| [1] |
FENG J W, FU J Z, YAO X H, et al. Triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) porous structures: from multi-scale design, precise additive manufacturing to multidisciplinary applications[J]. International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing, 2022, 4(2): 022001. doi: 10.1088/2631-7990/ac5be6
|
| [2] |
ZHANG J, XIE S C, JING K K, et al. Study on isotropic design of triply periodic minimal surface structures under an elastic modulus compensation mechanism[J]. Composite Structures, 2024, 342: 118266. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2024.118266
|
| [3] |
PENG C X, FOX K, QIAN M, et al. 3D printed sandwich beams with bioinspired cores: Mechanical performance and modelling[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 161: 107471. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2021.107471
|
| [4] |
CHEN R G, ZHANG W J, JIA Y F, et al. Ultra-stiff and quasi-elastic-isotropic triply periodic minimal surface structures designed by deep learning[J]. Materials & Design, 2024, 244: 113107.
|
| [5] |
JIN J L, WU S Q, YANG L, et al. Ni–Ti multicell interlacing Gyroid lattice structures with ultra-high hyperelastic response fabricated by laser powder bed fusion[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2024, 195: 104099. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2023.104099
|
| [6] |
SURJADI J U, GAO L B, DU H F, et al. Mechanical metamaterials and their engineering applications[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2019, 21(3): 1800864. doi: 10.1002/adem.201800864
|
| [7] |
SHI J P, ZHU L Y, LI L, et al. A TPMS-based method for modeling porous scaffolds for bionic bone tissue engineering[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 7395. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25750-9
|
| [8] |
HESSELMANN F, HALWES M, BONGARTZ P, et al. TPMS-based membrane lung with locally-modified permeabilities for optimal flow distribution[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12(1): 7160. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11175-y
|
| [9] |
TRIPATHI Y, SHUKLA M, BHATT A D. Implicit-function-based design and additive manufacturing of triply periodic minimal surfaces scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2019, 28(12): 7445-7451. doi: 10.1007/s11665-019-04457-6
|
| [10] |
ZOU S J, MU Y R, PAN B C, et al. Mechanical and biological properties of enhanced porous scaffolds based on triply periodic minimal surfaces[J]. Materials & Design, 2022, 219: 110803.
|
| [11] |
REN F X, ZHANG C D, LIAO W H, et al. Transition boundaries and stiffness optimal design for multi-TPMS lattices[J]. Materials & Design, 2021, 210: 110062.
|
| [12] |
YETIK O, ENGÜN S, KOK B, et al. Thermal management system of batteries using AlN reinforced TPMS-PCM composite material[J]. Energy, 2024, 313: 134137. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2024.134137
|
| [13] |
CUI Y L, GAIN A K, ZHANG L C, et al. Manufacture and property characterization of interconnected pore-gradient TPMS materials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2024, 892: 146100. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2024.146100
|
| [14] |
QIU N, WAN Y H, SHEN Y J, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on mechanical properties of TPMS structures[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2024, 261: 108657. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2023.108657
|
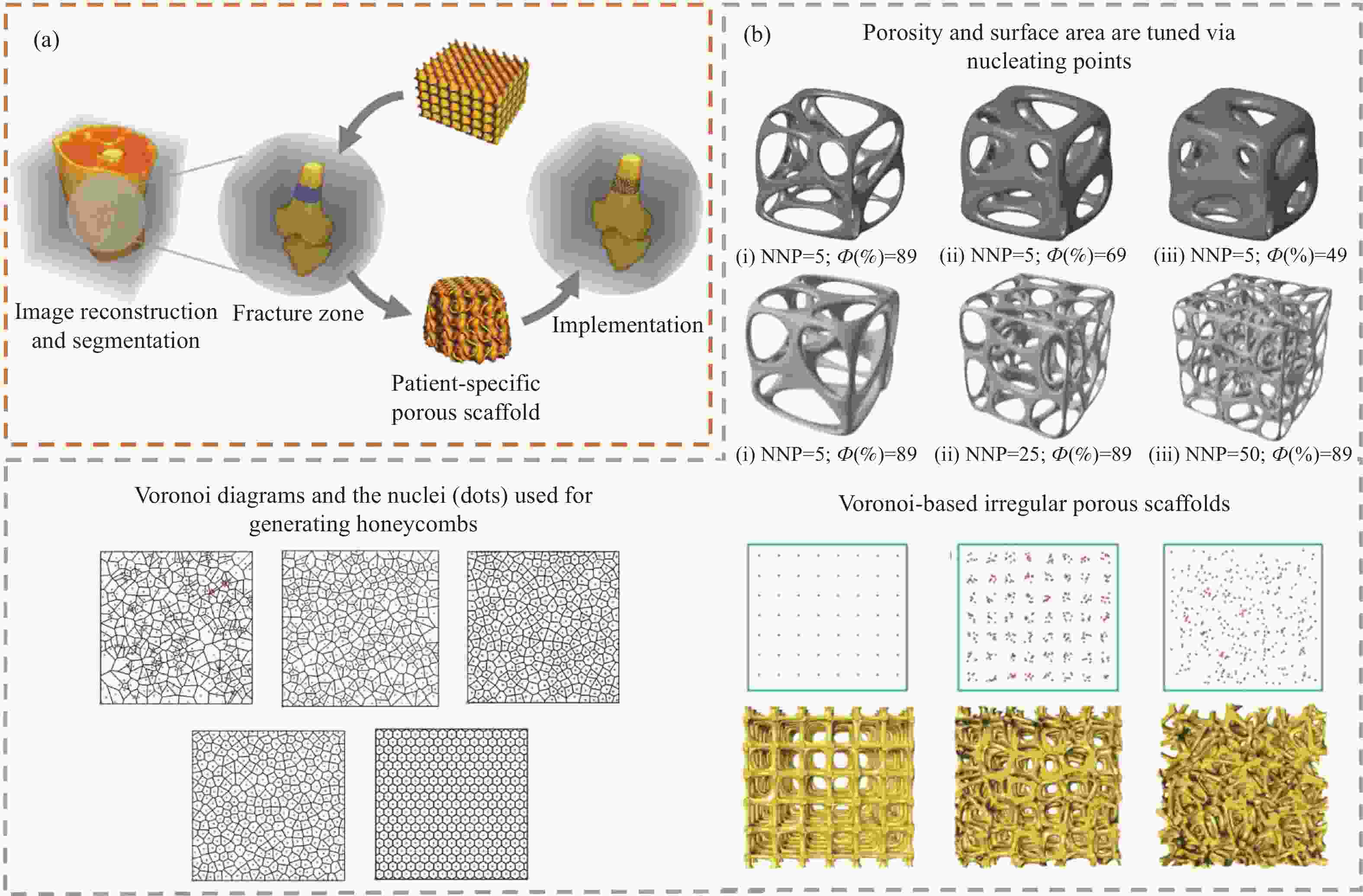
| [15] |
WANG Y Z, WU C Q, JI W J, et al. Machine learning-assisted precision inverse design research of ternary cathode materials: A new paradigm for material design[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2025, 680: 505-517. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2024.11.104
|
| [16] |
MI X X, TIAN L J, TANG A T, et al. A reverse design model for high-performance and low-cost magnesium alloys by machine learning[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2022, 201: 110881. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2021.110881
|
| [17] |
SONG Y, SUN Y W, ZOU Z W, et al. Systematic study of the thermal and hydraulic characteristics of a heat exchanger based on the Schwartz-D structure for aviation application[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 156: 107611. doi: 10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2024.107611
|
| [18] |
FENG J W, FU J Z, SHANG C, et al. Sandwich panel design and performance optimization based on triply periodic minimal surfaces[J]. Computer-Aided Design, 2019, 115: 307-322. doi: 10.1016/j.cad.2019.06.007
|
| [19] |
HUANG W S, NING H Y, LI N, et al. Thermal-hydraulic performance of TPMS-based regenerators in combined cycle aero-engine[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 250: 123510. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2024.123510
|
| [20] |
ZHANG Y, YAN Z J, SHEN M W, et al. Study on the thermal control performance of lightweight minimal surface lattice structures for aerospace applications[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2025, 261: 125110. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2024.125110
|
| [21] |
ZHANG T, ZHANG K F, LIU F, et al. Analysis of thermal storage behavior of composite phase change materials embedded with gradient-designed TPMS thermal conductivity enhancers: A numerical and experimental study[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 358: 122630. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.122630
|
| [22] |
NOVAK N, BOROVINŠEK M, AL-KETAN O, et al. Impact and blast resistance of uniform and graded sandwich panels with TPMS cellular structures[J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 300: 116174. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116174
|
| [23] |
ZHANG Y, CHEN Y G, LI J X, et al. Protective performance of hybrid triply periodic minimal surface lattice structure[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2024, 194: 111288. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.111288
|
| [24] |
NOVAK N, AL-KETAN O, KRSTULOVIĆ-OPARA L, et al. Quasi-static and dynamic compressive behaviour of sheet TPMS cellular structures[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 266: 113801. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113801
|
| [25] |
PHUNG-VAN P, HUNG P T, THAI C H. Small-dependent nonlinear analysis of functionally graded triply periodic minimal surface nanoplates[J]. Composite Structures, 2024, 335: 117986. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2024.117986
|
| [26] |
YAN X N. Research on design and impact protection performance of metal/ceramic heterogeneous lattice structure[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2021. (严效男. 金属/陶瓷异质点阵结构设计与冲击防护性能研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2021.YAN X N. Research on design and impact protection performance of metal/ceramic heterogeneous lattice structure[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2021.
|
| [27] |
CHEN Y Z, WANG C H, HSIEH T Y, et al. An efficient parameterized neural network enhanced multiscale finite element modeling for triply periodic minimal surface meta-structures and its applications for femur[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2024, 30: 6176-6194. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.05.023
|
| [28] |
SONG K L, WANG Z H, LAN J, et al. Porous structure design and mechanical behavior analysis based on TPMS for customized root analogue implant[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2021, 115: 104222. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2020.104222
|
| [29] |
WANG J E, SCHUTZEICHEL M, PLAUMANN B, et al. Multidisciplinary design optimisation of lattice-based battery housing for electric vehicles[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 12265. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60124-4
|
| [30] |
NOVAK N, KYTYR D, RADA V, et al. Compression behaviour of TPMS-filled stainless steel tubes[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2022, 852: 143680. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.143680
|
| [31] |
PANESAR A, ABDI M, HICKMAN D, et al. Strategies for functionally graded lattice structures derived using topology optimisation for Additive Manufacturing[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 19: 81-94. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2017.11.008
|
| [32] |
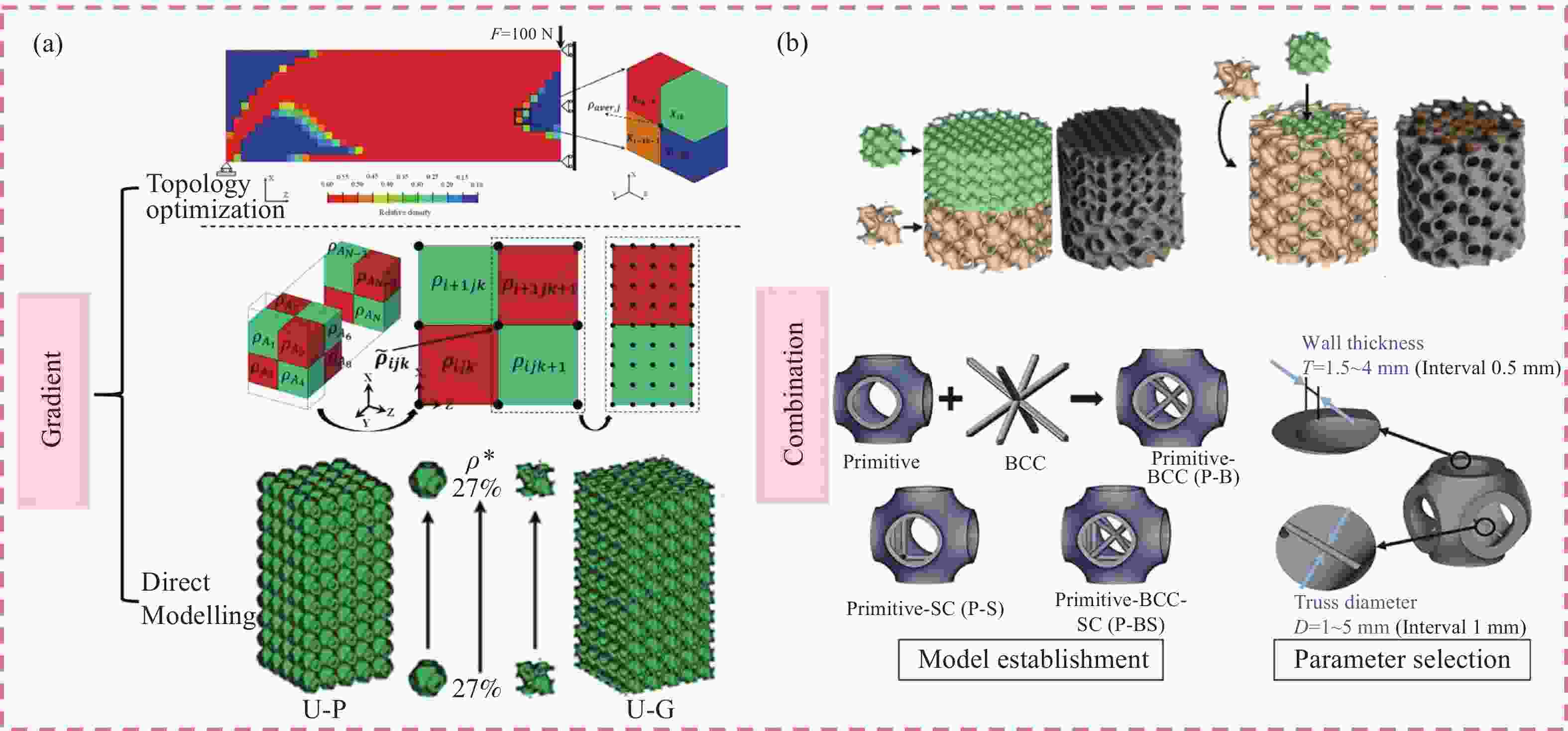
JIANG W M, LIAO W H, LIU T T, et al. A voxel-based method of multiscale mechanical property optimization for the design of graded TPMS structures[J]. Materials & Design, 2021, 204: 109655.
|
| [33] |
WANG H T. Research on the crashworthiness of automobile front longitudinal beam based on periodic minimal surface structure reinforcement[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019. (王赫庭. 基于周期极小曲面结构加强的汽车前纵梁防撞性研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019.WANG H T. Research on the crashworthiness of automobile front longitudinal beam based on periodic minimal surface structure reinforcement[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019.
|
| [34] |
ZHENG X J. Crashworthiness optimization design of a novel bionic hierarchical porous structure[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2020. (郑贤君. 新型仿生层级多孔结构的耐撞性优化设计[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2020.ZHENG X J. Crashworthiness optimization design of a novel bionic hierarchical porous structure[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2020.
|
| [35] |
SEEHANAM S, CHANCHAREON W, PROMOPPATUM P. Assessing the effect of manufacturing defects and non-Newtonian blood model on flow behaviors of additively manufactured Gyroid TPMS structures[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(5): e15711. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15711
|
| [36] |
KIM D Y, KIM H S, KAMATH S S, et al. TPMS-based auxetic structure for high-performance airless tires with variable stiffness depending on deformation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 11419. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62101-3
|
| [37] |
GIDE K M, BAGHERI Z S. Mechanical behavior and material modeling of fused filament fabricated PEEK based on TPMS lattices: a comparative study[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2024, 134(5): 2765-2780.
|
| [38] |
TYAGI S A, MANJAIAH M. Fine porous stainless steel TPMS cellular structures: Printability and post-processing evaluation[J]. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series D, 2024, 105(3): 2045-2052. doi: 10.1007/s40033-023-00598-0
|
| [39] |
YANG H. Research on modeling methods of porous structures[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2017. (杨辉. 多孔结构的建模方法研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2017.YANG H. Research on modeling methods of porous structures[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2017.
|
| [40] |
KARAKOÇ A. RegionTPMS—Region based triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS) for 3-D printed multiphase bone scaffolds with exact porosity values[J]. SoftwareX, 2021, 16: 100835. doi: 10.1016/j.softx.2021.100835
|
| [41] |
LEI H Y. Research on parametric modeling for active design of porous functional structures[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021. (雷鸿源. 面向多孔功能结构主动设计的参数化建模研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2021.LEI H Y. Research on parametric modeling for active design of porous functional structures[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021.
|
| [42] |
WANG G J, SHEN L D, ZHAO J F, et al. Design and compressive behavior of controllable irregular porous scaffolds: Based on Voronoi-Tessellation and for additive manufacturing[J]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2018, 4(2): 719-727.
|
| [43] |
SOTOMAYOR O E, TIPPUR H V. Role of cell regularity and relative density on elasto-plastic compression response of random honeycombs generated using Voronoi diagrams[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2014, 51(21): 3776-3786.
|
| [44] |
GÓMEZ S, VLAD M D, LÓPEZ J, et al. Design and properties of 3D scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2016, 42: 341-350. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.06.032
|
| [45] |
SHI X, LIAO W H, LIU T T, et al. Design optimization of multimorphology surface-based lattice structures with density gradients[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 117(7): 2013-2028.
|
| [46] |
FENG Y X, HUANG T, GONG Y H, et al. Stiffness optimization design for TPMS architected cellular materials[J]. Materials & Design, 2022, 222: 111078.
|
| [47] |
OZDEMIR M, SIMSEK U, KIZILTAS G, et al. A novel design framework for generating functionally graded multi-morphology lattices via hybrid optimization and blending methods[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2023, 70: 103560. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2023.103560
|
| [48] |
PARLAYAN O, OZDEMIR M, GAYIR C E, et al. A new sensitivity-based mapping scheme for topology optimization of graded TPMS designs[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2023, 129(7): 3197-3220.
|
| [49] |
GÜNTHER F, PILZ S, HIRSCH F, et al. Shape optimization of additively manufactured lattices based on triply periodic minimal surfaces[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2023, 73: 103659. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2023.103659
|
| [50] |
LI D W, DAI N, TANG Y L, et al. Design and optimization of graded cellular structures with triply periodic level surface-based topological shapes[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2019, 141(071402).
|
| [51] |
NGUYEN-XUAN H, TRAN K Q, THAI C H, et al. Modelling of functionally graded triply periodic minimal surface (FG-TPMS) plates[J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 315: 116981. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2023.116981
|
| [52] |
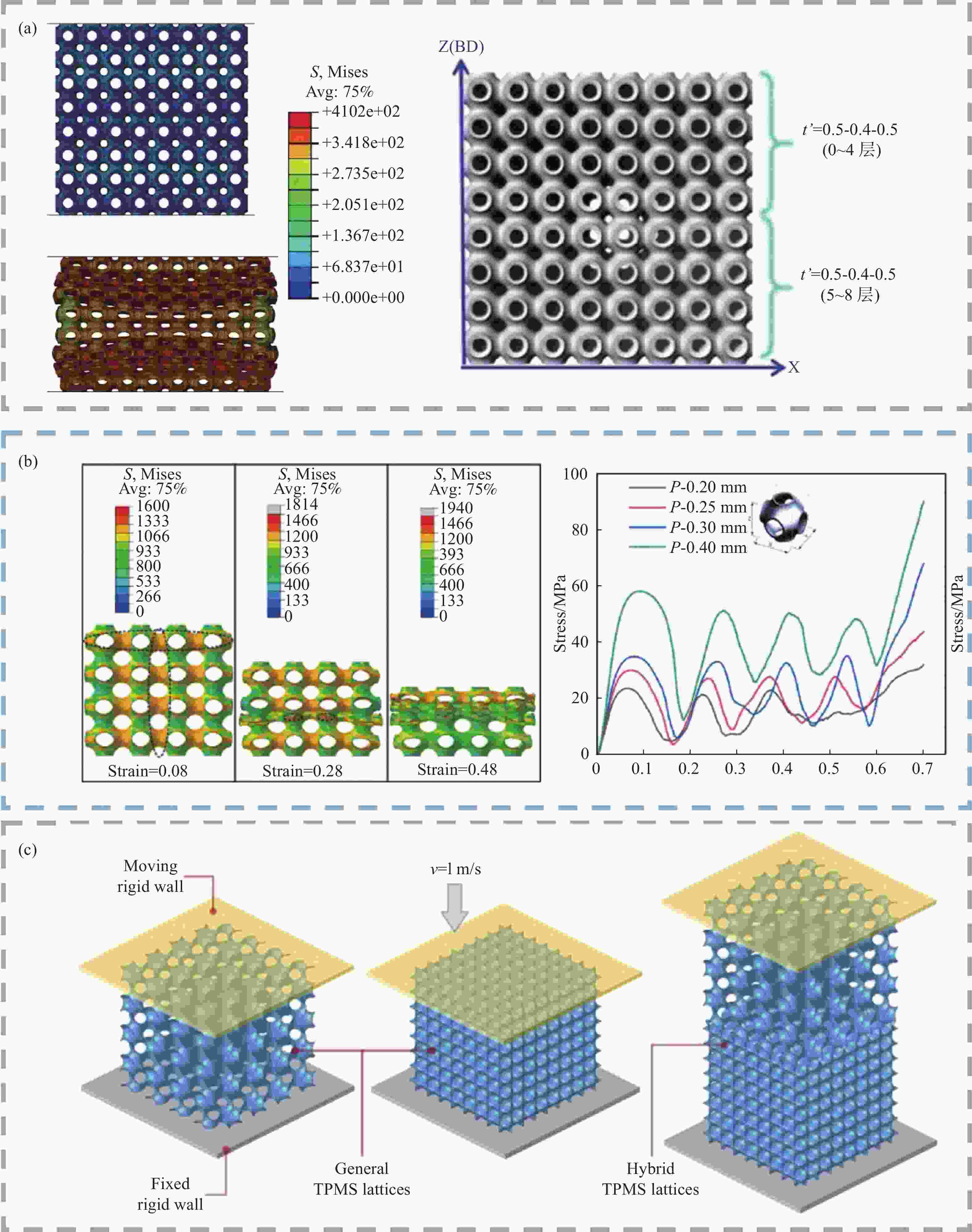
QIU N, ZHANG J Z, YUAN F Q, et al. Mechanical performance of triply periodic minimal surface structures with a novel hybrid gradient fabricated by selective laser melting[J]. Engineering Structures, 2022, 263: 114377. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2022.114377
|
| [53] |
LI K, LIAO R B, ZHENG Q C, et al. Design exploration of staggered hybrid minimal surface magnesium alloy bone scaffolds[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2024, 281: 109566. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2024.109566
|
| [54] |
CHEN Z Y, WU B S, CHEN X, et al. Energy absorption and impact resistance of hybrid triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) sheet-based structures[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2023, 37: 107352. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.107352
|
| [55] |
YE H L, TIAN F W, HE W L, et al. Mechanical and thermal property analysis and optimization design of hybrid lattice structure based on triply periodic minimal surfaces[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2024, 203: 112203. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2024.112203
|
| [56] |
NOVAK N, AL-KETAN O, BOROVINŠEK M, et al. Development of novel hybrid TPMS cellular lattices and their mechanical characterisation[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 15: 1318-1329. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.08.092
|
| [57] |
WANG H, TAN D W, LIU Z P, et al. On crashworthiness of novel porous structure based on composite TPMS structures[J]. Engineering Structures, 2022, 252: 113640. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2021.113640
|
| [58] |
ZHANG X Y. Research on SLM-formed sandwich structure based on three-periodic minimal surface[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2019. (张馨月. 基于三周期极小曲面的SLM成形夹芯结构研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2019.ZHANG X Y. Research on SLM-formed sandwich structure based on three-periodic minimal surface[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2019.
|
| [59] |
ZHONG M T. Research on gradient TPMS structure design and mechanical behavior of 316L stainless steel and NiTi shape memory alloy[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University, 2022. (钟敏婷. 316L不锈钢和NiTi形状记忆合金的梯度TPMS结构设计及力学行为研究[D]. 广州: 广州大学, 2022.ZHONG M T. Research on gradient TPMS structure design and mechanical behavior of 316L stainless steel and NiTi shape memory alloy[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University, 2022.
|
| [60] |
GUO W. Research on energy absorption and application of three-dimensional curved lattice structure[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2020. (郭文. 三维曲面点阵结构吸能及应用研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2020.GUO W. Research on energy absorption and application of three-dimensional curved lattice structure[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2020.
|
| [61] |
SUN Q D, SUN J, GUO K, et al. Compressive mechanical properties and energy absorption characteristics of SLM fabricated Ti6Al4V triply periodic minimal surface cellular structures[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2022, 166: 104241. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2022.104241
|
| [62] |
FENG G Z, LI S, XIAO L J, et al. Mechanical properties and deformation behavior of functionally graded TPMS structures under static and dynamic loading[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2023, 176: 104554. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2023.104554
|
| [63] |
ZHANG J, XIE S C, LI T, et al. A study of multi-stage energy absorption characteristics of hybrid sheet TPMS lattices[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 190: 110989. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2023.110989
|
| [64] |
LI C T. Research on morphology optimization and mechanical properties of mechanical metamaterials based on deep learning[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2021. (李长通. 基于深度学习的力学超材料形态优化及力学性能研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2021.LI C T. Research on morphology optimization and mechanical properties of mechanical metamaterials based on deep learning[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2021.
|
| [65] |
ZHANG J W, ZHAO J X, RONG Q G, et al. Machine learning guided prediction of mechanical properties of TPMS structures based on finite element simulation for biomedical titanium[J]. Materials Technology, 2022, 37(1): 1-8.
|
| [66] |
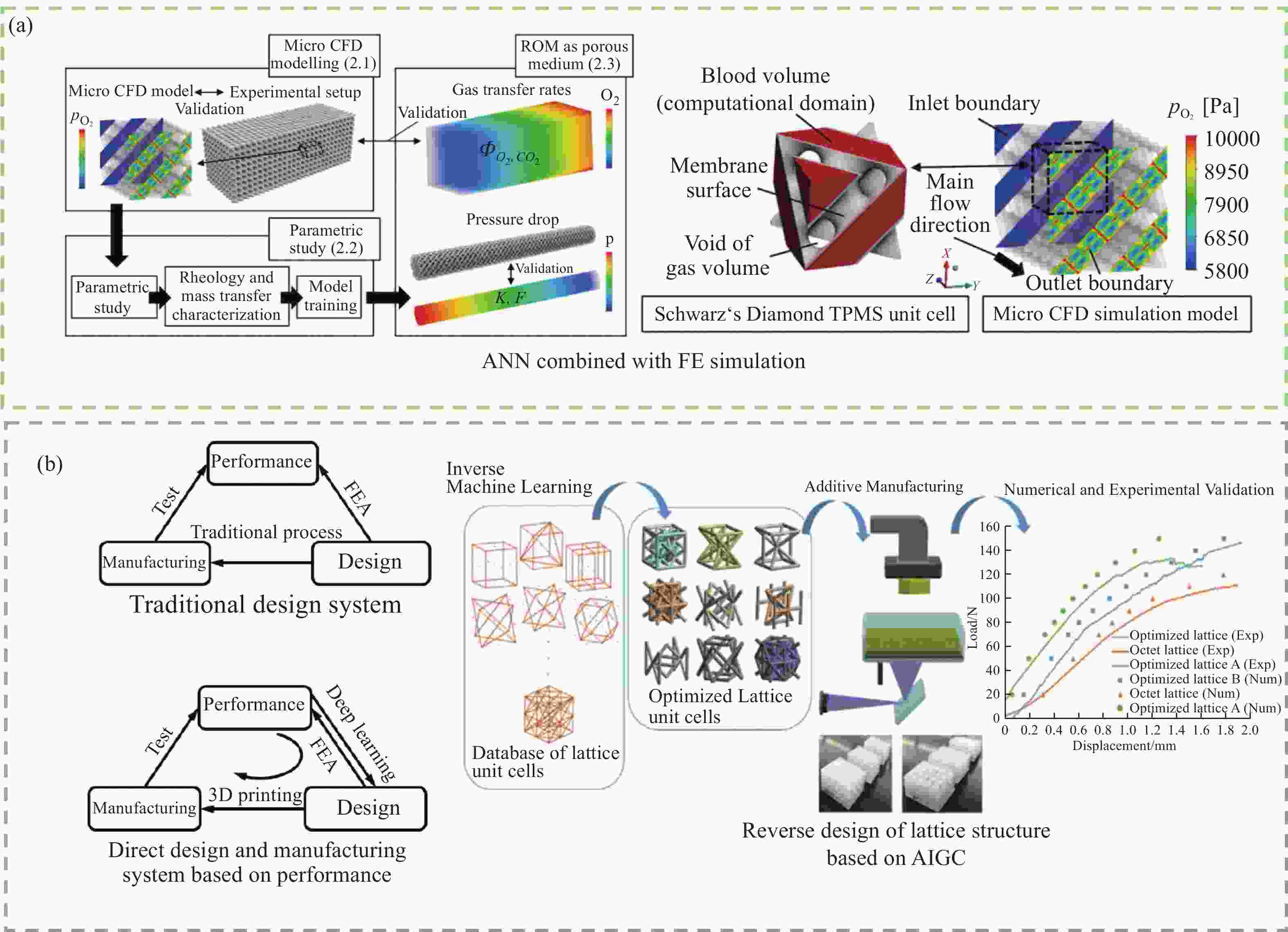
BARBIAN K P, HIRSCHWALD L T, LINKHORST J, et al. Flow and mass transfer prediction in anisotropic TPMS-structures as extracorporeal oxygenator membranes using reduced order modeling[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2024, 690: 122160. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2023.122160
|
| [67] |
HAN S Y, WANG Z, E-MELIGY M, et al. Nonlinear dynamic analysis of the FG-TPMS double-curved panels: Introducing SVM-DNN-RF algorithm to predict nonlinear dynamic information[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2024: 109785.
|
| [68] |
ZHANG H Q. Research on mechanical performance design system based on 3D printing and deep learning[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2019. (张汉青. 基于3D打印和深度学习的力学性能设计体系研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2019.ZHANG H Q. Research on mechanical performance design system based on 3D printing and deep learning[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2019.
|
| [69] |
WANG Y Z, ZENG Q L, WANG J Z, et al. Inverse design of shell-based mechanical metamaterial with customized loading curves based on machine learning and genetic algorithm[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 401: 115571. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2022.115571
|
| [70] |
HU B, WANG Z J, DU C, et al. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization accelerated design of TPMS structures[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2023, 244: 108085. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.108085
|
| [71] |
CHALLAPALLI A, PATEL D, LI G. Inverse machine learning framework for optimizing lightweight metamaterials[J]. Materials & Design, 2021, 208: 109937.
|
| [72] |
LI Z, LI J H, TIAN J H, et al. Performance-based inverse structural design of complex gradient triply periodic minimal surface structures based on a deep learning approach[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2024, 40: 109424. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2024.109424
|
| [73] |
LI Z, LI J H, TIAN J H, et al. Inverse design of cellular structures with the geometry of triply periodic minimal surfaces using generative artificial intelligence algorithms[J]. Engineering Structures, 2024, 321: 118988. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2024.118988
|
| [74] |
LI Z, LI J H, TIAN J H, et al. Design of nonlinear gradient sheet-based TPMS-lattice using artificial neural networks[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2024, 33: 223-234. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.09.051
|




 下载:
下载: