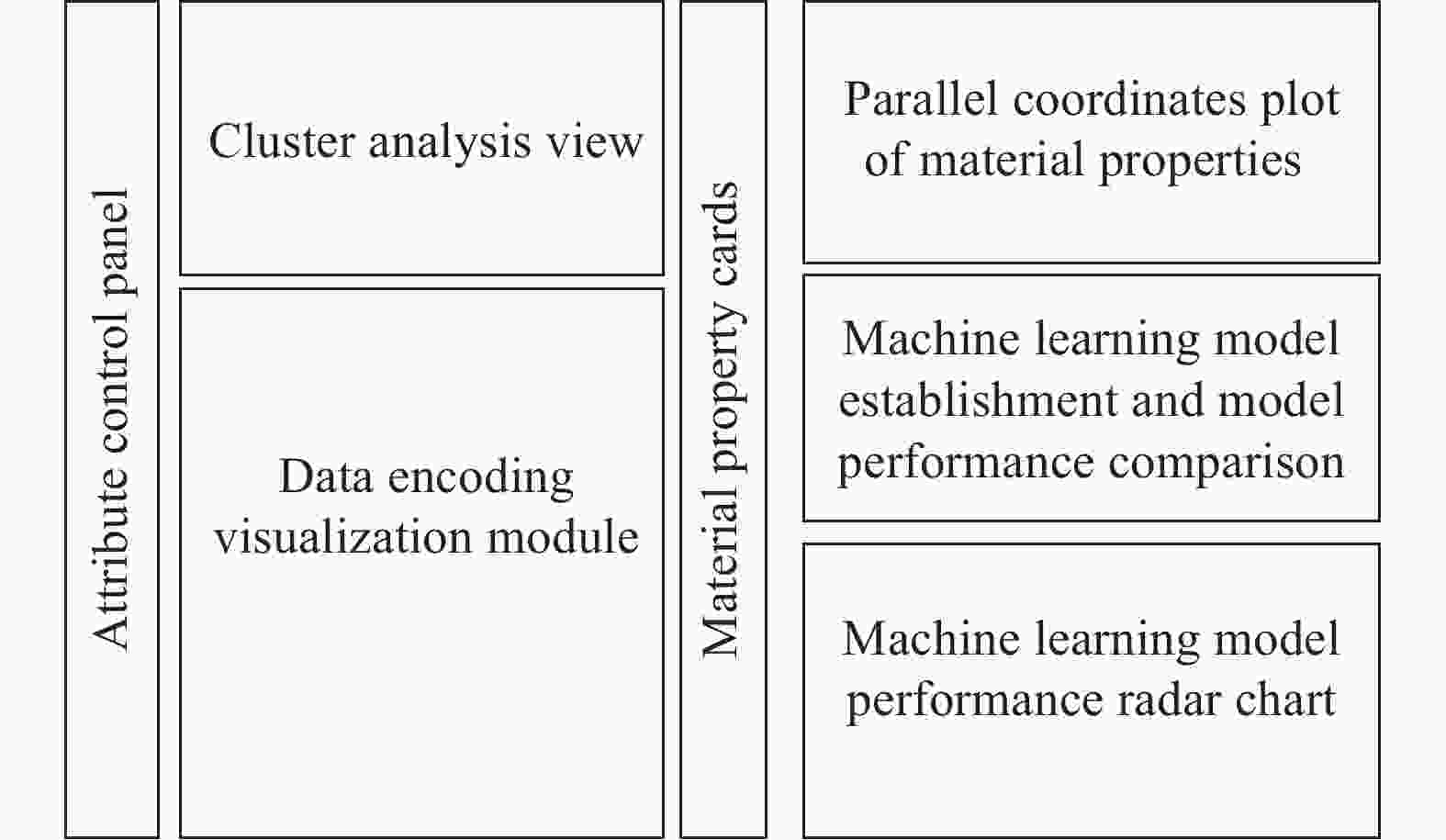
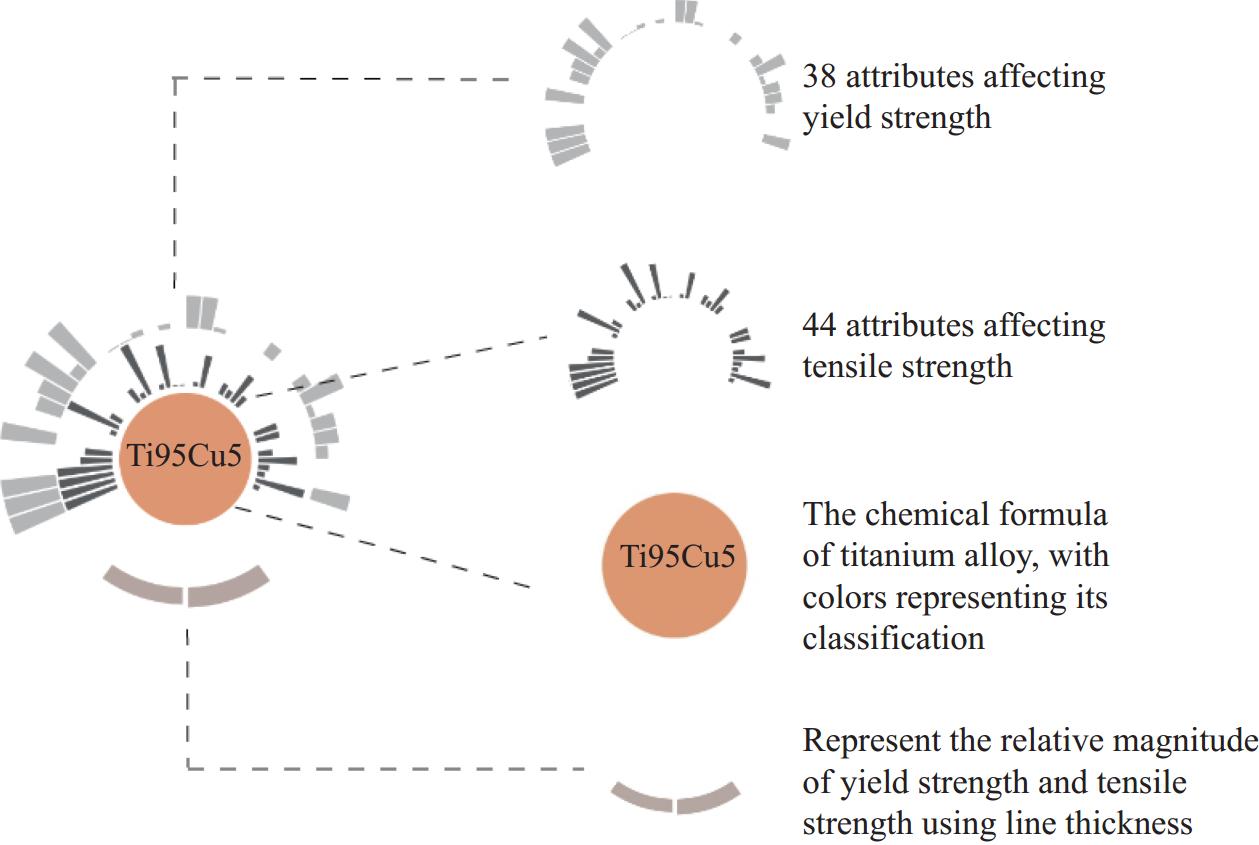
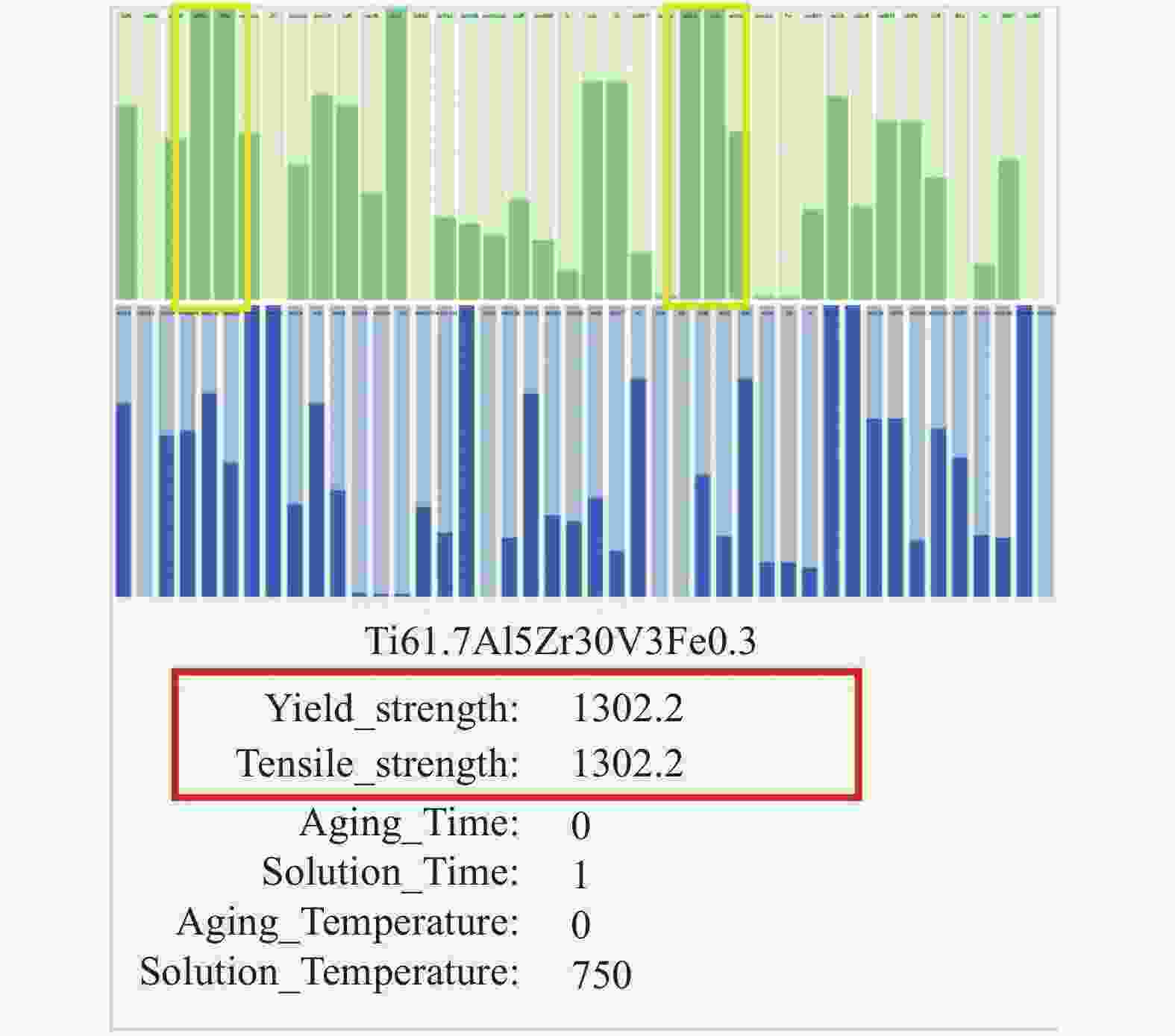
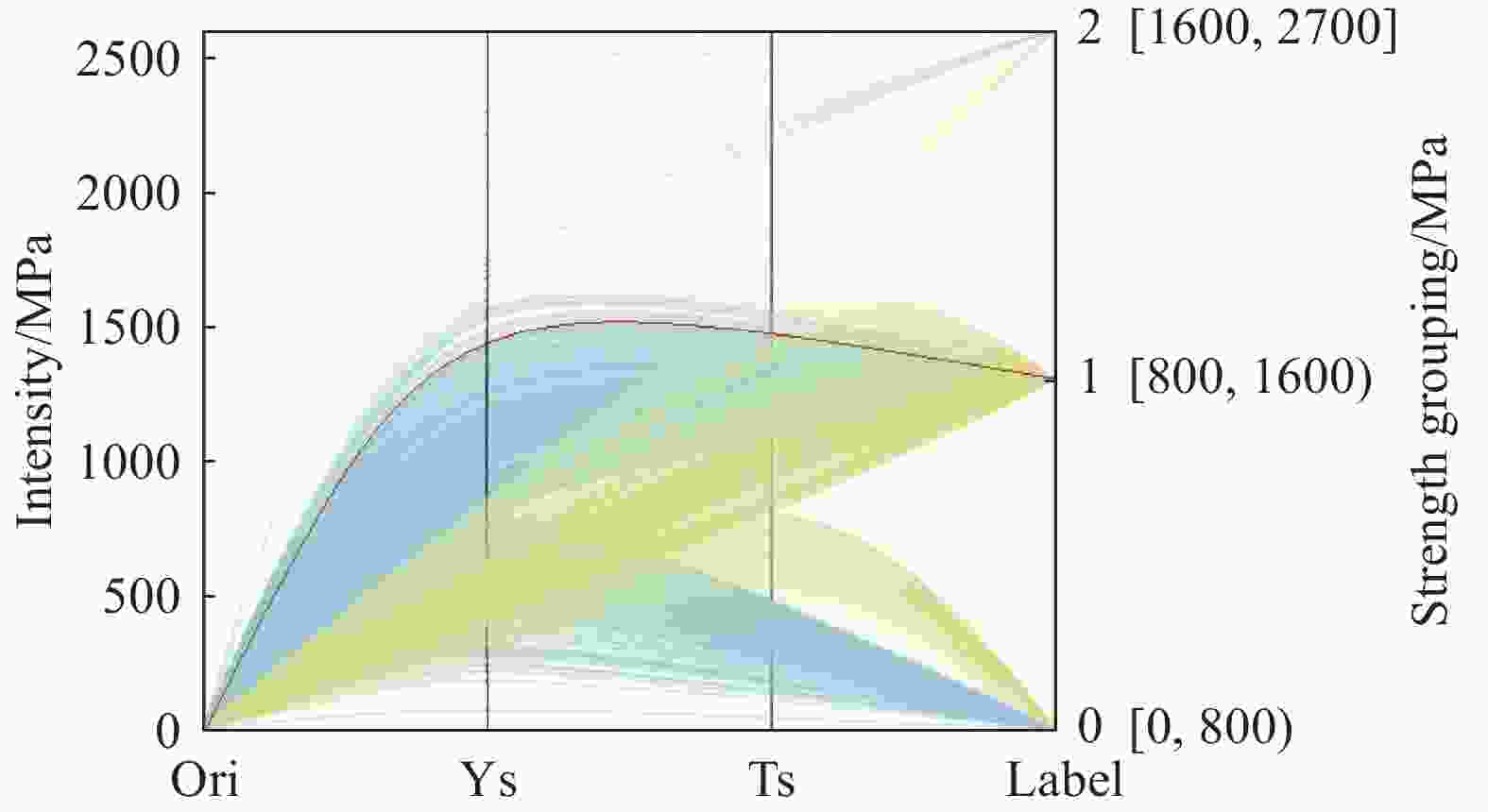
TAExplorer: visualizing key factors in titanium alloy performance
-
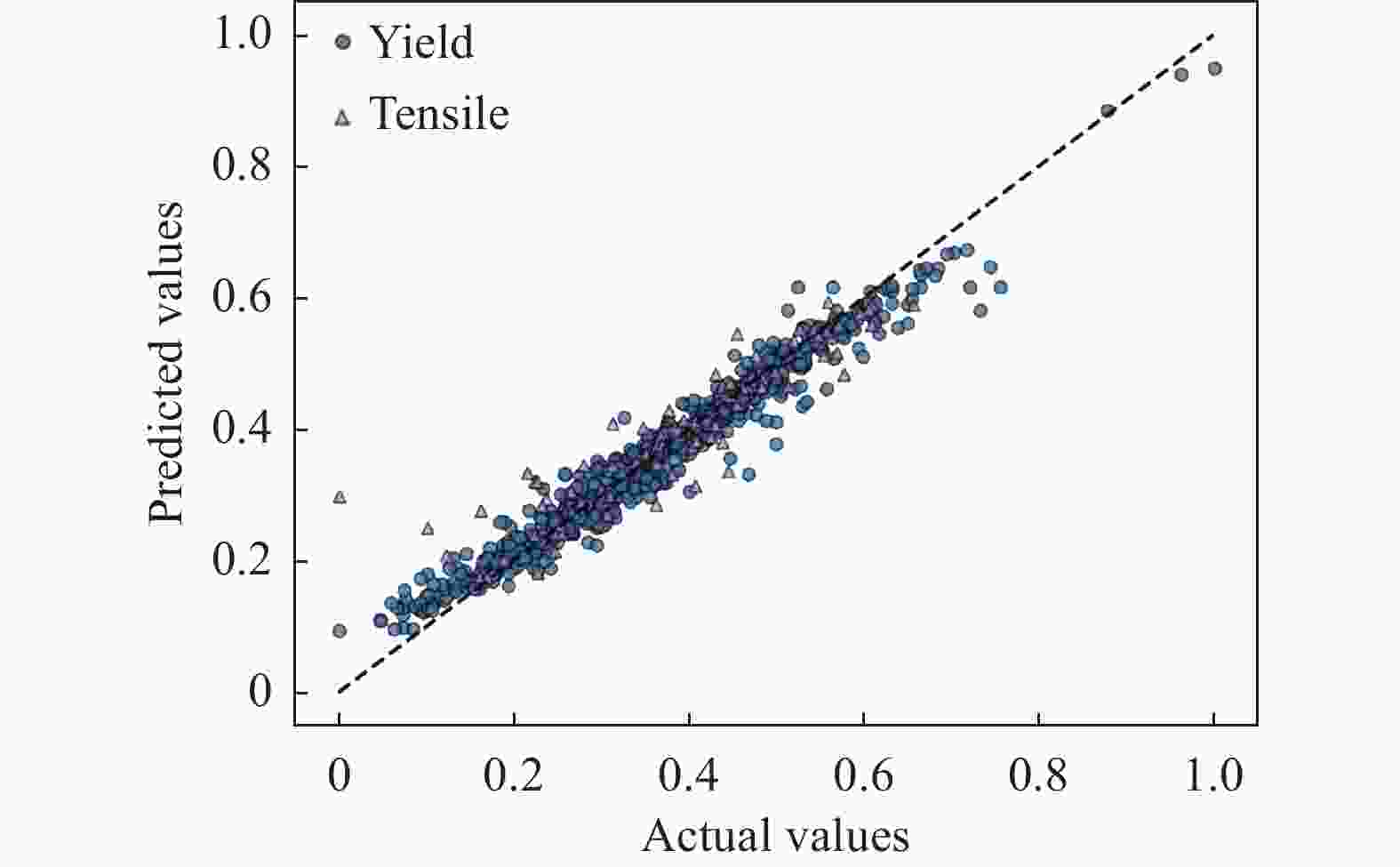
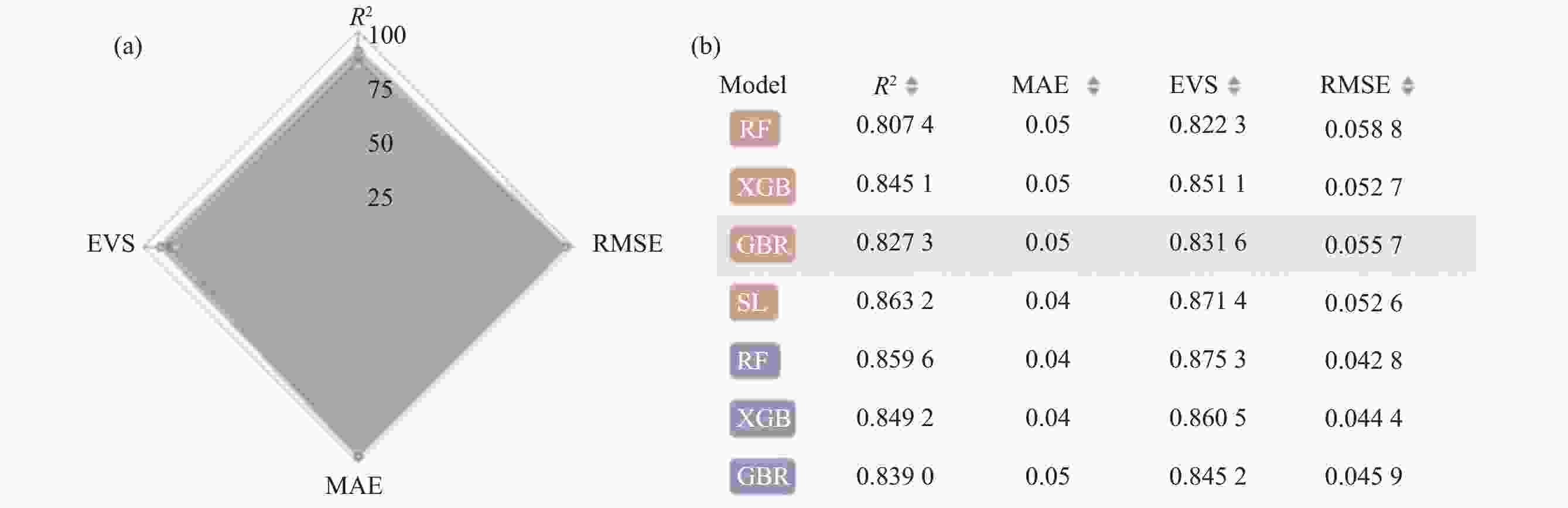
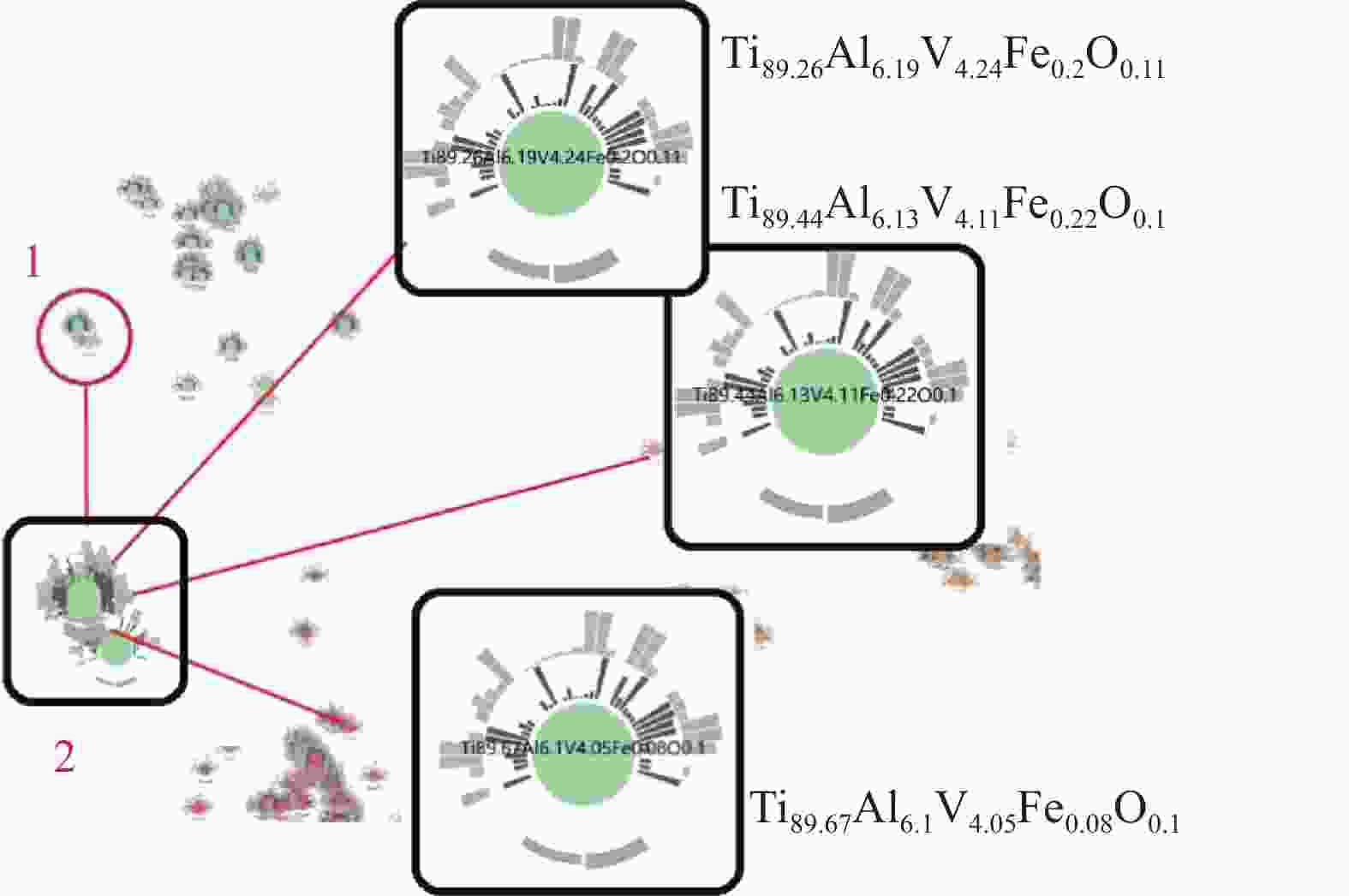
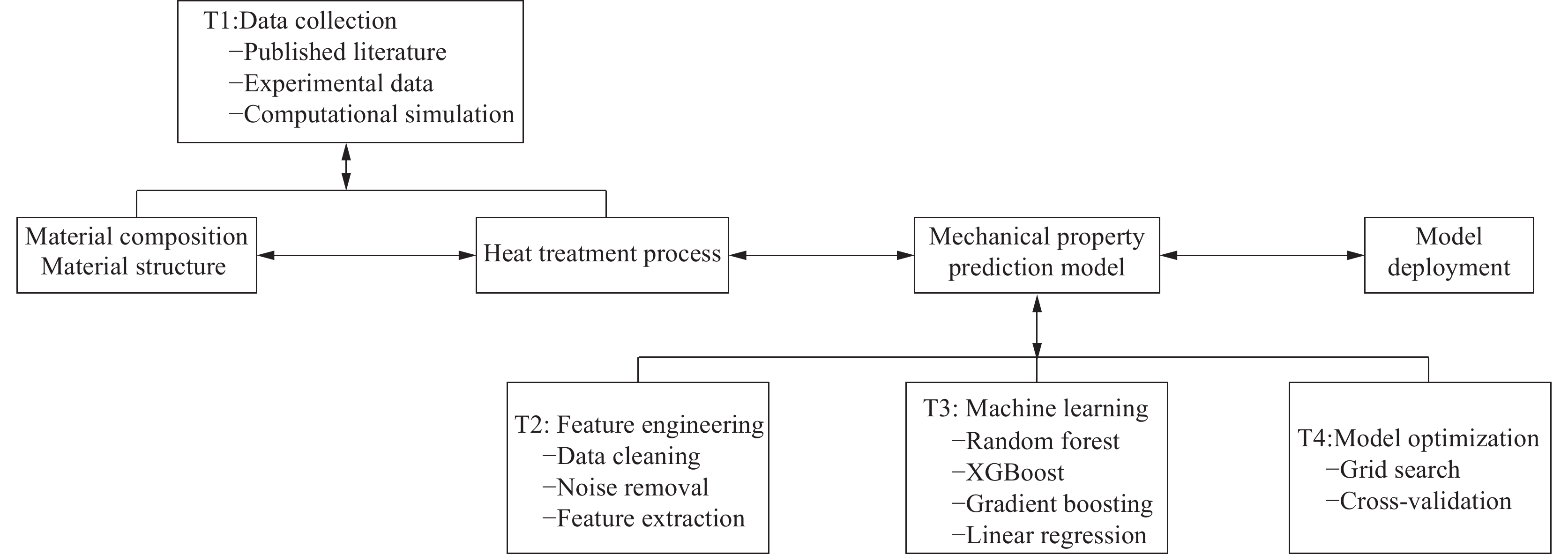
摘要: 钛合金具有高强度,优秀的耐腐蚀性和耐热性等特点,因此被航空航天、化工和医疗等领域广泛应用。由于钛合金的性能取决于它的结构特征,不同应用领域对于钛合金性能的要求不尽相同,专家们一直致力于通过试验试错方法来设计和获得具有目标性能的新材料,以及寻找影响钛合金性能的工艺因素。然而钛合金的制作工艺复杂,时间成本过长,利用传统方法来找到合适的材料非常困难。目前基于机器学习的方法被引入并用于材料预测,但是为领域专家设计的、能够对机器学习模型进行直观性能比较和分析的学习工具却很少。为此提出基于钛合金的交互式可视化分析系统TAExplorer,可以为专家提供多方面的参考。该系统采用多方面的可视化方案,旨在从各个角度进行分析,例如特征分布、数据相似性、模型性能以及结果呈现。专家们通过实际实验室试验进行了案例研究,最终结果证实了该系统的有效性和实用性。Abstract: Titanium alloys have the characteristics of high strength, excellent corrosion resistance and heat resistance, so they are widely used in aerospace, chemical and medical fields. Since the properties of titanium alloys depend on their structural characteristics and the requirements for titanium alloy properties vary from application to application, researchers have been working on designing and obtaining new materials with the targeted properties through experimental trial-and-error methods, as well as searching for process factors affecting the properties of titanium alloys. However, the production process of titanium alloy is complex, time-consuming, and it is very difficult to find the appropriate material by traditional methods. Machine learning based methods have currently being introduced and used for material prediction, but there are few learning tools designed for researchers that are capable of intuitively comparing and analyzing the performance of machine learning models. Herein, we propose TAExplorer, an interactive visualization and analysis system based on titanium alloys that can provide experts with multifaceted references. Our system employs a multifaceted visualization scheme that aims to analyze from various perspectives, such as feature distribution, data similarity, model performance, and result presentation. Experts have conducted case studies through practical laboratory experiments, and the final results confirm the effectiveness and practicality of our system.
-
Key words:
- titanium alloy /
- materials data /
- data visualization /
- machine learning
-
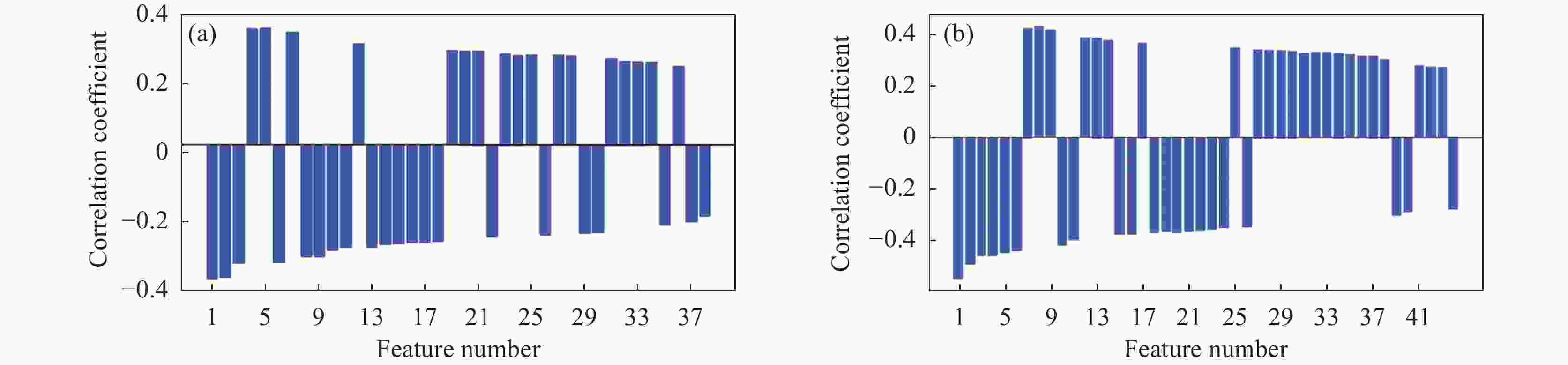
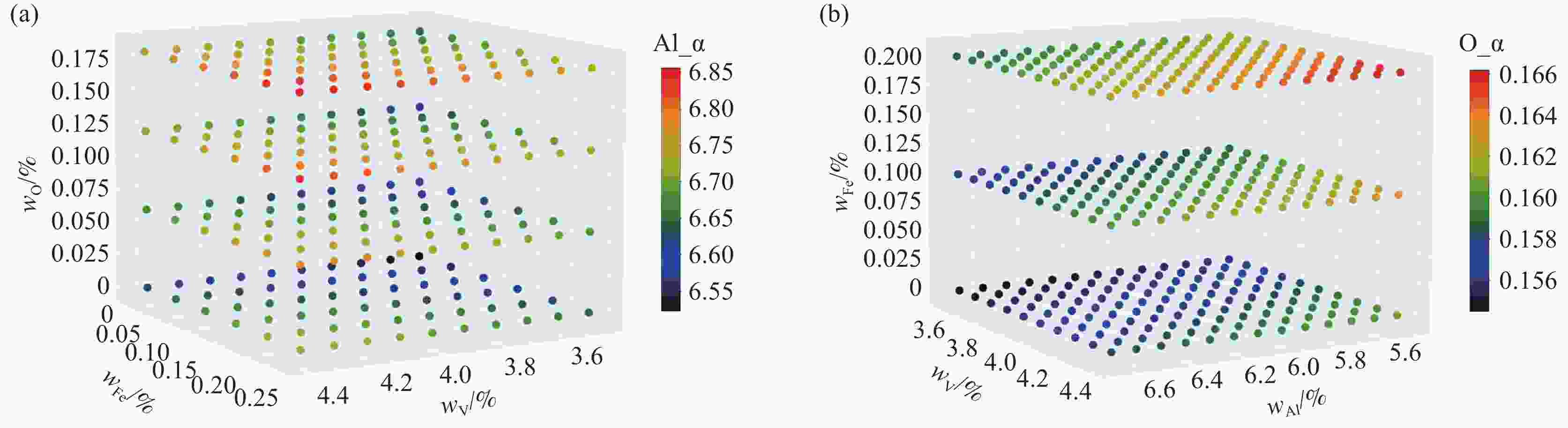
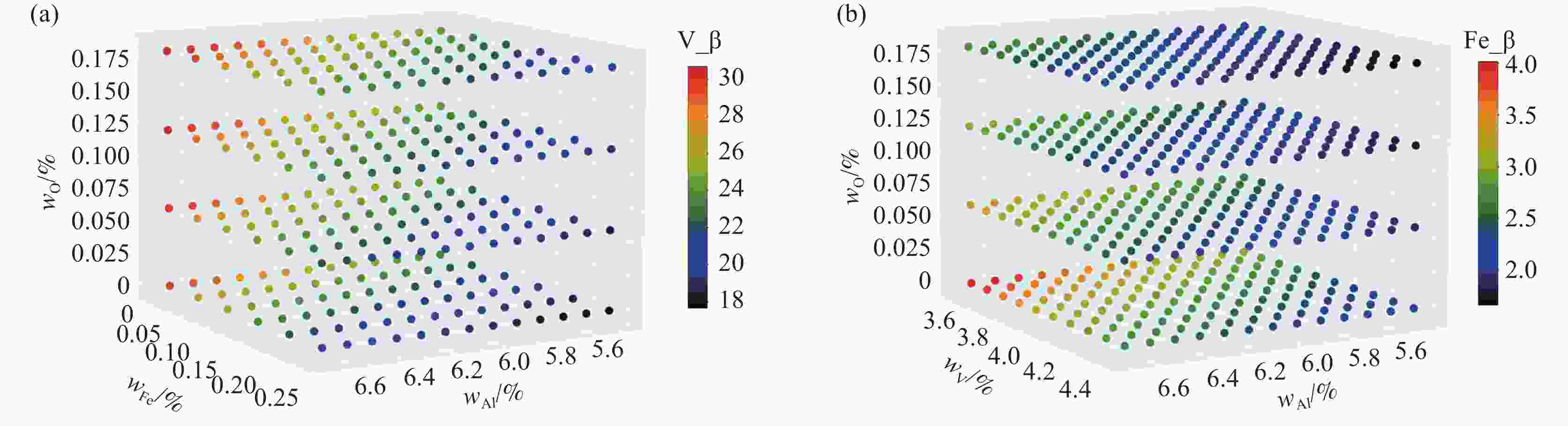
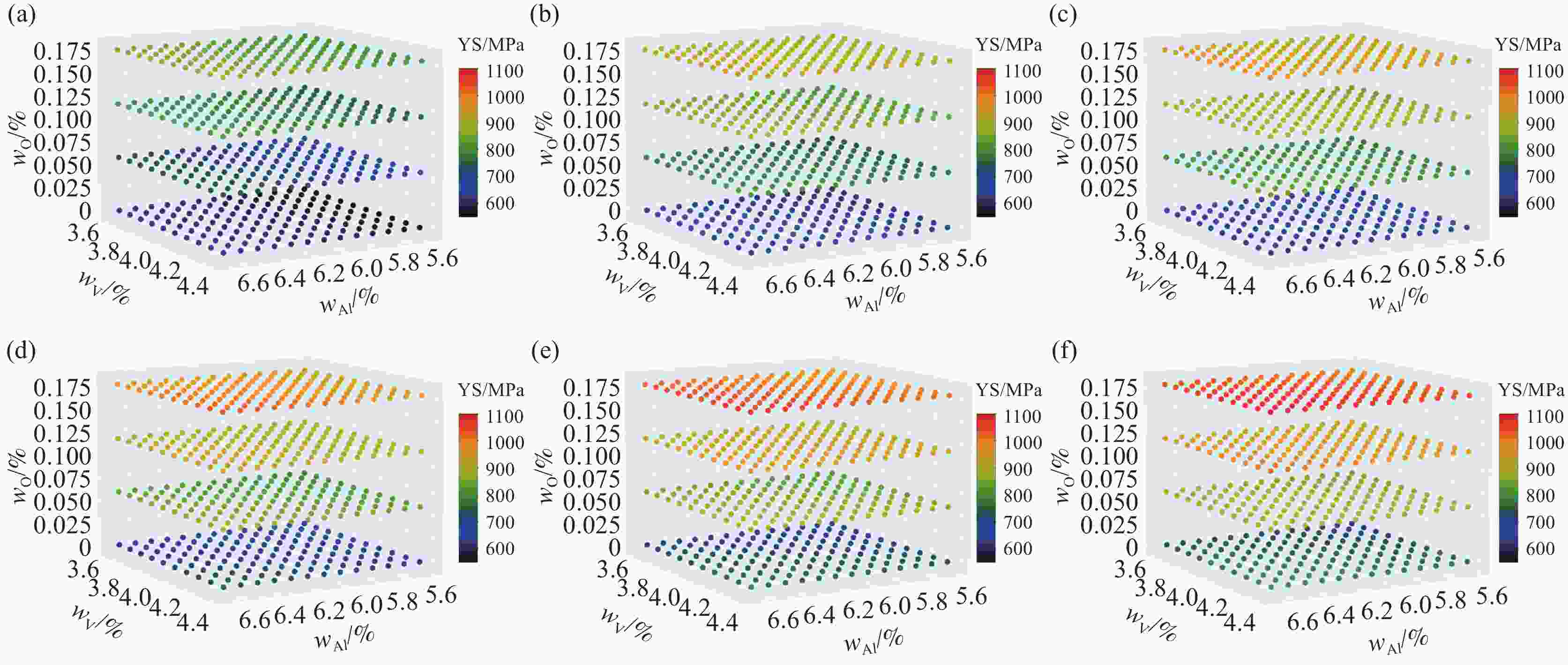
表 1 TC4钛合金的标准成分和计算选择的成分
Table 1. Standard composition and calculated selected composition of TC4 titanium alloy
Element Ti Al V Fe O Standard value Bal. 5.5~6.75 3.5~4.5 0~0.3 0~0.21 Calculated value Bal. Δ=0.1 Δ=0.1 Δ=0.05 Δ=0.03 -
[1] WILLIAMS J C, BOYER R R. Opportunities and issues in the application of titanium alloys for aerospace components[J]. Metals, 2020, 10(6): 705. doi: 10.3390/met10060705 [2] UHLMANN E, KERSTING R, KLEIN T B, et al. Additive manufacturing of titanium alloy for aircraft components[J]. Procedia Cirp, 2015, 35: 55-60. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2015.08.061 [3] WANG Z, YANG Q W, TANG C, et al. Optimization of acid leaching process for titanium slag after alkali leaching of scr catalyst[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2022(49): 1-2. [4] LIU X, CHU P K, DING C. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 2004, 47(3-4): 49-121. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2004.11.001 [5] ZHANG H, YAN N, LIANG H, et al. Phase transformation and microstructure control of Ti2AlNb-based alloys: A review[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 80: 203-216. [6] CUI C, HU B M, ZHAO L, et al. Titanium alloy production technology, market prospects and industry development[J]. Materials & Design, 2011, 32(3): 1684-1691. [7] VEIGA C, DAVIM J P, LOUREIRO A J R. Properties and applications of titanium alloys: a brief review[J]. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci, 2012, 32(2): 133-148. [8] KOSARAJU S, ANNE V G. Optimal machining conditions for turning Ti-6Al-4V using response surface methodology[J]. Advances in Manufacturing, 2013, 1(4): 329-339. doi: 10.1007/s40436-013-0047-9 [9] HASHMI K H, ZAKRIA G, RAZA M B, et al. Optimization of process parameters for high speed machining of Ti-6Al-4V using response surface methodology[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 85(5): 1847-1856. [10] SULAIMAN M A, CHE HARON C H, GHANI J A, et al. Optimization of turning parameters for titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V ELI using the response surface method (RSM)[J]. Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology (JAMT), 2013, 7(2). [11] MIA M, KHAN M A, DHAR N R. High-pressure coolant on flank and rake surfaces of tool in turning of Ti-6Al-4V: investigations on surface roughness and tool wear[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2017, 90(5): 1825-1834. [12] ALI KHAN M, JAFFERY S H I, KHAN M, et al. Statistical analysis of energy consumption, tool wear and surface roughness in machining of titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) under dry, wet and cryogenic conditions[J]. Mechanical sciences, 2019, 10(2): 561-573. doi: 10.5194/ms-10-561-2019 [13] GÜNAY M, KAÇAL A, TURGUT Y. Optimization of machining parameters in milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy using Taguchi method[J]. Engineering Sciences, 2011, 6(1): 428-440. [14] NAM J, LEE S W. Machinability of titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V) in environmentally-friendly micro-drilling process with nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication using nanodiamond particles[J]. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 2018, 5(1): 29-35. doi: 10.1007/s40684-018-0003-z [15] ELTAGGAZ A, NOUZIL I, DEIAB I. Machining Ti-6Al-4V alloy using nano-cutting fluids: Investigation and analysis[J]. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 2021, 5(2): 42. doi: 10.3390/jmmp5020042 [16] ZHU C, LI C, WU D, et al. A titanium alloys design method based on high-throughput experiments and machine learning[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 11: 2336-2353. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.02.055 [17] ZOU C, LI J, WANG W Y, et al. Integrating data mining and machine learning to discover high-strength ductile titanium alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2021, 202: 211-221. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.056 [18] OUTEIRO J, CHENG W, CHINESTA F, et al. Modelling and optimization of machining of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy using machine learning and design of experiments methods[J]. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 2022, 6(3): 58. doi: 10.3390/jmmp6030058 [19] LIU X, PENG Q, PAN S, et al. Machine learning assisted prediction of microstructures and Young’s modulus of biomedical multi-component β-Ti alloys[J]. Metals, 2022, 12(5): 796. doi: 10.3390/met12050796 [20] CHAI C, WANG Y, ZHAO S, et al. Machine learning-assisted design of low elastic modulus β-type medical titanium alloys and experimental validation[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2024, 238: 112902. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2024.112902 [21] PATURI U M R, PALAKURTHY S T, CHERUKU S, et al. Role of machine learning in additive manufacturing of titanium alloys—A review[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2023, 30(8): 5053-5069. doi: 10.1007/s11831-023-09969-y [22] ANGELINI M, SANTUCCI G, SCHUMANN H, et al. A review and characterization of progressive visual analytics[C]//Informatics. MDPI, 2018, 5(3): 31. [23] KAHNG M, ANDREWS P Y, KALRO A, et al. A cti v is: Visual exploration of industry-scale deep neural network models[J]. IEEE transactions on visualization and computer graphics, 2017, 24(1): 88-97. [24] LIU S, WANG X, LIU M, et al. Towards better analysis of machine learning models: A visual analytics perspective[J]. Visual Informatics, 2017, 1(1): 48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.visinf.2017.01.006 [25] LU J, CHEN W, MA Y, et al. Recent progress and trends in predictive visual analytics[J]. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2017, 11(2): 192-207. doi: 10.1007/s11704-016-6028-y [26] LU Y, GARCIA R, HANSEN B, et al. The state‐of‐the‐art in predictive visual analytics[C]//Computer Graphics Forum. 2017, 36(3): 539-562. [27] CHENG S, SHEN H, SHAN G, et al. Visual analysis of meteorological satellite data via model-agnostic meta-learning[J]. Journal of Visualization, 2021, 24(2): 301-315. doi: 10.1007/s12650-020-00704-4 [28] YUAN J, CHEN C, YANG W, et al. A survey of visual analytics techniques for machine learning[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2021, 7(1): 3-36. doi: 10.1007/s41095-020-0191-7 [29] SUN G D, WU Y C, LIANG R H, et al. A survey of visual analytics techniques and applications: State-of-the-art research and future challenges[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2013, 28(5): 852-867. doi: 10.1007/s11390-013-1383-8 [30] ANDRIENKO N, ANDRIENKO G. Visual analytics of movement: An overview of methods, tools and procedures[J]. Information visualization, 2013, 12(1): 3-24. doi: 10.1177/1473871612457601 [31] PREIM B, LAWONN K. A survey of visual analytics for public health[C]//Computer Graphics Forum. 2020, 39(1): 543-580. -




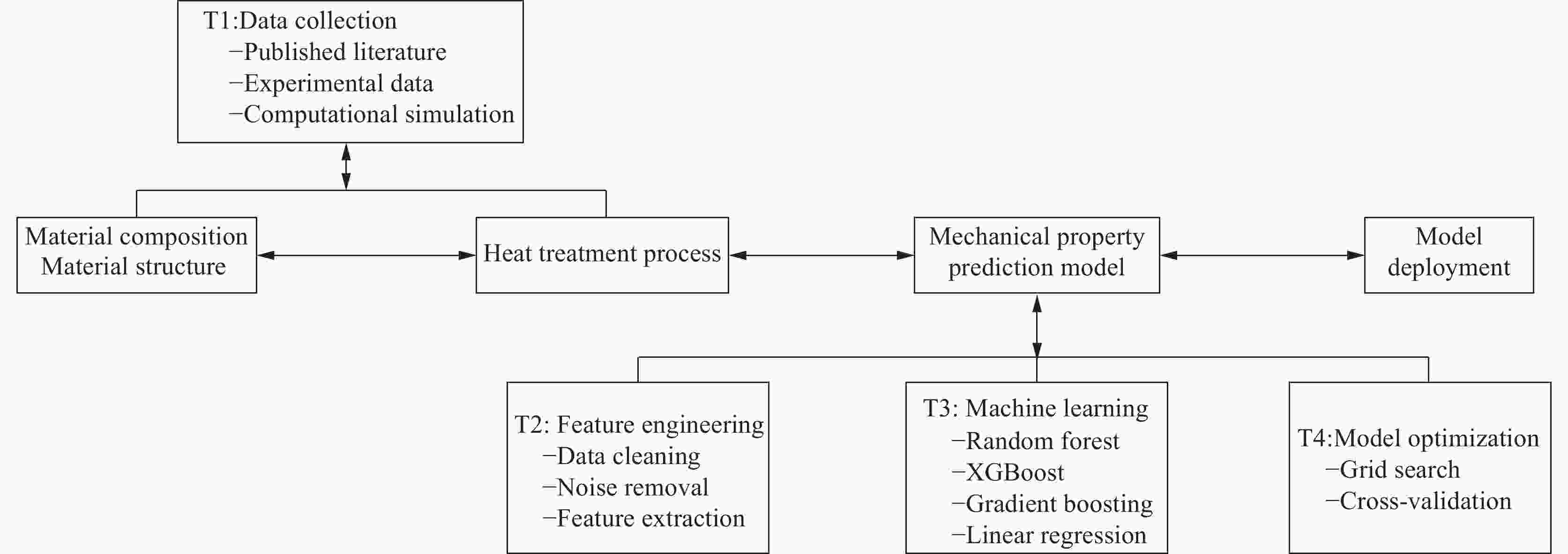
 下载:
下载: