Simulation study on the effect of VAR magnetic stirring process on the melt flow
-
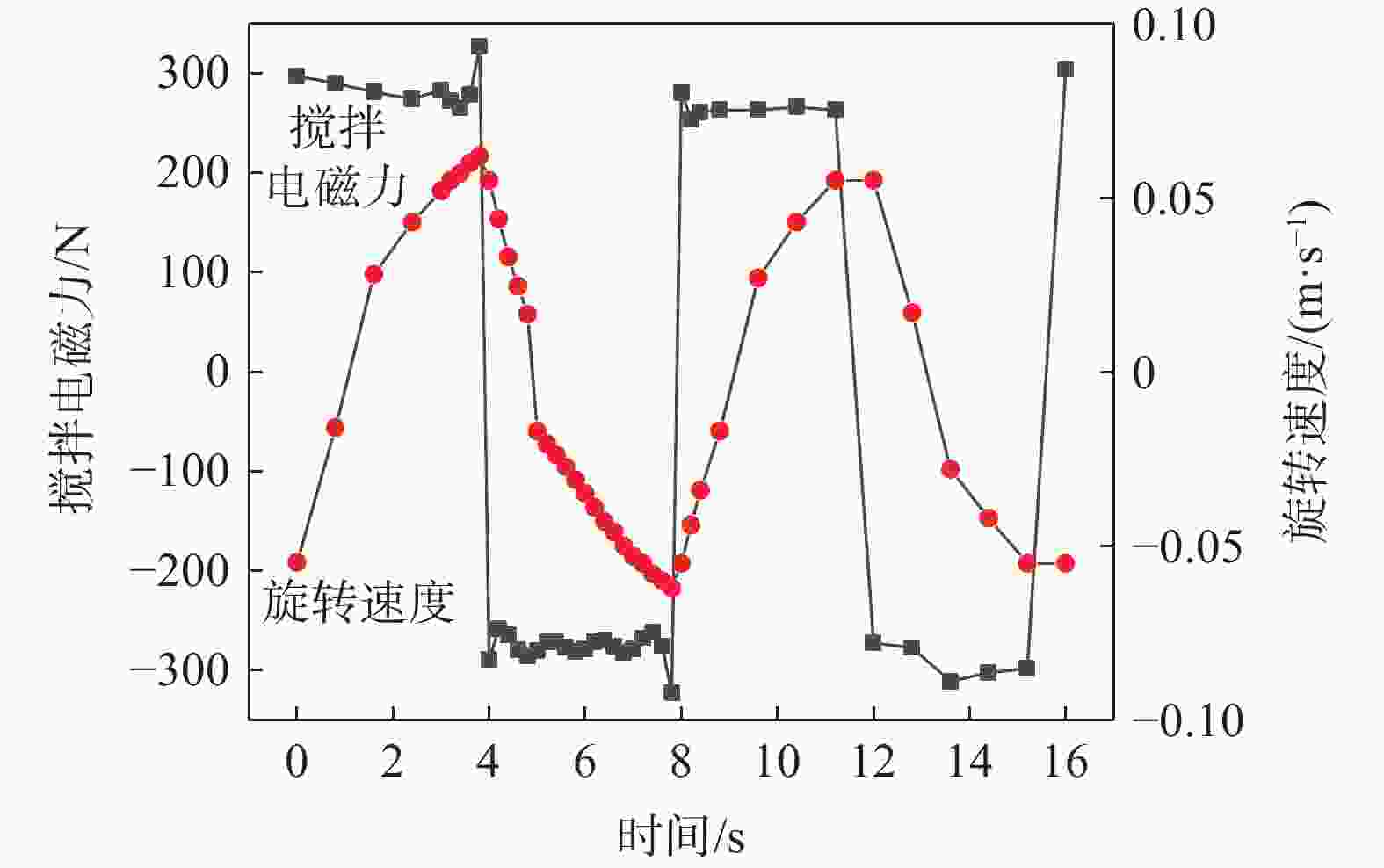
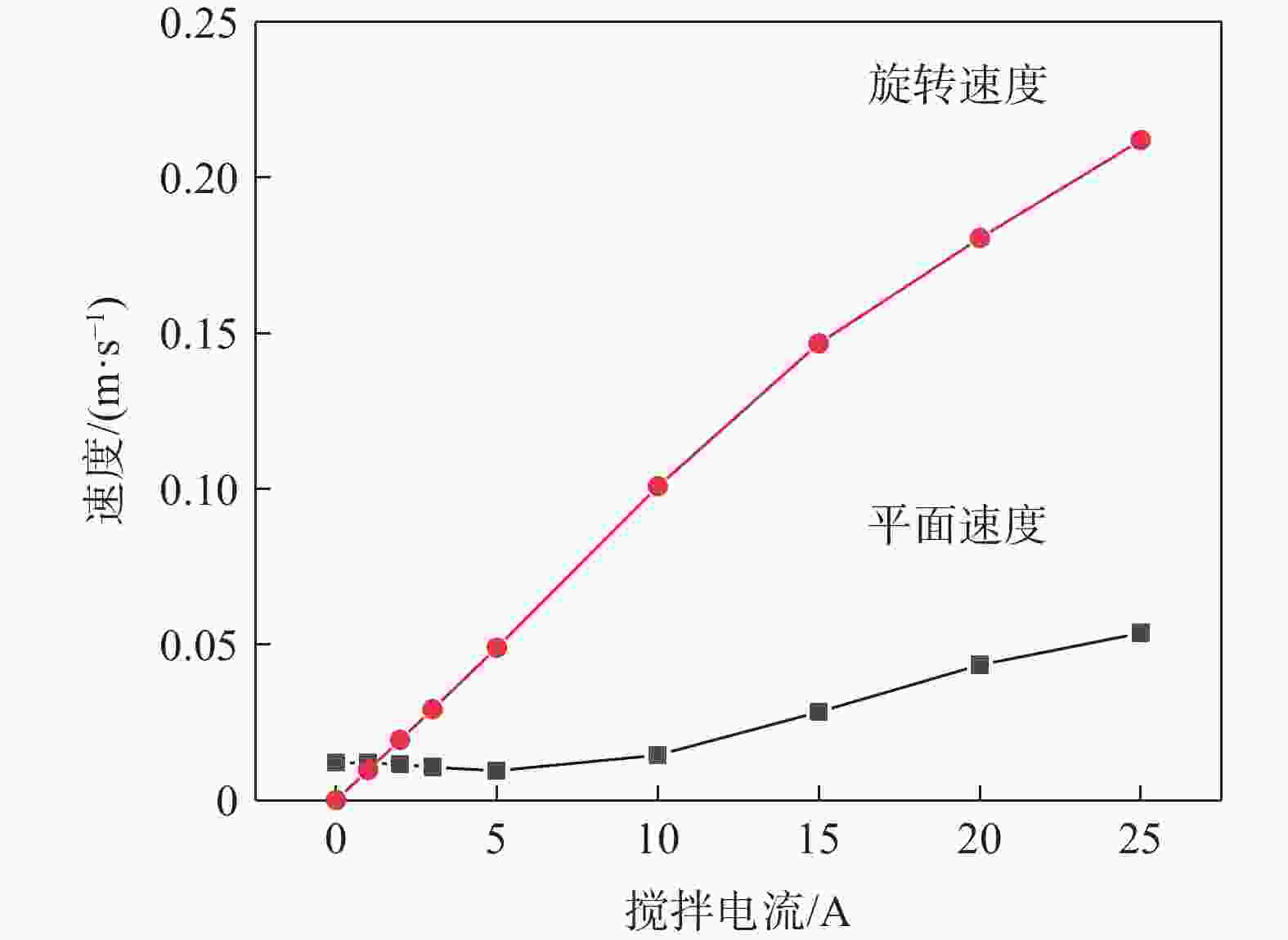
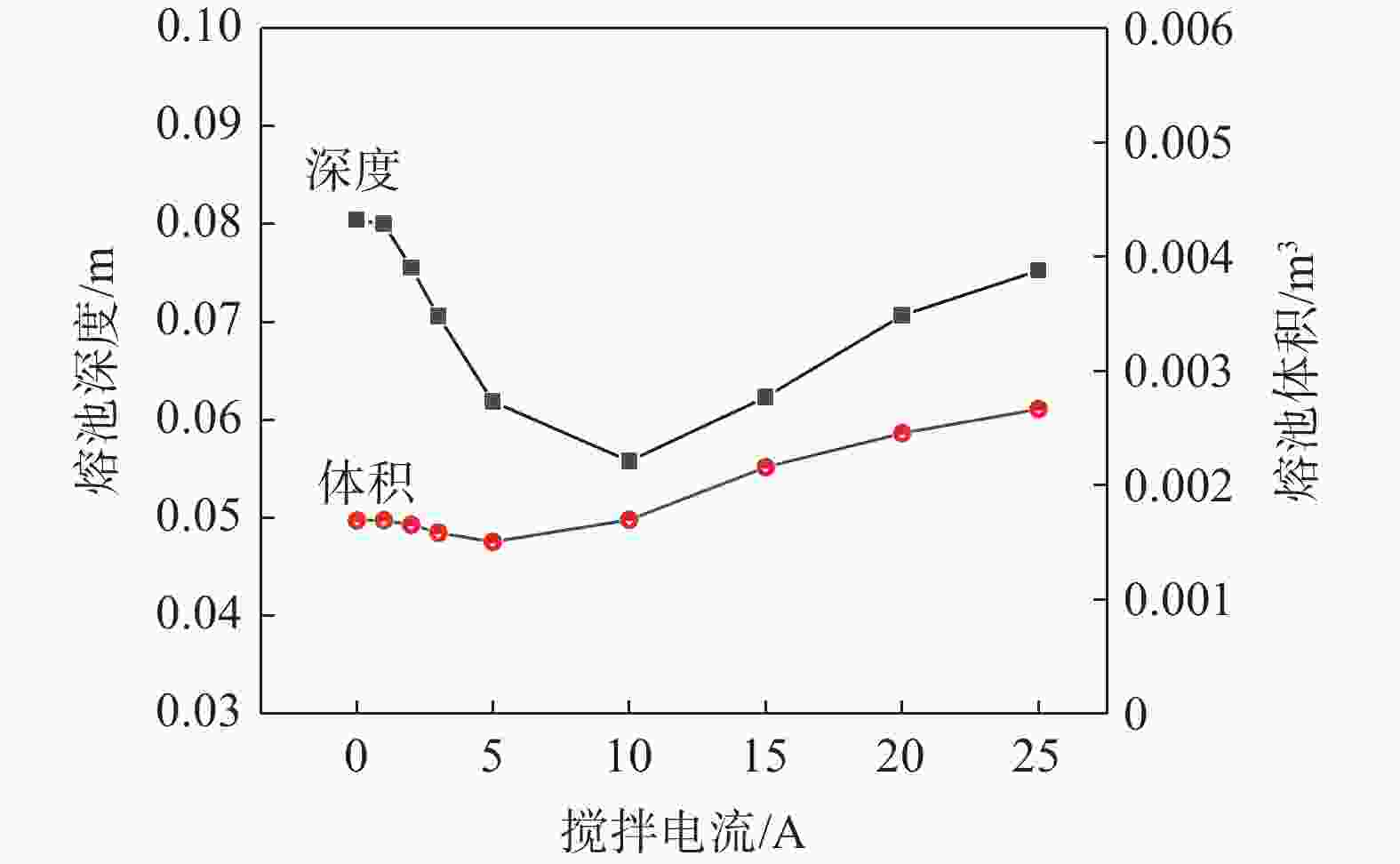
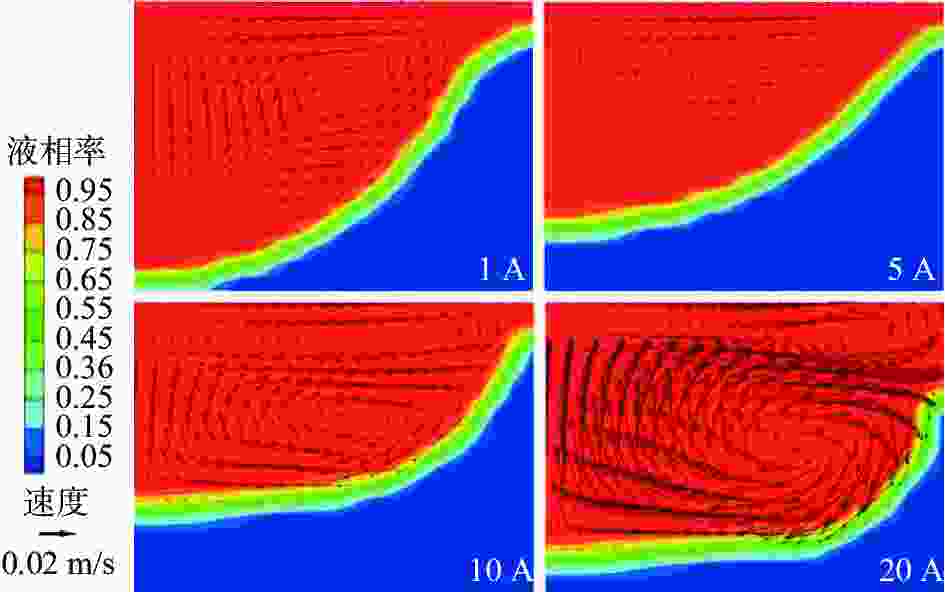
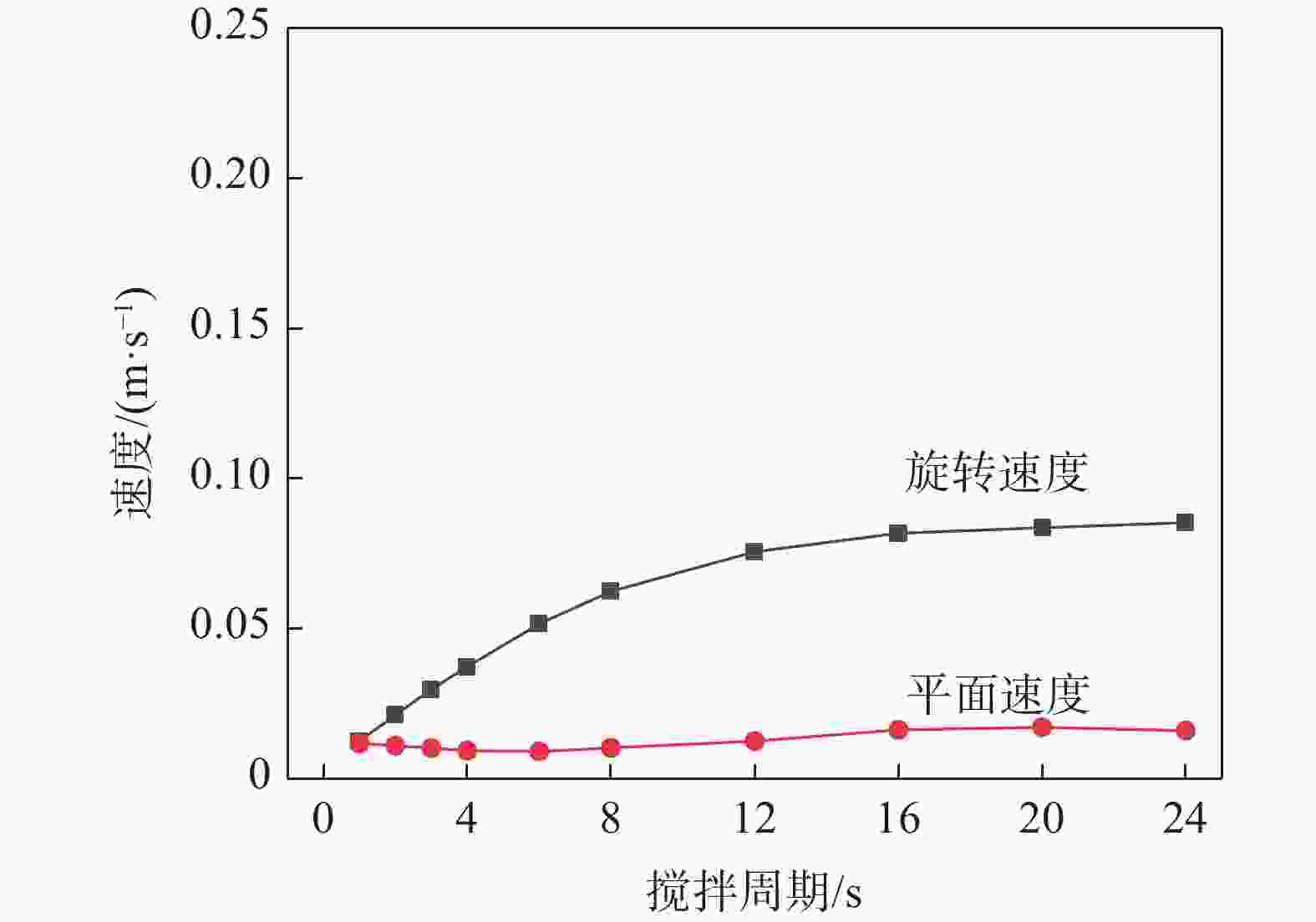
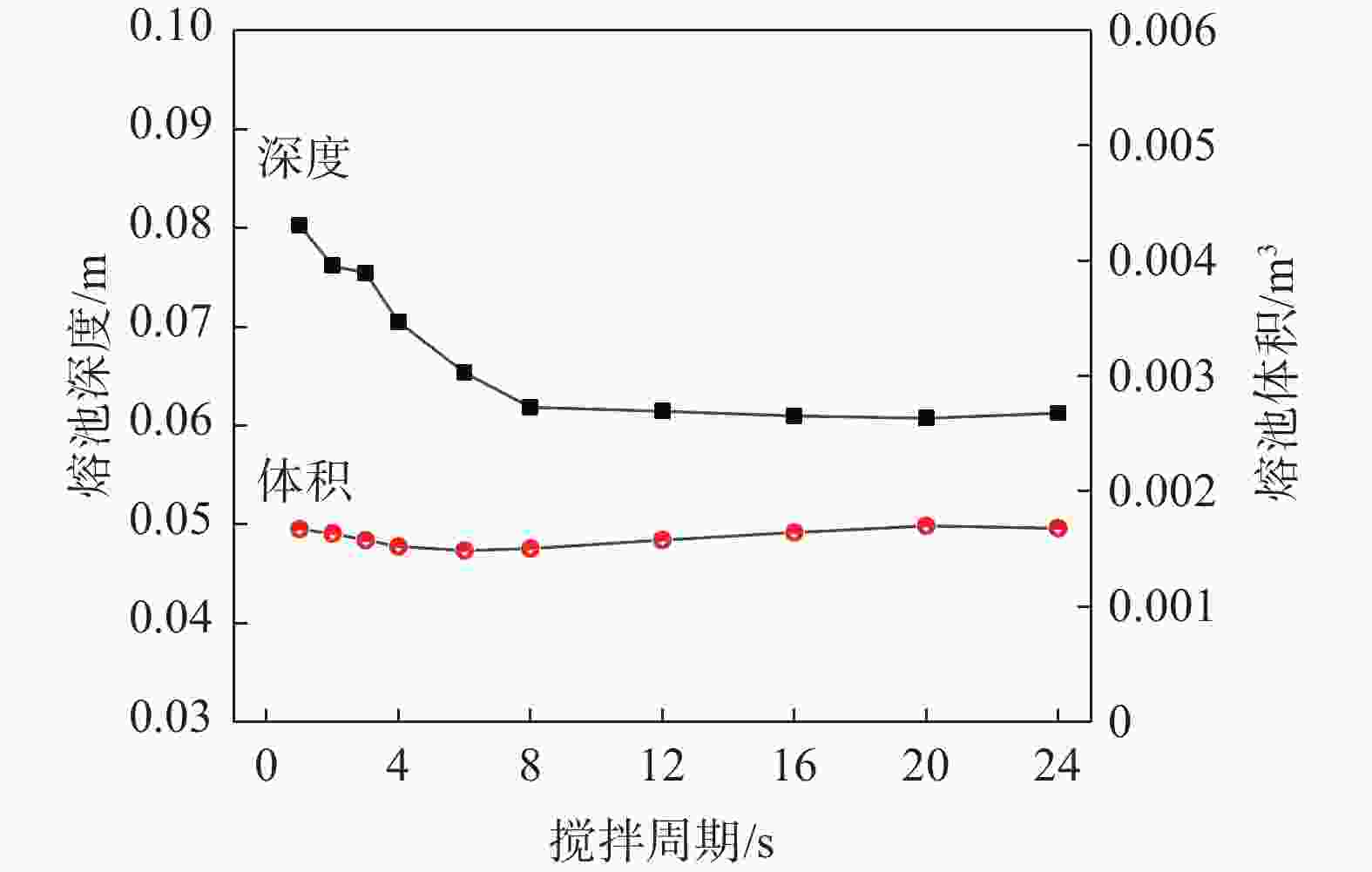
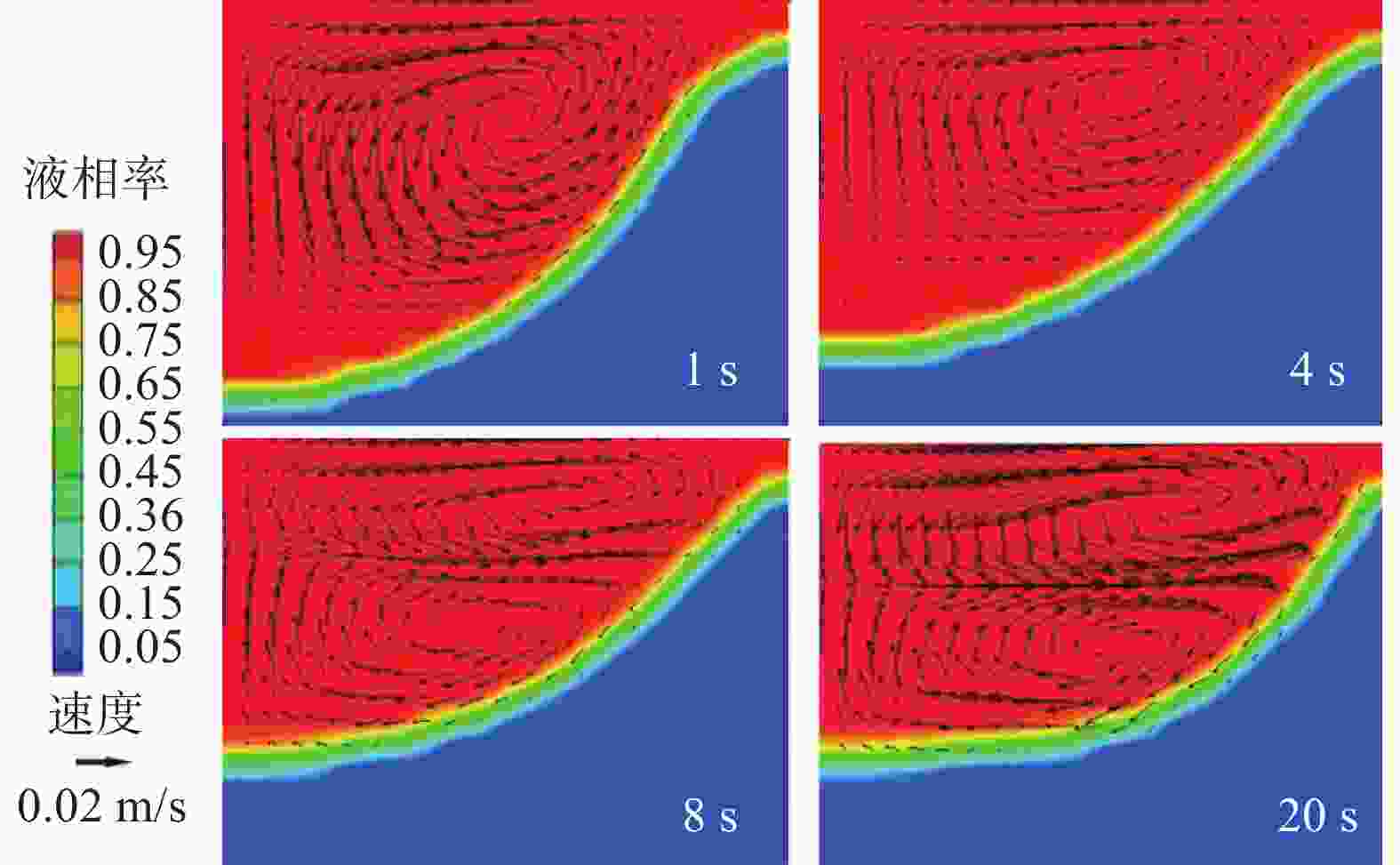
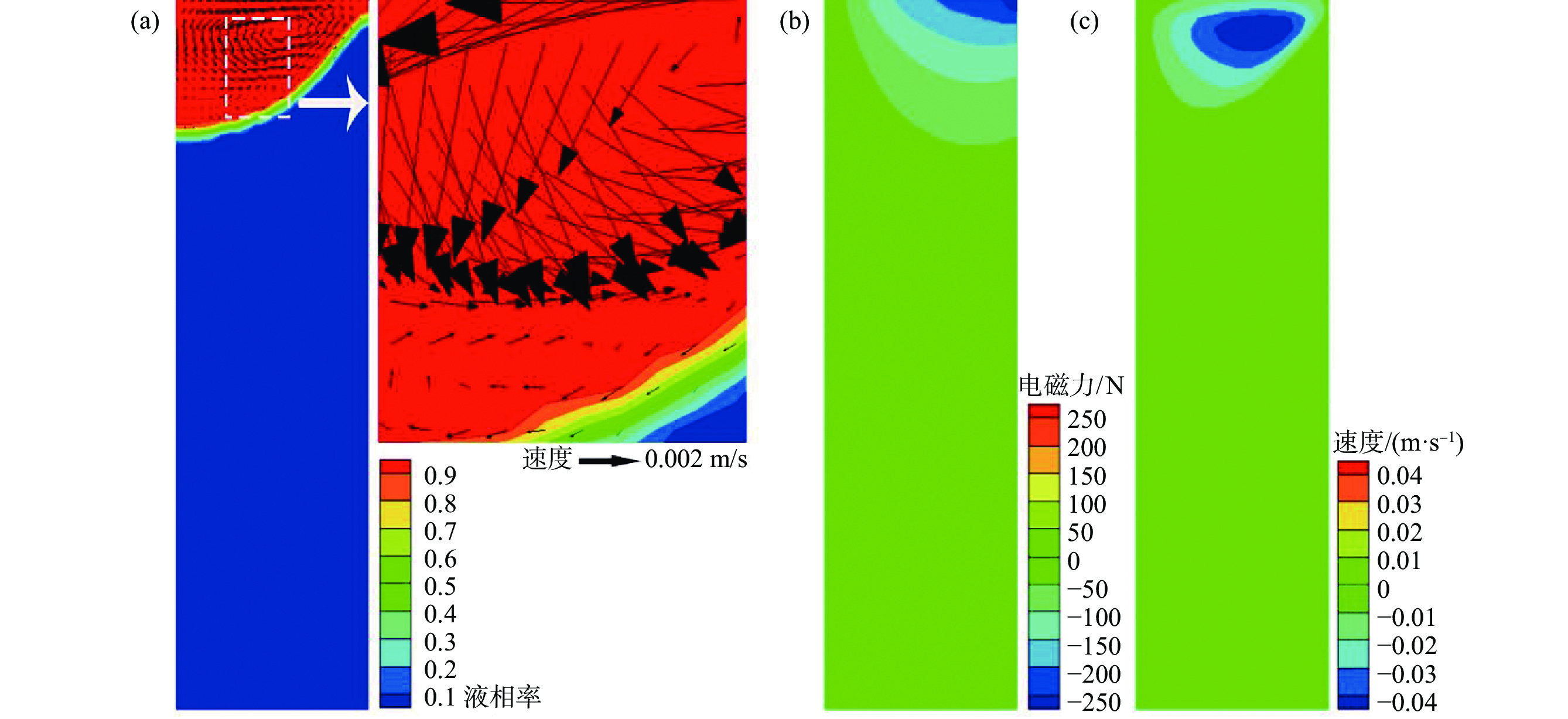
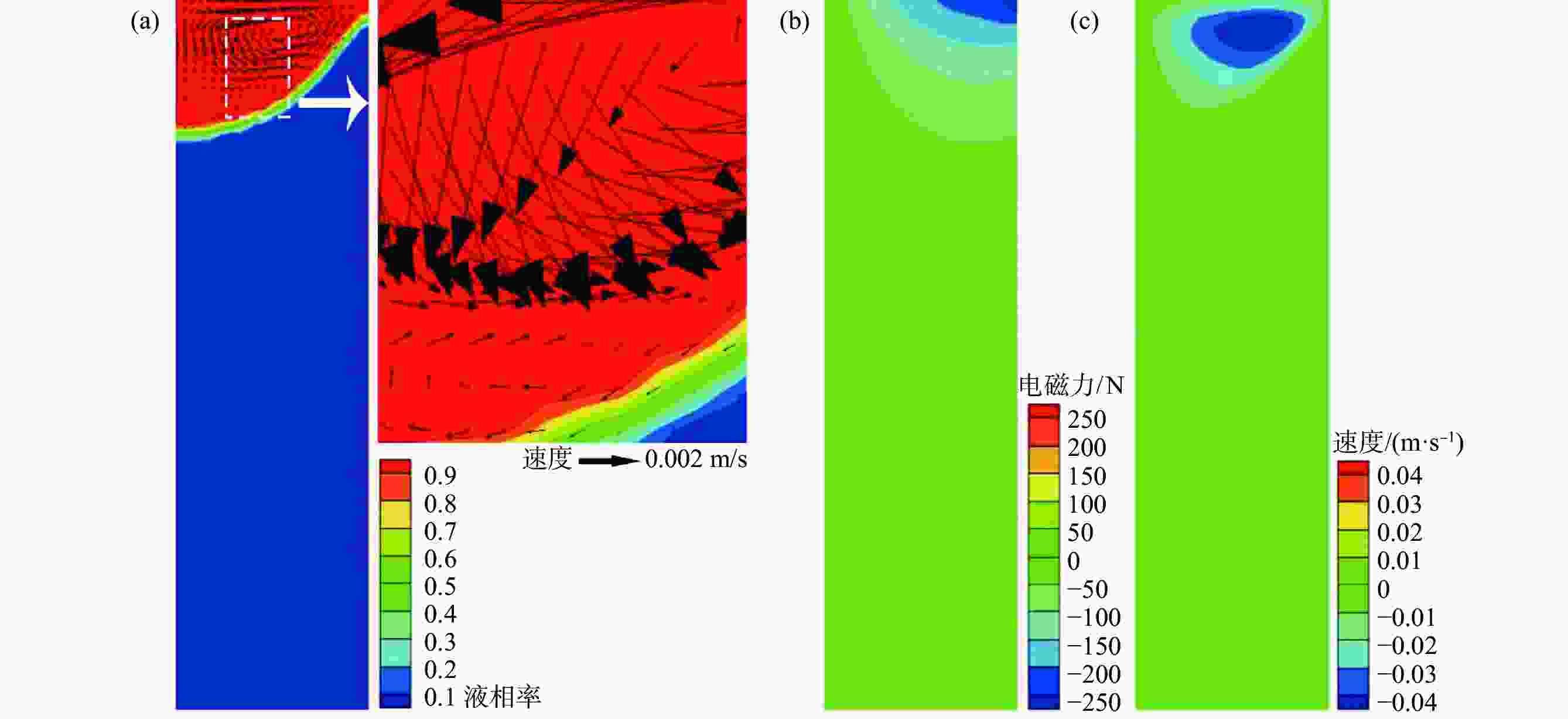
摘要: 真空自耗电弧熔炼中熔体的流动行为影响铸锭的凝固特性。熔体运动直接观测困难,因此通过模拟揭示熔体的流动行为非常关键。采用自主开发的三维模拟模型,研究了不同搅拌工艺参数下,熔炼过程中熔体的流动行为及熔池形貌。研究表明,随着搅拌电流从0.01 A逐步增加到25 A(搅拌周期为8 s),熔体旋转速度从0.0001 m/s近似线性增加到0.212 m/s,熔池逐渐宽化(由V形变成U形),熔池最大深度和熔池体积均存在一个明显的先下降后上升的过程。而随着搅拌周期从1 s逐步增加到24 s(搅拌电流为5 A),熔体旋转速度从0.0125 m/s快速增加到一个较大值(16 s时为0.0818 m/s)后趋于稳定,熔池逐渐宽化,熔池最大深度逐渐降低到一个最低值后趋于稳定。搅拌电流和搅拌周期均影响熔体的旋转及平面运动,但两者的影响机理存在一定的差异。Abstract: The flow behavior of melt in vacuum consumable arc melting affects the solidification characteristics of ingots. Direct observation of the melt motion is difficult, so revealing the flow behavior of the melt by simulation is crucial. In this paper, a self-developed three-dimensional simulation model was used to study the melt flow behavior and pool morphology during the melting process under different stirring process parameters. The research shows that with an increase in the stirring current from 0.01 A to 25 A (under a stirring period of 8 s), the rotational speed of the melt increases near-linearly from 0.0001 m/s to 0.212 m/s, and the molten pool gradually widens (from V-shaped to U-shaped). In the meanwhile, there is an obvious process of first decreasing and then increasing in the maximum depth and volume of the molten pool. As the stirring period increases from 1 s to 24 s (under a stirring current of 5 A), the rotational speed of the melt gradually increases from 0.0125 m/s to a high value (0.0818 m/s at 16 s) and then tends to stabilize. The molten pool gradually widens, and the maximum depth of the molten pool gradually decreases to a minimum value and then tends to stabilize. The stirring current and stirring period can affect the rotation and planar motion of the melt, but their affecting mechanisms are different.
-
Key words:
- titanium alloy /
- vacuum arc remelting /
- stirring magnetic field /
- molten flow
-
表 1 计算模型采用的物性参数[16]
Table 1. Physical parameters of the computational model
密度 /(kg·m−3) 扩散系数/(m2·s−1) 熔化潜热/(J·kg−1) Cr分配系数 液相线斜率 /(K·%−1) 溶质膨胀系数 /%−1 4170 4.0×10−9 3.77×105 0.75 −2.0 −0.35 比热容 /(J·kg−1·K−1) 热导率/(W·m−1·K−1) 热膨胀系数 /K−1 液相黏度/(kg·m−1·s−1) 电导率/(S·m−1) 磁导率/(H·m−1) 975 32.7 6.5×10−5 3.1×10−3 1.0×106 1.26×10−6 -
[1] Liu Xinxin. Research progress in preparation of vacuum consumable electrode EAF remelting technology of titanium alloys[J]. Industrial Heating, 2019,48(3):67−69. (刘欣欣. 真空自耗电弧熔炼制备钛合金技术的研究进展[J]. 工业加热, 2019,48(3):67−69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1639.2019.03.018Liu Xinxin. Research progress in preparation of vacuum consumable electrode EAF remelting technology of titanium alloys [J]. Industrial Heating, 2019, 48(3): 67-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1639.2019.03.018 [2] Lei Wenguang, Zhao Yongqing, Han Dong, et al. Development of melting technology for titanium and titanium alloys[J]. Materials Reports, 2016,30(5):101−106. (雷文光, 赵永庆, 韩栋, 等. 钛及钛合金熔炼技术发展现状[J]. 材料导报, 2016,30(5):101−106.Lei Wenguang, Zhao Yongqing, Han Dong, et al. Development of melting technology for titanium and titanium alloys [J]. Materials Reports, 2016, 30(5): 101-106. [3] Zhao Yongqing, Liu Junlin, Zhou Lian. Analysis on the segregation of typical β alloying elements of Cu, Fe and Cr in Ti alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005,34(4):531−538. (赵永庆, 刘军林, 周廉. 典型β型钛合金元素Cu, Fe和Cr的偏析规律[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2005,34(4):531−538. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2005.04.006Zhao Yongqing, Liu Junlin, Zhou Lian. Analysis on the segregation of typical β alloying elements of Cu, Fe and Cr in Ti alloys [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2005, 34(4): 531-538. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2005.04.006 [4] Liu Junlin, Zhao Yongqing, Zhou Lian. Segregation of Ti-2.5Cu, Ti-3Fe and Ti-3Cr alloy ingots[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004,33(7):731−735. (刘军林, 赵永庆, 周廉. Ti-2.5Cu, Ti-3Fe, Ti-3Cr合金铸锭的偏析[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2004,33(7):731−735. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2004.07.014Liu Junlin, Zhao Yongqing, Zhou Lian. Segregation of Ti-2.5 Cu, Ti-3 Fe and Ti-3 Cr alloy ingots [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004, 33(7): 731-735. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2004.07.014 [5] Hayakawa Hiroshi, Fukada Nobuo, Udagawa Takeshi, et al. Solidification structure and segregation in cast ingots of titanium alloy produced by vacuum arc consumable electrode method[J]. ISIJ International, 1991,31(8):775−784. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.31.775 [6] Zagrebelnyy Dmytro, Krane Matthew John M. Segregation development in multiple melt vacuum arc remelting[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2009,40(3):281−288. doi: 10.1007/s11663-008-9163-5 [7] Kou H, Zhang Y, Yang Z, et al. Liquid metal flow behavior during vacuum consumable arc remelting process for titanium[J]. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 2014,12(1):50−56. [8] Dobatkin V I, Anoshkin N F. Comparison of macrosegregation in titanium and aluminium alloy ingots[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 1999,263(2):224−229. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(98)01152-6 [9] Kondrashov E N, Musatov M I, Maksimov A Yu, et al. Calculation of the molten pool depth in vacuum arc remelting of alloy Vt3-1[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2007,16(1):19−25. doi: 10.1134/S1810232807010031 [10] Xiao Cong. Simulation and industrial validation of molten pool morphology and solidification structure of pure titanium during VAR process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,37(2):44−49, 83. (肖聪. 纯钛VAR熔池形貌和凝固组织模拟及其工业验证[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(2):44−49, 83. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.02.008Xiao Cong. Simulation and industrial validation of molten pool morphology and solidification structure of pure titanium during VAR process [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016, 37(2): 44-49, 83. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.02.008 [11] Li Pengfei, Li Jinshan, Sun Chang, et al. Multiscale modeling of the vacuum arc remelting process of titanium alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013,34(2):24−29. (李鹏飞, 李金山, 孙畅, 等. 钛合金真空自耗电弧熔炼过程的多尺度模拟[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2013,34(2):24−29. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2013.02.006Li Pengfei, Li Jinshan, Sun Chang, et al. Multiscale modeling of the vacuum arc remelting process of titanium alloy [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013, 34(2): 24-29. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2013.02.006 [12] Fan Kai, Wu Lincai, Li Junjie, et al. Numerical simulation of macrosegregation caused by buoyancy driven flow during VAR process for titanium alloys[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020,49(3):871−877. (樊凯, 吴林财, 李俊杰, 等. 钛合金VAR过程中自然对流下的宏观偏析行为模拟[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2020,49(3):871−877.Fan Kai, Wu Lincai, Li Junjie, et al. Numerical simulation of macrosegregation caused by buoyancy driven flow during VAR process for titanium alloys [J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020, 49(3): 871-877. [13] Huang Liqing, Wu Jingyang, Guo Jie, et al. Liquid metal flow behavior during vacuum consumable arc remelting process for titanium[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023,44(4):1−8. (黄立清, 吴京洋, 郭杰, 等. 钛合金VAR过程中自感电磁场对流场与偏析行为的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023,44(4):1−8. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2023.04.001Huang Liqing, Wu Jingyang, Guo Jie, et al. Liquid metal flow behavior during vacuum consumable arc remelting process for titanium [J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(4): 1-8. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2023.04.001 [14] 郭杰. TC17合金VAR铸锭宏/微观偏析及组织演化模拟[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2023.Guo Jie. Simulation of macro/micro segregation and microstructure evolution during the vacuum arc remelting of TC17 alloy [D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2023. [15] Davidson P A, He X, Lowe A J. Flow transitions in vacuum arc remelting[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2000,16(6):699−711. doi: 10.1179/026708300101508306 [16] Covino Bemard S, Cramer Stephen D. ASM Handbook [M]. USA: ASM International, 2003. -




 下载:
下载: