Study on process mineralogy and upgrading feasibility of a high-titanium and high-vanadium iron concentrate in Chaoyang, Liaoning
-
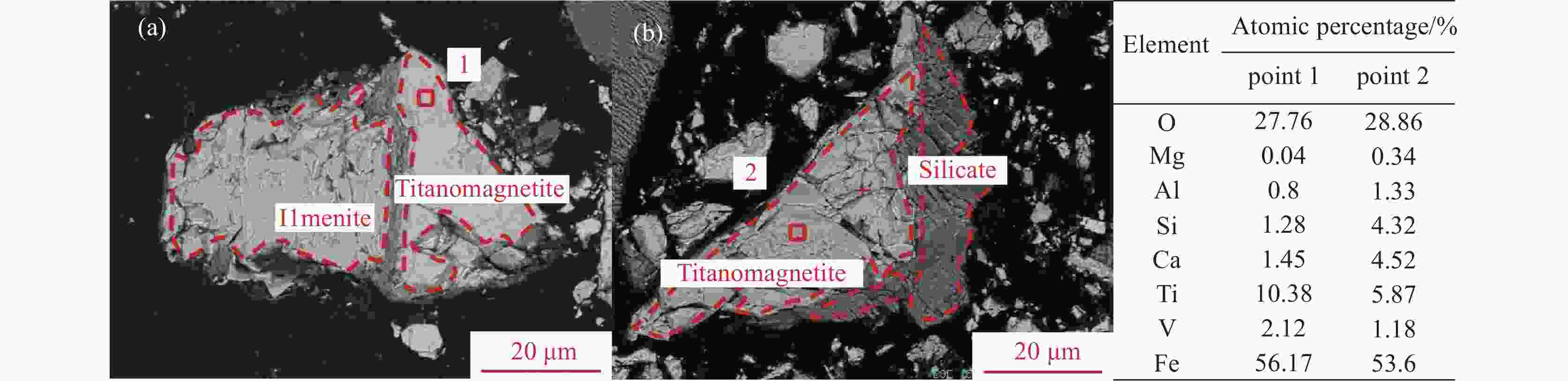
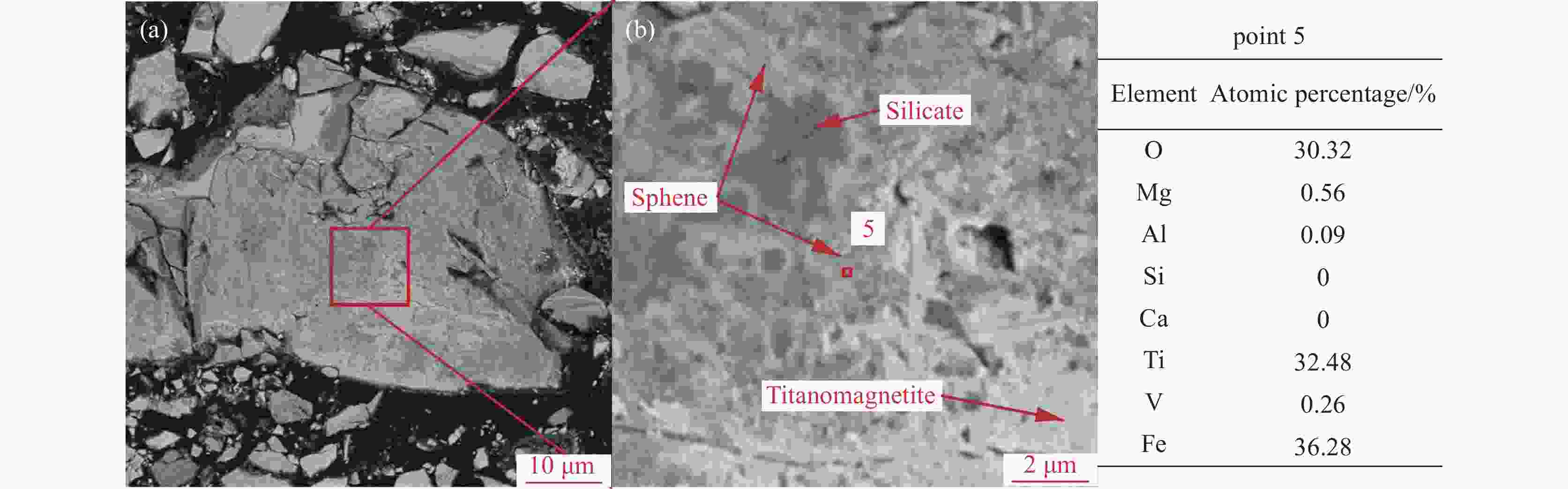
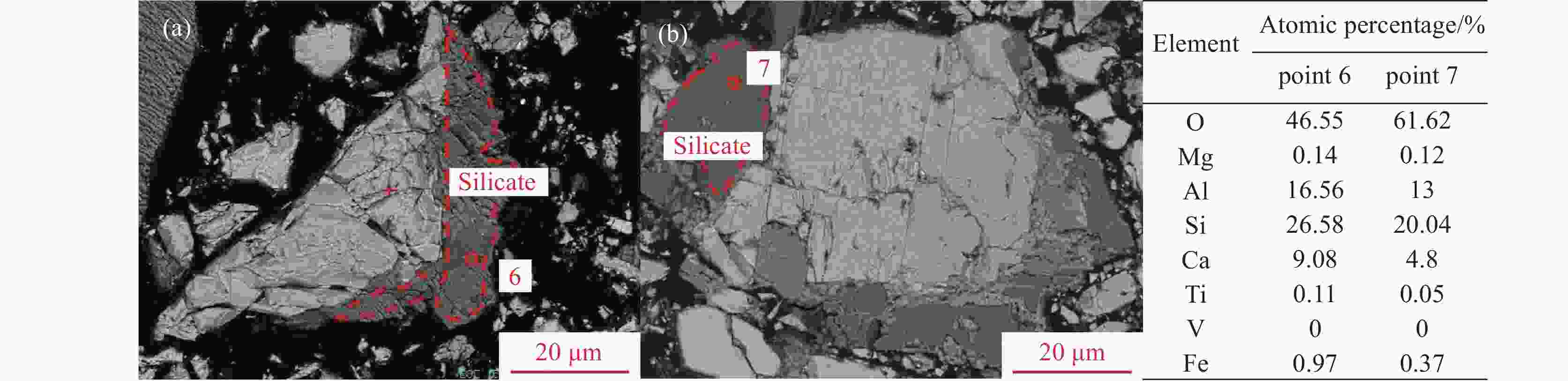
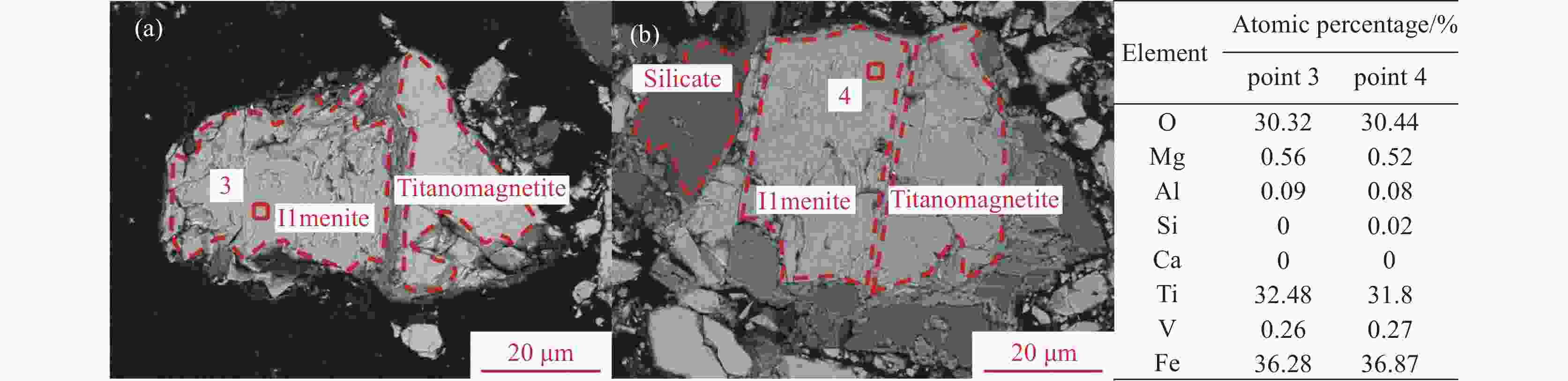
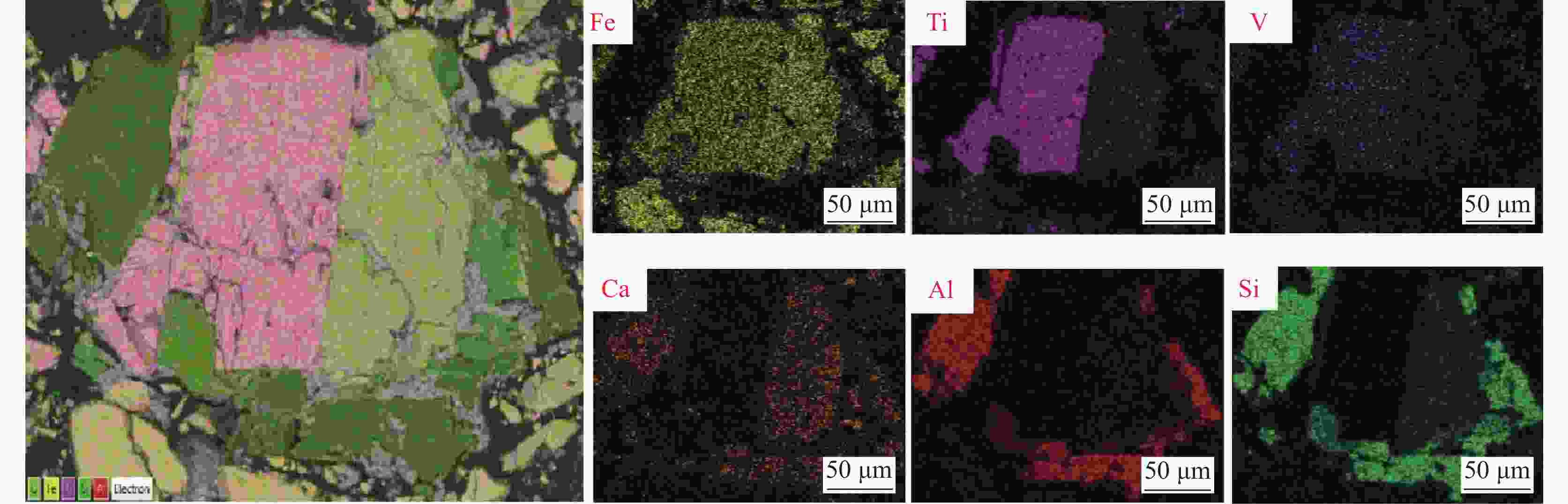
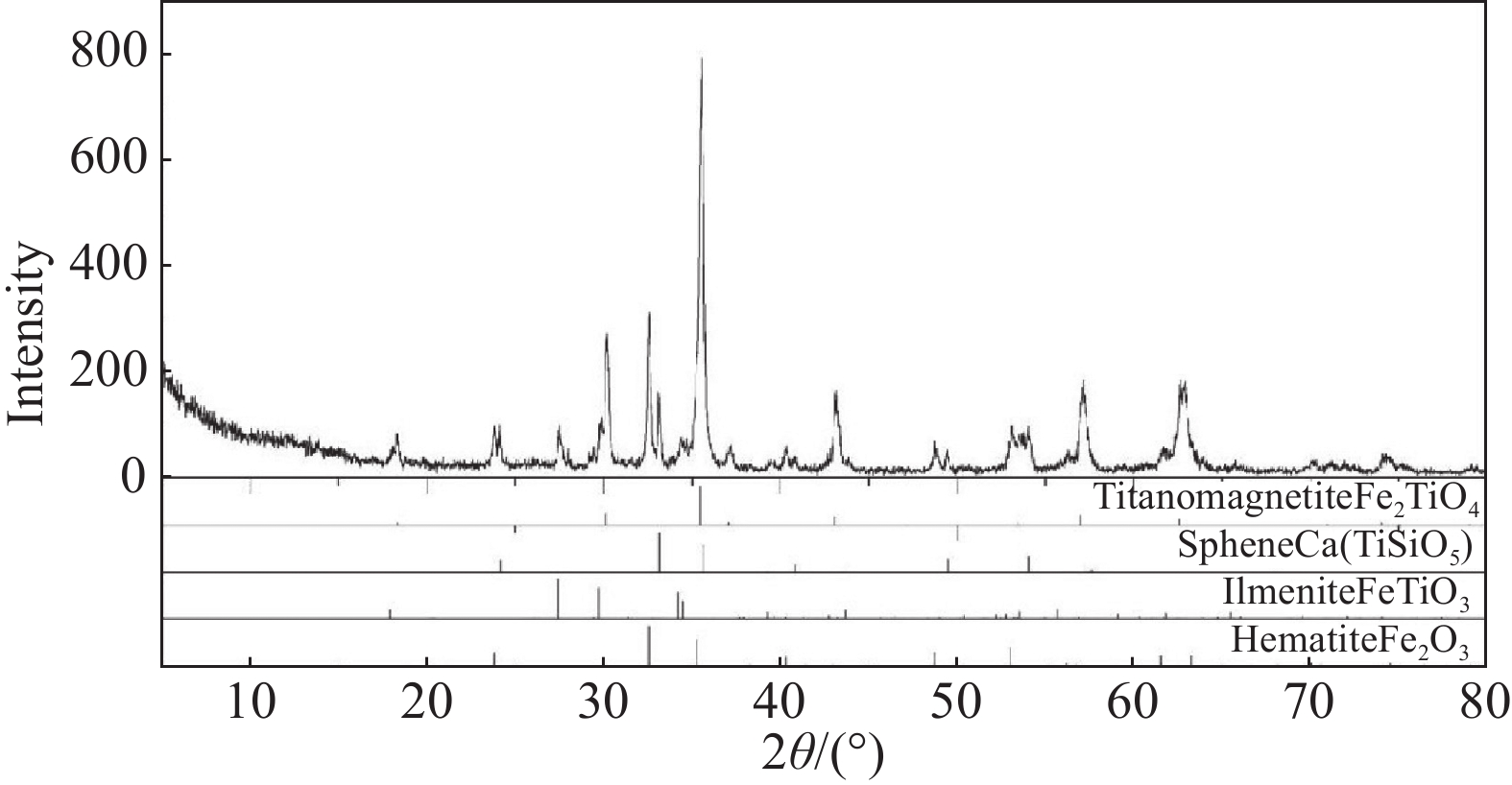
摘要: 辽宁朝阳地区发现了丰富的钒钛磁铁矿资源,其预选精矿的特征为具有高硅高钛高钒的显著特征。对该精矿进行工艺矿物学研究,探索进一步脱硅提质的可行性,对于该地区钒钛资源的深度开发利用具有重要意义。运用选矿工艺矿物学研究方法,查明了该精矿的主要矿物及其嵌布关系,铁精矿中有价矿物主要为钛磁铁矿、钛铁矿及少量的赤铁矿,脉石矿物主要为铁橄榄石和长石等硅酸盐矿物及少量的榍石。钒和钛主要赋存在钛磁铁矿是导致铁精矿高钒高钛的主要原因,钛磁铁矿之中嵌布着细小粒度的脉石,导致了铁精矿的高钙、高硅特征。通过细磨后磁选的手段可以有效地将该精矿提质。而钛磁铁矿中紧密嵌布的细小脉石颗粒通过细磨较难充分解离,部分钙、硅元素以常规细磨磁选较难去除,提质后精矿依然存在6.68%的SiO2和3.22%的CaO。Abstract: A vanadium-titanium magnetite resource has been discovered in Chaoyang, Liaoning, with the pre-selected concentrate being notable for high silicon, titanium, and vanadium content. Conducting process mineralogy research on this concentrate to explore the possibility of further silicon removal and quality enhancement is of great significance for the in-depth development and utilization of local vanadium-titanium resources. This study uses mineral processing and mineralogy research methods to identify the main minerals and their intergrowth relationships in the concentrate. The valuable minerals in the iron concentrate are mainly ilmenomagnetite, ilmenite, and a small amount of hematite. Gangue minerals are mainly silicate minerals like iron olivine and feldspar, along with a small quantity of sphene. The high vanadium and titanium content in the iron concentrate is mainly due to the presence of vanadium and titanium in ilmenomagnetite. The fine-grained gangue minerals intergrown with ilmenomagnetite lead to the high calcium and silicon content in the iron concentrate. After fine grinding and magnetic separation, the quality of the concentrate can be improved. However, due to the intimate intergrowth of fine-grained gangue minerals in ilmenomagnetite, it is difficult for conventional fine grinding and magnetic separation to fully liberate and remove the calcium and silicon elements. Therefore, even after quality improvement, the concentrate still contains 6.68% SiO2 and 3.22% CaO.
-
表 1 铁精矿的主要化学成分
Table 1. The major chemical components of iron ore
% TFe TiO2 V2O5 FeO SiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 S LOI 42.45 17.03 1.54 13.93 7.74 3.63 0.90 2.36 0.045 2.5 表 2 精矿矿物组成与含量
Table 2. Mineral composition and content of iron ore
% Titanomagnetite Ilmenite Fayalite Hematite 81.57 7.94 5.22 2.54 Feldspars Sphene Other gangue 1.53 0.96 0.24 表 3 铁元素在不同物相间分布率
Table 3. Inter-phase distribution rate of Fe
% Titanomagnetite Ilmenite Fayalite Hematite Sphene Total 86.92 6.02 3.44 3.26 0.36 100 表 4 钛元素在不同物相间分布率
Table 4. Inter-phase distribution rate of Ti
% Titanomagnetite Ilmenite Sphene Hematite Fayalite Total 76.68 21.51 1.09 0.66 0.06 100 表 5 精矿中主要含铁矿物粒度分布
Table 5. Grain size distribution of main minerals in iron concentrate
Size fraction/μm Titanomagnetite Ilmenite Fayalite Feldspars Yield/% Cumulative
yield/%Yield/% Cumulative
yield/%Yield/% Cumulative
yield/%Yield/% Cumulative
yield/%>500 2.89 2.89 2.80 2.80 12.11 12.11 10.41 10.41 (212, 500] 12.53 15.42 21.10 23.90 23.43 35.54 31.07 41.48 (150, 212] 17.55 32.97 25.90 49.80 22.13 57.67 20.70 62.18 (106, 150] 17.66 50.63 19.03 68.83 19.22 76.89 16.41 78.58 (75, 106] 15.43 66.06 15.03 83.86 10.26 87.15 9.35 87.93 (53, 75] 10.51 76.57 7.83 91.69 5.06 92.21 5.23 93.16 (38, 53] 6.72 83.29 3.27 94.96 3.10 95.31 2.55 95.71 (25, 38] 6.65 89.94 2.25 97.21 1.73 97.04 1.58 97.29 (10, 25] 9.48 99.42 2.65 99.86 2.77 99.81 2.51 99.80 ≤10 0.58 100 0.14 100 0.19 100 0.21 100 表 6 精矿中各物相解离度分析
Table 6. Dissociation degree of main minerals in iron concentrate
% Mineral Individual particles X≥80% 80%>X≥60% 60%>X≥40% 40%>X≥20% X<20% Titanomagnetite 73.13 11.13 8.22 4.04 2.47 1.01 Ilmenite 12.53 8.15 19.64 19.92 18.37 21.39 Fayalite 16.12 8.49 21.13 16.66 16.3 21.3 Hematite 27.8 6.33 13.03 7.53 8.39 36.93 Feldspars 8.42 1.88 11.82 26.39 17.07 34.42 表 7 提质精矿理论计算结果
Table 7. Theoretical calculation results of titanium enrichment concentrate
% Name TFe TiO2 V2O5 SiO2 CaO Enriched concentrate 42.46 18.26 1.64 6.17 3.88 Raw concentrate 42.45 17.03 1.54 7.74 3.63 表 8 精矿磁选提质试验结果
Table 8. Test results of magnetic separation for concentrate upgrading
% Magnetic field strength Yield TFe TiO2 V2O5 SiO2 CaO Feed concentrate 100 42.45 17.03 1.54 7.74 3.63 0.6 T Concentrate 91.01 43.99 18.21 1.57 6.68 3.22 Tailings 8.99 26.84 5.08 1.23 18.43 6.67 1.0 T Concentrate 96.37 43.85 17.59 1.56 6.95 3.69 Tailings 3.63 5.26 2.15 0.93 28.82 1.94 -
[1] WANG X Q. Blast furnace smelting of vanadium - titanium magnetite[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1994: 1-18. (王喜庆. 钒钦磁铁矿高炉冶炼[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1994: 1-18.WANG X Q. Blast furnace smelting of vanadium - titanium magnetite[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1994: 1-18. [2] YANG Z J, WANG F Y, LUO R F, et al. Magnetic separation enrichment method for ultra-fine vanadium - titanium magnetite in Western Sichuan[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019, 40(3): 26-29. (杨招君, 王丰雨, 罗荣飞, 等. 攀西超细粒级钒钛磁铁矿磁选富集方法[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019, 40(3): 26-29. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.03.005YANG Z J, WANG F Y, LUO R F, et al. Magnetic separation enrichment method for ultra-fine vanadium - titanium magnetite in Western Sichuan[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019, 40(3): 26-29. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.03.005 [3] YANG J Y, TANG Y, YANG K, et al. Leaching characteristics of vanadium in mine tailings and soils near a vanadium titanomagnetite mining site[J]. Hazard. Mater, 2014, 264: 498-504. [4] LIU F Y, XU L, CHEN C, et al. The occurrence state of titanium and prediction of theoretical indicators in a strongly altered vanadium - titanium magnetite in Western Sichuan[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Ore Dressing Section), 2024(6): 13-20, 39. (刘飞燕, 徐力, 陈超, 等. 攀西某强蚀变钒钛磁铁矿钛的赋存状态及理论指标预测[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2024(6): 13-20, 39.LIU F Y, XU L, CHEN C, et al. The occurrence state of titanium and prediction of theoretical indicators in a strongly altered vanadium - titanium magnetite in Western Sichuan[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Ore Dressing Section), 2024(6): 13-20, 39. [5] ZHANG L. Experimental study on the separation of titanium concentrate from the vanadium - titanium magnetite tailings in the western part of Liaoning Province [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2020. (张乐. 从辽西地区钒钛磁铁矿选铁尾矿中分选钛精矿的实验研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2020.ZHANG L. Experimental study on the separation of titanium concentrate from the vanadium - titanium magnetite tailings in the western part of Liaoning Province [D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2020. [6] LIU J S, XING Z X, CHENG G J, et al. Study on the grinding kinetics and magnetic separation of low-grade vanadiferous titanomagnetite concentrate[J]. Metals, 2022, 12(4): 575. [7] LIU Z X. Research and industrial practice on the upgrading and impurity reduction of the Baima vanadium - titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(3): 104-110. (刘志雄. 白马钒钛磁铁矿提质降杂研究及工业实践[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022, 43(3): 104-110.LIU Z X. Research and industrial practice on the upgrading and impurity reduction of the Baima vanadium - titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(3): 104-110. [8] LIU J S, XING Z X, CHENG G J, et al. Oxidation behavior of low-grade vanadiferous titanomagnetite concentrate with high titanium[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2024, 31: 329-341. [9] CHENG G J, XUE X X, GAO Z X, et al. Key technologies for the comprehensive utilization of high - vanadium and high - titanium magnetite resources in western Liaoning[C]// The Chinese Society for Metals. Proceedings of the 12th China Steelmaking Conference. (程功金, 薛向欣, 高子先, 等. 辽西高钒高钛型磁铁矿资源综合利用关键技术[C]// 中国金属学会. 第十二届中国钢铁年会论文集.CHENG G J, XUE X X, GAO Z X, et al. Key technologies for the comprehensive utilization of high - vanadium and high - titanium magnetite resources in western Liaoning[C]// The Chinese Society for Metals. Proceedings of the 12th China Steelmaking Conference. [10] XING B, HU X M, ZHANG J L, et al. Experimental study on the mineral processing of a vanadium - titanium magnetite in Chaoyang[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry Research, 2021(15): 172-174. (邢波, 胡秀明, 张金良, 等. 朝阳某钒钛磁铁矿选矿试验研究[J]. 当代化工研究, 2021(15): 172-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2021.15.084XING B, HU X M, ZHANG J L, et al. Experimental study on the mineral processing of a vanadium - titanium magnetite in Chaoyang[J]. Contemporary Chemical Industry Research, 2021(15): 172-174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2021.15.084 [11] DONG Z H, LI W B, LI Y J. Experimental study on the pre - enrichment of weathering - shell type vanadium - titanium magnetite in western Liaoning[J]. Metal Mines, 2019(2): 150-155. (董振海, 李文博, 李艳军. 辽西风化壳型钒钛磁铁矿预富集试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2019(2): 150-155.DONG Z H, LI W B, LI Y J. Experimental study on the pre - enrichment of weathering - shell type vanadium - titanium magnetite in western Liaoning[J]. Metal Mines, 2019(2): 150-155. [12] XU C B, ZHANG Y M, LIU T, et al. Process mineralogy study of a vanadium - titanium magnetite in western Liaoning[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Ore Dressing Section), 2018(3): 1-5, 41. (许承宝, 张一敏, 刘涛, 等. 辽西某钒钛磁铁矿工艺矿物学研究[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2018(3): 1-5, 41.XU C B, ZHANG Y M, LIU T, et al. Process mineralogy study of a vanadium - titanium magnetite in western Liaoning[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Ore Dressing Section), 2018(3): 1-5, 41. [13] ZHONG X, SHI Z X, GAO J. Process mineralogy discussion of the Baima vanadium - titanium magnetite in Western Sichuan[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2021, 41(10): 29-35. (钟祥, 史志新, 高健. 攀西地区白马钒钛磁铁矿工艺矿物学探讨[J]. 冶金分析, 2021, 41(10): 29-35. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.011357ZHONG X, SHI Z X, GAO J. Process mineralogy discussion of the Baima vanadium - titanium magnetite in Western Sichuan[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2021, 41(10): 29-35. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.011357 [14] YU H D, WANG L N, QU J K, et al. Process mineralogy characteristics and ore value of typical Chinese vanadium - titanium magnetites[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 41(2): 275-281. (于宏东, 王丽娜, 曲景奎, 等. 中国典型钒钛磁铁矿的工艺矿物学特征与矿石价值[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 41(2): 275-281. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2020.02.022YU H D, WANG L N, QU J K, et al. Process mineralogy characteristics and ore value of typical Chinese vanadium - titanium magnetites[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 41(2): 275-281. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2020.02.022 -




 下载:
下载: