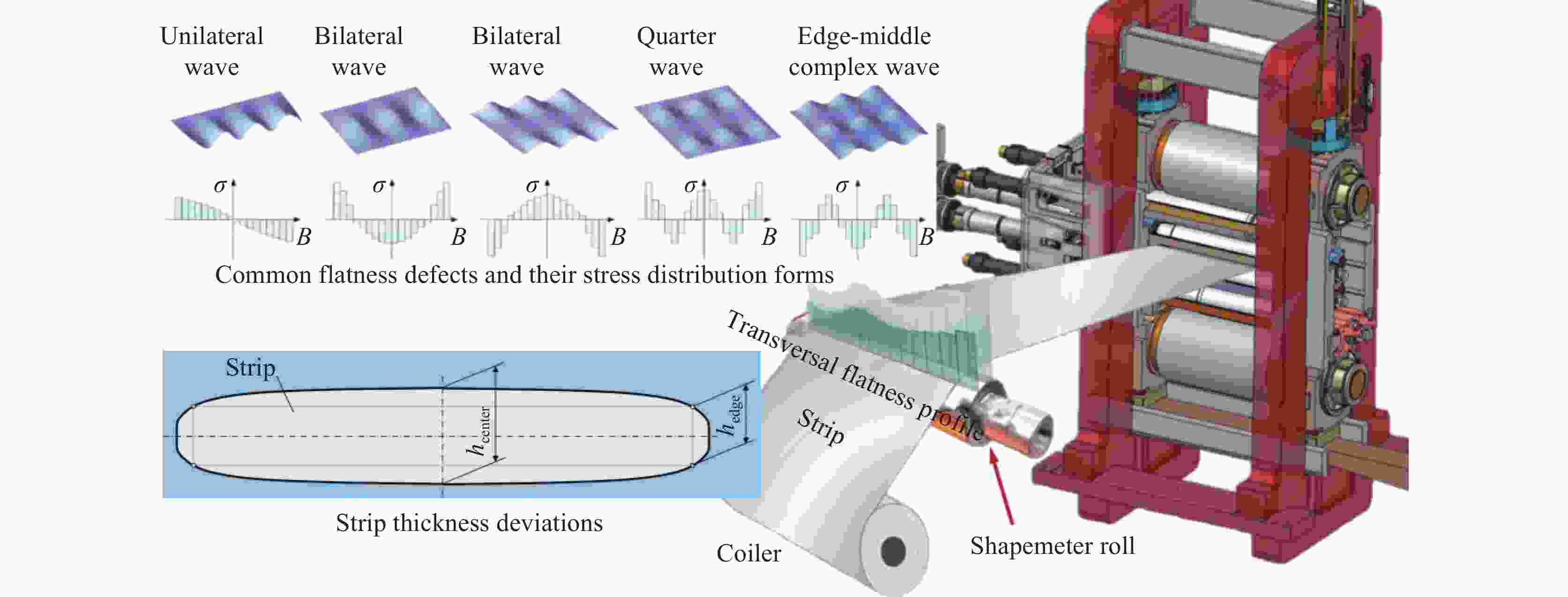
Deep applications of machine learning in cold strip rolling industry: opportunities and challenges
-
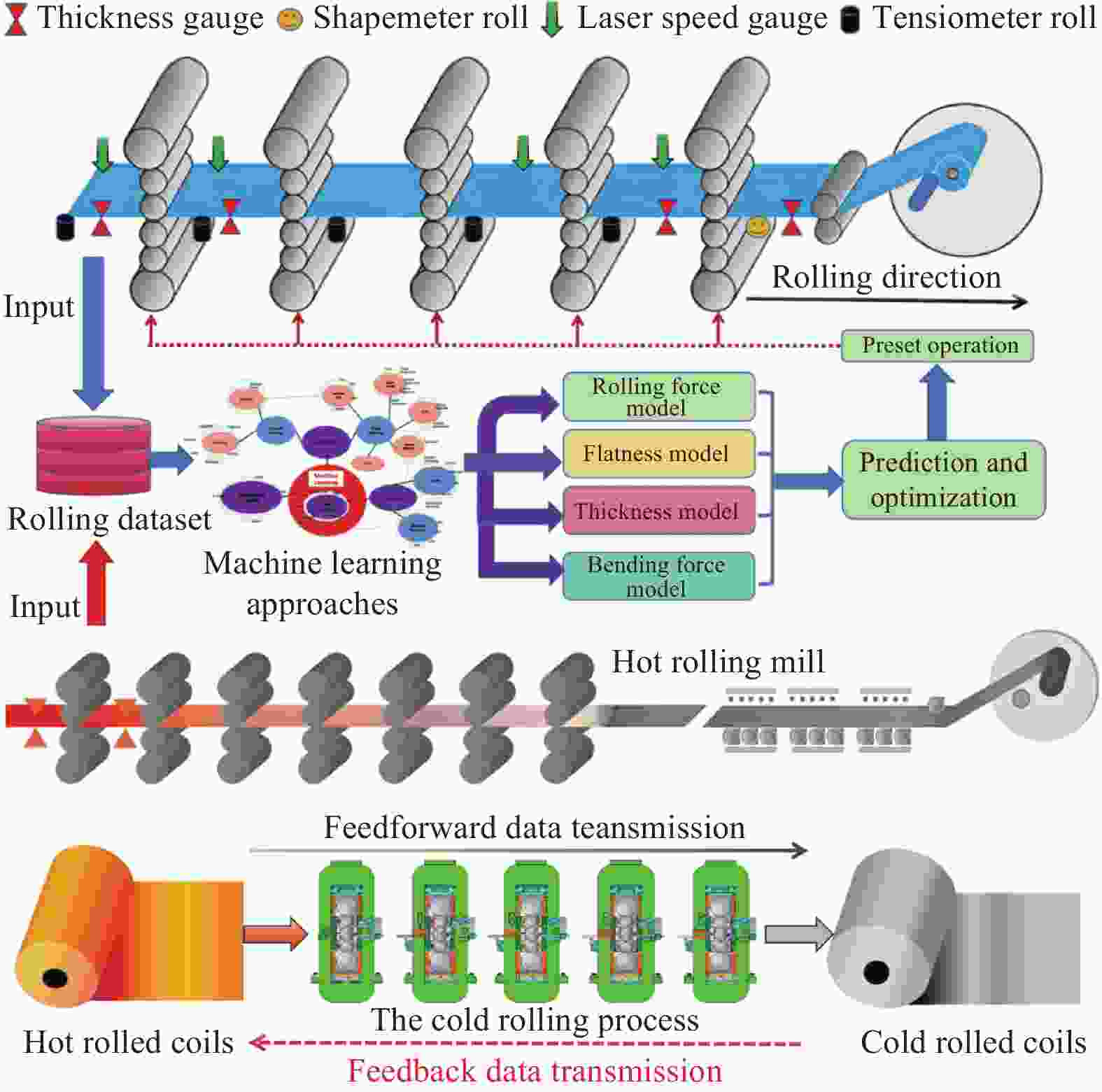
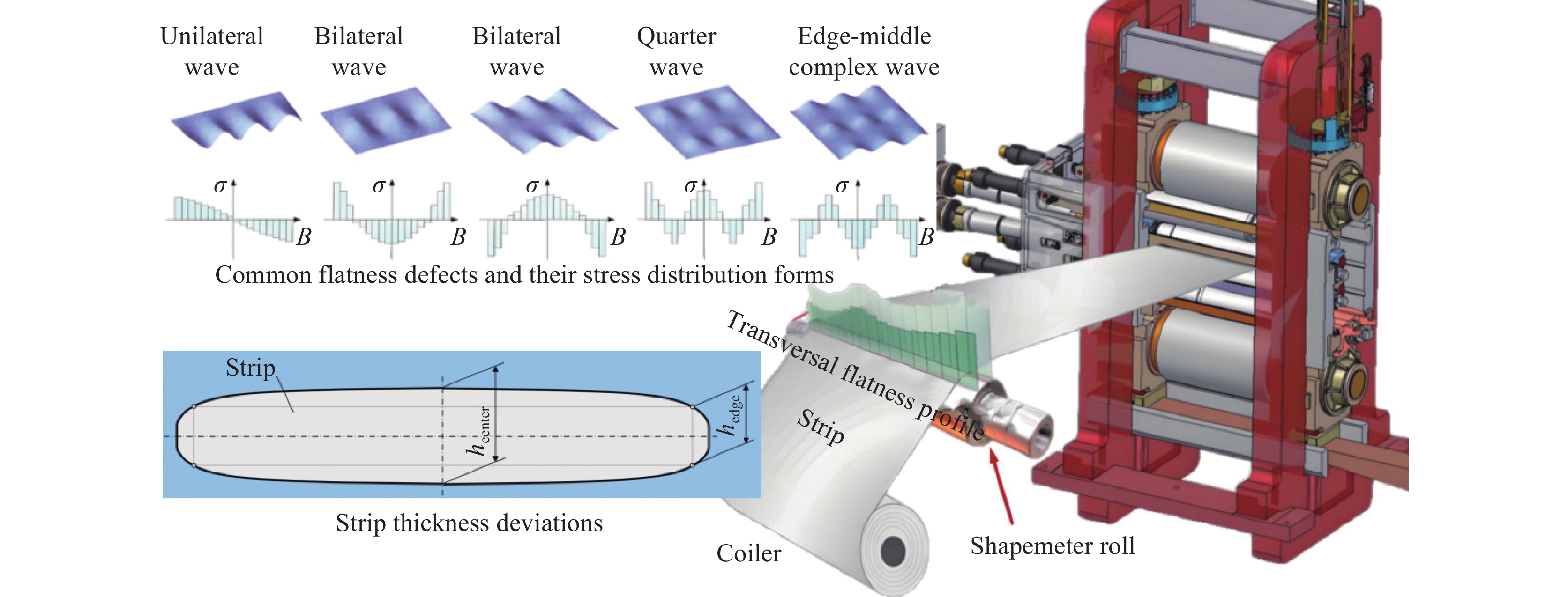
摘要: 板带冷轧是钢铁制造流程的关键环节,但长期以来面临着板形缺陷、厚度波动和轧机振动等问题,这些因素显著影响冷轧生产效率和产品质量。机器学习技术通过分析海量工艺数据,为实时预测和消除潜在缺陷提供解决方案。基于历史与实时数据,机器学习算法能够识别轧制力、辊缝、轧速等工艺参数与板形、厚度均匀性等质量指标间的复杂关联规律,实现工艺参数的动态优化,在保证产品一致性的同时有效降低废品率和停机时间。机器学习驱动的预测模型支持对轧制过程进行前瞻性调控,从源头上减少缺陷产生,提升整体效能。机器学习技术的应用不仅提高了冷轧过程的精度与可靠性,更带来显著的成本节约和产能提升。Abstract: The strip cold rolling process is a critical component of iron and steel manufacturing, yet it is often plagued by challenges such as flatness defects, thickness variations, and rolling mill vibrations, which can significantly impact productivity and product quality. Machine learning (ML) has emerged as a powerful tool to address these issues by analyzing vast amounts of process data to predict and mitigate potential defects in real-time. By leveraging historical and real-time data, ML algorithms can identify complex patterns and correlations between operational parameters (such as roll force, roll gap, and rolling speed)and key quality indicators like flatness and thickness uniformity. This enables the optimization of process parameters dynamically, ensuring consistent product quality while minimizing waste and downtime. Furthermore, ML-driven predictive models facilitate proactive adjustments to the rolling process, reducing the occurrence of defects and enhancing the overall efficiency. The integration of ML not only improves the precision and reliability of the cold rolling process but also leads to substantial cost savings and increased productivity.
-
Key words:
- Machine learning /
- cold rolling /
- flatness defects /
- thickness variations /
- rolling mill vibrations
-
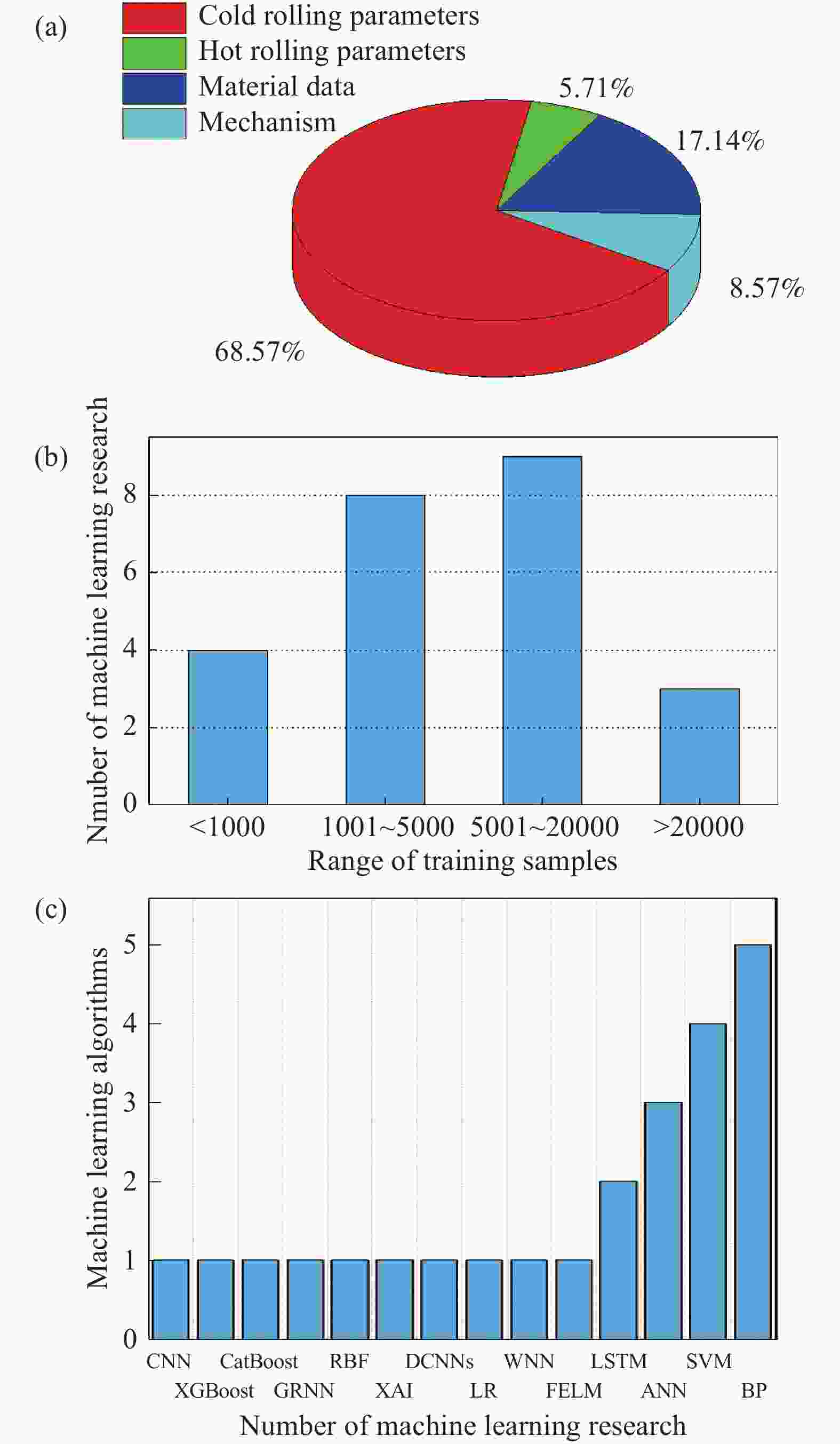
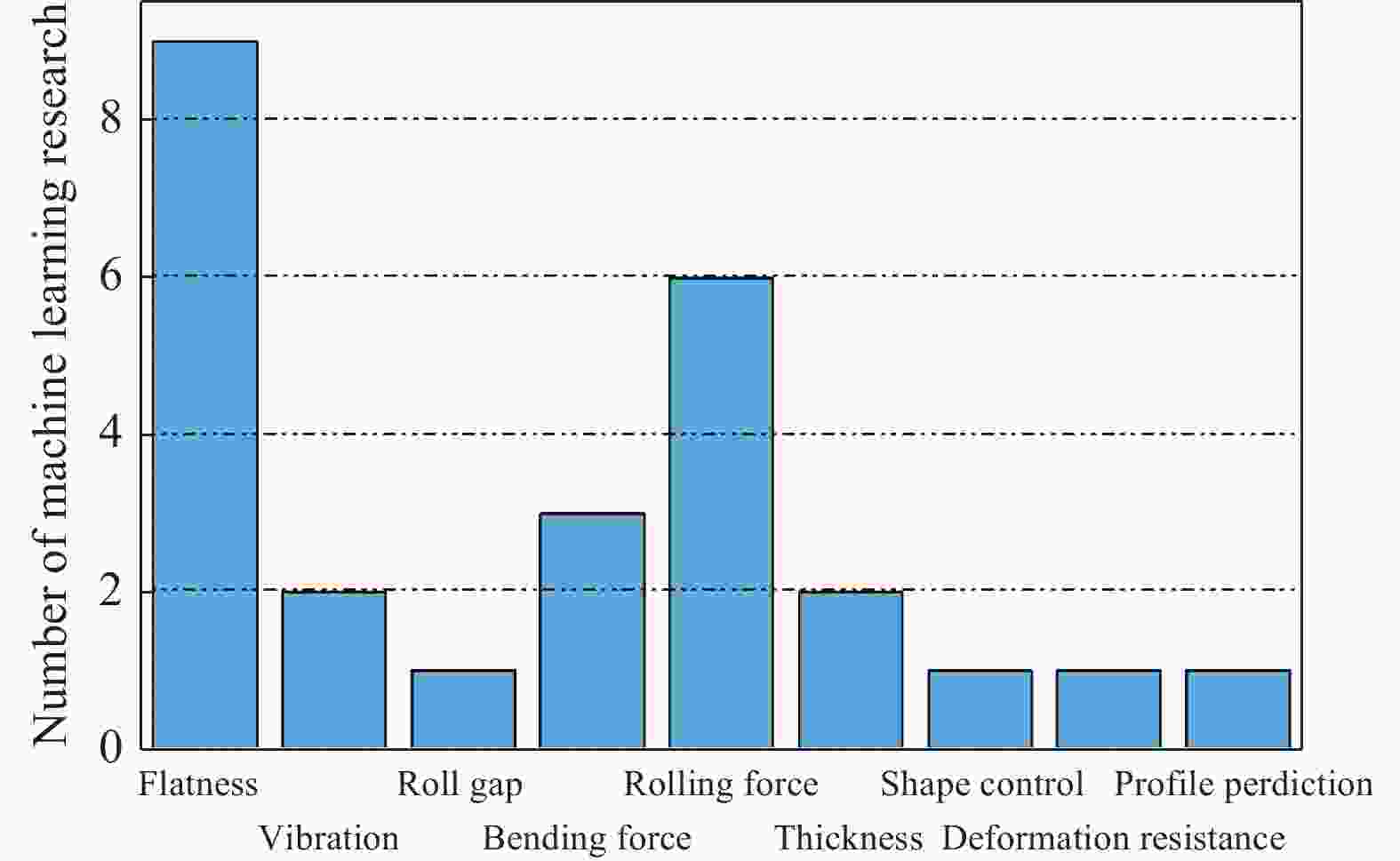
表 1 冷连轧智能预测与优化研究现状
Table 1. Research status of intelligent prediction and optimization in tandem cold rolling
Publications Model
applicationML method Applicable mill Data collection features Training
samplesEvaluation
metricSUN, et al.
(2020) [18]Flatness
prediction and optimizationKernel partial least square combined with artificial neural network (KPLS-ANN) 5-stand universal
crown mills
(UCM) cold
millsEntrance thickness, exit thickness, width, strip thickness, rolling force, rolling force tilting, work roll bending force, intermediate roll bending force, roll gap tilting, intermediate roll shifting, rolling speed, strip tension, tension tilting, coil diameter, steel grade, rolling mode 1553 groups
of samplesRMSE: 0.51,
MAE: 0.34,
MAPE: 0.09LU, et al.
(2020) [19]Rolling mill
vibration
predictionXGBoost
modelFive 6-high
tandem cold
rolling millsRolling speed, the cumulative rolling strip length of the work roll, strip deformation resistance, strip thickness at entry and exit point, total rolling force, back tension and front tension, work roll initial radius, work roll actual roughness, emulsion concentration, strip width, rraw thickness of hot strip, total reduction, roll vibration acceleration 2259 group
of vibration
data samplesR2: 0.779,
RMSE:0.0269 ,
MAE:0.0189 ,
MAPE: 9.7HU, et al.
(2020) [20]Roll gap
predictionChaos-Embedded Fuzzy Particle Swarm Optimization Optimized Support Vector Machine
(CF-PSO-SVM)1450 mm 5-stand
tandem cold
rolling millsEntry thickness, exit thickness, tension,
rolling speed, rolling force, roll gap, etc..7000 groups
of samplesR2: 0.994 1 续表1
Publications
and yearsModel
applicationML method Applicable mill Data collection sources and features Training
samplesEvaluation
metricSONG, et al.
(2021) [21]Bending Force prediction Chaos-Embedded Fuzzy Particle Swarm Optimization Optimized Support Vector Machine
(CF-PSO-SVM)1700 mm 5-stand tandem cold
rolling millsThe strip thickness before rolling, the strip thickness after rolling, the rolled strip width, the rolling speed, rolling force, shifting of intermediate roll , etc. 16000 group
of industrial
data samplesR2: 0.993 WANG, et al.
(2021) [22]Flatness
predictionConvolutional neural network (CNN) Tandem cold
rolling millsThe strip thickness before rolling, strip thickness after rolling, rolled strip width, rolling speed, forward slip, tension between stands, rolling force, shifting of intermediate roll, bending force of work roll, bending force of intermediate roll, flatness before rolling, flatness after final rolling 23000 groups
of samplesR2: 0.9555 CHEN, et al. (2022) [23] Rolling Force
Preset ModelGenetic Algorithm Optimized Backpropagation Neural Network (GA-BP) 1720 mm 5-stand universal crown
mills (UCM)
tandem cold
rolling millsYield strength, strip width, entry thickness, exit thickness, exit speed, unit back tension, unit forward tension, working roll radius 3500 groups
of samples98.76% HUANG, et al. (2022) [24] Thickness
predictionRadial basis function neural network based on variational Bayesian Gaussian mixture clustering algorithm (VBGM-RBF) six-high High
Crown (HC)
millsRolling force, rolling speed, strip width, etc. selected as input parameters, and the strip thickness after finish rolling as output
parameters16000 groups
of samplesR2: 0.9961 ,
RMSE:0.5053 CHEN, et al. (2022) [25] Rolling force
predictionGenetic algorithm
(GA)-feedback extreme learning machine (FELM)2030 mm 5-stand
strip tandem cold rolling millsEntry thickness, exit thickness, strip width, unit back tension, unit forward tension, rolling force, rolling speed, roll diameter, rolling length 700 groups
of samplesCHEN, et al. (2022) [26] Rolling force
predictionMayfly algorithm (MA)-Support Vector Machine (SVM) 1850 mm 5-stand
strip tandem cold
rolling millsEntry thickness, exit thickness, strip width, unit back tension, unit forward tension, rolling force, rolling speed, roll diameter, rolling length, raw roughness of rolling mill 800 groups
of samplesR2: 0.9793 ,
RMSE: 245.76YUAN, et al. (2022) [27] Flatness
predictionBP-MOPSO, multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm (MOPSO) 1720 mm 5-stand
6-roller strip
universal crown
mills (UCM)The strip thickness before rolling, strip thickness after rolling, rolled strip width, rolling speed, tension between stands, rolling force, intermediate roll shifting, work roll bending force, intermediate roll bending force, work roll wear, types of strip steel, fatness coefcient of the previous moment, entry crown, entry wedge 5000 groups
of samplesR2: 0.943 DING, et al. (2022) [28] Flatness
predictionCatBoost model 1450 mm 5-stand
strip tandem cold
rolling millsThe strip thickness before rolling, strip thickness after rolling, rolled strip width, rolling speed, tension between stands, rolling force, intermediate roll shifting, work roll bending force, intermediate roll bending force, work roll wear, types of strip steel, fatness coefcient of the previous moment 1225 groups
of samplesR2: 0.815,
RMSE: 0.666,
MAE: 0.436,
MAPE: 12.257CHEN, et al.
(2023) [29]Flatness
predictionAttention-Long-short-term memory (LSTM) model 1360 mm 4 stand
6-high cold
rolling millsEntrance thickness, exit thickness, strip width, yield strength of steel grade, rolling speed, forward tension, backward tension, rolling force, work roll bending force, shifting value of intermediate roll, tilting value of work roll tilt, 23 flatness data points of shape meter measurement points 68382 groups
of samplesR2: 0.971,
RMSE:1.209,
MAE: 0.825,
MSE:1.1454 ZHAO, et al.
(2023) [30]Flatness
prediction
and
optimizationartificial neural
network algorithm optimized by an artificial bee colony algorithm (ABC-ANN)1470 mm 5 stand
6-high cold
rolling mills
(UCM)Steel grade, temperature at exit of finish rolling, temperature at entry of coiler, thickness at exit of finish rolling, crown of strip, wedge of strip, width of strip, entry thickness, exit thickness of SCR, bending force of work roll, bending force of intermediate roll, shifting value of intermediate roll, rolling speed, tension from entry to exit of SCR, roll gap tilting, roll size 79181 groups
of samplesR2: 0.929,
RMSE:1.477,
MAE:1.2181 续表2
Publications Model
applicationML method Applicable mill Data collection features Training
samplesEvaluation
metricZHAO, et al. (2023) [31] Deformation
resistance
predictionBack propagation neural network optimized by the mind evolutionary
algorithm (MEA-BP)1420 mm 5-stand
6-high strip
cold rolling
millsEntrance thickness, exit thickness, relative reduction rate, cumulative reduction rate, rolling speed, finish rolling temperature, coiling temperature, hot rolling finished thickness, deformation resistance analytical model 1869 groups
of hot and
cold rolling
samples>95% YAN, et al. (2023) [32] Rolling force
predictionImproved Quantum Genetic Algorithm-Optimized Wavelet Neural Network (IQGA-WNN) ensemble learning 1450 mm 5- stand tandem cold
rolling millsRoll gap setting value, strip material, rolling speed, working roll diameter, working roll crown, entry thickness, exit thickness, intermediate roll crown, and intermediate roll diameter 1500 groups
of samples>93.75% XIA, et al. (2023) [33] Rolling force,
power and slipArtificial Neural Network (ANN) 5 stand tandem
cold rolling millsEffective radius, friction coefficient, reduction, average rolling pressure, angular velocity and tension 140 groups
of samples>94% SONG, et al. (2023) [34] Bending force prediction Hybrid fruit fly optimization algorithm (FOA)- generalized regression neural network (GRNN) 5 stand tandem
cold rolling millsEntrance thickness, exit thickness, rolled strip width, rolling force, shifting value of intermediate roll, target strip shape, actual strip shape 2000 groups
of samplesR2: 0.97, LI, et al. (2024) [35] Thickness
predictionDifferential Evolution Optimized Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Network (DE-BiLSTM) 1420 mm cold
rolling millsSteel grade, material parameters (e.g., hot-rolled finished thickness), and process parameters (e.g., coiling temperature) 98.3 % HAN, et al. (2024) [36] Profile
predictionPSO-BP algorithm 5-stand universal crown mill with work roll shifting (UCMW) tandem cold rolling mills Strip entry thickness, strip exit thickness, work roll diameter, strip width, strip deformation resistance, rolling force, front tension, back tension, friction coefficient, WRB, IMRB, WRS, IMRS 85 groups
of samplesGAO, et al.
(2024) [37]Variable speed
rolling force
predictionLong short-term memory (LSTM) network 5- stand tandem
cold rolling millsRolling length of work roll, raw thickness of hot strip, entry and exit thicknesses, rolling speed, entry and exit velocities, deformation resistance of strip, front and back tensions, actual position of roll gap, roll gap change rate, motor torque, power of internal plastic deformation, shear and tension, strip width, lubrication flow rate 10000 groups
of samplesR2: 0.9935 DING, et al.
(2024) [38]Flatness
predictioneXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) 5 stand universal
crown mills
(UCM) millsStrip set thickness, strip width, rolling speed, rolling force, work roll bending force, intermediate roll bending force, roll tilting, intermediate roll shifting, tension, theoretical tension deviation, measured strip thickness, measured strip speed, coil diameter, square coefficient of the flatness target curve, quadratic Coefficient of the flatness target curve, manual adjusting, automatic adjusting , theoretical rolling force deviation R2: 0.8867 ,
RMSE:0.912, MAE:0.5737 WANG, et al.
(2024) [39]Flatness
predictionDeep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) 1450 mm 5-stand
tandem cold
rolling millsStrip thickness, strip width, rolling speed, rolling force, work roll bending force, intermediate roll bending force, roll gap tilting value, intermediate roll shifting value, strip tension, tension difference, coil diameter, measured strip thickness, measured strip speed, coefficient of the square term of the flatness target curve, coefficient of the quadratic term of the flatness target curve, manual adjusting , automatic adjusting rolling force difference between OS and DS 1528 groups
of samplesR2: 0.8638 ,
RMSE:0.8469 ,
MAE: 0.2741 续表3
Publications Model
applicationML method Applicable mill Data collection features Training
samplesEvaluation
metricYANG, et al. (2024) [40] Flatness
predictionElite Adaptive Lévy Flight Bat Algorithm-Optimized Logistic Regression
(EALB-LR) ensemble model5-stand tandem
cold rolling
millsTension between stands, strip thickness, rolling speed between stands, rolling force between stands, actual roll gap length between stands, bending force of work roll, bending force of intermediate roll, speed after final rolling, tension after final rolling, rolling length, flatness after final rolling 10401 groups
of samplesR2: 0.9584 ,
MSE:1.2230 ,
MAE:0.4797 CHEN, et al.
(2024) [41]Vibration
predictionMulti-level network fusion 5 th stand at a
tandem cold
rolling millStrip entrance speed, back tension, front tension, raw thickness of cold strip, strip entrance thickness, strip exit thickness, rolling speed, rolling force, roll gap value 10000 group
of industrial
online data
samplesR2: 0.925,
RMSE:0.0011 CHEN, et al.
(2025) [42]Thickness
predictionRadial basis function neural network (RBF) 5-stand tandem
cold rolling
millsApply a random control signal sequence to the system in sequence based on the roll gap and speed, and record the output outlet thickness 5000 samples -
[1] TAKAMI K M, MAHMOUDI J, DAHLQUIST E, et al. Multivariable data analysis of a cold rolling control system to minimise defects[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2011, 54: 553-565. doi: 10.1007/s00170-010-2946-2 [2] FLORIANO B R, VARGAS A N, ISHIHARA J Y, et al. Neural-network-based model predictive control for consensus of nonlinear systems[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 116: 105327. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2022.105327 [3] ZONG N F, JING T, GEBELIN J C. Machine learning techniques for the comprehensive analysis of the continuous casting processes: Slab defects[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2025. [4] PITTNER J, SIMAAN M A. State-dependent riccati equation approach for optimal control of a tandem cold metal rolling process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2006, 42(3): 836-843. [5] ZONG N F, LIU H L, LI S, et al. Application status and prospects of machine learning in high-efficiency continuous casting manufacturing[J]. Angang Technology, 2025, 450(6): 23-33. (宗男夫, 刘宏亮, 李爽, 等. 机器学习在高效连铸制造中的应用现状及展望[J]. 鞍钢技术, 2025, 450(6): 23-33.ZONG N F, LIU H L, LI S, et al. Application status and prospects of machine learning in high-efficiency continuous casting manufacturing[J]. Angang Technology, 2025, 450(6): 23-33. [6] GEURTS P, ERNST D, WEHENKEL L, et al. Extremely randomized trees[J]. Machine learning, 2006, 63: 3-42. doi: 10.1007/s10994-006-6226-1 [7] SUTHAHARAN S. Machine learning models algorithms for big data classification: thinking with examples for effective learning, [M]. Berlin: Springer, 2016. [8] CHEN C, HUI Q, PEI Q, et al. CRML: A convolution regression model with machine learning for hydrology forecasting[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 133839-133849. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2941234 [9] ALLOGHANI M, Al-JUMEILY D, MUSTAFINA J, et al. A systematic review on supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms for data science[J]. Supervised Unsupervised Learn Data Sci. 2020, 3-21. [10] KAMESHWARAN K, MALARVIZHI K. Survey on clustering techniques in data mining[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2014, 5(2): 2272-2276. [11] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529-533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [12] KAELBLING L P, LITTMAN M L, MOORE A W. Reinforcement learning: a survey[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 1996, 4: 237-285. doi: 10.1613/jair.301 [13] WATKINS C W, DAYAN P. Q-learning[J]. Machine learning, 1992, 8: 279-292. [14] LIU Z. Artificial intelligence for engineers. basics and implementations[M].Berlin:Springer, 2025. [15] PANG G, SHEN C, CAO C, et al. Deep learning for anomaly detection: a review[J]. ACM Comput. Surv, 2021, 54(2): 1-38. [16] TERCAN H, TMEISEN T. Machine learning and deep learning based predictive quality in manufacturing: a systematic review[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2022, 33: 1879-1905. doi: 10.1007/s10845-022-01963-8 [17] HU Z Y, WEI Z H, SUN H, et al. Optimization of metal rolling control using soft computing approaches: a review[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2021, 28: 405-421. doi: 10.1007/s11831-019-09380-6 [18] SUN J, SHAN P F, WEI Z, et al. Data-based flatness prediction and optimization in tandem cold rolling[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2021, 11: 563-573. [19] LU X, SUN J, SONG Z X, et al. Prediction and analysis of cold rolling mill vibration based on a data-driven method[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 96: 106706. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106706 [20] HU Y, SUN J, PENG W, et al. A novel forecast model based on CF-PSO-SVM approach for predicting the roll gap in acceleration and deceleration process[J]. Engineering Computations, 2020, 38(3): 1117-1133. [21] SONG J, REN T Z, WANG K Y, et al. Optimization of work roll bending model in unsteady process of tandem cold rolling based on CF-PSO-SVM[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021, 11: 78-86. (宋君, 任廷志, 王奎越, 等. 基于CF-PSO-SVM的冷连轧非稳态工作辊弯辊模型优化[J]. 钢铁, 2021, 11: 78-86.SONG J, REN T Z, WANG K Y, et al. Optimization of work roll bending model in unsteady process of tandem cold rolling based on CF-PSO-SVM[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021, 11: 78-86. [22] WANG Y, LI C S, PENG L G, et al. Application of convolutional neural networks for prediction of strip flatness in tandem cold rolling process[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 68: 512-522. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.05.062 [23] CHEN L Z, SUN W Q, HE A R, et al. Research on thickness defect control of strip head based on GA-BP rolling force preset model[J]. Metals, 2022, 12: 924-940. doi: 10.3390/met12060924 [24] HUANG Y, ZHOU X M, GAO Z Y. Thickness prediction of thin strip cold rolling based on VBGM-RBF[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 120: 5865-5884. doi: 10.1007/s00170-022-09122-2 [25] CHEN S Z, BAI Y S, HOU J Q, et al. Rolling force prediction model for cold rolling based on GA-FELM[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 2022, 46(3): 46v224-229. (陈树宗, 白芸松, 侯佳琦, 等. 基于GA-FELM算法的冷轧轧制力预测模型[J]. 燕山大学学报, 2022, 46(3): 46v224-229. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2022.03.005CHEN S Z, BAI Y S, HOU J Q, et al. Rolling force prediction model for cold rolling based on GA-FELM[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 2022, 46(3): 46v224-229. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2022.03.005 [26] CHEN S Z, HOU J Q, BAI Y S, et al. Rolling force prediction model for cold rolling based on MA-SVM[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 2023, 47(5): 428-432. (陈树宗, 白芸松, 侯佳琦, 等. 基于MA-SVM算法的冷轧轧制力预测模型[J]. 燕山大学学报, 2023, 47(5): 428-432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2023.05.006CHEN S Z, HOU J Q, BAI Y S, et al. Rolling force prediction model for cold rolling based on MA-SVM[J]. Journal of Yanshan University, 2023, 47(5): 428-432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-791X.2023.05.006 [27] YUAN T H, SUN W Q, HE A R, et al. Research on quarter wave shape control of cold rolled high strength steel based on BP-MOPSO[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022, 122: 3867-3880. doi: 10.1007/s00170-022-10101-w [28] DING Y, DING C Y, SUN J, et al. Research on quarter wave shape control of cold rolled high strength steel based on BP-MOPSO[J]. Rolling, 2022, 39(6): 99-105. [29] CHEN Y F, PENG L G, WANG Y, et al. Prediction of tandem cold-rolled strip flatness based on Attention-LSTM model[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2023, 91: 110-121. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.02.048 [30] ZHAO J W, LI J D, YANG Q, et al. A novel paradigm of flatness prediction and optimization for strip tandem cold rolling by cloud-edge collaboration[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2023, 316: 117947. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2023.117947 [31] ZHAO J W, LI J D, QIE H T, et al. Online prediction of deformation resistance for strip tandem cold rolling based on data-driven[J]. Metals, 2023, 13: 737-756. doi: 10.3390/met13040737 [32] YAN Z W, BU H N, HU C Z, et al. Rolling force prediction during FGC process of tandem cold rolling based on IQGA-WNN ensemble learning[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2023, 125: 2869-2884. doi: 10.1007/s00170-023-10899-z [33] XIA J S, KHABAZ M K, PATRA I, et al. Using feed-forward perceptron Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model to determine the rolling force, power and slip of the tandem cold rolling[J]. ISA Transactions, 2023, 132: 353-363. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2022.06.009 [34] SONG J, WANG K Y, CAO Z H. Application of fruit fly optimization neural network in cold rolling bending model[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2023, 47(3): 116-125. (宋君, 王奎越, 曹忠华. 果蝇优化神经网络在冷轧弯辊模型中的应用[J]. 冶金自动化, 2023, 47(3): 116-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7059.2023.03.013SONG J, WANG K Y, CAO Z H. Application of fruit fly optimization neural network in cold rolling bending model[J]. Metallurgical Industry Automation, 2023, 47(3): 116-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7059.2023.03.013 [35] LI J D, ZHAO J W, WANG X C, et al. An industrial IoT-based deformation resistance prediction and thickness control method of cold-rolled strip in steel production systems[J]. Information Sciences, 2024, 674: 120735. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2024.120735 [36] HAN G M, LI H B, WANG G, et al. Prediction and control of profile for silicon steel strip in the whole tandem cold rolling based on PSO-BP algorithm[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2024, 120: 250-259. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2024.04.050 [37] CAO L, LI X, LI X H, et al. Variable speed rolling force prediction with theoretical and data-driven models[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2024, 264: 108833. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2023.108833 [38] DING C Y, YE J C, LEI J W, et al. An interpretable framework for high-precision flatness prediction in strip cold rolling[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2024, 329: 118452. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2024.118452 [39] WANG Q L, SUN J, HU Y J, et al. Deep learning-based flatness prediction via multivariate industrial data for steel strip during tandem cold rolling[J]. Expert Systems With Applications, 2024, 237: 121777. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121777 [40] YANG W Q, ZHAO Z T, ZHU L Y, et al. Strip flatness prediction of cold rolling based on ensemble methods[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2024, 31: 237-251. doi: 10.1007/s42243-023-01060-x [41] CHEN S Z, LIU Y X, WANG Y L, et al. Multi-dimension and multi-modal rolling mill vibration prediction model based on multi-level network fusion[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2024, 31: 3329-3348. doi: 10.1007/s11771-024-5762-9 [42] NIU Y Y, LI X J, DENG C, et al. RBF neural network-based distributed nonlinear model predictive control on tandem cold rolling stands[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2025, 35(6): 2451-2461. [43] BABAJAMALI Z, KHABAZ M K, AGHADAVOUDI F, et al. Pareto multi-objective optimization of tandem cold rolling settings for reductions and inter stand tension using Nsga-Ii[J]. ISA Transactions, 2022, 130: 399-408. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2022.04.002 [44] HAN H G, FU S J, SUN H Y, et al. Hierarchical nonlinear model predictive control with multi-time-scale for wastewater treatment process[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2021, 108: 125-135. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2021.11.002 -




 下载:
下载: