The creep-fatigue behavior of TC4 ELI alloy under simulated deep-sea environments
-
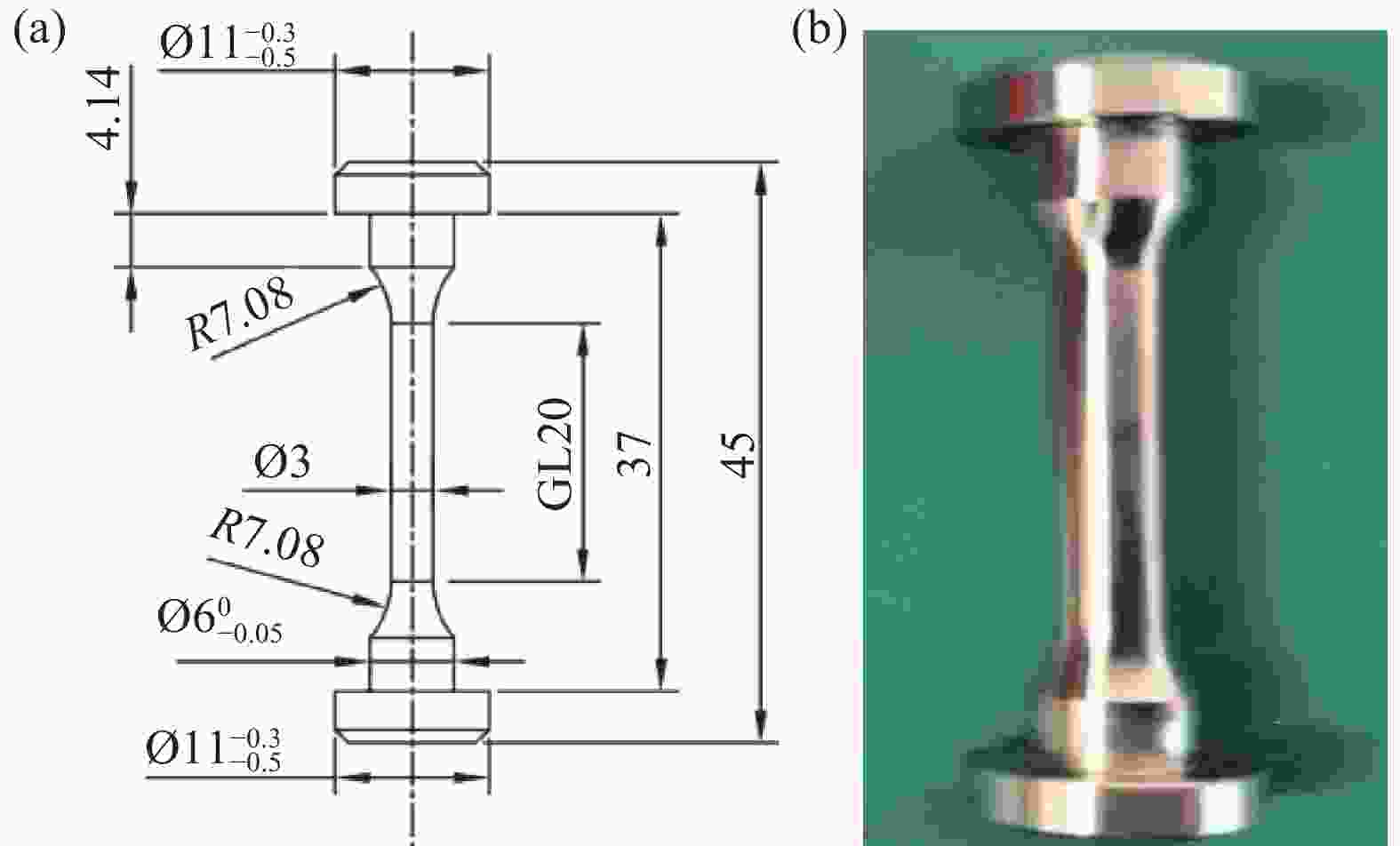
摘要: 针对TC4 ELI钛合金在深海多因素耦合环境下的蠕变-疲劳损伤机制不明问题,通过高压腐蚀试验系统,模拟南海200、600 m和
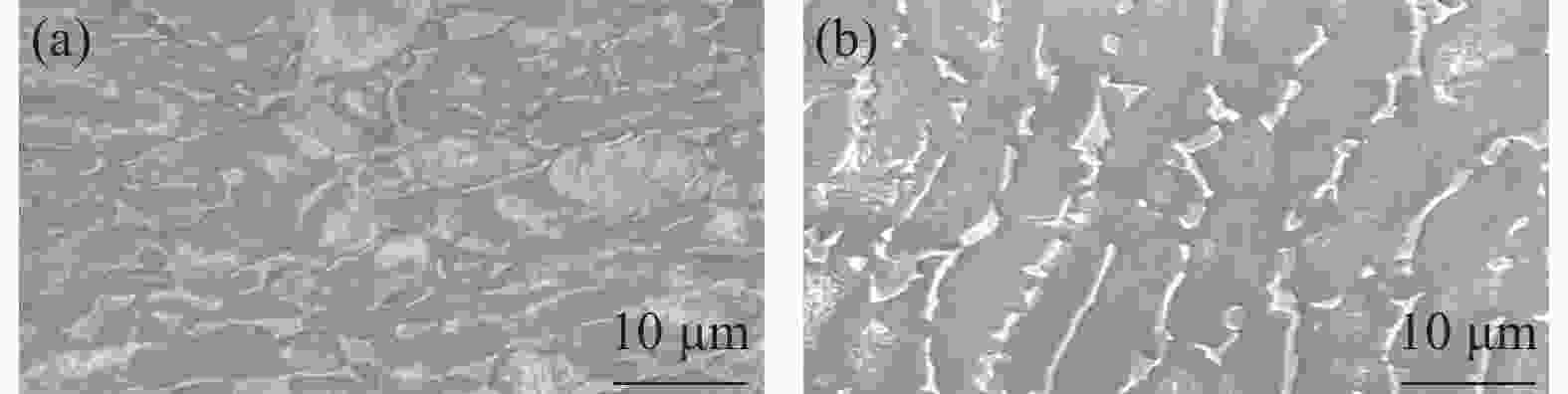
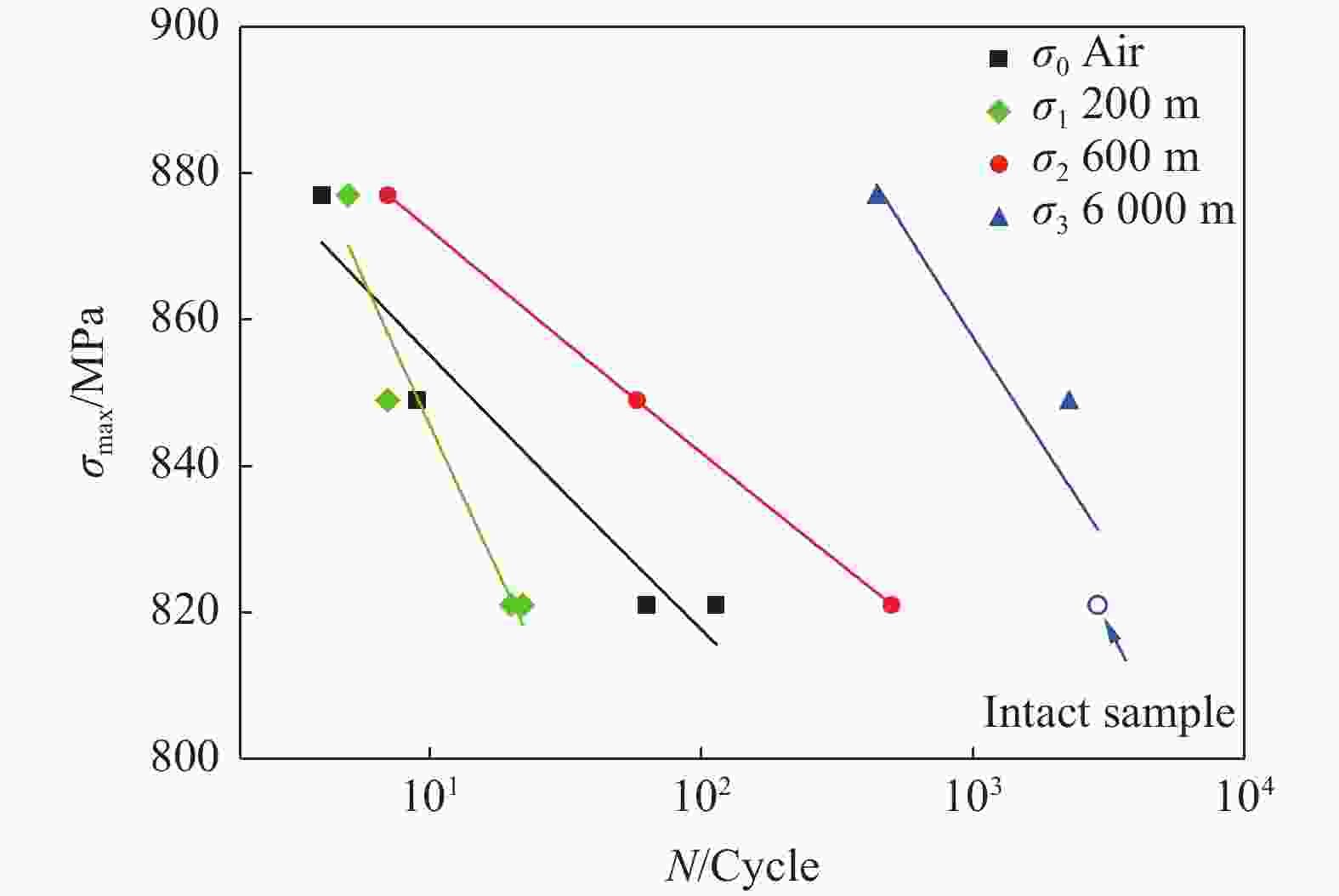
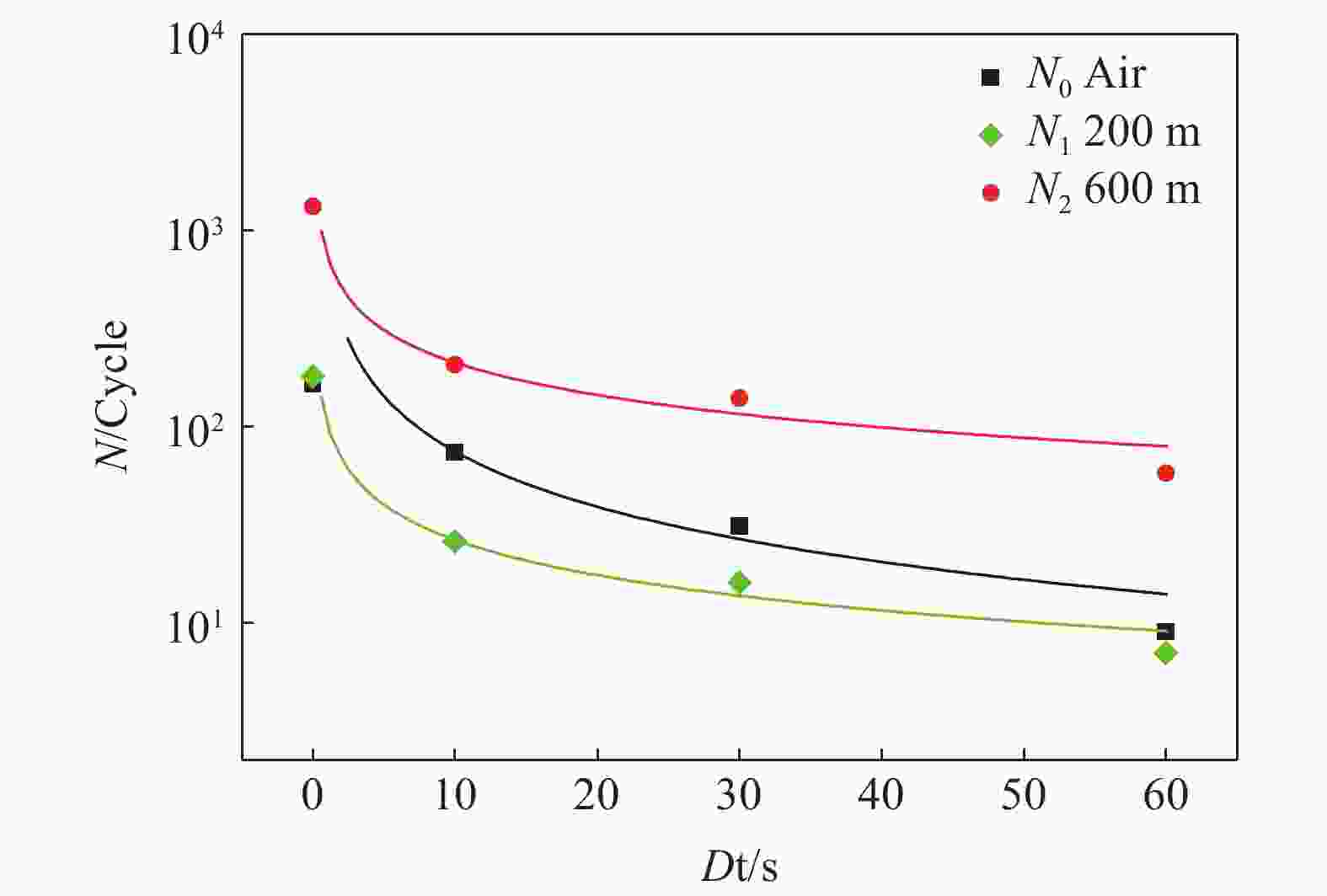
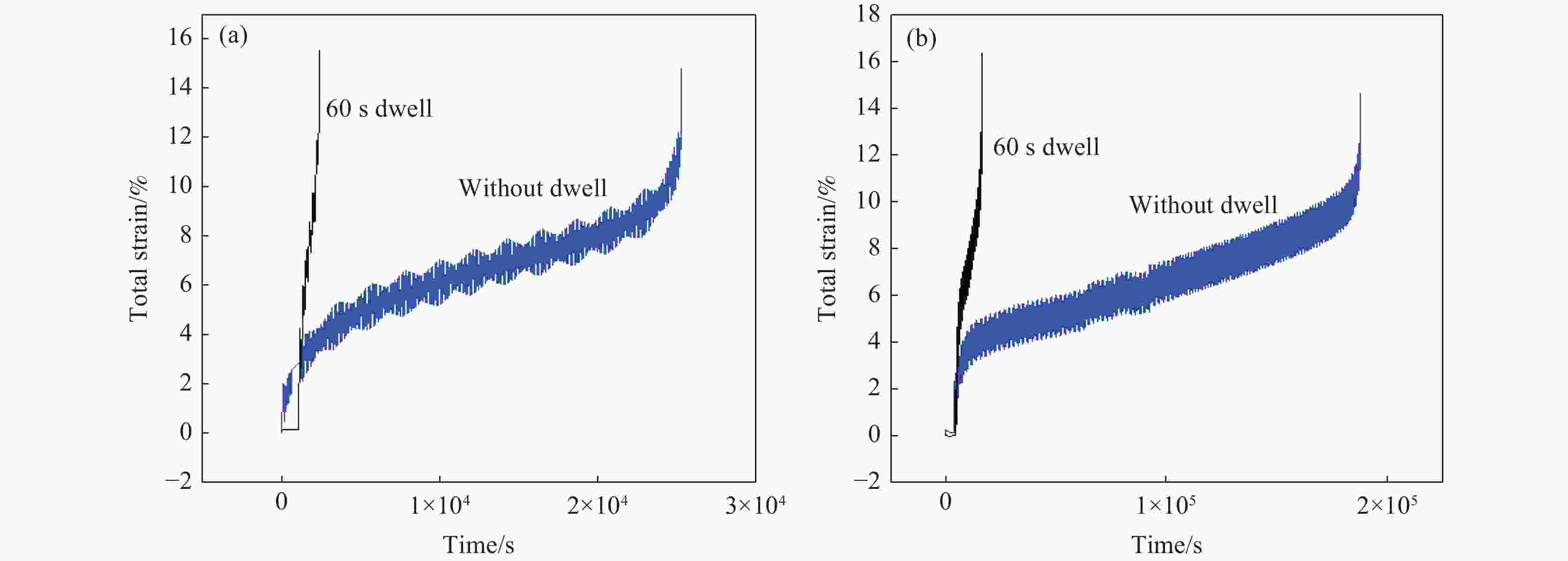
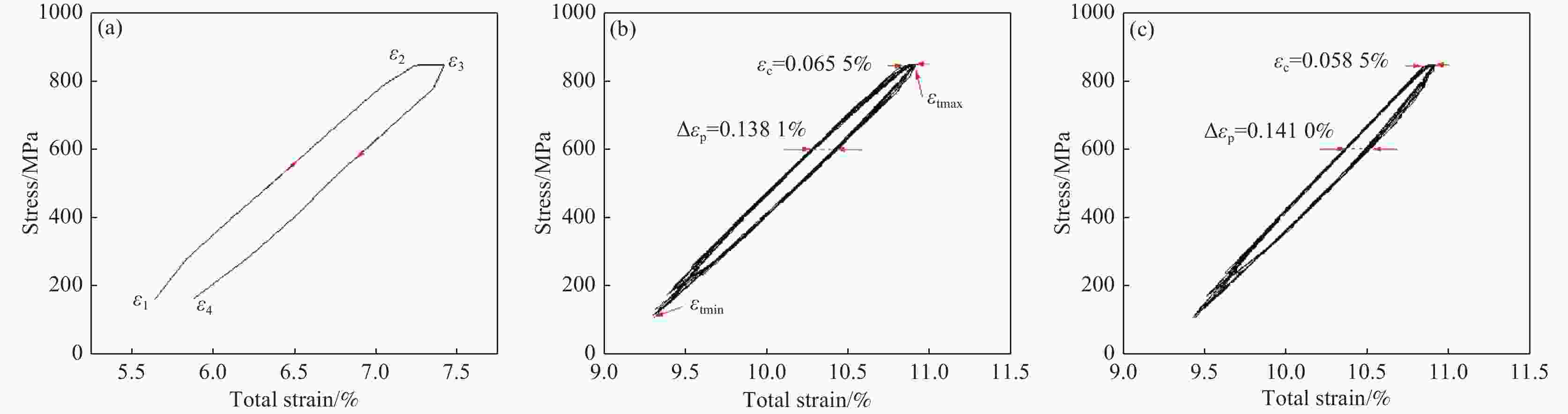
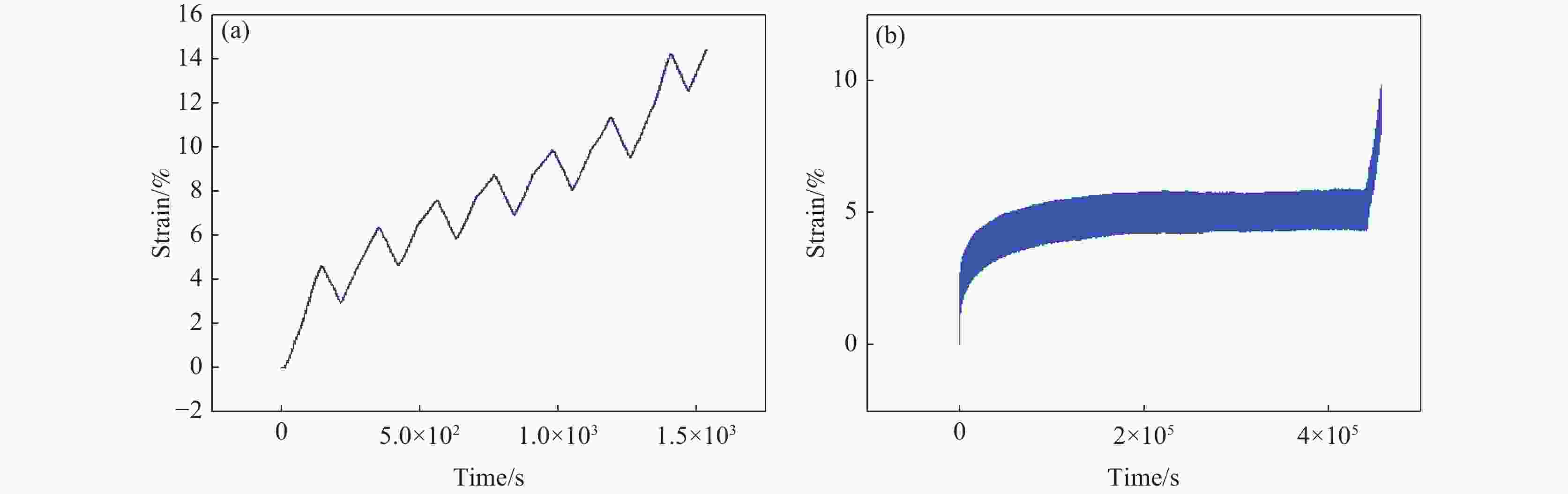
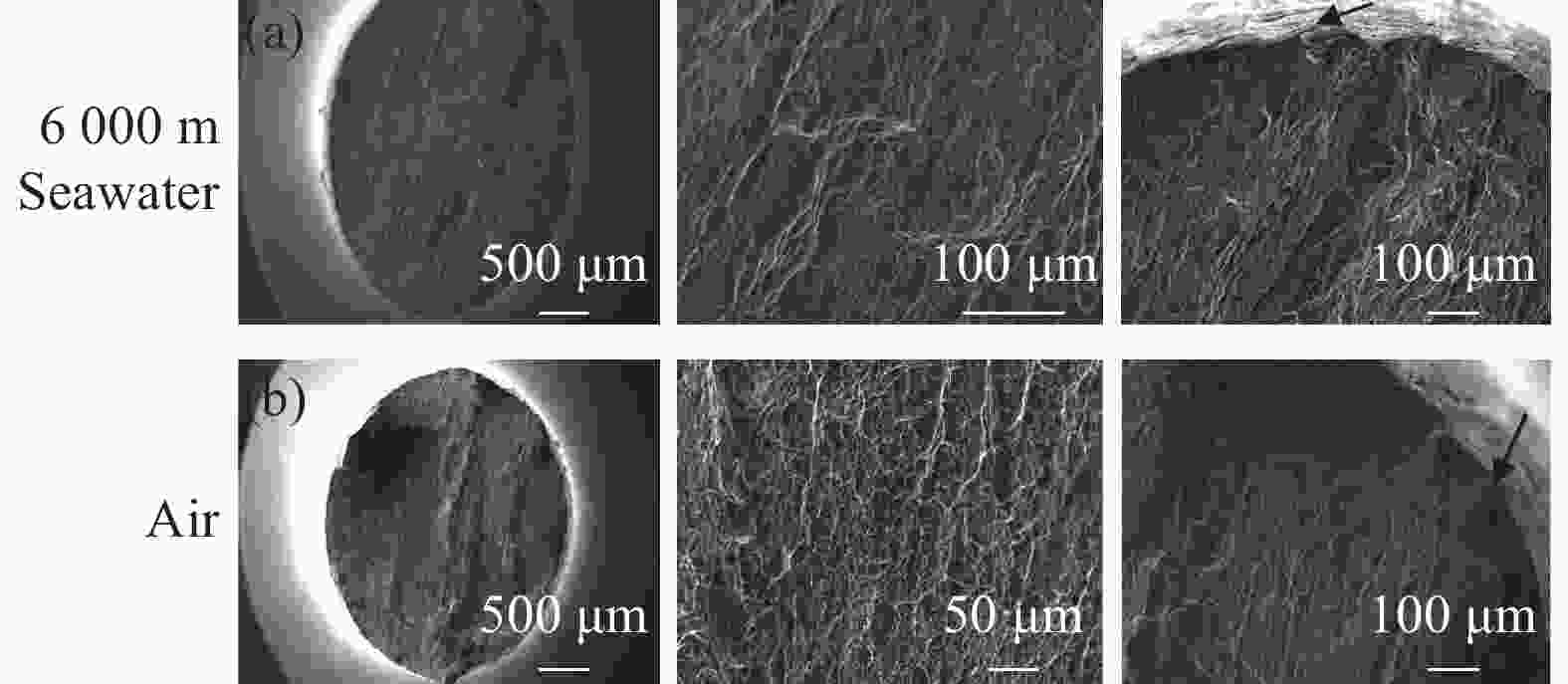
6000 m海水环境,系统研究了TC4 ELI合金的循环应力-寿命响应及损伤演化规律。试验给出了不同环境条件下TC4 ELI合金的循环应力-疲劳寿命数据。结果表明,模拟深海环境中蠕变-疲劳的循环应力-寿命关系可以用Basquin方程表征;有保载时间的蠕变-疲劳比纯疲劳的疲劳寿命显著降低;同等加载条件下疲劳过程的断裂应变量相当,疲劳寿命取决于应变增加的速率。扫描电镜观察到断口表面多源裂纹萌生,无明显扩展区,疲劳寿命主要为裂纹萌生寿命,表明深海环境与空气中裂纹萌生机制不同。Abstract: To address the unknown creep-fatigue damage mechanism of TC4 ELI titanium alloy in deep-sea multi-factor coupled environment, a high-pressure corrosion test system was used to simulate the seawater environment at 200, 600 m, and 6000 m in the South China Sea, and the cyclic stress life response and damage evolution law of TC4 ELI alloy were systematically studied. The experiment provided the cyclic stress-fatigue life data of TC4 ELI alloy under different environmental conditions. The results show that the cyclic stress-life relationship of creep-fatigue in the deep-sea environment can be characterized by the Basquin equation. The creep fatigue life with guaranteed load time is significantly reduced compared to that of pure fatigue; Under the same loading conditions, the fracture strain during the fatigue process is equivalent, and the fatigue life depends on the rate of strain increase. The stable stage of the cyclic strain-time curve shows the superimposed response of the creep rate and the plastic deformation of pure fatigue. Multiple-source crack initiations were observed on the fracture surface by Scanning Electron Microscopy, with no obvious crack propagation zone. The fatigue life is mainly the crack initiation life, indicating that the crack initiation mechanism is different in deep-sea environments and air.-
Key words:
- deep-sea environmental factors /
- creep-fatigue /
- fatigue life /
- crack initiation
-
表 1 试验材料的合金成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of TC4 ELI titanium alloy
% Al V Fe N H O Ti 5.99 3.91 0.034 0.0036 0.0024 0.050 Bal. 表 2 三种不同试验环境控制参数设定
Table 2. Three sets of environment parameters for test
Serial number Simulated water depth/m Hydrostatic pressure/MPa Dissolved oxygen×106 Temperature/ ℃ 1 200 2 8 27 2 600 6 2 9 3 6000 60 4 3 表 3 试验环境中蠕变-疲劳的应力-寿命方程(tD=60 s)
Table 3. Stress-life equation for creep fatigue in the test environment (tD=60 s)
Test depth/m Peak stress-fatigue life equation Air $ \mathit{\sigma}_0=894N^{-0.019\; 5} $ 200 $ {\sigma }_{1}=930{N}^{-0.041\;4} $ 600 $ {\sigma }_{2}=904{N}^{-0.015\;4} $ 6000 $ {\sigma }_{3}=1\;050{N}^{-0.029\;4} $ -
[1] ZHAO Y Q. Phase transformation and heat treatment of titanium alloys[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2012. (赵永庆. 钛合金相变及热处理[M]. 中南大学出版社, 2012.ZHAO Y Q. Phase transformation and heat treatment of titanium alloys[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2012. [2] FENG Y Q, JIA S X, WANG W Q, et al. Development of TC4 ELI titanium alloy hemisphere shell for manned submersible[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2016, 33(1): 19-22. (冯雅奇, 贾栓孝, 王韦琪, 等. 深潜器载人舱用TC4 ELI 钛合金半球壳的研制[J]. 钛工业进展, 2016, 33(1): 19-22.FENG Y Q, JIA S X, WANG W Q, et al. Development of TC4 ELI titanium alloy hemisphere shell for manned submersible[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2016, 33(1): 19-22. [3] LI Y H, YANG R, QING D G, et al. Effect of microstructure on tensile creep behavior of TC4ELI titanium alloy at roomtemperature[J]. World Nonferrous Metal, 2018(23): 180-181. (李有华, 杨蓉, 庆达嘎, 等. 显微组织对TC4ELI钛合金常温拉伸蠕变行为影响研究[J]. 世界有色金属, 2018(23): 180-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2018.23.102LI Y H, YANG R, QING D G, et al. Effect of microstructure on tensile creep behavior of TC4ELI titanium alloy at roomtemperature[J]. World Nonferrous Metal, 2018(23): 180-181. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2018.23.102 [4] XI G Q, QIU J K, LEI J F, et al. Room temperature creep behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2021, 35(12): 881-892. (席国强, 邱建科, 雷家峰, 等. Ti-6Al-4V合金的室温蠕变行为[J]. 材料研究学报, 2021, 35(12): 881-892.XI G Q, QIU J K, LEI J F, et al. Room temperature creep behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2021, 35(12): 881-892. [5] DONG Y C, FANG Z G, CHANG H, et al. Service performance of titanium alloy in marine environment[J]. Materials China, 2020, 39(3): 185-190. (董月成, 方志刚, 常辉, 等. 海洋环境下钛合金主要服役性能研究[J]. 中国材料进展, 2020, 39(3): 185-190.DONG Y C, FANG Z G, CHANG H, et al. Service performance of titanium alloy in marine environment[J]. Materials China, 2020, 39(3): 185-190. [6] ZHOU J L, LI X G, CHENG X Q, et al. Research progress on corrosion of metallic materials in deep sea environment[J]. Corros. Sci. Prot. Technol. , 2010, 22: 47. (周建龙, 李晓刚, 程学群, 等. 深海环境下金属及合金材料腐蚀研究进展[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2010, 22: 47.ZHOU J L, LI X G, CHENG X Q, et al. Research progress on corrosion of metallic materials in deep sea environment[J]. Corros. Sci. Prot. Technol. , 2010, 22: 47. [7] FU Z X, LI X F, LUO L Z. Research progress on corrosion fatigue of metal materials[J]. Equipment Enviromental Engineering, 2019, 16(7): 71-75. (符朝旭, 黎小锋 , 罗来正. 金属材料腐蚀疲劳研究进展[J]. 装备环境工程, 2019, 16(7): 71-75.FU Z X, LI X F, LUO L Z. Research progress on corrosion fatigue of metal materials[J]. Equipment Enviromental Engineering, 2019, 16(7): 71-75. [8] LIN J H, DAN Z H, LU J F, et al. Research status and prospect on marine corrosion of titanium alloys in deep ocean environments[J]. Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 2020, 49: 1090. (林俊辉, 淡振华, 陆嘉飞, 等. 深海腐蚀环境下钛合金海洋腐蚀的发展现状及展望[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2020, 49: 1090.LIN J H, DAN Z H, LU J F, et al. Research status and prospect on marine corrosion of titanium alloys in deep ocean environments[J]. Rare Met. Mater. Eng., 2020, 49: 1090. [9] LI Y H, ZHANG W X, CHEN X L, et al. Research and application status of titanium alloys for marine engineering[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2022, 39(1): 43-48. (李永华, 张文旭, 陈小龙, 等. 海洋工程用钛合金研究与应用现状[J]. 钛工业进展, 2022, 39(1): 43-48.LI Y H, ZHANG W X, CHEN X L, et al. Research and application status of titanium alloys for marine engineering[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2022, 39(1): 43-48. [10] ZHU S P, HUANG H Z, HE L P, et al. Improved generalized strain energy damage function method for high temperature low cycle fatigue-creep[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2011, 32(8): 1445-1452. (朱顺鹏, 黄洪钟, 何俐萍, 等. 高温低周疲劳-蠕变的改进型广义应变能损伤函数方法[J]. 航空学报, 2011, 32(8): 1445-1452.ZHU S P, HUANG H Z, HE L P, et al. Improved generalized strain energy damage function method for high temperature low cycle fatigue-creep[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2011, 32(8): 1445-1452. [11] LIU Y Y, ZHAO Z H, WANG G S, et al. Effect of the over-aging degree on high cycle fatigue properties of an ultra-high strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2024, 918: 147428. [12] TANG S J. Sdudy on microstructure, properties and room temperature creep of TC4 ELI sheet[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2021. (汤苏晋. TC4 ELI板材组织性能及室温蠕变研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2021.TANG S J. Sdudy on microstructure, properties and room temperature creep of TC4 ELI sheet[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2021. [13] WANG L, WANG K, LI Y Q, et al. Low-cycle fatigue properties of TC4 ELI titanium alloy[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2018, 35(2): 17-21. (王雷, 王琨, 李艳青, 等. TC4 ELI钛合金低周疲劳性能研究[J]. 钛工业进展, 2018, 35(2): 17-21.WANG L, WANG K, LI Y Q, et al. Low-cycle fatigue properties of TC4 ELI titanium alloy[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2018, 35(2): 17-21. [14] HONG Y S, FANG B. Microscopic process and description for the initiation and propagation of short fatigue cracks[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 1993, 23(4): 468-486. (洪友士, 方彪. 疲劳短裂纹萌生及发展的细观过程和理论[J]. 力学进展, 1993 23(4): 468-486.HONG Y S, FANG B. Microscopic process and description for the initiation and propagation of short fatigue cracks[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 1993, 23(4): 468-486. [15] SUN Y Y, CHANG H, FANG Z G. et al. Effect of microstructure on low cycle fatigue property of TC4 ELI titanium alloy[J]. Rare Met. Mater. Eng, 2020, 49(5): 1623-1628. -




 下载:
下载: