation in a HSLA steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 145: 479-489. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2018.09.013 [19] MANDAL S, BHOWMIK N, TEWARY N K, et al. Austenite grain growth and effect of austenite grain size on bainitic transformation[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2022, 38(7): 409-418. doi: 10.1080/02670836.2022.2045547 [20] WANG L F, HE P, HAN L, et al. Stress-strain analysis and yield strength prediction of austenite deformation of a medium carbon alloy steel[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2023, 31(1): 43-48. (王礼凡, 何平, 韩理, 等. 中碳合金钢奥氏体变形应力应变分析及屈服强度的预测[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2023, 31(1): 43-48. doi: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20220040WANG L F, HE P, HAN L, et al. Stress-strain analysis and yield strength prediction of austenite deformation of a medium carbon alloy steel[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2023, 31(1): 43-48. doi: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20220040 [21] ZHOU J H, GUAN K Z. Resistance to plastic deformation of metals[M]. Beijing: China Machine PRESS, 1989: 60-63. (周纪华, 管克智. 金属塑性变形阻力[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1989: 60-63.ZHOU J H, GUAN K Z. Resistance to plastic deformation of metals[M]. Beijing: China Machine PRESS, 1989: 60-63. -




 下载:
下载: