Study on microalloying and heat treatment process of spring steel 55SiCrV
-
摘要: 在弹簧钢55SiCr成分基础上进行钒微合金化处理,获得了55SiCrV,通过淬火+回火正交试验、显微组织观察、力学性能测试和X射线衍射等手段,研究并分析了淬火+回火工艺对弹簧钢55SiCrV微观组织和力学性能的影响,结果表明:0.20%V的添加可使55SiCrV组织中存在大量弥散均匀分布的10~35 nm含钒析出相,强化效果最佳。淬火+回火处理可以改变55SiCrV的显微组织比例,其中的残余奥氏体可以降低强度和增加塑性,55SiCrV获得最佳力学性能匹配(Rm=1 815 MPa、Z=28%)的热处理工艺为900 ℃淬火+430 ℃回火,对应其残余奥氏体含量为2.3%。Abstract: In this paper 55SiCrV steel was obtained by V microalloying based on the composition of 55SiCr spring steel, the effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of 55SiCrV was studied by means of orthogonal test of quenching and tempering, microstructure observation, mechanical properties test and X-ray diffraction. The experimental results show that there are a large number of 10 ~ 35 nm vanadium containing precipitates in the microstructure of 55SiCrV (0.20% V), and the corresponding strengthening effect is the best. Quenching and tempering processes can change the microstructure proportion of 55SiCrV, in which retained austenite can reduce the strength and increase the plasticity, the best matching of mechanical properties (Rm=1 815 MPa, Z=28%) of 55SiCrV is obtained by following process combination o f quenching at 900 ℃ and tempering at 430 ℃, and the content of resulted retained austenite is 2.3%.
-
Key words:
- spring steel /
- 55SiCrV /
- microalloying /
- quenching /
- tempering /
- mechanical properties
-
0. 引言
微合金化处理是一种常用的改善钢材性能的方法,通过部分合金元素的适量添加可以显著改变材料的微观组织转变曲线[1-2],进而结合一定的热处理手段可优化材料显微组织和力学性能,不同的微合金元素种类和添加量对材料的组织转变影响差异很大。钒是目前最常用的微合金化元素之一,可通过细化组织晶粒和从铁素体中析出强化相来提高材料强度[3]。55SiCrV是在传统弹簧钢55SiCr基础上加入钒元素研制而成的一种新钢种,被证明性能显著优于55SiCr,受到弹簧行业的广泛关注[4-6]。含钒弹簧钢55SiCrV由于钢中同时存在钒合金和碳、氮元素,使得第二相析出类型较复杂,因此受到其热处理工艺的影响较大。已有试验表明[1,7]:钒微合金钢中的析出相主要为碳氮复合相,根据其溶解度积差异在不同温度阶段循序形成并互溶,且其中的细小碳化物、氮化物和碳氮化物可阻止高温奥氏体发生再结晶及长大,从而达到细晶强化的效果;此外,钒元素的适量添加可以显著增强弹簧钢的屈服比,降低其脱碳敏感性[8],因此对于改善其冶金表面质量具有明显的效果。
弹簧钢下游用户的深加工过程涉及酸洗-磷化-拉拔-油淬火-回火-涂油-收卷等系列加工,其中淬火+回火工艺是决定弹簧钢微观组织与强度级别的关键环节[5],而材料的微合金化处理会显著改变其显微组织转变特点,因此仅适当的热处理工艺才能最大程度地发挥微合金化作用[9],弹簧钢的热处理工艺是其应用技术的核心内容。
55SiCrV已被证实可用于制作高强度汽车用悬挂簧和气门簧,是国内强度最高的弹簧钢系列之一,但对于55SiCrV具体成分、组织和性能之间的研究却较为缺乏[10]。笔者对常见的商业用55SiCr弹簧钢进行不同含量的钒微合金化处理,确定了空冷条件下合适的钒添加量,通过淬火+回火正交试验对弹簧钢的热处理工艺进行模拟,并结合显微组织观察、力学性能测试和X射线衍射等手段,通过对比研究试样在不同热处理工艺下的微观组织和力学性能变化,以期掌握55SiCrV强化机理,助力优化国产弹簧钢性能。
1. 试验材料及方法
在55SiCr成分基础上,通过中试工厂50 kg真空感应炉冶炼了7炉55SiCrV,将不同炉次试验钢以微合金元素钒含量作为变量,1#~7#试验钢的目标钒添加量分别为0、0.05%、0.10%、0.15%、0.20%、0.25%、0.30%,实际测定主要化学成分见表1,其中P和S控制要求分别为≤0.020%和≤0.015%。将7炉55SiCrV的钢板加工成拉伸试样,测量不同钒含量55SiCrV试样在空冷条件下的屈服强度Rp0.2和抗拉强度Rm,定量分析钒含量对材料力学性能的影响。
采用中试工厂轧机将50 kg试验钢炮弹锭轧制成厚16 mm,宽300 mm的钢板,钢锭加热及轧钢温度模拟55SiCr轧制温度,具体工艺参数见表2,每炉钢经锯床切割加工成16 mm钢板待用。
表 1 试样主要化学成分Table 1. Main chemical constituents of samples% 编号 C Si Mn Cr V 1# 0.59 1.44 0.80 0.70 0 2# 0.56 1.42 0.75 0.69 0.06 3# 0.56 1.38 0.76 0.70 0.11 4# 0.56 1.44 0.78 0.71 0.16 5# 0.56 1.40 0.73 0.69 0.19 6# 0.56 1.40 0.74 0.70 0.25 7# 0.56 1.41 0.76 0.71 0.29 表 2 55SiCrV试验钢轧制工艺参数Table 2. Rolling process parametersof tested steel 55SiCrV加热温度/℃ 开轧温度/℃ 终轧温度/℃ 1150±20 1050±20 950±50 参考弹簧钢实际深加工过程进行其热处理工艺模拟,将5#试样(0.19% V)加工成标准拉伸样进行热处理,拉伸样在电阻加热炉内保温15 min,加热温度分别为850、900、950、1000 ℃,取出随即置于油池中进行淬火,然后将试样钢在430 ℃和450 ℃下进行回火处理,回火时间分别为30 min和60 min,具体热处理参数与对应试验编号见表3。通过拉伸试验机对热处理后的试样进行抗拉强度Rm和面缩率Z测量,采用CMT5105式万能试验机参照标准GB/T 228—2002执行,每炉钢至少检测5件试样,取其平均数作为统计结果。
表 3 热处理工艺及试验编号Table 3. Heat treatment processes and their test number编号 加热温度/℃ 回火工艺 温度/℃ 时间/min 1-1# 850 430 30 1-2# 850 450 30 2-1# 900 430 30 2-2# 900 450 30 3-1# 950 430 30 3-2# 950 450 30 3-3# 950 430 60 3-4# 950 450 60 4-1# 1000 430 30 4-2# 1000 450 30 2. 试验结果分析及讨论
2.1 钒含量对55SiCrV力学性能的影响
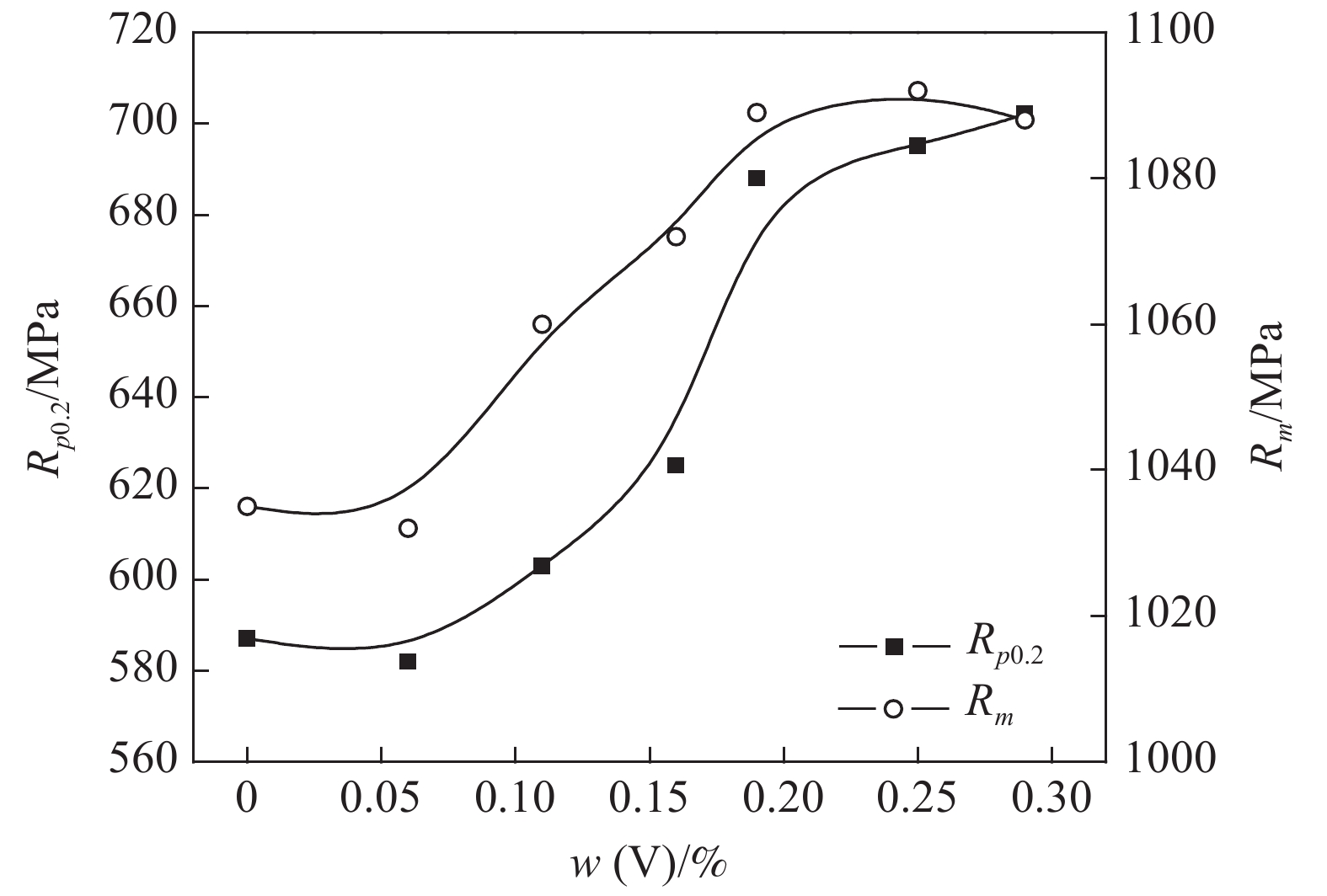
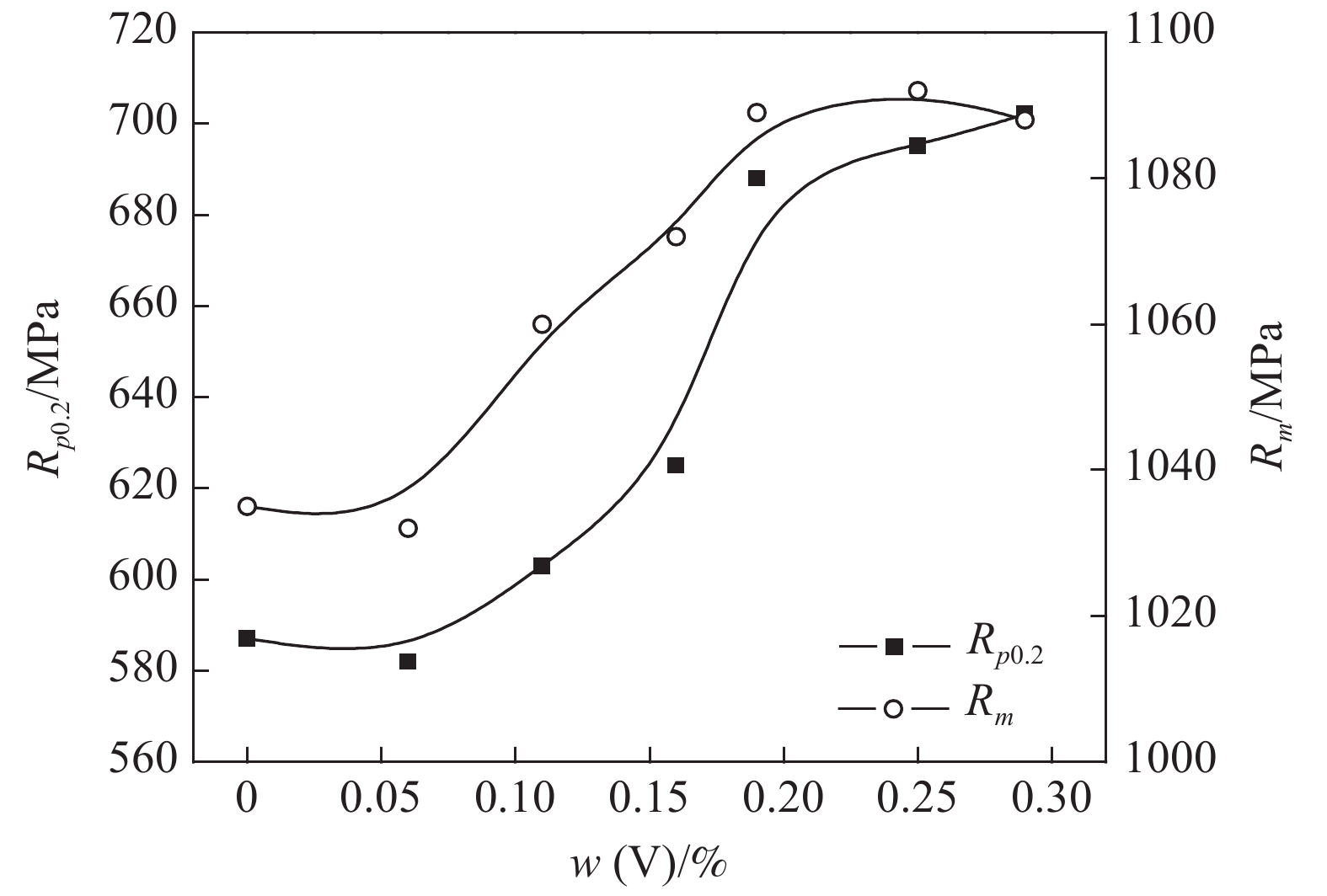
对7炉55SiCrV空冷试样的力学性能进行统计,绘制钒含量对55SiCrV屈服强度Rp0.2和抗拉强度Rm的影响曲线,如图1所示。
结合表1和图1进行分析,尽管1#和2#试样的钒含量相差0.06%,但试样的屈服强度与抗拉强度相差不大,1#试验略高于2#试样,主要原因是1#试样的碳含量为0.59%,高于2#~5#试样的0.56%,且其中的硅含量和锰含量均不低于其他试样,由于碳硅锰是主要的强化元素,由此产生的强化作用与0.06%V产生的沉淀强化相抵消,造成了1#和2#试样强度接近。
对比2#~7#试验的强度数据,在材料其他元素差异不明显且试样均为空冷处理条件下,钒的加入使钢的强度得到明显的提升。其中当钒含量从0.16%提升至0.19%过程中(2#~5#试验),材料的屈服和抗拉强度随着钒含量的增加呈近似线性变化;但随着钒含量的进一步提高,材料的强度并未出现预期的增加,且0.29%V试样的抗拉强度略低于0.25%V试样。不同钒含量试样均采用空冷处理,与实际生产过程中的控制冷却差异较大,该试验主要是为了定量研究化学成分对材料强度的影响。从图1材料强度与钒含量的变化曲线中可以看出,钒含量超过0.20%后,材料的强度升高趋势显著降低,而且钒含量的过量添加会导致其中的析出相尺寸过大,具有恶化塑性的趋势[3],因此可确定0.20%V是55SiCrV的适宜添加量。
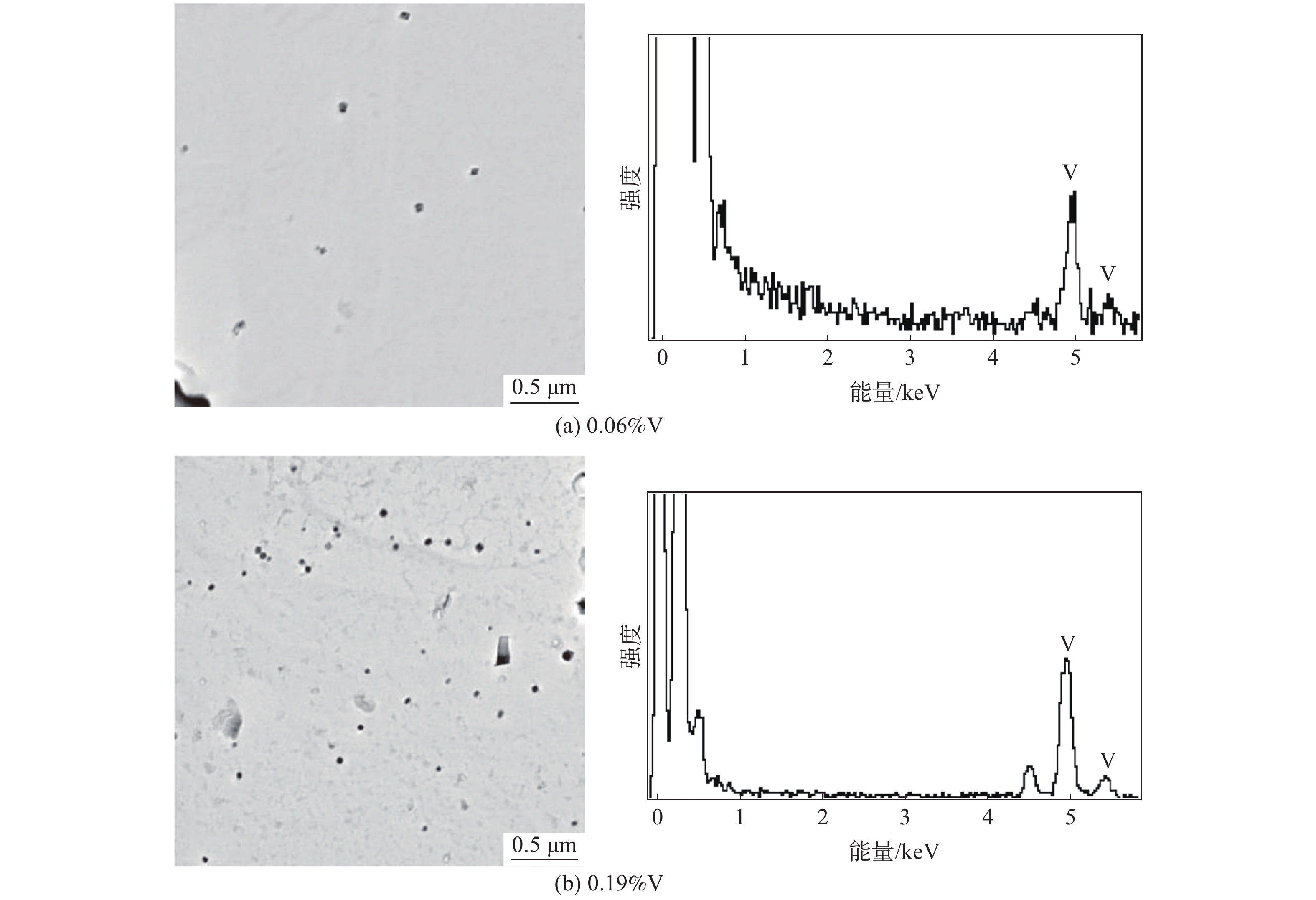
55SiCrV钢中添加钒含量由0.06%提高到0.19%,其屈服强度和抗拉强度增幅分别达到106 MPa和57 MPa,通过二次复型法对2#(0.06%V)和5#(0.19%V)试样的析出相进行TEM观察,结果如图2所示,两试样中的析出相形态均为不规则球形或矩形,析出相分布较均匀,成分一致,主要为含钒析出相,2#试样(0.06%V)的析出相颗粒明显少于5#(0.19%V)试样。经测量,尺寸范围集中于40~140 nm,而5#试样析出相主要范围为10~35 nm,其次为35~80 nm。
与其他强化元素不同的是,钒元素能在低温下进入奥氏体中,V(C,N)钒析出相在材料的冷却阶段大量析出,发挥沉淀强化作用。钒元素的沉淀强化作用可按照Orowan 机制进行解释,位错线在析出相颗粒附近滑移绕过发生缠结进而提高材料的强度[7],滑移面上的析出相颗粒数量越多,强化效果越好,5#(0.19%V)试样析出相颗粒更多,强化效果更强,显微组织与性能趋势一致。
2.2 热处理对55SiCrV组织和性能的影响
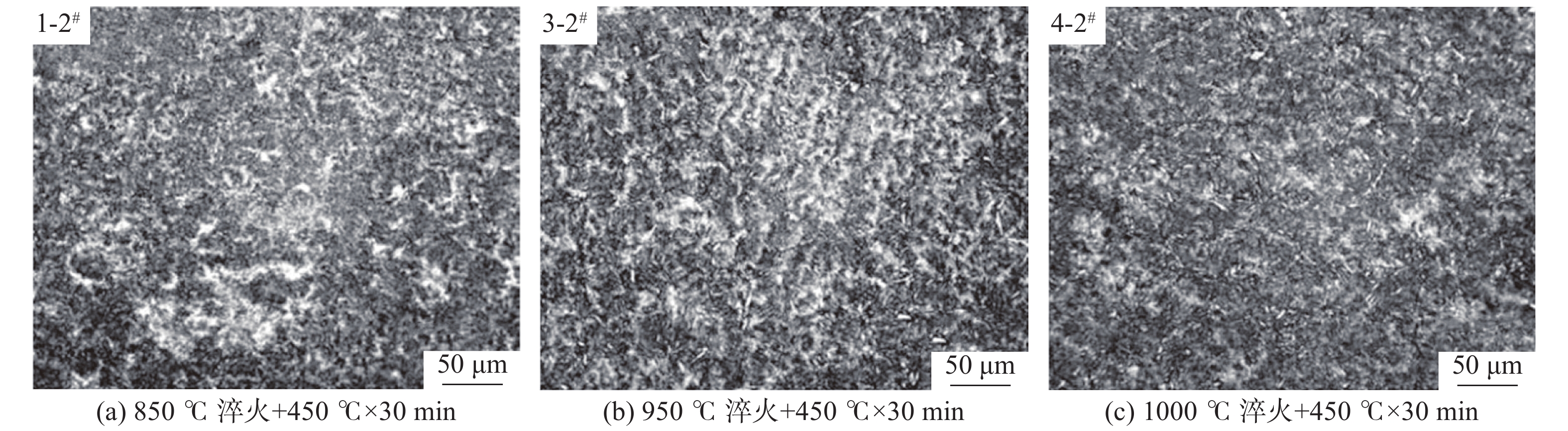
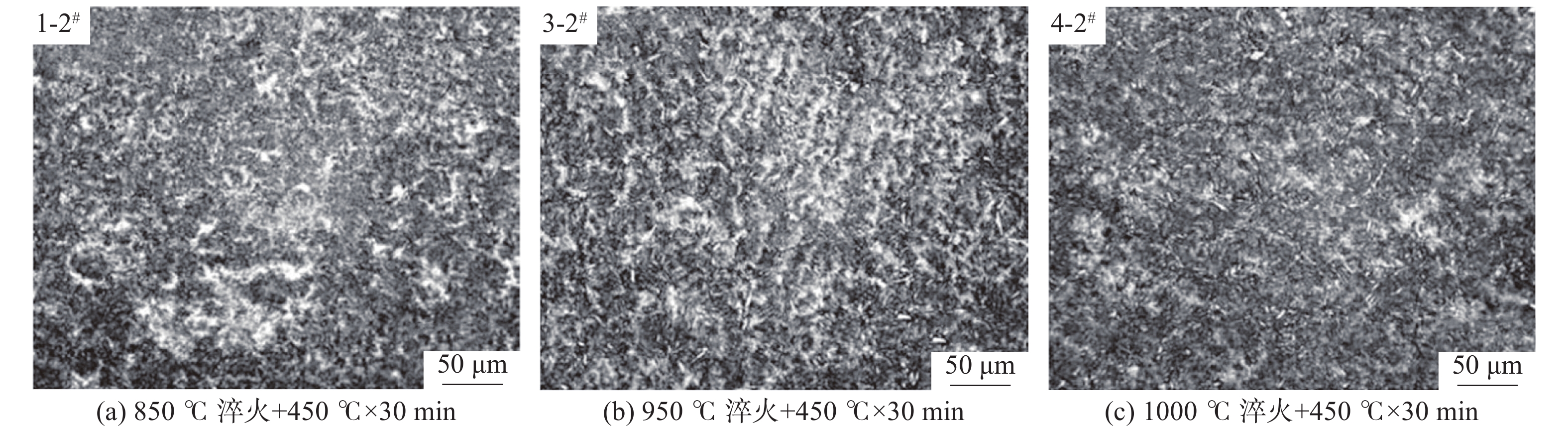
图3为0.19%V的55SiCrV试样经不同热处理后的金相组织,由图3可以看出,试样经淬火+回火处理后的组织主要为回火屈氏体+回火马氏体+残余奥氏体,但含量的比例不一致,其中回火屈氏体对应金相图片的黑色区域,回火马氏体对应白色区域,残余奥氏体对应白色点状区域。采用X射线衍射仪定量分析试样残余奥氏体组织含量,结果见表4,在不同热处理工艺下,2-1#、3-2#试样残余奥氏体含量达到极值,分别为2.3%和5.4%。
对热处理试样进行力学性能检测,结果见表5,可以看出:3-1#~3-4#采用相同的淬火温度,而回火温度和时间不同,当分别在450 ℃和430 ℃回火30 min条件下,如3-1#和3-2#试样,强度下降约 110 MPa,面缩率提高13%;3-1#和3-3#试样在相同的淬火温度(950 ℃)与回火温度(430 ℃)下,随着回火时间由30 min延长至60 min,试样强度下降 82 MPa,面缩率保持17%不变;而对比3-2#和3-4#试样,在950 ℃淬火和450 ℃回火时,试样的强度下降了75 MPa,面缩也下降6%,因此材料的抗拉强度随着淬火温度的升高而下降,而回火时间的延长会一定程度的降低试样的强度,但无法提高其塑性。
表 4 试验钢残余奥氏体含量Table 4. Retained austenite content of tested steels编号 加热温度/℃ 回火工艺 残余奥氏体含量/% 温度/℃ 时间/min 1-1# 850 430 30 3.6 1-2# 850 450 30 3.0 2-1# 900 430 30 2.3 2-2# 900 450 30 4.6 3-1# 950 430 30 4.8 3-2# 950 450 30 5.4 3-3# 950 430 60 5.1 3-4# 950 450 60 5.0 4-1# 1000 430 30 4.3 4-2# 1000 450 30 2.9 表 5 试验钢力学性能测试结果Table 5. Mechanical properties of tested steels编号 加热温度/℃ 回火工艺 Rm/MPa Z/% 温度/℃ 时间/min 1-1# 850 430 30 1 867 13 1-2# 850 450 30 1728 17 2-1# 900 430 30 1 815 28 2-2# 900 450 30 1739 17 3-1# 950 430 30 1 805 17 3-2# 950 450 30 1695 30 3-3# 950 430 60 1723 17 3-4# 950 450 60 1620 24 4-1# 1000 430 30 1694 28 4-2# 1000 450 30 1685 29 在表5中不同淬火-回火温度组合下,当回火温度保持430 ℃,淬火温度由950 ℃提高至1000 ℃时(3-1#和4-1#试样),强度由1 805 MPa下降至1 694 MPa,降幅超过100 MPa;而当回火温度为450 ℃时,3-2#和4-2#试样的强度差值仅为10 MPa,说明430℃低温回火时对其淬火温度的变化更为敏感,随着回火温度提高至 450 ℃,淬火温度对强度的影响作用显著降低。
综合对比本次试验结果,热处理工艺可以改变55SiCrV的显微组织,进而影响其力学性能,其中残余奥氏体会降低试样的强度且增加其塑性。55SiCrV的最佳性能匹配为2-1#试样,对应热处理工艺为900 ℃淬火+430 ℃回火,此时强度达到1 815 MPa,且具备28%的面缩率,对应的残余奥氏体含量为2.3%;而最佳的塑性则在3-2#工艺(30%,950 ℃淬火+450 ℃回火),对应的残余奥氏体含量为5.4%,可适用于制造部分塑性要求特别高的材料。
3. 结论
对55SiCr弹簧钢进行钒微合金化处理,得到55SiCrV;然后通过淬火+回火正交试验、显微组织观察、力学性能测试和X射线衍射等手段,获得了不同热处理工艺对55SiCrV微观组织和力学性能变化,形成结论如下:
1)55SiCrV的适宜钒添加量约为0.20%,可获得大量弥散均匀分布的10~35 nm含钒析出相,并获得最佳的强化效果;当钒添加量超过0.20%后,材料的强度不会继续提高,且存在塑性恶化风险。
2)55SiCrV的抗拉强度随着淬火温度的升高而下降,回火时间的延长也会一定程度上降低试样的强度,且无法提高其塑性;淬火+回火处理通过改变材料的显微组织比例来影响其力学性能, 900 ℃淬火+430 ℃×30 min回火热处理时可以获得最佳力学性能匹配(Rm=1 815 MPa、Z=28%)。
3)55SiCrV组织中的残余奥氏体可起到降低强度和增加塑性的作用,900 ℃淬火+430℃×30 min回火时残余奥氏体含量为2.3%;而获得最佳塑性(Z=30%)的工艺为950 ℃淬火+450 ℃回火,对应的残余奥氏体含量为5.4%。
-
表 1 试样主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical constituents of samples
% 编号 C Si Mn Cr V 1# 0.59 1.44 0.80 0.70 0 2# 0.56 1.42 0.75 0.69 0.06 3# 0.56 1.38 0.76 0.70 0.11 4# 0.56 1.44 0.78 0.71 0.16 5# 0.56 1.40 0.73 0.69 0.19 6# 0.56 1.40 0.74 0.70 0.25 7# 0.56 1.41 0.76 0.71 0.29 表 2 55SiCrV试验钢轧制工艺参数
Table 2. Rolling process parametersof tested steel 55SiCrV
加热温度/℃ 开轧温度/℃ 终轧温度/℃ 1150±20 1050±20 950±50 表 3 热处理工艺及试验编号
Table 3. Heat treatment processes and their test number
编号 加热温度/℃ 回火工艺 温度/℃ 时间/min 1-1# 850 430 30 1-2# 850 450 30 2-1# 900 430 30 2-2# 900 450 30 3-1# 950 430 30 3-2# 950 450 30 3-3# 950 430 60 3-4# 950 450 60 4-1# 1000 430 30 4-2# 1000 450 30 表 4 试验钢残余奥氏体含量
Table 4. Retained austenite content of tested steels
编号 加热温度/℃ 回火工艺 残余奥氏体含量/% 温度/℃ 时间/min 1-1# 850 430 30 3.6 1-2# 850 450 30 3.0 2-1# 900 430 30 2.3 2-2# 900 450 30 4.6 3-1# 950 430 30 4.8 3-2# 950 450 30 5.4 3-3# 950 430 60 5.1 3-4# 950 450 60 5.0 4-1# 1000 430 30 4.3 4-2# 1000 450 30 2.9 表 5 试验钢力学性能测试结果
Table 5. Mechanical properties of tested steels
编号 加热温度/℃ 回火工艺 Rm/MPa Z/% 温度/℃ 时间/min 1-1# 850 430 30 1 867 13 1-2# 850 450 30 1728 17 2-1# 900 430 30 1 815 28 2-2# 900 450 30 1739 17 3-1# 950 430 30 1 805 17 3-2# 950 450 30 1695 30 3-3# 950 430 60 1723 17 3-4# 950 450 60 1620 24 4-1# 1000 430 30 1694 28 4-2# 1000 450 30 1685 29 -
[1] (文波. 碳化钒在Fe-C-V微合金钢中的析出行为研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2011.)Wen Bo. Precipitation behavior of vanadium carbide in Fe-C-V microalloyed steel[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2011. [2] Hong Guohua, Yang Shunhu, Xiao Bo, et al. Production status and development prospect of spring steel at home and abroad[J]. Modern Metallurgy, 2009,(1):10−13. (洪国华, 杨顺虎, 肖波, 等. 国内外弹簧钢的生产现状和发展前景[J]. 现代冶金, 2009,(1):10−13. [3] Lu Jun, Zeng Yu, Zhang Chi, et al. Research progress of steel for automotive engine valve spring[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2008,(11):5−9, 18. (卢俊, 曾渝, 张弛, 等. 汽车发动机气门弹簧用钢研究进展[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2008,(11):5−9, 18. [4] Zhang Zhonghua, Wan Genjie, Cai Haiyan, et al. Development of 55SiCrV high strength spring steel wire[J]. Metal Products, 2006,(1):43−45. (张忠铧, 万根节, 蔡海燕, 等. 55SiCrV高强度弹簧钢线材的开发[J]. 金属制品, 2006,(1):43−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4226.2006.01.017 [5] Ke Xiaotao, Lu Xiangyang. Effect of vanadium on relaxation resistance of Si Mn spring steel[J]. Special Steel, 2007,28(6):4−6. (柯晓涛, 卢向阳. 钒对Si-Mn系弹簧钢松弛抗力的影响[J]. 特殊钢, 2007,28(6):4−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8620.2007.06.002 [6] Ma Mingtu, Li Zhigang, Lu Xiangyang. Effect of vanadium on decarburization sensitivity of 35Si MnB spring steel[J]. Special Steel, 2001,(5):11−13. (马鸣图, 李志刚, 卢向阳. 钒对35Si MnB弹簧钢脱碳敏感性的影响[J]. 特殊钢, 2001,(5):11−13. [7] Xu Dexiang, Yin Zhongda. High strength of spring steel and effect of alloying elements[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2003,28(12):30−36. (徐德祥, 尹锺大. 弹簧钢高强度化及合金元素的作用[J]. 金属热处理, 2003,28(12):30−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6051.2003.12.010 [8] Xie Yuanlin. Alloying effect and application of vanadium in steel[J]. Special Steel Technology, 2015,(1):1−5. (谢元林. 钒在钢中的合金化作用及应用[J]. 特钢技术, 2015,(1):1−5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0971.2015.01.001 [9] (崔娟, 刘雅政, 黄学启. 控轧控冷工艺对含钒弹簧钢组织性能的影响[C]//2007中国钢铁年会论文集. 2007.)Cui Juan, Liu Yazheng, Huang Xueqi. Effect of controlled rolling and controlled cooling process on microstructure and properties of spring steel containing vanadium[C]//Proceedings of 2007 China Steel Annual Conference. 2007. [10] Jiang Ting, Wang Kaizhong, Yu Tongren, et al. Effect of heat treatment process on mechanical properties and microstructure of 55SiCrV spring steel[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2019,44(10):96−98. (姜婷, 汪开忠, 于同仁, 等. 热处理工艺对弹簧钢 55SiCrV力学性能和组织的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2019,44(10):96−98. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载: